Size and Shape Filtering of Malignant Cell Clusters within Breast Tumors Identifies Scattered Individual Epithelial Cells as the Most Valuable Histomorphological Clue in the Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Characteristics
2.2. Prognostic Performance of the Clinicopathological Features
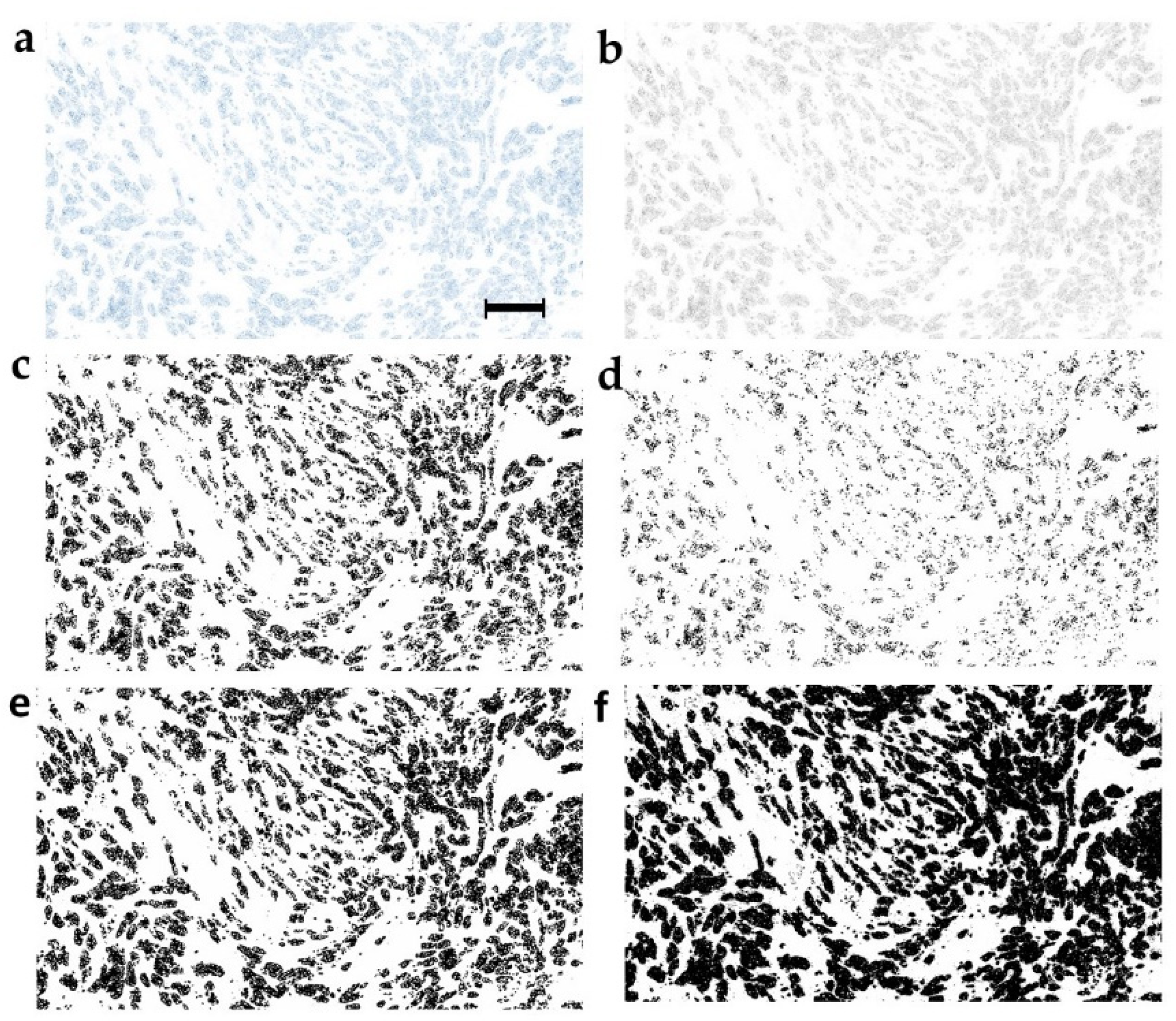
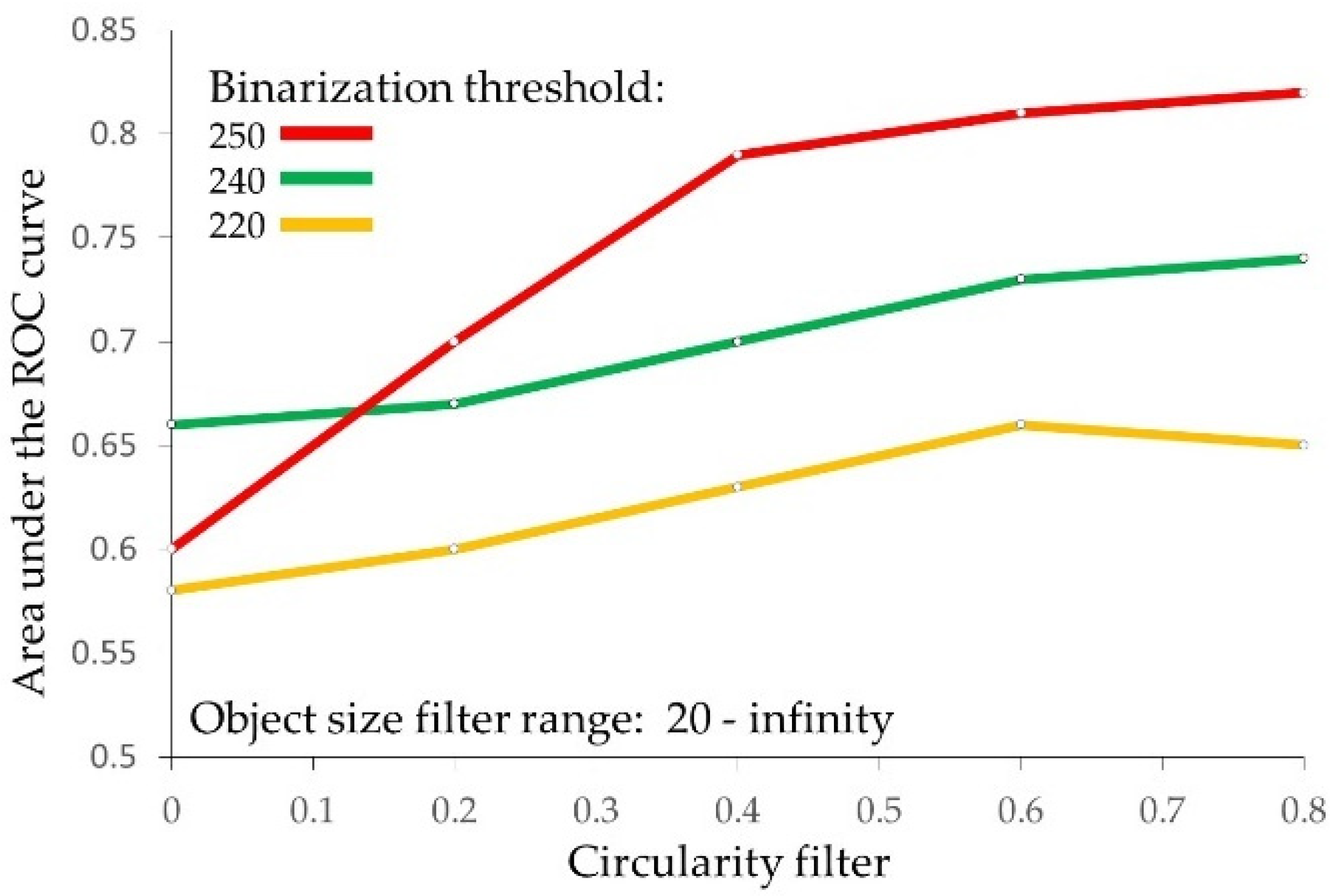
2.3. Optimization of the Image Binarization as the Strategy for Prognostic Performance Improvement
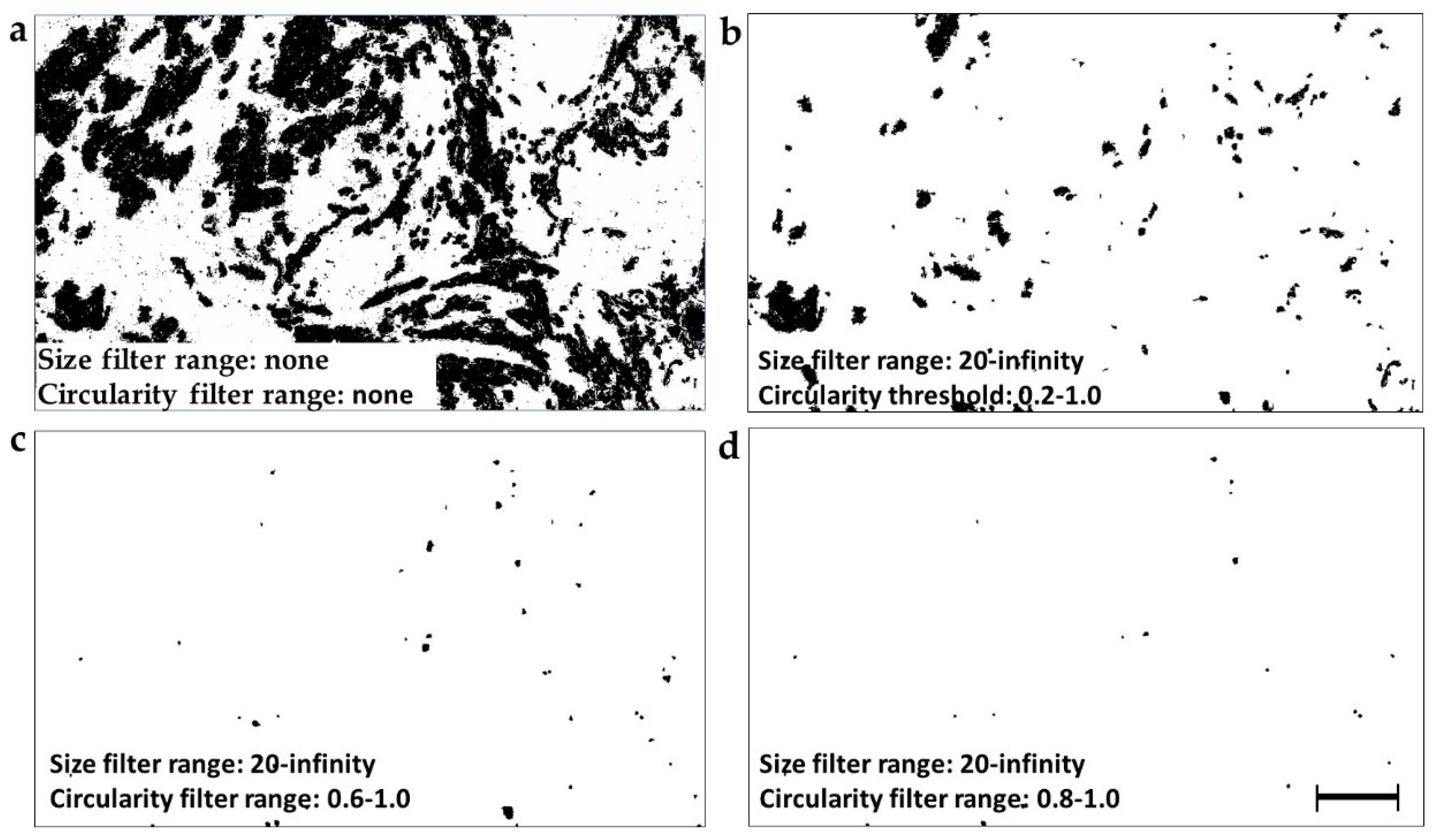
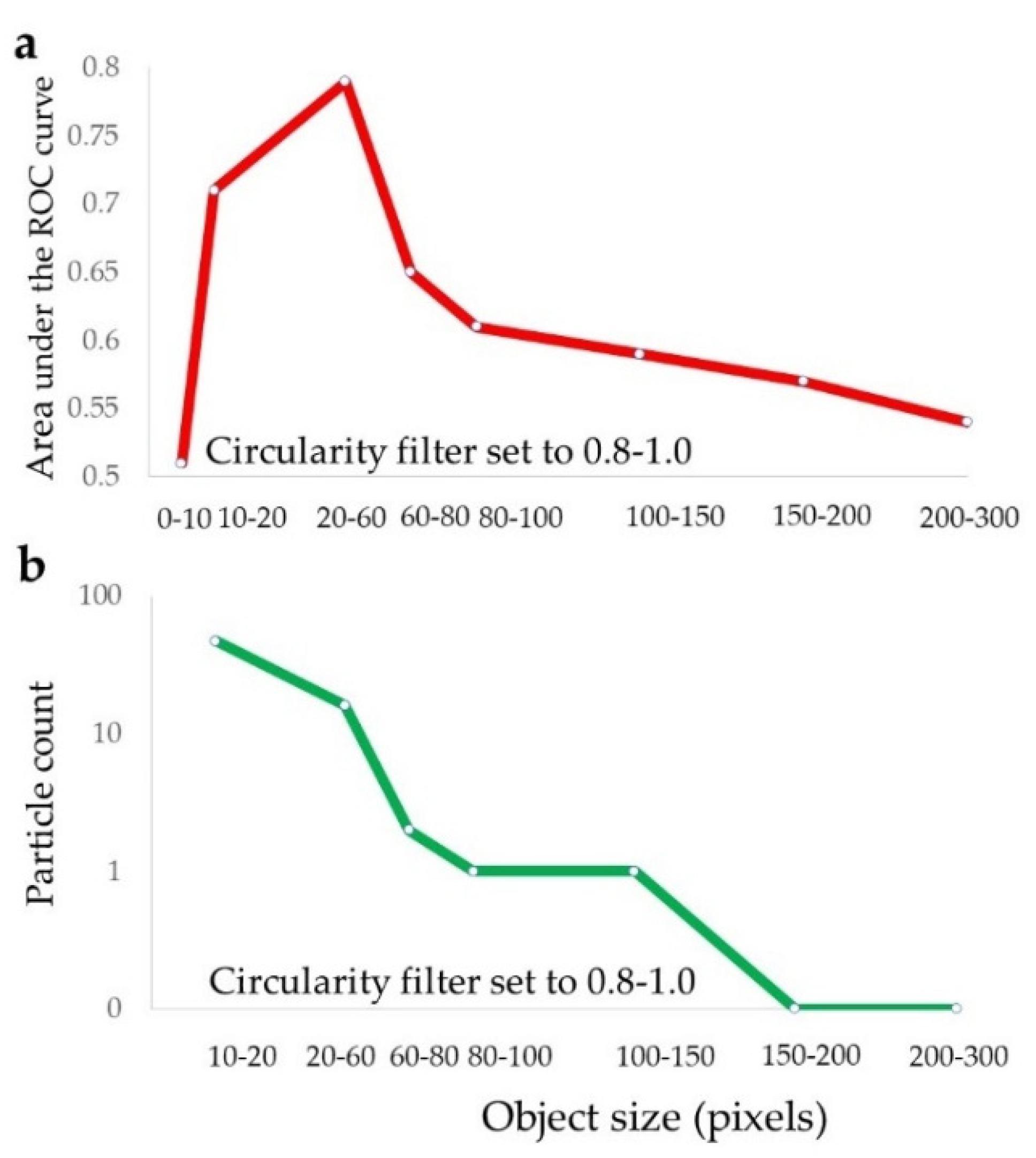
2.4. Selection of Different Particle Subsets by the Circularity and Size Filtration
2.5. Identification of the Prognostically Optimal Particle Subset and the Consisting Particles
2.6. Multivariate Analysis of the Clinicopathological and Particle Analysis Features
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Approval Statement
4.2. Patient Group
4.3. HER2 Amplification Testing
4.4. Study Design
4.5. Image Analysis Workflow
4.6. Immunostaining
4.7. Selection of Tissue Sections
4.8. Image Acquisition
4.9. Stain Decomposition
4.10. Image Binarization
4.11. Image Analysis
4.12. Prognostic Evaluation
4.13. Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajkovic, N.; Vujasinovic, T.; Kanjer, K.; Milosevic, N.T.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D.; Radulovic, M. Prognostic biomarker value of binary and grayscale breast tumor histopathology images. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drukker, C.A.; van Tinteren, H.; Schmidt, M.K.; Rutgers, E.J.; Bernards, R.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Van’t Veer, L.J. Long-term impact of the 70-gene signature on breast cancer outcome. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 143, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnitt, S.J. Classification and prognosis of invasive breast cancer: From morphology to molecular taxonomy. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23 (Suppl. 2), S60–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, B. Oncotype DX Test Offers Guidance For Women Debating Chemotherapy. Biotechnol. Healthc. 2006, 3, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orucevic, A.; Chen, J.; McLoughlin, J.M.; Heidel, R.E.; Panella, T.; Bell, J. Is the TNM staging system for breast cancer still relevant in the era of biomarkers and emerging personalized medicine for breast cancer—An institution’s 10-year experience. Breast J. 2015, 21, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elston, C.W.; Gresham, G.A.; Rao, G.S.; Zebro, T.; Haybittle, J.L.; Houghton, J.; Kearney, G. The cancer research campaign (King’s/Cambridge trial for early breast cancer: Clinico-pathological aspects. Br. J. Cancer 1982, 45, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buyse, M.; Loi, S.; van’t Veer, L.; Viale, G.; Delorenzi, M.; Glas, A.M.; d’Assignies, M.S.; Bergh, J.; Lidereau, R.; Ellis, P.; et al. Validation and clinical utility of a 70-gene prognostic signature for women with node-negative breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.M.; Hveem, T.; Pretorius, M.; Oukrif, D.; Nielsen, B.; Albregtsen, F.; Lovat, L.B.; Novelli, M.R.; Danielsen, H.E. Comparison of nuclear texture analysis and image cytometric DNA analysis for the assessment of dysplasia in Barrett’s oesophagus. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1218–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavicius, A.; Laurinaviciene, A.; Dasevicius, D.; Elie, N.; Plancoulaine, B.; Bor, C.; Herlin, P. Digital image analysis in pathology: Benefits and obligation. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2012, 35, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angell, H.K.; Gray, N.; Womack, C.; Pritchard, D.I.; Wilkinson, R.W.; Cumberbatch, M. Digital pattern recognition-based image analysis quantifies immune infiltrates in distinct tissue regions of colorectal cancer and identifies a metastatic phenotype. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurinavicius, A.; Plancoulaine, B.; Laurinaviciene, A.; Herlin, P.; Meskauskas, R.; Baltrusaityte, I.; Besusparis, J.; Dasevi Ius, D.; Elie, N.; Iqbal, Y.; et al. A methodology to ensure and improve accuracy of Ki67 labelling index estimation by automated digital image analysis in breast cancer tissue. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2014, 16, R35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aeffner, F.; Zarella, M.D.; Buchbinder, N.; Bui, M.M.; Goodman, M.R.; Hartman, D.J.; Lujan, G.M.; Molani, M.A.; Parwani, A.V.; Lillard, K.; et al. Introduction to Digital Image Analysis in Whole-slide Imaging: A White Paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. Inform. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkovic, N.; Kolarevic, D.; Kanjer, K.; Milosevic, N.T.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D.; Radulovic, M. Comparison of Monofractal, Multifractal and gray level Co-occurrence matrix algorithms in analysis of Breast tumor microscopic images for prognosis of distant metastasis risk. Biomed. Microdevices 2016, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajkovic, N.; Li, X.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Kanjer, K.; Radulovic, M.; Milosevic, N.T. The Pan-Cytokeratin Staining Intensity and Fractal Computational Analysis of Breast Tumor Malignant Growth Patterns Prognosticate the Occurrence of Distant Metastasis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambasco, M.; Eliasziw, M.; Magliocco, A.M. Morphologic complexity of epithelial architecture for predicting invasive breast cancer survival. J. Transl. Med. 2010, 8, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujasinovic, T.; Pribic, J.; Kanjer, K.; Milosevic, N.T.; Tomasevic, Z.; Milovanovic, Z.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D.; Radulovic, M. Gray-Level Co-Occurrence Matrix Texture Analysis of Breast Tumor Images in Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk. Microsc. Microanal. 2015, 21, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, A.; Niemiec, J.; Ambicka, A.; Mucha-Malecka, A.; Rys, J.; Mitus, J.; Wysocki, W.M.; Cichocka, A.; Jakubowicz, J. Survival of breast cancer patients according to changes in expression of selected markers between primary tumor and lymph node metastases. Biomark. Med. 2016, 10, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tambasco, M.; Magliocco, A.M. Relationship between tumor grade and computed architectural complexity in breast cancer specimens. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.W.; Qu, A.P.; Yuan, J.P.; Chen, C.; Sun, S.R.; Hu, M.B.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Computer-based image studies on tumor nests mathematical features of breast cancer and their clinical prognostic value. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, F.; Cao, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. The prognostic value of tumor budding in invasive breast cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2013, 209, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Pineda, E.; Adamo, B.; Galvan, P.; Fernandez, A.; Gaba, L.; Diez, M.; Viladot, M.; Arance, A.; Munoz, M. Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast 2015, 24 (Suppl. 2), S26–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.H.; Sangoi, A.R.; Leung, S.; Marinelli, R.J.; Nielsen, T.O.; van de Vijver, M.J.; West, R.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Koller, D. Systematic analysis of breast cancer morphology uncovers stromal features associated with survival. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 108ra113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voutsadakis, I.A. Prognostic role of tumor budding in breast cancer. World J. Exp. Med. 2018, 8, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prall, F. Tumour budding in colorectal carcinoma. Histopathology 2007, 50, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salhia, B.; Trippel, M.; Pfaltz, K.; Cihoric, N.; Grogg, A.; Ladrach, C.; Zlobec, I.; Tapia, C. High tumor budding stratifies breast cancer with metastatic properties. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 150, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Mathisen, A.F.; Funch Richardt, N.; Vander Plaetsen, A.S.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Stender, H.; Hillig, T. Feasibility of single-cell analysis of model cancer and foetal cells in blood after isolation by cell picking. Tumour Biol. 2019, 41, 1010428318823361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Liang, G.; Xie, X.; Jiang, W.; Tan, L.; Sanders, A.J.; Liu, Z.; Ling, Y.; Zhong, W.; Tian, Z.; et al. Incorporating MicroRNA into Molecular Phenotypes of Circulating Tumor Cells Enhances the Prognostic Accuracy for Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Oncologist 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez Cubero, M.J.; Lorente, J.A.; Robles-Fernandez, I.; Rodriguez-Martinez, A.; Puche, J.L.; Serrano, M.J. Circulating Tumor Cells: Markers and Methodologies for Enrichment and Detection. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1634, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwanenburg, A.; Lock, S. Why validation of prognostic models matters? Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 127, 370–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rykala, J.; Przybylowska, K.; Majsterek, I.; Pasz-Walczak, G.; Sygut, A.; Dziki, A.; Kruk-Jeromin, J. Angiogenesis markers quantification in breast cancer and their correlation with clinicopathological prognostic variables. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2011, 17, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brankovic-Magic, M.V.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D.B.; Neskovic-Konstantinovic, Z.B.; Kanjer, K.S.; Spuzic, I.V. Variations in the content of steroid receptors in breast cancer. Comparison between primary tumors and metastatic lesions. Acta Oncol. 1992, 31, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic-Rakovic, N.; Jovanovic, D.; Neskovic-Konstantinovic, Z.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D. Prognostic value of HER2 gene amplification detected by chromogenic in situ hybridization (CISH) in metastatic breast cancer. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2007, 82, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorovic-Rakovic, N.; Jovanovic, D.; Neskovic-Konstantinovic, Z.; Nikolic-Vukosavljevic, D. Comparison between immunohistochemistry and chromogenic in situ hybridization in assessing HER-2 status in breast cancer. Pathol. Int. 2005, 55, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Plataniotis, K.N. A Complete Color Normalization Approach to Histopathology Images Using Color Cues Computed From Saturation-Weighted Statistics. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 1862–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nature Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efron, B. Bootstrap Methods: Another Look at the Jackknife. Ann. Stat. 1979, 7, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | n | Metastasis (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| HER2 status | ||
| HER2− | 80 | 21 |
| HER2+ | 22 | 20 |
| ER status (cut off = 20 fmol/mg) | ||
| ER− | 32 | 13 |
| ER+ | 70 | 23 |
| PR status (cut off = 10 fmol/mg) | ||
| PR− | 64 | 25 |
| PR+ | 38 | 17 |
| Tumor size (cm) | ||
| ≤ 2 | 73 | 12 |
| 2–5 | 26 | 37 |
| ≥ 5 | 2 | 50 |
| Nodal status | ||
| N0 | 102 | 20 |
| N+ | 0 | 0 |
| Histologic grade | ||
| G1 | 9 | 33 |
| G2 | 92 | 17 |
| G3 | 1 | 0 |
| Count of individual scattered epithelial cells c | ||
| Low count (0–7.6) | 60 | 5 |
| High count (8.3–37.0) | 42 | 40 |
| Metastasis | ||
| lungs | 8 | 100 |
| bones | 7 | 100 |
| liver | 3 | 100 |
| skin | 1 | 100 |
| muscle | 1 | 100 |
| none | 82 | 0 |
| Parameter | AUC | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.60 | 0.15 | 0.48–0.73 |
| Tumor size | 0.65 | 0.04 * | 0.51–0.78 |
| Grade | 0.45 | 0.50 | 0.31–0.60 |
| ER | 0.60 | 0.14 | 0.46–0.75 |
| PR | 0.48 | 0.80 | 0.33–0.63 |
| HER2+ | 0.49 | 0.45 | 0.32–0.67 |
| HER2-enriched | 0.47 | 0.67 | 0.33–0.61 |
| Triple negative | 0.46 | 0.55 | 0.32–0.60 |
| Parameter | AUC/95% CI b/p-Value b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Binarization: auto Circularity: 0.0–1.0 Size: 20-infinity | Binarization: 220 Circularity: 0.0–1.0 Size: 20-infinity | Binarization: 240 Circularity: 0.0–1.0 Size: 20-infinity | Binarization: 250 Circularity: 0.0–1.0 Size: 20-infinity | |
| Count | 0.57 0.46–0.71 0.31 | 0.58 0.44–0.71 0.29 | 0.66 0.53–0.80 0.03 * | 0.60 0.47–0.73 0.18 |
| Total area | 0.37 0.25–0.50 0.08 | 0.35 0.22–0.49 0.04 * | 0.35 0.24–0.47 0.04 * | 0.54 0.39–0.68 0.63 |
| Average size | 0.40 0.27–0.53 0.15 | 0.37 0.23–0.50 0.06 | 0.33 0.21–0.46 0.02 * | 0.44 0.29–0.59 0.41 |
| Circularity | 0.67 0.55–0.78 0.02 * | 0.59 0.45–0.73 0.21 | 0.65 0.59–0.81 0.04 * | 0.62 0.50–0.75 0.09 |
| Solidity | 0.62 0.50–0.73 0.11 | 0.54 0.39–0.68 0.61 | 0.57 0.43–0.70 0.37 | 0.57 0.43–0.71 0.32 |
| Parameter | AUC a | 95% CI | p-Value | HR b | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 0.82 | 0.72–0.90 | 0.000 * | 14.8 | 5.3–242 | 0.001 * |
| Total area | 0.77 | 0.68–0.86 | 0.000 * | 17.2 | 5.7–230 | 0.001 * |
| Average size | 0.63 | 0.54–0.77 | 0.03 * | 11.9 | 2.1–28.8 | 0.001 * |
| Circularity | 0.62 | 0.51–0.74 | 0.09 | 12.8 | 3.3–61.6 | 0.02 * |
| Feature | p-Value a | HR | 95%CI a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.03 | 5.5 | 1.4–1264869 |
| Count | 0.001 | 16.1 | 5.7–344551 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vranes, V.; Rajković, N.; Li, X.; Plataniotis, K.N.; Raković, N.T.; Milovanović, J.; Kanjer, K.; Radulovic, M.; Milošević, N.T. Size and Shape Filtering of Malignant Cell Clusters within Breast Tumors Identifies Scattered Individual Epithelial Cells as the Most Valuable Histomorphological Clue in the Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk. Cancers 2019, 11, 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101615
Vranes V, Rajković N, Li X, Plataniotis KN, Raković NT, Milovanović J, Kanjer K, Radulovic M, Milošević NT. Size and Shape Filtering of Malignant Cell Clusters within Breast Tumors Identifies Scattered Individual Epithelial Cells as the Most Valuable Histomorphological Clue in the Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk. Cancers. 2019; 11(10):1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101615
Chicago/Turabian StyleVranes, Velicko, Nemanja Rajković, Xingyu Li, Konstantinos N. Plataniotis, Nataša Todorović Raković, Jelena Milovanović, Ksenija Kanjer, Marko Radulovic, and Nebojša T. Milošević. 2019. "Size and Shape Filtering of Malignant Cell Clusters within Breast Tumors Identifies Scattered Individual Epithelial Cells as the Most Valuable Histomorphological Clue in the Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk" Cancers 11, no. 10: 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101615
APA StyleVranes, V., Rajković, N., Li, X., Plataniotis, K. N., Raković, N. T., Milovanović, J., Kanjer, K., Radulovic, M., & Milošević, N. T. (2019). Size and Shape Filtering of Malignant Cell Clusters within Breast Tumors Identifies Scattered Individual Epithelial Cells as the Most Valuable Histomorphological Clue in the Prognosis of Distant Metastasis Risk. Cancers, 11(10), 1615. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11101615






