Liver-Targeting Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Potently Suppress Hepatocellular Tumor Growth as Standalone Agents
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
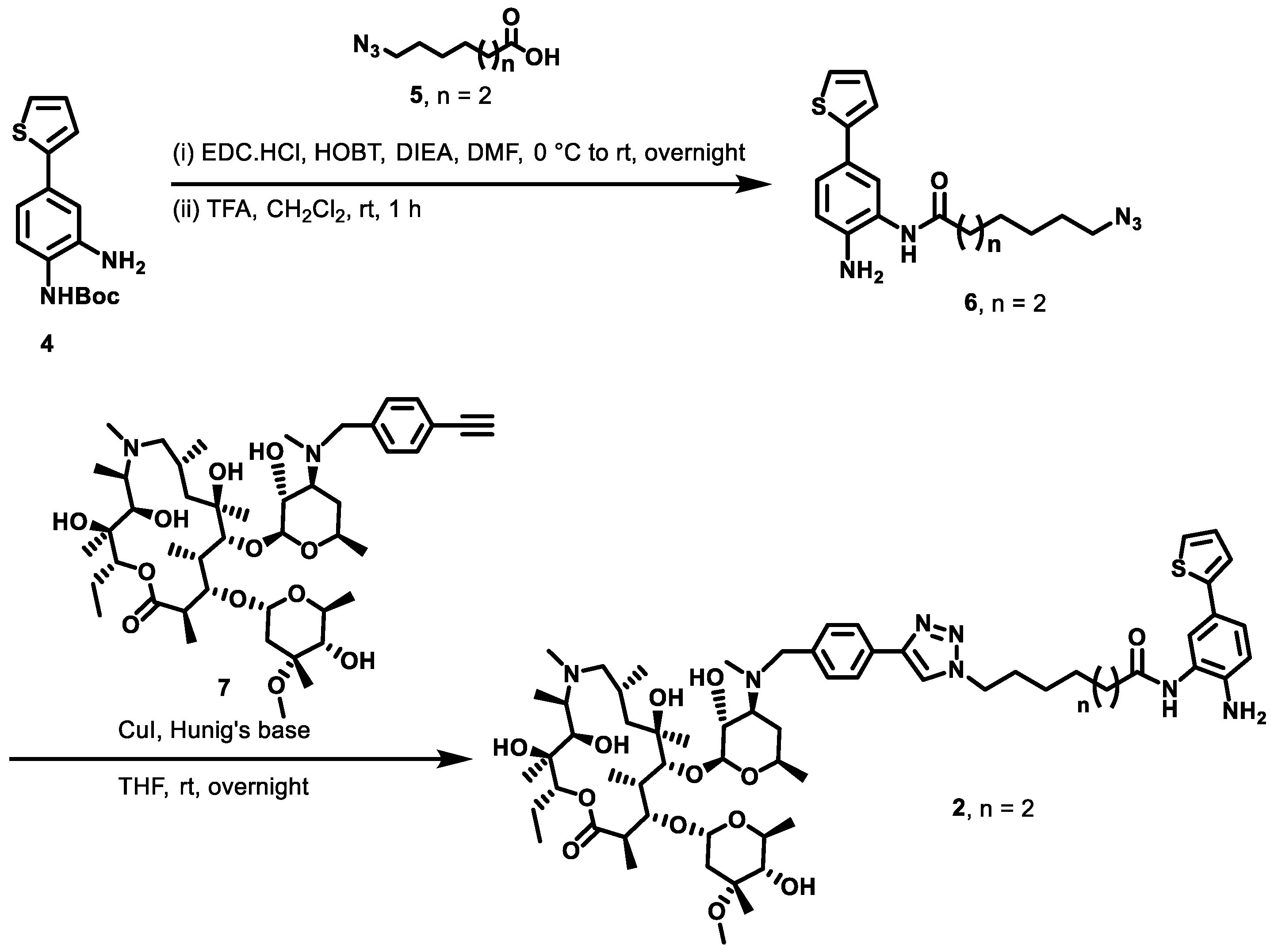
2.1. Macrolide-Based Class I HDACi: Design Rationale and Synthesis
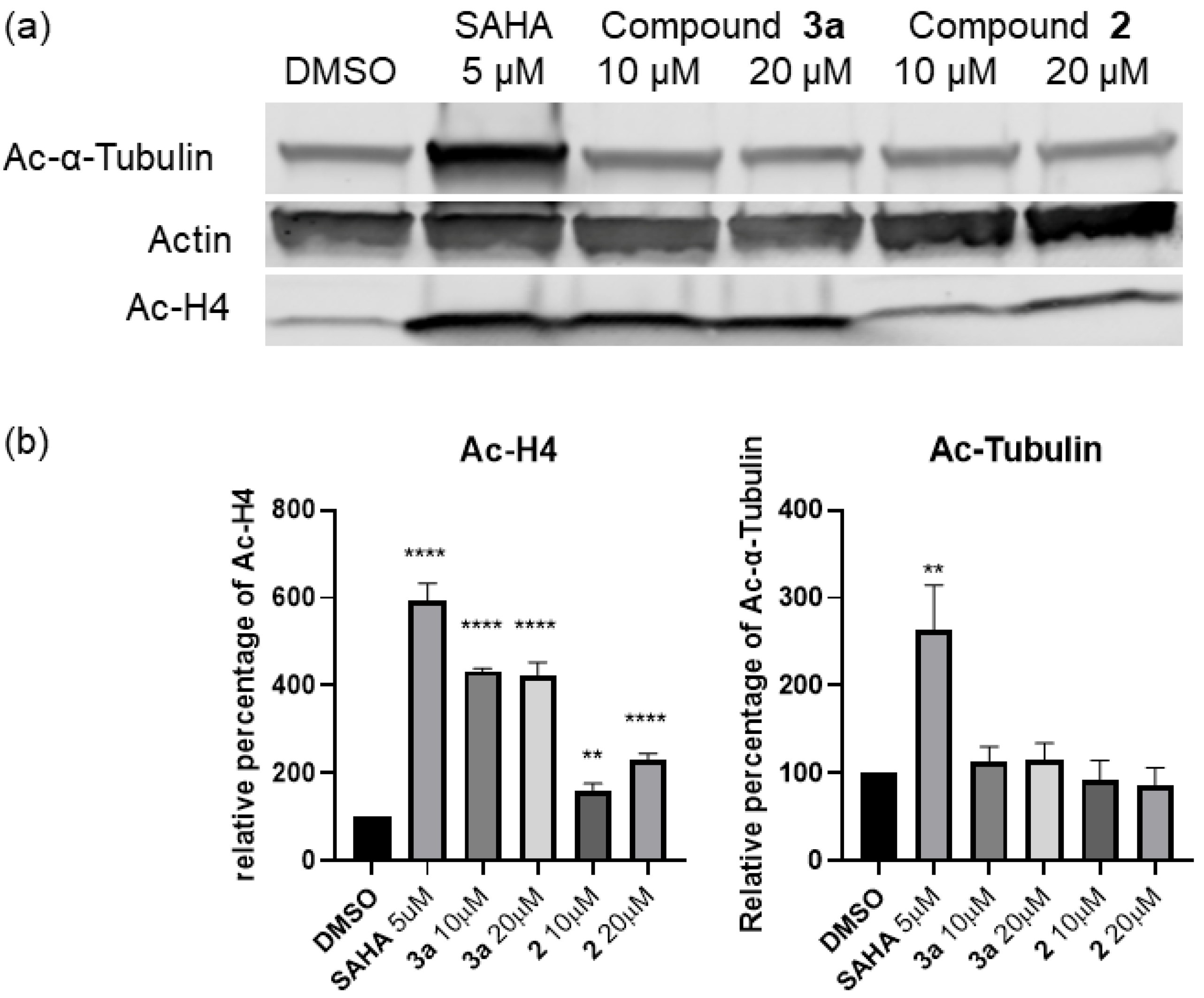
2.2. In Vitro Profiling, Whole Cell Activity, and Intracellular Target Validation
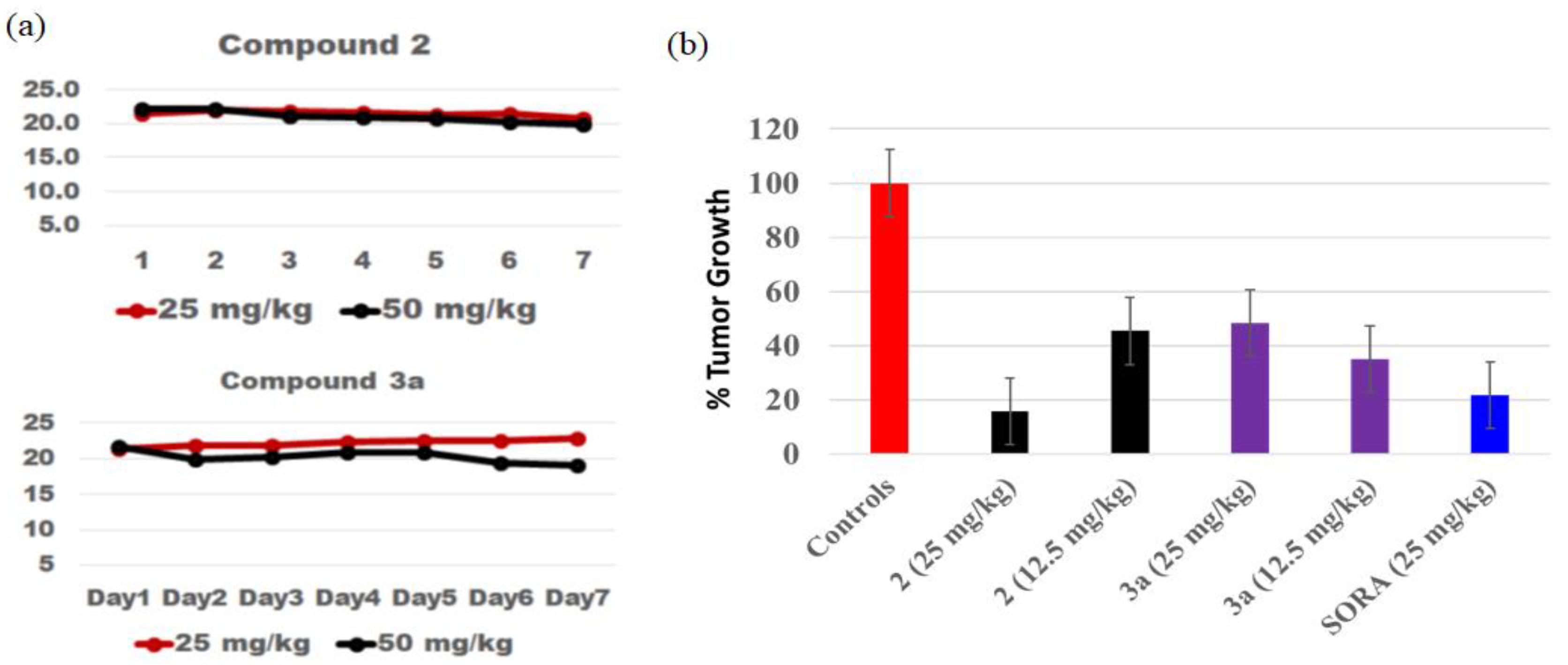
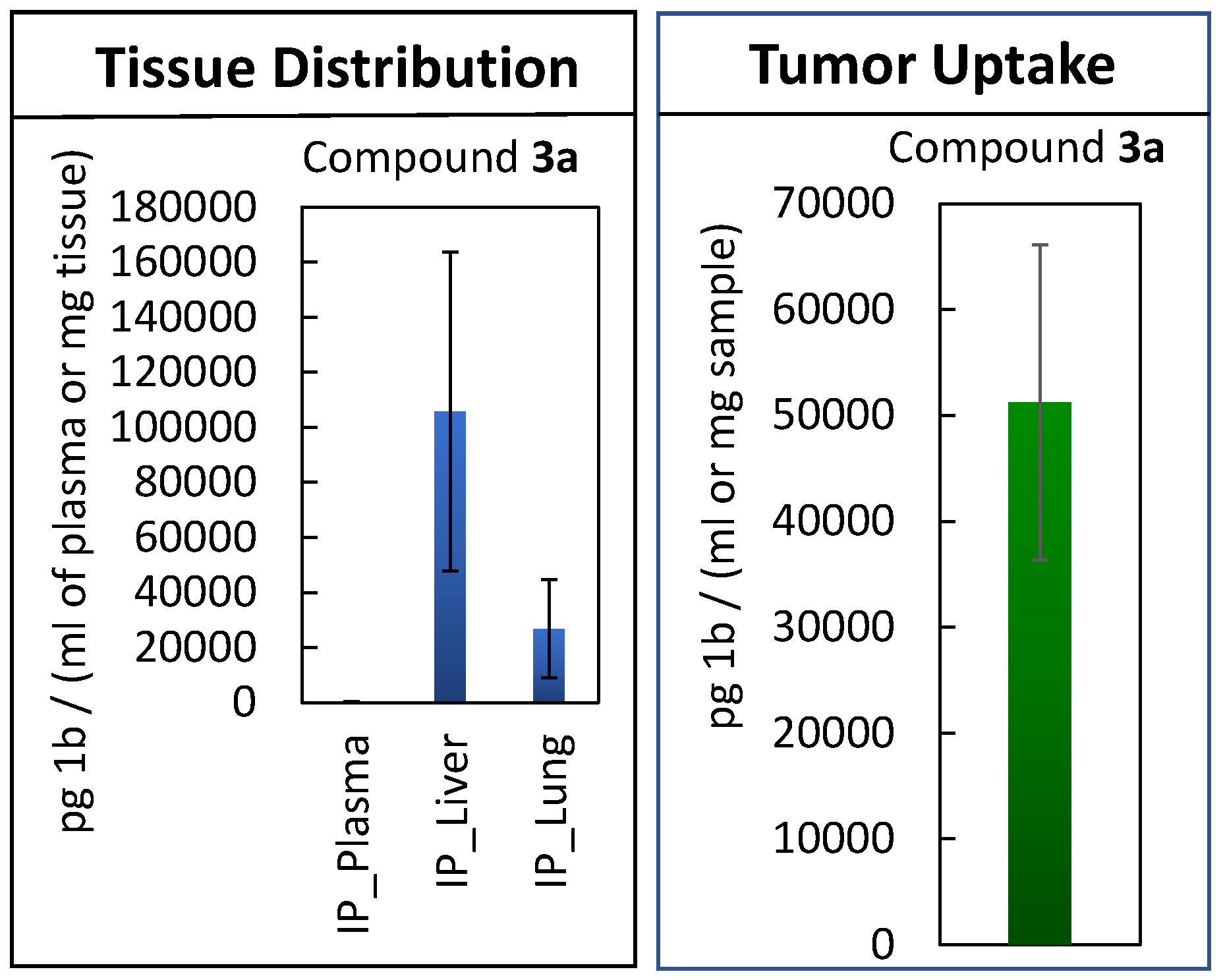
2.3. Maximum Tolerated Dose Determination, In Vivo Efficacy Study, and Tissue Distribution
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemical and Reagents
4.2. Molecular Docking and Compound Synthesis
4.3. HDAC Assay
4.4. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.5. Cell Colony Formation and Hep3B Cell Viability Assay
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Flow Cytometry
4.8. Maximum Tolerated Dose Determination
4.9. Tissue Distribution Studies
4.10. Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry
4.11. In Vivo Efficacy Studies
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Cancer Society. Global Cancer Facts & Figures, 4th ed.; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, B.D.; Goncalves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Obesity and Cancer Mechanisms: Cancer Metabolism. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 4277–4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts & Figures 2020; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Fuster, J.; Bruix, J. Intention-to-treat analysis of surgical treatment for early hepatocellular carcinoma: Resection versus transplantation. Hepatology 1999, 30, 1434–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferro, V.; Regalia, E.; Doci, R.; Andreola, S.; Pulvirenti, A.; Bozzetti, F.; Montalto, F.; Ammatuna, M.; Morabito, A.; Gennari, L. Liver Transplantation for the Treatment of Small Hepatocellular Carcinomas in Patients with Cirrhosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viveiros, P.; Riaz, A.; Lewandowski, R.J.; Mahalingam, D. Current State of Liver-Directed Therapies and Combinatory Approaches with Systemic Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC). Cancers 2019, 11, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.-F.; Oliveira, A.C.d.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilmi, M.; Neuzillet, C.; Calderaro, J.; Lafdil, F.; Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Rousseau, B. Angiogenesis and immune checkpoint inhibitors as therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: Current knowledge and future research directions. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montella, L.; Addeo, R. Targeted Therapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma—Overview of HCC Pathophysiology and Drug Targets; Future Medicine Ltd.: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, W.; Chung, H.C.; Chan, S.L.; Wang, L.Z.; Lim, R.; Picus, J.; Boyer, M.; Mo, F.K.F.; Koh, J.; Rha, S.Y.; et al. Epigenetic Therapy Using Belinostat for Patients With Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Phase I/II Study With Biomarker and Pharmacokinetic Analysis of Tumors From Patients in the Mayo Phase II Consortium and the Cancer Therapeutics Research Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.B.; Sung, F.; Tao, Q.; Poon, F.F.; Lui, V.W.; Yeo, W.; Chan, S.L.; Chan, A.T. The preclinical activity of the histone deacetylase inhibitor PXD101 (belinostat) in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Investig. New Drugs 2010, 28, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikimaru, T.; Taketomi, A.; Yamashita, Y.; Shirabe, K.; Hamatsu, T.; Shimada, M.; Maehara, Y. Clinical significance of histone deacetylase 1 expression in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncology 2007, 72, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freese, K.; Seitz, T.; Dietrich, P.; Lee, S.M.L.; Thasler, W.E.; Bosserhoff, A.; Hellerbrand, C. Histone deacetylase expressions in hepatocellular carcinoma and functional effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors on liver cancer cells in vitro. Cancers 2019, 11, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.-Y.; Xie, H.-J.; Li, Z.; Kong, L.-F.; Ding, Y.-Z. Analysis of miRNAs related to abnormal HDAC1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2016, 9, 21482–21489. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, J.K.; Jung, K.H.; Eun, J.W.; Bae, H.J.; Kim, M.G.; Chang, Y.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, H.; et al. HDAC1 Inactivation Induces Mitotic Defect and Caspase-Independent Autophagic Cell Death in Liver Cancer. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Bao, J.; Ye, F.; Shi, Y.; Bu, H. Loss of histone deacetylases 1 and 2 in hepatocytes impairs murine liver regeneration through Ki67 depletion. Hepatology 2013, 58, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryder, B.E.; Sodji, Q.H.; Oyelere, A.K. Targeted cancer therapy: Giving histone deacetylase inhibitors all they need to succeed. Future Med. Chem. 2012, 4, 505–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toh, T.B.; Lim, J.J.; Chow, E.K.-H. Epigenetics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Trans. Med. 2019, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panobinostat and Sorafenib in Treating Patients with Liver Cancer That is Metastatic and/or Cannot Be Removed by Surgery. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00873002 (accessed on 20 March 2020).
- Sorafenib and Vorinostat in Treating Patients with Advanced Liver Cancer. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01075113 (accessed on 20 August 2019).
- Tsilimigras, D.I.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Moris, D.; Spartalis, E.; Pawlik, T.M. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic perspective. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 27, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwakwari, S.C.; Patil, V.; Guerrant, W.; Oyelere, A.K. Macrocyclic Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 1423–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardi, P.M.; Cole, K.E.; Dowling, D.P.; Christianson, D.W. Structure, mechanism, and inhibition of histone deacetylases and related metalloenzymes. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Porter, N.J.; Mahendran, A.; Breslow, R.; Christianson, D.W. Unusual zinc-binding mode of HDAC6-selective hydroxamate inhibitors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13459–13464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morphy, R.; Rankovic, Z. Designed Multiple Ligands. An Emerging Drug Discovery Paradigm. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 6523–6543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrant, W.; Patil, V.; Canzoneri, J.C.; Oyelere, A.K. Dual Targeting of Histone Deacetylase and Topoisomerase II with Novel Bifunctional Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 1465–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrant, W.; Patil, V.; Canzoneri, J.; Yao, L.P.; Hood, R.; Oyelere, A.K. Dual-acting histone deacetylase-topoisomerase I inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 3283–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gryder, B.E.; Rood, M.K.; Johnson, K.A.; Patil, V.; Raftery, E.D.; Yao, L.-P.D.; Rice, M.; Azizi, B.; Doyle, D.; Oyelere, A.K. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Equipped with Estrogen Receptor Modulation Activity. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 5782–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gryder, B.E.; Akbashev, M.J.; Rood, M.K.; Raftery, E.D.; Meyers, W.M.; Dillard, P.; Khan, S.; Oyelere, A.K. Selectively Targeting Prostate Cancer with Antiandrogen Equipped Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 2550–2560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, L.; Mustafa, N.; Tan, E.C.; Poulsen, A.; Singh, P.; Duong-Thi, M.-D.; Lee, J.X.T.; Ramanujulu, P.M.; Chng, W.J.; Yen, J.J.Y.; et al. Design and Synthesis of Ligand Efficient Dual Inhibitors of Janus Kinase (JAK) and Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Based on Ruxolitinib and Vorinostat. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 8336–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Fathi, S.; Mortley, S.; Mohiuddin, M.; Jang, Y.C.; Oyelere, A.K. Pyrimethamine conjugated histone deacetylase inhibitors: Design, synthesis and evidence for triple negative breast cancer selective cytotoxicity. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyelere, A.K.; Chen, P.C.; Guerrant, W.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Hood, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Y. Nonpeptide Macrocyclic Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mwakwari, S.C.; Guerrant, W.; Patil, V.; Khan, S.I.; Tekwani, B.L.; Gurard-Levin, Z.A.; Mrksich, M.; Oyelere, A.K. Nonpeptide Macrocyclic Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitors Derived from Tricyclic Ketolide. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 6100–6111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tapadar, S.; Fathi, S.; Raji, I.; Omesiete, W.; Kornacki, J.R.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Miyata, M.; Mitsutake, K.; Li, J.-D.; Mrksich, M.; et al. A structure–activity relationship of non-peptide macrocyclic histone deacetylase inhibitors and their anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 7543–7564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoepelman, I.M.; Schneider, M.M.E. Azithromycin: The first of the tissue-selective azalides. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 1995, 5, 145–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carceles, C.M.; Fernandez-Varon, E.; Marin, P.; Escudero, E. Tissue disposition of azithromycin after intravenous and intramuscular administration to rabbits. Vet. J. 2007, 174, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, A.; Conejo, M.C.; García, I.; Perea, E.J. Factors affecting the intracellular accumulation and activity of azithromycin. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1995, 35, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandizzi, C.; Malizia, T.; Batoni, G.; Ghelardi, E.; Baschiera, F.; Bruschini, P.; Senesi, S.; Campa, M.; Tacca, M.D. Distribution of azithromycin in plasma and tonsil tissue after repeated oral administration of 10 or 20 milligrams per kilogram in pediatric patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1594–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danesi, R.; Lupetti, A.; Barbara, C.; Ghelardi, E.; Chella, A.; Malizia, T.; Senesi, S.; Angeletti, C.A.; Tacca, M.D.; Campa, M. Comparative distribution of azithromycin in lung tissue of patients given oral daily doses of 500 and 1000 mg. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2003, 51, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreaden, E.C.; Mwakwari, S.C.; Austin, L.A.; Kieffer, M.J.; Oyelere, A.K.; El-Sayed, M.A. Small Molecule-Gold Nanorod Conjugates Selectively Target and Induce Macrophage Cytotoxicity towards Breast Cancer Cells. Small 2012, 8, 2819–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crooke, S.N.; Schimer, J.; Raji, I.; Oyelere, A.K.; Finn, M.G. Lung Tissue Delivery of Virus-Like Particles Mediated by Macrolide Antibiotics. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.M.A.; Davison, R.S.; Bliss, E.; McGee, J.O.D. Macrophages in human breast disease: A quantitative immunohistochemical study. Br. J. Cancer 1988, 57, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradei, O.M.; Mallais, T.C.; Frechette, S.; Paquin, I.; Tessier, P.E.; Leit, S.M.; Fournel, M.; Bonfils, C.; Trachy-Bourget, M.-C.; Liu, J.; et al. Novel aminophenyl benzamide-type histone deacetylase inhibitors with enhanced potency and selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 5543–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witter, D.J.; Harrington, P.; Wilson, K.J.; Chenard, M.; Fleming, J.C.; Haines, B.; Kral, A.M.; Secrist, J.P.; Miller, T.A. Optimization of biaryl Selective HDAC1&2 Inhibitors (SHI-1:2). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 726–731. [Google Scholar]
- Bressi, J.C.; Jennings, A.J.; Skene, R.; Wu, Y.; Melkus, R.; Jong, R.D.; O’Connell, S.; Grimshaw, C.E.; Navre, M.; Gangloff, A.R. Exploration of the HDAC2 foot pocket: Synthesis and SAR of substituted N-(2-aminophenyl)benzamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3142–3145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, F.F.; Lundh, M.; Kaya, T.; McCarren, P.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Gale, J.P.; Galbo, T.; Fisher, S.L.; Meier, B.C.; et al. An Isochemogenic Set of Inhibitors to Define the Therapeutic Potential of Histone Deacetylases in β-Cell Protection. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sodji, Q.H.; Kornacki, J.R.; McDonald, J.F.; Mrksich, M.; Oyelere, A.K. Design and structure activity relationship of tumor-homing histone deacetylase inhibitors conjugated to folic and pteroic acids. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 96, 340–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seo, Y.J.; Kang, Y.; Muench, L.; Reid, A.; Caesar, S.; Jean, L.; Wagner, F.; Holson, E.; Haggarty, S.J.; Weiss, P.; et al. Image-Guided Synthesis Reveals Potent Blood-Brain Barrier Permeable Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiyama, M.; Tominaga, H.; Shiga, M.; Sasamoto, K.; Ohkura, Y.; Ueno, K. A combined assay of cell viability and in vitro cytotoxicity with a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt, neutral red and crystal violet. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1996, 19, 1518–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carlisi, D.; Vassallo, B.; Lauricella, M.; Emanuele, S.; D’Anneo, A.; Di Leonardo, E.; Di Fazio, P.; Vento, R.; Tesoriere, G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors induce in human hepatoma HepG2 cells acetylation of p53 and histones in correlation with apoptotic effects. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Y.-S.; Kashida, Y.; Kulp, S.K.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, D.; Hung, J.-H.; Tang, M.; Lin, Z.-Z.; Chen, T.-J.; Chen, A.-L.; et al. Efficacy of a Novel Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor in Murine Models of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehara, T.; Liu, X.; Fujimoto, J.; Friedman, S.L.; Takahashi, H. Expression and role of Bcl-xL in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Hepatology 2001, 34, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.-C.; Huang, H.-H.; Lai, C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-J.; Liou, J.-P.; Lai, M.-J.; Li, Y.-H.; Teng, C.-M.; Yang, C.-R. Novel histone deacetylase inhibitor MPT0G009 induces cell apoptosis and synergistic anticancer activity with tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand against human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 402–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raji, I.; Yadudu, F.; Janeira, E.; Fathi, S.; Szymczak, L.; Kornacki, J.R.; Komatsu, K.; Li, J.-D.; Mrksich, M.; Oyelere, A.K. Bifunctional Conjugates with Potent Inhibitory Activity Towards Cyclooxygenase and Histone Deacetylase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 1202–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marrocco, D.L.; Tilley, W.D.; Bianco-Miotto, T.; Evdokiou, A.; Scher, H.I.; Rifkind, R.A.; Marks, P.A.; Richon, V.M.; Bulter, L.M. Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (vorinostat) represses androgen receptor expression and acts synergistically with an androgen receptor antagonist to inhibit prostate cancer cell proliferation. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reilberger, T.; Chen, Y.; Ramjiawan, R.R.; Hato, T.; Fan, C.; Samuel, R.; Roberge, S.; Huang, P.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Zhu, A.X.; et al. An orthotopic mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma with underlying liver cirrhosis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1264–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lachenmayer, A.; Toffanin, S.; Cabellos, L.; Alsinet, C.; Hoshida, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Minguez, B.; Tsai, H.-W.; Ward, S.C.; Thung, S.; et al. Combination therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Additive preclinical efficacy of the HDAC inhibitor panobinostatwith sorafenib. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1343–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svechnikova, I.; Gray, S.G.; Kundrotiene, J.; Ponthan, F.; Kogner, P.; Ekstrom, T.J. Apoptosis and tumor remission in liver tumor xenografts by 4-phenylbutyrate. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 22, 579–588. [Google Scholar]
- Coradini, D.; Zorzet, S.; Rossin, R.; Scarlata, I.; Pellizzaro, C.; Turrin, C.; Bello, M.; Cantoni, S.; Speranza, A.; Sava, G.; et al. Inhibition of hepatocellular carcinomas in vitro and hepatic metastases in vivo in mice by the histone deacetylase inhibitor HA-But. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 4822–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Enzymes | 1 (IC50, nM) |
|---|---|
| HDAC1 | 2.7 |
| HDAC2 | 8.1 |
| HDAC3/NCOR2 | 1.7 |
| HDAC4 | 1904 |
| HDAC5 | 1773 |
| HDAC6 | 1.7 |
| HDAC7 | 2621 |
| HDAC8 | 839 |
| HDAC9 | 6910 |
| HDAC10 | 4.5 |
| HDAC11 | 7361 |
| Enzymes | 2 (IC50, nM) | 3a (IC50, nM) | 3b (IC50, nM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDAC1 | 509 | 3800 | NI |
| HDAC2 | 3454 | 9200 | NI |
| HDAC3/NCOR2 | NI | 3000 | 2400 |
| HDAC4 | NI | NI | NT |
| HDAC5 | NI | NI | NT |
| HDAC6 | NI | NI | NI |
| HDAC7 | NI | NI | NT |
| HDAC8 | NI | NI | NI |
| HDAC9 | NI | NI | NT |
| HDAC10 | 2285 | 3000 | NT |
| HDAC11 | NI | NI | NT |
| Cell Lines IC50 (µM) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compounds | Hep-G2 | Huh7 | SK-HEP1 | Hep3B | Kupffer |
| 1 | 16.08 | 25.54 | 28.21 | 2.82 | >100 |
| 2 | 3.27 | 1.48 | 3.08 | 3.51 | >100 |
| 3a | 6.76 | 3.82 | 3.83 | 4.61 | >100 |
| 3b | 6.93 | 3.56 | 9.02 | 6.60 | NT |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tapadar, S.; Fathi, S.; Wu, B.; Sun, C.Q.; Raji, I.; Moore, S.G.; Arnold, R.S.; Gaul, D.A.; Petros, J.A.; Oyelere, A.K. Liver-Targeting Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Potently Suppress Hepatocellular Tumor Growth as Standalone Agents. Cancers 2020, 12, 3095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113095
Tapadar S, Fathi S, Wu B, Sun CQ, Raji I, Moore SG, Arnold RS, Gaul DA, Petros JA, Oyelere AK. Liver-Targeting Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Potently Suppress Hepatocellular Tumor Growth as Standalone Agents. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113095
Chicago/Turabian StyleTapadar, Subhasish, Shaghayegh Fathi, Bocheng Wu, Carrie Q. Sun, Idris Raji, Samuel G. Moore, Rebecca S. Arnold, David A. Gaul, John A. Petros, and Adegboyega K. Oyelere. 2020. "Liver-Targeting Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Potently Suppress Hepatocellular Tumor Growth as Standalone Agents" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113095
APA StyleTapadar, S., Fathi, S., Wu, B., Sun, C. Q., Raji, I., Moore, S. G., Arnold, R. S., Gaul, D. A., Petros, J. A., & Oyelere, A. K. (2020). Liver-Targeting Class I Selective Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Potently Suppress Hepatocellular Tumor Growth as Standalone Agents. Cancers, 12(11), 3095. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113095







