Differential MicroRNA Landscape Triggered by Estrogens in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) of Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors
Abstract
1. Introduction
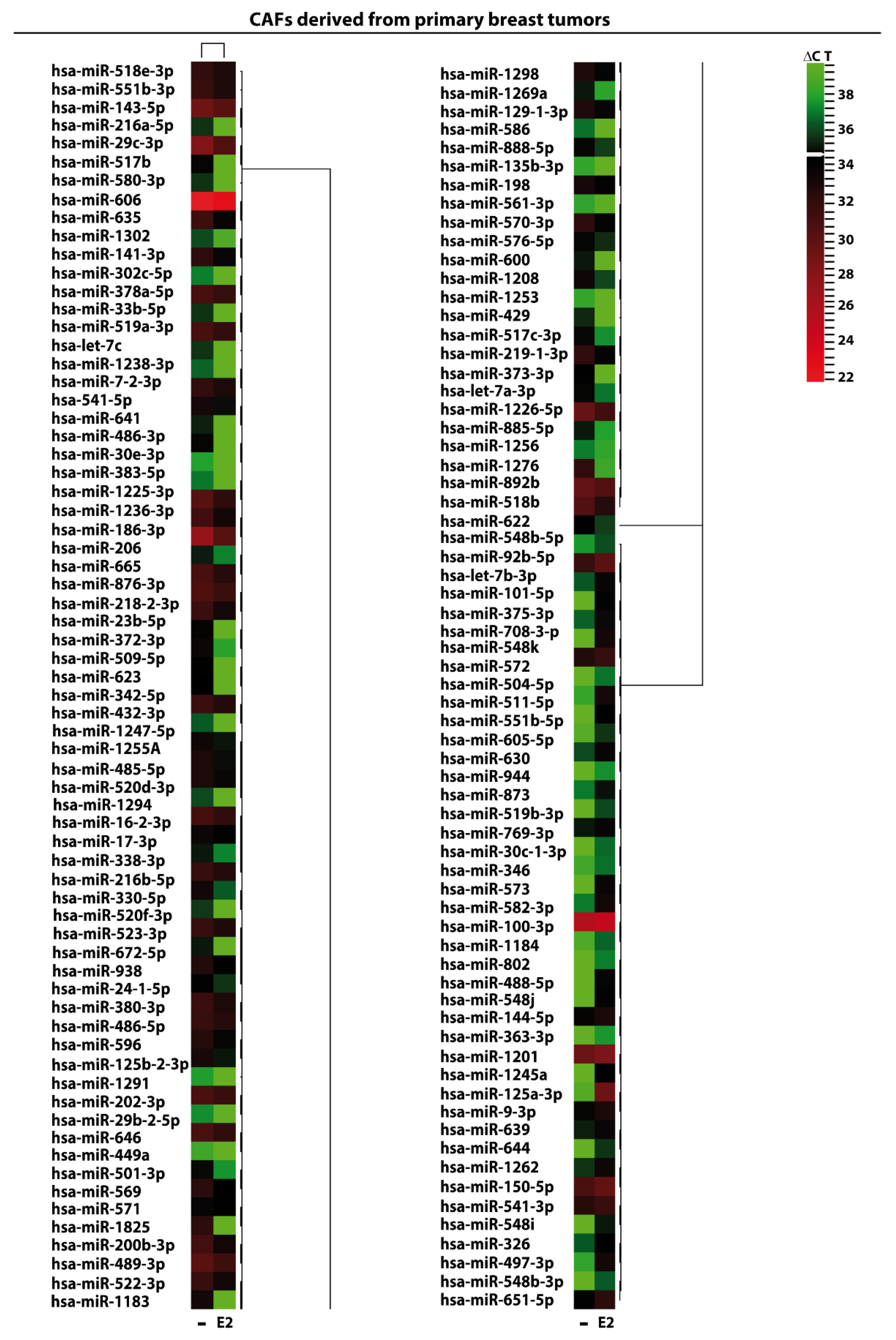
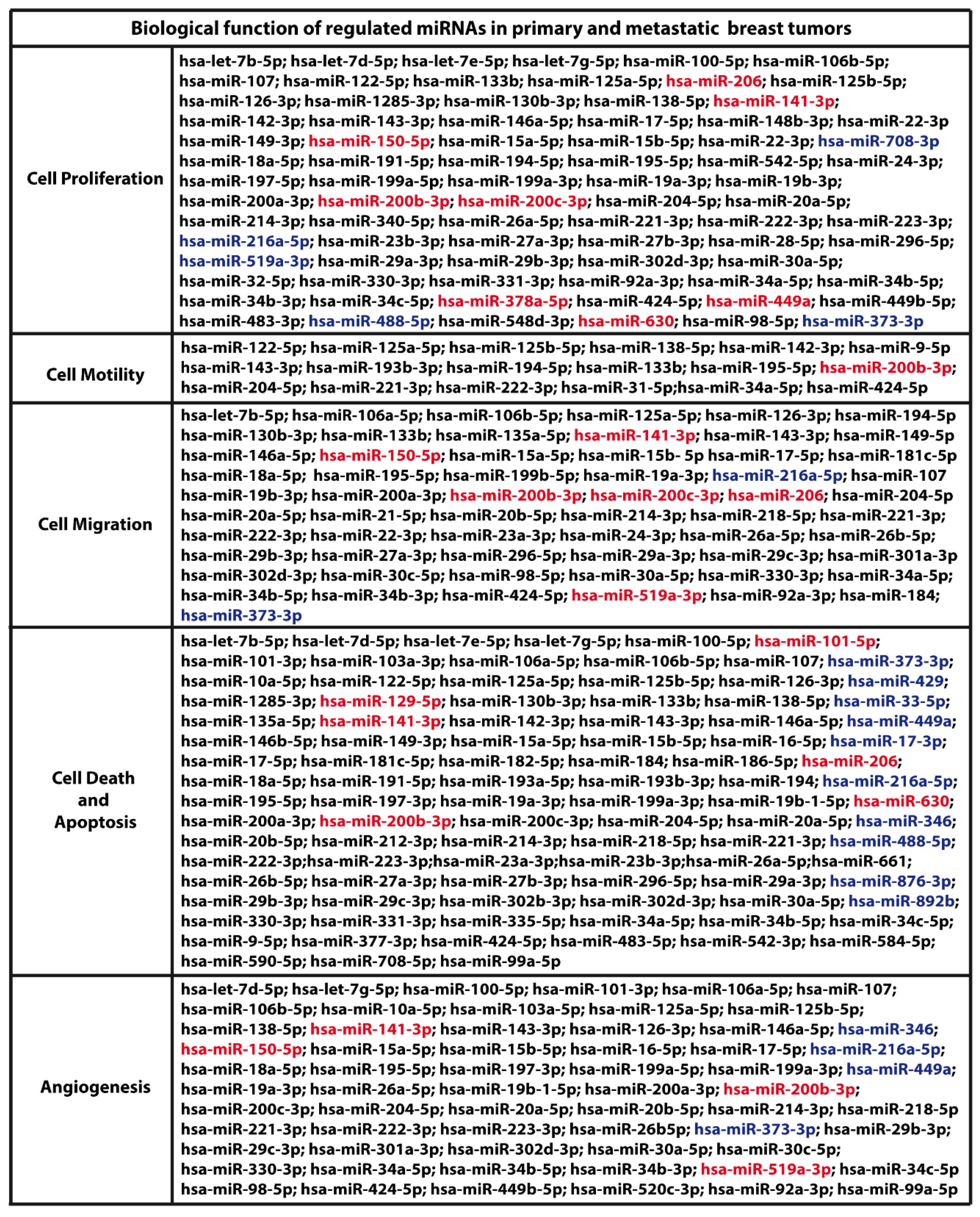
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Reagents
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Immunofluorescence Microscopy
3.4. RNA Extraction
3.5. miRNA Expression Profiling
3.6. Data Analysis
3.7. Declarations: Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.; Naishadham, D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2013, 63, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scully, O.J.; Bay, B.H.; Yip, G.; Yu, Y. Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2012, 9, 311–320. [Google Scholar]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiga, K.; Hara, M.; Nagasaki, T.; Sato, T.; Takahashi, H.; Takeyama, H. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Their Characteristics and Their Roles in Tumor Growth. Cancers 2015, 7, 2443–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhood, B.; Najafi, M.; Mortezaee, K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Secretions, interactions, and therapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichmuller, S.B.; Osen, W.; Mandelboim, O.; Seliger, B. Immune modulatory microRNAs involved in tumor attack and tumor immune escape. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, Y.; Raz, Y.; Cohen, N.; Ben-Shmuel, A.; Schwartz, H.; Geiger, T.; Erez, N. Tumor-derived osteopontin reprograms normal mammary fibroblasts to promote inflammation and tumor growth in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orimo, A.; Gupta, P.B.; Sgroi, D.C.; Arenzana-Seisdedos, F.; Delaunay, T.; Naeem, R.; Carey, V.J.; Richardson, A.L.; Weinberg, R.A. Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell 2005, 121, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J. Estrogen receptors: Therapies targeted to receptor subtypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lappano, R.; Maggiolini, M. GPER is involved in the functional liaison between breast tumor cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2018, 176, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brechbuhl, H.M.; Finlay-Schultz, J.; Yamamoto, T.M.; Gillen, A.E.; Cittelly, D.M.; Tan, A.C.; Sams, S.B.; Pillai, M.M.; Elias, A.D.; Robinson, W.A.; et al. Fibroblast Subtypes Regulate Responsiveness of Luminal Breast Cancer to Estrogen. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1710–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cirillo, F.; Pellegrino, M.; Malivindi, R.; Rago, V.; Avino, S.; Muto, L.; Dolce, V.; Vivacqua, A.; Rigiracciolo, D.C.; De Marco, P.; et al. GPER is involved in the regulation of the estrogen-metabolizing CYP1B1 enzyme in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 106608–106624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, P.; Lappano, R.; De Francesco, E.M.; Cirillo, F.; Pupo, M.; Avino, S.; Vivacqua, A.; Abonante, S.; Picard, D.; Maggiolini, M. GPER signalling in both cancer-associated fibroblasts and breast cancer cells mediates a feedforward IL1β/IL1R1 response. Sci. Rep. 2016, 13, 24354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Chang, W.; Fang, B.; Qin, J.; Qu, X.; Cheng, F. Estrogen-induced SDF-1α production promotes the progression of ER-negative breast cancer via the accumulation of MDSCs in the tumor microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Liu, M.; Luo, S.; Yu, T.; Wu, C.; Yang, G.; Tu, G. Dynamic monitoring of GPER-mediated estrogenic effects in breast cancer associated fibroblasts: An alternative role of estrogen in mammary carcinoma development. Steroids 2016, 112, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marco, P.; Cirillo, F.; Vivacqua, A.; Malaguarnera, R.; Belfiore, A.; Maggiolini, M. Novel Aspects Concerning the Functional Cross-Talk between the Insulin/IGF-I System and Estrogen Signaling in Cancer Cells. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2015, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pupo, M.; Vivacqua, A.; Perrotta, I.; Pisano, A.; Aquila, S.; Abonante, S.; Gasperi-Campani, A.; Pezzi, V.; Maggiolini, M. The nuclear localization signal is required for nuclear GPER translocation and function in breast Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs). Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 376, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, A.; Romeo, E.; De Marco, P.; De Francesco, E.M.; Abonante, S.; Maggiolini, M. GPER mediates the Egr-1 expression induced by 17β-estradiol and 4-hydroxitamoxifen in breast and endometrial cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 133, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggiolini, M.; Picard, D. The unfolding stories of GPR30, a new membrane-bound estrogen receptor. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 204, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, D.P.; Lappano, R.; Albanito, L.; Madeo, A.; Maggiolini, M.; Picard, D. Estrogenic GPR30 signalling induces proliferation and migration of breast cancer cells through CTGF. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, A.; Sebastiani, A.; Miglietta, A.M.; Rigiracciolo, D.C.; Cirillo, F.; Galli, G.R.; Talia, M.; Santolla, M.F.; Lappano, R.; Giordano, F.; et al. miR-338-3p Is Regulated by Estrogens through GPER in Breast Cancer Cells and Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs). Cells 2018, 7, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.F.; Li, D.M.; Shi, Z.M.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.M.; Ge, X.; Liu, X.; Qian, Y.C.; Wen, Y.Y.; Zhen, L.L.; et al. Estrogen regulates miRNA expression: Implication of estrogen receptor and miR-124/AKT2 in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36940–36955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinge, C.M. miRNAs regulated by estrogens, tamoxifen, and endocrine disruptors and their downstream gene targets. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418 Pt 3, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivacqua, A.; De Marco, P.; Santolla, M.F.; Cirillo, F.; Pellegrino, M.; Panno, M.L.; Abonante, S.; Maggiolini, M. Estrogenic gper signaling regulates mir144 expression in cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts (cafs). Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16573–16587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Hamo, R.; Efroni, S. MicroRNA regulation of molecular pathways as a generic mechanism and as a core disease phenotype. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1594–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chira, P.; Vareli, K.; Sainis, I.; Papandreou, C.; Briasoulis, E. Alterations of MicroRNAs in Solid Cancers and Their Prognostic Value. Cancers 2010, 2, 1328–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandujano-Tinoco, E.A.; García-Venzor, A.; Melendez-Zajgla, J.; Maldonado, V. New emerging roles of microRNAs in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018, 171, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Croce, C.M. The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2016, 1, 15004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipan, V.; Zorc, M.; Kunej, T. MicroRNA Polymorphisms in Cancer: A Literature Analysis. Cancers 2015, 7, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, L.R.; Bulun, S.E. Estrogen production and action. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, S116–S124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.; Homaei, A.; Raju, A.B.; Meher, B.R. Estrogen: The necessary evil for human health, and ways to tame it. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.H.; Chu, N.M.; Lin, Y.F.; Kao, S.H. G-Protein Coupled Estrogen Receptor in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptors in breast carcinogenesis and endocrine therapy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Gu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, A.; Jing, X.; Zhao, L.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L. Estrogen promotes progression of hormone-dependent breast cancer through CCL2-CCR2 axis by upregulation of Twist via PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.F.; Shi, Z.M.; Li, D.M.; Qian, Y.C.; Ren, Y.; Bai, X.M.; Xie, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Ge, X.; Liu, W.-T.; et al. Estrogen-induced miR-196a elevation promotes tumor growth and metastasis via targeting SPRED1 in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S.; He, H.; Chen, Q. Estradiol induces HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; He, H.; Chen, Q.; Yue, W. GPER mediated estradiol reduces miR-148a to promote HLA-G expression in breast cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, L.; Pantel, K.; Kang, Y. Tumor metastasis: Moving new biological insights into the clinic. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1450–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchsbaum, R.J.; Oh, S.Y. Breast Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cancers 2016, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Sakai, R. Direct Interaction between Carcinoma Cells and Cancer Associated Fibroblasts for the Regulation of Cancer Invasion. Cancers 2015, 7, 2054–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezawa, Y.; Orimo, A. The roles of tumor- and metastasis-promoting carcinoma-associated fibroblasts in human carcinomas. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 675–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L. MicroRNA and Metastasis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2016, 132, 165–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, A.; Brown, J.A.; Kerin, M.J. Metastatic breast cancer: The potential of miRNA for diagnosis and treatment monitoring. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, R.U.; Miyazaki, H.; Ochiya, T. The Roles of MicroRNAs in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2015, 7, 598–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepp, M.; Ströse, A.J.; Haier, J. Dysregulation of miRNA Expression in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) and Its Consequences on the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2017, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Hou, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wang, L.; Luo, H.; Tang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, M. MiRNA expression analysis of cancer-associated fibroblasts and normal fibroblasts in breast cancer. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 2051–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piasecka, D.; Braun, M.; Kordek, R.; Sadej, R.; Romanska, H. MicroRNAs in regulation of triple-negative breast cancer progression. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 144, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, A.; Muoio, M.G.; Miglietta, A.M.; Maggiolini, M.; Department of Pharmacy, Health and Nutritional Sciences, University of Calabria, Rende, (CS), Italy. Personal observation, 2019.
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioinformatics & Evolutionary Genomics. Available online: http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/Venn/ (accessed on 4 March 2019).










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vivacqua, A.; Muoio, M.G.; Miglietta, A.M.; Maggiolini, M. Differential MicroRNA Landscape Triggered by Estrogens in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) of Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors. Cancers 2019, 11, 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030412
Vivacqua A, Muoio MG, Miglietta AM, Maggiolini M. Differential MicroRNA Landscape Triggered by Estrogens in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) of Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors. Cancers. 2019; 11(3):412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030412
Chicago/Turabian StyleVivacqua, Adele, Maria Grazia Muoio, Anna Maria Miglietta, and Marcello Maggiolini. 2019. "Differential MicroRNA Landscape Triggered by Estrogens in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) of Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors" Cancers 11, no. 3: 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030412
APA StyleVivacqua, A., Muoio, M. G., Miglietta, A. M., & Maggiolini, M. (2019). Differential MicroRNA Landscape Triggered by Estrogens in Cancer Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) of Primary and Metastatic Breast Tumors. Cancers, 11(3), 412. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11030412






