IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
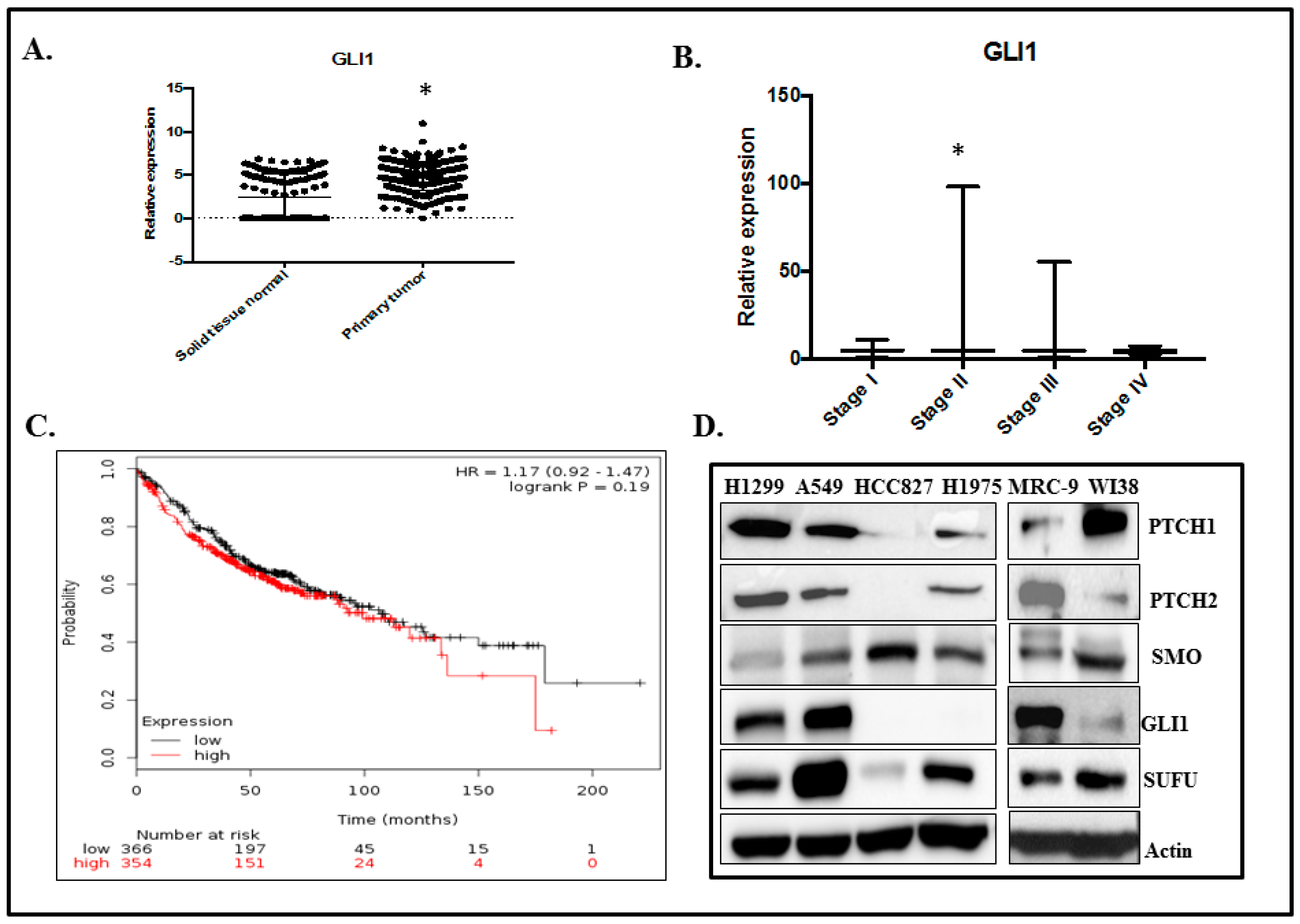
2.1. GLI1 Expression in Lung Adenocarcinoma
2.2. GLI1 Expression Is Reduced in H1299-IL24 Cells
2.3. IL-24 Regulates ATM-DDR Pathway in Lung Cancer Cells
2.4. IL-24 Induces DNA Damage in H1299 Lung Cancer Cells
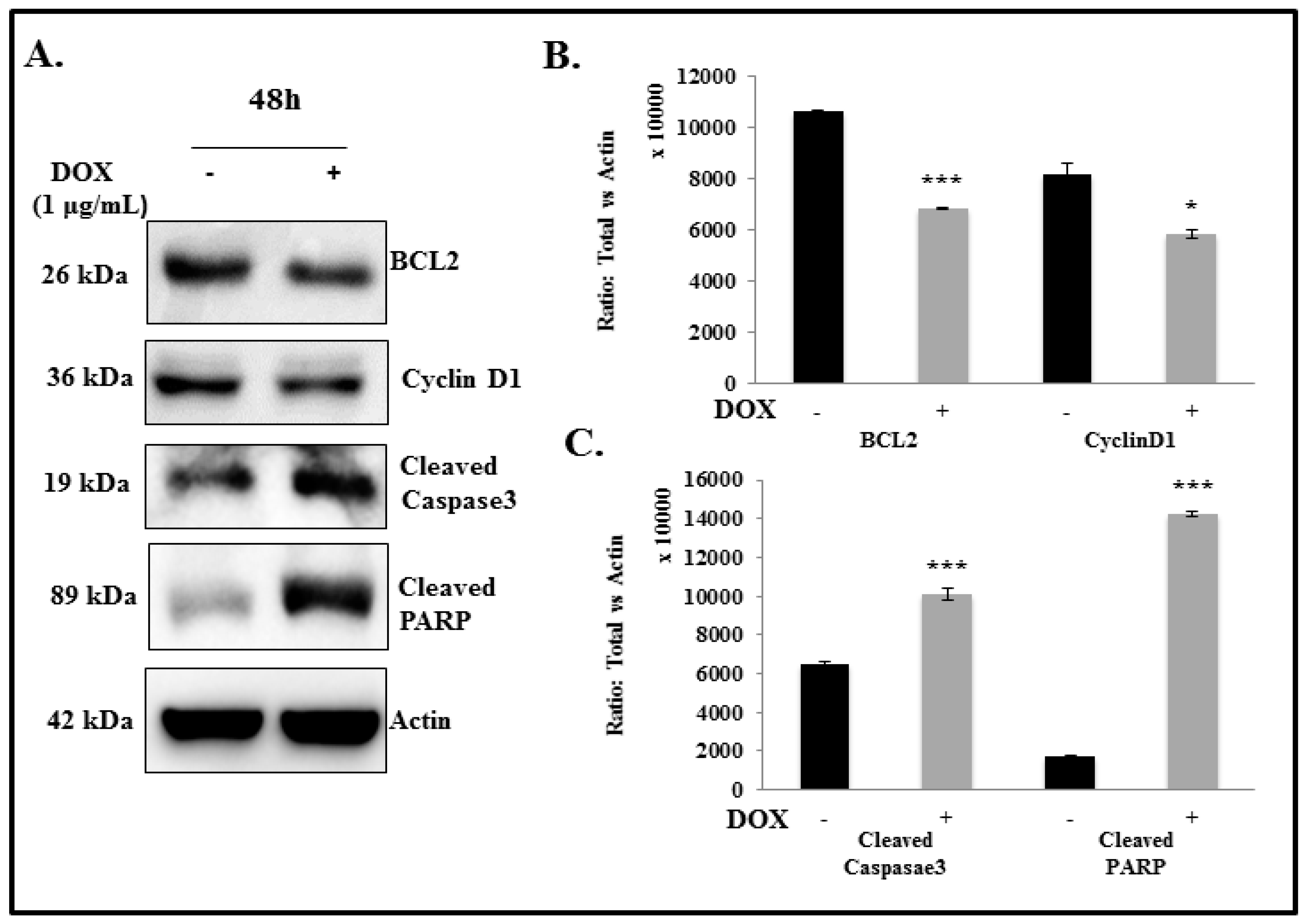
2.5. IL-24 Triggers Apoptosis in H1299 Lung Cancer Cells
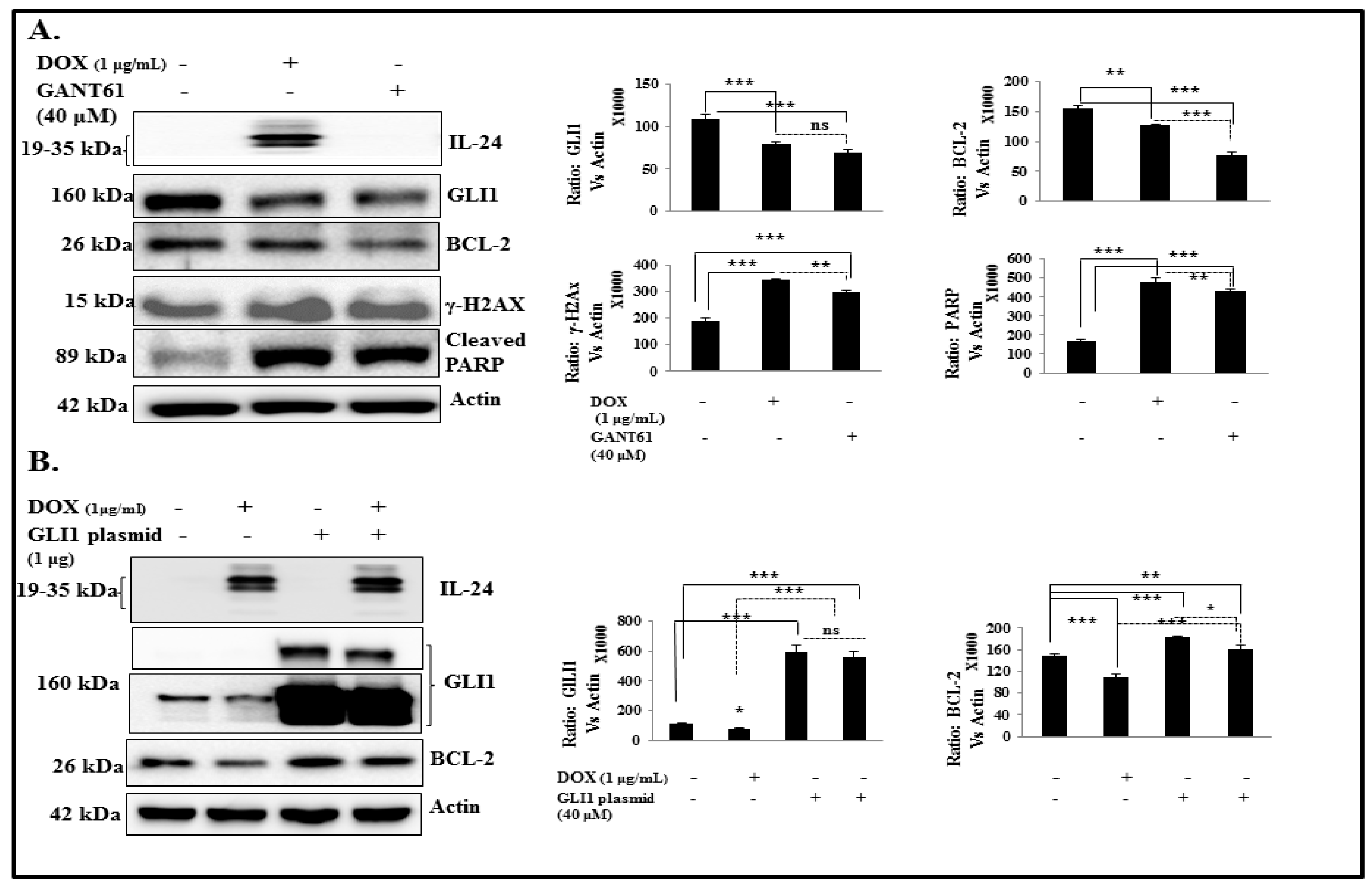
2.6. IL-24 Induces DNA Damage and Apoptosis via GLI1 Inhibition
2.7. IL-24 Downregulates GLI1, Even under Treatment with Exogenous SHH Ligand
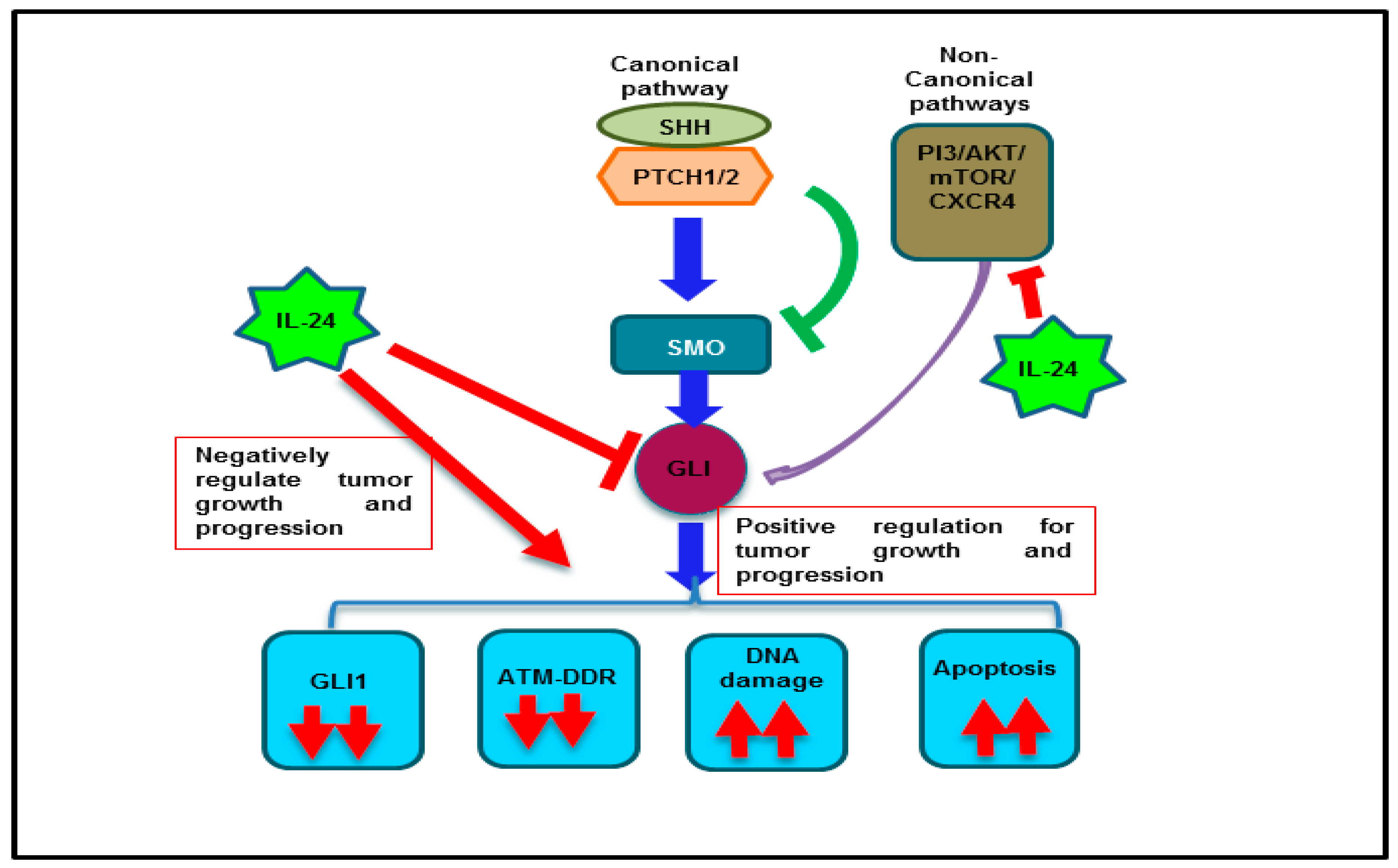
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Stable Transfection of Inducible IL-24 Plasmid Vector in H1299 Cells
4.2. Transient Transfection of IL-24 Plasmid
4.3. Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.4. Exogenous SHH Treatment to NSCLC Cells
4.5. GLI1 Overexpression Studies
4.6. Immunofluorescence Assay
4.7. Comet Assay
4.8. TCGA Lung Adenocarcinoma (LUAD) Data
4.9. Determination of GLI1 Expression in LUAD Pathological Stages
4.10. Survival Curve Analysis
4.11. Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.12. Western Blotting Analysis
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natukula, K.; Jamil, K.; Pingali, U.R.; Suresh Attili, V.S.; Naidu Madireddy, U.R. Survival analysis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with platinum based chemotherapy in combination with paclitaxel, gemcitabine and etoposide. Asian Pac. J. Cancer. Prev. 2013, 14, 4661–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Cai, Y. Clinical observation and prognostic analysis of pemetrexed plus platinum as first-line treatment in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer. Prev. 2013, 14, 6267–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cao, W.; Li, A.W.; Ren, S.X.; Chen, X.X.; Li, W.; Gao, G.H.; He, Y.Y.; Zhou, C.C. Efficacy of first-line chemotherapy affects the second-line setting response in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer. Prev. 2014, 15, 6799–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Di, B.S.; Wei, K.P.; Tian, J.H.; Xiao, X.J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Yu, Q.; Yang, K.H.; Ge, L.; Huang, W.H. Effectiveness and safety of pemetrexed versus docetaxel as a treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 3419–3424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kiziltan, H.S.; Bayir, A.G.; Tastekin, D.; Coban, G.; Eris, A.H.; Aydin, T.; Mayadagli, A. Outcome of daily cisplatin with thoracic chemoradiotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with comorbid disorders: A pilot study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer. Prev. 2014, 15, 8591–8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daga, A.; Ansari, A.; Patel, S.; Mirza, S.; Rawal, R.; Umrania, V. Current drugs and drug targets in non-small cell lung cancer: Limitations and opportunities. Asian Pac. J. Cancer. Prev. 2015, 16, 4147–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, J.W.; Sequist, L.V. Exciting new targets in lung cancer therapy: ALK, IGF-1R, HDAC, and Hh. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2010, 11, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brechbiel, J.; Miller-Moslin, K.; Adjei, A.A. Crosstalk between hedgehog and other signaling pathways as a basis for combination therapies in cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Xie, G.; Fan, Q.; Xie, J. Activation of the hedgehog-signaling pathway in human cancer and the clinical implications. Oncogene 2010, 29, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasca di Magliano, M.; Hebrok, M. Hedgehog signalling in cancer formation and maintenance. Nature Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonnissen, A.; Isebaert, S.; Haustermans, K. Targeting the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: Beyond Smoothened. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13899–13913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.C.; Fuller, C.; Hogg, T.L.; Dalton, J.; Finkelstein, D.; Lau, C.C.; Chintagumpala, M.; Adesina, A.; Ashley, D.M.; Kellie, S.J.; et al. Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1924–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibat, A.; Missiaglia, E.; Rosenberger, A.; Pritchard-Jones, K.; Shipley, J.; Hahn, H.; Fulda, S. Activation of the hedgehog pathway confers a poor prognosis in embryonal and fusion gene-negative alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6323–6330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tostar, U.; Malm, C.J.; Meis-Kindblom, J.M.; Kindblom, L.G.; Toftgård, R.; Undén, A.B. Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: A possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J. Pathol. 2006, 208, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiesslich, T.; Mayr, C.; Wachter, J.; Bach, D.; Fuereder, J.; Wagner, A.; Alinger, B.; Pichler, M.; Di Fazio, P.; Ocker, M.; et al. Activated hedgehog pathway is a potential target for pharmacological intervention in biliary tract cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 396, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Nakamura, M.; Tasaki, A.; Yamanaka, N.; Nakashima, H.; Nomura, M.; Kuroki, S.; Katano, M. Hedgehog signaling pathway is a new therapeutic target for patients with breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6071–6074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ten Haaf, A.; Bektas, N.; von Serenyi, S.; Losen, I.; Arweiler, E.C.; Hartmann, A.; Knüchel, R.; Dahl, E. Expression of the glioma-associated oncogene homolog (GLI) 1 in human breast cancer is associated with unfavourable overall survival. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souzaki, M.; Kubo, M.; Kai, M.; Kameda, C.; Tanaka, H.; Taguchi, T.; Tanaka, M.; Onishi, H.; Katano, M. Hedgehog signaling pathway mediates the progression of non-invasive breast cancer to invasive breast cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karhadkar, S.S.; Bova, G.S.; Abdallah, N.; Dhara, S.; Gardner, D.; Maitra, A.; Isaacs, J.T.; Berman, D.M.; Beachy, P.A. Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature 2004, 431, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, T.K.; Kang, C.S.; Choi, Y.J. Hedgehog signaling protein expression and its association with prognostic parameters in prostate cancer: A retrospective study from the view point of new 2010 anatomic stage/prognostic groups. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 104, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnat, F.; Duquet, A.; Malerba, M.; Zbinden, M.; Mas, C.; Gervaz, P.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Human colon cancer epithelial cells harbour active HEDGEHOG-GLI signalling that is essential for tumour growth, recurrence, metastasis and stem cell survival and expansion. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.C.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, X.B.; Qin, G.Q.; Cai, C.; Liang, Y.X.; Han, Z.D.; Dai, Q.S.; Chen, Y.R.; Zheng, G.H.; et al. Expression of hedgehog pathway components is associated with bladder cancer progression and clinical outcome. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2012, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Z.; Bi, A.; Chen, D.; Gao, L.; Yin, Z.; Luo, L. Activation of hedgehog signaling pathway in human non-small cell lung cancers. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauth, M.; Toftgard, R. Non-canonical activation of GLI transcription factors: Implications for targeted anti-cancer therapy. Cell Cycle 2007, 6, 2458–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, Y.; Tanaka, N. The Hedgehog Signaling Networks in Lung Cancer: The Mechanisms and Roles in Tumor Progression and Implications for Cancer Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7969286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palle, K.; Mani, C.; Tripathi, K.; Athar, M. Aberrant GLI1 Activation in DNA Damage Response, Carcinogenesis and Chemoresistance. Cancers 2015, 7, 2330–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yauch, R.L.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.P.; Alicke, B.; Januario, T.; Ahn, C.P.; Holcomb, T.; Pujara, K.; Stinson, J.; Callahan, C.A.; Tang, T.; et al. Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 2009, 326, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhashilkar, A.M.; Schrock, R.D.; Hindi, M.; Liao, J.; Sieger, K.; Kourouma, F.; Zou-Yang, X.H.; Onishi, E.; Takh, O.; Vedvick, T.S.; et al. Melanoma differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7): A novel anti-tumor gene for cancer gene therapy. Mol. Med. 2001, 7, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, E.G.; Mumm, J.B.; Poindexter, N.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Yang, X.H.; Retter, M.W.; Hill, P.; Chada, S.; Grimm, E.A. The protein product of the tumor suppressor gene, melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7, exhibits immunostimulatory activity and is designated IL-24. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 6041–6046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeki, T.; Mhashilkar, A.; Swanson, X.; Zou-Yang, X.H.; Sieger, K.; Kawabe, S.; Branch, C.D.; Zumstein, L.; Meyn, R.E.; Roth, J.A.; et al. Inhibition of human lung cancer growth following adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene expression in vivo. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4558–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellerhorst, J.A.; Prieto, V.G.; Ekmekcioglu, S.; Broemeling, L.; Yekell, S.; Chada, S.; Grimm, E.A. Loss of MDA-7 expression with progression of melanoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Miyahara, R.; Kawano, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Yanagihara, K.; Otake, Y.; Katakura, H.; Wada, H.; Tanaka, F. Expression of MDA-7/IL-24 and its clinical significance in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1198–1202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Molecular targets and signaling pathways regulated by interleukin (IL)-24 in mediating its antitumor activities. J. Mol. Signal. 2013, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, R.; Ito, I.; Gopalan, B.; Saito, Y.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Chada, S. Ectopic production of MDA-7/IL-24 inhibits invasion and migration of human lung cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2004, 9, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Jin, J.; Shanker, M.; Lauderdale, J.; Bates, J.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.D.; Archibald, S.J.; Hubin, T.J.; Ramesh, R. IL-24 inhibits lung cancer cell migration and invasion by disrupting the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling axis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.W.; Nemunaitis, J.; Su, D.; Zhang, Y.; Cunningham, C.; Senzer, N.; Netto, G.; Rich, D.; Mhashilkar, A.; Parker, K.; et al. Intratumoral injection of INGN 241, a nonreplicating adenovector expressing the melanoma-differentiation associated gene-7 (mda-7/IL24): Biologic outcome in advanced cancer patients. Mol. Ther. 2005, 11, 160–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panneerselvam, J.; Shanker, M.; Jin, J.; Branch, C.D.; Muralidharan, R.; Zhao, Y.D.; Chada, S.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Phosphorylation of interleukin (IL)-24 is required for mediating its anti-cancer activity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16271–16286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowsheen, S.; Yang, E.S. The intersection between DNA damage response and cell death pathways. Exp. Oncol. 2012, 34, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Mazumdar, T.; Devecchio, J.; Agyeman, A.; Shi, T.; Houghton, J.A. Blocking Hedgehog survival signaling at the level of the GLI genes induces DNA damage and extensive cell death in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5904–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazumdar, T.; Devecchio, J.; Shi, T.; Jones, J.; Agyeman, A.; Houghton, J.A. Hedgehog signaling drives cellular survival in human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Walter, V.; Hayes, D.N.; Onaitis, M. Hedgehog-GLI signaling inhibition suppresses tumor growth in squamous lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1566–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, A.; Mazumdar, T.; Houghton, J.A. Regulation of DNA damage following termination of Hedgehog (HH) survival signaling at the level of the GLI genes in human colon cancer. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasibhatla, S.; Brunner, T.; Genestier, L.; Echeverri, F.; Mahboubi, A.; Green, D.R. DNA damaging agents induce expression of Fas ligand and subsequent apoptosis in T lymphocytes via the activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Mol. Cell 1998, 1, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norbury, C.J.; Zhivotovsky, B. DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 2797–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickstrom, M.; Dyberg, C.; Shimokawa, T.; Milosevic, J.; Baryawno, N.; Fuskevåg, O.M.; Larsson, R.; Kogner, P.; Zaphiropoulos, P.G.; Johnsen, J.I. Targeting the hedgehog signal transduction pathway at the level of GLI inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Peng, X.; Yuan, X.; Huang, D.; Chen, J.; Lu, Q.; Lv, N.; Luo, S. Suppression of growth and migration by blocking the Hedgehog signaling pathway in gastric cancer cells. Cell. Oncol. (Dordr) 2013, 36, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.W.; Kita, Y.; Frank, D.J.; Majewski, R.R.; Konicek, B.A.; Nobrega, M.A.; Jacob, H.; Walterhouse, D.; Iannaccone, P. Gene expression profiling leads to identification of GLI1-binding elements in target genes and a role for multiple downstream pathways in GLI1-induced cell transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5548–5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, O.; Hennen, E.; Koch, I.; Lindner, M.; Eickelberg, O. Gli1 mediates lung cancer cell proliferation and Sonic Hedgehog-dependent mesenchymal cell activation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, R.; Mhashilkar, A.M.; Tanaka, F.; Saito, Y.; Branch, C.D.; Sieger, K.; Mumm, J.B.; Stewart, A.L.; Boquoi, A.; Dumoutier, L.; et al. Melanoma differentiation-associated gene 7/interleukin (IL)-24 is a novel ligand that regulates angiogenesis via the IL-22 receptor. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5105–5113. [Google Scholar]
- Broustas, C.G.; Lieberman, H.B. DNA damage response genes and the development of cancer metastasis. Radiat. Res. 2014, 181, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derheimer, F.A.; Kastan, M.B. Multiple roles of ATM in monitoring and maintaining DNA integrity. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3675–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Guo, X.; Qian, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, C.; Brinkman, K.L.; Serrano-Gonzalez, M.; Jope, R.S.; Zhou, B.; Engler, D.A.; et al. Activation of the ATM-Snail pathway promotes breast cancer metastasis. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 4, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golding, S.E.; Rosenberg, E.; Valerie, N.; Hussaini, I.; Frigerio, M.; Cockcroft, X.F.; Chong, W.Y.; Hummersone, M.; Rigoreau, L.; Menear, K.A.; et al. Improved ATM kinase inhibitor KU-60019 radiosensitizes glioma cells, compromises insulin, AKT and ERK prosurvival signaling, and inhibits migration and invasion. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2894–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, N.; Miyagawa, K. Targeting DNA damage response in cancer therapy. Cancer Sci. 2014, 105, 370–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, A.M.; Ryan, A.J. ATM and ATR as therapeutic targets in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 149, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulany, M.; Mihatsch, J.; Holler, M.; Chaachouay, H.; Rodemann, H.P. Cisplatin-mediated radiosensitization of non-small cell lung cancer cells is stimulated by ATM inhibition. Radiother. Oncol. 2014, 111, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeki, T.; Mhashilkar, A.; Chada, S.; Branch, C.; Roth, J.A.; Ramesh, R. Tumor-suppressive effects by adenovirus-mediated mda-7 gene transfer in non-small cell lung cancer cell in vitro. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 2051–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, S.; Tam, J.; Roth, J.A.; Sokolov, K.; Ramesh, R. EGFR-targeted plasmonic magnetic nanoparticles suppress lung tumor growth by abrogating G2/M cell-cycle arrest and inducing DNA damage. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 3825–3839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Munshi, A.; Brooks, C.; Liu, J.; Hobbs, M.L.; Meyn, R.E. Gefitinib radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer cells by suppressing cellular DNA repair capacity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paschoud, S.; Dogar, A.M.; Kuntz, C.; Grisoni-Neupert, B.; Richman, L.; Kuhn, L.C. Destabilization of interleukin-6 mRNA requires a putative RNA stem-loop structure, an AU-rich element, and the RNA-binding protein AUF1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 8228–8241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Mehta, M.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage. Cancers 2019, 11, 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121879
Panneerselvam J, Srivastava A, Mehta M, Chen A, Zhao YD, Munshi A, Ramesh R. IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121879
Chicago/Turabian StylePanneerselvam, Janani, Akhil Srivastava, Meghna Mehta, Allshine Chen, Yan D. Zhao, Anupama Munshi, and Rajagopal Ramesh. 2019. "IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121879
APA StylePanneerselvam, J., Srivastava, A., Mehta, M., Chen, A., Zhao, Y. D., Munshi, A., & Ramesh, R. (2019). IL-24 Inhibits Lung Cancer Growth by Suppressing GLI1 and Inducing DNA Damage. Cancers, 11(12), 1879. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121879







