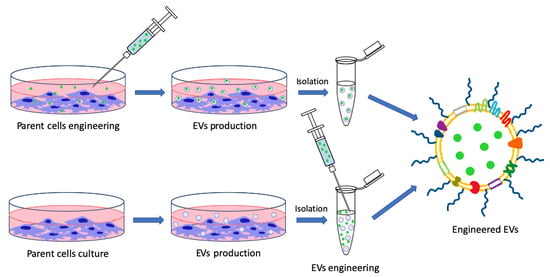
Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Reliable Tool in Cancer Nanomedicine
Abstract
Share and Cite
Susa, F.; Limongi, T.; Dumontel, B.; Vighetto, V.; Cauda, V. Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Reliable Tool in Cancer Nanomedicine. Cancers 2019, 11, 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121979
Susa F, Limongi T, Dumontel B, Vighetto V, Cauda V. Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Reliable Tool in Cancer Nanomedicine. Cancers. 2019; 11(12):1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121979
Chicago/Turabian StyleSusa, Francesca, Tania Limongi, Bianca Dumontel, Veronica Vighetto, and Valentina Cauda. 2019. "Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Reliable Tool in Cancer Nanomedicine" Cancers 11, no. 12: 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121979
APA StyleSusa, F., Limongi, T., Dumontel, B., Vighetto, V., & Cauda, V. (2019). Engineered Extracellular Vesicles as a Reliable Tool in Cancer Nanomedicine. Cancers, 11(12), 1979. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11121979