Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
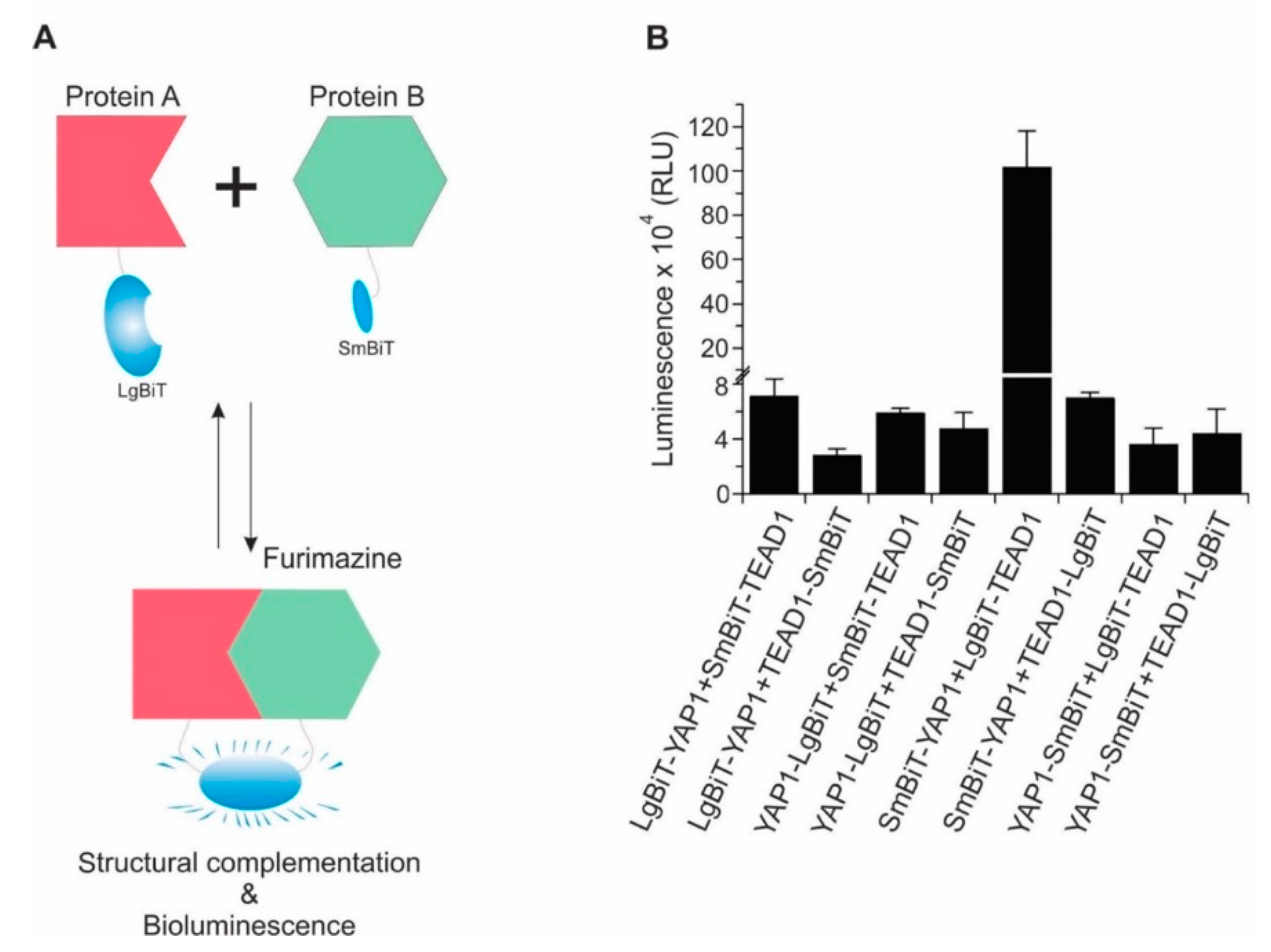
2.1. Design and Development of a Highly Sensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensor
2.2. Validation of YAP/TAZ–TEAD–BS In Vivo and In Vitro
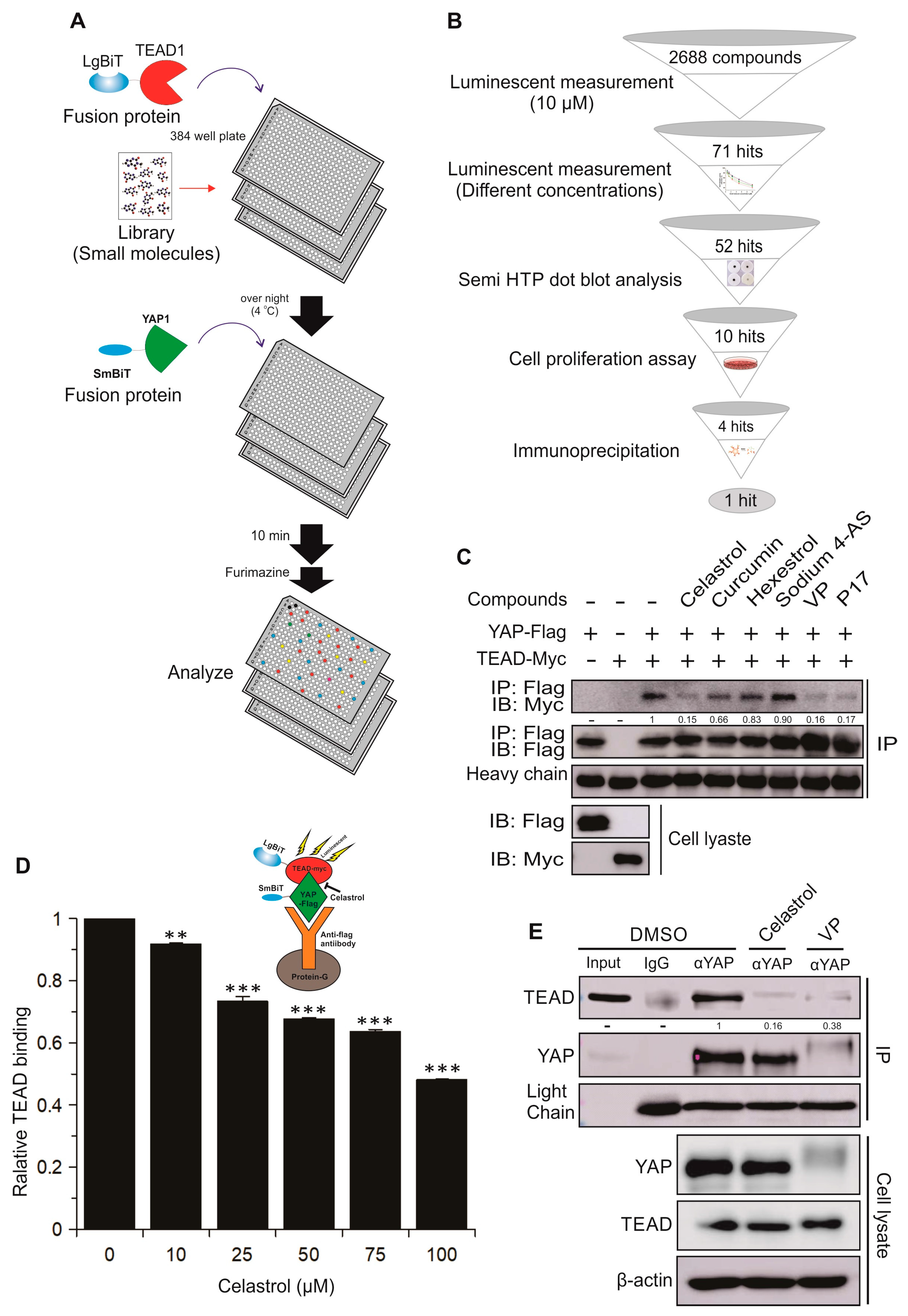
2.3. Identification and Validation of Novel Small Molecule Drugs Disrupting the YAP–TEAD Interaction Using the YAP–TEAD Biosensor
2.4. Celastrol Inhibits TEAD-Dependent Target Genes Expression, Cell Proliferation, Cell Viability, Migration, and Colony Formation in Lung and Breast Cancer Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid Construction
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. NanoLuc Luciferase (NanoBiT) Assay
4.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.5. Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Clonogenic Assay
4.7. Wound Healing Assay
4.8. Western Blotting and Antibodies
4.9. Semi HTP Dot Blot Analysis of Inhibition of Small Molecule Drugs on YAP–TEAD Interactions
4.10. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.11. Bioluminescence Imaging (BLI)
4.12. Fusion Protein Purification
4.13. Small Molecule Screen
4.14. Reporter Luciferase Assay
4.15. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR
4.16. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Yang, X. The roles of the Hippo pathway in cancer metastasis. Cell. Signal. 2016, 28, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Xu, T. Molecular mechanism of size control in development and human diseases. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, I.M.; Halder, G. Hippo-YAP/TAZ signalling in organ regeneration and regenerative medicine. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.X.; Zhao, B.; Guan, K.L. Hippo Pathway in Organ Size Control, Tissue Homeostasis, and Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 811–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zygulska, A.L.; Krzemieniecki, K.; Pierzchalski, P. Hippo pathway-brief overview of its relevance in cancer. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 311–335. [Google Scholar]
- Maugeri-Sacca, M.; De Maria, R. The Hippo pathway in normal development and cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 186, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, Y.T.; Guerrero-Castilla, A.; Cano, M.; Muñoz, M.F.; Ayala, A.; Argüelles, S. Dysregulation of the Hippo pathway signaling in aging and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 143, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Guan, K.L. The YAP and TAZ transcription co-activators: Key downstream effectors of the mammalian Hippo pathway. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, Y.; Chun, A.; Cheung, K.; Rashidi, B.; Yang, X. Tumor suppressor LATS1 is a negative regulator of oncogene YAP. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 5496–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wei, X.; Li, W.; Udan, R.S.; Yang, Q.; Kim, J.; Xie, J.; Ikenoue, T.; Yu, J.; Li, L.; et al. Inactivation of YAP oncoprotein by the Hippo pathway is involved in cell contact inhibition and tissue growth control. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, S.; Park, S.Y.; Park, H.W. Regulation of the Hippo pathway in cancer biology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 2303–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, T.; Ghahremani, M.; Yang, X. The Role of YAP and TAZ in Angiogenesis and Vascular Mimicry. Cells 2019, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taha, Z.; Janse van Rensburg, H.J.; Yang, X. The Hippo Pathway: Immunity and Cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azad, T.; Nouri, K.; Van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Maritan, S.M.; Wu, L.; Hao, Y.; Montminy, T.; Yu, J.; Khanal, P.; Mulligan, L.M.; et al. A gain-of-functional screen identifies the Hippo pathway as a central mediator of receptor tyrosine kinases during tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Hu, T.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhu, L.; Rong, Y.; Shen, H.; Luk, J.M.; et al. Targeting Hippo pathway by specific interruption of YAP-TEAD interaction using cyclic YAP-like peptides. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.K.; Cunningham, C.N. Targeting the Hippo Pathway and Cancer through the TEAD Family of Transcription Factors. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 81–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, R.; Yu, F.X. Targeting the Hippo Pathway for Anti-cancer Therapies. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 4104–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Chittenden, Y.; Huang, B.; Shim, J.S.; Chen, Q.; Lee, S.-J.; Anders, R.A.; Liu, J.O.; Pan, D. Genetic and pharmacological disruption of the TEAD-YAP complex suppresses the oncogenic activity of YAP. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1300–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ramakrishnan, S.K.; Triner, D.; Centofanti, B.; Maitra, D.; Győrffy, B.; Sebolt-Leopold, J.S.; Dame, M.K.; Varani, J.; Brenner, D.E.; et al. Tumor-selective proteotoxicity of verteporfin inhibits colon cancer progression independently of YAP1. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Yang, X. Targeting the Hippo Pathway for Breast Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel) 2018, 10, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Xie, M.; Scott, A.W.; Jin, J.; Ma, L.; Dong, X.; Skinner, H.D.; Johnson, R.L.; Ding, S.; Ajani, J.A. A Novel YAP1 Inhibitor Targets CSC-Enriched Radiation-Resistant Cells and Exerts Strong Antitumor Activity in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pobbati, A.V.; Han, X.; Hung, A.W.; Weiguang, S.; Huda, N.; Chen, G.-Y.; Kang, C.; Chia, C.S.B.; Luo, X.; Hong, W.; et al. Targeting the Central Pocket in Human Transcription Factor TEAD as a Potential Cancer Therapeutic Strategy. Structure 2015, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Shen, H.C.; Yan, S.F.; Mayweg, A.V.; Xu, Z.; Qin, N.; Wong, J.C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Structure-Based Design and Synthesis of Potent Cyclic Peptides Inhibiting the YAP-TEAD Protein-Protein Interaction. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 5, 993–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, Y.; Firer, M.; Gellerman, G. Recent Innovations in Peptide Based Targeted Drug Delivery to Cancer Cells. Biomedicines 2016, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.A.; Sessions, R.B.; Shoemark, D.K.; Williams, C.; Ebrahimighaei, R.; McNeill, M.C.; Crump, M.P.; McKay, T.R.; Harris, G.; Newby, A.C.; et al. Antiproliferative and Antimigratory Effects of a Novel YAP-TEAD Interaction Inhibitor Identified Using in Silico Molecular Docking. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnick, J.S.; Janes, J.; Kim, S.; Chang, J.Y.; Sipes, D.G.; Gunderson, D.; Jarnes, L.; Matzen, J.T.; Garcia, M.E.; Hood, T.L.; et al. An efficient rapid system for profiling the cellular activities of molecular libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3153–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smirnova, N.A.; Haskew-Layton, R.E.; Basso, M.; Hushpulian, D.M.; Payappilly, J.B.; Speer, R.E.; Ahn, Y.-H.; Rakhman, I.; Cole, P.A.; Pinto, J.T.; et al. Development of Neh2-luciferase reporter and its application for high throughput screening and real-time monitoring of Nrf2 activators. Chem. Biol. 2011, 18, 752–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Binkowski, B.F.; Butler, B.L.; Stecha, P.F.; Lewis, M.K.; Wood, K.V. Novel genetically encoded biosensors using firefly luciferase. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, D.V.; Ugarova, N.N. Firefly Luciferase-based Fusion Proteins and their Applications in Bioanalysis. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 436–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Nouri, K.; Van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Hao, Y.; Yang, X. Monitoring Hippo Signaling Pathway Activity Using a Luciferase-based Large Tumor Suppressor (LATS) Biosensor. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, 139, e58416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Lightbody, E.D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V.R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; et al. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K.; Azad, T.; Lightbody, E.; Khanal, P.; Nicol, C.J.; Yang, X. A kinome-wide screen using a NanoLuc LATS luminescent biosensor identifies ALK as a novel regulator of the Hippo pathway in tumorigenesis and immune evasion. FASEB J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Tashakor, A.; Hosseinkhani, S. Split-luciferase complementary assay: Applications, recent developments, and future perspectives. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5541–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.T., Jr.; Miller, S.C. Beyond D-luciferin: Expanding the scope of bioluminescence imaging in vivo. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.P.; Unch, J.; Binkowski, B.F.; Valley, M.P.; Butler, B.L.; Wood, M.G.; Otto, P.; Zimmerman, K.; Vidugiris, G.; Machleidt, T.; et al. Engineered luciferase reporter from a deep sea shrimp utilizing a novel imidazopyrazinone substrate. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1848–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, C.G.; Ehlerding, E.B.; Cai, W. NanoLuc: A Small Luciferase Is Brightening Up the Field of Bioluminescence. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.S.; Schwinn, M.K.; Hall, M.P.; Zimmerman, K.; Otto, P.; Lubben, T.H.; Butler, B.L.; Binkowski, B.F.; Machleidt, T.; Kirkland, T.A.; et al. NanoLuc Complementation Reporter Optimized for Accurate Measurement of Protein Interactions in Cells. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhao, B.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Dong, Z.; Yang, H.; Guan, K.-L.; Xu, Y. Structural insights into the YAP and TEAD complex. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. Targeting the Hippo pathway to improve response to chemotherapy. In Targeting Cell Survival Pathways to Enhance Response to Chemotherapy; Elsevier: London, UK, 2018; pp. 165–189. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, K.J.; Mo, J.-S.; Han, S.-H.; Park, W.-C.; Kim, H.-S.; Yun, K.-J.; Chae, S.-C.; Mo, J.; Han, S.; Park, W.; et al. MicroRNA 375 regulates proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells by suppressing the CTGF-EGFR signaling pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Mukherjee, T.; Bishayee, A. Molecular targets of celastrol in cancer: Recent trends and advancements. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 128, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, K.; Fansa, E.K.; Amin, E.; Dvorsky, R.; Gremer, L.; Willbold, D.; Schmitt, L.; Timson, D.J.; Ahmadian, M.R. IQGAP1 Interaction with RHO Family Proteins Revisited: Kinetic and Equilibrium Evidence for Multiple Distinct Binding Sites. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 26364–26376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nouri, K.; Azad, T.; Ling, M.; van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Pipchuk, A.; Shen, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X. Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensors. Cancers 2019, 11, 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101596
Nouri K, Azad T, Ling M, van Rensburg HJJ, Pipchuk A, Shen H, Hao Y, Zhang J, Yang X. Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensors. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101596
Chicago/Turabian StyleNouri, Kazem, Taha Azad, Min Ling, Helena J. Janse van Rensburg, Alexander Pipchuk, He Shen, Yawei Hao, Jianmin Zhang, and Xiaolong Yang. 2019. "Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensors" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101596
APA StyleNouri, K., Azad, T., Ling, M., van Rensburg, H. J. J., Pipchuk, A., Shen, H., Hao, Y., Zhang, J., & Yang, X. (2019). Identification of Celastrol as a Novel YAP-TEAD Inhibitor for Cancer Therapy by High Throughput Screening with Ultrasensitive YAP/TAZ–TEAD Biosensors. Cancers, 11(10), 1596. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101596





