MicroRNA 452 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing VEGFA Expression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MIR452 Expression Level in Human CRC Tissues and Cell Lines
2.2. Differential mRNA Expression Profiling of MIR452-Overexpressing Cells
2.3. Identification of the MIR452 Target Genes
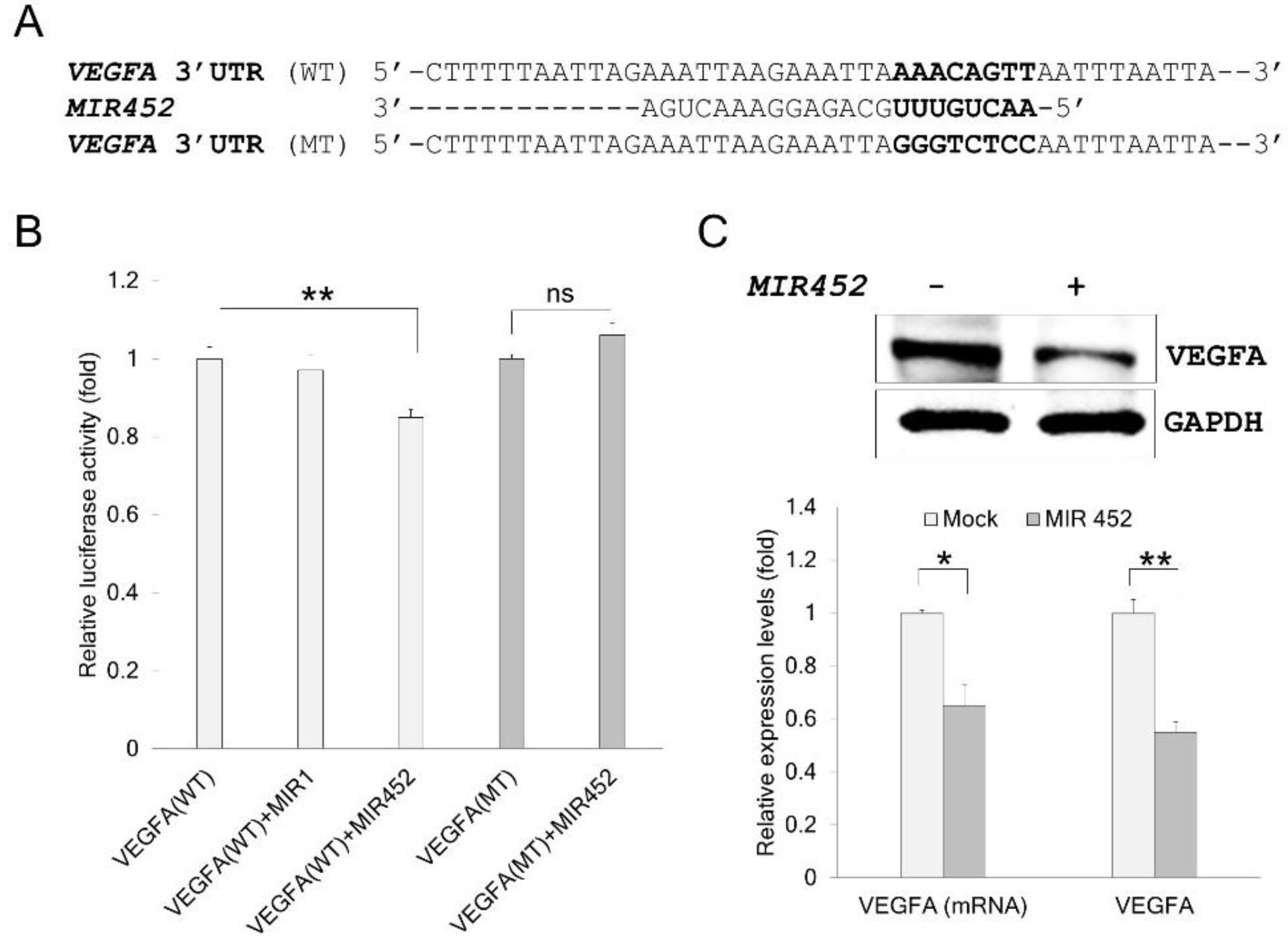
2.4. VEGFA Was a Direct Target of MIR452
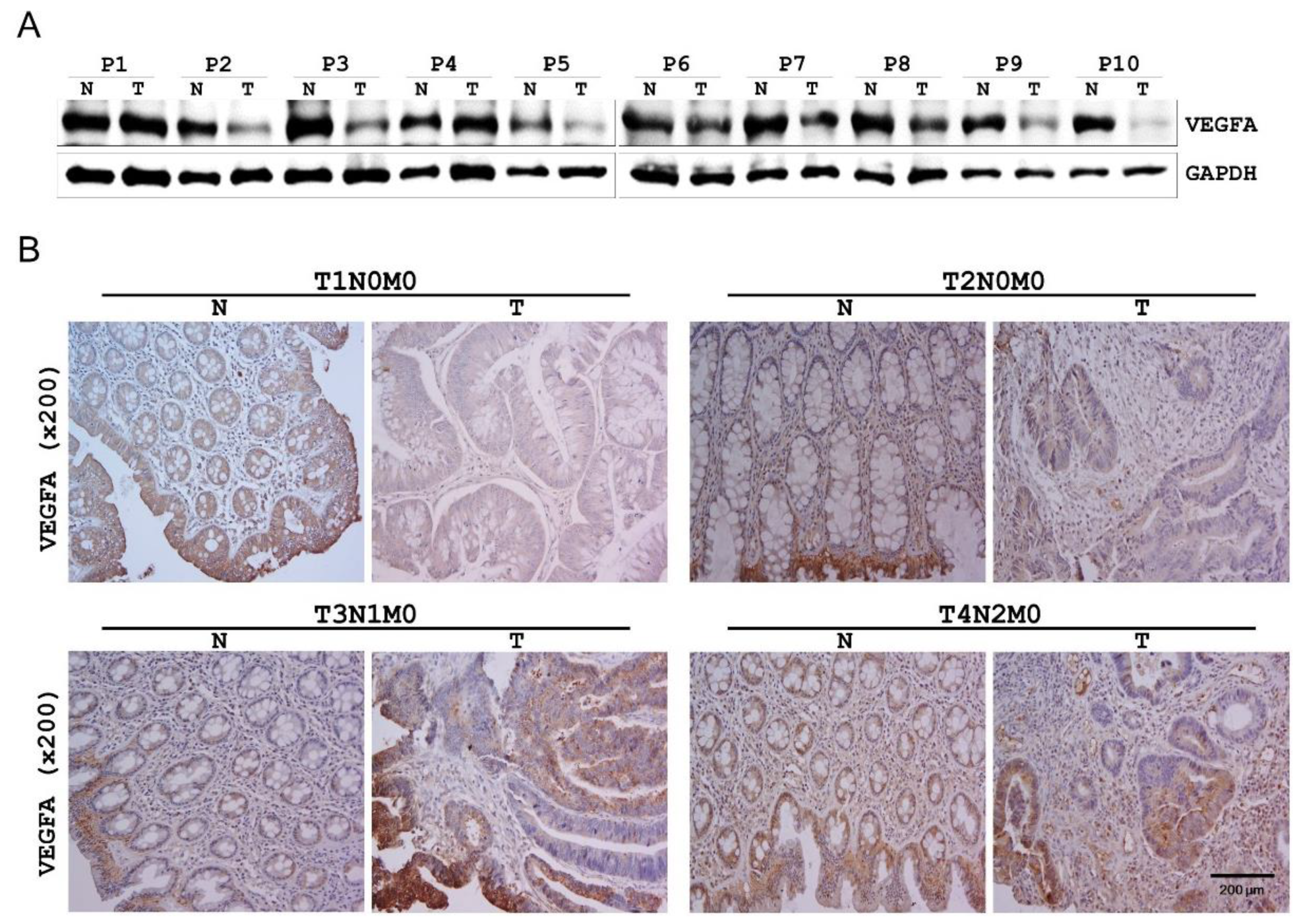
2.5. VEGFA Expression in Human CRC Tissues
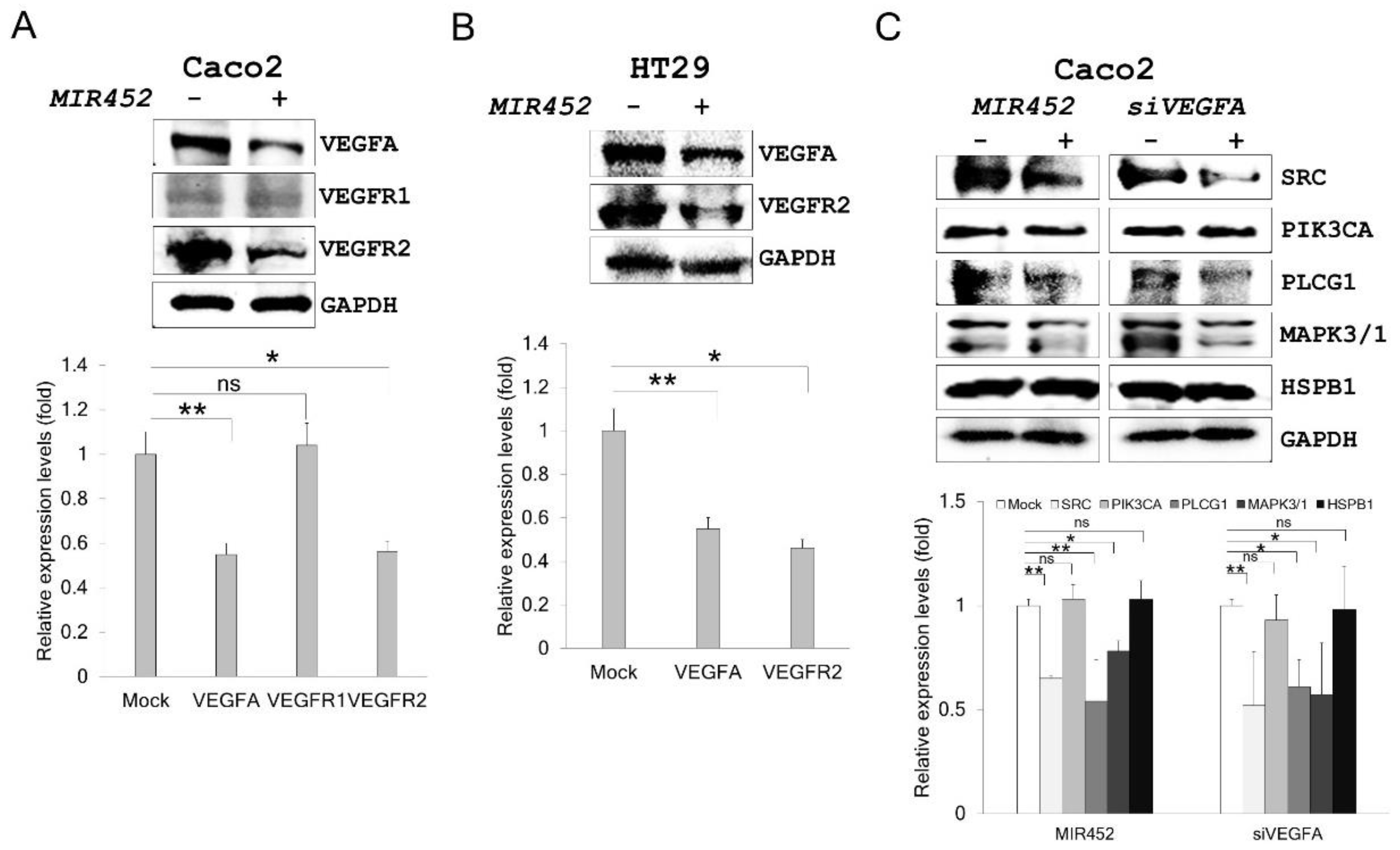
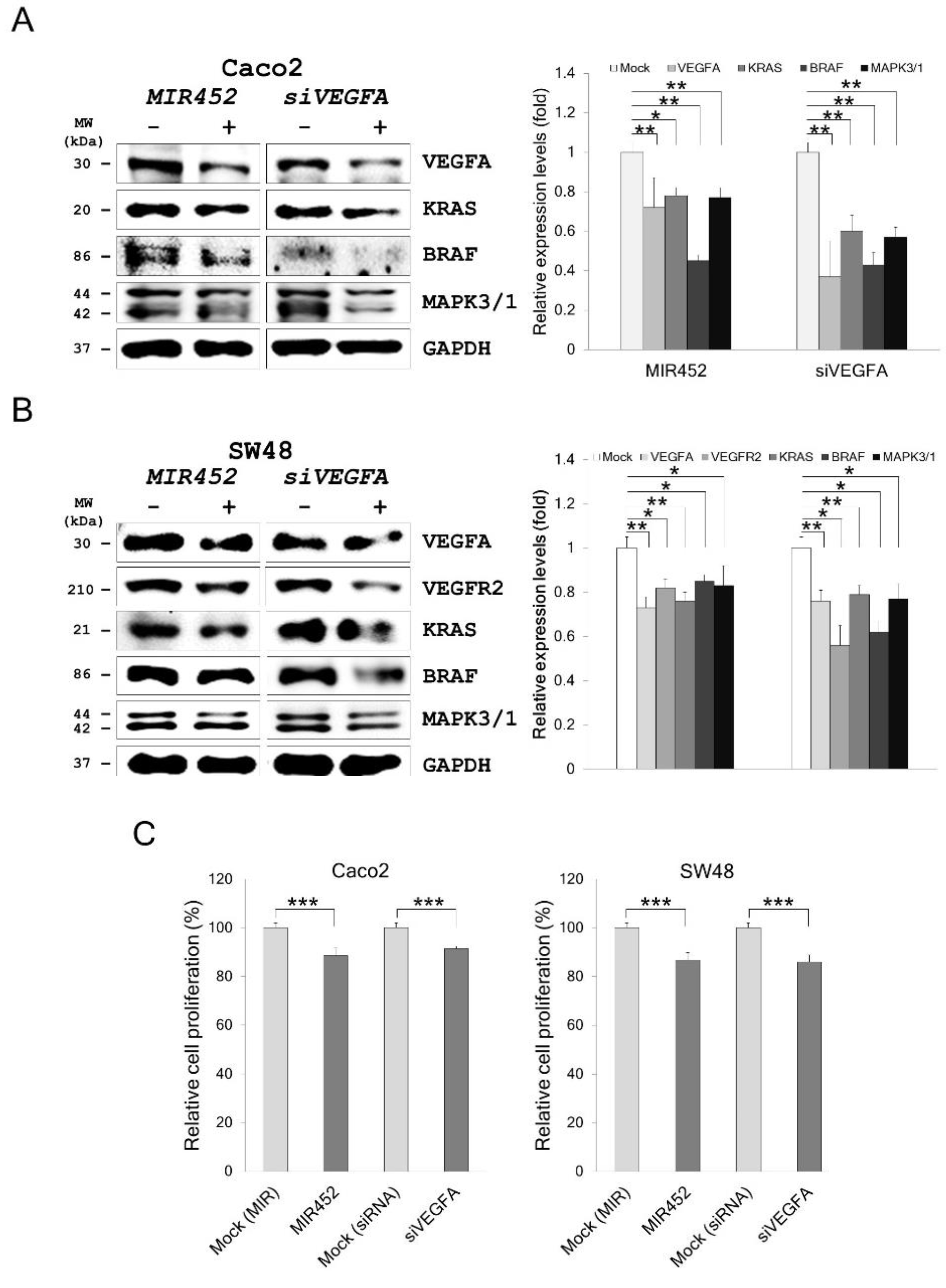
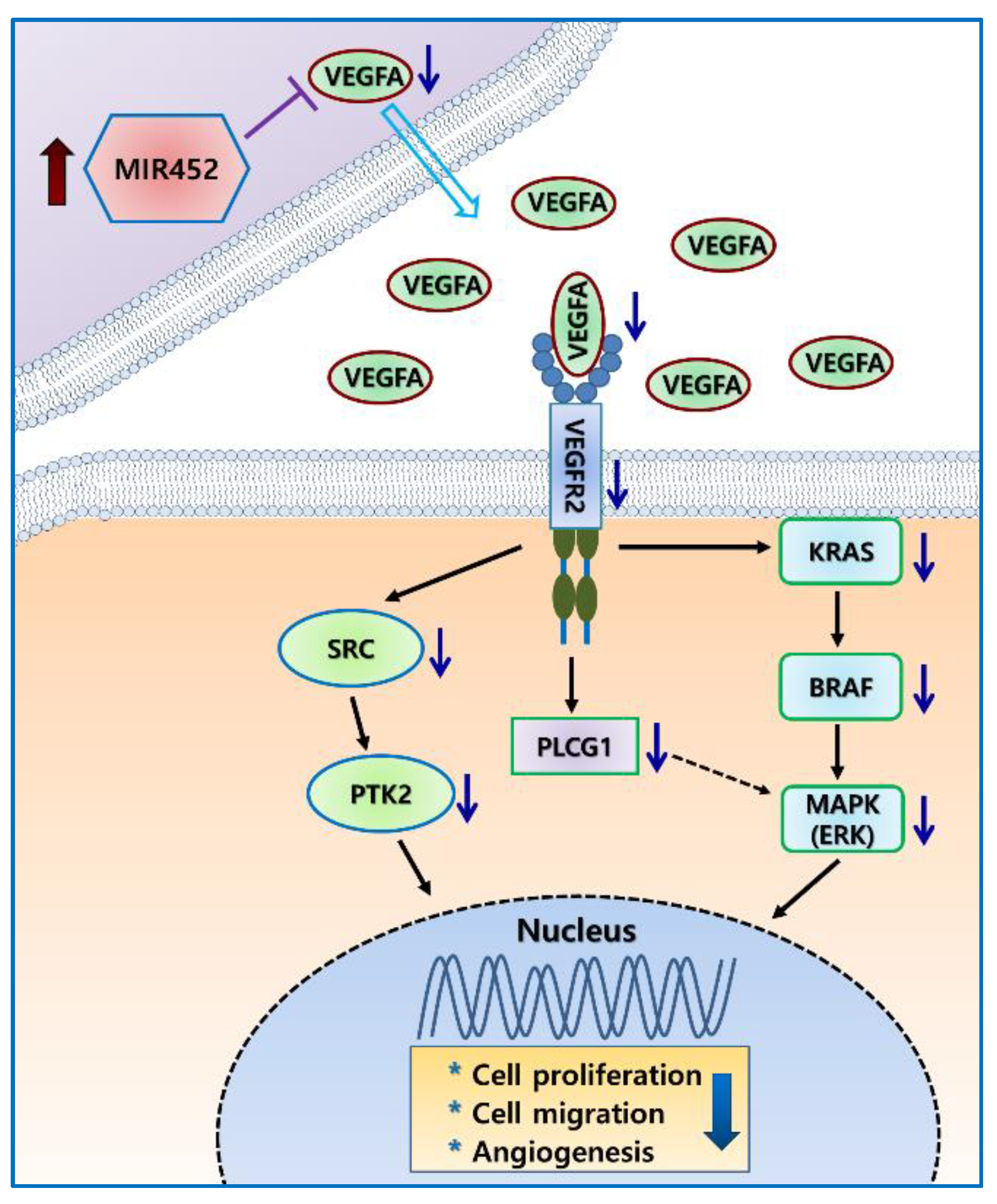
2.6. MIR452 Regulated the VEGFA–Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling Pathway in CRC Cells
2.7. MIR452 Regulated VEGFA-Mediated VEGFR2–SRC–Protein Tyrosine Kinase 2 (PTK2) Signaling
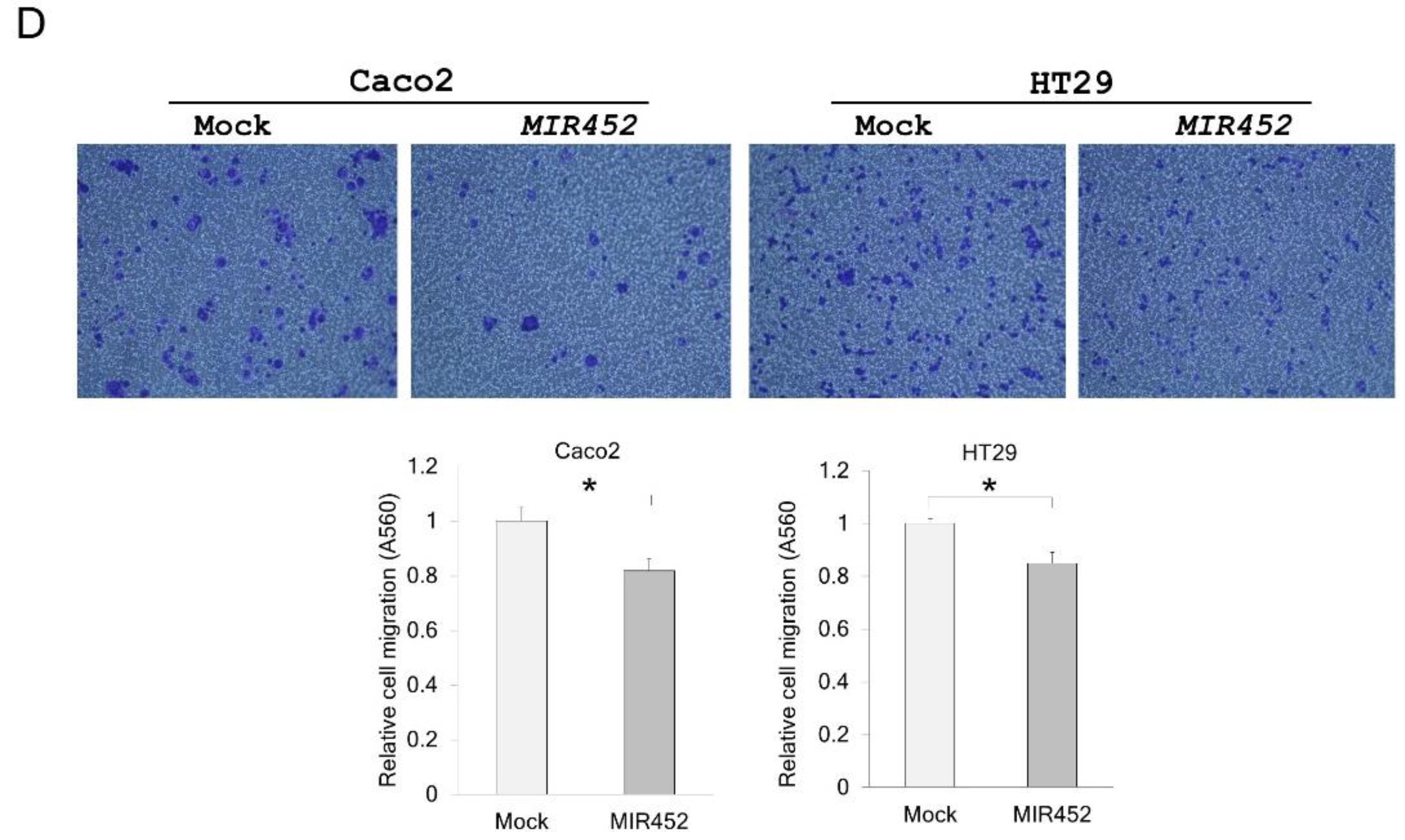
2.8. Migration of the Cells Transfected with the MIR452 Mimic or siVEGFA
2.9. MIR452 Regulated VEGFA-Mediated VEGFR2–KRAS GTPase Proto-Oncogene (KRAS)–B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase (BRAF) Signaling
2.10. MIR452 Inhibited CRC Cell Proliferation
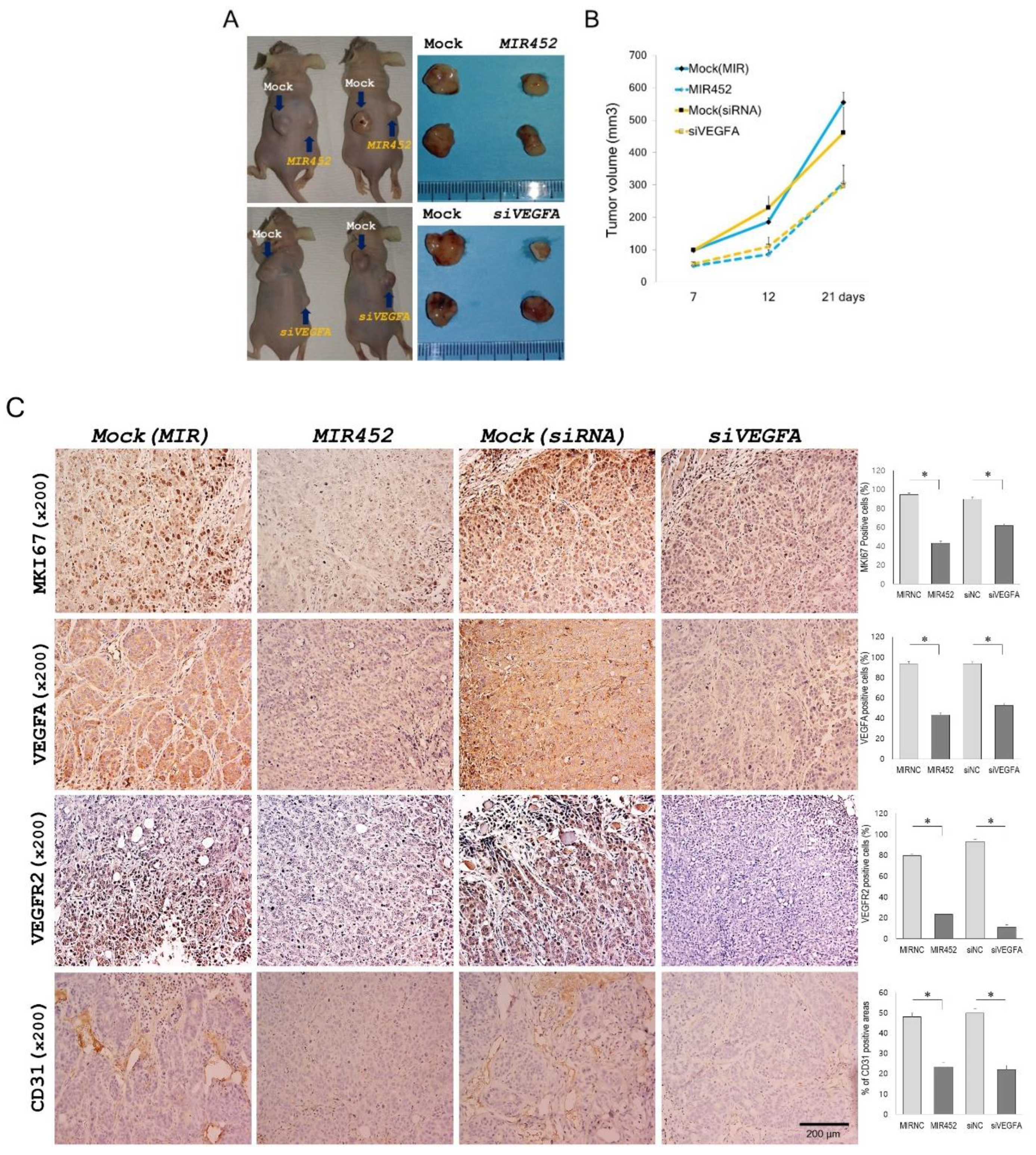
2.11. Effect of MIR452 on the Growth of Xenografted CRC Cells in Mice
2.12. Histopathology of the Tumors Derived from the Xenografts of MIR452-Transfected CRC Cells
2.13. MIR452 Inhibited Angiogenesis by VEGFA Downregulation in the Rat Aortic Ring Model
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Tissue Samples
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.4. Transfection and Oligonucleotides
4.5. Identification of the MIR452 Target Genes by mRNA Expression Profiling
4.6. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.7. MIR452 Target Prediction by Bioinformatics
4.8. Antibodies and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Transwell Migration Assays
4.10. Xenograft Model
4.11. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.12. Rat Aortic Ring Angiogenesis Assay
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O′keefe, S.J. Diet, microorganisms and their metabolites, and colon cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 691–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pit, U.; Martin, N.; Rubens, B.; Serge, H.; Elisabeth, L. Hypoxia- and microRNA-induced metabolic reprogramming of tumor-initiating cells. Cells 2019, 8, 528–543. [Google Scholar]
- Goradel, N.H.; Mohammadi, N.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Farhood, B.; Negahdari, B.; Sahebkar, A. Regulation of tumor angiogenesis by microRNAs: State of the art. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serocki, M.; Bartoszewska, S.; Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Ochocka, R.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: A novel therapeutic target. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garzon, R.; Fabbri, M.; Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression and function in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2005, 12, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, E.A.; Fridman, M.V.; Loginov, V.I.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Morozov, S.G. Molecular mechanisms in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Role of miRNAs and hypermethylated miRNA genes in crucial oncogenic pathways and processes. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.; Dasgupta, P.; Bhat, N.S.; Shahryari, V.; Shiina, M.; Hashimoto, Y.; Majid, S.; Deng, G.; Saini, S.; Tabatabai, Z.L.; et al. Elevated miR-182-5p associates with renal cancer cell mitotic arrest through diminished MALAT-1 expression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1750–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borzi, C.; Calzolari, L.; Ferretti, A.M.; Caleca, L.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G.; Fortunato, O. c-Myc shuttled by tumour-derived extracellular vesicles promotes lung bronchial cell proliferation through miR-19b and miR-92a. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Ao, X.; Liu, Y.; Ding, D.; Jiao, W.J.; Yu, Z.; Zhai, W.X.; Dong, S.H.; He, Y.Q.; Guo, H.; et al. MicroRNA-608 Promotes apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells treated with doxorubicin through the inhibition of TFAP4. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.C.; Wells, J.M.; Chow, K.H.; Huang, H.; Yuan, M.; Saxena, T.; Melnick, M.A.; Politi, K.; Asara, J.M.; Costa, D.B. miR-147b-mediated TCA cycle dysfunction and pseudohypoxia initiate drug tolerance to EGFR inhibitors in lung adenocarcinoma. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 460–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, L.; Meijer, J.; Schubert, S.; Matin, F.; Batra, J. Assessment of miR-98-5p, miR-152-3p, miR-326 and miR-4289 expression as biomarker for prostate cancer diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Al-Muftah, M.A.; Al-Kowari, M.K.; Abuaqel, S.W.J.; Al-Rumaihi, K.; Al-Bozom, I.; Li, P.; Chouchane, L. Targeting Wnt/EZH2/microRNA-708 signaling pathway inhibits neuroendocrine differentiation in prostate cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Pi, J.; Zou, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, T.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, H.; et al. microRNA arm-imbalance in part from complementary targets mediated decay promotes gastric cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Hong, L.L.; Wang, K.L.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.L.; Lei, L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Cheng, X.D.; Ling, Z.Q. Deregulation of CSMD1 targeted by microRNA-10b drives gastric cancer progression through the NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 15, 2075–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, M.; Chen, W.; Chen, T.; Tang, Q.; He, Z. microRNA-17 functions as an oncogene by downregulating Smad3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aydin, Y.; Kurt, R.; Song, K.; Lin, D.; Osman, H.; Youngquist, B.; Scott, J.W.; Shores, N.J.; Thevenot, P.; Cohen, A.; et al. Hepatic stress response in HCV infection promotes STAT3-mediated inhibition of HNF4A-miR-122 feedback loop in liver fibrosis and cancer progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Schooneveld, E.; Wouters, M.C.; Van der Auwera, I.; Peeters, D.J.; Wildiers, H.; Van Dam, P.A.; Vergote, I.; Vermeulen, P.B.; Dirix, L.Y.; Van Laere, S.J. Expression profiling of cancerous and normal breast tissues identifies microRNAs that are differentially expressed in serum from patients with (metastatic) breast cancer and healthy volunteers. Breast Cancer Res. 2012, 14, R34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, K.; Wu, J.; Shi, L.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.; Li, M.; Song, L. Downregulation of miR-452 promotes stem-like traits and tumorigenicity of gliomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3429–3438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Sheng, Q.; Jiang, C.; Shu, J.; Chen, J.; Nie, Z.; Lv, Z.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-452 promotes tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 389, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Toh, H.C.; Chow, P.; Chung, A.Y.F.; Meyers, D.J.; Cole, P.A.; Ooi, L.L.; Lee, C.G. MicroRNA-224 is upregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma through epigenetic mechanisms. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerla, S.; Lindgren, D.; Kvist, A.; Frigyesi, A.; Staaf, J.; Persson, H.; Liedberg, F.; Chebil, G.; Gudjonsson, S.; Borg, A.; et al. MiRNA expression in urothelial carcinomas: Important roles of miR-10a, miR-222, miR-125b, miR-7 and miR-452 for tumor stage and metastasis, and frequent homozygous losses of miR-31. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 2236–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.S.; Alam, K.J.; Kang, I.H.; Park, W.C.; Seo, G.S.; Choi, S.C.; Kim, H.S.; Moon, H.B.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.C. MicroRNA 196B regulates FAS-mediated apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2843–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.S.; Alam, K.J.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.C. MicroRNA 429 regulates mucin gene expression and secretion in murine model of colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2016, 10, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, D.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Danielsen, S.A.; Eknæs, M.; Hektoen, M.; Lind, G.E.; Lothe, R.A. Epigenetic and genetic features of 24 colon cancer cell lines. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibner, G.; Kimsa-Furdzik, M.; Francuz, T. Relevance of MicroRNAs as potential diagnostic and prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 27, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- To, K.K.; Tong, C.W.; Wu, M.; Cho, W.C. MicroRNAs in the prognosis and therapy of colorectal cancer: From bench to bedside. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2949–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, H.L.; Mercurio, A.M. VEGF targets the tumour cell. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibuya, M. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF) and Its Receptor (VEGFR) Signaling in Angiogenesis: A Crucial Target for Anti- and Pro-Angiogenic Therapies. Genes Cancer. 2011, 2, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, J.A.; Dvorak, A.M.; Dvorak, H.F. VEGF-A and the induction of pathological angiogenesis. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2007, 2, 251–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Bi, N.; Wu, L.; Ding, X.; Men, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Shi, S.; Song, Y.; et al. MicroRNA-29c functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting VEGFA in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Pan, J.S.; Jin, L.X.; Wu, J.; Ren, Y.D.; Chen, P.; Xiao, C.; Han, J. MicroRNA-17~92 inhibits colorectal cancer progression by targeting angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zou, C.; Pan, L.; Xu, Y.; Qi, W.; Ma, G.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, P. MicroRNA-140-5p inhibits the progression of colorectal cancer by targeting VEGFA. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 1123–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; van de Ven, R.A.H.; Zaganjor, E.; Ng, M.R.; Barakat, A.; Demmers, J.J.P.G.; Finley, L.W.S.; Gonzalez Herrera, K.N.; Hung, Y.P.; Harris, I.S. Inhibition of epithelial cell migration and Src/FAK signaling by SIRT3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7057–7062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, D.; Yao, Q.; Zhan, C.; Le-Meng, Z.; Liu, H.; Cai, Y.; Tu, C.; Li, X.; Zou, Y.; Zhang, S. MicroRNA-146a promote cell migration and invasion in human colorectal cancer via carboxypeptidase M/src-FAK pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 22674–22684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, N.; Pang, B.; Tong, D.; Sun, D.; Sun, H.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W.; Meng, X.; Bai, J.; et al. TRIB1 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion through activation MMP-2 via FAK/Src and ERK pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 47931–47942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N. VEGF in signaling and disease: Beyond discovery and development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, J.M.; Hurwitz, H.I. Understanding and targeting resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2013, 4, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Comunanza, V.; Bussolino, F. Therapy for cancer: strategy of combining anti-angiogenic and target therapies. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 5, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.J.; Mo, J.S.; Han, S.H.; Park, W.C.; Kim, H.S.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.C. MicroRNA 375 regulates proliferation and migration of colon cancer cells by suppressing the CTGF-EGFR signaling pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mo, J.S.; Han, S.H.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.C. MicroRNA 429 regulates the expression of CHMP5 in the inflammatory colitis and colorectal cancer cells. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Symbol | Accession | Gene Name | Chromosome Location | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARGLU1 | NM_018011 | arginine and glutamate rich 1 | 13q33.3 | - |
| ASB8 | NM_024095 | ankyrin repeat and SOCS box containing 8 | 12q13.11 | - |
| BCAS2 | NM_005872 | breast carcinoma amplified sequence 2 | 1p13.2 | - |
| BTF3L4 | NM_152265 | basic transcription factor 3-like 4 | 1p32.3 | - |
| CDK5R1 | NM_003885 | cyclin-dependent kinase 5, regulatory subunit 1 | 17q11.2 | neuron-specific activator |
| CLK1 | NM_004071 | CDC-like kinase 1 | 2q33 | protein kinases |
| DCUN1D1 | NM_020640 | DCN1, defective in cullin neddylation 1, domain containing 1 | 3q26.3 | - |
| FAM134B | NM_001034850 | family with sequence similarity 134, member B | 5p15.1 | transmembrane protein (Golgi) |
| FAM8A1 | NM_016255 | family with sequence similarity 8, member A1 | 6p23 | - |
| FBXW5 | NM_018998 | F-box and WD repeat domain containing 5 | 9q34.3 | ubiquitination |
| GTF2E1 | NM_005513 | general transcription factor IIE, polypeptide 1, alpha 56 kDa | 3q21-q24 | transcription factor |
| GTF2H1 | NM_005316 | general transcription factor IIH, polypeptide 1, 62 kDa | 11p15-p14 | transcription factor |
| IL20RA | NM_014432 | interleukin 20 receptor subunit alpha | 6q23.3 | cytokine receptor |
| METTL10 | NM_212554 | methyltransferase like 10 | 10q26.13 | - |
| MTFR1 | NM_014637 | mitochondrial fission regulator 1 | 8q13.1 | mitochondrial protein |
| NOL8 | NM_017948 | nucleolar protein 8 | 9p22.31 | - |
| PER2 | NM_022817 | period circadian clock 2 | 2q37.3 | - |
| PKN2 | NM_006256 | protein kinase N2 | 1p22.2 | - |
| PLEKHA1 | NM_001001974 | pleckstrin homology domain containing, family A | 10q26.13 | adapter protein |
| PPL | NM_002705 | periplakin | 16p13.3 | desmosomes component |
| SHC1 | NM_001130040 | SHC adaptor protein 1 | 1q21.3 | adapter protein |
| TAF5L | NM_001025247 | TATA-box binding protein associated factor 5 like | 1q42.13 | histone acetylase complex |
| THNSL2 | NM_018271 | threonine synthase-like 2 | 2p11.2 | threonine synthase |
| THUMPD1 | NM_017736 | THUMP domain containing 1 | 16p12.3 | - |
| TMPRSS2 | NM_005656 | transmembrane protease, serine 2 | 21q22.3 | serine protease |
| VEGFA | NM_001025366 | vascular endothelial growth factor A | 6p12 | growth factor |
| WTAP | NM_004906 | Wilms tumor 1 associated protein | 6q25-q27 | tumor suppressor gene |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mo, J.S.; Park, W.C.; Choi, S.-C.; Yun, K.J.; Chae, S.-C. MicroRNA 452 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing VEGFA Expression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101613
Mo JS, Park WC, Choi S-C, Yun KJ, Chae S-C. MicroRNA 452 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing VEGFA Expression. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101613
Chicago/Turabian StyleMo, Ji Su, Won Cheol Park, Suck-Chei Choi, Ki Jung Yun, and Soo-Cheon Chae. 2019. "MicroRNA 452 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing VEGFA Expression" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101613
APA StyleMo, J. S., Park, W. C., Choi, S.-C., Yun, K. J., & Chae, S.-C. (2019). MicroRNA 452 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Cell Migration, and Angiogenesis in Colorectal Cancer by Suppressing VEGFA Expression. Cancers, 11(10), 1613. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101613




