YAP/TAZ Signalling in Colorectal Cancer: Lessons from Consensus Molecular Subtypes
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. YAP/TAZ in Colorectal Cancer: From Cells to Patients
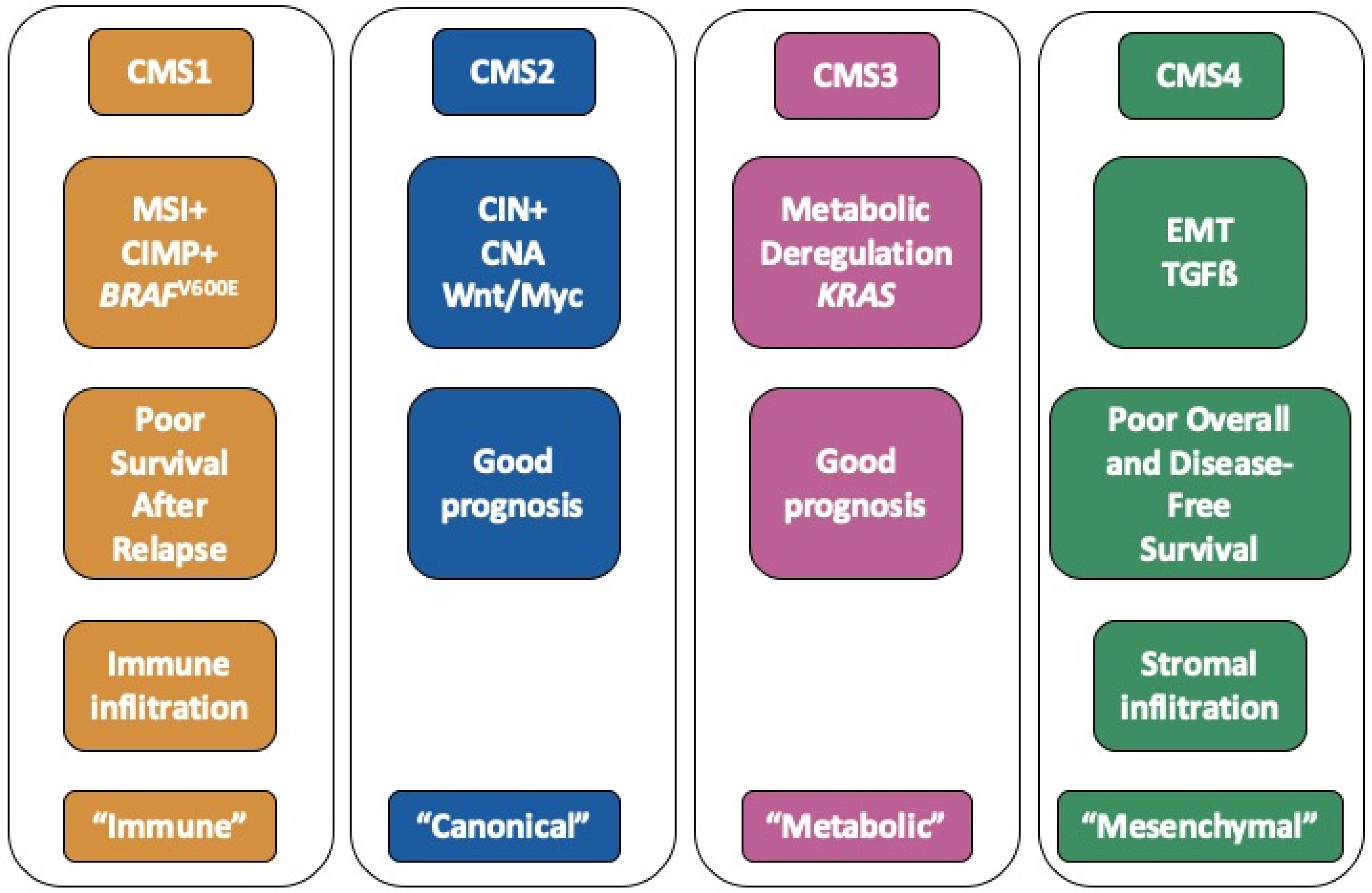
2.1. Clinical Data
2.2. Insight from Animal Models
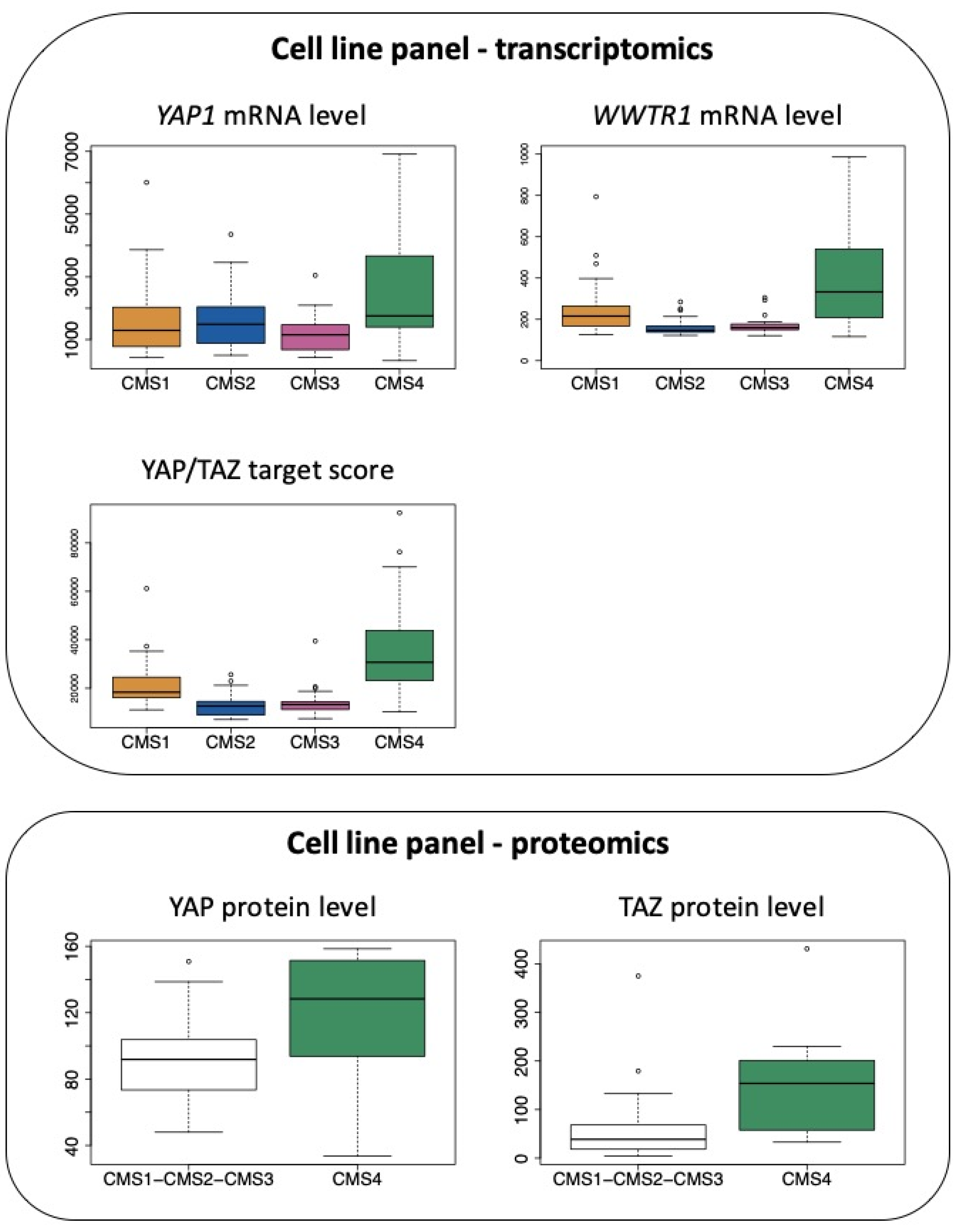
2.3. The Cellular Scale
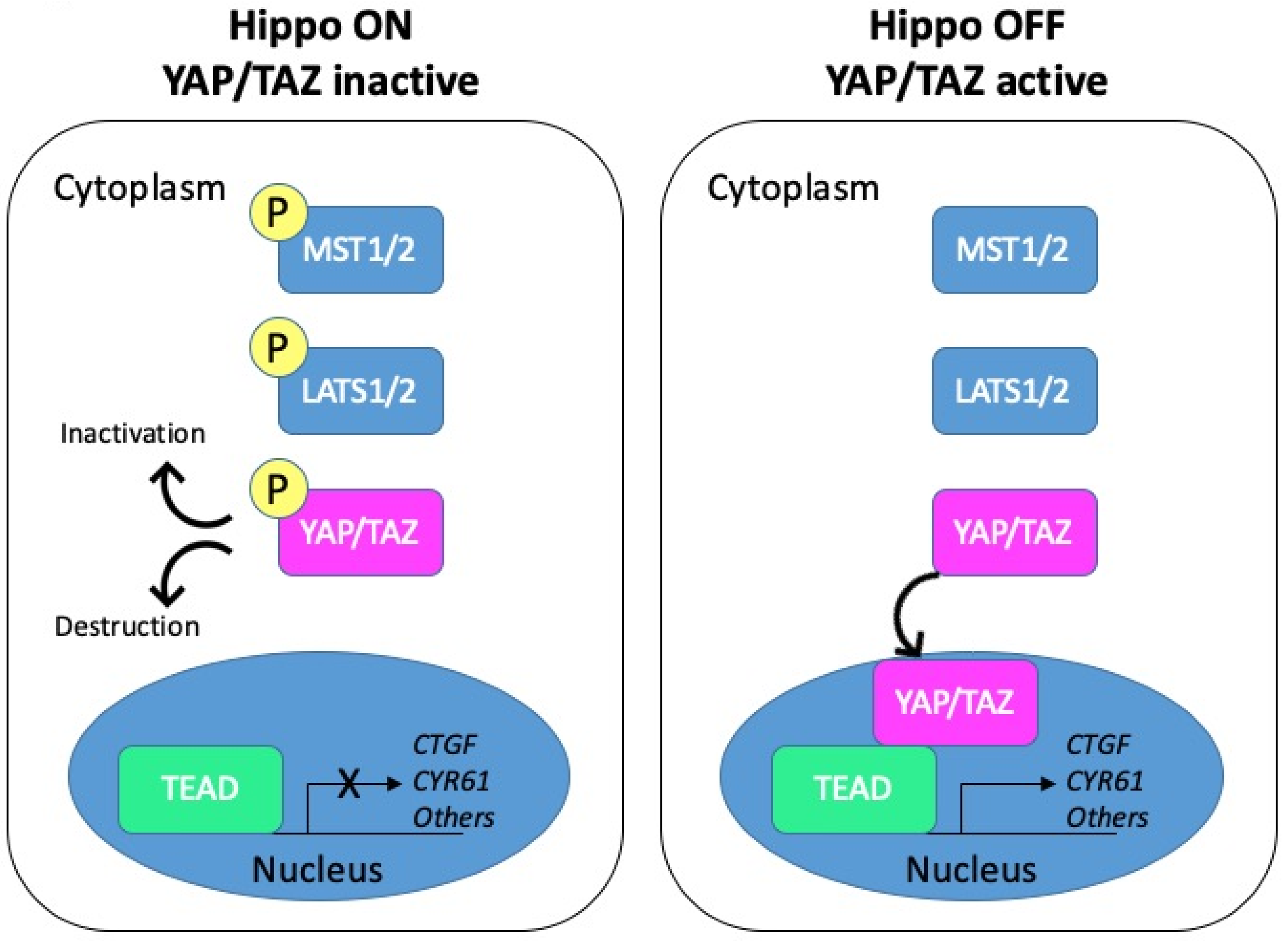
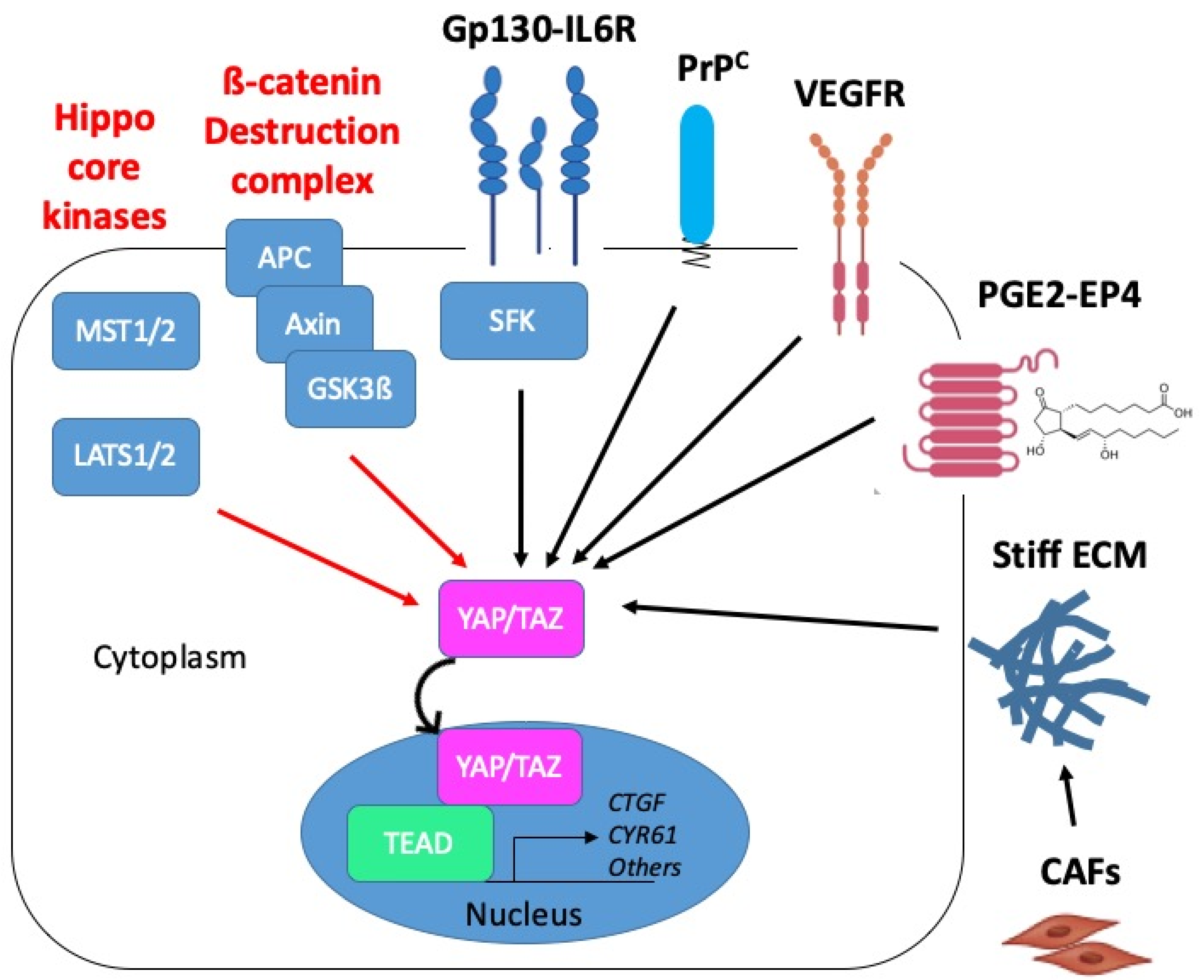
3. Upstream Pathways
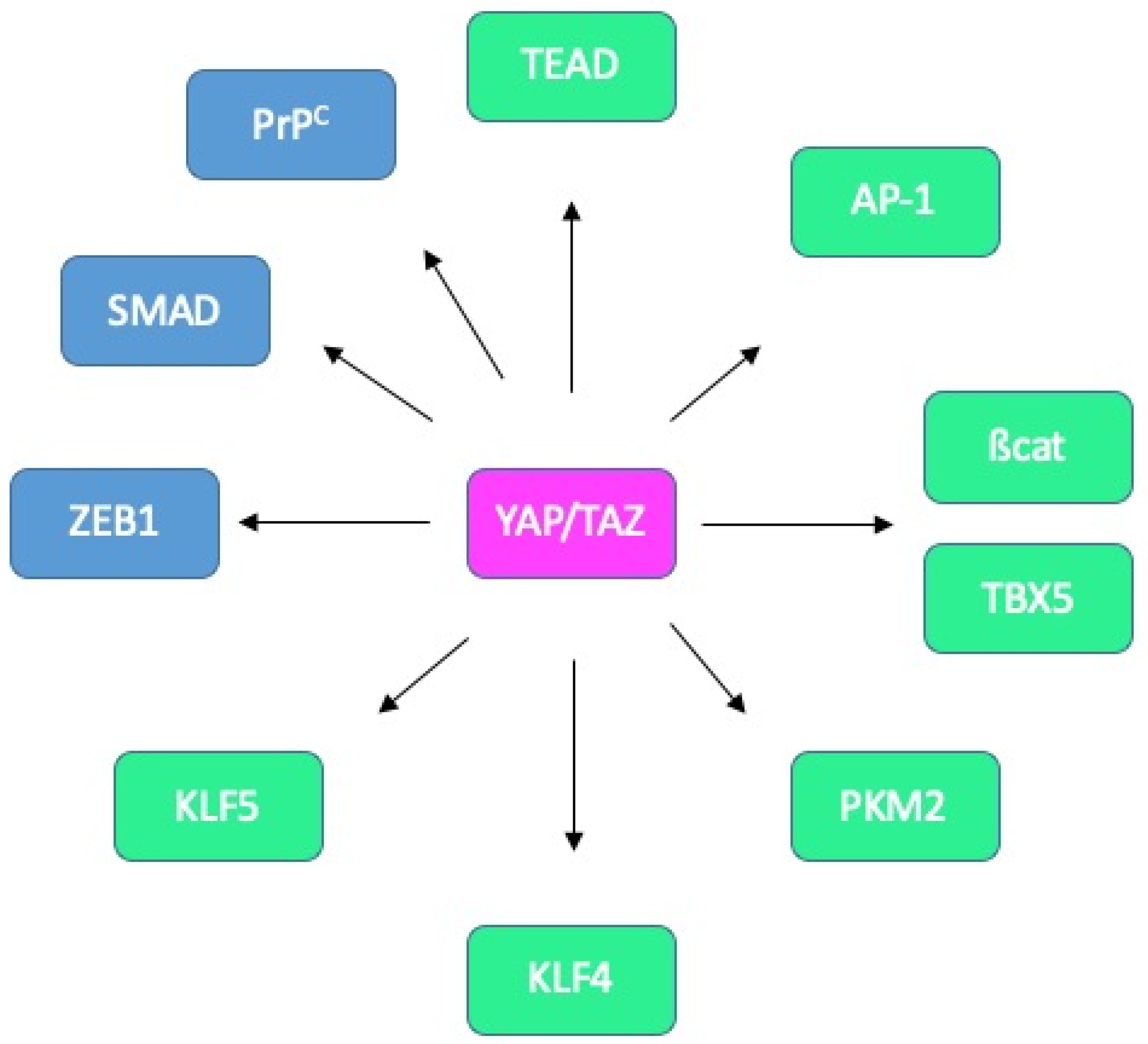
4. Choosing the Adequate Partner
5. Conclusions/Future Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Punt, C.J.A.; Koopman, M.; Vermeulen, L. From tumour heterogeneity to advances in precision treatment of colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinney, J.; Dienstmann, R.; Wang, X.; de Reyniès, A.; Schlicker, A.; Soneson, C.; Marisa, L.; Roepman, P.; Nyamundanda, G.; Angelino, P.; et al. The consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becht, E.; de Reyniès, A.; Giraldo, N.A.; Pilati, C.; Buttard, B.; Lacroix, L.; Selves, J.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Laurent-Puig, P.; Fridman, W.H. Immune and stromal classification of colorectal cancer is associated with molecular subtypes and relevant for precision immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 4057–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van den Braak, R.R.J.C.; Ten Hoorn, S.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Tuynman, J.B.; Smid, M.; Wilting, S.M.; Martens, J.W.M.; Punt, C.J.A.; Foekens, J.A.; Medema, J.P.; et al. Interconnectivity between molecular subtypes and tumor stage in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dienstmann, R.; Vermeulen, L.; Guinney, J.; Kopetz, S.; Tejpar, S.; Tabernero, J. Consensus molecular subtypes and the evolution of precision medicine in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, E.; Eason, K.; Cervantes, A.; Salazar, R.; Sadanandam, A. Context matters-consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer as biomarkers for clinical trials. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D. The hippo signaling pathway in development and cancer. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 491–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harvey, K.F.; Zhang, X.; Thomas, D.M. The Hippo pathway and human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Meng, Z.; Chen, R.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo pathway: Biology and pathophysiology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2019, 88, 577–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varelas, X. The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ and YAP in development, homeostasis and disease. Development 2014, 141, 1614–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.-X.; Meng, Z.; Plouffe, S.W.; Guan, K.-L. Hippo pathway regulation of gastrointestinal tissues. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 201–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanconato, F.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ at the roots of cancer. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 783–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huyghe, J.R.; Bien, S.A.; Harrison, T.A.; Kang, H.M.; Chen, S.; Schmit, S.L.; Conti, D.V.; Qu, C.; Jeon, J.; Edlund, C.K.; et al. Discovery of common and rare genetic risk variants for colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuen, H.-F.; McCrudden, C.M.; Huang, Y.-H.; Tham, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, S.-D.; Hong, W. TAZ expression as a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.-D.; McCrudden, C.M.; Yuen, H.-F.; Leung, K.L.; Hong, W.-J.; Kwok, H.F. Association between the expression levels of TAZ, AXL and CTGF and clinicopathological parameters in patients with colon cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marisa, L.; de Reynies, A.; Duval, A.; Selves, J.; Gaub, M.P.; Vescovo, L.; Etienne-Grimaldi, M.C.; Schiappa, R.; Guenot, D.; Ayadi, M.; et al. Gene expression classification of colon cancer into molecular subtypes: Characterization, validation, and prognostic value. PLoS Med. 2013, 10, e1001453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touil, Y.; Igoudjil, W.; Corvaisier, M.; Dessein, A.-F.; Vandomme, J.; Monté, D.; Stechly, L.; Skrypek, N.; Langlois, C.; Grard, G.; et al. Colon cancer cells escape 5FU chemotherapy-induced cell death by entering stemness and quiescence associated with the c-Yes/YAP axis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, K.-W.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, S.-B.; Sohn, B.H.; Lee, H.-S.; Jang, H.-J.; Park, Y.-Y.; Kopetz, S.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, S.C.; et al. Significant association of oncogene YAP1 with poor prognosis and cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Sobrero, A.; Van Krieken, J.H.; Aderka, D.; Aguilar, E.A.; Bardelli, A.; Benson, A.; Bodoky, G.; et al. ESMO consensus guidelines for the management of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 1386–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhardt, A.A.; Gayyed, M.F.; Klein, A.P.; Dong, J.; Maitra, A.; Pan, D.; Montgomery, E.A.; Anders, R.A. Expression of Yes-associated protein in common solid tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2008, 39, 1582–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Shi, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Yang, A.; Wen, W.; Zhu, Q. Overexpression of YAP and TAZ is an independent predictor of prognosis in colorectal cancer and related to the proliferation and metastasis of colon cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, C.; Li, Q.; Xu, K.; Wang, E. Clinical and prognostic significance of Yes-associated protein in colorectal cancer. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 2169–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, E.R.; Morikawa, T.; Butler, B.L.; Shrestha, K.; de la Rosa, R.; Yan, K.S.; Fuchs, C.S.; Magness, S.T.; Smits, R.; Ogino, S.; et al. Restriction of intestinal stem cell expansion and the regenerative response by YAP. Nature 2013, 493, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Maglic, D.; Dill, M.T.; Mojumdar, K.; Ng, P.K.-S.; Jeong, K.J.; Tsang, Y.H.; Moreno, D.; Bhavana, V.H.; et al. Comprehensive molecular characterization of the Hippo signaling pathway in cancer. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 1304–1317.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Lu, Y.; Akbani, R.; Ju, Z.; Roebuck, P.L.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.-Y.; Broom, B.M.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; Kane, D.W.; et al. TCPA: A resource for cancer functional proteomics data. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1046–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camargo, F.D.; Gokhale, S.; Johnnidis, J.B.; Fu, D.; Bell, G.W.; Jaenisch, R.; Brummelkamp, T.R. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H.; Barry, E.; Yin, Y.; Lawrence, E.; Dawson, D.; Willis, J.E.; Markowitz, S.D.; Camargo, F.D.; et al. Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E1312–E1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Heijden, M.; Vermeulen, L. Stem cells in homeostasis and cancer of the gut. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Maitra, A.; Anders, R.A.; Taketo, M.M.; Pan, D. β-Catenin destruction complex-independent regulation of Hippo-YAP signaling by APC in intestinal tumorigenesis. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fodde, R.; Smits, R.; Clevers, H. APC, signal transduction and genetic instability in colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2001, 1, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-catenin signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregorieff, A.; Liu, Y.; Inanlou, M.R.; Khomchuk, Y.; Wrana, J.L. Yap-dependent reprogramming of Lgr5(+) stem cells drives intestinal regeneration and cancer. Nature 2015, 526, 715–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzolin, L.; Panciera, T.; Soligo, S.; Enzo, E.; Bicciato, S.; Dupont, S.; Bresolin, S.; Frasson, C.; Basso, G.; Guzzardo, V.; et al. YAP/TAZ incorporation in the β-catenin destruction complex orchestrates the Wnt response. Cell 2014, 158, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayyaz, A.; Kumar, S.; Sangiorgi, B.; Ghoshal, B.; Gosio, J.; Ouladan, S.; Fink, M.; Barutcu, S.; Trcka, D.; Shen, J.; et al. Single-cell transcriptomes of the regenerating intestine reveal a revival stem cell. Nature 2019, 569, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulis, M.; Kaklamanos, A.; Schernthanner, M.; Bielecki, P.; Zhao, J.; Kaffe, E.; Frommelt, L.-S.; Qu, R.; Knapp, M.S.; Henriques, A.; et al. Paracrine orchestration of intestinal tumorigenesis by a mesenchymal niche. Nature 2020, 580, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.; Xiol, J.; Dill, M.T.; Yuan, W.-C.; Panero, R.; Roper, J.; Osorio, F.G.; Maglic, D.; Li, Q.; Gurung, B.; et al. Regenerative reprogramming of the intestinal stem cell state via Hippo signaling suppresses metastatic colorectal cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 27, 590–604.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fessler, E.; Medema, J.P. Colorectal cancer subtypes: Developmental origin and microenvironmental regulation. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stastna, M.; Janeckova, L.; Hrckulak, D.; Kriz, V.; Korinek, V. Human colorectal cancer from the perspective of mouse models. Genes 2019, 10, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackstadt, R.; van Hooff, S.R.; Leach, J.D.; Cortes-Lavaud, X.; Lohuis, J.O.; Ridgway, R.A.; Wouters, V.M.; Roper, J.; Kendall, T.J.; Roxburgh, C.S.; et al. Epithelial NOTCH signaling rewires the tumor microenvironment of colorectal cancer to drive poor-prognosis subtypes and metastasis. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 319–336.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tschaharganeh, D.F.; Chen, X.; Latzko, P.; Malz, M.; Gaida, M.M.; Felix, K.; Ladu, S.; Singer, S.; Pinna, F.; Gretz, N.; et al. Yes-associated protein up-regulates Jagged-1 and activates the Notch pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1530–1542.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sveen, A.; Bruun, J.; Eide, P.W.; Eilertsen, I.A.; Ramirez, L.; Murumägi, A.; Arjama, M.; Danielsen, S.A.; Kryeziu, K.; Elez, E.; et al. Colorectal cancer consensus molecular subtypes translated to preclinical models uncover potentially targetable cancer cell dependencies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 794–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Konsavage, W.M.; Kyler, S.L.; Rennoll, S.A.; Jin, G.; Yochum, G.S. Wnt/β-catenin signaling regulates Yes-associated protein (YAP) gene expression in colorectal carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11730–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, R.; Halder, G. The two faces of Hippo: Targeting the Hippo pathway for regenerative medicine and cancer treatment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azzolin, L.; Zanconato, F.; Bresolin, S.; Forcato, M.; Basso, G.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Role of TAZ as mediator of Wnt signaling. Cell 2012, 151, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, J.; Li, S.; Chi, P.; Xu, Z.; Lu, X.; Huang, Y. Lentivirus-mediated RNA interference targeting WWTR1 in human colorectal cancer cells inhibits cell proliferation in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Q.; Gao, X.; Yu, T.; Yuan, L.; Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, G.; Jiao, C.; Zhou, W.; Huang, Q.; et al. REGγ controls Hippo signaling and reciprocal NF-κB-YAP regulation to promote colon cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2015–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneron, A.M.; Ludwig, R.L.; Vousden, K.H. Cytoplasmic ASPP1 inhibits apoptosis through the control of YAP. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2430–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.-W.; Lin, P.-L.; Wang, L.; Huang, C.-C.; Lee, H. The YAP1/SIX2 axis is required for DDX3-mediated tumor aggressiveness and cetuximab resistance in KRAS-wild-type colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 1114–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-Y.; Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, B.-X.; Cheng, C.-H.; Chen, K.-C.; Lin, C.-W. Podocalyxin-like protein 1 regulates TAZ signaling and stemness properties in colon cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, X.; Ye, J.; Shang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, R. Ascl2 activation by YAP1/KLF5 ensures the self-renewability of colon cancer progenitor cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109301–109318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosenbluh, J.; Nijhawan, D.; Cox, A.G.; Li, X.; Neal, J.T.; Schafer, E.J.; Zack, T.I.; Wang, X.; Tsherniak, A.; Schinzel, A.C.; et al. β-Catenin-driven cancers require a YAP1 transcriptional complex for survival and tumorigenesis. Cell 2012, 151, 1457–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhou, X.; Wang, T.; Feng, X.; Sun, Y.-P.; Xiong, Y.; Yuan, H.-X.; Guan, K.-L. Endothelin promotes colorectal tumorigenesis by activating YAP/TAZ. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2413–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, D.D.; Xue, W.; Krall, E.B.; Bhutkar, A.; Piccioni, F.; Wang, X.; Schinzel, A.C.; Sood, S.; Rosenbluh, J.; Kim, J.W.; et al. KRAS and YAP1 converge to regulate EMT and tumor survival. Cell 2014, 158, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Sabnis, A.J.; Chan, E.; Olivas, V.; Cade, L.; Pazarentzos, E.; Asthana, S.; Neel, D.; Yan, J.J.; Lu, X.; et al. The Hippo effector YAP promotes resistance to RAF- and MEK-targeted cancer therapies. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Sheng, X.; Tian, Y.; Deng, M.; Du, S.; Lv, C.; Li, G.; Pan, Y.; Song, Y.; et al. Secreted stromal protein ISLR promotes intestinal regeneration by suppressing epithelial Hippo signaling. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.-D.; Lu, X.-X.; Gan, W.-J.; Li, X.-M.; He, X.-S.; Zhang, S.; Ji, Q.-H.; Zhou, F.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.-R.; et al. RARγ downregulation contributes to colorectal tumorigenesis and metastasis by derepressing the Hippo-Yap pathway. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3813–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, H.-S.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Sun, H.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Gou, X.-M.; Yu, X.-Y.; Huang, Y.-H. Loss of HACE1 promotes colorectal cancer cell migration via upregulation of YAP1. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9663–9672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.-H.; Kuo, C.-C.; Lin, B.-X.; Huang, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-W. Elevation of YAP promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and tumor aggressiveness in colorectal cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 350, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, D.C.; Kang, J.H.; Hamza, B.; King, E.M.; Lamar, J.M.; Manalis, S.R.; Hynes, R.O. YAP enhances tumor cell dissemination by promoting intravascular motility and reentry into systemic circulation. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 3867–3879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; Xue, X.; Shah, Y.M. Hypoxia-inducible factor 2α (HIF-2α) promotes colon cancer growth by potentiating Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17046–17056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greenhough, A.; Bagley, C.; Heesom, K.J.; Gurevich, D.B.; Gay, D.; Bond, M.; Collard, T.J.; Paraskeva, C.; Martin, P.; Sansom, O.J.; et al. Cancer cell adaptation to hypoxia involves a HIF-GPRC5A-YAP axis. EMBO Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, S.; Beaulieu, J.-F. The Hippo pathway effector YAP1 regulates intestinal epithelial cell differentiation. Cells 2020, 9, 1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, C.; Chen, L.; Lai, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Jeong, J.-H. Combinational inhibition of EGFR and YAP reverses 5-Fu resistance in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 5432–5439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Gu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, B.; Xie, J. Functional significance of Hippo/YAP signaling for drug resistance in colorectal cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2018, 57, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnekamp, J.F.; van Hooff, S.R.; Prasetyanti, P.R.; Kandimalla, R.; Buikhuisen, J.Y.; Fessler, E.; Ramesh, P.; Lee, K.A.S.T.; Bochove, G.G.W.; de Jong, J.H.; et al. Consensus molecular subtypes of colorectal cancer are recapitulated in in vitro and in vivo models. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medico, E.; Russo, M.; Picco, G.; Cancelliere, C.; Valtorta, E.; Corti, G.; Buscarino, M.; Isella, C.; Lamba, S.; Martinoglio, B.; et al. The molecular landscape of colorectal cancer cell lines unveils clinically actionable kinase targets. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roumeliotis, T.I.; Williams, S.P.; Gonçalves, E.; Alsinet, C.; Del Castillo Velasco-Herrera, M.; Aben, N.; Ghavidel, F.Z.; Michaut, M.; Schubert, M.; Price, S.; et al. Genomic determinants of protein abundance variation in colorectal cancer cells. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 2201–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Le Corre, D.; Ghazi, A.; Balogoun, R.; Pilati, C.; Aparicio, T.; Martin-Lannerée, S.; Marisa, L.; Djouadi, F.; Poindessous, V.; Crozet, C.; et al. The cellular prion protein controls the mesenchymal-like molecular subtype and predicts disease outcome in colorectal cancer. EBioMedicine 2019, 46, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antony, J.; Huang, R.Y.-J. AXL-driven EMT state as a targetable conduit in cancer. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3725–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lamouille, S.; Xu, J.; Derynck, R. Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 178–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, J.-Y.; Yu, C.-Y.; Bao, Y.-J.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Yang, S.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hong, J.; Fang, J.-Y. TEAD4 promotes colorectal tumorigenesis via transcriptionally targeting YAP1. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex. 2018, 17, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, H.-B.; Kim, M.; Park, Y.-S.; Park, I.; Kim, T.; Yang, S.-Y.; Cho, C.J.; Hwang, D.; Jung, J.-H.; Markowitz, S.D.; et al. Prostaglandin E2 activates YAP and a positive-signaling loop to promote colon regeneration after colitis but also carcinogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Xie, C.; Lu, N. Crosstalk between Hippo signalling and miRNAs in tumour progression. FEBS J. 2017, 284, 1045–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, K.; Wu, L.-W.; Grivennikov, S.I.; de Jong, P.R.; Lian, I.; Yu, F.-X.; Wang, K.; Ho, S.B.; Boland, B.S.; Chang, J.T.; et al. A gp130-Src-YAP module links inflammation to epithelial regeneration. Nature 2015, 519, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, K.; Moroishi, T.; de Jong, P.R.; Krawczyk, M.; Grebbin, B.M.; Luo, H.; Xu, R.-H.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Schweiger, C.; Wang, K.; et al. YAP-IL-6ST autoregulatory loop activated on APC loss controls colonic tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1643–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Totaro, A.; Panciera, T.; Piccolo, S. YAP/TAZ upstream signals and downstream responses. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panciera, T.; Azzolin, L.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Mechanobiology of YAP and TAZ in physiology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yui, S.; Azzolin, L.; Maimets, M.; Pedersen, M.T.; Fordham, R.P.; Hansen, S.L.; Larsen, H.L.; Guiu, J.; Alves, M.R.P.; Rundsten, C.F.; et al. YAP/TAZ-dependent reprogramming of colonic epithelium links ECM remodeling to tissue regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 35–49.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirsch, T.Z.; Martin-Lannerée, S.; Mouillet-Richard, S. Functions of the prion protein. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2017, 150, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manni, G.; Lewis, V.; Senesi, M.; Spagnolli, G.; Fallarino, F.; Collins, S.J.; Mouillet-Richard, S.; Biasini, E. The cellular prion protein beyond prion diseases. Swiss Med. Wkly. 2020, 150, w20222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Lannerée, S.; Hirsch, T.Z.; Hernandez-Rapp, J.; Halliez, S.; Vilotte, J.L.; Launay, J.M.; Mouillet-Richard, S. PrPC from stem cells to cancer. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2014, 2, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Besnier, L.S.; Cardot, P.; Da Rocha, B.; Simon, A.; Loew, D.; Klein, C.; Riveau, B.; Lacasa, M.; Clair, C.; Rousset, M.; et al. The cellular prion protein PrPc is a partner of the Wnt pathway in intestinal epithelial cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 3313–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravard, A.; Auvré, F.; Fantini, D.; Bernardino-Sgherri, J.; Sissoëff, L.; Daynac, M.; Xu, Z.; Etienne, O.; Dehen, C.; Comoy, E.; et al. The prion protein is critical for DNA repair and cell survival after genotoxic stress. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 904–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jongen, J.M.J.; van der Waals, L.M.; Trumpi, K.; Laoukili, J.; Peters, N.A.; Schenning-van Schelven, S.J.; Govaert, K.M.; Rinkes, I.H.M.B.; Kranenburg, O. Downregulation of DNA repair proteins and increased DNA damage in hypoxic colon cancer cells is a therapeutically exploitable vulnerability. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86296–86311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azad, T.; van Rensburg, H.J.J.; Lightbody, E.D.; Neveu, B.; Champagne, A.; Ghaffari, A.; Kay, V.R.; Hao, Y.; Shen, H.; Yeung, B.; et al. A LATS biosensor screen identifies VEGFR as a regulator of the Hippo pathway in angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, T.; Ghahremani, M.; Yang, X. The role of YAP and TAZ in angiogenesis and vascular mimicry. Cells 2019, 8, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panciera, T.; Citron, A.; Di Biagio, D.; Battilana, G.; Gandin, A.; Giulitti, S.; Forcato, M.; Bicciato, S.; Panzetta, V.; Fusco, S.; et al. Reprogramming normal cells into tumour precursors requires ECM stiffness and oncogene-mediated changes of cell mechanical properties. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbazán, J.; Vignjevic, D.M. Cancer associated fibroblasts: Is the force the path to the dark side? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 56, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauviel, A.; Nallet-Staub, F.; Varelas, X. Integrating developmental signals: A Hippo in the (path)way. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1743–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Varelas, X.; Wrana, J.L. Coordinating developmental signaling: Novel roles for the Hippo pathway. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, P.; Han, X.; Zheng, B.; DeRan, M.; Yu, J.; Jarugumilli, G.; Deng, H.; Pan, D.; Luo, X.; Wu, X. Autopalmitoylation of TEAD Proteins Regulates Transcriptional Output of the Hippo Pathway. Available online: https://pubmed-ncbi-nlm-nih-gov.proxy.insermbiblio.inist.fr/26900866/ (accessed on 21 September 2020).
- Lin, K.C.; Moroishi, T.; Meng, Z.; Jeong, H.-S.; Plouffe, S.W.; Sekido, Y.; Han, J.; Park, H.W.; Guan, K.-L. Regulation of Hippo pathway transcription factor TEAD by p38 MAPK-induced cytoplasmic translocation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiao, S.; Li, C.; Hao, Q.; Miao, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z. VGLL4 targets a TCF4-TEAD4 complex to coregulate Wnt and Hippo signalling in colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diamantopoulou, Z.; White, G.; Fadlullah, M.Z.H.; Dreger, M.; Pickering, K.; Maltas, J.; Ashton, G.; MacLeod, R.; Baillie, G.S.; Kouskoff, V.; et al. TIAM1 antagonizes TAZ/YAP both in the destruction complex in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus to inhibit invasion of intestinal epithelial cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 621–634.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zanconato, F.; Forcato, M.; Battilana, G.; Azzolin, L.; Quaranta, E.; Bodega, B.; Rosato, A.; Bicciato, S.; Cordenonsi, M.; Piccolo, S. Genome-wide association between YAP/TAZ/TEAD and AP-1 at enhancers drives oncogenic growth. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1218–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-C.; Ling, H.-H.; Chiang, M.-C.; Chung, C.-H.; Lee, W.-Y.; Chu, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; Lai, Y.-W.; Tsai, I.-L.; et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer rewrites metabolic program through a Glut3-YAP-dependent signaling circuit. Theranostics 2019, 9, 2526–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imajo, M.; Ebisuya, M.; Nishida, E. Dual role of YAP and TAZ in renewal of the intestinal epithelium. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudhoff, M.J.; Braam, M.J.S.; Freeman, S.A.; Wong, D.; Rattray, D.G.; Wang, J.; Antignano, F.; Snyder, K.; Refaeli, I.; Hughes, M.R.; et al. SETD7 controls intestinal regeneration and tumorigenesis by regulating Wnt/β-catenin and Hippo/YAP signaling. Dev. Cell 2016, 37, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feldker, N.; Ferrazzi, F.; Schuhwerk, H.; Widholz, S.A.; Guenther, K.; Frisch, I.; Jakob, K.; Kleemann, J.; Riegel, D.; Bönisch, U.; et al. Genome-wide cooperation of EMT transcription factor ZEB1 with YAP and AP-1 in breast cancer. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, W.; Mossmann, D.; Kleemann, J.; Mock, K.; Meisinger, C.; Brummer, T.; Herr, R.; Brabletz, S.; Stemmler, M.P.; Brabletz, T. ZEB1 turns into a transcriptional activator by interacting with YAP1 in aggressive cancer types. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemer, S.E.; Szymaniak, A.D.; Varelas, X. The transcriptional regulators TAZ and YAP direct transforming growth factor β-induced tumorigenic phenotypes in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 13461–13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crozet, C.; Vézilier, J.; Delfieu, V.; Nishimura, T.; Onodera, T.; Casanova, D.; Lehmann, S.; Béranger, F. The truncated 23-230 form of the prion protein localizes to the nuclei of inducible cell lines independently of its nuclear localization signals and is not cytotoxic. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2006, 32, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strom, A.; Wang, G.-S.; Picketts, D.J.; Reimer, R.; Stuke, A.W.; Scott, F.W. Cellular prion protein localizes to the nucleus of endocrine and neuronal cells and interacts with structural chromatin components. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mouillet-Richard, S.; Laurent-Puig, P. YAP/TAZ Signalling in Colorectal Cancer: Lessons from Consensus Molecular Subtypes. Cancers 2020, 12, 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113160
Mouillet-Richard S, Laurent-Puig P. YAP/TAZ Signalling in Colorectal Cancer: Lessons from Consensus Molecular Subtypes. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113160
Chicago/Turabian StyleMouillet-Richard, Sophie, and Pierre Laurent-Puig. 2020. "YAP/TAZ Signalling in Colorectal Cancer: Lessons from Consensus Molecular Subtypes" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113160
APA StyleMouillet-Richard, S., & Laurent-Puig, P. (2020). YAP/TAZ Signalling in Colorectal Cancer: Lessons from Consensus Molecular Subtypes. Cancers, 12(11), 3160. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113160





