Combination of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Up-To-Seven Criteria as a Useful Predictor for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Clinical Characteristics of Patients
2.2. Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after TACE
2.3. Factors Associated with Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after TACE
2.4. Predictive Performance of M2BPGi for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after TACE
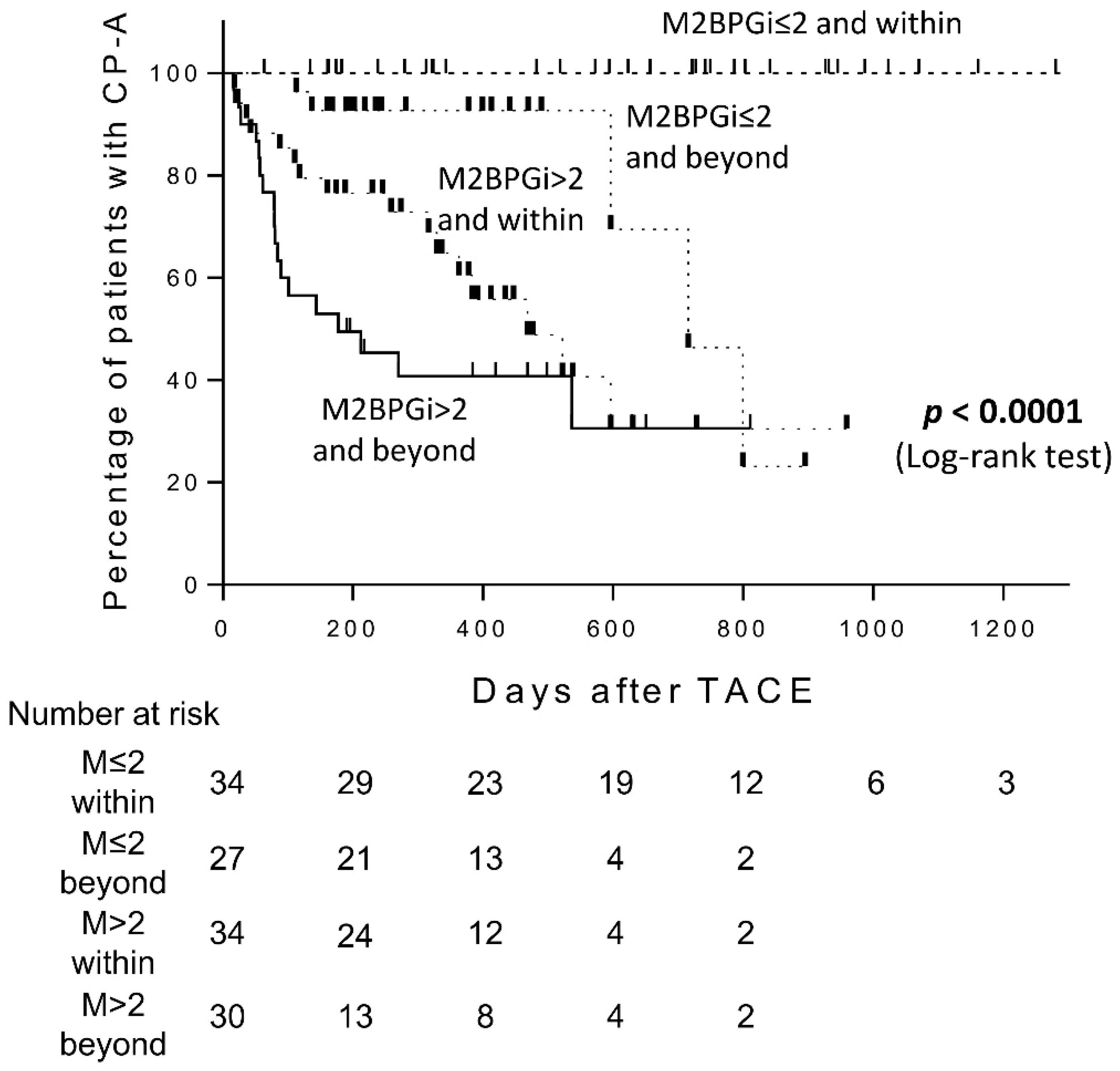
2.5. Predictive Performance of M2BPGi and Up-To-Seven Criteria Combination for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after TACE
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Transarterial Chemoembolization Procedure
4.3. Follow-Up Schedule and Retreatment Strategy
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galle, P.R.; Forner, A.; Llovet, J.M.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Schirmacher, P.; Vilgrain, V. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eso, Y.; Marusawa, H. Novel approaches for molecular targeted therapy against hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Kudo, M.; Hirooka, M.; Koizumi, Y.; Hiasa, Y.; Tajiri, K.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Ochi, H.; et al. Hepatic Function during Repeated TACE Procedures and Prognosis after Introducing Sorafenib in Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Multicenter Analysis. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, RS.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forner, A.; Gilabert, M.; Bruix, J.; Raoul, J.L. Treatment of intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toshima, T.; Shirabe, K.; Ikegami, T.; Yoshizumi, T.; Kuno, A.; Togayachi, A.; Gotoh, M.; Narimatsu, H.; Korenaga, M.; Mizokami, M.; et al. A novel serum marker, glycosylated Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein (WFA(+)-M2BP), for assessing liver fibrosis. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiyoshi, M.; Kuno, A.; Gotoh, M.; Fukai, M.; Yokoo, H.; Kamachi, H.; Kamiyama, T.; Korenaga, M.; Mizokami, M.; Narimatsu, H.; et al. Clinicopathological characteristics and diagnostic performance of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein as a preoperative serum marker of liver fibrosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, M.; Miyake, T.; Kuno, A.; Imai, Y.; Sawai, Y.; Hino, K.; Hara, Y.; Hige, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Yamada, G.; et al. Association between Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding protein and the fibrosis stage of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eso, Y.; Takai, A.; Taura, K.; Takahashi, K.; Ueda, Y.; Marusawa, H.; Seno, H. Association of Mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer level with nutritional status in chronic liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, S.; Chiba, T.; Ooka, Y.; Kanogawa, N.; Motoyama, T.; Suzuki, E.; Tawada, A.; Kanai, F.; Yoshikawa, M.; Yokosuka, O. Efficacy of sorafenib in intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients refractory to transarterial chemoembolization. Oncology 2014, 87, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arizumi, T.; Ueshima, K.; Minami, T.; Kono, M.; Chishina, H.; Takita, M.; Kitai, S.; Inoue, T.; Yada, N.; Hagiwara, S.; et al. Effectiveness of Sorafenib in Patients with Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization (TACE) Refractory and Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2015, 4, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kuno, A.; Ikehara, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Ito, K.; Matsuda, A.; Sekiya, S.; Hige, S.; Sakamoto, M.; Kage, M.; Mizokami, M.; et al. A serum “sweet-doughnut” protein facilitates fibrosis evaluation and therapy assessment in patients with viral hepatitis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narimatsu, H. Development of M2BPGi: A novel fibrosis serum glyco-biomarker for chronic hepatitis/cirrhosis diagnostics. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2015, 12, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Kong, W.; Liu, L.; Chi, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Qu, L.; Qi, Y.; et al. Accuracy of M2BPGi, compared with Fibro Scan®, in analysis of liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis C. BMC Gastroenterol. 2017, 17, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagata, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Nishimura-Sakurai, Y.; Asano, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Miyoshi, M.; Kaneko, S.; Goto, F.; Otani, S.; Kawai-Kitahata, F.; et al. Serial measurement of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2-binding protein is useful for predicting liver fibrosis and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C patients treated with IFN-based and IFN-free therapy. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 956–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, N.; Nojima, M.; Iio, E.; Matsunami, K.; Toyoda, H.; Murakami, S.; Inoue, T.; Ogawa, S.; Kumada, T.; Tanaka, Y. High levels of serum Mac-2-binding protein glycosylation isomer (M2BPGi) predict the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis B patients treated with nucleot(s)ide analogues. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, Y.; Tsuchiya, K.; Kurosaki, M.; Takeguchi, T.; Takeguchi, Y.; Okada, M.; Wang, W.; Kubota, Y.; Goto, T.; Komiyama, Y.; et al. Up-to-seven criteria as a useful predictor for tumor downstaging to within Milan criteria and Child-Pugh grade deterioration after initial conventional transarterial chemoembolization. Hepatol. Res. 2018, 48, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Llovet, J.M.; Miceli, R.; Bhoori, S.; Schiavo, M.; Mariani, L.; Camerini, T.; Roayaie, S.; Schwartz, M.E.; Grazi, G.L.; et al. Predicting survival after liver transplantation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma beyond the Milan criteria: A retrospective, exploratory analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, H.; Ohkawa, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Sakakibara, M.; Imanaka, K.; Tamura, T.; Sueyoshi, H.; Takada, R.; Fukutake, N.; Uehara, H.; et al. Subclassification of patients with intermediate-stage (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage-B) hepatocellular carcinoma using the up-to-seven criteria and serum tumor markers. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, M.; Cabibbo, G.; Piscaglia, F.; Zavaglia, C.; Grieco, A.; Villa, E.; Cammà, C.; Colombo, M.; SOFIA Study Group. Field-practice study of sorafenib therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective multicenter study in Italy. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2055–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; S Sulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanai, T.; Shiraki, M.; Ohnishi, S.; Miyazaki, T.; Ideta, T.; Kochi, T.; Imai, K.; Suetsugu, A.; Takai, K.; Shimizu, M.; et al. Impact of serum glycosylated Wisteria floribunda agglutinin positive Mac-2 binding protein levels on liver functional reserves and mortality in patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2015, 45, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamasaki, K.; Tateyama, M.; Abiru, S.; Komori, A.; Nagaoka, S.; Saeki, A.; Hashimoto, S.; Sasaki, R.; Bekki, S.; Kugiyama, Y.; et al. Elevated serum levels of Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predict the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients. Hepatology 2014, 60, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bolondi, L.; Burroughs, A.; Dufour, J.F.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Piscaglia, F.; Raoul, J.L.; Sangro, B. Heterogeneity of patients with intermediate (BCLC B) Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Proposal for a subclassification to facilitate treatment decisions. Semin. Liver Dis. 2012, 32, 348–359. [Google Scholar]



| Variable | n = 125 |
|---|---|
| Age (years, range) | 74.3 ± 8.86 (41–88) |
| Gender (Male vs. Female) | 96/29 |
| Child-Pugh score (score of 5 vs. score of 6) | 69/56 |
| Etiology (HBV vs. HCV vs. non-B non-C) | 12/64/49 |
| Treatment history (Naïve vs. recurrence) | 30/95 |
| Up-to-seven criteria (within vs. beyond) | 68/57 |
| Tumor number | 4.47 ± 3.67 |
| Maximum tumor size (cm) | 4.86 ± 9.45 |
| Number of TACE procedures | 1.95 ± 1.23 |
| AST (IU/L) | 47.8 ± 30.5 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 35.1 ± 30.3 |
| Platelets (×104/μL) | 14.8 ± 9.92 |
| ALB (g/dL) | 3.68 ± 0.43 |
| T-Bil (mg/dL) | 0.82 ± 0.31 |
| PT (%) | 90.5 ± 14.8 |
| AFP (ng/mL) | 3506 ± 14194 |
| DCP (mAU/mL) | 2900 ± 9532 |
| FIB-4 index | 5.59 ± 4.00 |
| M2BPGi (cut-off index) | 3.31 ± 3.01 |
| Variable | No. of Cases | Univariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | ||
| Age (>75 vs. ≤75) | 69/56 | 1.30 (0.69–2.50) | 0.4130 |
| Gender (Female vs. Male) | 29/96 | 2.97 (1.55–5.57) | 0.0013 |
| ALB (≤3.5 g/dL vs. >3.5 g/dL) | 48/77 | 3.48 (1.82–6.82) | 0.0002 |
| T-Bil (>1.0 mg/dL vs. ≤1.0 mg/dL) | 28/97 | 2.76 (1.43–5.20) | 0.0003 |
| PT (≤80% vs. >80%) | 36/89 | 2.07 (1.08–3.89) | 0.0281 |
| Platelets (≤10 × 104/μL vs. >10 × 104/μL) | 38/87 | 1.73 (0.89–3.29) | 0.1031 |
| AFP (>100 ng/mL vs. ≤100 ng/mL) | 52/73 | 1.61 (0.84–3.06) | 0.1490 |
| DCP (>100 mAU/mL vs. ≤100 mAU/mL) | 77/48 | 1.56 (0.80–3.19) | 0.1975 |
| FIB-4 index (>4.00 vs. ≤4.00) | 70/55 | 2.48 (1.27–5.23) | 0.0074 |
| M2BPGi (>2.00 COI vs. ≤2.00 COI) | 64/61 | 10.86 (4.55–32.2) | <0.0001 |
| Up-to-seven criteria (Beyond vs. Within) | 57/68 | 2.35 (1.24–4.58) | 0.0098 |
| Variable | No. of Cases | Multivariate Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p Value | ||
| Gender (Female vs. Male) | 29/96 | 2.00 (1.00–3.94) | 0.0515 |
| FIB-4 index (>4.00 vs. ≤4.00) | 70/55 | 0.63 (0.28–1.48) | 0.2794 |
| M2BPGi (>2.00 COI vs. ≤2.00 COI) | 64/61 | 12.41 (4.55–40.3) | <0.0001 |
| Up-to-seven criteria (Beyond vs. Within) | 57/68 | 1.96 (1.01–3.90) | 0.0479 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eso, Y.; Takai, A.; Takahashi, K.; Ueda, Y.; Taura, K.; Marusawa, H.; Seno, H. Combination of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Up-To-Seven Criteria as a Useful Predictor for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030405
Eso Y, Takai A, Takahashi K, Ueda Y, Taura K, Marusawa H, Seno H. Combination of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Up-To-Seven Criteria as a Useful Predictor for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2019; 11(3):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030405
Chicago/Turabian StyleEso, Yuji, Atsushi Takai, Ken Takahashi, Yoshihide Ueda, Kojiro Taura, Hiroyuki Marusawa, and Hiroshi Seno. 2019. "Combination of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Up-To-Seven Criteria as a Useful Predictor for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 11, no. 3: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030405
APA StyleEso, Y., Takai, A., Takahashi, K., Ueda, Y., Taura, K., Marusawa, H., & Seno, H. (2019). Combination of Mac-2 Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer and Up-To-Seven Criteria as a Useful Predictor for Child-Pugh Grade Deterioration after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 11(3), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030405







