Efficacy and Toxicity of Weekly Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as Induction or Palliative Treatment in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
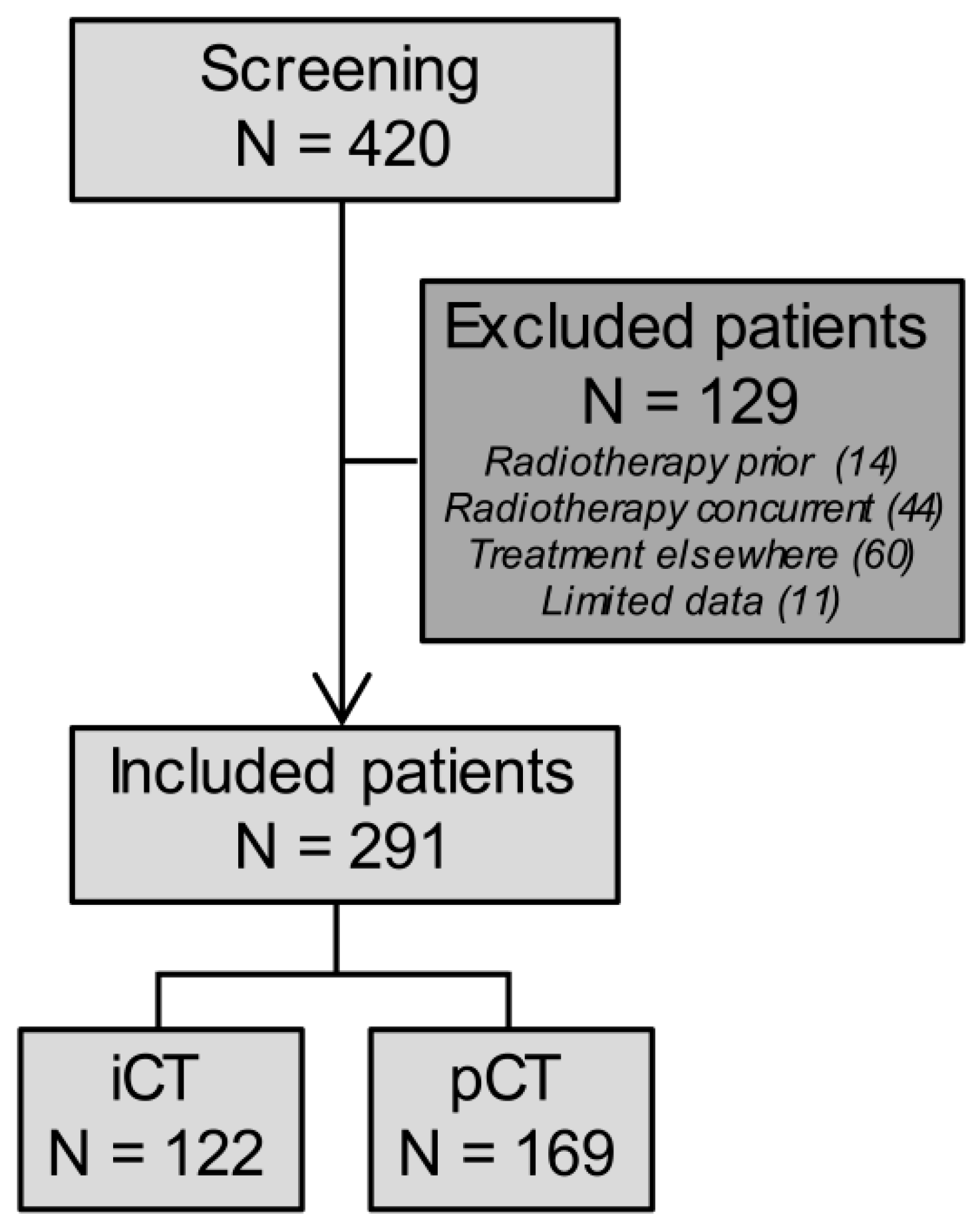
2.1. Patient, Tumor, and Treatment Characteristics
2.2. Toxicity
2.3. Efficacy
2.4. Predictive and Prognostic Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Treatment
4.3. Data
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.; Forman, D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hur, C.; Miller, M.; Kong, C.Y.; Dowling, E.C.; Nattinger, K.J.; Dunn, M.; Feuer, E.J. Trends in esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence and mortality. Cancer 2013, 119, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Ferlay, J.; Forman, D. Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological subtype in 2012. Gut 2015, 64, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, J.; Smyth, E.; Cunningham, D.; Lagergren, P. Oesophageal cancer. Lancet 2017, 390, 2383–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin-Fenton, D.P.; Murray, L.J.; Whiteman, D.C.; Cardwell, C.; Webb, P.M.; Jordan, S.J.; Corley, D.A.; Sharp, L.; Lagergren, J.; Barrett’s Esophagus, A.C.I. Reproductive and sex hormonal factors and oesophageal and gastric junction adenocarcinoma: A pooled analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2067–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhuang, H.; Liu, Y. The association between obesity factor and esophageal caner. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2012, 3, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubo, A.; Cook, M.B.; Shaheen, N.J.; Vaughan, T.L.; Whiteman, D.C.; Murray, L.; Corley, D.A. Sex-specific associations between body mass index, waist circumference and the risk of Barrett’s oesophagus: A pooled analysis from the international BEACON consortium. Gut 2013, 62, 1684–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohanes, P.; Yang, D.; Chhibar, R.S.; Labonte, M.J.; Winder, T.; Ning, Y.; Gerger, A.; Benhaim, L.; Paez, D.; Wakatsuki, T.; et al. Influence of sex on the survival of patients with esophageal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, I.; Norman, A.R.; Cunningham, D.; Waters, J.S.; Oates, J.; Ross, P.J. Multivariate prognostic factor analysis in locally advanced and metastatic esophago-gastric cancer—Pooled analysis from three multicenter, randomized, controlled trials using individual patient data. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 2395–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polee, M.B.; Hop, W.C.; Kok, T.C.; Eskens, F.A.; van der Burg, M.E.; Splinter, T.A.; Siersema, P.D.; Tilanus, H.W.; Stoter, G.; van der Gaast, A. Prognostic factors for survival in patients with advanced oesophageal cancer treated with cisplatin-based combination chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Araujo, J.L.; Altorki, N.K.; Sonett, J.R.; Rodriguez, A.; Sungur-Stasik, K.; Spinelli, C.F.; Neugut, A.I.; Abrams, J.A. Variation by stage in the effects of prediagnosis weight loss on mortality in a prospective cohort of esophageal cancer patients. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eloubeidi, M.A.; Desmond, R.; Arguedas, M.R.; Reed, C.E.; Wilcox, C.M. Prognostic factors for the survival of patients with esophageal carcinoma in the U.S.: The importance of tumor length and lymph node status. Cancer 2002, 95, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chau, I.; Norman, A.R.; Cunningham, D.; Oates, J.; Hawkins, R.; Iveson, T.; Nicolson, M.; Harper, P.; Seymour, M.; Hickish, T. The impact of primary tumour origins in patients with advanced oesophageal, oesophago-gastric junction and gastric adenocarcinoma—Individual patient data from 1775 patients in four randomised controlled trials. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, J.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Hulshof, M.; van Hagen, P.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzinger, P.C.; Mayer, R.J. Esophageal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2241–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ancona, E.; Ruol, A.; Castoro, C.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Merigliano, S.; Santi, S.; Bonavina, L.; Peracchia, A. First-line chemotherapy improves the resection rate and long-term survival of locally advanced (T4, any N, M0) squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: Final report on 163 consecutive patients with 5-year follow-up. Ann. Surg. 1997, 226, 714–723; discussion 723–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, H.; Yamasaki, M.; Kurokawa, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Nakajima, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Mori, M.; Doki, Y. Clinical relevance of induction triplet chemotherapy for esophageal cancer invading adjacent organs. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 106, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Hatooka, S.; Ura, T.; Abe, T.; Takahari, D.; Shitara, K.; Nomura, M.; Kondo, C.; Mizota, A.; Yatabe, Y.; et al. Docetaxel plus 5-fluorouracil and cisplatin (DCF) induction chemotherapy for locally advanced borderline-resectable T4 esophageal cancer. Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 3535–3541. [Google Scholar]
- Homs, M.Y.; vd Gaast, A.; Siersema, P.D.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Kuipers, E.J. Chemotherapy for metastatic carcinoma of the esophagus and gastro-esophageal junction. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2006, 4, CD004063. [Google Scholar]
- Janmaat, V.T.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van der Gaast, A.; Mathijssen, R.H.; Bruno, M.J.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Kuipers, E.J.; Spaander, M.C. Palliative chemotherapy and targeted therapies for esophageal and gastroesophageal junction cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 11, CD004063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ter Veer, E.; Haj Mohammad, N.; van Valkenhoef, G.; Ngai, L.L.; Mali, R.M.A.; Anderegg, M.C.; van Oijen, M.G.H.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M. The Efficacy and Safety of First-line Chemotherapy in Advanced Esophagogastric Cancer: A Network Meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, N.H.; ter Veer, E.; Ngai, L.; Mali, R.; van Oijen, M.G.; van Laarhoven, H.W. Optimal first-line chemotherapeutic treatment in patients with locally advanced or metastatic esophagogastric carcinoma: Triplet versus doublet chemotherapy: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2015, 34, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutch Cancer Clinical Practice Guidelines. Available online: https://www.oncoline.nl/oesofaguscarcinoom (accessed on 5 May 2019).
- Dijksterhuis, W.P.M.; van Oijen, M.G.H.; Verhoeven, R.H.A.; van Laarhoven, H.W.M. Diversity of first-line palliative systemic treatments for esophagogastric cancer patients with synchronous metastases: A real world evidence study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polee, M.B.; Sparreboom, A.; Eskens, F.A.; Hoekstra, R.; van de Schaaf, J.; Verweij, J.; Stoter, G.; van der Gaast, A. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of weekly paclitaxel and carboplatin in patients with metastatic esophageal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosteller, R.D. Simplified calculation of body-surface area. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 1098. [Google Scholar]
- Levey, A.S.; Coresh, J.; Greene, T.; Marsh, J.; Stevens, L.A.; Kusek, J.W.; Van Lente, F.; Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration. Expressing the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate with standardized serum creatinine values. Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honing, J.; Smit, J.K.; Muijs, C.T.; Burgerhof, J.G.; de Groot, J.W.; Paardekooper, G.; Muller, K.; Woutersen, D.; Legdeur, M.J.; Fiets, W.E.; et al. A comparison of carboplatin and paclitaxel with cisplatinum and 5-fluorouracil in definitive chemoradiation in esophageal cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, D.; Starling, N.; Rao, S.; Iveson, T.; Nicolson, M.; Coxon, F.; Middleton, G.; Daniel, F.; Oates, J.; Norman, A.R.; et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meerten, E.; Eskens, F.A.; van Gameren, E.C.; Doorn, L.; van der Gaast, A. First-line treatment with oxaliplatin and capecitabine in patients with advanced or metastatic oesophageal cancer: A phase II study. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1348–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, H.; Verweij, J.; Nooter, K.; Sparreboom, A. Cremophor EL: The drawbacks and advantages of vehicle selection for drug formulation. Eur. J. Cancer 2001, 37, 1590–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Moiseyenko, V.M.; Tjulandin, S.; Majlis, A.; Constenla, M.; Boni, C.; Rodrigues, A.; Fodor, M.; Chao, Y.; Voznyi, E.; et al. Phase III study of docetaxel and cisplatin plus fluorouracil compared with cisplatin and fluorouracil as first-line therapy for advanced gastric cancer: A report of the V325 Study Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4991–4997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dank, M.; Zaluski, J.; Barone, C.; Valvere, V.; Yalcin, S.; Peschel, C.; Wenczl, M.; Goker, E.; Cisar, L.; Wang, K.; et al. Randomized phase III study comparing irinotecan combined with 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid to cisplatin combined with 5-fluorouracil in chemotherapy naive patients with advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, T.J.; An, G.L.; Zhao, X.H.; Tian, F.; Li, X.H.; Lian, J.W.; Pan, B.R.; Gu, S.Z. Combined treatment of oxaliplatin and capecitabine in patients with metastatic esophageal squamous cell cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polee, M.B.; Eskens, F.A.; van der Burg, M.E.; Splinter, T.A.; Siersema, P.D.; Tilanus, H.W.; Verweij, J.; Stoter, G.; van der Gaast, A. Phase II study of bi-weekly administration of paclitaxel and cisplatin in patients with advanced oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 86, 669–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kok, T.C.; Van der Gaast, A.; Dees, J.; Eykenboom, W.M.; Van Overhagen, H.; Stoter, G.; Tilanus, H.W.; Splinter, T.A. Cisplatin and etoposide in oesophageal cancer: A phase II study. Rotterdam Oesophageal Tumour Study Group. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 980–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yokota, T.; Kato, K.; Hamamoto, Y.; Tsubosa, Y.; Ogawa, H.; Ito, Y.; Hara, H.; Ura, T.; Kojima, T.; Chin, K.; et al. Phase II study of chemoselection with docetaxel plus cisplatin and 5-fluorouracil induction chemotherapy and subsequent conversion surgery for locally advanced unresectable oesophageal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Batran, S.E.; Hartmann, J.T.; Probst, S.; Schmalenberg, H.; Hollerbach, S.; Hofheinz, R.; Rethwisch, V.; Seipelt, G.; Homann, N.; Wilhelm, G.; et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: A study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polee, M.B.; Kok, T.C.; Siersema, P.D.; Tilanus, H.W.; Splinter, T.A.; Stoter, G.; Van der Gaast, A. Phase II study of the combination cisplatin, etoposide, 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid in patients with advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Anticancer Drugs 2001, 12, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, J.A.; Fodor, M.B.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Moiseyenko, V.M.; Chao, Y.; Cabral Filho, S.; Majlis, A.; Assadourian, S.; Van Cutsem, E. Phase II multi-institutional randomized trial of docetaxel plus cisplatin with or without fluorouracil in patients with untreated, advanced gastric, or gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5660–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Custodio, A.; Carmona-Bayonas, A.; Jimenez-Fonseca, P.; Sanchez, M.L.; Viudez, A.; Hernandez, R.; Cano, J.M.; Echavarria, I.; Pericay, C.; Mangas, M.; et al. Nomogram-based prediction of survival in patients with advanced oesophagogastric adenocarcinoma receiving first-line chemotherapy: A multicenter prospective study in the era of trastuzumab. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1526–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundelof, M.; Lagergren, J.; Ye, W. Patient demographics and lifestyle factors influencing long-term survival of oesophageal cancer and gastric cardia cancer in a nationwide study in Sweden. Eur. J. Cancer 2008, 44, 1566–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Analysis Working Group: Asan University; BC Cancer Agency; Brigham and Women’s Hospital; Broad Institute; Brown University; Case Western Reserve University; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Duke University; Greater Poland Cancer Centre; et al. Integrated genomic characterization of oesophageal carcinoma. Nature 2017, 541, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Cohen, D.J. Pharmacotherapy for metastatic esophageal cancer: Where do we need to improve? Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2019, 20, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Bendell, J.; Calvo, E.; Kim, J.W.; Ascierto, P.A.; Sharma, P.; Ott, P.A.; Peltola, K.; Jaeger, D.; Evans, J.; et al. CheckMate-032 Study: Efficacy and Safety of Nivolumab and Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Patients With Metastatic Esophagogastric Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2836–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, T.; Hamamoto, Y.; Kato, K.; Ura, T.; Kojima, T.; Tsushima, T.; Hironaka, S.; Hara, H.; Satoh, T.; Iwasa, S.; et al. Nivolumab treatment for oesophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: An open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.K.; Boku, N.; Satoh, T.; Ryu, M.H.; Chao, Y.; Kato, K.; Chung, H.C.; Chen, J.S.; Muro, K.; Kang, W.K.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer refractory to, or intolerant of, at least two previous chemotherapy regimens (ONO-4538-12, ATTRACTION-2): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 2461–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashi, K.; Kei, M.; Eric, F.; Chih-Hung, H.; Toshikazu, M.; Sung-Bae, K.; Se-Hoon, L.; Jaafar, B.; Ken, K.; Shen, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy as second-line therapy for advanced esophageal cancer: Phase III KEYNOTE-181 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, T.W.; Blackstone, E.H.; Rusch, V.W. 7th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: Esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) Version 4.03; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 14 June 2010.
- Eisenhauer, E.A.; Therasse, P.; Bogaerts, J.; Schwartz, L.H.; Sargent, D.; Ford, R.; Dancey, J.; Arbuck, S.; Gwyther, S.; Mooney, M.; et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur. J. Cancer 2009, 45, 228–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | iCT (N = 122) | pCT (N = 169) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 93 (76%) | 138 (82%) |
| Female | 29 (24%) | 31 (18%) |
| Age (years) | ||
| Median (IQR) | 64 (58–69) | 61 (55–68) |
| Performance Status | ||
| WHO 0 | 28 (23%) | 49 (29%) |
| WHO 1 | 73 (60%) | 90 (53%) |
| WHO 2 | 7 (6%) | 5 (3%) |
| Unknown | 14 (12%) | 25 (13%) |
| Ethnic Origin | ||
| Caucasian | 93 (76%) | 120 (71%) |
| African | 1 (0.8%) | 3 (2%) |
| Asian | 0 | 4 (2%) |
| Unknown | 28 (23%) | 42 (25%) |
| BSA (m2) a | ||
| Mean (SD) | 1.91 (0.22) | 1.89 (0.21) |
| eGFR (mL/min) b | ||
| Median (IQR) | 93 (84–99) | 92 (78–100) |
| Unknown | 21 (17%) | 45 (27%) |
| Smoking | ||
| Never | 15 (12%) | 31 (18%) |
| Before diagnosis | 22 (18%) | 36 (21%) |
| Current | 80 (66%) | 91 (54%) |
| Unknown | 5 (4%) | 11 (7%) |
| Alcohol | ||
| Never | 24 (20%) | 29 (17%) |
| Before diagnosis | 54 (44%) | 81 (48%) |
| Current | 37 (30%) | 48 (28%) |
| Unknown | 7 (6%) | 11 (7%) |
| Tumor Location | ||
| Proximal | 23 (19%) | 8 (5%) |
| Middle | 29 (24%) | 26 (15%) |
| Distal | 57 (47%) | 123 (73%) |
| GE-junction | 13 (11%) | 10 (6%) |
| Multiple locations | 0 | 2 (1%) |
| Tumor Type | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 61 (50%) | 117 (70%) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 59 (48%) | 48 (28%) |
| Other c | 2 (2%) | 3 (2%) |
| Unknown | 0 | 1 (1%) |
| Tumor Differentiation | ||
| Good | 7 (6%) | 3 (2%) |
| Moderate | 38 (31%) | 50 (30%) |
| Poor | 48 (39%) | 74 (44%) |
| Unknown | 29 (24%) | 42 (25%) |
| T-stage | ||
| T1b | 0 | 3 (2%) |
| T2 | 5 (4%) | 12 (7%) |
| T3 | 66 (54%) | 112 (66%) |
| T4a | 27 (22%) | 23 (14%) |
| T4b | 24 (20%) | 13 (8%) |
| N-stage | ||
| N0 | 12 (10%) | 21 (12%) |
| N1 | 49 (40%) | 69 (41%) |
| N2 | 48 (39%) | 56 (33%) |
| N3 | 13 (11%) | 23 (14%) |
| M-stage | ||
| M0 | 71 (58%) | 15 (9%) |
| M1 | 51 (42%) | 155 (91%) |
| Metastases Location | ||
| Lymph nodes | 50 (41%) | 72 (43%) |
| Liver | 0 | 19 (11%) |
| Lungs | 0 | 3 (2%) |
| Other | 0 | 18 (11%) |
| Multiple locations | 1 (1%) | 42 (25%) |
| Not applicable | 71 (58%) | 15 (9%) |
| Disease Stage | ||
| IB | 1 (1%) | 0 |
| IIA | 5 (4%) | 2 (1%) |
| IIB | 1 (1%) | 2 (1%) |
| IIIA | 17 (14%) | 4 (2%) |
| IIIB | 13 (11%) | 2 (1%) |
| IIIC | 34 (28%) | 5 (3%) |
| IV | 51 (42%) | 154 (91%) |
| Carboplatin dose (mg) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 477 (90) | 486 (95) |
| Paclitaxel dose (mg) | ||
| Mean (SD) | 191 (22) | 187 (22) |
| Number of treatment cycles d | ||
| Median (IQR) | 7 (6–9) | 8 (6–9) |
| iCT (N = 122) | pCT (N = 169) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade ≥3 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade ≥3 | |
| Overall Toxicity | 114 (93%) | 111 (91%) | 86 (71%) | 167 (99%) | 154 (91%) | 131 (78%) |
| Gastrointestinal Toxicity | ||||||
| Anorexia | 21 (17%) | 5 (4%) | 1 (1%) | 35 (21%) | 9 (5%) | 3 (2%) |
| Nausea | 39 (32%) | 8 (7%) | 1 (1%) | 68 (40%) | 10 (6%) | 3 (2%) |
| Vomiting | 19 (16%) | 4 (3%) | 0 | 27 (16%) | 5 (3%) | 3 (2%) |
| Diarrhea | 20 (16%) | 1 (1%) | 2 (2%) | 21 (12%) | 10 (6%) | 2 (1%) |
| Constipation | 31 (25%) | 10 (8%) | 0 | 57 (34%) | 15 (9%) | 0 |
| Mucositis | 4 (3%) | 2 (2%) | 0 | 17 (10%) | 0 | 1 (1%) |
| Other Toxicity | ||||||
| Alopecia | 32 (26%) | 40 (33%) | NA | 50 (30%) | 65 (39%) | NA |
| Dermatitis | 9 (7%) | 2 (2%) | 0 | 10 (6%) | 4 (2%) | 0 |
| Fatigue | 59 (48%) | 25 (21%) | 1 (1%) | 82 (49%) | 36 (21%) | 5 (3%) |
| Sensory Neuropathy | 27 (22%) | 3 (3%) | 0 | 40 (24%) | 4 (2%) | 0 |
| Motoric Neuropathy | 1 (2%) | 0 | 0 | 3 (2%) | 6 (4%) | 0 |
| Hematological Toxicity | ||||||
| Anemia | 57 (47%) | 58 (48%) | 6 (5%) | 86 (51%) | 64 (38%) | 17 (10%) |
| Thrombocytopenia | 67 (55%) | 22 (18%) | 13 (11%) | 83 (49%) | 27 (16%) | 22 (13%) |
| Leukocytopenia | 7 (6%) | 56 (46%) | 43 (35%) | 18 (11%) | 74 (44%) | 52 (31%) |
| Neutropenia | 0 | 21 (17%) | 82 (67%) | 0 | 24 (14%) | 113 (67%) |
| Other blood value alterations | ||||||
| Creatinine Increase | 6 (5%) | 0 | 0 | 6 (4%) | 0 | 0 |
| AST Increase | 21 (17%) | 0 | 1 (1%) | 29 (17%) | 2 (1%) | 4 (2%) |
| ALT Increase | 20 (16%) | 3 (3%) | 0 | 20 (12%) | 3 (2%) | 2 (1%) |
| GGT Increase | 20 (16%) | 4 (3%) | 1 (1%) | 25 (15%) | 14 (8%) | 12 (7%) |
| AP Increase | 19 (16%) | 0 | 0 | 25 (15%) | 1 (1%) | 6 (4%) |
| Bilirubin Increase | 12 (10%) | 5 (4%) | 0 | 7 (4%) | 7 (4%) | 3 (2%) |
| Clinical Consequences | iCT (N = 122) | pCT (N = 169) | ||||
| No | Yes: toxicity | Yes: other | No | Yes: toxicity | Yes: other | |
| Febrile Neutropenia | 118 (97%) | 4 (3%) | NA | 163 (96%) | 6 (4%) | NA |
| Dose reduction Carboplatin | 117 (96%) | 1 (1%) | 3 (3%) a | 126 (75%) | 1 (1%) | 4 (2%) a |
| Dose reduction Paclitaxel | 97 (79%) | 1 (1%) | 24 (20%) a | 126 (75%) | 1 (1%) | 40 (24%) a |
| Treatment delay | 64 (53%) | 51 (42%) | 7 (6%) | 84 (50%) | 72 (43%) | 11 (7%) |
| Premature end of treatment * | 95 (78%) | 14 (12%) | 13 (11%) b | 109 (64%) | 29 (17%) | 31 (19%) b |
| Hospitalization | 96 (79%) | 18 (15%) | 8 (7%) | 140 (83%) | 17 (10%) | 12 (7%) |
| iCT (N = 122) | pCT (N = 169) | |
|---|---|---|
| Response after 6 cycles | ||
| Complete Response | 1 (1%) | 2 (1%) |
| Partial Response | 57 (47%) | 72 (43%) |
| Stable Disease | 46 (38%) | 56 (33%) |
| Progressive Disease | 11 (9%) | 23 (14%) |
| Unknown | 7 (6%) | 16 (10%) |
| Treatment afterwards a | ||
| Carboplatin-Paclitaxel b | 13 (11%) | 14 (8%) |
| Chemotherapy Other c | 8 (7%) | 18 (11%) |
| Definitive Chemoradiotherapy d | 9 (7%) | 1 (1%) |
| Esophagectomy | 43 (35%) | 7 (4%) |
| PFS (months; median (IQR)) | ||
| All patients | 12.4 (7.1–45.3) | 8.2 (5.1–14.5) |
| No CRT or esophagectomy afterwards | 9.0 (4.3–13.4) | 8.0 (5.0–13.2) |
| CRT or esophagectomy afterwards | 22.1 (12.4–114.2) | 18.1 (14.8–122.2) |
| OS (months; median [IQR]) | ||
| All patients | 15.6 (9.7–36.3) | 10.9 (6.5–18.3) |
| No CRT or esophagectomy afterwards | 11.8 (7.3–18.6) | 10.6 (6.4–17.2) |
| CRT or esophagectomy afterwards | 26.8 (15.4–91.7) | 23.1 (14.8–28.0) |
| Baseline Factor | Induction Chemotherapy (iCT) | Palliative Chemotherapy (pCT) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progression Free Survival | Overall Survival | Progression Free Survival | Overall Survival | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis | |||||||||||||||||
| HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | HR | 95% CI | P | |
| Sex (M vs. F) | 0.77 | 0.45–1.29 | 0.319 | 0.83 | 0.51–1.34 | 0.443 | 1.00 | 0.63–1.59 | 0.989 | 0.90 | 0.58–1.39 | 0.623 | ||||||||||||
| Age | 1.01 | 0.98–1.03 | 0.600 | 1.01 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.496 | 1.00 | 0.98–1.03 | 0.738 | 1.00 | 0.98–1.02 | 0.892 | ||||||||||||
| BSA | 0.89 | 0.30–2.62 | 0.835 | 0.63 | 0.24–1.64 | 0.341 | 0.80 | 0.33–1.94 | 0.618 | 0.30 | 0.13–0.69 | 0.005 | 0.34 | 0.12–0.91 | 0.032 | |||||||||
| WHO (1 vs. 0) | 1.31 | 0.77–2.23 | 0.322 | 2.20 | 1.30–3.72 | 0.003 | 1.87 | 1.06–3.29 | 0.031 | 1.34 | 0.90–2.01 | 0.154 | 1.70 | 1.16–2.48 | 0.006 | 1.69 | 1.13–2.52 | 0.011 | ||||||
| Alcohol (vs never) History Current | 1.03 1.50 | 0.44–2.43 0.76–2.96 | 0.311 | 1.49 1.98 | 0.64–3.49 0.95–4.14 | 0.114 | 0.71 0.90 | 0.40–1.29 0.57–1.44 | 0.498 | 0.83 0.87 | 0.50–1.40 0.56–1.34 | 0.767 | ||||||||||||
| Smoking (vs never) History Current | 1.17 2.22 | 0.63–2.18 1.14–4.33 | 0.032 0.619 0.019 | 1.28 2.61 | 0.60–2.75 1.17–5.85 | 0.522 0.020 | 1.40 2.42 | 0.76–2.60 1.26–4.63 | 0.015 0.281 0.008 | 0.92 1.02 | 0.55–1.53 0.58–1.78 | 0.883 | 0.92 0.98 | 0.57–1.47 0.59–1.63 | 0.915 | |||||||||
| Year of diagnosis | 1.03 | 0.96–1.10 | 0.381 | 1.01 | 0.95–1.08 | 0.689 | 1.06 | 1.01–1.12 | 0.016 | 1.06 | 1.01–1.12 | 0.028 | 1.01 | 0.96–1.05 | 0.833 | |||||||||
| Tumor location (vs proximal) Middle Junction/Cardia Multiple locations | 1.17 0.99 0.94 NA | 0.57–2.43 0.52–1.91 0.37–2.41 NA | 0.937 | 0.79 0.67 0.55 | 0.43–1.45 0.39–1.16 0.24–1.26 | 0.429 | 0.32 0.59 0.69 0.85 | 0.12–0.89 0.24–1.45 0.22–2.11 0.16–4.42 | 0.100 0.029 0.246 0.513 0.849 | 0.29 0.55 0.68 0.73 | 0.10–0.80 0.22–1.36 0.22–2.08 0.14–3.80 | 0.017 0.193 0.498 0.705 | 0.27 0.45 0.46 0.87 | 0.12–0.63 0.22–0.94 0.18–1.17 0.18–4.13 | 0.045 0.002 0.033 0.103 0.859 | 0.27 0.54 0.49 | 0.11–0.65 0.26–1.15 0.18–1.33 | 0.004 0.110 0.160 | ||||||
| Histology (SCC vs. AC) | 1.06 | 0.66–1.68 | 0.816 | 1.22 | 0.80–1.86 | 0.354 | 0.56 | 0.36–0.86 | 0.008 | 0.76 | 0.52–1.10 | 0.146 | ||||||||||||
| Differentiation (poor vs. good/moderate) | 1.40 | 0.83–2.37 | 0.206 | 1.15 | 0.71–1.86 | 0.572 | 1.06 | 0.70–1.63 | 0.776 | 1.06 | 0.72–1.56 | 0.761 | ||||||||||||
| T-stage (iCT: vs. T2/T3, pCT: vsT1b/T2) T3 T4A T4B | NA 1.28 1.61 | NA 0.74–2.22 0.86–3.00 | 0.305 | NA 0.98 2.20 | NA 0.57–1.68 1.32–3.66 | 0.014 NA 0.948 0.003 | NA 1.01 1.82 | NA 0.56–1.81 1.02–3.25 | NA 0.984 0.044 | 1.85 1.68 1.36 | 0.98–3.48 0.76–3.71 0.56–3.28 | 0.204 | 2.03 2.13 1.59 | 1.11–3.71 1.03–4.41 0.71–3.55 | 0.076 | |||||||||
| N-stage (vs N0) N1 N2 N3 | 0.72 0.83 0.79 | 0.29–1.75 0.35–2.00 0.28–2.25 | 0.888 | 0.93 0.94 0.77 | 0.47–1.83 0.48–1.86 0.33–1.82 | 0.935 | 0.92 1.17 1.15 | 0.51–1.65 0.65–2.12 0.59–2.24 | 0.704 | 1.03 1.14 1.23 | 0.60–1.76 0.65–1.98 0.65–2.33 | 0.867 | ||||||||||||
| M-stage (vs M0) | 0.97 | 0.61–1.53 | 0.880 | 0.90 | 0.59–1.38 | 0.634 | 2.72 | 1.00–7.38 | 0.050 | 1.05 | 0.58–1.90 | 0.877 | ||||||||||||
| Metastases location: Nodal Liver Other Multiple locations | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.78 3.43 2.36 2.51 | 0.71–4.48 1.26–9.33 0.85–6.57 0.98–6.44 | 0.048 0.219 0.016 0.099 0.055 | 1.00 1.26 1.14 1.16 | 0.54–1.86 0.57–2.77 0.54–2.42 0.60–2.23 | 0.916 | ||||||||||||
| Liver metastases (Y vs. No) | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 1.47 | 1.02–2.13 | 0.040 | 1.12 | 0.78–1.60 | 0.534 | ||||||||||||
| Hemoglobin (mmoL/L) | 0.99 | 0.79–1.26 | 0.961 | 0.83 | 0.67–1.03 | 0.087 | 0.95 | 0.80–1.12 | 0.520 | 0.86 | 0.74–0.00 | 0.052 | ||||||||||||
| Thrombocytes (109/L) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.010 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.001 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.020 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.025 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.695 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.684 | ||||||
| Leukocytes (109/L) | 1.05 | 0.97–1.13 | 0.206 | 1.04 | 0.97–1.11 | 0.270 | 1.01 | 0.99–1.03 | 0.478 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.735 | ||||||||||||
| Neutrophils (109/L) | 1.05 | 0.96–1.14 | 0.310 | 1.04 | 0.96–1.12 | 0.312 | 1.01 | 0.97–1.05 | 0.696 | 1.01 | 0.95–1.08 | 0.660 | ||||||||||||
| ASAT (U/L) | 1.00 | 0.97–1.03 | 0.958 | 0.99 | 0.97–1.02 | 0.599 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.145 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.883 | ||||||||||||
| ALAT (U/L) | 1.00 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.880 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.01 | 0.633 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.767 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.475 | ||||||||||||
| LD (U/L) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.396 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.716 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.908 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.414 | ||||||||||||
| GGT (U/L) | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.301 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.193 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.608 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.973 | ||||||||||||
| AP (U/L) | 1.01 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.056 | 1.02 | 1.00–1.03 | 0.023 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.01 | 0.183 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.948 | 1.00 | 1.00–1.00 | 0.943 | |||||||||
| Bilirubin (µmol/L) | 1.01 | 0.95–1.07 | 0.836 | 1.02 | 0.96–1.08 | 0.596 | 1.00 | 0.96–1.03 | 0.953 | 1.01 | 0.97–1.04 | 0.722 | ||||||||||||
| Kreatinin (µmol/L) | 0.99 | 0.97–1.00 | 0.114 | 1.00 | 0.98–1.01 | 0.665 | 1.00 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.552 | 0.99 | 0.98–1.01 | 0.356 | ||||||||||||
| Patients (N) | Age (Median) | Esophageal Tumor (%) | GEJ Tumor * (%) | Gastric Tumor (%) | Adenocarcinoma (%) | Locally Advanced (%) | Metastatic Disease (%) | Overall Response (%) | Median PFS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fluorouracil, Cisplatin [33] | 224 | 55 | 0 | 25 | 75 | 90 | 3 | 97 | 25 | 3.7 | 8.6 |
| Fluorouracil, Cisplatin [34] | 163 | 59 | 0 | 19 | 81 | 100 | 5 | 95 | 26 | 4.2 | 8.7 |
| Fluorouracil, Cisplatin [17] | 163 | 56 a | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 32 | NR | 11.0 |
| Fluorouracil, Oxaliplatin [31] | 51 | 60 | NR | NR | 0 | 88 | NR | NR | 39 | 5.3 | 8.0 |
| Fluorouracil, Oxaliplatin [35] | 64 | 63 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 41 | 4.0 | 10.0 |
| Docetaxel, Cisplatin [41] | 76 | 57 | 0 | 26 | 74 | 100 | 5 | 95 | 20 | 5.0 | 10.5 |
| Paclitaxel, Cisplatin [36] | 51 | 56 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 61 | 10 | 90 | 43 | NR | 9.0 |
| Etoposide, Cisplatin [37] | 73 | 60 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 96 | 45 | NR | 8.5 |
| Epirubicin, Cisplatin, Fluorouracil [30] | 263 | 65 | 35 | 29 | 36 | 90 | 21 | 80 | 41 | 6.2 | 9.9 |
| Epirubicin, Cisplatin, Capecitabine [30] | 250 | 64 | 30 | 28 | 42 | 90 | 23 | 77 | 46 | 6.7 | 9.9 |
| Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil [30] | 245 | 61 | 30 | 23 | 37 | 86 | 23 | 77 | 42 | 6.5 | 9.3 |
| Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin, Capecitabine [30] | 244 | 62 | 34 | 22 | 44 | 87 | 24 | 58 | 48 | 7.0 | 11.2 |
| Docetaxel, Cisplatin, Fluorouracil [38] | 48 | 66 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 81 | 19 | 31 | 17.6 | NR b |
| Docetaxel, Cisplatin, Fluorouracil [33] | 221 | 55 | 0 | 19 | 81 | 89 | 3 | 96 | 37 | 5.6 | 9.2 |
| Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid, Cisplatin [39] | 108 | 64 | 0 | 22 | 78 | 100 | 9 | 91 | 25 | 3.9 | 8.8 |
| Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid, Oxaliplatin [39] | 112 | 64 | 0 | 18 | 82 | 100 | 3 | 97 | 35 | 5.8 | 10.7 |
| Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid, Irinotecan [34] | 170 | 58 | 0 | 20 | 80 | 100 | 4 | 96 | 32 | 5.0 | 9.0 |
| Fluorouracil, Folinic Acid, Cisplatin, Etoposide [40] | 69 | 55 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 81 | 34 | NR | 9.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
de Man, F.M.; van Eerden, R.A.G.; Oomen-de Hoop, E.; Veraart, J.N.; van Doorn, N.; van Doorn, L.; van der Gaast, A.; Mathijssen, R.H.J. Efficacy and Toxicity of Weekly Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as Induction or Palliative Treatment in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060826
de Man FM, van Eerden RAG, Oomen-de Hoop E, Veraart JN, van Doorn N, van Doorn L, van der Gaast A, Mathijssen RHJ. Efficacy and Toxicity of Weekly Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as Induction or Palliative Treatment in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2019; 11(6):826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060826
Chicago/Turabian Stylede Man, Femke M., Ruben A.G. van Eerden, Esther Oomen-de Hoop, Joris N. Veraart, Nadia van Doorn, Leni van Doorn, Ate van der Gaast, and Ron H.J. Mathijssen. 2019. "Efficacy and Toxicity of Weekly Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as Induction or Palliative Treatment in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Patients" Cancers 11, no. 6: 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060826
APA Stylede Man, F. M., van Eerden, R. A. G., Oomen-de Hoop, E., Veraart, J. N., van Doorn, N., van Doorn, L., van der Gaast, A., & Mathijssen, R. H. J. (2019). Efficacy and Toxicity of Weekly Carboplatin and Paclitaxel as Induction or Palliative Treatment in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Patients. Cancers, 11(6), 826. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060826






