Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Pathological Diagnosis and Mechanism of Thrombus Formation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Mechanism of Thrombus Formation (Virchow’s Triad)
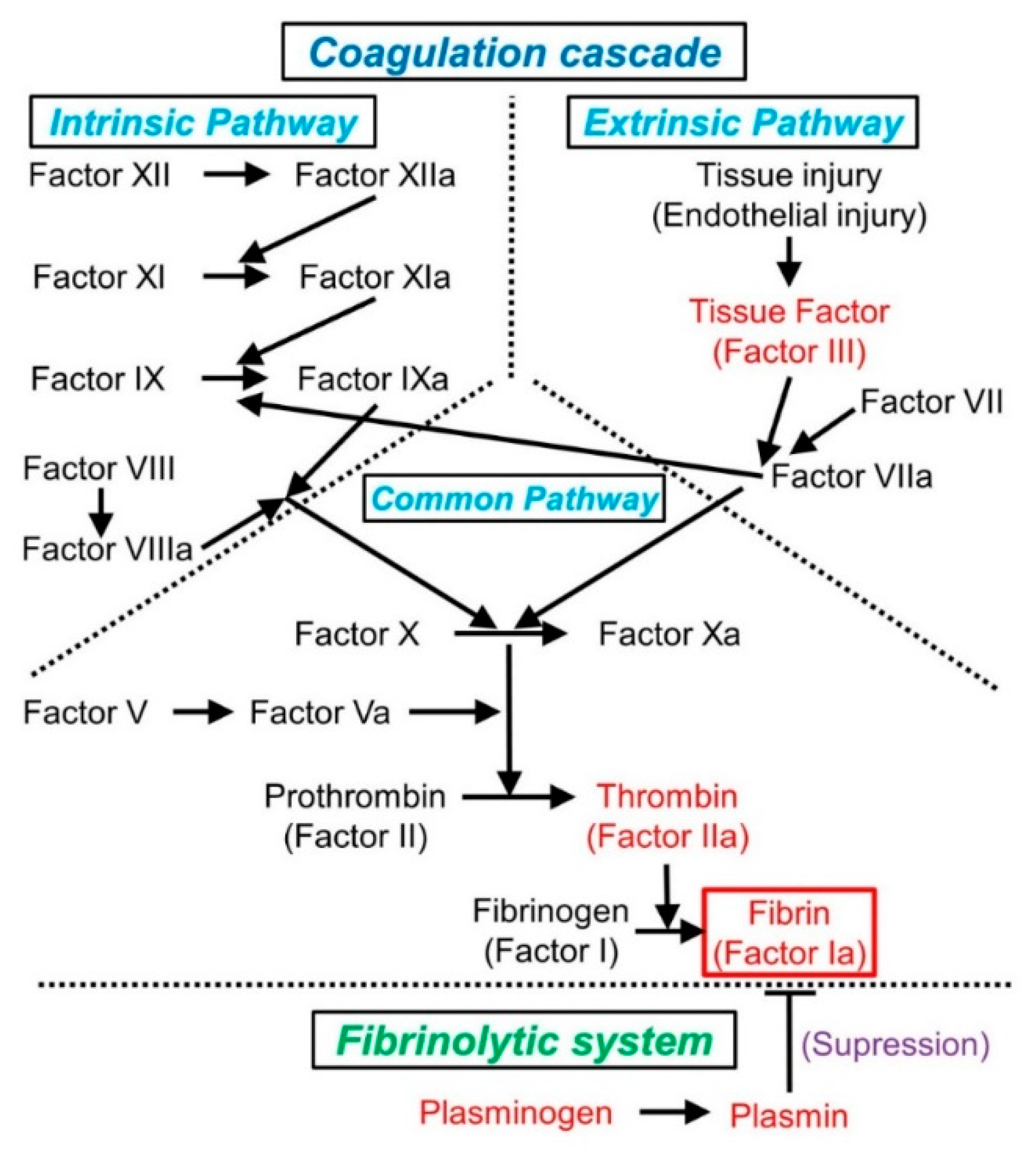
2.1. Normal Hemostasis and the Coagulation Cascade
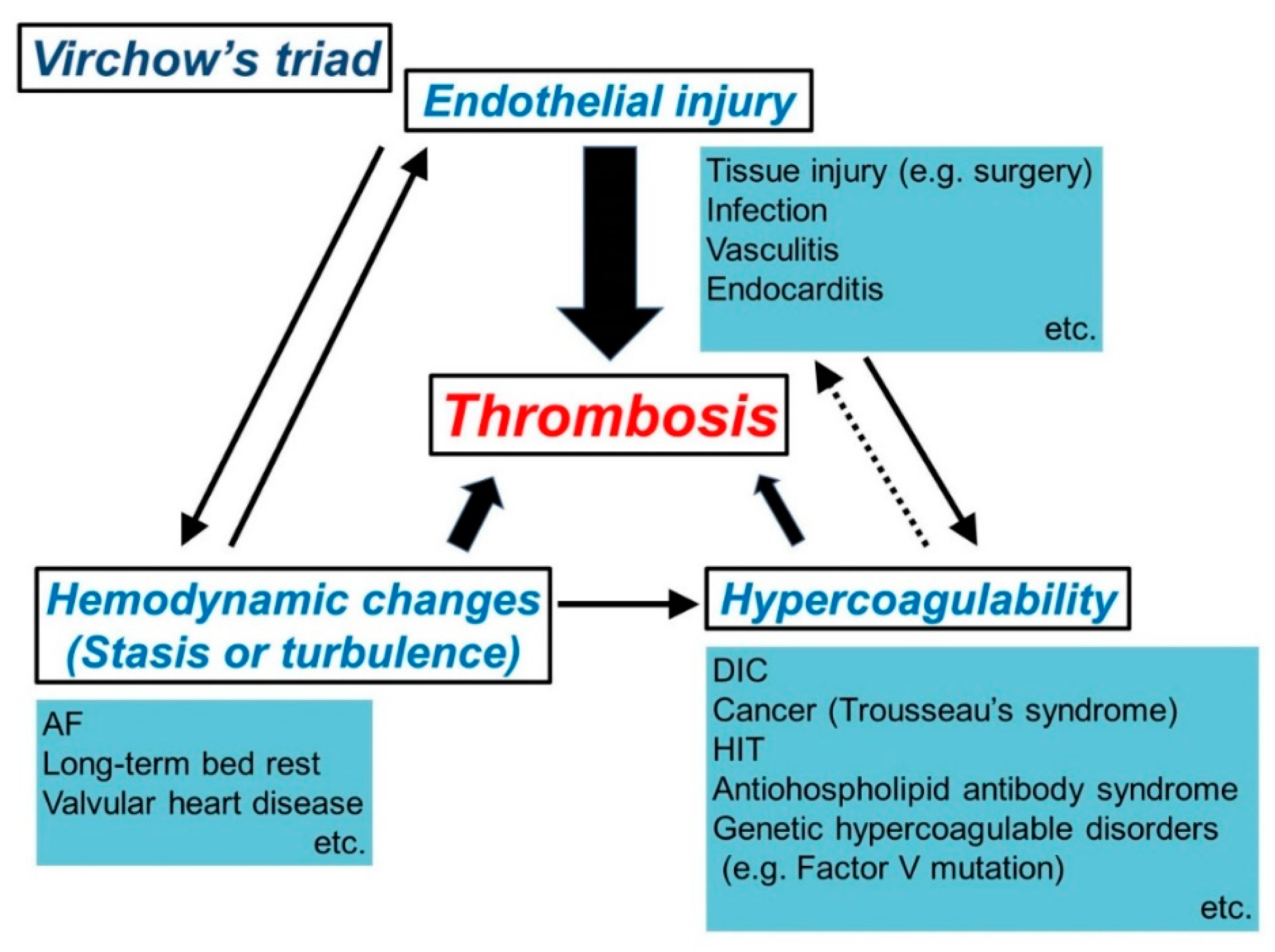
2.2. Mechanism of Thrombosis (Virchow’s Triad)
2.3. Recent Molecular Studies on Thrombosis
3. Trousseau’s Syndrome
3.1. Overview
3.2. Clinical Characteristics Related to Cerebral Thromboembolism
3.3. Pathogenesis
3.4. Association with Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lung Cancer Surgery
4. Mechanism of Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer
4.1. Overview
4.2. Pulmonary Vein Stump (PVS)
4.3. Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
4.4. Possibility of Cancer-Associated Hypercoagulability
5. Thrombectomy and Thrombus Pathology in Practice
5.1. Development of Thrombectomy
5.2. General Principles of Thrombus Pathology
5.3. Examples of Thrombus Pathology
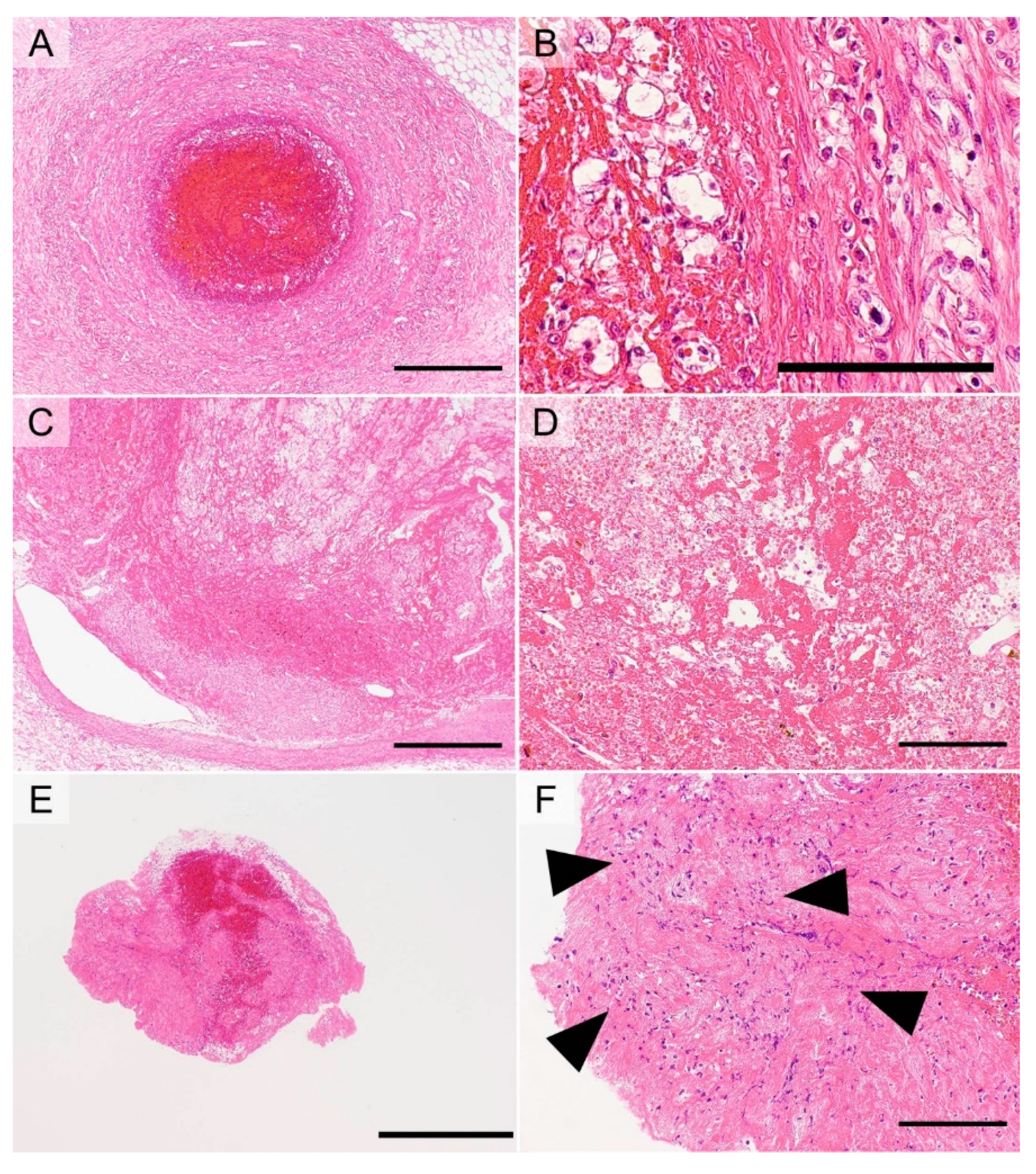
5.3.1. Thromboembolism Due to Disseminated Intravascular Coagulopathy (DIC)
5.3.2. Coronary Atherogenic Thrombus
5.3.3. Atherogenic Thrombus in Cerebral Thromboembolism
5.3.4. Thrombus Due to Thrombophlebitis
5.3.5. Thrombus Due to PTE Resulting from DVT
5.3.6. AF-Associated Cardiogenic Thrombus in Cerebral Thromboembolism
5.4. Utility of Thrombus Pathology for Pharmacotherapy
6. Use of Thrombus Pathology to Treat Post-Lobectomy Stroke
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | atrial fibrillation |
| APTT | activated partial thromboplastin time |
| DIC | disseminated intravascular coagulopathy |
| DVT | deep vein thrombosis |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| KLF | Krüppel-like factor |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| NBTE | nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| PT | prothrombin time |
| PTE | pulmonary thromboembolism |
| PVS | pulmonary vein stump |
| TF | tissue factor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, K. Lung Cancer: Understanding Its Molecular Pathology and the 2015 WHO Classification. Front. Oncol. 2017, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, C.J. The “lazarus response” in treatment-naive, poor performance status patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and epidermal growth factor receptor mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1350–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hida, T.; Seto, T.; Horinouchi, H.; Maemondo, M.; Takeda, M.; Hotta, K.; Hirai, F.; Kim, Y.H.; Matsumoto, S.; Ito, M.; et al. Phase II study of ceritinib in alectinib-pretreated patients with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-rearranged metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer in Japan: ASCEND-9. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrelli, F.; Maltese, M.; Tomasello, G.; Conti, B.; Borgonovo, K.; Cabiddu, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Ghidini, M.; Passalacqua, R.; Barni, S.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Predictors of PD-L1 Expression in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin. Lung Cancer 2018, 19, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; Cappuzzo, F.; Rocco, G.; Palmer, J.D.; van Zandwijk, N.; Blackhall, F.; Le, X.; Pennell, N.A.; et al. A consensus on the role of osimertinib in non-small cell lung cancer from the AME Lung Cancer Collaborative Group. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 3909–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Ucar, A.E.; Delgado Roel, M. Indication for VATS sublobar resections in early lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl. 3), S194–S199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.S.; Richards, W.G.; Jaklitsch, M.T.; Gill, R.; Chirieac, L.R.; Colson, Y.L.; Mohiuddin, K.; Mentzer, S.J.; Bueno, R.; Sugarbaker, D.J.; et al. Lobectomy versus sublobar resection for small (2 cm or less) non-small cell lung cancers. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2011, 92, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, F.; Flehinger, B.J.; Martini, N. Complications of surgery in the treatment of carcinoma of the lung. Chest 1982, 82, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, P.M.; Truong, M.T.; Godoy, M.C.B. Postoperative Imaging and Complications in Resection of Lung Cancer. Semin. Ultrasound CT MRI 2018, 39, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uramoto, H.; Nakanishi, R.; Fujino, Y.; Imoto, H.; Takenoyama, M.; Yoshimatsu, T.; Oyama, T.; Osaki, T.; Yasumoto, K. Prediction of pulmonary complications after a lobectomy in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Thorax 2001, 56, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillai, J.B.; Barnard, S. Cancer immunology. Cardiac tamponade: A rare complication after pulmonary lobectomy. Interact. Cardiovasc. Thorac. Surg. 2003, 2, 657–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Pang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chen, G.; Miao, F. A malformed staple causing cardiac tamponade after lobectomy. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2012, 94, 2107–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojiri, T.; Inoue, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Maeda, H.; Shintani, Y.; Sawabata, N.; Hamasaki, T.; Okumura, M. Impact of cardiopulmonary complications of lung cancer surgery on long-term outcomes. Surg. Today 2015, 45, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, B.T.; Schumacher, H.C.; Wang, S.; Shaefi, S.; Berman, M.F. Perioperative acute ischemic stroke in noncardiac and nonvascular surgery: Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes. Anesthesiology 2009, 110, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, T.; Suzuki, H.; Nagato, K.; Nakajima, T.; Iwata, T.; Yoshida, S.; Yoshino, I. Is left upper lobectomy for lung cancer a risk factor for cerebral infarction? Surg. Today 2016, 46, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Sato, S.; Okumura, M.; Niwa, H.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Date, H.; Nakajima, J.; Usuda, J.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Frequency of cerebral infarction after pulmonary resection: A multicenter, retrospective study in Japan. Surg. Today 2018, 48, 571–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaka, K.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Kato, T.; Muto, J.; Nakada-Kubota, R.; Sasaki, T.; Matsui, Y. Thrombosis in the pulmonary vein stump after left upper lobectomy as a possible cause of cerebral infarction. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1924–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaka, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Uemura, S.; Shoji, Y.; Hayama, S.; Ichimura, T.; Senmaru, N.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Matsui, Y. Blood stasis may cause thrombosis in the left superior pulmonary vein stump after left upper lobectomy. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 9, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaka, K.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Takahashi, Y.; Kawase, H.; Hayama, S.; Ichimura, T.; Senmaru, N.; Honma, N.; Matsui, Y. Left upper lobectomy can be a risk factor for thrombosis in the pulmonary vein stump. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2014, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usui, G.; Takayama, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Katano, T.; Yanagiya, M.; Kusakabe, M.; Miura, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Horiuchi, H.; Okubo, S. Cerebral Embolism Caused by Thrombus in the Pulmonary Vein Stump after Left Lower Lobectomy: A Case Report and Literature Review. Intern. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.N. Hemodynamic disorders, thromboembolic disease, and shock. In Pathologic Basis of Diseases, 8th ed.; Kumar, V., Abbas, A.K., Fausto, N., Aster, J.C., Eds.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2004; pp. 111–134. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M.; Monroe, D.M. Coagulation 2006: A modern view of hemostasis. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2007, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Bendeck, M.; Gotlieb, A.I. Vascular Pathobiology: Atherosclerosis and Large Vessel Disease. In Cardiovascular Pathology, 4th ed.; Buja, L.M., Butany, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 85–124. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, M.; Monroe, D.M., 3rd. A cell-based model of hemostasis. Thromb. Haemost. 2001, 85, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roselli, M.; Riondino, S.; Mariotti, S.; La Farina, F.; Ferroni, P.; Guadagni, F. Clinical models and biochemical predictors of VTE in lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2014, 33, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdol Razak, N.B.; Jones, G.; Bhandari, M.; Berndt, M.C.; Metharom, P. Cancer-Associated Thrombosis: An Overview of Mechanisms, Risk Factors, and Treatment. Cancers 2018, 10, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushman, M. Epidemiology and risk factors for venous thrombosis. Semin. Hematol. 2007, 44, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Zuka, M.; Liu, J.; Russell, S.; Dent, J.; Guerrero, J.A.; Forsyth, J.; Maruszak, B.; Gartner, T.K.; Felding-Habermann, B.; et al. Platelet glycoprotein Ib alpha supports experimental lung metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9024–9028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaan, R.; Strange, C. Use of multitarget tyrosine kinase inhibitors to attenuate platelet-derived growth factor signalling in lung disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 170061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskovičová, N.; Petřek, M.; Eickelberg, O.; Heinzelmann, K. Platelet-derived growth factor signaling in the lung. From lung development and disease to clinical studies. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 263–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambas, K.; Mitroulis, I.; Ritis, K. The emerging role of neutrophils in thrombosis-the journey of TF through NETs. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkmann, V.; Reichard, U.; Goosmann, C.; Fauler, B.; Uhlemann, Y.; Weiss, D.S.; Weinrauch, Y.; Zychlinsky, A. Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria. Science 2004, 303, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimball, A.S.; Obi, A.T.; Diaz, J.A.; Henke, P.K. The emerging role of NETs in venous thrombosis and immunothrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeiler, S.; Stark, K.; Massberg, S.; Engelmann, B. Propagation of thrombosis by neutrophils and extracellular nucleosome networks. Haematologica 2017, 102, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.W.; Qiu, H.; Jo, H. MicroRNA-663 upregulated by oscillatory shear stress plays a role in inflammatory response of endothelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2011, 300, H1762–H1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Z.; Cui, Q.; Xi, J.; Li, Y.S.; Chien, S.; Wang, N. MicroRNA-19a mediates the suppressive effect of laminar flow on cyclin D1 expression in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3240–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, D.; Owens, G.K. Smooth muscle cell phenotypic switching in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 95, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Davies, P.F. Site-specific microRNA-92a regulation of Kruppel-like factors 4 and 2 in atherosusceptible endothelium. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Xu, X.; Deng, S.; Luo, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, T.; Lei, G.; Zhang, F.; Yang, C.; et al. Methylation of kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) associates with its expression and non-small cell lung cancer progression. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2024–2037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sun, M.; Zang, C.; Ma, P.; He, J.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Shu, Y. Upregulated long non-coding RNA AGAP2-AS1 represses LATS2 and KLF2 expression through interacting with EZH2 and LSD1 in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Ying, X.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Luo, X.; Xie, S.; Wang, Q.C.; Hu, W.; Wang, L. The novel KLF4/PLAC8 signaling pathway regulates lung cancer growth. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loyer, X.; Vion, A.C.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varki, A. Trousseau’s syndrome: Multiple definitions and multiple mechanisms. Blood 2007, 110, 1723–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trousseau, A. Phlegmasia alba dolens. Clin. Med. l’Hotel-Dieu Paris 1865, 3, 654–712. [Google Scholar]
- Sack, G.H., Jr.; Levin, J.; Bell, W.R. Trousseau’s syndrome and other manifestations of chronic disseminated coagulopathy in patients with neoplasms: Clinical, pathophysiologic, and therapeutic features. Medicine 1977, 56, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristinsson, S.Y.; Turesson, I. The association of cancer and venous thrombosis: Yes, Trousseau is right...again! Leuk. Lymphoma 2011, 52, 734–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, G.J.; Weitz, H.H. Venous thrombosis and cancer: What would Dr. Trousseau teach today? Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 440–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graus, F.; Rogers, L.R.; Posner, J.B. Cerebrovascular complications in patients with cancer. Medicine 1985, 64, 16–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineo, G.F.; Regoeczi, E.; Hatton, M.W.; Brain, M.C. The activation of coagulation by extracts of mucus: A possible pathway of intravascular coagulation accompanying adenocarcinomas. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1973, 82, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Bick, R.L. Cancer-associated thrombosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 109–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callander, N.; Rapaport, S.I. Trousseau’s syndrome. West. J. Med. 1993, 158, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callander, N.S.; Varki, N.; Rao, L.V. Immunohistochemical identification of tissue factor in solid tumors. Cancer 1992, 70, 1194–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, L.A.; Ladisch, S. Tumor gangliosides enhance alpha2 beta1 integrin-dependent platelet activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1316, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denko, N.C.; Giaccia, A.J. Tumor hypoxia, the physiological link between Trousseau’s syndrome (carcinoma-induced coagulopathy) and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 795–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Romano, G.; Di Leva, G.; Nuovo, G.; Jeon, Y.J.; Ngankeu, A.; Sun, J.; Lovat, F.; Alder, H.; Condorelli, G.; et al. EGFR and MET receptor tyrosine kinase-altered microRNA expression induces tumorigenesis and gefitinib resistance in lung cancers. Nat. Med. 2011, 18, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, C.; Sabatino, G.; Medico, E.; Girolami, F.; Follenzi, A.; Reato, G.; Sottile, A.; Naldini, L.; Comoglio, P.M. The MET oncogene drives a genetic programme linking cancer to haemostasis. Nature 2005, 434, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlmann, E.J.; Dunitz, J.M.; Fiol, M.E. Pulmonary vein thrombosis after lung transplantation presenting as stroke. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2009, 28, 209–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, N.; Fukuda, H.; Handa, A.; Kawasaki, T.; Kurosaki, Y.; Chin, M.; Yamagata, S. Histological examination of Trousseau syndrome-related thrombus retrieved through acute endovascular thrombectomy: Report of 2 cases. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2016, 25, e227–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtaka, K.; Hida, Y.; Kaga, K.; Iimura, Y.; Shiina, N.; Muto, J.; Hirano, S. Pulmonary vein thrombosis after video-assisted thoracoscopic left upper lobectomy. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2012, 143, e3–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Usui, G.; Matsumoto, J.; Hashimoto, H.; Katano, T.; Kusakabe, M.; Horiuchi, H.; Okubo, S. Thrombus reformation in the pulmonary vein stump confirmed 16 months after cerebral embolism on the day after left upper lobectomy for lung cancer. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, e225–e227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, D.J.; Piccini, J.P.; Wang, T.; Zheng, J.; Malaisrie, S.C.; Holmes, D.R.; Suri, R.M.; Mack, M.J.; Badhwar, V.; Jacobs, J.P.; et al. Association between left atrial appendage occlusion and readmission for thromboembolism among patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing concomitant cardiac surgery. JAMA 2018, 319, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; Gersh, B.J.; Holmes, D.R., Jr.; Melduni, R.M.; Johnsrud, D.O.; Sangaralingham, L.R.; Shah, N.D.; Noseworthy, P.A. Association of aurgical left atrial appendage occlusion with subsequent stroke and mortality among patients undergoing cardiac surgery. JAMA 2018, 319, 2116–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadiyaram, V.K.; Mohanty, S.; Gianni, C.; Trivedi, C.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Burkhardt, D.J.; Gallinghouse, J.G.; Hranitzky, P.M.; Horton, R.P.; Sanchez, J.E.; et al. Thromboembolic events and need for anticoagulation therapy following left atrial appendage occlusion in patients with electrical isolation of the appendage. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaporciyan, A.A.; Correa, A.M.; Rice, D.C.; Roth, J.A.; Smythe, W.R.; Swisher, S.G.; Walsh, G.L.; Putnam, J.B., Jr. Risk factors associated with atrial fibrillation after noncardiac thoracic surgery: Analysis of 2588 patients. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2004, 127, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haïssaguerre, M.; Jaïs, P.; Shah, D.C.; Takahashi, A.; Hocini, M.; Quiniou, G.; Garrigue, S.; Le Mouroux, A.; Le Métayer, P.; Clémenty, J. Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathan, H.; Eliakim, M. The junction between the left atrium and the pulmonary veins. An anatomic study of human hearts. Circulation 1966, 34, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, I.; Hájková, P.; Kvasnicka, J.; Kholová, I. Myocardial sleeves of pulmonary veins and atrial fibrillation: A postmortem histopathological study of 100 subjects. Virchows Arch. 2006, 449, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, A.; Kamata, T.; Iwasa, T.; Watanabe, S.; Tsuta, K. Myocardial Sleeve Tissues in Surgical Lung Specimens. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2015, 39, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oral, H.; Pappone, C.; Chugh, A.; Good, E.; Bogun, F.; Pelosi, F., Jr.; Bates, E.R.; Lehmann, M.H.; Vicedomini, G.; Augello, G.; et al. Circumferential pulmonary-vein ablation for chronic atrial fibrillation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 934–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- January, C.T.; Wann, L.S.; Calkins, H.; Chen, L.Y.; Cigarroa, J.E.; Cleveland, J.C., Jr.; Ellinor, P.T.; Ezekowitz, M.D.; Field, M.E.; Furie, K.L.; et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association task force on clinical practice guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, M.; Demchuk, A.M.; Menon, B.K.; Eesa, M.; Rempel, J.L.; Thornton, J.; Roy, D.; Jovin, T.G.; Willinsky, R.A.; Sapkota, B.L.; et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.C.; Mitchell, P.J.; Kleinig, T.J.; Dewey, H.M.; Churilov, L.; Yassi, N.; Yan, B.; Dowling, R.J.; Parsons, M.W.; Oxley, T.J.; et al. Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1009–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovin, T.G.; Chamorro, A.; Cobo, E.; de Miquel, M.A.; Molina, C.A.; Rovira, A.; San Román, L.; Serena, J.; Abilleira, S.; Ribó, M.; et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 hours after stroke with a mismatch between deficit and infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for stroke at 6 to 16 hours with selection by perfusion imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grau, A.J.; Weimar, C.; Buggle, F.; Heinrich, A.; Goertler, M.; Neumaier, S.; Glahn, J.; Brandt, T.; Hacke, W.; Diener, H.C. Risk factors, outcome, and treatment in subtypes of ischemic stroke: The German stroke data bank. Stroke 2001, 32, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Schubert, M.; Förschler, A.; Prothmann, S.; Kreiser, K.; Zimmer, C.; Riegger, J.; Bauer, J.; Neff, F.; Kehl, V.; et al. The impact of histological clot composition in embolic stroke. Clin. Neuroradiol. 2016, 26, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeckh-Behrens, T.; Kleine, J.F.; Zimmer, C.; Neff, F.; Scheipl, F.; Pelisek, J.; Schirmer, L.; Nguyen, K.; Karatas, D.; Poppert, H. Thrombus histology suggests cardioembolic cause in cryptogenic stroke. Stroke 2016, 47, 1864–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sporns, P.B.; Hanning, U.; Schwindt, W.; Velasco, A.; Minnerup, J.; Zoubi, T.; Heindel, W.; Jeibmann, A.; Niederstadt, T.U. Ischemic stroke: What does the histological composition tell us about the origin of the thrombus? Stroke 2017, 48, 2206–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, B.F.; Waterman, A.D.; Shannon, W.; Boechler, M.; Rich, M.W.; Radford, M.J. Validation of clinical classification schemes for predicting stroke: Results from the National Registry of Atrial Fibrillation. JAMA 2001, 285, 2864–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patell, R.; Gutierrez, A.; Rybicki, L.; Khorana, A.A. Usefulness of CHADS2 and CHA2DS2-VASc scores for stroke prediction in patients with cancer and atrial fibrillation. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, 2182–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hashimoto, H.; Usui, G.; Tsugeno, Y.; Sugita, K.; Amori, G.; Morikawa, T.; Inamura, K. Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Pathological Diagnosis and Mechanism of Thrombus Formation. Cancers 2019, 11, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040488
Hashimoto H, Usui G, Tsugeno Y, Sugita K, Amori G, Morikawa T, Inamura K. Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Pathological Diagnosis and Mechanism of Thrombus Formation. Cancers. 2019; 11(4):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040488
Chicago/Turabian StyleHashimoto, Hirotsugu, Genki Usui, Yuta Tsugeno, Keisuke Sugita, Gulanbar Amori, Teppei Morikawa, and Kentaro Inamura. 2019. "Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Pathological Diagnosis and Mechanism of Thrombus Formation" Cancers 11, no. 4: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040488
APA StyleHashimoto, H., Usui, G., Tsugeno, Y., Sugita, K., Amori, G., Morikawa, T., & Inamura, K. (2019). Cerebral Thromboembolism after Lobectomy for Lung Cancer: Pathological Diagnosis and Mechanism of Thrombus Formation. Cancers, 11(4), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11040488




