Liposomal Irinotecan for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer in a Preclinical Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Liposomal Irinotecan (Lipo-IRI)
2.2. Stability of Lipo-IRI
2.3. In Vitro Cell Viability of Irinotecan
2.4. Chromatographic Analysis of Lipo-IRI
2.5. Plasma Pharmacokinetics and Bio-Distribution of Lipo-IRI
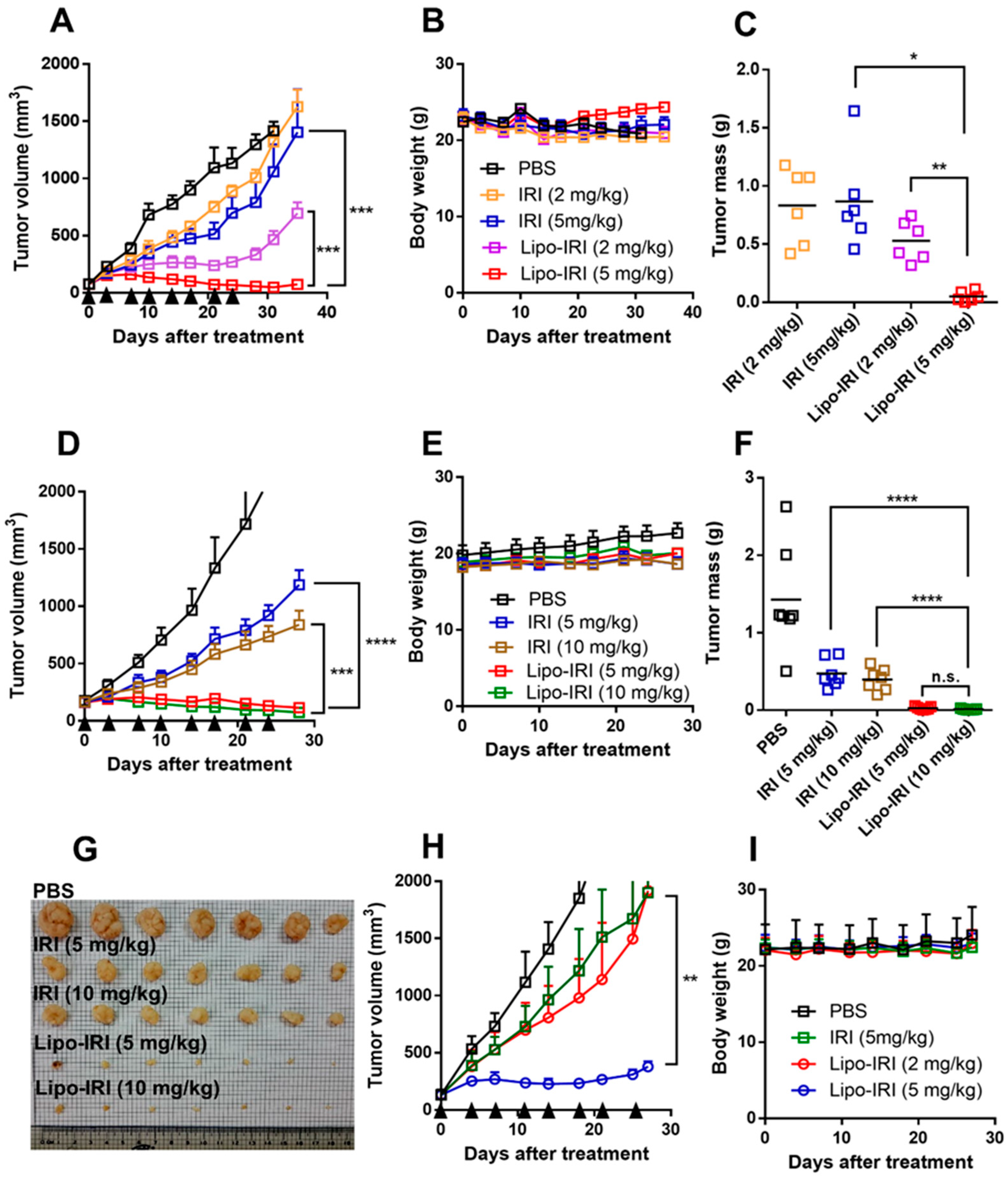
2.6. In Vivo Therapeutic Efficacy of Liposomal Irinotecan
2.7. Side Effects of Irinotecan
2.8. Generation of Targeting Liposome pHCT74-Lipo-IRI and Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Efficacy in Large Tumor-Bearing Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Animals
4.2. Liposomal Drug Preparation
4.3. Phosphorus Content Analysis
4.4. Characterization of Lipo-IRI
4.5. Quantification of Lipo-IRI
4.6. In Vitro Release Profile
4.7. Cell Viability Assay
4.8. Pharmacokinetics and Bio-Distribution Study
4.9. In Vivo Anti-Tumor Efficacy in Small Tumor Models
4.10. Toxicity and Side Effects
4.11. Combination Targeted Therapy in Large Tumor Model In Vivo
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, S.L.; Wike, J.M.; Kato, I.; Lewis, D.R.; Michaud, F. A population-based study of colorectal cancer histology in the United States, 1998–2001. Cancer 2006, 107, 1128–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, B.; Lieberman, D.A.; McFarland, B.; Andrews, K.S.; Brooks, D.; Bond, J.; Dash, C.; Giardiello, F.M.; Glick, S.; Johnson, D.; et al. Screening and surveillance for the early detection of colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps, 2008: A joint guideline from the American Cancer Society, the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer, and the American College of Radiology. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 1570–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moertel, C.G.; Schutt, A.J.; Reitemeier, R.J.; Hahn, R.G. Phase II study of camptothecin (NSC-100880) in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Chemother. Rep. Part 1 1972, 56, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Muggia, F.M.; Creaven, P.J.; Hansen, H.H.; Cohen, M.H.; Selawry, O.S. Phase I clinical trial of weekly and daily treatment with camptothecin (NSC-100880): Correlation with preclinical studies. Cancer Chemother. Rep. Part 1 1972, 56, 515–521. [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg, R.P.; Caranfa, M.J.; Holden, K.G.; Jakas, D.R.; Gallagher, G.; Mattern, M.R.; Mong, S.M.; Bartus, J.O.; Johnson, R.K.; Kingsbury, W.D. Modification of the hydroxy lactone ring of camptothecin: Inhibition of mammalian topoisomerase I and biological activity. J. Med. Chem. 1989, 32, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiang, Y.H.; Lihou, M.G.; Liu, L.F. Arrest of replication forks by drug-stabilized topoisomerase I-DNA cleavable complexes as a mechanism of cell killing by camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 5077–5082. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giovanella, B.C.; Harris, N.; Mendoza, J.; Cao, Z.; Liehr, J.; Stehlin, J.S. Dependence of anticancer activity of camptothecins on maintaining their lactone function. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 922, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immordino, M.L.; Dosio, F.; Cattel, L. Stealth liposomes: Review of the basic science, rationale, and clinical applications, existing and potential. Int. J. Nanomed. 2006, 1, 297–315. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiang, Y.H.; Liu, L.F. Identification of mammalian DNA topoisomerase I as an intracellular target of the anticancer drug camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.L. Irinotecan (CPT-11): Recent developments and future directions—Colorectal cancer and beyond. Oncologist 2001, 6, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparreboom, A.; de Jonge, M.J.; de Bruijn, P.; Brouwer, E.; Nooter, K.; Loos, W.J.; van Alphen, R.J.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Stoter, G.; Verweij, J. Irinotecan (CPT-11) metabolism and disposition in cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 2747–2754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.P.; Yang, X.X.; Chan, S.Y.; Xu, A.L.; Duan, W.; Zhu, Y.Z.; Sheu, F.S.; Boelsterli, U.A.; Chan, E.; Zhang, Q.; et al. St. John’s wort attenuates irinotecan-induced diarrhea via down-regulation of intestinal pro-inflammatory cytokines and inhibition of intestinal epithelial apoptosis. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 216, 225–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Alencar, N.M.; da Silveira Bitencourt, F.; de Figueiredo, I.S.; Luz, P.B.; Lima-Junior, R.C.; Aragao, K.S.; Magalhaes, P.J.; de Castro Brito, G.A.; Ribeiro, R.A.; de Freitas, A.P.; et al. Side-Effects of Irinotecan (CPT-11), the Clinically Used Drug for Colon Cancer Therapy, Are Eliminated in Experimental Animals Treated with Latex Proteins from Calotropis procera (Apocynaceae). Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.L.; Kuhn, J.G.; Schaaf, L.J.; Rodriguez, G.I.; Eckhardt, S.G.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Rinaldi, D.A.; Hammond, L.A.; Hodges, S.; Sharma, A.; et al. Phase I dose-finding and pharmacokinetic trial of irinotecan (CPT-11) administered every two weeks. Ann. Oncol. 2001, 12, 1631–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanterman, J.; Sade-Feldman, M.; Biton, M.; Ish-Shalom, E.; Lasry, A.; Goldshtein, A.; Hubert, A.; Baniyash, M. Adverse immunoregulatory effects of 5FU and CPT11 chemotherapy on myeloid-derived suppressor cells and colorectal cancer outcomes. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6022–6035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.W. Liposome-based drug delivery in breast cancer treatment. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoarau, D.; Delmas, P.; David, S.; Roux, E.; Leroux, J.C. Novel long-circulating lipid nanocapsules. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yarmolenko, P.S.; Zhao, Y.; Landon, C.; Spasojevic, I.; Yuan, F.; Needham, D.; Viglianti, B.L.; Dewhirst, M.W. Comparative effects of thermosensitive doxorubicin-containing liposomes and hyperthermia in human and murine tumours. Int. J. Hyperth. 2010, 26, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dromi, S.; Frenkel, V.; Luk, A.; Traughber, B.; Angstadt, M.; Bur, M.; Poff, J.; Xie, J.; Libutti, S.K.; Li, K.C.; et al. Pulsed-high intensity focused ultrasound and low temperature-sensitive liposomes for enhanced targeted drug delivery and antitumor effect. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2722–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Khan, S.; Wang, Y.F.; Kamath, N.; Sarkar, A.K.; Ahmad, A.; Sheikh, S.; Ali, S.; Carbonaro, D.; Zhang, A.; et al. Preclinical safety, pharmacokinetics and antitumor efficacy profile of liposome-entrapped SN-38 formulation. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, E.; Alnajim, J.; Anantha, M.; Zastre, J.; Yan, H.; Webb, M.; Waterhouse, D.; Bally, M. A novel liposomal irinotecan formulation with significant anti-tumour activity: Use of the divalent cation ionophore A23187 and copper-containing liposomes to improve drug retention. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 68, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, D.C.; Meyer, O.; Hong, K.; Kirpotin, D.B.; Papahadjopoulos, D. Optimizing liposomes for delivery of chemotherapeutic agents to solid tumors. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 691–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greish, K.; Fang, J.; Inutsuka, T.; Nagamitsu, A.; Maeda, H. Macromolecular therapeutics: Advantages and prospects with special emphasis on solid tumour targeting. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2003, 42, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northfelt, D.W.; Martin, F.J.; Working, P.; Volberding, P.A.; Russell, J.; Newman, M.; Amantea, M.A.; Kaplan, L.D. Doxorubicin encapsulated in liposomes containing surface-bound polyethylene glycol: Pharmacokinetics, tumor localization, and safety in patients with AIDS-related Kaposi’s sarcoma. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1996, 36, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Hong, R.L.; Wu, H.C. Alpha-Enolase-binding peptide enhances drug delivery efficiency and therapeutic efficacy against colorectal cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 290ra291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathijssen, R.H.; van Alphen, R.J.; Verweij, J.; Loos, W.J.; Nooter, K.; Stoter, G.; Sparreboom, A. Clinical pharmacokinetics and metabolism of irinotecan (CPT-11). Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 2182–2194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawato, Y.; Aonuma, M.; Hirota, Y.; Kuga, H.; Sato, K. Intracellular roles of SN-38, a metabolite of the camptothecin derivative CPT-11, in the antitumor effect of CPT-11. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 4187–4191. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, E.; Alnajim, J.; Anantha, M.; Taggar, A.; Thomas, A.; Edwards, K.; Karlsson, G.; Webb, M.; Bally, M. Transition metal-mediated liposomal encapsulation of irinotecan (CPT-11) stabilizes the drug in the therapeutically active lactone conformation. Pharm. Res. 2006, 23, 2799–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patankar, N.; Anantha, M.; Ramsay, E.; Waterhouse, D.; Bally, M. The role of the transition metal copper and the ionophore A23187 in the development of Irinophore CTM. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taggar, A.S.; Alnajim, J.; Anantha, M.; Thomas, A.; Webb, M.; Ramsay, E.; Bally, M.B. Copper-topotecan complexation mediates drug accumulation into liposomes. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nichols, J.W.; Bae, Y.H. EPR: Evidence and fallacy. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danhier, F. To exploit the tumor microenvironment: Since the EPR effect fails in the clinic, what is the future of nanomedicine? J. Control. Release 2016, 244, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drummond, D.C.; Noble, C.O.; Guo, Z.; Hong, K.; Park, J.W.; Kirpotin, D.B. Development of a highly active nanoliposomal irinotecan using a novel intraliposomal stabilization strategy. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3271–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsuka, K.; Inoue, S.; Kameyama, M.; Kanetoshi, A.; Fujimoto, T.; Takaoka, K.; Araya, Y.; Shida, A. Intracellular conversion of irinotecan to its active form, SN-38, by native carboxylesterase in human non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2003, 41, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Yan, B.; Humerickhouse, R.; Dolan, M.E. Irinotecan activation by human carboxylesterases in colorectal adenocarcinoma cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2696–2700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Zhang, W.; Ma, M.K.; McLeod, H.L. Human carboxylesterase 2 is commonly expressed in tumor tissue and is correlated with activation of irinotecan. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2605–2611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Armand, J.P. CPT-11: Clinical experience in phase I studies. Semin. Oncol. 1996, 23, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rothenberg, M.L.; Meropol, N.J.; Poplin, E.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Wadler, S. Mortality associated with irinotecan plus bolus fluorouracil/leucovorin: Summary findings of an independent panel. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 3801–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B., 3rd; Ajani, J.A.; Catalano, R.B.; Engelking, C.; Kornblau, S.M.; Martenson, J.A., Jr.; McCallum, R.; Mitchell, E.P.; O’Dorisio, T.M.; Vokes, E.E.; et al. Recommended guidelines for the treatment of cancer treatment-induced diarrhea. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swami, U.; Goel, S.; Mani, S. Therapeutic targeting of CPT-11 induced diarrhea: A case for prophylaxis. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 777–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurita, A.; Kado, S.; Kaneda, N.; Onoue, M.; Hashimoto, S.; Yokokura, T. Modified irinotecan hydrochloride (CPT-11) administration schedule improves induction of delayed-onset diarrhea in rats. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2000, 46, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kehrer, D.F.; Sparreboom, A.; Verweij, J.; de Bruijn, P.; Nierop, C.A.; van de Schraaf, J.; Ruijgrok, E.J.; de Jonge, M.J. Modulation of irinotecan-induced diarrhea by cotreatment with neomycin in cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1136–1141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Sawyer, M.B.; Field, C.J.; Dieleman, L.A.; Baracos, V.E. Nutritional modulation of antitumor efficacy and diarrhea toxicity related to irinotecan chemotherapy in rats bearing the ward colon tumor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 7146–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kase, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Togashi, Y.; Kamataki, T. Relevance of irinotecan hydrochloride-induced diarrhea to the level of prostaglandin E2 and water absorption of large intestine in rats. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 75, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klebanoff, S.J. Myeloperoxidase: Friend and foe. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 77, 598–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heldin, C.H.; Rubin, K.; Pietras, K.; Ostman, A. High interstitial fluid pressure-An obstacle in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.H.; Liu, I.J.; Lu, R.M.; Wu, H.C. Advancement and applications of peptide phage display technology in biomedical science. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taieb, J.; Lecomte, T.; Aparicio, T.; Asnacios, A.; Mansourbakht, T.; Artru, P.; Fallik, D.; Spano, J.P.; Landi, B.; Lledo, G.; et al. FOLFIRI.3, a new regimen combining 5-fluorouracil, folinic acid and irinotecan, for advanced pancreatic cancer: Results of an Association des Gastro-Enterologues Oncologues (Gastroenterologist Oncologist Association) multicenter phase II study. Ann. Oncol. 2007, 18, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teufel, A.; Steinmann, S.; Siebler, J.; Zanke, C.; Hohl, H.; Adami, B.; Schroeder, M.; Klein, O.; Hohler, T.; Galle, P.R.; et al. Irinotecan plus folinic acid/continuous 5-fluorouracil as simplified bimonthly FOLFIRI regimen for first-line therapy of metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.T.; Siveke, J.T.; Wang-Gillam, A.; Li, C.P.; Bodoky, G.; Dean, A.P.; Shan, Y.S.; Jameson, G.S.; Macarulla, T.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Survival with nal-IRI (liposomal irinotecan) plus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin versus 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in per-protocol and non-per-protocol populations of NAPOLI-1: Expanded analysis of a global phase 3 trial. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 105, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Gillam, A.; Hubner, R.A.; Siveke, J.T.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Belanger, B.; de Jong, F.A.; Mirakhur, B.; Chen, L.T. NAPOLI-1 phase 3 study of liposomal irinotecan in metastatic pancreatic cancer: Final overall survival analysis and characteristics of long-term survivors. Eur. J. Cancer 2019, 108, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.; Lin, C.T.; Wu, H.C. Hepatocellular carcinoma cell-specific peptide ligand for targeted drug delivery. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, G.R. Phosphorus assay in column chromatography. J. Biol. Chem. 1959, 234, 466–468. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Warner, D.L.; Burke, T.G. Simple and versatile high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the simultaneous quantitation of the lactone and carboxylate forms of camptothecin anticancer drugs. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1997, 691, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.-R.; Lee, M.-H.; Li, W.-S.; Wu, H.-C. Liposomal Irinotecan for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer in a Preclinical Model. Cancers 2019, 11, 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030281
Huang J-R, Lee M-H, Li W-S, Wu H-C. Liposomal Irinotecan for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer in a Preclinical Model. Cancers. 2019; 11(3):281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030281
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jiao-Ren, Mei-Hsien Lee, Wen-Shan Li, and Han-Chun Wu. 2019. "Liposomal Irinotecan for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer in a Preclinical Model" Cancers 11, no. 3: 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030281
APA StyleHuang, J.-R., Lee, M.-H., Li, W.-S., & Wu, H.-C. (2019). Liposomal Irinotecan for Treatment of Colorectal Cancer in a Preclinical Model. Cancers, 11(3), 281. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030281




