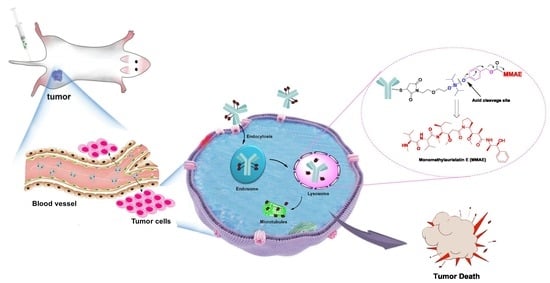
Novel Silyl Ether-Based Acid-Cleavable Antibody-MMAE Conjugates with Appropriate Stability and Efficacy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Design and Synthesis of Silyl Ether-Based ADC Payload
2.2. Antibody Conjugation
2.3. The Stability Assays of the Conjugate in Plasma
2.4. Effect of Acidity on ADC Stability
2.5. In Vitro Potency Assay
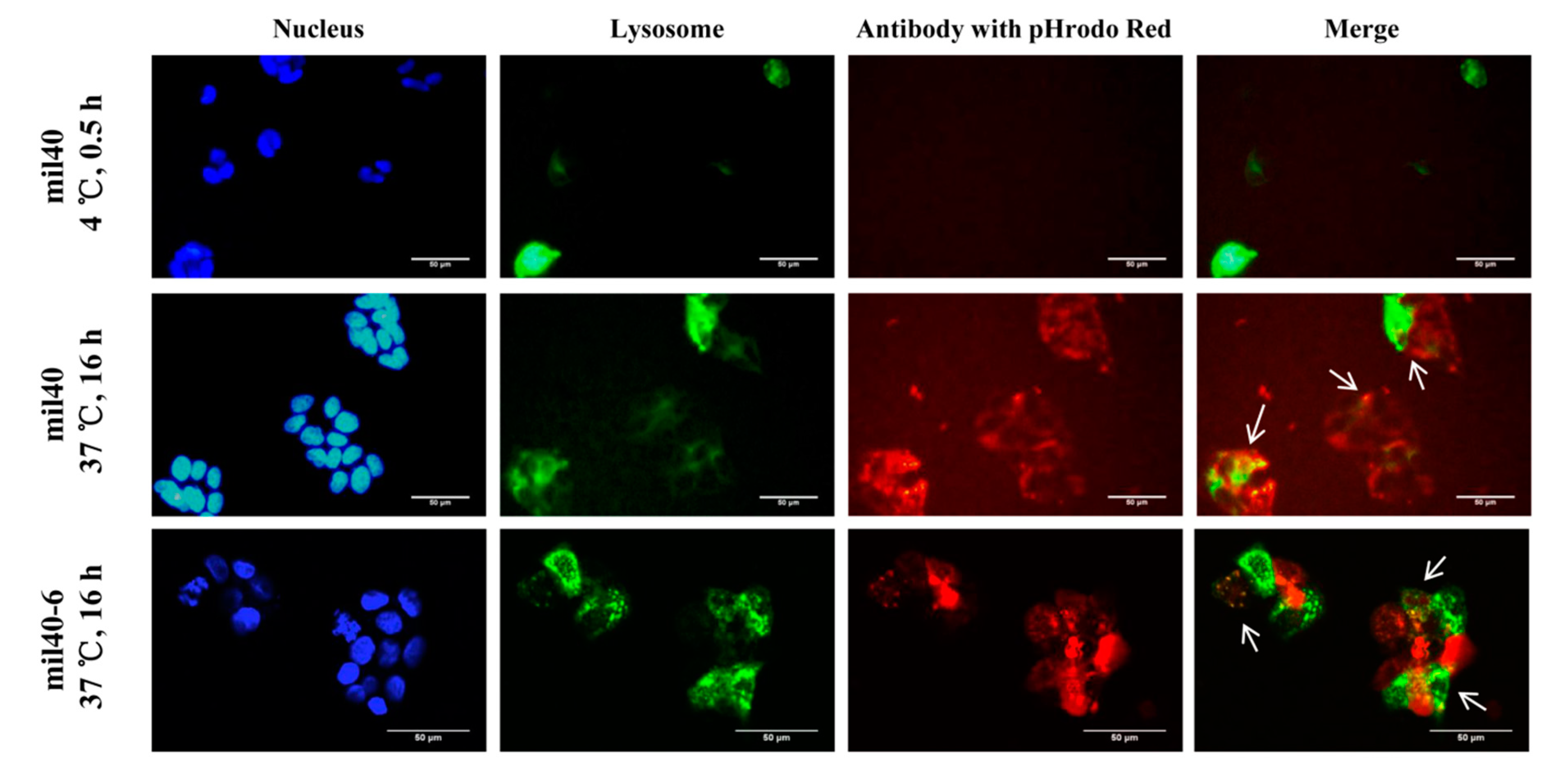
2.6. Trafficking Assay by Fluorescence Microscopy
2.7. Linker Composition on Inhibition of Microtubule Polymerization
2.8. Cell Cycle Effects
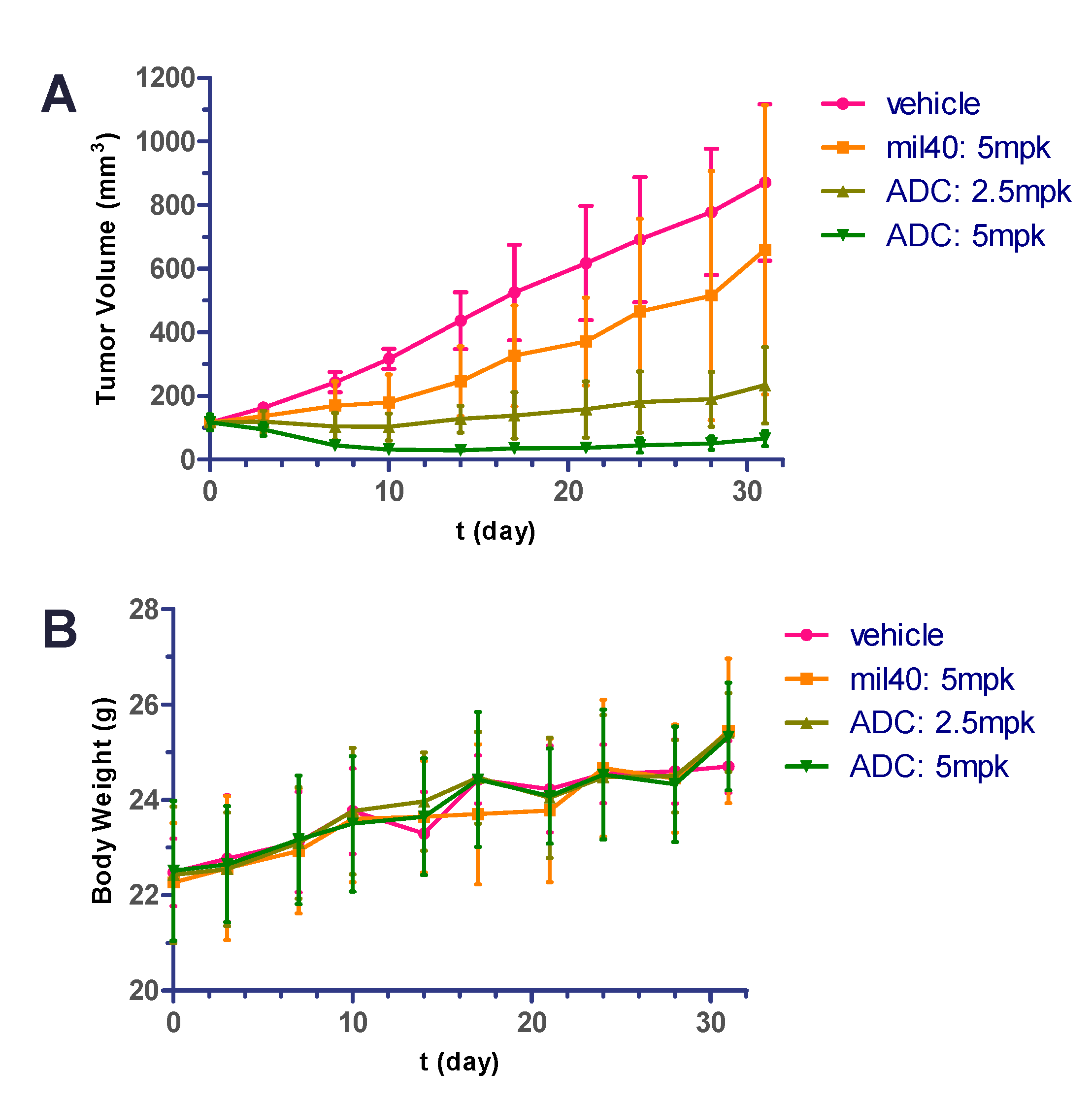
2.9. In Vivo Potency in Xenografted Nude Mice
2.10. Hematology Safety Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Synthesis of the Silyl Ether-Based Linker-MMAE Conjugate
4.2.1. Synthesis of 1-(2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2,5-dione (2)
4.2.2. Synthesis of 4-(((2-(2-(2,5-dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)ethoxy)ethoxy)diisopropylsilyl)-oxy) benzaldehyde (3)
4.2.3. Synthesis of 1-(2-(2-(((4-(hydroxymethyl)phenoxy)diisopropylsilyl)oxy)ethoxy)ethyl)-1H- pyrrole-2,5-dione (4)
4.2.4. Synthesis of 4-(((2-(2-(2,5-dioxo-2,5-dihydro-1H-pyrrol-1-yl)ethoxy)ethoxy)diisopropylsilyl)-oxy) benzyl(4-nitrophenyl) carbonate (5)
4.2.5. Synthesis of the Linker-MMAE Conjugate (Compound 6)
4.3. Preparation of Reagents and Antibody-Drug Conjugates
4.4. The Stability Assays of Linker and ADC in Plasma
4.5. Effect of Acidity Difference on the Drug Release Process
4.6. Evaluation of ADC for Cancer Cell Killing in Vitro
4.7. Endocytosis and Transport for the Silyl Ether-Based ADC
4.8. Microtubule Polymerization Assay
4.9. Cell Cycle Arrest in HER2-Positive Cancer Cells
4.10. In Vivo Antitumor Activity in Human Gastric Xenograft Tumors
4.11. Hematology Analysis during Treatment
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peters, C.; Brown, S. Antibody-drug conjugates as novel anti-cancer chemotherapeutics. Biosci. Rep. 2015, 35, e00225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez, H.L.; Cardarelli, P.M.; Deshpande, S.; Gangwar, S.; Schroeder, G.M.; Vite, G.D.; Borzilleri, R.M. Antibody-drug conjugates: Current status and future directions. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 869–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q. Site-specific antibody conjugation for ADC and beyond. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, Y.; Kopeček, J.; Yang, J. A new construct of antibody-drug conjugates for treatment of B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 103, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gébleux, R.; Stringhini, M.; Casanova, R.; Soltermann, A.; Neri, D. Non-internalizing antibody-drug conjugates display potent anti-cancer activity upon proteolytic release of monomethyl auristatin E in the subendothelial extracellular matrix. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1670–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolot, R.S.; Basu, S.; Million, R.P. Antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2013, 12, 259–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Goetsch, L.; Dumontet, C.; Corvaia, N. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2017, 16, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, R. Drawing lessons from the clinical development of antibody-drug conjugates. Drug. Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 30, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebleux, R.; Casi, G. Antibody-drug conjugates: Current status and future perspectives. Pharm. Ther. 2016, 167, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekholm, F.S.; Pynnonen, H.; Vilkman, A.; Pitkanen, V.; Helin, J.; Saarinen, J.; Satomaa, T. Introducing glycolinkers for the functionalization of cytotoxic drugs and applications in antibody-drug conjugation chemistry. ChemMedChem 2016, 11, 2501–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Smith, S.W.; Ghone, S.; Tomczuk, B. Current ADC linker chemistry. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 3526–3540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantis, N.; Banerji, U. Antibody-drug conjugates-an emerging class of cancer treatment. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, M.R.; Canakci, M.; Li, L.; Zhuang, J.; Osborne, B.; Thayumanavan, S. Field guide to challenges and opportunities in antibody-drug conjugates for chemists. Bioconjug. Chem. 2015, 26, 2198–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchikama, K.; An, Z. Antibody-drug conjugates: Recent advances in conjugation and linker chemistries. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, J.R.; Grinstein, S.; Orlowski, J. Sensors and regulators of intracellular pH. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolting, B. Linker technologies for antibody-drug conjugates. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 1045, 71–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cardillo, T.M.; Govindan, S.V.; Sharkey, R.M.; Trisal, P.; Goldenberg, D.M. Humanized anti-trop-2 igg-sn-38 conjugate for effective treatment of diverse epithelial cancers: Preclinical studies in human cancer xenograft models and monkeys. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3157–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, N.; Setua, S.; Kashyap, V.K.; Khan, S.; Jaggi, M.; Yallapu, M.M.; Chauhan, S.C. Antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy: Chemistry to clinical implications. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Chari, R.V.; Miller, M.L.; Widdison, W.C. Antibody-drug conjugates: An emerging concept in cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 3796–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.; Wang, E.S. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2018, 11, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Kano, Y.; Akutsu, M.; Tsunoda, S.; Izumi, T.; Yazawa, Y.; Miyawaki, S.; Mano, H.; Furukawa, Y. The cytotoxic effects of gemtuzumab ozogamicin (mylotarg) in combination with conventional antileukemic agents by isobologram analysis in vitro. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 4589–4596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moussa, E.M.; Panchal, J.P.; Moorthy, B.S.; Blum, J.S.; Joubert, M.K.; Narhi, L.O.; Topp, E.M. Immunogenicity of therapeutic protein aggregates. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 417–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adem, Y.T.; Schwarz, K.A.; Duenas, E.; Patapoff, T.W.; Galush, W.J.; Esue, O. Auristatin antibody drug conjugate physical instability and the role of drug payload. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Arnst, K.E.; Miller, D.D.; Li, W. Tubulin inhibitor-based antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Molecules 2017, 22, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vankemmelbeke, M.; Durrant, L. Third-generation antibody drug conjugates for cancer therapy-a balancing act. Deliv 2016, 7, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senter, P.D.; Sievers, E.L. The discovery and development of brentuximab vedotin for use in relapsed Hodgkin lymphoma and systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doronina, S.O.; Bovee, T.D.; Meyer, D.W.; Miyamoto, J.B.; Anderson, M.E.; Morris-Tilden, C.A.; Senter, P.D. Novel peptide linkers for highly potent antibody-auristatin conjugate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1960–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderna, A.; Leverett, C.A. Recent advances in the development of new auristatins: Structural modifications and application in antibody drug conjugates. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anami, Y.; Yamazaki, C.M.; Xiong, W.; Gui, X.; Zhang, N.; An, Z.; Tsuchikama, K. Glutamic acid-valine-citrulline linkers ensure stability and efficacy of antibody-drug conjugates in mice. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.A.; Sievers, E.L.; Stadtmauer, E.A.; Lowenberg, B.; Estey, E.H.; Dombret, H.; Theobald, M.; Voliotis, D.; Bennett, J.M.; Richie, M.; et al. Final report of the efficacy and safety of gemtuzumab ozogamicin (mylotarg) in patients with cd33-positive acute myeloid leukemia in first recurrence. Cancer 2005, 104, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, S.C.; Benjamin, D.R.; Jeffrey, S.C.; Okeley, N.M.; Meyer, D.L.; Sanderson, R.J.; Senter, P.D. Contribution of linker stability to the activities of anticancer immunoconjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Chen, T.; Zhang, P.; Ling, C.-C. Controlled acid-mediated regioselectiveo-desilylations for multifunctionalization of cyclodextrins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2014, 2014, 5793–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, T.; Lu, X. Controlled release of silyl ether camptothecin from thiol-ene click chemistry-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Acta Biomaterijalia 2017, 51, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parrott, M.C.; Luft, J.C.; Byrne, J.D.; Fain, J.H.; Napier, M.E.; Desimone, J.M. Tunable bifunctional silyl ether cross-linkers for the design of acid-sensitive biomaterials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17928–17932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, K.S.; Finniss, M.C.; Schorzman, A.N.; Kuijer, J.L.; Luft, J.C.; Bowerman, C.J.; Napier, M.E.; Haroon, Z.A.; Zamboni, W.C.; DeSimone, J.M. Particle replication in nonwetting templates nanoparticles with tumor selective alkyl silyl ether docetaxel prodrug reduces toxicity. Nano. Lett. 2014, 14, 1472–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Assadi, M.G.; Golipour, N. Synthesis and characterization of methylsalicylate and acetaminophen silyl ether canditates for prodrugs. Main Group Chem. 2006, 5, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finniss, M.C.; Chu, K.S.; Bowerman, C.J.; Luft, J.C.; Haroon, Z.A.; DeSimone, J.M. A versatile acid-labile linker for antibody–drug conjugates. Med. Chem. Commun. 2014, 5, 1355–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, S. Development and properties of valine-alanine based antibody-drug conjugates with monomethyl auristatin e as the potent payload. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendriks, B.S.; Klinz, S.G.; Reynolds, J.G.; Espelin, C.W.; Gaddy, D.F.; Wickham, T.J. Impact of tumor HER2/ERBB2 expression level on HER2-targeted liposomal doxorubicin-mediated drug delivery: Multiple low-affinity interactions lead to a threshold effect. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis Phillips, G.D.; Li, G.; Dugger, D.L.; Crocker, L.M.; Parsons, K.L.; Mai, E.; Blattler, W.A.; Lambert, J.M.; Chari, R.V.; Lutz, R.J.; et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-dm1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 9280–9290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, J.P.M.; Vassileva, V.; Robinson, E.; Morais, M.; Smith, M.E.B.; Pedley, R.B.; Caddick, S.; Baker, J.R.; Chudasama, V. Use of a next generation maleimide in combination with THIOMAB™ antibody technology delivers a highly stable, potent and near homogeneous THIOMAB™ antibody-drug conjugate (TDC). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24828–24832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.; Okouneva, T.; Manna, T.; Miller, H.P.; Schmid, S.; Arthaud, L.; Luduena, R.; Jordan, M.A.; Wilson, L. Mechanism of action of the microtubule-targeted antimitotic depsipeptide tasidotin (formerly ILX-651) and its major metabolite tasidotin c-carboxylate. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3767–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maderna, A.; Doroski, M.; Subramanyam, C.; Porte, A.; Leverett, C.A.; Vetelino, B.C.; Chen, Z.; Risley, H.; Parris, K.; Pandit, J.; et al. Discovery of cytotoxic dolastatin 10 analogues with n-terminal modifications. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 10527–10543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Dong, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, X.; Huang, M.; Li, S.; Ma, W.; et al. HER2-targeted antibody drug conjugates for ovarian cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, C.L.; Gordon, K.A.; Toki, B.E.; Yamane, A.K.; Hering, M.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Petroziello, J.M.; Ryan, M.C.; Smith, L.; Simon, R.; et al. Lymphocyte activation antigen CD70 expressed by renal cell carcinoma is a potential therapeutic target for anti-CD70 antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Yu, C.; Jiang, J.; Huang, C.; Yao, X.; Xu, Q.; Yu, F.; Lou, L.; Fang, J. An anti-her2 antibody conjugated with monomethyl auristatin e is highly effective in her2-positive human gastric cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Le, H.; Cruz-Chuh, J.D.; Bobba, S.; Guo, J.; Staben, L.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Kozak, K.R.; Lewis Phillips, G.D.; et al. Immolation of p-aminobenzyl ether linker and payload potency and stability determine the cell-killing activity of antibody-drug conjugates with phenol-containing payloads. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianolio, D.A.; Rouleau, C.; Bauta, W.E.; Lovett, D.; Cantrell, W.R., Jr.; Recio, A., 3rd; Wolstenholme-Hogg, P.; Busch, M.; Pan, P.; Stefano, J.E.; et al. Targeting HER2-positive cancer with dolastatin 15 derivatives conjugated to trastuzumab, novel antibody-drug conjugates. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2012, 70, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. Cac10-vcmmae, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin e conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trail, P. Antibody drug conjugates as cancer therapeutics. Antibodies 2013, 2, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrott, M.C.; Finniss, M.; Luft, J.C.; Pandya, A.; Gullapalli, A.; Napier, M.E.; DeSimone, J.M. Incorporation and controlled release of silyl ether prodrugs from print nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7978–7982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trail, P.A.; Willner, D.; Lasch, S.J.; Henderson, A.J.; Hofstead, S.; Casazza, A.M.; Firestone, R.A.; Hellstrom, I.; Hellstrom, K.E. Cure of xenografted human carcinomas by BR96-doxorubicin immunoconjugates. Science 1993, 261, 212–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghaert, E.R.; Khandke, K.M.; Sridharan, L.; Dougher, M.; DiJoseph, J.F.; Kunz, A.; Hamann, P.R.; Moran, J.; Chaudhary, I.; Damle, N.K. Determination of pharmacokinetic values of calicheamicin-antibody conjugates in mice by plasmon resonance analysis of small (5 microl) blood samples. Cancer Chemother. Pharm. 2008, 61, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, M.N.; Sugarman, S.; Murray, J.; Ostroff, J.B.; Healey, D.; Jones, D.; Daniel, C.R.; LeBherz, D.; Brewer, H.; Onetto, N.; et al. PhaseI trial of the anti-lewis y drug immunoconjugate BR96-doxorubicin in patients with lewis y-expressing epithelial tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindan, S.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Moon, S.J.; Hansen, H.J.; Goldenberg, D.M. Ceacam5-targeted therapy of human colonic and pancreatic cancer xenografts with potent labetuzumab-sn-38 immunoconjugates. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2009, 15, 6052–6061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, R.W.; Boutin, R.H.; Nedelman, M.A.; Lister-James, J.; Dean, R.T. Enhanced kidney clearance with an ester-linked 99mtc-radiolabeled antibody fab’-chelator conjugate. Bioconjug. Chem. 2002, 1, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, S.C.; Andreyka, J.B.; Bernhardt, S.X.; Kissler, K.M.; Kline, T.; Lenox, J.S.; Moser, R.F.; Nguyen, M.T.; Okeley, N.M.; Stone, I.J.; et al. Development and properties of β-glucuronide linkers for monoclonal antibody-drug conjugates. Bioconjug. Chem. 2006, 17, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Cell Lines | HER2 Status | ADC | mil40 | MMAE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (nM) | Max. Inhibition | IC50 (nM) | Max. Inhibition | IC50 (nM) | Max. Inhibition | ||
| BT-474 | HER2+++ | 0.170 | 50.50% | 0.323 | 61.25% | 0.400 | 40.65% |
| NCI-N87 | HER2+++ | 0.028 | 93.54% | 1.157 | 45.80% | 0.369 | 68.22% |
| MDA-MB-453 | HER2++ | 0.101 | 87.30% | 0.315 | 34.80% | 0.295 | 83.79% |
| MCF-7 | HER2− | 7.742 | 47.8% | >1000 | - | 0.688 | 77.64% |
| MDA-MB-231 | HER2− | >1000 | - | >1000 | - | 1.156 | 53.4% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Fan, S.; Xiao, D.; Xie, F.; Li, W.; Zhong, W.; Zhou, X. Novel Silyl Ether-Based Acid-Cleavable Antibody-MMAE Conjugates with Appropriate Stability and Efficacy. Cancers 2019, 11, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070957
Wang Y, Fan S, Xiao D, Xie F, Li W, Zhong W, Zhou X. Novel Silyl Ether-Based Acid-Cleavable Antibody-MMAE Conjugates with Appropriate Stability and Efficacy. Cancers. 2019; 11(7):957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070957
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yanming, Shiyong Fan, Dian Xiao, Fei Xie, Wei Li, Wu Zhong, and Xinbo Zhou. 2019. "Novel Silyl Ether-Based Acid-Cleavable Antibody-MMAE Conjugates with Appropriate Stability and Efficacy" Cancers 11, no. 7: 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070957
APA StyleWang, Y., Fan, S., Xiao, D., Xie, F., Li, W., Zhong, W., & Zhou, X. (2019). Novel Silyl Ether-Based Acid-Cleavable Antibody-MMAE Conjugates with Appropriate Stability and Efficacy. Cancers, 11(7), 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11070957