The Chalcone Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
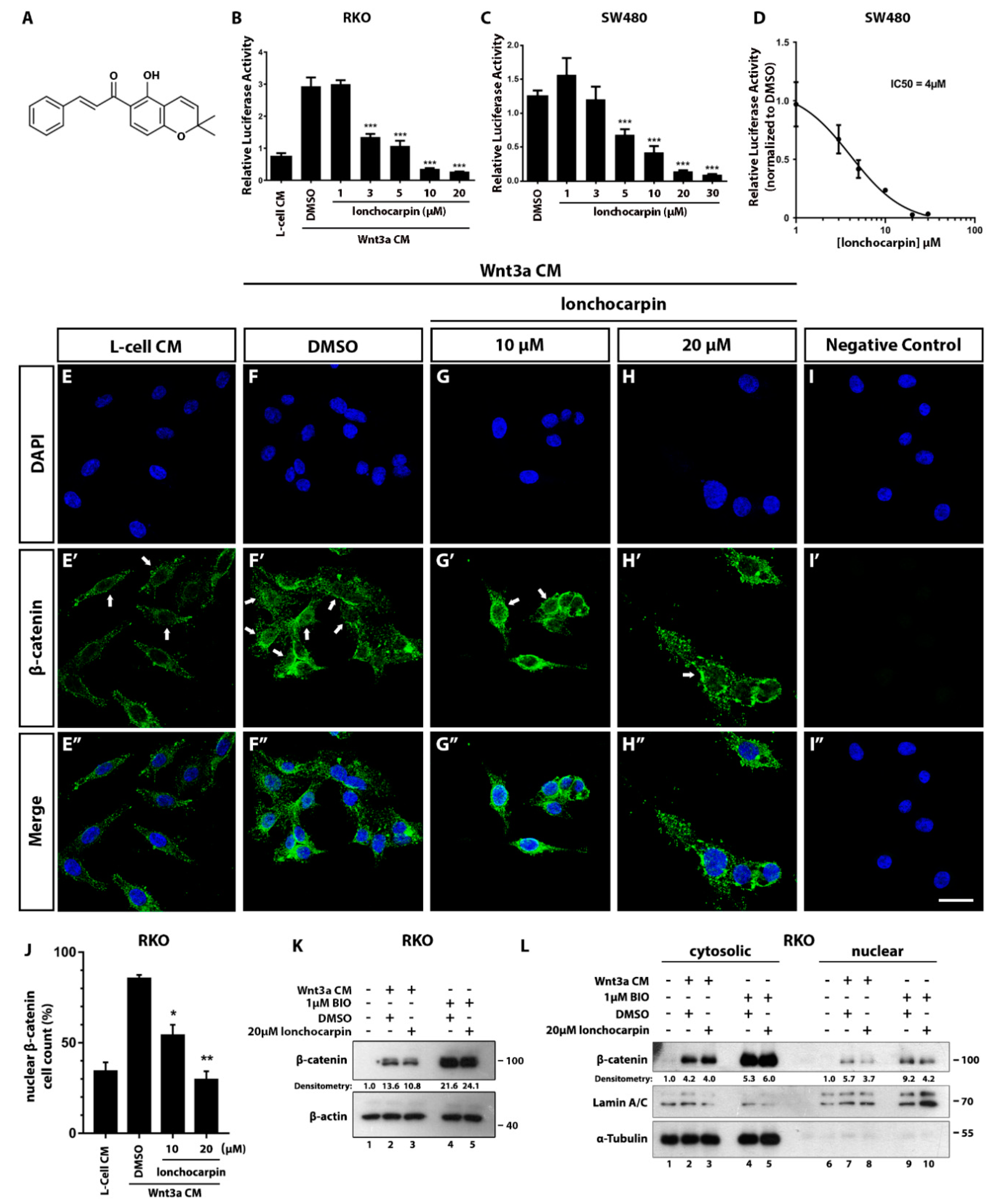
2.1. Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway and Reduces Nuclear β-Catenin Levels
2.2. Lonchocarpin Inhibits the Canonical Wnt Pathway Downstream of the Destruction Complex
2.3. Lonchocarpin Treatment Disturbs Xenopus laevis Embryos Axial Patterning and Rescues Wnt Overactivation Phenotypes
2.4. Lonchocarpin Reduces HCT116, SW480, and DLD-1 Cell Proliferation
2.5. Lonchocarpin Reduces Cell Migration in HCT116, SW480, and DLD-1 Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
2.6. Lonchocarpin Decreases Cell Proliferation in Azoxymethane (AOM)/Dextran Sulfate Sodium (DSS) Induced Adenocarcinomas
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Chemical Compounds
4.2. Wnt/β-Catenin Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.3. Immunocytochemistry
4.4. Immunoblotting and Cell Fractionation
4.5. Xenopus laevis Embryo Manipulations
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Scratch Assay
4.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.9. AOM/DSS Protocol
4.10. Tissue Processing, Histopathology, H&E, and Immunofluorescence
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Network, C.G.A. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kinzler, K.; Nilbert, M.; Vogelstein, B.; Bryan, T.; Levy, D.; Smith, K.; Preisinger, A.; Hedge, P.; Markham, A. Identification of a gene located at chromosome 5q21 that is mutated in colorectal cancers. Science 1991, 251, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miki, T.; Yasuda, S.Y.; Kahn, M. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Embryonic Stem Cell Self-renewal and Somatic Cell Reprogramming. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2011, 7, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Amerongen, R.; Nusse, R. Towards an integrated view of Wnt signaling in development. Development 2009, 136, 3205–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.-E.; Huang, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, A.; Semonov, M.V.; MacDonald, B.T.; Zhang, X.; Abreu, J.G.; Peng, L.; et al. Wnt stabilization of β-catenin reveals principles for morphogen receptor-scaffold assemblies. Science 2013, 340, 867–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- MacDonald, B.T.; Tamai, K.; He, X. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: Components, Mechanisms, and Diseases. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tortelote, G.G.; Reis, R.R.; de Almeida Mendes, F.; Abreu, J.G. Complexity of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway: Searching for an activation model. Cell. Signal. 2017, 40, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M. Can we safely target the WNT pathway? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larabell, C.A.; Torres, M.; Rowning, B.A.; Yost, C.; Miller, J.R.; Wu, M.; Kimelman, D.; Moon, R.T. Establishment of the Dorso-ventral Axis in Xenopus Embryos Is Presaged by Early Asymmetries in β-Catenin That Are Modulated by the Wnt Signaling Pathway. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 136, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maia, L.A.; Velloso, I.; Abreu, J.G. Advances in the use of Xenopus for successful drug screening. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, A.P.; Moon, R.T. Ectopic expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 in Xenopus embryos leads to duplication of the embryonic axis. Cell 1989, 58, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, C.A.; Hanson, A.J.; Schneider, J.; Tahinci, E.; Orton, D.; Cselenyi, C.S.; Jernigan, K.K.; Meyers, K.C.; Hang, B.I.; Waterson, A.G.; et al. Small-molecule inhibition of Wnt signaling through activation of casein kinase 1α. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2010, 6, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, T.; Kohno, H.; Suzuki, R.; Yamada, Y.; Sugie, S.; Mori, H. A novel inflammation-related mouse colon carcinogenesis model induced by azoxymethane and dextran sodium sulfate. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, R.; Kohno, H.; Sugie, S.; Takahashi, M.; Wakabayashi, K. Colonic adenocarcinomas rapidly induced by the combined treatment with 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine and dextran sodium sulfate in male ICR mice possess β-catenin gene mutations and increases immunoreactivity for β-catenin, cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Amado, N.G.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Menezes, F.S.; Da Silva, J.F.M.; Neto, V.M.; Abreu, J.G. Isoquercitrin isolated from Hyptis fasciculata reduces glioblastoma cell proliferation and changes β-catenin cellular localization. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2009, 20, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, N.G.; Predes, D.; Moreno, M.M.; Carvalho, I.O.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Flavonoids and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling: Potential Role in Colorectal Cancer Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 12094–12106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fonseca, B.F.; Predes, D.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Reis, A.H.; Amado, N.G.; Cayres, M.C.L.; Kuster, R.M.; Oliveira, F.L.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Derricin and Derricidin Inhibit Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppress Colon Cancer Cell Growth In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, Z.; Hung, M.S.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, T.; Gong, M.; Zhi, X.; Jablon, D.M.; You, L. Promoter demethylation of WIF-1 by epigallocatechin-3-gallate in lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, M.; Velmurugan, B.; Tyagi, A.; Agarwal, C.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin Suppresses Growth of Human Colorectal Carcinoma SW480 Cells in Culture and Xenograft through Down-regulation of β-Catenin-Dependent Signaling. Neoplasia 2010, 12, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Landesman-Bollag, E.; Song, D.H.; Mourez, R.R.; Sussman, D.J.; Cardiff, R.D.; Sonenshein, G.E.; Seldin, D.C. Protein kinase CK2: Signaling and tumorigenesis in the mammary gland. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 227, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Li, R.; Sarkar, S.H.; Sarkar, F.H. Regulation of Akt/FOXO3a/GSK-3β/AR signaling network by isoflavone in prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 27707–27716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, C.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Hahm, E.R.; Park, S.; Kim, H.K.; Yang, C.H. Quercetin, a potent inhibitor against β-catenin/Tcf signaling in SW480 colon cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Hwang, W.; Kim, Y.S.; Park, D. Isorhamnetin-induced anti-adipogenesis is mediated by stabilization of β-catenin protein. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.H.; Sussman, D.J.; Seldin, D.C. Endogenous Protein Kinase CK2 Participates in Wnt Signaling in Mammary Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 23790–23797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baudrenghien, J.; Jadot, J.; Huis, R. Etablissement de la formule de structure de la lonchocarpine. Bull. Soc. Roy. Sci. Liège 1949, 18, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Cursino, L.M.C.; Lima, N.M.; Murillo, R.; Nunez, C.V.; Merfort, I.; Humar, M. Isolation of Flavonoids from Deguelia duckeana and Their Effect on Cellular Viability, AMPK, eEF2, eIF2 and eIF4E. Molecules 2016, 21, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korinek, V.; Barker, N.; Morin, P.J.; Van Wichen, D.; De Weger, R.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Clevers, H. Constitutive transcriptional activation by a β-catenin-Tcf complex in APC−/− colon carcinoma. Science 1997, 275, 1784–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Munemitsu, S.; Albert, I.; Rubinfeld, B.; Polakis, P. Deletion of an amino-terminal sequence beta-catenin in vivo and promotes hyperphosporylation of the adenomatous polyposis coli tumor suppressor protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 4088–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trosset, J.Y.; Dalvit, C.; Knapp, S.; Fasolini, M.; Veronesi, M.; Mantegani, S.; Gianellini, L.M.; Catana, C.; Sundström, M.; Stouten, P.F. Inhibition of protein–protein interactions: The discovery of druglike β-catenin inhibitors by combining virtual and biophysical screening. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2006, 64, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Abreu, J.G.; Yokota, C.; MacDonald, B.T.; Singh, S.; Coburn, K.L.A.; Cheong, S.-M.; Zhang, M.M.; Ye, Q.-Z.; Hang, H.C.; et al. Tiki1 is required for head formation via Wnt cleavage-oxidation and inactivation. Cell 2012, 149, 1565–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amado, N.G.; Fonseca, B.F.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Reis, A.H.; Simas, A.B.C.; Kuster, R.M.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Effects of natural compounds on Xenopus embryogenesis: A potential read out for functional drug discovery targeting Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2103–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.; Gwak, J.; Park, S.; Yang, C.S. Green tea polyphenol EGCG suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting GSK-3β- and PP2A-independent β-catenin phosphorylation/degradation. BioFactors 2014, 40, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amado, N.G.; Predes, D.; Fonseca, B.F.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Reis, A.H.; Dudenhoeffer, A.C.; Borges, H.L.; Mendes, F.A.; Abreu, J.G. Isoquercitrin suppresses colon cancer cell growth in vitro by targeting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35456–35467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cunha, G.M.D.; Fontenele, J.B.; Nobre Júnior, H.V.; de Sousa, F.C.; Silveira, E.R.; Nogueira, N.A.; de Moraes, M.O.; Viana, G.S.; Costa-Lotufo, L.V. Cytotoxic activity of chalcones isolated from Lonchocarpus sericeus (Pocr.) Kunth. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staal, F.; Famili, F.; Garcia Perez, L.; Pike-Overzet, K. Aberrant Wnt signaling in leukemia. Cancers 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhou, D.; Li, X.Z.; Jiang, Z.; Tan, C.; Wei, X.Y.; Ling, J.; Jing, J.; Liu, F.; Li, N. A natural chalcone induces apoptosis in lung cancer cells: 3D-QSAR, docking and an in vivo/vitro assay. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Robertis, M.; Massi, E.; Poeta, M.L.; Carotti, S.; Morini, S.; Cecchetelli, L.; Signori, E.; Fazio, V.M. The AOM/DSS murine model for the study of colon carcinogenesis: From pathways to diagnosis and therapy studies. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.E.; Wani, M.C.; Cook, C.; Palmer, K.H.; McPhail, A.A.; Sim, G. Plant antitumor agents. I. The isolation and structure of camptothecin, a novel alkaloidal leukemia and tumor inhibitor from camptotheca acuminata. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1966, 88, 3888–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, M.E.; Wani, M.C. Discovery to clinic. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 803, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikazawa, N.; Tanaka, H.; Tasaka, T.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, M.; Onishi, H.; Katano, M. Inhibition of Wnt signaling pathway decreases chemotherapy-resistant side-population colon cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2041–2048. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, T.; Ambrosi, G.; Wandmacher, A.; Rauscher, B.; Betge, J.; Rindtorff, N.; Häussler, R.; Hinsenkamp, I.; Bamberg, L.; Hessling, B.; et al. MEK inhibitors activate Wnt signalling and induce stem cell plasticity in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; VanCleave, A.; Helmuth, R.; Torres, H.; Rickel, K.; Wollenzien, H.; Sun, H.; Zeng, E.; Zhao, J.; Tao, J. Targeting the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human osteosarcoma cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36780–36792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.J.; Hsu, L.S.; Shia, Y.T.; Lin, M.W.; Lin, C.M. The β-catenin/TCF complex as a novel target of resveratrol in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbain, N.H.; Salim, N.; Wui, W.T.; Basri, M.; Rahman, M.B.A. Optimization of Quercetin loaded Palm Oil Ester Based Nanoemulsion Formulation for Pulmonary Delivery. J. Oleo Sci. 2018, 67, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakran, M.; Shegokar, R.; Sahoo, N.G.; Al Shaal, L.; Li, L.; Müller, R.H. Fabrication of quercetin nanocrystals: Comparison of different methods. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2012, 80, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Pakade, Y.B.; Singh, B.; Yadav, S.C. Development of biodegradable nanoparticles for delivery of quercetin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 80, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, P. Bioavailability and metabolism of the flavonol quercetin in the pig. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pool, H.; Quintanar, D.; Figueroa, J.D.D.; Mano, C.M.; Bechara, J.E.H.; Godínez, L.A.; Mendoza, S.; Godí Nez, L.A. Antioxidant Effects of Quercetin and Catechin Encapsulated into PLGA Nanoparticles. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.C.D.; Mors, W. Chalcones of the root bark of Derris sericea. Phytochemistry 1972, 11, 3023–3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwkoop, P.; Faber, J. Normal Table of Xenopus Laevis; North-Holland Publishing, Co.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1967. [Google Scholar]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Predes, D.; Oliveira, L.F.S.; Ferreira, L.S.S.; Maia, L.A.; Delou, J.M.A.; Faletti, A.; Oliveira, I.; Amado, N.G.; Reis, A.H.; Fraga, C.A.M.; et al. The Chalcone Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation. Cancers 2019, 11, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121968
Predes D, Oliveira LFS, Ferreira LSS, Maia LA, Delou JMA, Faletti A, Oliveira I, Amado NG, Reis AH, Fraga CAM, et al. The Chalcone Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121968
Chicago/Turabian StylePredes, Danilo, Luiz F. S. Oliveira, Laís S. S. Ferreira, Lorena A. Maia, João M. A. Delou, Anderson Faletti, Igor Oliveira, Nathalia G. Amado, Alice H. Reis, Carlos A. M. Fraga, and et al. 2019. "The Chalcone Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121968
APA StylePredes, D., Oliveira, L. F. S., Ferreira, L. S. S., Maia, L. A., Delou, J. M. A., Faletti, A., Oliveira, I., Amado, N. G., Reis, A. H., Fraga, C. A. M., Kuster, R., Mendes, F. A., Borges, H. L., & Abreu, J. G. (2019). The Chalcone Lonchocarpin Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling and Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation. Cancers, 11(12), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121968





