Prognostic Value of the Pace of Tumor Progression as Assessed by Serial 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan and Liquid Biopsy in Refractory Colorectal Cancer: The CORIOLAN Trial
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
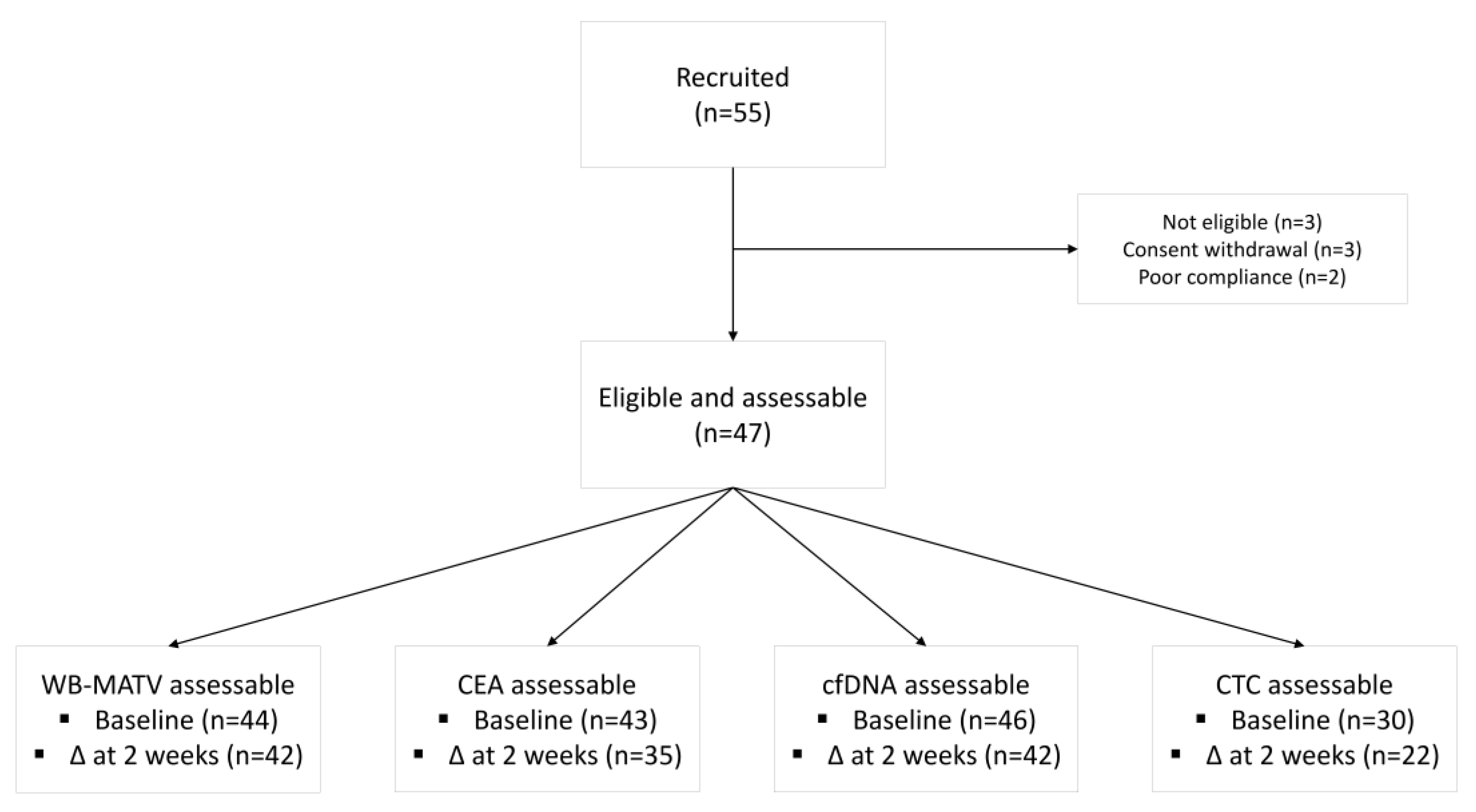
2.1. Study Design and Patient Population
2.2. Study Procedures
2.3. Metabolic Imaging-Based Assessments
2.4. Circulating Free DNA (cfDNA)
2.5. Circulating Tumor Cell (CTC) count
2.6. Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA)
2.7. Study Objectives
2.8. Statistical Considerations
2.9. Approvals and Consent
3. Results
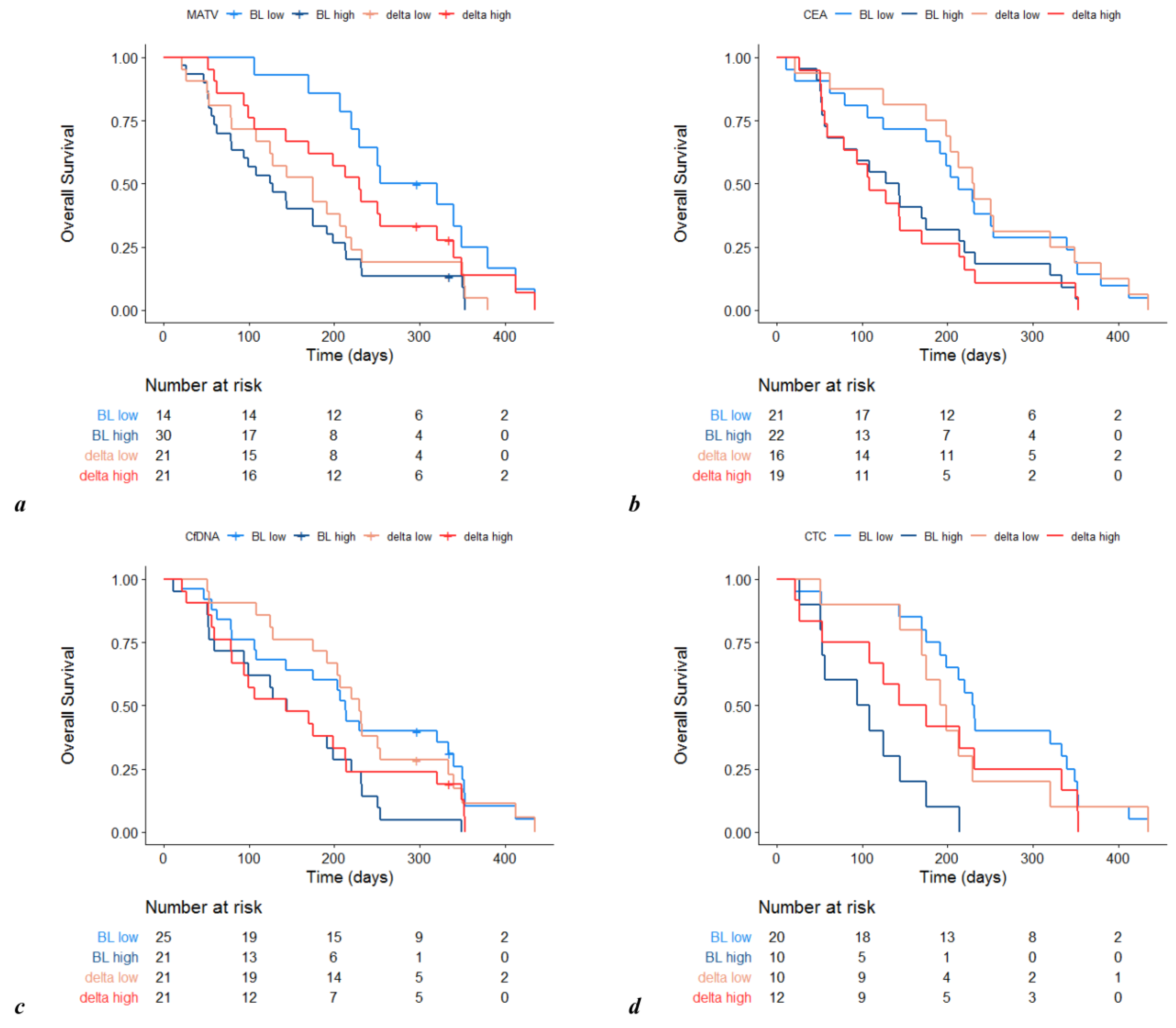
3.1. Prognostic Value of Metabolic Imaging Parameters
3.2. Other Prognostic Factors at Baseline
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cremolini, C.; Loupakis, F.; Antoniotti, C.; Lupi, C.; Sensi, E.; Lonardi, S.; Mezi, S.; Tomasello, G.; Ronzoni, M.; Zaniboni, A.; et al. FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab as first-line treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: Updated overall survival and molecular subgroup analyses of the open-label, phase 3 TRIBE study. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venook, A.P.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Lenz, H.J.; Innocenti, F.; Fruth, B.; Meyerhardt, J.A.; Schrag, D.; Greene, C.; O’Neil, B.H.; Atkins, J.N.; et al. Effect of First-Line Chemotherapy Combined with Cetuximab or Bevacizumab on Overall Survival in Patients with KRAS Wild-Type Advanced or Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 317, 2392–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grothey, A.; Sargent, D.; Goldberg, R.M.; Schmoll, H.-J. Survival of Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer Improves with the Availability of Fluorouracil-Leucovorin, Irinotecan, and Oxaliplatin in the Course of Treatment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2004, 22, 1209–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, D.A.; Ahmad, B.B.; Chen, Q.; Ayer, T.; Howard, D.H.; Lipscomb, J.; El-Rayes, B.F.; Flowers, C.R. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Regorafenib for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 3727–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, S.K.; Hay, J.W.; Barzi, A. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Regorafenib and TAS-102 in Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in the United States. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, e751–e761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grothey, A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Sobrero, A.; Siena, S.; Falcone, A.; Ychou, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bouché, O.; Mineur, L.; Barone, C.; et al. Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2013, 381, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qin, S.; Xu, R.; Yau, T.C.-C.; Ma, B.B.Y.; Pan, H.; Xu, J.; Bai, Y.; Chi, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. Regorafenib plus best supportive care versus placebo plus best supportive care in Asian patients with previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer (CONCUR): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Miceli, R.; Rimassa, L.; Lonardi, S.; Aprile, G.; Mennitto, A.; Marmorino, F.; Bozzarelli, S.; Antonuzzo, L.; Tamburini, E.; et al. Estimating 12-week death probability in patients with refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: The Colon Life nomogram. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM procedure guidelines for tumour imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woff, E.; Hendlisz, A.; Ameye, L.; García, C.; Kamoun, T.; Guiot, T.; Paesmans, M.; Flamen, P. Validation of Metabolically Active Tumor Volume and Total Lesion Glycolysis as 18F-FDG PET/CT–Derived Prognostic Biomarkers in Chemorefractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 60, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Woff, E.; Kehagias, P.; Vandeputte, C.; Ameye, L.; Guiot, T.; Paesmans, M.; Hendlisz, A.; Flamen, P. Combining 18F-FDG PET/CT–Based Metabolically Active Tumor Volume and Circulating Cell-Free DNA Significantly Improves Outcome Prediction in Chemorefractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Relationship of Circulating Tumor Cells to Tumor Response, Progression-Free Survival, and Overall Survival in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3213–3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendlisz, A.; Golfinopoulos, V.; Garcia, C.; Covas, A.; Emonts, P.; Ameye, L.; Paesmans, M.; Deleporte, A.; Machiels, G.; Toussaint, E.; et al. Serial FDG–PET/CT for early outcome prediction in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer undergoing chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1687–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köhne, C.-H.; Cunningham, D.; Di Costanzo, F.; Glimelius, B.; Blijham, G.; Aranda, E.; Scheithauer, W.; Rougier, P.; Palmer, M.; Wils, J.; et al. Clinical determinants of survival in patients with 5-fluorouracil-based treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: Results of a multivariate analysis of 3825 patients. Ann. Oncol. 2002, 13, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renfro, L.A.; Goldberg, R.M.; Grothey, A.; Sobrero, A.; Adams, R.; Seymour, M.T.; Heinemann, V.; Schmoll, H.-J.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Hurwitz, H.; et al. Clinical Calculator for Early Mortality in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: An Analysis of Patients from 28 Clinical Trials in the Aide et Recherche en Cancérologie Digestive Database. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1929–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamfjord, J.; Guren, T.K.; Dajani, O.; Johansen, J.; Glimelius, B.; Sorbye, H.; Pfeiffer, P.; Lingjærde, O.; Tveit, K.; Kure, E.; et al. Total circulating cell-free DNA as a prognostic biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer before first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mayer, R.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Falcone, A.; Yoshino, T.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Mizunuma, N.; Yamazaki, K.; Shimada, Y.; Tabernero, J.; Komatsu, Y.; et al. Randomized Trial of TAS-102 for Refractory Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
| Variable | N | % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years)(median/range) | 65 | 38–82 | |
| Sex | Male | 25 | 53 |
| Female | 22 | 47 | |
| ECOG PS | 0 | 17 | 36 |
| 1 | 30 | 64 | |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | ≤25 | 22 | 47 |
| >25 | 25 | 53 | |
| Tumor sidedness | Right | 10 | 21 |
| Left | 33 | 70 | |
| Unknown | 4 | 9 | |
| RAS status | Wild type | 22 | 47 |
| Mutant | 25 | 53 | |
| Number prior systemic therapies (median/range) | 5 | 2–8 | |
| Number of metastatic sites | ≤2 | 20 | 43 |
| >2 | 27 | 57 | |
| Peritoneal metastases | Absent | 33 | 70 |
| Present | 14 | 30 | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | <11 | 16 | 34 |
| ≥11 | 31 | 66 | |
| NL ratio | <5 | 28 | 60 |
| ≥5 | 18 | 38 | |
| Unknown | 1 | 2 | |
| ALP (IU/L) | <300 | 34 | 73 |
| ≥300 | 10 | 21 | |
| Unknown | 3 | 6 | |
| Colon Life score (%) (median/range) | 30% | 10–94 | |
| WB-MATV (cm3) | <100 | 14 | 30 |
| ≥100 | 30 | 64 | |
| Unknown | 3 | 6 | |
| cfDNA (ng/mL) | <50 | 25 | 53 |
| ≥50 | 21 | 45 | |
| Unknown | 1 | 2 | |
| CTC count (/mL) | <3 | 20 | 53 |
| ≥3 | 10 | 45 | |
| Unknown | 17 | 2 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Camera, S.; Akin Telli, T.; Woff, E.; Vandeputte, C.; Kehagias, P.; Guiot, T.; Critchi, G.; Wissam, Y.; Bregni, G.; Trevisi, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of the Pace of Tumor Progression as Assessed by Serial 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan and Liquid Biopsy in Refractory Colorectal Cancer: The CORIOLAN Trial. Cancers 2020, 12, 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102752
Camera S, Akin Telli T, Woff E, Vandeputte C, Kehagias P, Guiot T, Critchi G, Wissam Y, Bregni G, Trevisi E, et al. Prognostic Value of the Pace of Tumor Progression as Assessed by Serial 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan and Liquid Biopsy in Refractory Colorectal Cancer: The CORIOLAN Trial. Cancers. 2020; 12(10):2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102752
Chicago/Turabian StyleCamera, Silvia, Tugba Akin Telli, Erwin Woff, Caroline Vandeputte, Pashalina Kehagias, Thomas Guiot, Gabriela Critchi, Yacine Wissam, Giacomo Bregni, Elena Trevisi, and et al. 2020. "Prognostic Value of the Pace of Tumor Progression as Assessed by Serial 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan and Liquid Biopsy in Refractory Colorectal Cancer: The CORIOLAN Trial" Cancers 12, no. 10: 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102752
APA StyleCamera, S., Akin Telli, T., Woff, E., Vandeputte, C., Kehagias, P., Guiot, T., Critchi, G., Wissam, Y., Bregni, G., Trevisi, E., Pretta, A., Senti, C., Leduc, S., Gkolfakis, P., Hoerner, F., Rothé, F., Sclafani, F., Flamen, P., Deleporte, A., & Hendlisz, A. (2020). Prognostic Value of the Pace of Tumor Progression as Assessed by Serial 18F-FDG PET/CT Scan and Liquid Biopsy in Refractory Colorectal Cancer: The CORIOLAN Trial. Cancers, 12(10), 2752. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102752





