Temperature Compensation Method for MEMS Ring Gyroscope Based on PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF and FTTA-LSTM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
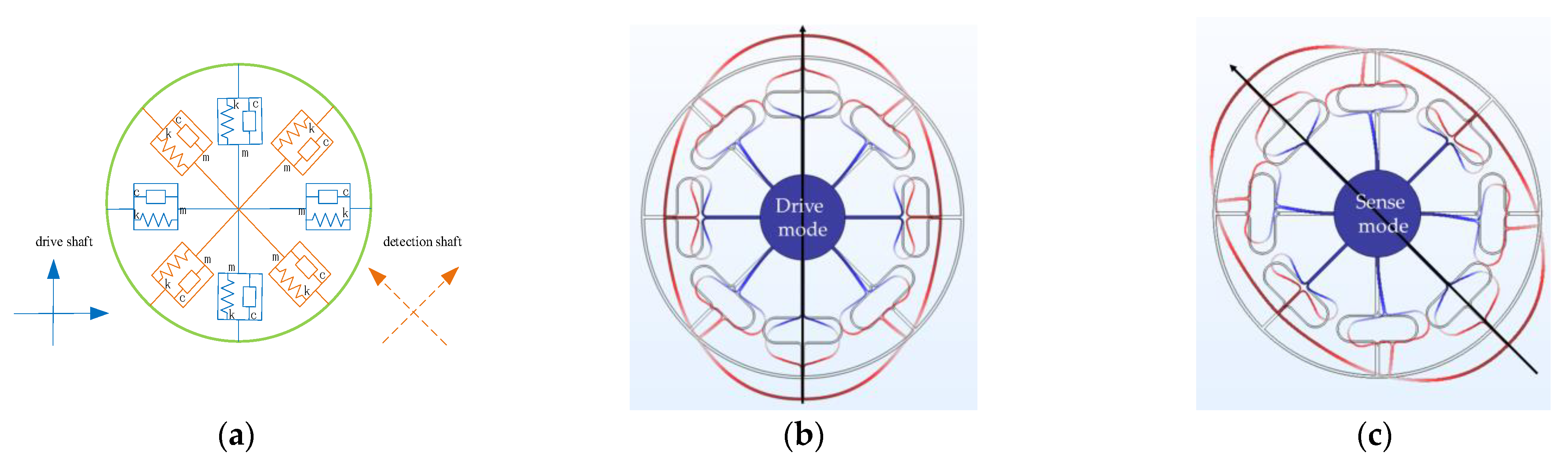
2. Introduction to MEMS Ring Gyroscope
3. Parallel Processing Methods
3.1. Empirical Mode Decomposition (EMD)
3.2. Time-Varying Filter-Based Empirical Mode Decomposition (TVFEMD)
3.3. Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO)
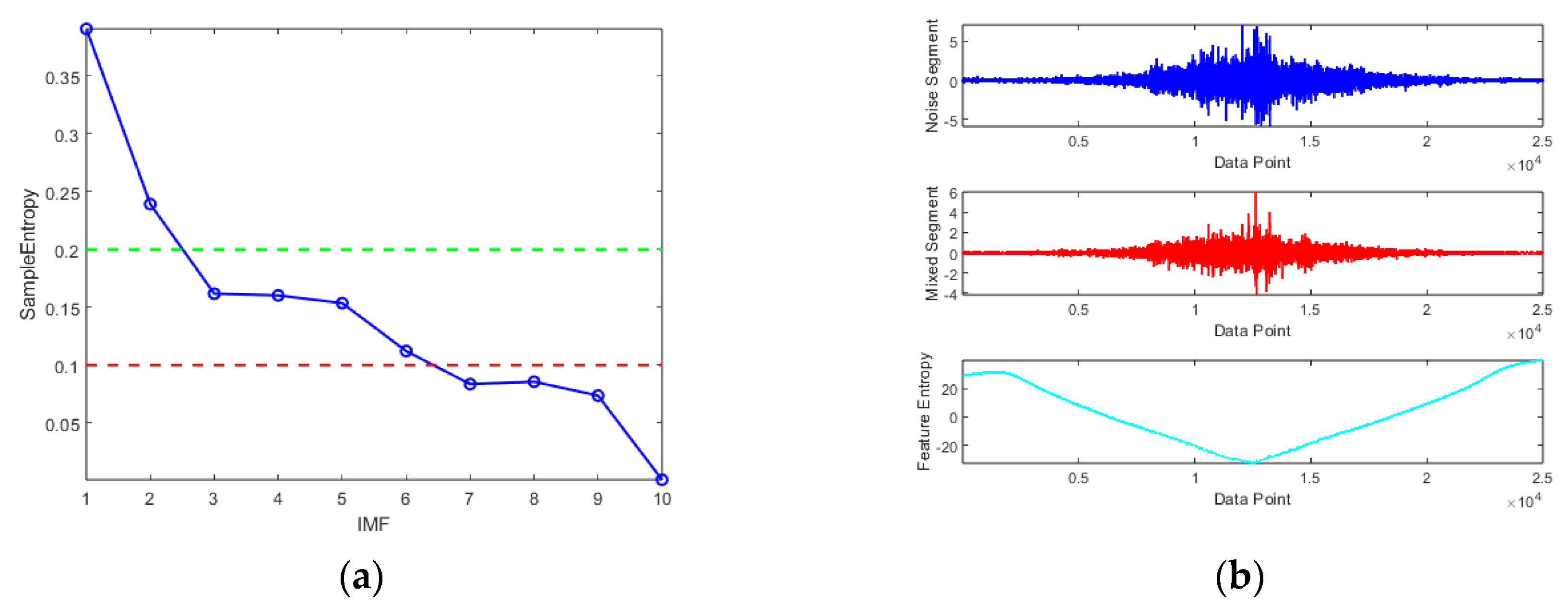
3.4. Sample Entropy (SE)
3.5. Time–Frequency Peak Filtering (TFPF)
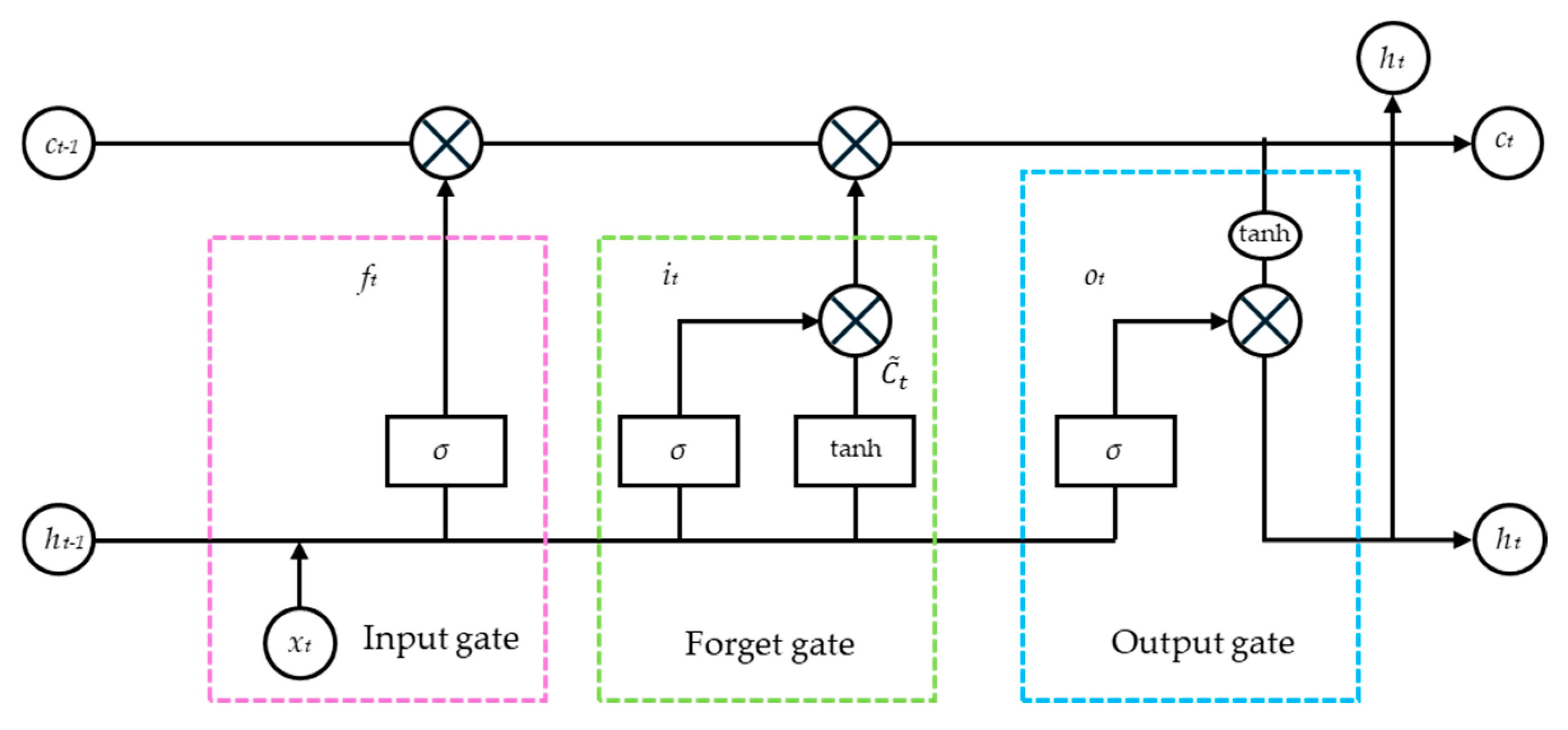
3.6. Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network (LSTM)
3.7. Football Team Training Algorithm (FTTA)
3.7.1. Team Training
3.7.2. Group Training
3.7.3. Individual Extra Training
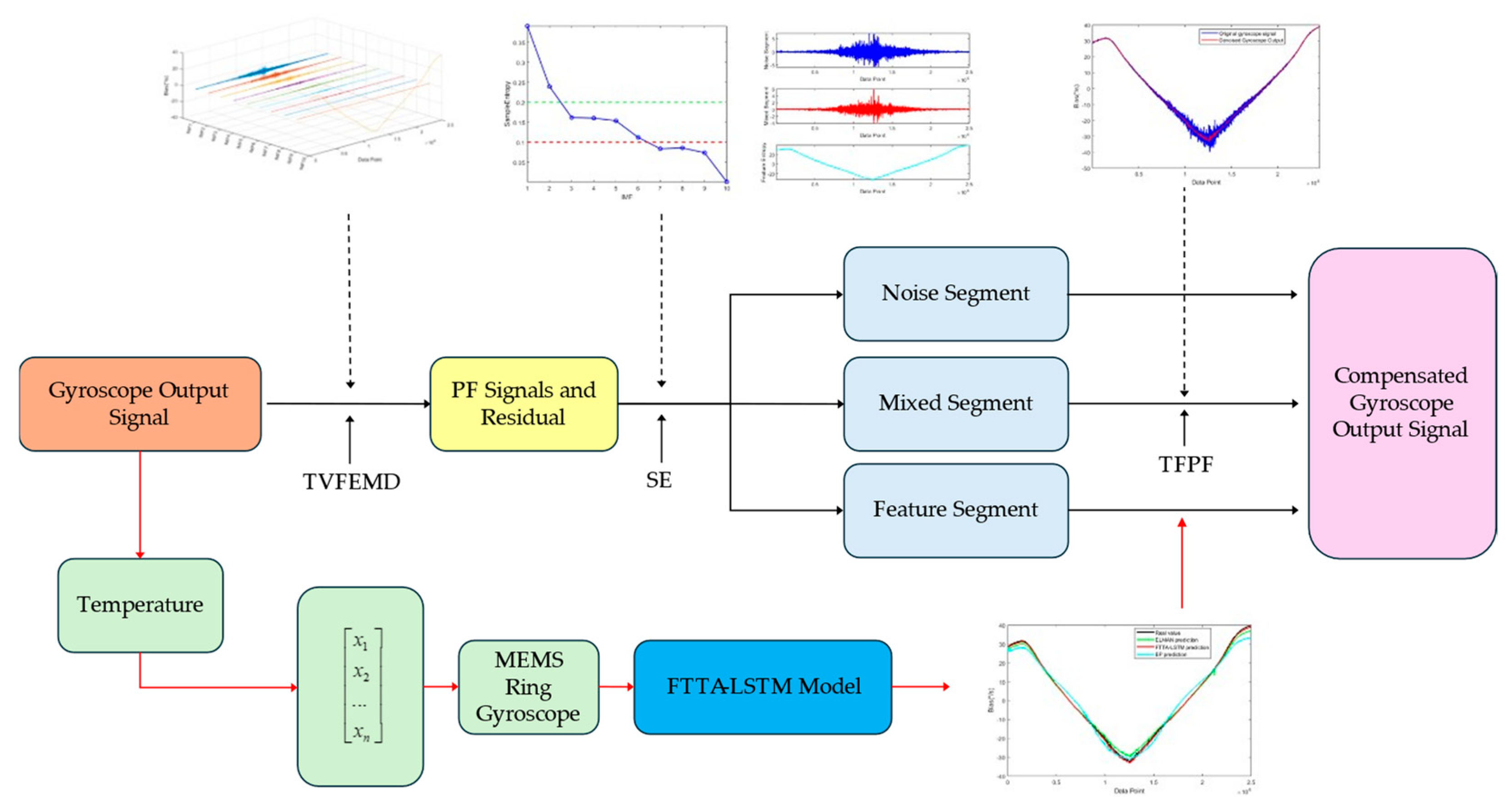
3.8. Temperature Compensation Model
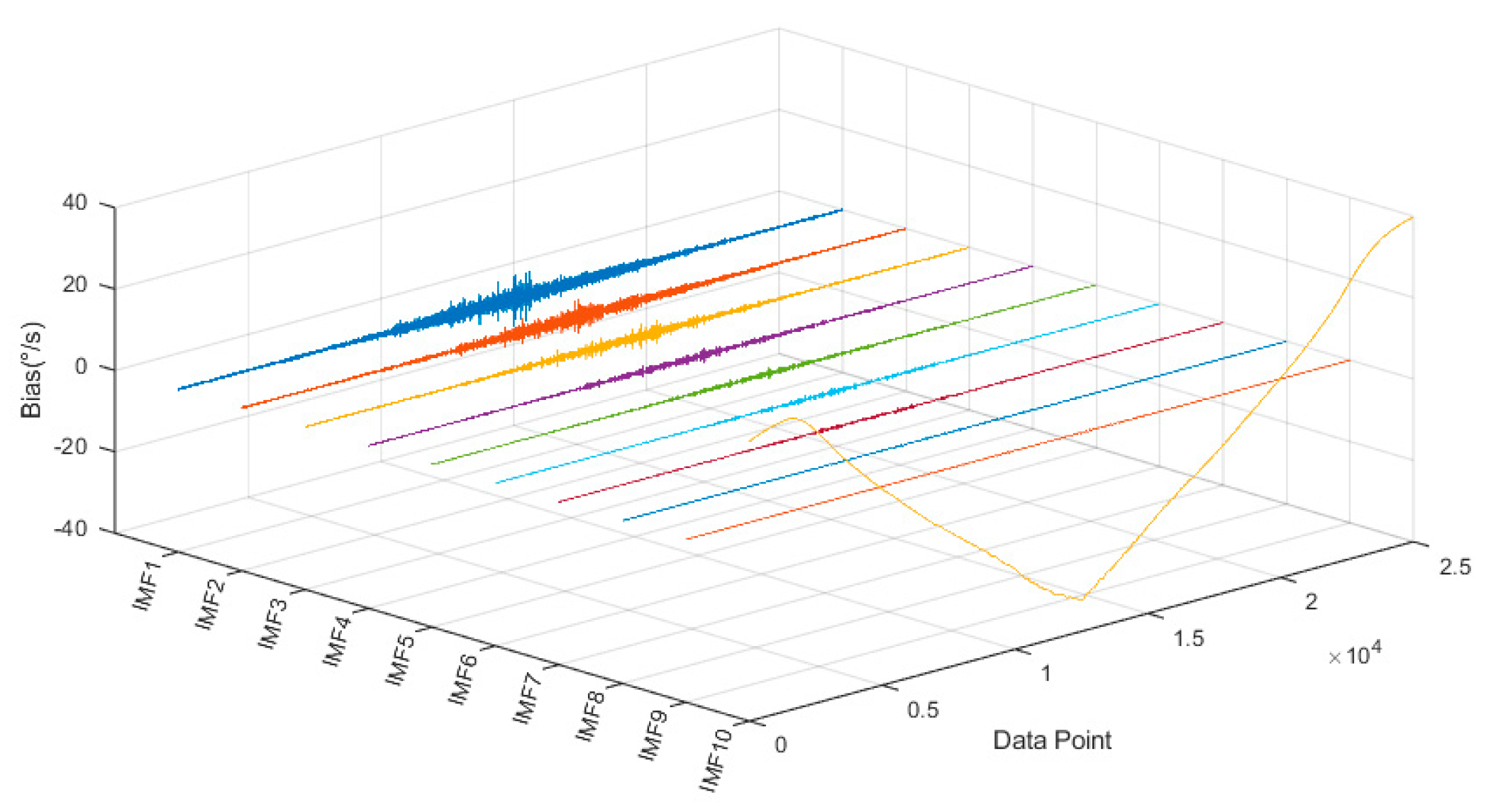
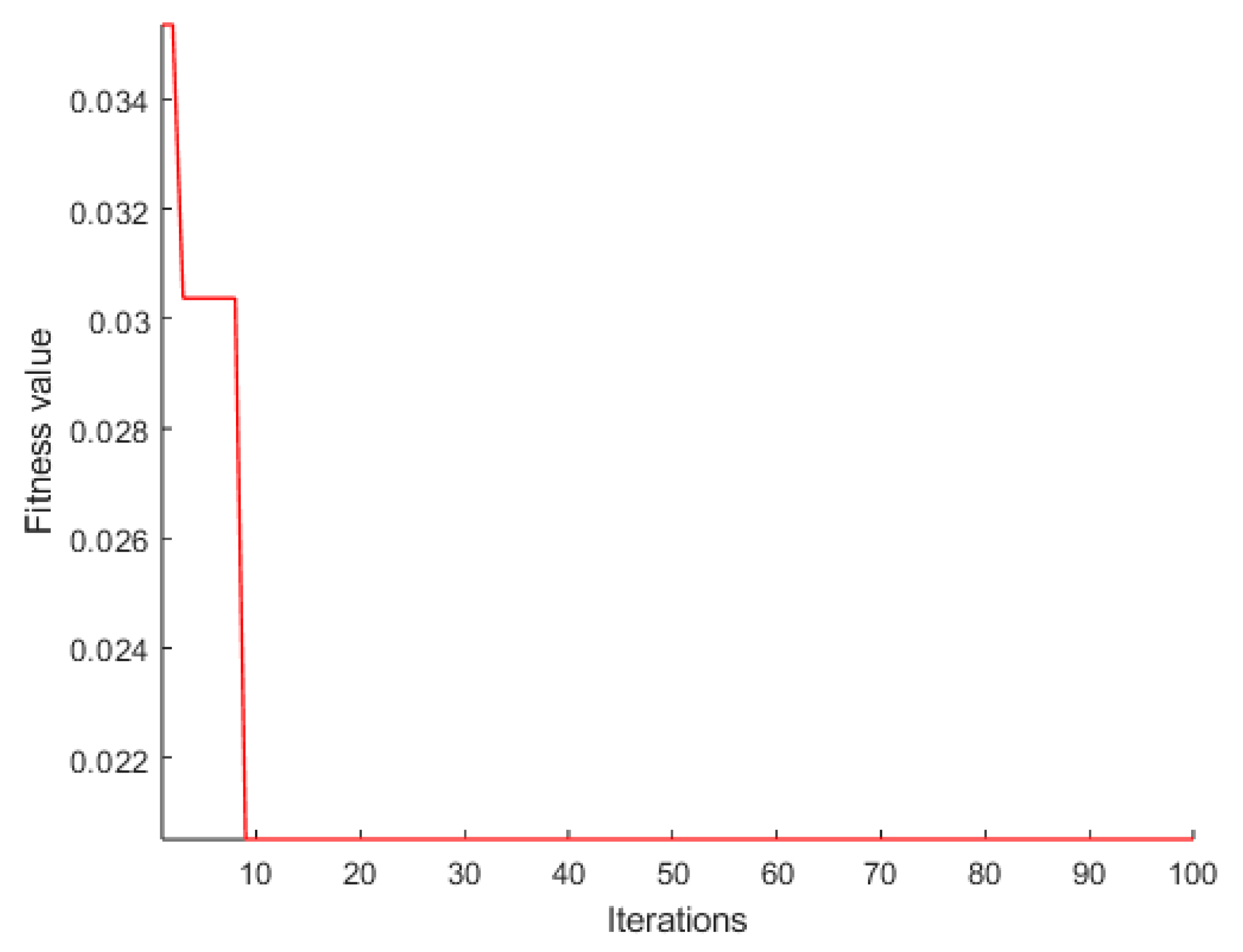
3.8.1. Optimizing TVFEMD Decomposition Parameters Using PSO
3.8.2. Temperature Compensation Using the FTTA-LSTM Model
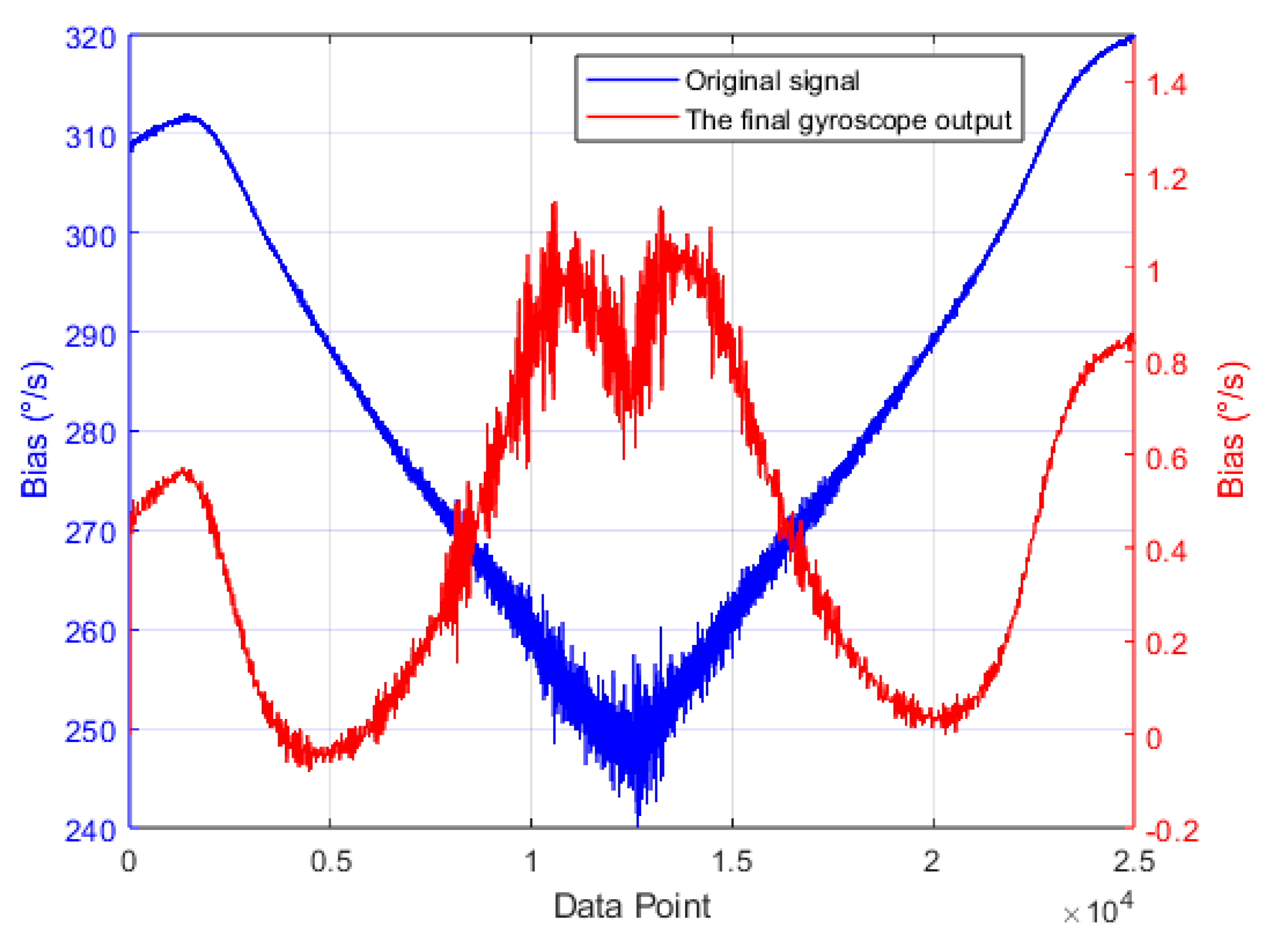
3.8.3. Generating the Final Compensation Signal
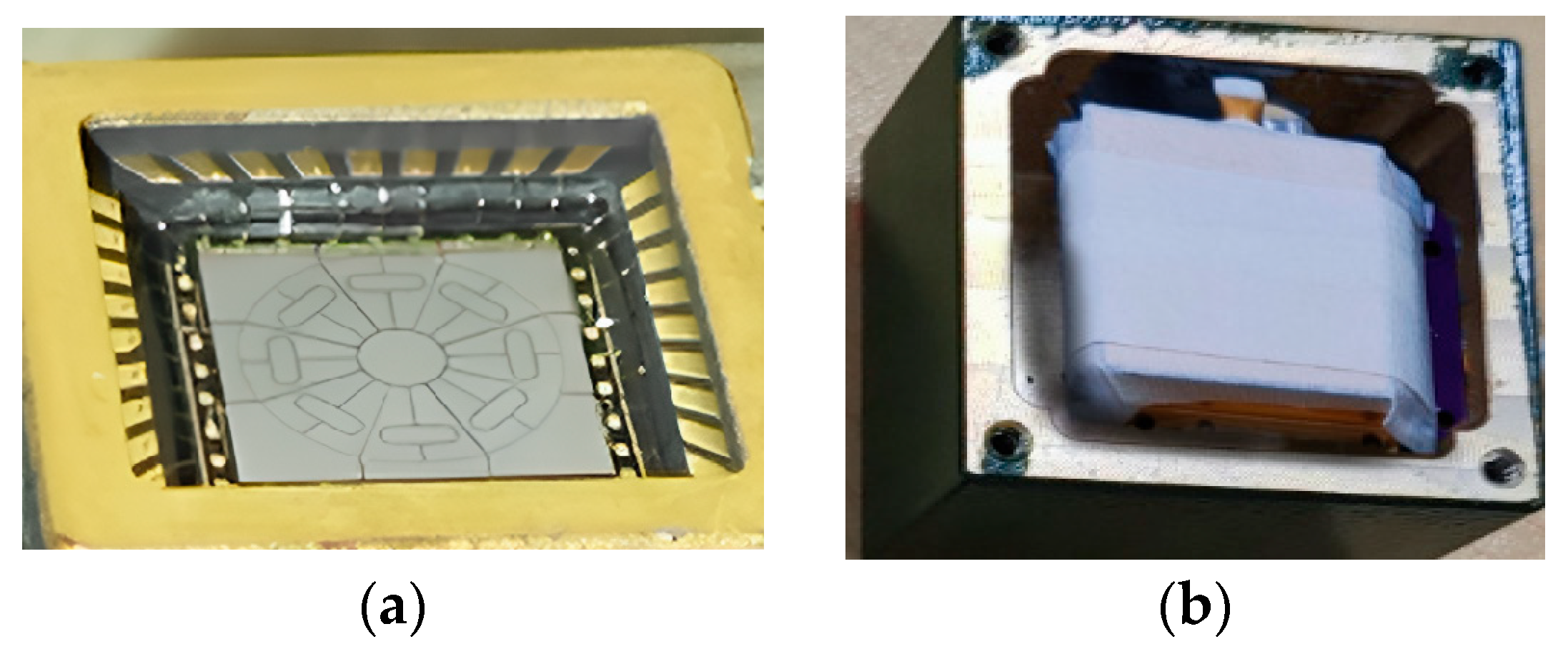
4. Experiment
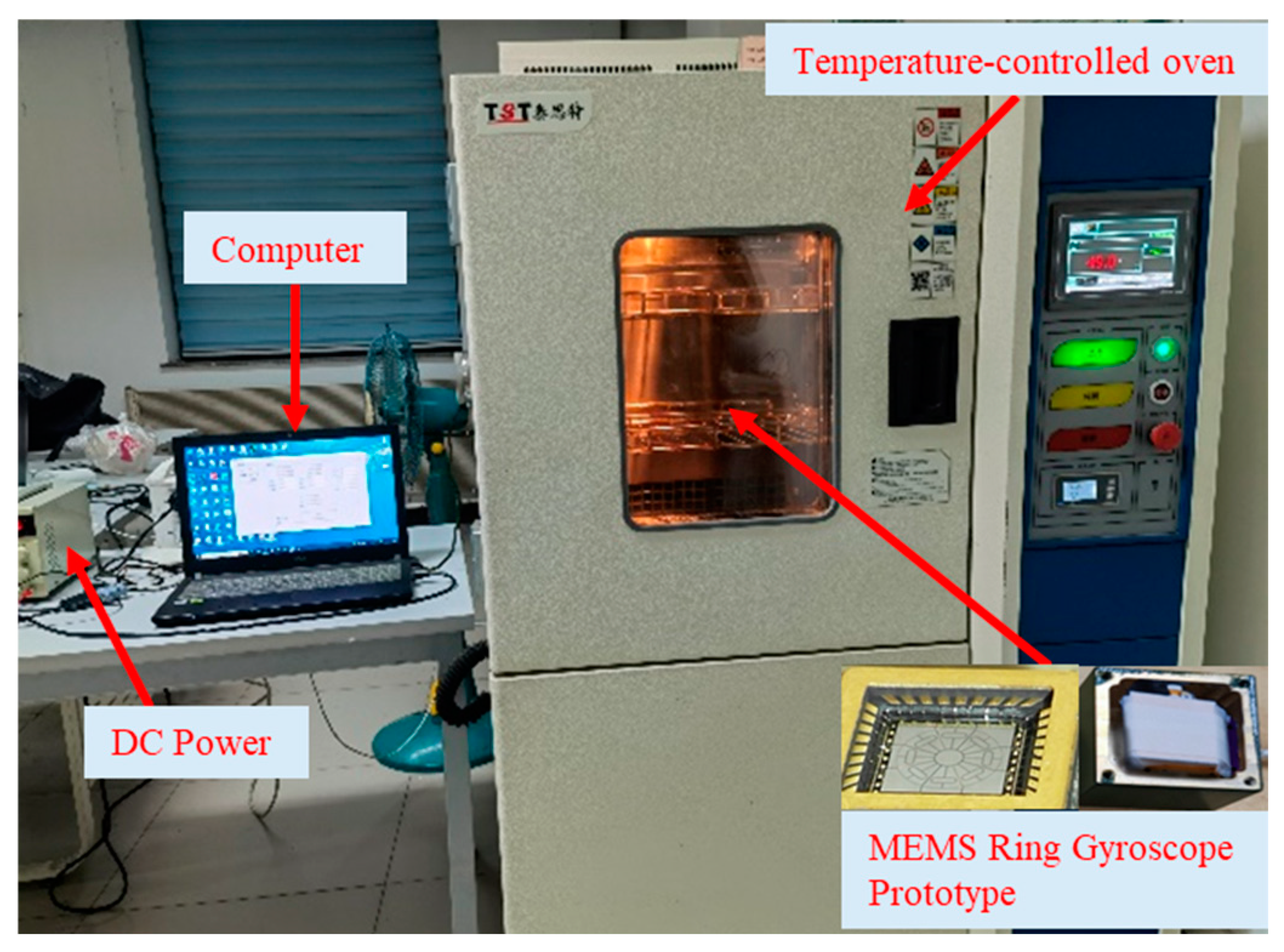
4.1. The Temperature Experimental Process
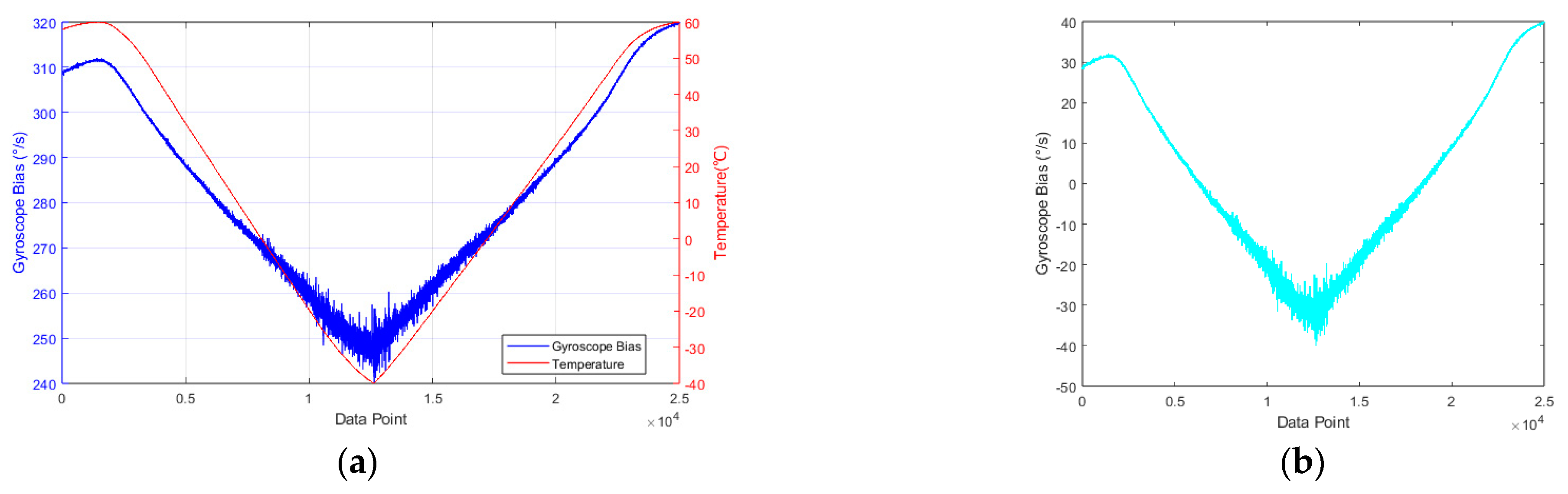
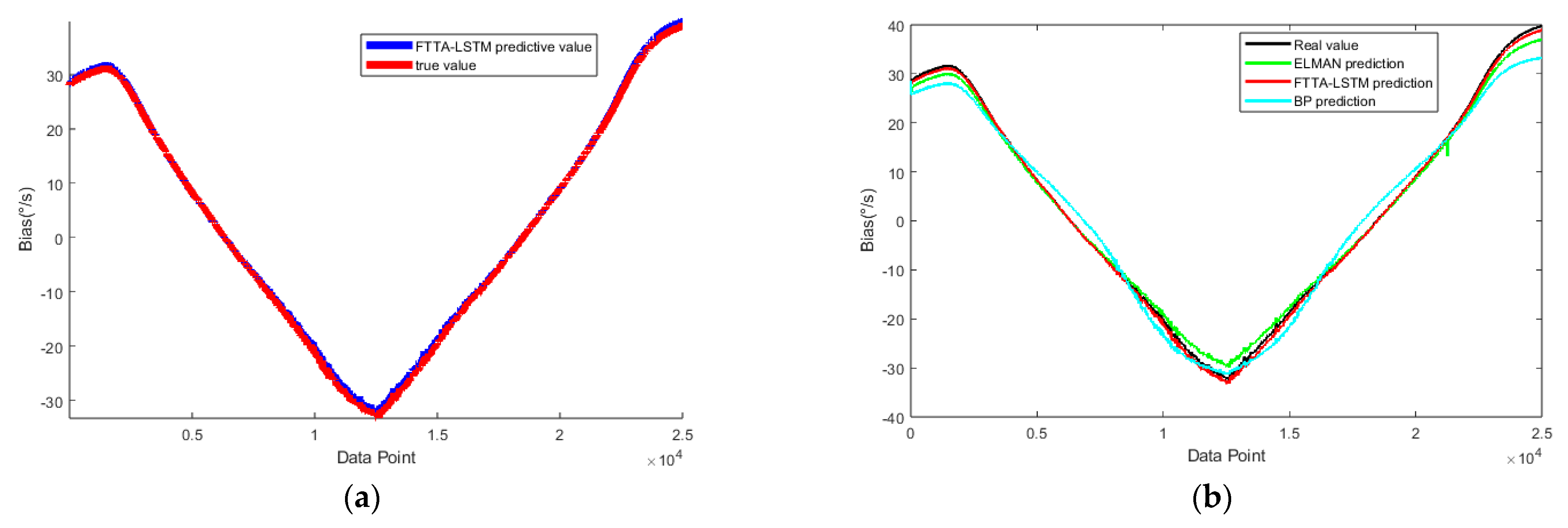
4.2. The Experimental Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, R.; Ma, T.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Chang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Wei, W.; Cao, H. A New Dual-Mass MEMS Gyroscope Fault Diagnosis Platform. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, H.; Duan, X. Hybrid Temperature Compensation Model of MEMS Gyroscope Based on Genetic Particle Swarm Optimization Variational Modal Decomposition and Improved Backpropagation. Sens. Mater. 2021, 33, 2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, G.; Bestetti, M.; Gadola, M. Silicon MEMS inertial sensors evolution over a quarter century. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2021, 31, 084002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, W.A.; Howard, I.; Mazhar, I.; McKee, K. A review of MEMS vibrating gyroscopes and their reliability issues in harsh environments. Sensors 2022, 22, 7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, R.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, V. Errors in micro-electro-mechanical systems inertial measurement and a review on present practices of error modelling. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2018, 40, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdinc, T. On-Chip Compensation of Stress, Temperature, and Nonlinearity in a MEMS Gyroscope. Ph.D. Thesis, Carnegie Mellon University, Atlanta, GA, USA, 2016; p. 9625347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazdrowicz, J.; Napieralski, A. “Temperature Change Leverage on Performance of MEMS Rotational Motion Sensors,” Intersociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems. 2019. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Temperature-Change-Leverage-on-Performance-of-MEMS-Nazdrowicz-Napieralski/a4b1a433f49b9cfc01d86cfa2b922126eff4fb79 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Li, K.; Cui, R.; Cai, Q.; Wei, W.; Shen, C.; Tang, J.; Shi, Y.; Cao, H.; Liu, J. A Fusion Algorithm for Real-Time Temperature Compensation and Noise Suppression with a Double U-Beam Vibration Ring Gyroscope. IEEE Sens. J. 2024, 24, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Huang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cao, H. MEMS gyroscope temperature compensation based on drive mode vibration characteristic control. Micromachines 2019, 10, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhao, Q. Bias thermal stability improvement of MEMS gyroscope with quadrature motion correction and temperature self-sensing compensation. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Li, H. Investigation of a vacuum packaged MEMS gyroscope architecture’s temperature robustness. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 2013, 41, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Woo, J.K.; Najafi, K.; Lee, S.; Mitchell, J.; Challoner, D. ±2 ppm frequency drift and 300x reduction of bias drift of commercial 6-axis inertial measurement units using a low-power oven-control micro platform. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE SENSORS, Busan, Republic of Korea, 1–4 November 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Dai, B.; Liu, X.; Xu, L.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X. The on-chip temperature compensation and temperature control research for the silicon micro-gyroscope. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 21, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Zhao, F.; Kang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Hu, D.; Liu, J.; Cao, H. A Novel Parallel Processing Model for Noise Reduction and Temperature Compensation of MEMS Gyroscope. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Y.-H.; Peng, C.-C. An ARMA-based digital twin for MEMS gyroscope drift dynamics modeling and real-time compensation. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X. Temperature Energy Influence Compensation for MEMS Vibration Gyroscope Based on RBF NN-GA-KF Method. Shock. Vib. 2018, 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhou, Y.; Shu, X. Compensation of fiber optic gyroscope vibration error based on VMD and FPA-WT. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2022, 33, 115104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Qin, P.; Sun, X.-M.; Li, Y. An automatic parameter setting variational mode decomposition method for vibration signals. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2024, 20, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S. Study on mode mixing problem of empirical mode decomposition. In Proceedings of the 2016 Joint International Information Technology, Mechanical and Electronic Engineering, Xi’an, China, 4–5 October 2016; Atlantis Press: Xi’an, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Niu, X. MEMS gyroscope temperature compensation based on SSA-RBF neural network. In Proceedings of the 2022 5th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Pattern Recognition, Xiamen, China, 23–25 September 2022; ACM: Xiamen, China, 2022; pp. 109–114. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Miao, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, P.; Wu, X.; Xi, X.; Xiao, D. A temperature drift suppression method of mode-matched MEMS gyroscope based on a combination of mode reversal and multiple regression. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cao, H. Improved VMD-ELM algorithm for MEMS gyroscope of temperature compensation model based on CNN-LSTM and PSO-SVM. Micromachines 2022, 13, 2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Chai, B.; Cheng, R.; Wang, Y. Temperature drift compensation of a MEMS accelerometer based on DLSTM and ISSA. Sensors 2023, 23, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cao, H. Temperature compensation model of MEMS multi-ring disk solid wave gyroscope based on RIME-VMD and PSO-DBN multi fusion algorithm. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2025, 385, 116285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Pan, Y.; Li, K.; He, L.; Wang, Q.; Wang, W. Modeling and Reliability Analysis of MEMS Gyroscope Rotor Parameters under Vibrational Stress. Micromachines 2024, 15, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, J. Short-term air quality prediction based on EMD-transformer-BiLSTM. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Cui, Y.; Gu, Y.; Wang, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, K.; Cao, H. Temperature drift compensation for four-mass vibration MEMS gyroscope based on EMD and hybrid filtering fusion method. Micromachines 2023, 14, 971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, C.; Dong, H. Study on displacement by integrating acceleration of vibration screening excitation platform based on EBKA-TVF-EMD. Heliyon 2025, 11, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviran, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Ghezelbash, R. Optimized AI-MPM: Application of PSO for tuning the hyperparameters of SVM and RF algorithms. Comput. Geosci. 2025, 195, 105785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, R.; Xu, J.; Huang, B.; Xu, H.; Peng, M.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J.; Gu, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; et al. A temperature compensation approach for micro-electro-mechanical systems accelerometer based on gated recurrent unit–attention and robust local mean decomposition–sample entropy–time-frequency peak filtering. Micromachines 2024, 15, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Cui, R.; Liu, W.; Ma, T.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, C.; Shi, Y. Dual mass MEMS gyroscope temperature drift compensation based on TFPF-MEA-BP algorithm. Sens. Rev. 2021, 41, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, M.; Gao, J.; Li, A.; Zhang, X.; Shen, C.; Cao, H. Micromechanical gyroscope temperature compensation based on combined LSTM-SVM-DBN algorithm. Sens. Actuators Phys. 2024, 369, 115128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1431-2004; IEEE Standard Specification Format Guide and Test Procedure for Coriolis Vibratory Gyros. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 1–78. [CrossRef]
- IEEE Std 1554-2005; IEEE Recommended Practice for Inertial Sensor Test Equipment, Instrumentation, Data Acquisition, and Analysis. IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; pp. 1–145. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, L.; Yu, J.; Ren, Y.; Chen, K.; Cao, H.; Xie, H. Temperature Compensation for MEMS Accelerometer Based on a Fusion Algorithm. Micromachines 2024, 15, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
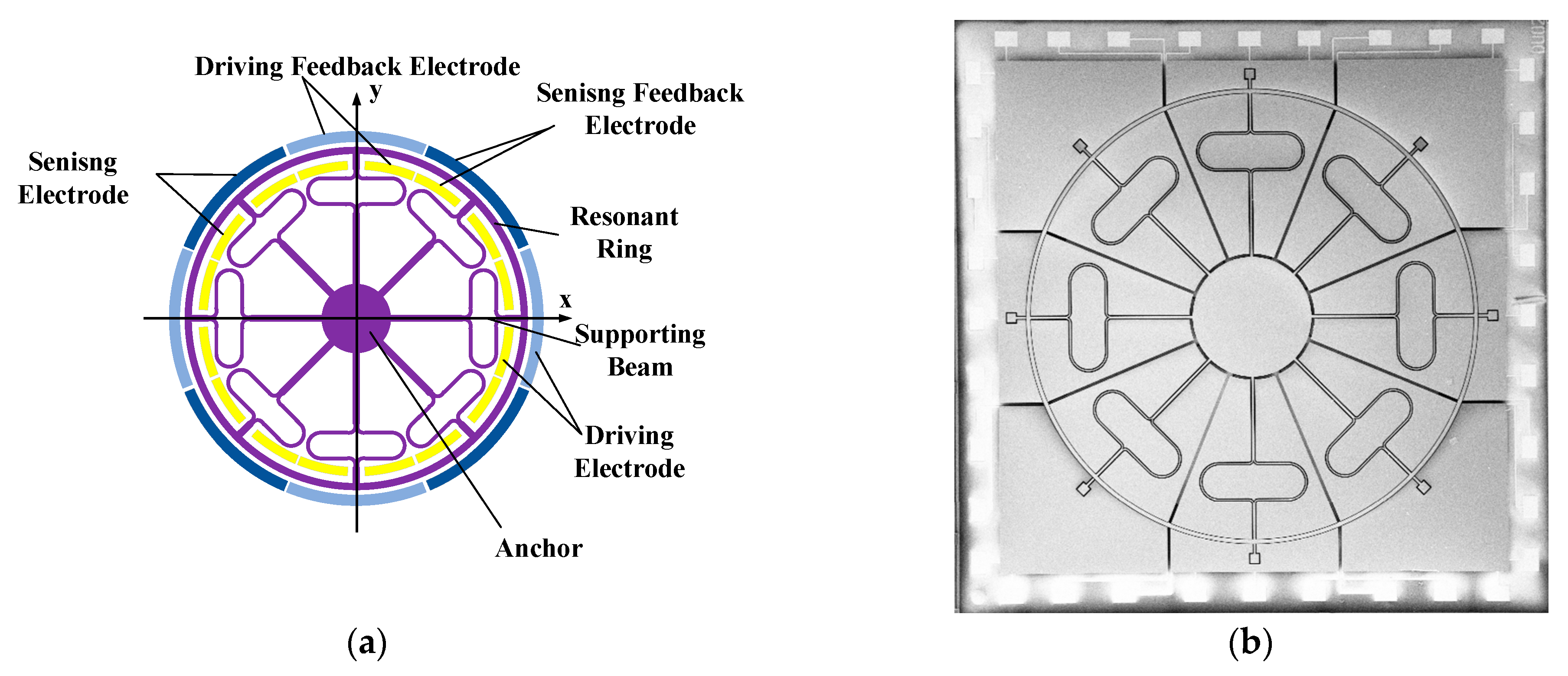




| Parameter | Characteristic | Parameter | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| ra | Radius of anchor | Rr | Radius of resonant ring |
| l1 | Length of straight beam i | b | Width of beam ii, iii, iv, v, vi |
| r1 | Radius of curved beam ii, v | 2b | Width of beam i, vii |
| l2 | Length of straight beam iii, vi | br | Width of the resonant ring |
| r2 | Radius of curved beam iv | h | Thickness of the structural |
| l3 | Length of straight beam vii | d | Electrode gap |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| pop | Population Size |
| dim | Particle Dimension |
| [lb,ub] | Particle Position Boundaries |
| [vmin,vmax] | Particle Velocity Boundaries |
| c1 = c2 | Learning Factor |
| Data | Mean Absolute Error (MAE) | Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) |
|---|---|---|
| raw data | 0.4301 | 0.7634 |
| PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF | 0.0096 | 0.0440 |
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| pop | Population Size |
| dim | Particle Dimension |
| [lb,ub] | Particle Position Boundaries |
| maxgen | Number of Iterations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, H.; Ye, W.; Liu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, H. Temperature Compensation Method for MEMS Ring Gyroscope Based on PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF and FTTA-LSTM. Micromachines 2025, 16, 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050507
Huang H, Ye W, Liu L, Wang W, Wang Y, Cao H. Temperature Compensation Method for MEMS Ring Gyroscope Based on PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF and FTTA-LSTM. Micromachines. 2025; 16(5):507. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050507
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Hongqiao, Wen Ye, Li Liu, Wenjing Wang, Yan Wang, and Huiliang Cao. 2025. "Temperature Compensation Method for MEMS Ring Gyroscope Based on PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF and FTTA-LSTM" Micromachines 16, no. 5: 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050507
APA StyleHuang, H., Ye, W., Liu, L., Wang, W., Wang, Y., & Cao, H. (2025). Temperature Compensation Method for MEMS Ring Gyroscope Based on PSO-TVFEMD-SE-TFPF and FTTA-LSTM. Micromachines, 16(5), 507. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi16050507







