Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Myeloma Cells Cultured in a Three-Dimensional, Reconstructed Bone Marrow Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MM Cells Cultured in 3D Form Large Clusters
2.2. STAT3 Activity in MM Cells is Increased in 3D Culture
2.3. STAT3 Activation in MM-3D Cells Is Dependent on the 3D Environment
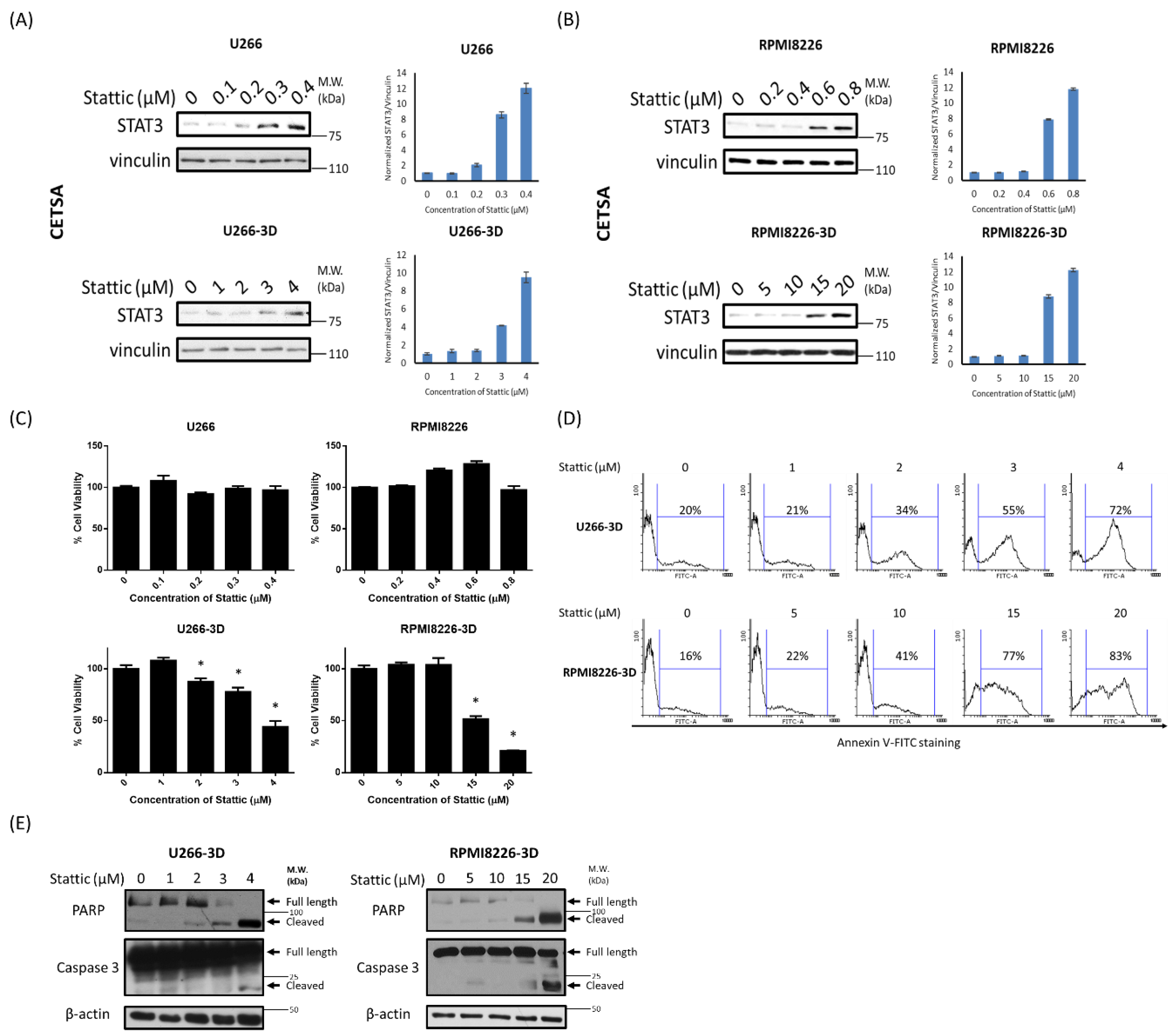
2.4. STAT3 Inhibition Is Effective in Decreasing Cell Growth of MM-3D Cells
2.5. STAT3 Inhibition Sensitizes MM-3D Cells to Bortezomib
2.6. Gene Expression Profiling in MM-3D Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines, Patient Samples and Materials
4.2. 3D Culture
4.3. Preparation of Cells for Immunocytochemistry
4.4. DNA Pulldown Assay
4.5. Cellular Thermal Shift Assay (CETSA)
4.6. Cell Viability and Apoptosis Assays
4.7. Oligonucleotide Array
4.8. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Kievit, F.M.; Erickson, A.E.; Silber, J.R.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Zhang, M. Culture on 3D chitosan-hyaluronic acid scaffolds enhances stem cell marker expression and drug resistance in human glioblastoma cancer stem cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 3173–3181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, E.K.F.; Darling, E.M.; Kulangara, K.; Guilak, F.; Leong, K.W. Nanotopography-induced changes in focal adhesions, cytoskeletal organization, and mechanical properties of human mesenchymal stem cells. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1299–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Spagnoli, G.C.; Martin, I.; Ploegert, S.; Demougin, P.; Heberer, M.; Reschner, A. Three-dimensional culture of melanoma cells profoundly affects gene expression profile: A high density oligonucleotide array study. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 204, 522–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischbach, C.; Chen, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Schmelzle, T.; Brugge, J.S.; Polverini, P.J.; Mooney, D.J. Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Roman, N.; Stevenson, K.; Gilmour, L.; Hamilton, G.; Chalmers, A.J. A novel 3D human glioblastoma cell culture system for modeling drug and radiation responses. Neuro. Oncol. 2016, 17, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gozzetti, A.; Candi, V.; Papini, G.; Bocchia, M. Therapeutic advancements in multiple myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, N. Epidemiology of multiple myeloma. In Recent Results in Cancer Research; Moehler, T., Goldschmidt, H., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; Volume 183, pp. 25–35. ISBN 9783540857716. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Buadi, F.K.; Zeldenrust, S.R.; Dingli, D.; Russell, S.J.; Lust, J.A.; et al. Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood 2008, 111, 2516–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankbar, B.; Padró, T.; Leo, R.; Feldmann, B.; Kropff, M.; Mesters, R.M.; Serve, H.; Berdel, W.E.; Kienast, J. Vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin-6 in paracrine tumor-stromal cell interactions in multiple myeloma. Blood 2000, 95, 2630–2636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Menu, E.; Asosingh, K.; Van Riet, I.; Croucher, P.; Van Camp, B.; Vanderkerken, K. Myeloma cells (5TMM) and their interactions with the marrow microenvironment. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2004, 33, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, A.W.; Huang, Y.W.; Zhang, B.Q.; Netto, G.; Vitetta, E.S.; Stone, M.J. Heterotransplantation of human multiple myeloma cell lines in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. Anticancer Res. 1993, 13, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calimeri, T.; Battista, E.; Conforti, F.; Neri, P.; Di Martino, M.T.; Rossi, M.; Foresta, U.; Piro, E.; Ferrara, F.; Amorosi, A.; et al. A unique three-dimensional SCID-polymeric scaffold (SCID-synth-hu) model for in vivo expansion of human primary multiple myeloma cells. Leukemia 2011, 25, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrarini, M.; Mazzoleni, G.; Steimberg, N.; Belloni, D.; Ferrero, E. Innovative models to assess multiple myeloma biology and the impact of drugs. InTech 2013, 39–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrarini, M.; Steimberg, N.; Ponzoni, M.; Belloni, D.; Berenzi, A.; Girlanda, S.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Mazzoleni, G.; Ferrero, E. Ex-Vivo dynamic 3-D culture of human tissues in the RCCSTM bioreactor allows the study of multiple myeloma biology and response to therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Puente, P.; Muz, B.; Gilson, R.C.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; King, J.; Achilefu, U.; Vij, R.; Azab, A.K. 3D tissue-engineered bone marrow as a novel model to study pathophysiology and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirshner, J.; Thulien, K.J.; Martin, L.D.; Debes Marun, C.; Reiman, T.; Belch, A.R.; Pilarski, L. A unique three-dimensional model for evaluating the impact of therapy on multiple myeloma. Blood 2008, 112, 2935–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parikh, M.R.; Belch, A.R.; Pilarski, L.M.; Kirshner, J. A Three-dimensional tissue culture model to study primary human bone marrow and its malignancies. J. Vis. Exp. 2014, e50947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Veirman, K.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Lub, S.; De Beule, N.; Thielemans, K.; Bautmans, I.; Oyajobi, B.O.; De Bruyne, E.; Menu, E.; Lemaire, M. Multiple myeloma induces Mcl-1 expression and survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10532–10547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romagnoli, M.; Séveno, C.; Wuillème-Toumi, S.; Amiot, M.; Bataille, R.; Minvielle, S.; Barillé-Nion, S. The imbalance between Survivin and Bim mediates tumour growth and correlates with poor survival in patients with multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 145, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spets, H.; Stromberg, T.; Georgii-Hemming, P.; Siljason, J.; Nilsson, K.; Jernberg-Wiklund, H. Expression of the bcl-2 family of pro- and anti-apoptotic genes in multiple myeloma and normal plasma cells. Regulation during interleukin-6 (IL-6)-induced growth and survival. Eur. J. Haematol. 2002, 69, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.D.; Baladandayuthapani, V.; Lin, H.; Mulligan, G.; Li, B.-Z.; Esseltine, D.L.W.; Qi, L.; Xu, J.; Hunziker, W.; Barlogie, B.; et al. Tight jnction protein 1 modulates proteasome capacity and proteasome inhibitor sensitivity in multiple myeloma via EGFR/JAK1/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, A.C.; Shishodia, S.; Reuben, J.M.; Weber, D.; Alexanian, R.; Raj-Vadhan, S.; Estrov, Z.; Talpaz, M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Nuclear factor–κB and STAT3 are constitutively active in CD138 + cells derived from multiple myeloma patients, and suppression of these transcription factors leads to apoptosis. Blood 2004, 103, 3175–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Galletti, S.; Garavelli, S.; Platonova, N.; Paoli, A.; Basile, A.; Taiana, E.; Neri, A.; Chiaramonte, R. Notch signaling deregulation in multiple myeloma: A rational molecular target. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26826–26840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezieau, S.; Devilder, M.-C.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Mellerin, M.-P.; Puthier, D.; Pennarun, E.; Rapp, M.J.; Harousseau, J.L.; Moisan, J.P.; Bataille, R. High incidence of N and K-Ras activating mutations in multiple myeloma and primary plasma cell leukemia at diagnosis. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 18, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Leong, T.; Quam, L.; Billadeau, D.; Kay, N.E.; Greipp, P.; Van ness, B. Activating mutations of N- and K-ras in multiple myeloma show different clinical associations: Analysis of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Phase III Trial. Blood 1996, 88, 2699–2706. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, M.; Cao, B.; Hou, T.; Mao, X. Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 21, 3173–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinbrunn, T.; Stühmer, T.; Gattenlöhner, S.; Rosenwald, A.; Mottok, A.; Unzicker, C.; Einsele, H.; Chatterjee, M.; Bargou, R.C. Mutated RAS and constitutively activated Akt delineate distinct oncogenic pathways, which independently contribute to multiple myeloma cell survival. Blood 2011, 117, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuchs, O. Targeting of NF-kappaB signaling pathway, other signaling pathways and epigenetics in therapy of multiple myeloma. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2013, 13, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Medeiros, L.J.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Yared, M.A.; Tsioli, P.; Leventaki, V.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Herling, M.; Amin, H.M.; Lai, R. Differential expression and clinical significance of tyrosine-phosphorylated STAT3 in ALK+ and ALK− anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 3692–3699. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kolosenko, I.; Grandér, D.; Tamm, K.P. IL-6 activated JAK/STAT3 pathway and sensitivity to Hsp90 inhibitors in multiple myeloma. Curr. Med. Chem. 2014, 46, 3042–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Liu, J.; Yang, M.; Huang, N.; Zhong, Y.; Zeng, T.; Wei, R.; Wu, Z.; Xiao, C.; Cao, X.; et al. Cucurbitacin B exerts anti-cancer activities in human multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo by modulating multiple cellular pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5800–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenne, A.-T.; Ro, T.B.; Waage, A.; Sundan, A.; Borset, M.; Hjorth-Hansen, H. Interleukin-21 is a growth and survival factor for human myeloma cells. Blood 2002, 99, 3756–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schust, J.; Sperl, B.; Hollis, A.; Mayer, T.U.; Berg, T. Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and dimerization. Chem. Biol. 2006, 13, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafari, R.; Almqvist, H.; Axelsson, H.; Ignatushchenko, M.; Lundbäck, T.; Nordlund, P.; Martinez Molina, D. The cellular thermal shift assay for evaluating drug target interactions in cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2100–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Farach-Carson, M.C.; Jia, X. Three-dimensional in vitro tumor models for cancer research and drug evaluation. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 1256–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, R.; Broglie, J.J.; Adcock, A.F.; Yang, L. Three-dimensional cell culture systems and their applications in drug discovery and cell-based biosensors. Assay Drug Dev. Technol. 2014, 12, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, V.M.; Petersen, O.W.; Wang, F.; Larabell, C.A.; Briand, P.; Damsky, C.; Bissell, M.J. Reversion of the malignant phenotype of human breast cells in three-dimensional culture and in vivo by integrin blocking antibodies. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 137, 231–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lee, W.Y.; Siegel, D.S.; Tolias, P.; Zilberberg, J. Patient-specific 3D microfluidic tissue model for multiple myeloma. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2014, 20, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastinne, T.; Leleu, X.; Duhamel, A.; Moreau, A.S.; Franck, G.; Andrieux, J.; Lai, J.L.; Coiteux, V.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Bauters, F.; et al. Plasma cell growth fraction using Ki-67 antigen expression identifies a subgroup of multiple myeloma patients displaying short survival within the ISS stage I. Eur. J. Haematol. 2007, 79, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Di Liberto, M.; Jayabalan, D.; Liang, J.; Ely, S.; Bretz, J.; Shaffer, A.L.; Louie, T.; Chen, I.; Randolph, S.; et al. Prolonged early G 1 arrest by selective CDK4/CDK6 inhibition sensitizes myeloma cells to cytotoxic killing through cell cycle-coupled loss of IRF4. Blood 2012, 120, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catley, L.; Weisberg, E.; Kiziltepe, T.; Tai, Y.T.; Hideshima, T.; Neri, P.; Tassone, P.; Atadja, P.; Chauhan, D.; Munshi, N.C.; et al. Aggresome induction by proteasome inhibitor bortezomib and alpha-tubulin hyperacetylation by tubulin deacetylase (TDAC) inhibitor LBH589 are synergistic in myeloma cells. Blood 2006, 108, 3441–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, P.G.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Schlossman, R.L.; Munshi, N.C.; Wen, P.; Briemberg, H.; Kuter, D.; Oaklander, A.-L.; Lonial, S.; Hassoun, H.; et al. Phase II trial of single agent bortezomib (VELCADE®) in patients with previously untreated multiple myeloma (MM). Blood 2004, 104, 336. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, P.G.; Barlogie, B.; Berenson, J.; Singhal, S.; Jagannath, S.; Irwin, D.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Srkalovic, G.; Alsina, M.; Alexanian, R.; et al. A phase 2 study of bortezomib in relapsed, refractory myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nierste, B.A.; Gunn, E.J.; Whiteman, K.R.; Lutz, R.J.; Kirshner, J. Maytansinoid immunoconjugate IMGN901 is cytotoxic in a three-dimensional culture model of multiple myeloma. Am. J. Blood Res. 2016, 6, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gunn, E.J.; Williams, J.T.; Huynh, D.T.; Iannotti, M.J.; Han, C.; Barrios, F.J.; Kendall, S.; Glackin, C.A.; Colby, D.A.; Kirshner, J. The natural products parthenolide and andrographolide exhibit anti-cancer stem cell activity in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, M.C.; Jeong, H.; Son, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Han, D.; Goughnour, P.C.; Kang, T.; Kwon, N.H.; Moon, H.E.; Paek, S.H.; et al. Novel morphologic and genetic analysis of cancer cells in a 3D microenvironment identifies STAT3 as a regulator of tumor permeability barrier function. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-F.; Lai, R. STAT3 in cancer-friend or foe? Cancers 2014, 6, 1408–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, D.E.; Lee, C. What does Stat3 do? J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.F.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Devgan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Albanese, C.; Darnell, J.E. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell 1999, 98, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bommert, K.; Bargou, R.C.; Stühmer, T. Signalling and survival pathways in multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siveen, K.S.; Sikka, S.; Surana, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.P.; Tan, B.K.H.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 136–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K.C. Molecular mechanisms of novel therapeutic approaches for multiple myeloma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 927–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, S.; Brancalion, A.; Mandato, E.; Tubi, L.Q.; Colpo, A.; Pizzi, M.; Cappellesso, R.; Zaffino, F.; Di Maggio, S.A.; Cabrelle, A.; et al. Protein kinase CK2 inhibition down modulates the NF-κB and STAT3 survival pathways, enhances the cellular proteotoxic stress and synergistically boosts the cytotoxic effect of bortezomib on multiple myeloma and mantle cell Lymphoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.; Yang, S.; Weatherburn, C.; Gibson, J.; Ho, P.J.; Suen, H.; Hart, D.; Joshua, D. Phospho-flow detection of constitutive and cytokine-induced pSTAT3/5, pAKT and pERK expression highlights novel prognostic biomarkers for patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2015, 29, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Shi, M.; Xia, D.; Zhao, K.; Zeng, L.; Yao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Niu, M.; et al. Piperlongumine induces apoptosis and reduces bortezomib resistance by inhibiting STAT3 in multiple myeloma cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 73497–73508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Peng, H.; Luo, Y.; Deng, M.; Li, R.; Dai, C.; Xu, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Icaritin suppresses multiple myeloma, by inhibiting IL-6/JAK2/STAT3. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10460–10472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Benson, D.M.; Deangelis, S.; Bakan, C.E.; Li, P.K.; Li, C.; Lin, J. A small molecule, LLL12 inhibits constitutive STAT3 and IL-6-induced STAT3 signaling and exhibits potent growth suppressive activity in human multiple myeloma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, S.-H.; Ahn, S.; Choi, H.-W.; Shin, M.-G.; Lee, S.; Yang, D.-H.; Ahn, J.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.J. STAT3 expression is associated with poor survival in non-elderly adult patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood Res. 2017, 52, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, A.; Ito, A.; Iitsuka, H.; Tsuneyama, K.; Miyazono, T.; Murakami, J.; Shibahara, N.; Sakurai, H.; Saiki, I.; Nakayama, T.; et al. Role of chemokine CX3CL1 in progression of multiple myeloma via CX3CR1 in bone microenvironments. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2935–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shain, K.H.; Yarde, D.N.; Meads, M.B.; Huang, M.; Jove, R.; Hazlehurst, L.A.; Dalton, W.S. Beta-1 integrin adhesion enhances IL-6-mediated STAT3 signaling in myeloma cells: Implications for microenvironment influence on tumor survival and proliferation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Yan, F.; Zhao, D.; Lv, M.; Liang, X.; Dai, H.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, J.; Sun, X.; et al. Reelin promotes the adhesion and drug resistance of multiple myeloma cells via integrin β1 signaling and STAT3. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9844–9858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rozovski, U.; Grgurevic, S.; Bueso-Ramos, C.; Harris, D.M.; Li, P.; Liu, Z.; Wu, J.Y.; Jain, P.; Wierda, W.; Burger, J.; et al. Aberrant LPL expression, driven by STAT3, mediates free fatty acid metabolism in CLL cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 944–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaner, D.E.; Lee, E.; Shi, Y.; Wen, F.; Li, Y.; Tung, S.; Gary-Gouy, H.; Dalloul, A.; Ceddia, R.; Gorzcynski, R. PPAR-alpha is a therapeutic target for chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1090–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloni, D.; Marcatti, M.; Ponzoni, M.; Ciceri, F.; Veschini, L.; Corti, A.; Caligaris Cappio, F.; Ferrarini, M.; Ferrero, E. Angiopoietin-2 in bone marrow milieu promotes multiple myeloma-associated angiogenesis. Exp. Cell Res. 2015, 330, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Tang, J.; Jiang, J.; Chen, Z. New insights into the roles of CHOP-induced apoptosis in ER stress. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 629–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canino, C.; Luo, Y.; Marcato, P.; Blandino, G.; Pass, H.I.; Cioce, M. A STAT3-NFkB/DDIT3/CEBPβ axis modulates ALDH1A3 expression in chemoresistant cell subpopulations. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12637–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| IL6 | 5′-TCCAGTTGCCTTCTTGGGAC-3′ | 5′-GTACTCCAGAAGACCAGAGG-3′ |
| IL21 | 5′-TGTGAATGACTTGGTCCCTGAA-3′ | 5′-AACAGGAAAAAGCTGACCAC-3′ |
| IL10 | 5′-GCCTAACATGCTTCGAGATC-3′ | 5′-TGATGTCTGGGTCTTGGTTC-3′ |
| LPL | 5′-ACAAGAGAGAACCAGACTCCAA-3′ | 5′-GCGGACACTGGGTAATGCT-3′ |
| ANGPT2 | 5′-AACTTTCGGAAGAGCATGGAC-3′ | 5′-CGAGTCATCGTATTCGAGCGG-3′ |
| DDIT3 | 5′-GGAAACAGAGTGGTCATTCCC-3′ | 5′-CTGCTTGAGCCGTTCATTCTC-3′ |
| CA9 | 5′-GGATCTACCTACTGTTGAGGCT-3′ | 5′-CATAGCGCCAATGACTCTGGT-3′ |
| GAPDH | 5′-GGTCTCCTCTGACTTCAACAGCG-3′ | 5′-ACCACCCTGTTGCTGTAGCCAA-3′ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-H.; Molavi, O.; Alshareef, A.; Haque, M.; Wang, Q.; Chu, M.P.; Venner, C.P.; Sandhu, I.; Peters, A.C.; Lavasanifar, A.; et al. Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Myeloma Cells Cultured in a Three-Dimensional, Reconstructed Bone Marrow Model. Cancers 2018, 10, 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060206
Huang Y-H, Molavi O, Alshareef A, Haque M, Wang Q, Chu MP, Venner CP, Sandhu I, Peters AC, Lavasanifar A, et al. Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Myeloma Cells Cultured in a Three-Dimensional, Reconstructed Bone Marrow Model. Cancers. 2018; 10(6):206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060206
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yung-Hsing, Ommoleila Molavi, Abdulraheem Alshareef, Moinul Haque, Qian Wang, Michael P. Chu, Christopher P. Venner, Irwindeep Sandhu, Anthea C. Peters, Afsaneh Lavasanifar, and et al. 2018. "Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Myeloma Cells Cultured in a Three-Dimensional, Reconstructed Bone Marrow Model" Cancers 10, no. 6: 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060206
APA StyleHuang, Y.-H., Molavi, O., Alshareef, A., Haque, M., Wang, Q., Chu, M. P., Venner, C. P., Sandhu, I., Peters, A. C., Lavasanifar, A., & Lai, R. (2018). Constitutive Activation of STAT3 in Myeloma Cells Cultured in a Three-Dimensional, Reconstructed Bone Marrow Model. Cancers, 10(6), 206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers10060206






