Age-Related Alterations in Immune Contexture Are Associated with Aggressiveness in Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
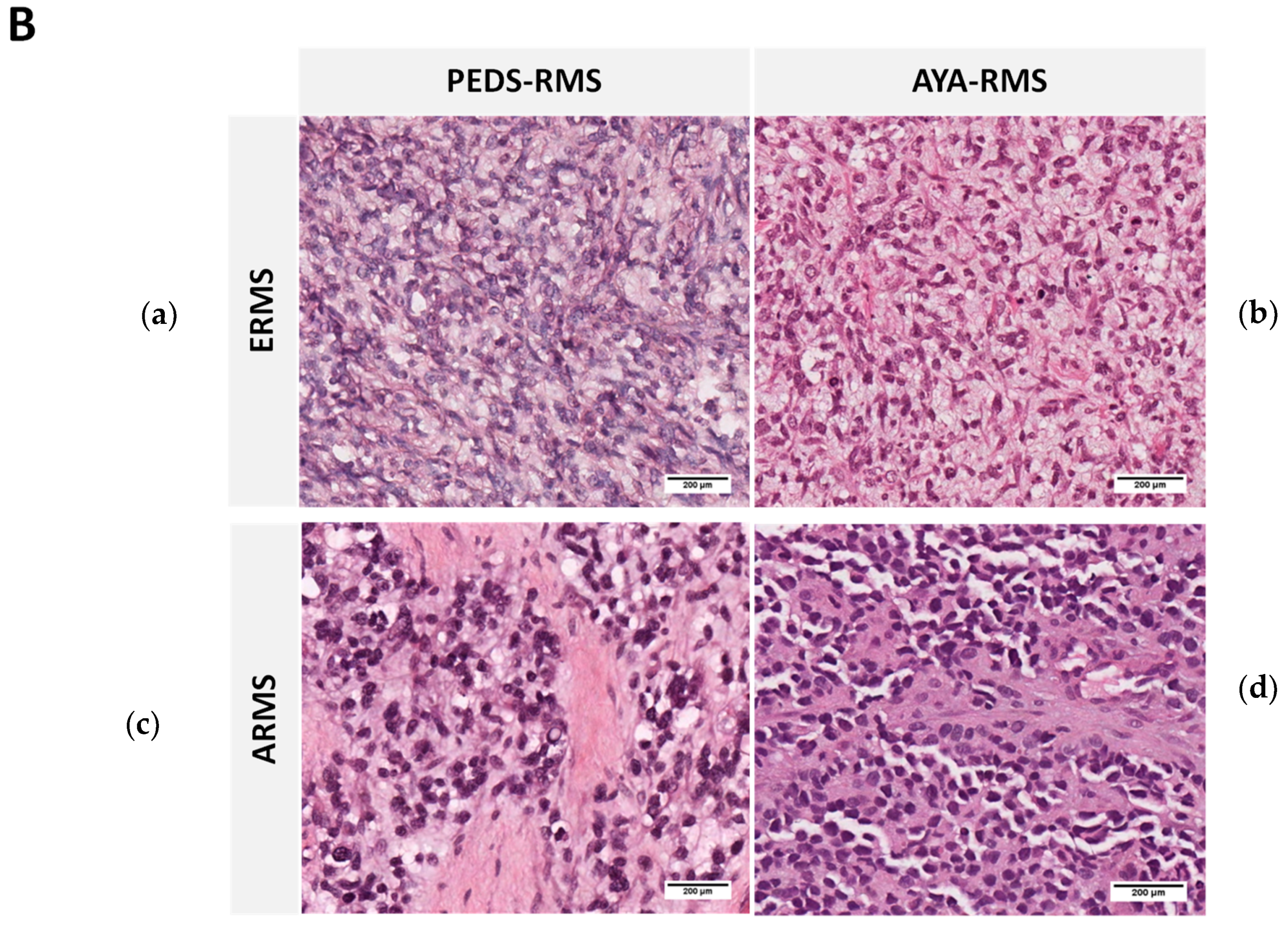
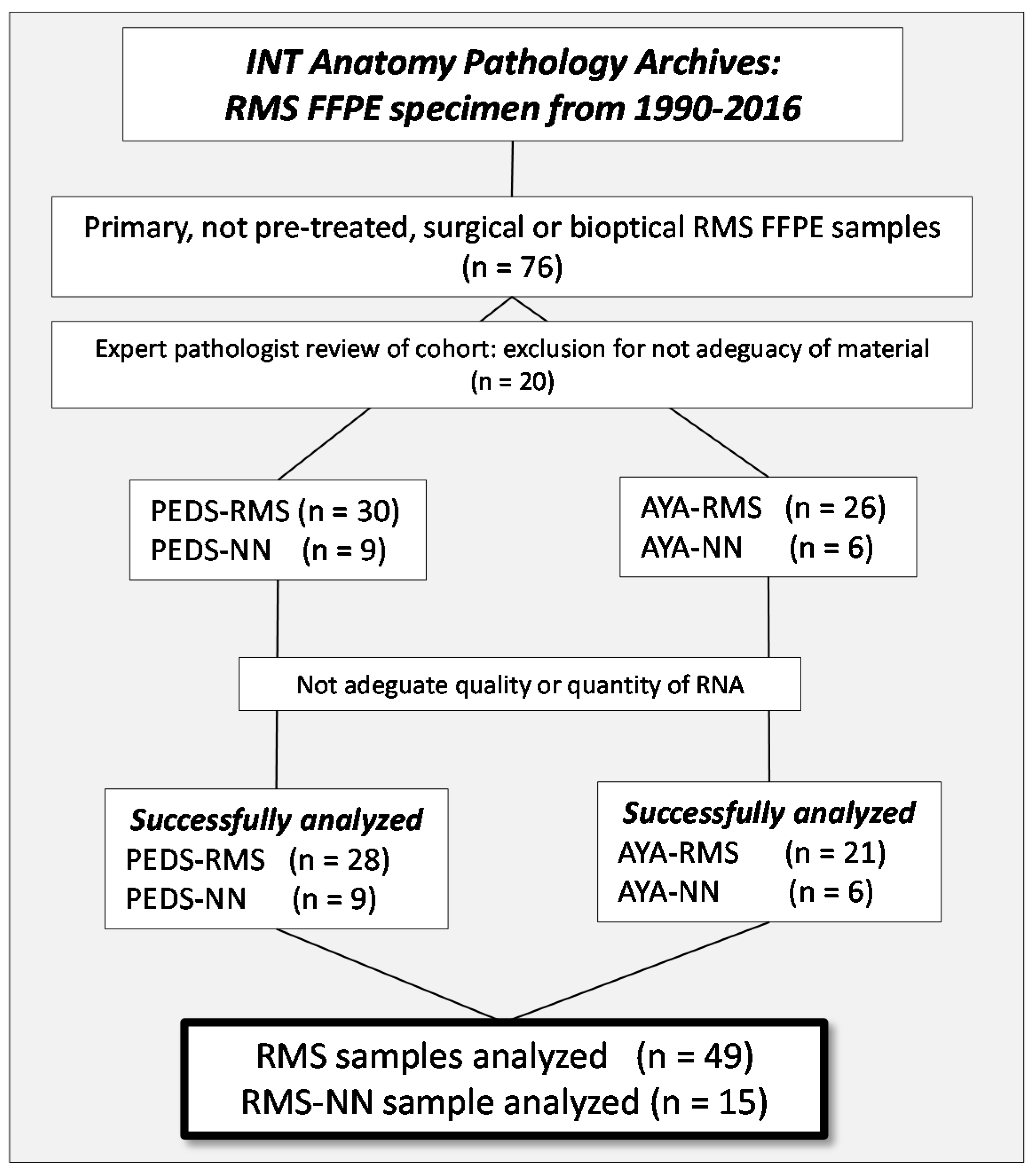
2.1. Clinico-Pathological Features of the Studied RMS Series
2.2. Age-Related miRNA Expression in RMS
2.3. Age-Related Gene Expression Assessment
2.4. Integration of miRNA Expression and GEP Data
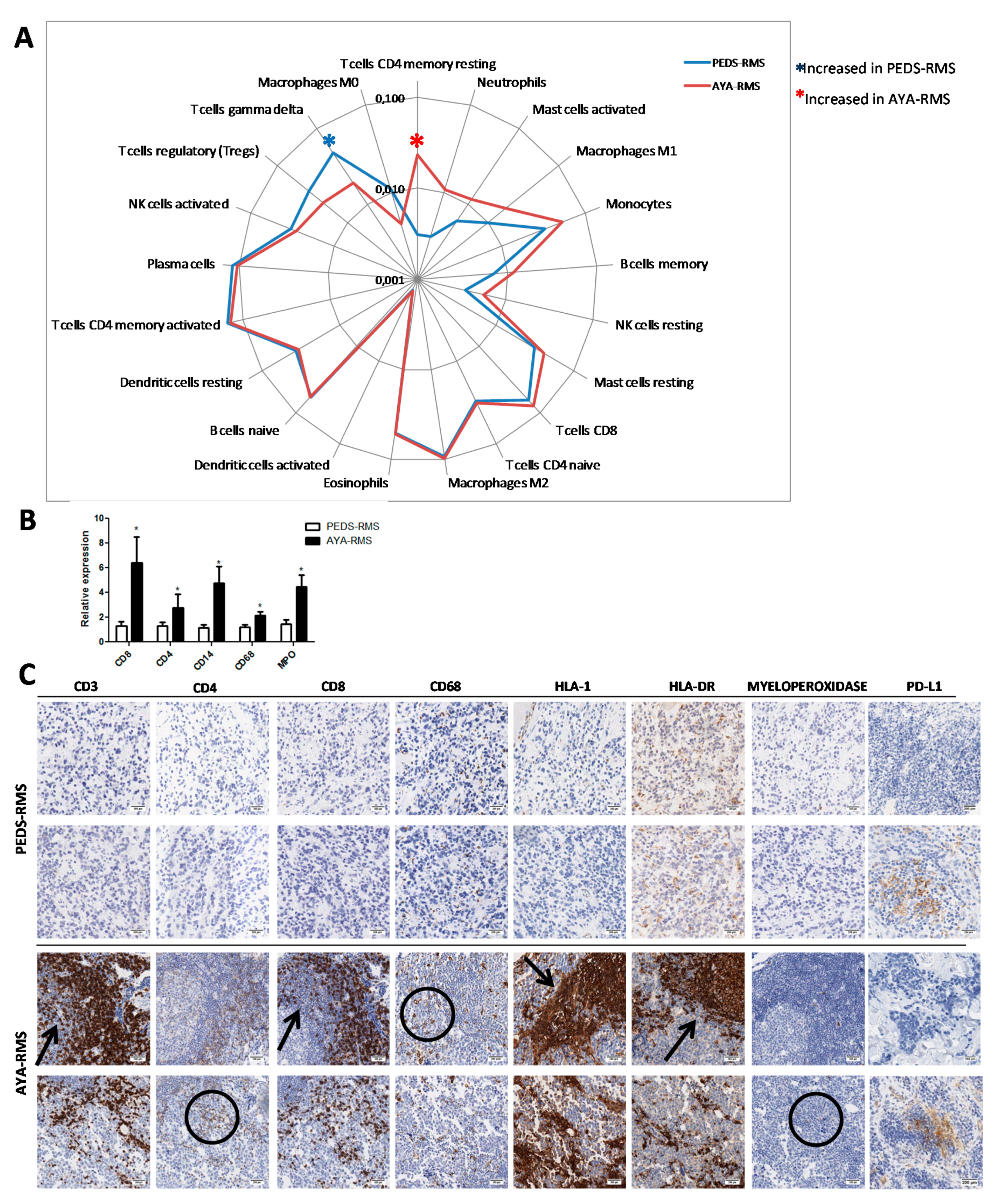
2.5. Assessment of Specific Immune Cell Tumor Infiltration
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples Selection
4.2. RNA Extraction from FFPE
4.3. miRNAs Profiling
4.4. Real-Time PCR
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. miRNAs In Situ Hybridization (ISH)
4.7. Gene Expression Profiling
4.8. Bioinformatic Analysis
4.9. miRNA-mRNA Integration Analysis
5. Conclusions
Data Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sultan, I.; Qaddoumi, I.; Yaser, S.; Rodriguez-Galindo, C.; Ferrari, A. Comparing Adult and Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma in the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results Program, 1973 to 2005: An Analysis of 2,600 Patients. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3391–3397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trama, A.; Botta, L.; Foschi, R.; Ferrari, A.; Stiller, C.; Desandes, E.; Maule, M.M.; Merletti, F.; Gatta, G.; the EUROCARE-5 Working Group. Survival of European Adolescents and Young Adults Diagnosed with Cancer in 2000–07: Population-Based Data from EUROCARE-5. Lancet. Oncol. 2016, 17, 896–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.; Miceli, R.; Casanova, M.; Meazza, C.; Favini, F.; Luksch, R.; Catania, S.; Fiore, M.; Morosi, C.; Mariani, L. The Symptom Interval in Children and Adolescents with Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Cancer 2010, 116, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Trama, A.; De Paoli, A.; Bergeron, C.; Merks, J.H.; Jenney, M.; Orbach, D.; Chisholm, J.C.; Gallego, S.; Glosli, H.; et al. Access to Clinical Trials for Adolescents with Soft Tissue Sarcomas: Enrollment in European Pediatric Soft Tissue Sarcoma Study Group (EpSSG) Protocols. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2017, 64, e26348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Casanova, M. New Concepts for the Treatment of Pediatric Nonrhabdomyosarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2005, 5, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamaschi, L.; Bertulli, R.; Casanova, M.; Provenzano, S.; Chiaravalli, S.; Gasparini, P.; Collini, P.; Sangalli, C.; Gandola, L.; Diletto, B.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma in Adults: Analysis of Treatment Modalities in a Prospective Single-Center Series. Med. Oncol. 2019, 36, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shern, J.F.; Chen, L.; Chmielecki, J.; Wei, J.S.; Patidar, R.; Rosenberg, M.; Ambrogio, L.; Auclair, D.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.K.; et al. Comprehensive Genomic Analysis of Rhabdomyosarcoma Reveals a Landscape of Alterations Affecting a Common Genetic Axis in Fusion-Positive and Fusion-Negative Tumors. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, E.; McEvoy, J.; Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Honnell, V.; Ocarz, M.; Gordon, B.; Dapper, J.; Blankenship, K.; Yang, Y.; et al. Identification of Therapeutic Targets in Rhabdomyosarcoma through Integrated Genomic, Epigenomic, and Proteomic Analyses. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. Causes and Consequences of microRNA Dysregulation. Cancer J. 2012, 18, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, M.V.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA Dysregulation in Cancer: Diagnostics, Monitoring and Therapeutics. A Comprehensive Review. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osada, H.; Takahashi, T. let-7 and miR-17-92: Small-Sized Major Players in Lung Cancer Development. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Dutta, A. The Tumor Suppressor microRNA let-7 Represses the HMGA2 Oncogene. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, J.; Vinklarek, J.; Bienertova-Vasku, J.; Slaby, O. MicroRNAs involved in skeletal muscle development and their roles in rhabdomyosarcoma pathogenesis. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2013, 60, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bersani, F.; Lingua, M.F.; Morena, D.; Foglizzo, V.; Miretti, S.; Lanzetti, L.; Carrà, G.; Morotti, A.; Ala, U.; Provero, P.; et al. Deep Sequencing Reveals a Novel miR-22 Regulatory Network with Therapeutic Potential in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6095–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taulli, R.; Bersani, F.; Foglizzo, V.; Linari, A.; Vigna, E.; Ladanyi, M.; Tuschl, T.; Ponzetto, C. The Muscle-Specific microRNA miR-206 Blocks Human Rhabdomyosarcoma Growth in Xenotransplanted Mice by Promoting Myogenic Differentiation. J. Clin. Invest. 2009, 119, 2366–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichek, J.L.; Duan, F.; Smith, L.M.; Gustafson, D.M.; O’Connor, R.S.; Zhang, C.; Dunlevy, M.J.; Gastier-Foster, J.M.; Barr, F.G. Genomic and Clinical Analysis of Amplification of the 13q31 Chromosomal Region in Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 1463–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imam, J.S.; Buddavarapu, K.; Lee-Chang, J.S.; Ganapathy, S.; Camosy, C.; Chen, Y.; Rao, M.K. MicroRNA-185 Suppresses Tumor Growth and Progression by Targeting the Six1 Oncogene in Human Cancers. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4971–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davicioni, E.; Finckenstein, F.G.; Shahbazian, V.; Buckley, J.D.; Triche, T.J.; Anderson, M.J. Identification of a PAX-FKHR Gene Expression Signature that Defines Molecular Classes and Determines the Prognosis of Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcomas. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 6936–6946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davicioni, E.; Anderson, J.R.; Buckley, J.D.; Meyer, W.H.; Triche, T.J. Gene Expression Profiling for Survival Prediction in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcomas: A Report from the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1240–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebrack, B.J. Psychological, Social, and Behavioral Issues for Young Adults with Cancer. Cancer 2011, 117, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drost, F.M.; Mols, F.; Kaal, S.E.; Stevens, W.B.; Van Der Graaf, W.T.; Prins, J.B.; Husson, O. Psychological Impact of Lymphoma on Adolescents and Young Adults: Not a Matter of Black or White. J. Cancer Surviv. 2016, 10, 726–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husson, O.; Zebrack, B.J. Psychometric Evaluation of an Adolescent and Young Adult Module of the Impact of Cancer Instrument. J. Adolesc. Young Adult Oncol. 2017, 6, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, L.B.; Rabkin, C.S.; Brown, L.M.; Allan, J.M.; Alter, B.P.; Ambrosone, C.B.; Begg, C.B.; Caporaso., N.; Chanock, S.; DeMichele., A.; et al. Cancer Survivorship—Genetic Susceptibility and Second Primary Cancers: Research Strategies and Recommendations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 15–25. [PubMed]
- Ferrari, A.; Dileo, P.; Casanova, M.; Bertulli, R.; Meazza, C.; Gandola., L.; Navarria, P.; Collini, P.; Gronchi, A.; Olmi, P.; et al. Rhabdomyosarcoma in Adults. A Retrospective Analysis of 171 Patients Treated at a Single Institution. Cancer 2003, 98, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komdeur, R.; Klunder, J.; Van Der Graaf, W.T.; van den Berg, E.; de Bont, E.S.; Hoekstra, H.J.; Molenaar, W.M. Multidrug Resistance Proteins in Rhabdomyosarcomas: Comparison Between Children and Adults. Cancer 2003, 97, 1999–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Q.W.; Lung, R.W.; Law, P.T.; Lai, P.B.; Chan, K.Y.; To, K.F.; Wong, N. MicroRNA-223 is Commonly Repressed in Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Potentiates Expression of Stathmin1. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, Z.; Guo, F.; Qin, X.; Liu, B.; Lei, Z.; Song, Z.; Sun, L.; Zhang, H.T.; You, J.; et al. miR-223 Regulates Migration and Invasion by Targeting Artemin in Human Esophageal Carcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Li, H.; Jia, C.Y.; Cheng, W.; Yu, M.; Peng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Dong, Y.W.; Shao, K.; et al. MicroRNA-223 Regulates FOXO1 Expression and Cell Proliferation. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1038–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorhoi, A.; Iannaccone, M.; Farinacci, M.; Fae, K.C.; Schreiber, J.; Moura-Alves, P.; Nouailles, G.; Mollenkopf, H.J.; Oberbeck-Müller, D.; Jörg, S.; et al. MicroRNA-223 Controls Susceptibility to Tuberculosis by Regulating Lung Neutrophil Recruitment. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 4836–4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.P.; Shin, Y.J.; Panda, A.C.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, S.M.; Bahn, Y.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Kwon, E.S.; Baek, S.J.; et al. miR-431 Promotes Differentiation and Regeneration of Old Skeletal Muscle by Targeting Smad4. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1605–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, H.; Zhai, L.; Zou, X.; Meng, J.; Zhong, R.; Li, C.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, D. MicroRNA-431 Accelerates Muscle Regeneration and Ameliorates Muscular Dystrophy by Targeting Pax7 in Mice. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornson, C.R.; Cheung, T.H.; Liu, L.; Tripathi, P.V.; Steeper, K.M.; Rando, T.A. Notch Signaling is Necessary to Maintain Quiescence in Adult Muscle Stem Cells. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Shin, M.S.; Cheon, M.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, C.; Kim, W.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Jang, B.G. GREM1 is Expressed in the Cancer-Associated Myofibroblasts of Basal Cell Carcinomas. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schatton, D.; Pla-Martin, D.; Marx, M.C.; Hansen, H.; Mourier, A.; Nemazanyy, I.; Pessia, A.; Zentis, P.; Corona, T.; Kondylis, V.; et al. CLUH Regulates Mitochondrial Metabolism by Controlling Translation and Decay of Target mRNAs. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 675–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourteymour, S.; Hjorth, M.; Lee, S.; Holen, T.; Langleite, T.M.; Jensen, J.; Birkeland, K.I.; Drevon, C.A.; Eckardt, K. Dual specificity phosphatase 5 and 6 are oppositely regulated in human skeletal muscle by acute exercise. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flanagan-Steet, H.; Hannon, K.; McAvoy, M.J.; Hullinger, R.; Olwin, B.B. Loss of FGF Receptor 1 Signaling Reduces Skeletal Muscle Mass and Disrupts Myofiber Organization in the Developing Limb. Dev. Biol. 2000, 218, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahim, M.; Smith, R.; Burghardt, R.; Safe, S. Role of Sp Proteins in Regulation of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression and Proliferation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6740–6749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, S.C.; Law, M.E.; Corsino, P.E.; Law, B.K. TGF-beta antiproliferative effects in tumor suppression. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.) 2012, 4, 749–766. [Google Scholar]
- Kajita, Y.; Kato, T., Jr.; Tamaki, S.; Furu, M.; Takahashi, R.; Nagayama, S.; Aoyama, T.; Nishiyama, H.; Nakamura, E.; Katagiri, T.; et al. The Transcription Factor Sp3 Regulates the Expression of a Metastasis-Related Marker of Sarcoma, Actin Filament-Associated Protein 1-like 1 (AFAP1L1). PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e49709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyson, K.A.; Stover, B.D.; Grippin, A.; Mendez-Gomez, H.R.; Lagmay, J.; Mitchell, D.A.; Sayour, E.J. Emerging Trends in Immunotherapy for Pediatric Sarcomas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentles, A.J.; Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Bratman, S.V.; Feng, W.; Kim, D.; Nair, V.S.; Xu, Y.; Khuong, A.; Hoang, C.D.; et al. The Prognostic Landscape of Genes and Infiltrating Immune Cells across Human Cancers. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Niu, C.; Cui, J. Gamma-Delta (Gammadelta) T Cells: Friend or Foe in Cancer Development? J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Elements of Cancer Immunity and the Cancer-Immune Set Point. Nature 2017, 541, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambros, V. The Functions of Animal microRNAs. Nature 2004, 431, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Cecco, L.; Giannoccaro, M.; Marchesi, E.; Bossi, P.; Favales, F.; Locati, L.D.; Licitra, L.; Pilotti, S.; Canevari, S. Integrative miRNA-Gene Expression Analysis Enables Refinement of Associated Biology and Prediction of Response to Cetuximab in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Cancer. Genes 2017, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fortunato, O.; Boeri, M.; Verri, C.; Conte, D.; Mensah, M.; Suatoni, P.; Pastorino, U.; Sozzi, G. Assessment of Circulating microRNAs in Plasma of Lung Cancer Patients. Molecules 2014, 19, 3038–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, G.; Bergamaschi, L.; Ferrari, A.; Renne, S.L.; Collini, P.; Gardelli, C.; Barisella, M.; Centonze, G.; Chiaravalli, S.; Paolino, C.; et al. PD-L1 Assessment in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Pilot Study. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, O.; Borzi, C.; Milione, M.; Centonze, G.; Conte, D.; Boeri, M.; Verri, C.; Moro, M.; Facchinetti, F.; Andriani, F.; et al. Circulating mir-320a Promotes Immunosuppressive Macrophages M2 Phenotype Associated with Lung Cancer Risk. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2746–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Affymetrix. Available online: http://www.affymetrix.com/support/technical/byproduct.affx?product=expressionconsole (accessed on 1 September 2019).
- CIBERSORT. Available online: https://cibersort.stanford.edu/ (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Newman, A.M.; Liu, C.L.; Green, M.R.; Gentles, A.J.; Feng, W.; Xu, Y.; Hoang, C.D.; Diehn, M.; Alizadeh, A.A. Robust Enumeration of Cell Subsets from Tissue Expression Profiles. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Statistical Software, Version 3.5.2. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Bioconductor. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/ (accessed on 6 September 2019).
- Huber, W.; Carey, V.J.; Gentleman, R.; Anders, S.; Carlson, M.; Carvalho, B.S.; Bravo, H.C.; Davis, S.; Gatto, L.; Girke, T.; et al. Orchestrating High-Throughput Genomic Analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bioconductor ComplexHeatmap. Available online: https://www.bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/ComplexHeatmap.html (accessed on 8 September 2019).
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. miRNet—Dissecting miRNA-Target Interactions and Functional Associations Through Network-Based Visual Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cytoscape. Available online: https://cytoscape.org/ (accessed on 2 September 2019).
- Sales, G.; Coppe, A.; Bisognin, A.; Biasiolo, M.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Romualdi, C. MAGIA, A Web-Based Tool for miRNA and Genes Integrated Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W352–W359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| # of Cases (%) | PEDS 0–14 Years (%) | AYA 15–34 Years (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (No. of subjects) | 49 | 28 | 21 | |
| Gender | Male | 26 (53) | 13 (46) | 13 (62) |
| Female | 23 (47) | 15 (54) | 8 (38) | |
| Histology | Embryonal | 29 (59) | 20 (71) | 9 (43) |
| Alveolar | 20 (41) | 8 (29) | 12 (57) | |
| Alveolar Fusion Status | Positive | 10 | 5 | 5 |
| Negative | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Not performed | 5 | 0 | 5 | |
| Primary site | ||||
| Favorable site | Orbits | 2 (4) | 2 (7) | 0 (0) |
| Genito-urinary | 21 (42) | 10 (36) | 11 (52) | |
| Head and Neck | 3 (6) | 2 (7) | 1 (5) | |
| Unfavorable site | Bladder-prostate | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (9) |
| Limbs | 7 (14) | 6 (21) | 1 (5) | |
| Parameningeal | 10 (20) | 5 (18) | 5 (24) | |
| Others | 4 (8) | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | |
| NA | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1(5) | |
| Tumor Stage | T1 | 16 (33) | 15 (54) | 1 (5) |
| T2 | 32 (65) | 13 (46) | 19 (90) | |
| NA | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| Lymph node involvement | N0 | 34 (69) | 23 (82) | 11 (52) |
| N1 | 14 (28) | 5 (18) | 9 (43) | |
| NA | 1(2) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| Presence of metastasis | M0 | 36 (73) | 23 (82) | 13 (62) |
| M1 | 12 (25) | 5 (18) | 7 (33) | |
| NA | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| IRS | 1 | 9 (18) | 5 (18) | 4 (19) |
| 2 | 4 (8) | 1 (4) | 3 (14) | |
| 3 | 23 (47) | 17 (60) | 6 (29) | |
| 4 | 12 (25) | 5 (18) | 7 (33) | |
| NA | 1 (2) | 0 (0) | 1 (5) | |
| Overall Survival | 1°CR | 25 (51) | 16 (57) | 9 (43) |
| 2° CR | 2 (4) | 2 (7) | 0 (0) | |
| DOD | 19 (39) | 9 (32) | 10 (47) | |
| Dead of other causes | 1 (2) | 1 (4) | 0 (0) | |
| NA | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (9) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gasparini, P.; Fortunato, O.; De Cecco, L.; Casanova, M.; Iannó, M.F.; Carenzo, A.; Centonze, G.; Milione, M.; Collini, P.; Boeri, M.; et al. Age-Related Alterations in Immune Contexture Are Associated with Aggressiveness in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091380
Gasparini P, Fortunato O, De Cecco L, Casanova M, Iannó MF, Carenzo A, Centonze G, Milione M, Collini P, Boeri M, et al. Age-Related Alterations in Immune Contexture Are Associated with Aggressiveness in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers. 2019; 11(9):1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091380
Chicago/Turabian StyleGasparini, Patrizia, Orazio Fortunato, Loris De Cecco, Michela Casanova, Maria Federica Iannó, Andrea Carenzo, Giovanni Centonze, Massimo Milione, Paola Collini, Mattia Boeri, and et al. 2019. "Age-Related Alterations in Immune Contexture Are Associated with Aggressiveness in Rhabdomyosarcoma" Cancers 11, no. 9: 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091380
APA StyleGasparini, P., Fortunato, O., De Cecco, L., Casanova, M., Iannó, M. F., Carenzo, A., Centonze, G., Milione, M., Collini, P., Boeri, M., Dugo, M., Gargiuli, C., Mensah, M., Segale, M., Bergamaschi, L., Chiaravalli, S., Sensi, M. L., Massimino, M., Sozzi, G., & Ferrari, A. (2019). Age-Related Alterations in Immune Contexture Are Associated with Aggressiveness in Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancers, 11(9), 1380. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11091380








