Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
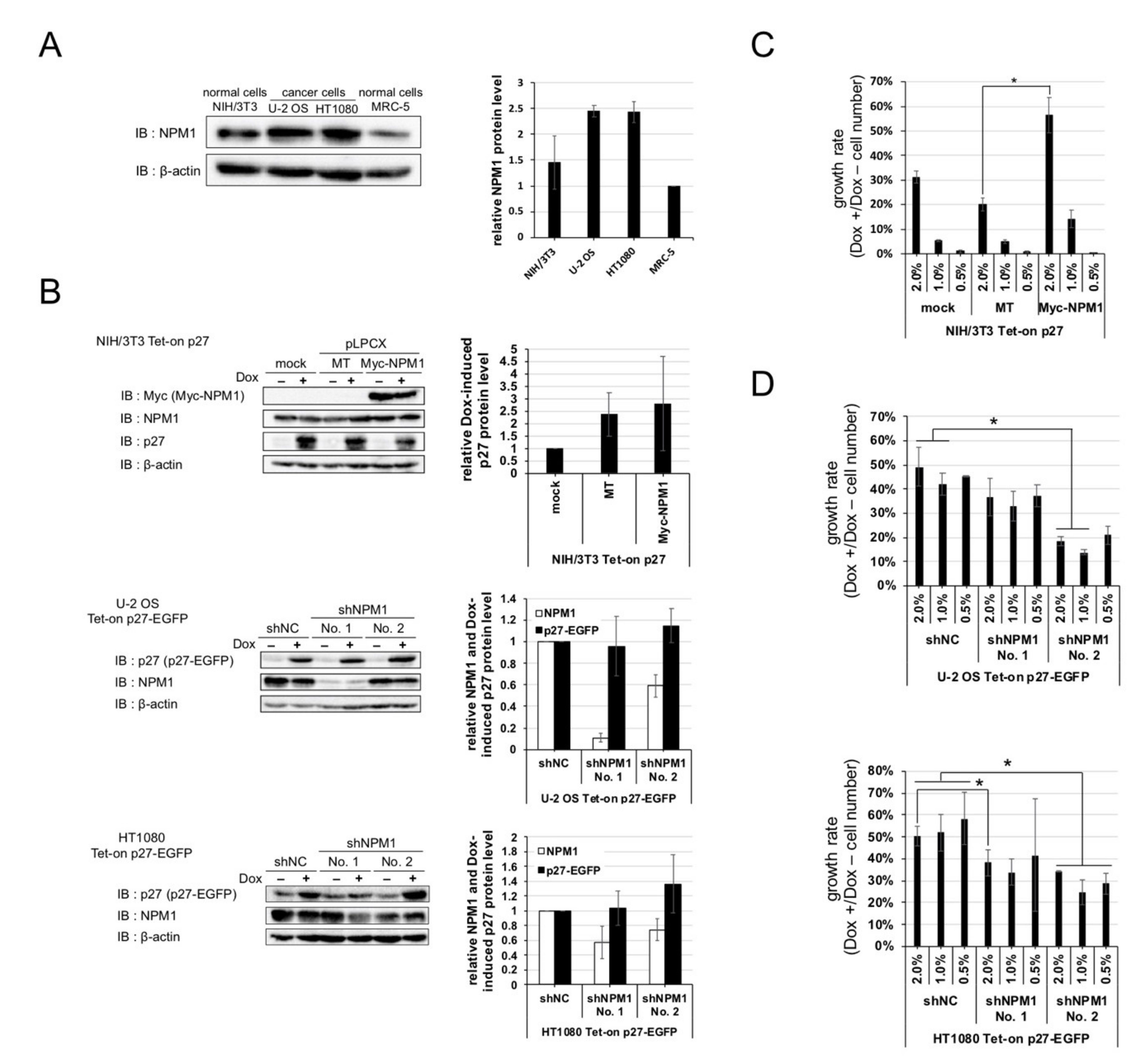
2.1. Overexpression of p27 in Cancer and Normal Cells
2.2. Screening for Qualitative Functional Suppressor(s) of p27
2.3. Nucleophosmin Isoform 1 (NPM1) Interacts with p27
2.4. Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27 Function In Vitro
2.5. NPM1 Suppresses p27 Function in Xenografted Tumors in Mouse
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture
4.2. Plasmids
4.3. Transfection and Flow Cytometry
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Establishment of Cell Lines Carrying Dox-Inducible p27 Constructs
4.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.7. Preparation of Cell Extracts and Immunoprecipitation
4.8. Proteomic Screening for p27-Interacting Factors
4.9. Yeast Two-Hybrid Assay
4.10. RNA Interference
4.11. Mouse Xenograft Model
4.12. Immunofluorescence of Tumors
4.13. Quantification and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartek, J.; Lukas, J. DNA damage checkpoints: From initiation to recovery or adaptation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polyak, K.; Lee, M.H.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Koff, A.; Roberts, J.M.; Tempst, P.; Massagué, J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell 1994, 78, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Patten, A.K.; Massagué, J.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal structure of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor bound to the cyclin A-Cdk2 complex. Nature 1996, 382, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagui, T.K.; Cui, D.; Roy, S.; Mohapatra, S.; Shor, A.C.; Ma, L.; Pledger, W.J. Inhibition of p27Kip1 gene transcription by mitogens. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrano, A.C.; Eytan, E.; Hershko, A.; Pagano, M. SKP2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK inhibitor p27. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, M.; Yoshimoto, T.; Crook, M.F.; Nallamshetty, S.; True, A.; Nabel, G.J.; Nabel, E.G. A growth factor-dependent nuclear kinase phosphorylates p27(Kip1) and regulates cell cycle progression. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3390–3401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, M.H.; Mavila, N.; Wang, W.H.; Alvarez, S.V.; Hall, M.C.; Andrisani, O.M. Time-dependent activation of Phox2a by the cyclic AMP pathway modulates onset and duration of p27Kip1 transcription. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 4878–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trabosh, V.A.; Divito, K.A.; D Aguda, B.; Simbulan-Rosenthal, C.M.; Rosenthal, D.S. Sequestration of E12/E47 and suppression of p27KIP1 play a role in Id2-induced proliferation and tumorigenesis. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1252–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hengst, L.; Reed, S.I. Translational control of p27Kip1 accumulation during the cell cycle. Science 1996, 271, 1861–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, S.S. The function of p27 KIP1 during tumor development. Exp. Mol. Med. 2009, 41, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polyak, K.; Kato, J.Y.; Solomon, M.J.; Sherr, C.J.; Massague, J.; Roberts, J.M.; Koff, A. p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loda, M.; Cukor, B.; Tam, S.W.; Lavin, P.; Fiorentino, M.; Draetta, G.F.; Jessup, J.M.; Pagano, M. Increased proteasome-dependent degradation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in aggressive colorectal carcinomas. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, P.L.; Malone, K.E.; Heagerty, P.J.; Alexander, G.M.; Gatti, L.A.; Firpo, E.J.; Daling, J.R.; Roberts, J.M. Expression of cell-cycle regulators p27Kip1 and cyclin E, alone and in combination, correlate with survival in young breast cancer patients. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasui, W.; Kudo, Y.; Semba, S.; Yokozaki, H.; Tahara, E. Reduced expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1 is associated with advanced stage and invasiveness of gastric carcinomas. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1997, 88, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatabe, Y.; Masuda, A.; Koshikawa, T.; Nakamura, S.; Kuroishi, T.; Osada, H.; Takahashi, T.; Mitsudomi, T. p27KIP1 in human lung cancers: differential changes in small cell and non-small cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 1042–1047. [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama, K.; Ishida, N.; Shirane, M.; Inomata, A.; Inoue, T.; Shishido, N.; Horii, I.; Loh, D.Y. Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell 1996, 85, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fero, M.L.; Rivkin, M.; Tasch, M.; Porter, P.; Carow, C.E.; Firpo, E.; Polyak, K.; Tsai, L.H.; Broudy, V.; Perlmutter, R.M.; et al. A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell 1996, 85, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kiyokawa, H.; Kineman, R.D.; Manova-Todorova, K.O.; Soares, V.C.; Hoffman, E.S.; Ono, M.; Khanam, D.; Hayday, A.C.; Frohman, L.A.; Koff, A. Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1). Cell 1996, 85, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fero, M.L.; Randel, E.; Gurley, K.E.; Roberts, J.M.; Kemp, C.J. The murine gene p27Kip1 is haplo-insufficient for tumour suppression. Nature 1998, 396, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guan, X. A crosstalk imbalance between p27(Kip1) and its interacting molecules enhances breast carcinogenesis. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Ji, F.; Deng, Y.; Tang, C.; Yang, S.; Xi, Q.; Liu, R.; Di, W. Knockdown of CRM1 inhibits the nuclear export of p27(Kip1) phosphorylated at serine 10 and plays a role in the pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvetkov, L.M.; Yeh, K.H.; Lee, S.J.; Sun, H.; Zhang, H. p27(Kip1) ubiquitination and degradation is regulated by the SCF(Skp2) complex through phosphorylated Thr187 in p27. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 661–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujita, N.; Sato, S.; Katayama, K.; Tsuruo, T. Akt-dependent phosphorylation of p27Kip1 promotes binding to 14-3-3 and cytoplasmic localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 28706–28713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masciullo, V.; Sgambato, A.; Pacilio, C.; Pucci, B.; Ferrandina, G.; Palazzo, J.; Carbone, A.; Cittadini, A.; Mancuso, S.; Scambia, G.; et al. Frequent loss of expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 3790–3794. [Google Scholar]
- Box, J.K.; Paquet, N.; Adams, M.N.; Boucher, D.; Bolderson, E.; O’Byrne, K.J.; Richard, D.J. Nucleophosmin: from structure and function to disease development. BMC Mol. Biol. 2016, 17, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Maggi, L.B.; Brady, S.N.; Apicelli, A.J.; Dai, M.S.; Lu, H.; Weber, J.D. Nucleophosmin is essential for ribosomal protein L5 nuclear export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 3798–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Savkur, R.S.; Olson, M.O. Preferential cleavage in pre-ribosomal RNA byprotein B23 endoribonuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 4508–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Budhu, A.; Forgues, M.; Wang, X.W. Temporal and spatial control of nucleophosmin by the Ran-Crm1 complex in centrosome duplication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 7, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, F.X.; Shao, H.Y.; Chen, X.C.; Tan, S.; Zhang, H.J.; Miao, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.-C.; Zhang, L. Knockdown of NPM1 by RNA interference inhibits cells proliferation and induces apoptosis in leukemic cell line. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 8, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korgaonkar, C.; Hagen, J.; Tompkins, V.; Frazier, A.A.; Allamargot, C.; Quelle, F.W.; Quelle, D.E. Nucleophosmin (B23) targets ARF to nucleoli and inhibits its function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Falini, B.; Nicoletti, I.; Martelli, M.F.; Mecucci, C. Acute myeloid leukemia carrying cytoplasmic/mutated nucleophosmin (NPMc+ AML): biologic and clinical features. Blood 2007, 109, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, S.W.; Kirstein, M.N.; Valentine, M.B.; Dittmer, K.G.; Shapiro, D.N.; Saltman, D.L.; Look, A.T. Fusion of a kinase gene, ALK, to a nucleolar protein gene, NPM, in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Science 1994, 263, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahana, K.; Bhat, K.P.; Jin, A.; Itahana, Y.; Hawke, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Zhang, Y. Tumor suppressor ARF degrades B23, a nucleolar protein involved in ribosome biogenesis and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Fry, E.A. Aberrant expression of p14. Tumor Microenviron. 2018, 1, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.L.; Weintraub, H. Expression of achaete-scute homolog 3 in Xenopus embryos converts ectodermal cells to a neural fate. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1434–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoshimura, M.; Asai, K.; Sadaie, Y.; Yoshikawa, H. Interaction of Bacillus subtilis extracytoplasmic function (ECF) sigma factors with the N-terminal regions of their potential anti-sigma factors. Microbiology 2004, 150, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clurman, B.E.; Sheaff, R.J.; Thress, K.; Groudine, M.; Roberts, J.M. Turnover of cyclin E by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is regulated by cdk2 binding and cyclin phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1996, 10, 1979–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chibazakura, T.; McGrew, S.G.; Cooper, J.A.; Yoshikawa, H.; Roberts, J.M. Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase activity during mitotic exit and maintenance of genome stability by p21, p27, and p107. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4465–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chibazakura, T.; Kamachi, K.; Ohara, M.; Tane, S.; Yoshikawa, H.; Roberts, J.M. Cyclin A promotes S-phase entry via interaction with the replication licensing factor Mcm7. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- James, P.; Halladay, J.; Craig, E.A. Genomic libraries and a host strain designed for highly efficient two-hybrid selection in yeast. Genetics 1996, 144, 1425–1436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Shi, M.; Chen, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Shen, B.; Deng, X.; Xie, J.; Zhan, X.; Peng, C. NPM1 activates metabolic changes by inhibiting FBP1 while promoting the tumorigenicity of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21443–21451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kometani, T.; Arai, T.; Chibazakura, T. Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells. Cancers 2020, 12, 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102886
Kometani T, Arai T, Chibazakura T. Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells. Cancers. 2020; 12(10):2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102886
Chicago/Turabian StyleKometani, Tatsuya, Takuya Arai, and Taku Chibazakura. 2020. "Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells" Cancers 12, no. 10: 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102886
APA StyleKometani, T., Arai, T., & Chibazakura, T. (2020). Increased Expression of NPM1 Suppresses p27Kip1 Function in Cancer Cells. Cancers, 12(10), 2886. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12102886




