Automated Gleason Scoring and Tumor Quantification in Prostate Core Needle Biopsy Images Using Deep Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Pathologist-Based Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Acquisition and Digitization
4.2. Data Annotation
4.3. Automated Gleason Scoring System
4.4. Evaluation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Data and Code Availability
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Network, N.C.C. Prostate Cancer Early Detection (Version 2. 2019). Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/prostate_detection.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Epstein, J.I.; Allsbrook, W.C., Jr.; Amin, M.B.; Egevad, L.L. The 2005 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2005, 29, 1228–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A. The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleason, D.F.; Mellinger, G.T. Prediction of prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological grading and clinical staging. J. Urol. 1974, 111, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, P.A.; Moch, H.; Cubilla, A.L.; Ulbright, T.M.; Reuter, V.E. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs-Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allsbrook, W.C., Jr.; Mangold, K.A.; Johnson, M.H.; Lane, R.B.; Lane, C.G.; Epstein, J.I. Interobserver reproducibility of Gleason grading of prostatic carcinoma: General pathologist. Hum. Pathol. 2001, 32, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, T.A.; Eruyar, A.T.; Cebeci, O.O.; Memik, O.; Ozcan, L.; Kuskonmaz, I. Interobserver variability in Gleason histological grading of prostate cancer. Scand. J. Urol. 2016, 50, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierorazio, P.M.; Walsh, P.C.; Partin, A.W.; Epstein, J.I. Prognostic Gleason grade grouping: Data based on the modified Gleason scoring system. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I.; Zelefsky, M.J.; Sjoberg, D.D.; Nelson, J.B.; Egevad, L.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Vickers, A.J.; Parwani, A.V.; Reuter, V.E.; Fine, S.W.; et al. A Contemporary Prostate Cancer Grading System: A Validated Alternative to the Gleason Score. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.D.; Dunstan, R.W. Whole-slide imaging and automated image analysis: Considerations and opportunities in the practice of pathology. Vet. Pathol. 2014, 51, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colling, R.; Pitman, H.; Oien, K.; Rajpoot, N.; Macklin, P. Artificial intelligence in digital pathology: A roadmap to routine use in clinical practice. J. Pathol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litjens, G.; Kooi, T.; Bejnordi, B.E.; Setio, A.A.A.; Ciompi, F.; Ghafoorian, M.; van der Laak, J.; van Ginneken, B.; Sanchez, C.I. A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 42, 60–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, T.; Aresta, G.; Castro, E.; Rouco, J.; Aguiar, P.; Eloy, C.; Polónia, A.; Campilho, A. Classification of breast cancer histology images using Convolutional Neural Networks. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bychkov, D.; Linder, N.; Turkki, R.; Nordling, S.; Kovanen, P.E.; Verrill, C.; Walliander, M.; Lundin, M.; Haglund, C.; Lundin, J. Deep learning based tissue analysis predicts outcome in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Roa, A.; Gilmore, H.; Basavanhally, A.; Feldman, M.; Ganesan, S.; Shih, N.N.C.; Tomaszewski, J.; Gonzalez, F.A.; Madabhushi, A. Accurate and reproducible invasive breast cancer detection in whole-slide images: A Deep Learning approach for quantifying tumor extent. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehteshami Bejnordi, B.; Veta, M.; Johannes van Diest, P.; van Ginneken, B.; Karssemeijer, N.; Litjens, G.; van der Laak, J.; Hermsen, M.; Manson, Q.F.; Balkenhol, M.; et al. Diagnostic Assessment of Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases in Women With Breast Cancer. JAMA 2017, 318, 2199–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertosun, M.G.; Rubin, D.L. Automated Grading of Gliomas using Deep Learning in Digital Pathology Images: A modular approach with ensemble of convolutional neural networks. AMIA Annu. Symp. Proc. 2015, 2015, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Golden, J.A. Deep Learning Algorithms for Detection of Lymph Node Metastases From Breast Cancer: Helping Artificial Intelligence Be Seen. JAMA 2017, 318, 2184–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, M.E.; Scott, M.L.J.; Scorer, P.W.; Söderberg, M.; Balcerzak, D.; Barker, C. Relevance of deep learning to facilitate the diagnosis of HER2 status in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.-H.; Zhang, C.; Berry, G.J.; Altman, R.B.; Ré, C.; Rubin, D.L.; Snyder, M. Predicting non-small cell lung cancer prognosis by fully automated microscopic pathology image features. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanella, G.; Werneck Krauss Silva, V.; Fuchs, T.J. Terabyte-scale Deep Multiple Instance Learning for Classification and Localization in Pathology. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.06983. [Google Scholar]
- Litjens, G.; Sanchez, C.I.; Timofeeva, N.; Hermsen, M.; Nagtegaal, I.; Kovacs, I.; Hulsbergen-van de Kaa, C.; Bult, P.; van Ginneken, B.; van der Laak, J. Deep learning as a tool for increased accuracy and efficiency of histopathological diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, E.; Fricker, K.S.; Moret, M.; Rupp, N.; Hermanns, T.; Fankhauser, C.; Wey, N.; Wild, P.J.; Ruschoff, J.H.; Claassen, M. Automated Gleason grading of prostate cancer tissue microarrays via deep learning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, K.; Foote, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, P.C.; Wulczyn, E.; Tan, F.; Olson, N.; Smith, J.L.; Mohtashamian, A.; Wren, J.H.; et al. Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for improving Gleason scoring of prostate cancer. NPJ Digit. Med. 2019, 2, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Fedorov, A.; Fennessy, F.; Kikinis, R.; Gao, Y. Large scale digital prostate pathology image analysis combining feature extraction and deep neural network. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.02678. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, M.B.; Lin, D.W.; Gore, J.L.; Srigley, J.R.; Samaratunga, H.; Egevad, L.; Rubin, M.; Nacey, J.; Carter, H.B.; Klotz, L.; et al. The critical role of the pathologist in determining eligibility for active surveillance as a management option in patients with prostate cancer: Consensus statement with recommendations supported by the College of American Pathologists, International Society of Urological Pathology, Association of Directors of Anatomic and Surgical Pathology, the New Zealand Society of Pathologists, and the Prostate Cancer Foundation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138, 1387–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, J.I. Prognostic significance of tumor volume in radical prostatectomy and needle biopsy specimens. J. Urol. 2011, 186, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintal, M.M.; Meirelles, L.R.; Freitas, L.L.; Magna, L.A.; Ferreira, U.; Billis, A. Various morphometric measurements of cancer extent on needle prostatic biopsies: Which is predictive of pathologic stage and biochemical recurrence following radical prostatectomy? Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2011, 43, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimo, F.; Vollmer, R.T.; Corcos, J.; Kotar, K.; Begin, L.R.; Humphrey, P.A.; Bismar, T.A. Prognostic value of various morphometric measurements of tumour extent in prostate needle core tissue. Histopathology 2008, 53, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-C.; Zhu, Y.; Papandreou, G.; Schroff, F.; Adam, H. Encoder-Decoder with Atrous Separable Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.02611v3. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-local Neural Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.07971v3. [Google Scholar]
- Welcome to Python.org. Available online: https://python.org (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- OpenCV. Available online: https://opencv.org (accessed on 10 July 2019).
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- PyTorch. Available online: https://pytorch.org (accessed on 10 July 2019).




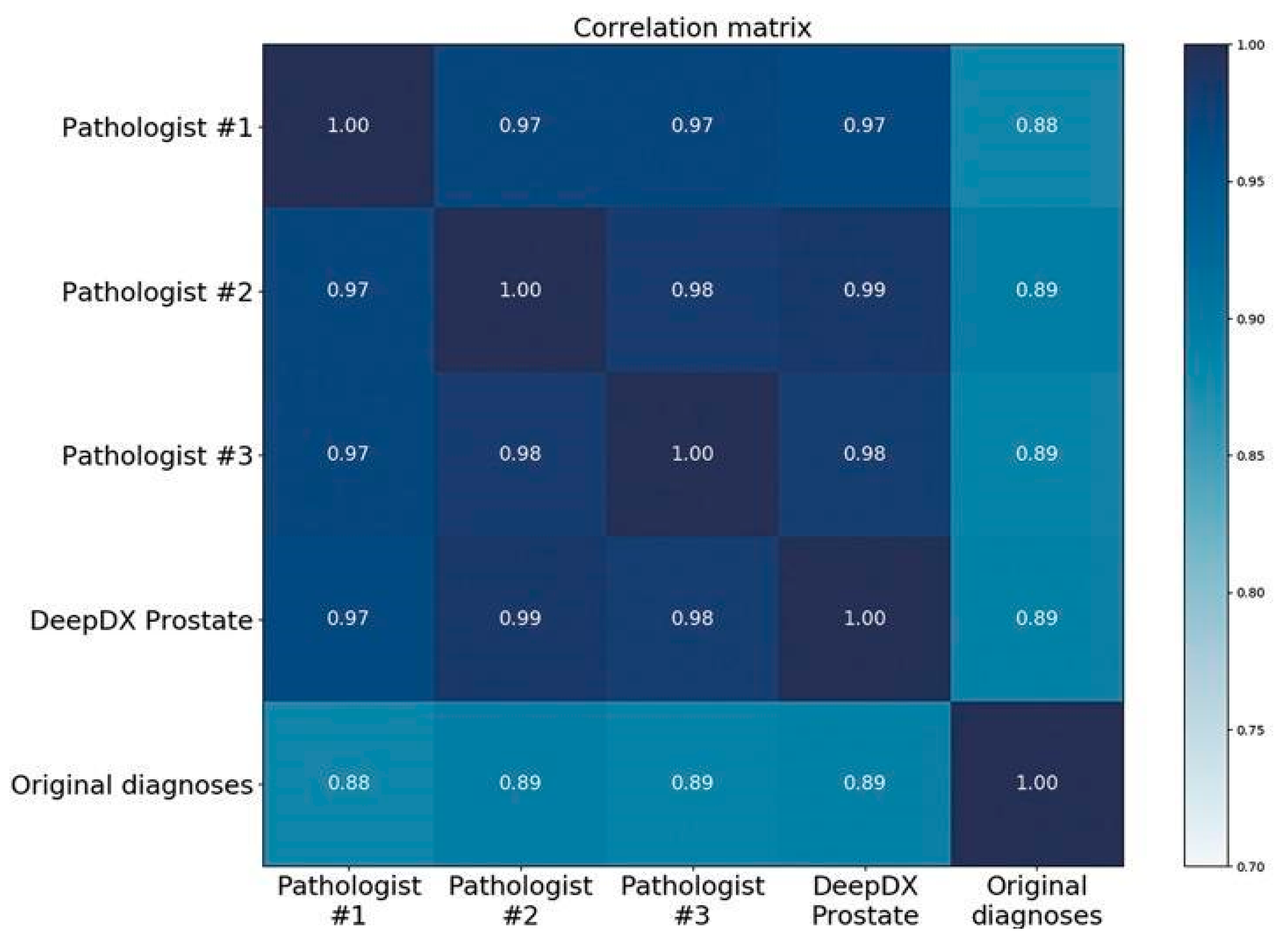
| DeepDx Prostate | Reference Standard | Original Diagnoses | Pathologist 1 | Pathologist 2 | Pathologist 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeepDx Prostate | - | 0.615/0.907 | 0.440/0.811 | 0.550/0.875 | 0.606/0.906 | 0.615/0.916 |
| Reference standard | 0.615/0.907 | - | 0.524/0.870 | 0.781/0.955 | 0.809/0.952 | 0.794/0.943 |
| Original diagnoses | 0.440/0.811 | 0.524/0.870 | - | 0.488/0.865 | 0.494/0.854 | 0.514/0.852 |
| Pathologist 1 * | 0.550/0.875 | 0.781/0.955 | 0.488/0.865 | - | 0.590/0.904 | 0.574/0.896 |
| Pathologist 2 | 0.606/0.906 | 0.809/0.952 | 0.494/0.854 | 0.590/0.904 | - | 0.682/0.920 |
| Pathologist 3 | 0.615/0.916 | 0.794/0.943 | 0.514/0.852 | 0.574/0.896 | 0.682/0.920 | - |
| Difficulty | DeepDx Prostate | Reference Standard | Original Diagnoses | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | DeepDx Prostate | ‒ | 0.656/0.958 | 0.634/0.853 |
| Reference standard | 0.656/0.958 | ‒ | 0.611/0.836 | |
| Original diagnoses | 0.634/0.853 | 0.611/0.836 | ‒ | |
| Medium | DeepDx Prostate | ‒ | 0.529/0.856 | 0.311/0.709 |
| Reference standard | 0.529/0.856 | ‒ | 0.423/0.799 | |
| Original diagnoses | 0.311/0.709 | 0.423/0.799 | ‒ | |
| Hard | DeepDx Prostate | ‒ | 0.224/0.525 | 0.255/0.508 |
| Reference standard | 0.224/0.525 | ‒ | 0.224/0.683 | |
| Original diagnoses | 0.255/0.508 | 0.224/0.683 | ‒ |
| Difficulty | Pathologist 1 * | Pathologist 2 | Pathologist 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Easy | Pathologist 1 * | ‒ | 0.931/0.990 | 1.000/1.000 |
| Pathologist 2 | 0.931/0.990 | ‒ | 0.931/0.990 | |
| Pathologist 3 | 1.000/1.000 | 0.931/0.990 | ‒ | |
| Medium | Pathologist 1 * | ‒ | 0.488/0.836 | 0.463/0.820 |
| Pathologist 2 | 0.488/0.836 | ‒ | 0.599/0.863 | |
| Pathologist 3 | 0.463/0.820 | 0.599/0.863 | ‒ | |
| Hard | Pathologist 1 * | ‒ | 0.273/0.636 | 0.382/0.815 |
| Pathologist 2 | 0.273/0.636 | ‒ | 0.219/0.733 | |
| Pathologist 3 | 0.382/0.815 | 0.219/0.733 | ‒ |
| Category | Discovery | Validation (Original Hospital Diagnosis) | Validation (Reference Standards) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Benign | 645 | 188 | 203 |
| ASAP * | 0 | 11 | 8 |
| Grade Group 1 | 145 | 100 | 67 |
| Grade Group 2 | 131 | 100 | 111 |
| Grade Group 3 | 27 | 101 | 92 |
| Grade Group 4 | 122 | 100 | 61 |
| Grade Group 5 | 63 | 100 | 158 |
| Total | 1133 | 700 | 700 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ryu, H.S.; Jin, M.-S.; Park, J.H.; Lee, S.; Cho, J.; Oh, S.; Kwak, T.-Y.; Woo, J.I.; Mun, Y.; Kim, S.W.; et al. Automated Gleason Scoring and Tumor Quantification in Prostate Core Needle Biopsy Images Using Deep Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Pathologist-Based Assessment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121860
Ryu HS, Jin M-S, Park JH, Lee S, Cho J, Oh S, Kwak T-Y, Woo JI, Mun Y, Kim SW, et al. Automated Gleason Scoring and Tumor Quantification in Prostate Core Needle Biopsy Images Using Deep Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Pathologist-Based Assessment. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121860
Chicago/Turabian StyleRyu, Han Suk, Min-Sun Jin, Jeong Hwan Park, Sanghun Lee, Joonyoung Cho, Sangjun Oh, Tae-Yeong Kwak, Junwoo Isaac Woo, Yechan Mun, Sun Woo Kim, and et al. 2019. "Automated Gleason Scoring and Tumor Quantification in Prostate Core Needle Biopsy Images Using Deep Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Pathologist-Based Assessment" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121860
APA StyleRyu, H. S., Jin, M.-S., Park, J. H., Lee, S., Cho, J., Oh, S., Kwak, T.-Y., Woo, J. I., Mun, Y., Kim, S. W., Hwang, S., Shin, S.-J., & Chang, H. (2019). Automated Gleason Scoring and Tumor Quantification in Prostate Core Needle Biopsy Images Using Deep Neural Networks and Its Comparison with Pathologist-Based Assessment. Cancers, 11(12), 1860. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121860





