9G TestTM Cancer/Lung: A Desirable Companion to LDCT for Lung Cancer Screening
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
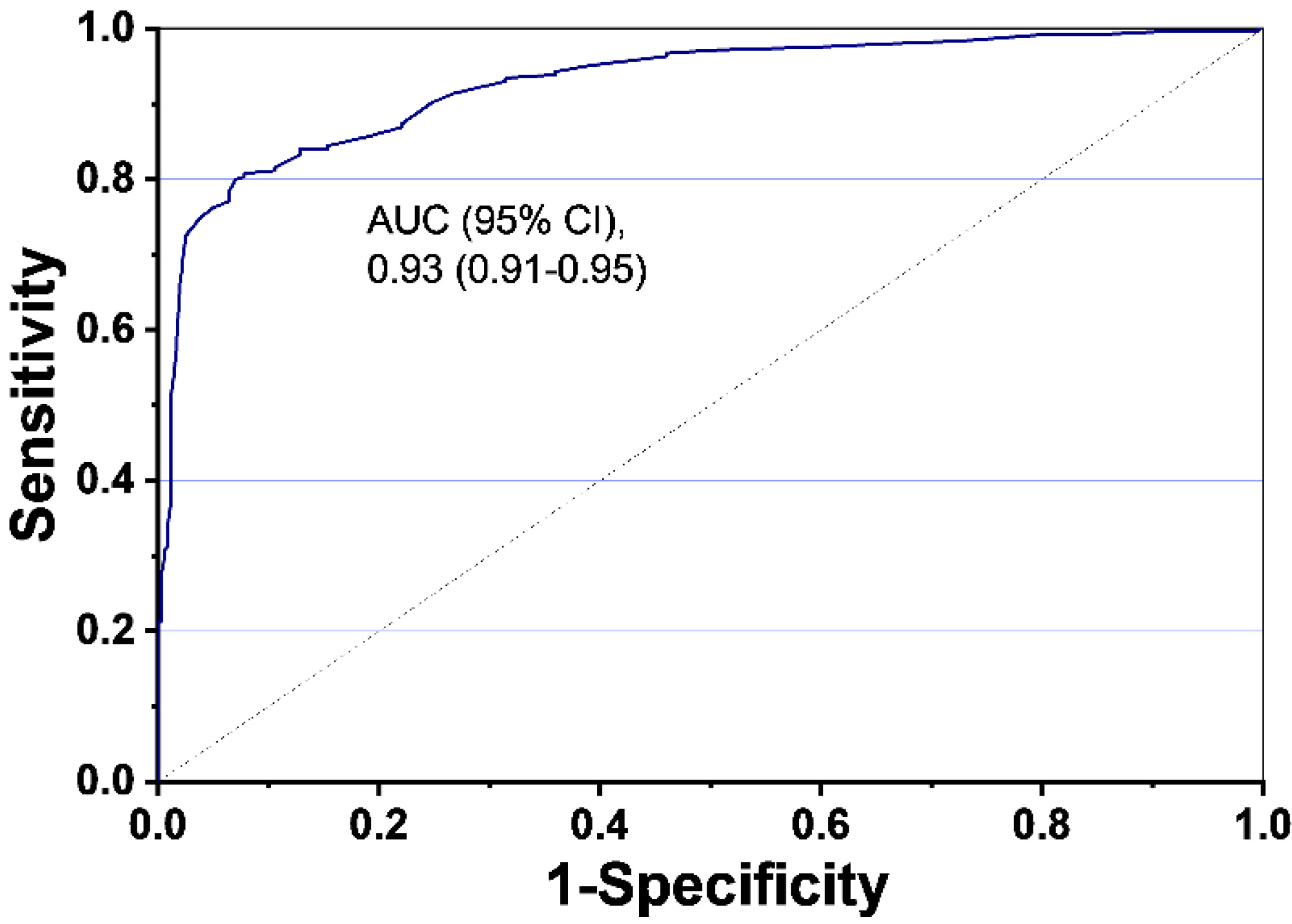
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Determination of Lung Cancer Index Using 9G Test™ Cancer/Lung Test
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 7–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Shen, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, H. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) versus other cancer screenings in early diagnosis of lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2018, 97, e11233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, F.R.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Mulshine, J.L.; Kwon, R.; Curran, W.J.; Wu, Y.-L.; Paz-Ares, L. Lung cancer: Current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V.; et al. The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: Proposals for Revision of the TNM Stage Groupings in the Forthcoming (Eighth) Edition of the TNM Classification for Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maldonado, S.G.; Motsch, E.; Trotter, A.; Kauczor, H.; Heussel, C.; Hermann, S.; Zeissig, S.R.; Delorme, S.; Kaaks, R. Overdiagnosis in lung cancer screening: Estimates from the German Lung Cancer Screening Intervention Trial. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patz, E.F., Jr.; Pinsky, P.; Gatsonis, C.; Sicks, J.D.; Kramer, B.S.; Tammemägi, M.C.; Chiles, C.; Black, W.C.; Aberle, D.R.; NLST Overdiagnosis Manuscript Writing Team. Overdiagnosis in Low-Dose Computed Tomography Screening for Lung Cancer. JAMA Intern. Med. 2014, 174, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.-Z.; Kuo, P.-L.; Huang, Y.-L.; Tang, E.-K.; Chen, C.-S.; Wu, M.-T.; Lin, Y.-P. Differences in lung cancer characteristics and mortality rate between screened and non-screened cohorts. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcus, P.M.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Zweig, M.H.; Harris, A.; Offord, K.P.; Fontana, R.S. Extended lung cancer incidence follow-up in the Mayo Lung Project and over diagnosis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, M.M.; Hocking, W.G.; Kvale, P.A.; Andriole, G.L.; Buys, S.S.; Church, T.R.; Crawford, E.D.; Fouad, M.N.; Isaacs, C.; Reding, D.J.; et al. Screening by chest radiograph and lung cancer mortality: The Prostate, Lung, Colorectal, and Ovarian (PLCO) randomized trial. JAMA 2011, 306, 1865–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, N.; Motsch, E.; Trotter, A.; Heussel, C.P.; Dienemann, H.; Schnabel, P.A.; Kauczor, H.; Maldonado, S.G.; Miller, A.B.; Kaaks, R.; et al. Lung cancer mortality reduction by LDCT screening—Results from the randomized German LUSI trial. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, L.M.; Peled, N.; Ajona, D.; Boeri, M.; Field, J.K.; Sozzi, G.; Pio, R.; Zulueta, J.; Javier, J.; Spira, A.; et al. Biomarkers in Lung Cancer Screening: Achievements, Promises, and Challenges. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, R.A.; Ba, K.S.A.; Brooks, D.; Fedewa, S.A.; Manassaram-Baptiste, D.; Saslow, D.; Wender, R.C. Cancer screening in the United States, 2019: A review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2019, 69, 184–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henschke, C.I.; McCauley, D.I.; Yankelevitz, D.F.; Naidich, D.P.; McGuinness, G.; Miettinen, O.S.; Libby, D.M.; Pasmantier, M.W.; Koizumi, J.; Altorki, N.K.; et al. Early Lung Cancer Action Project: Overall design and findings from baseline screening. Lancet 1999, 354, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, M.; Cavuto, S.; Lutman, F.R.; Brambilla, G.; Chiesa, G.; Ceresoli, G.; Passera, E.; Angeli, E.; Chiarenza, M.; Aranzulla, G.; et al. DANTE Study Group. A randomized study of lung cancer screening with spiral computed tomography (the DANTE Trial): Three-year results. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Lung Screening Trial Research Team; Aberle, D.R.; Adams, A.M.; Berg, C.D.; Black, W.C.; Clapp, J.D.; Fagerstrom, R.M.; Gareen, I.F.; Gatsonis, C.; Marcus, P.M.; et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sozzi, G.; Boeri, M. Potential biomarkers for lung cancer screening. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Fahrmann, J.F.; Kim, K.; DeFelice, B.C.; Taylor, S.L.; Gandara, D.R.; Yoneda, K.Y.; Cooke, D.T.; Fiehn, O.; Kelly, K.; Miyamoto, S. Investigation of Metabolomic Blood Biomarkers for Detection of Adenocarcinoma Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 1716–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carozzi, F.M.; Bisanzi, S.; Carrozzi, L.; Falaschi, F.; Pegna, A.L.; Mascalchi, M.; Picozzi, G.; Peluso, M.; Sani, C.; Greco, L.; et al. Multimodal lung cancer screening using the ITALUNG biomarker panel and low dose computed tomography. Results of the ITALUNG biomarker study. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bamji-Stocke, S.; Van Berkel, V.; Miller, D.M.; Frieboes, H.B. A review of metabolism-associated biomarkers in lung cancer diagnosis and treatment. Metabolomics 2018, 14, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zheng, J.; Ahmed, R.; Huang, G.; Reid, J.; Mandal, R.; Maksymuik, A.; Sitar, D.S.; Tappia, P.S.; Ramjiawan, B.; et al. A High-Performing Plasma Metabolite Panel for Early-Stage Lung Cancer Detection. Cancers 2020, 12, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dent, A.G.; Sutedja, T.G.; Zimmerman, P.V. Exhaled breath analysis for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2013, 5 (Suppl 5), S540–S550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhu, W.; Xie, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, M. Ultrasensitive Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA of Lung Cancer via an Enzymatically Amplified SERS-Based Frequency Shift Assay. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 18145–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Guan, Z.; Cuk, K.; Brenner, H.; Zhang, Y. Circulating microRNA biomarkers for lung cancer detection in Western populations. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 4849–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquette, C.-H.; Boutros, J.; Benzaquen, J.; Ferreira, M.; Pastre, J.; Pison, C.; Padovani, B.; Bettayeb, F.; Fallet, V.; Guibert, N.; et al. Circulating tumour cells as a potential biomarker for lung cancer screening: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Li, X.; Ren, T.; Yin, Y. Autoantibodies as diagnostic biomarkers for lung cancer: A systematic review. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kammer, M.N.; Massion, P.P. Noninvasive biomarkers for lung cancer diagnosis, where do we stand? J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 3317–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.; Chapman, C.J.; Holdenrieder, S.; Murray, A.; Robertson, C.; Wood, W.C.; Maddison, P.; Healey, G.; Fairley, G.H.; Barnes, A.C.; et al. Clinical validation of an autoantibody test for lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Sun, S.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Che, Y.; Huang, J.; Mao, S.; Lei, Y.; et al. Utility of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 as a serum protein biomarker for the early detection of non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter in vitro diagnostic clinical trial. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, K.W.; Einvik, G.; Brekke, P.H.; Omland, T. Cardiac Troponin T Increase in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke with and without Cancer. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lyon, A.R. Disparate worlds drawing closer together: Cardiovascular biomarkers predict cancer outcomes in treatment-naïve patients. Heart 2015, 101, 1853–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thålin, C.; Demers, M.; Blomgren, B.; Wong, S.L.; Von Arbin, M.; Von Heijne, A.; Laska, A.C.; Wallén, H.; Wagner, D.D.; Aspberg, S. NETosis promotes cancer-associated arterial microthrombosis presenting as ischemic stroke with troponin elevation. Thromb. Res. 2016, 139, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesterova, M.; Johnson, N.; Cheadle, C.; Cho-Chung, Y. Autoantibody biomarker opens a new gateway for cancer diagnosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agarwal, S.; Saini, S.; Parashar, D.; Verma, A.; Sinha, A.; Jagadish, N.; Batra, A.; Suri, S.; Gupta, A.; Ansari, A.S.; et al. The novel cancer-testis antigen A-kinase anchor protein 4 (AKAP4) is a potential target for immunotherapy of ovarian serous carcinoma. OncoImmunology 2013, 2, e24270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Leypoldt, F.; Kaya, Z.; Bieber, K.; McLachlan, S.M.; Komorowski, L.; Luo, J.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Hammers, C.M.; et al. Mechanisms of Autoantibody-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pavo, N.; Raderer, M.; Hülsmann, M.; Neuhold, S.; Adlbrecht, C.; Strunk, G.; Goliasch, G.; Gisslinger, H.; Steger, G.G.; Hejna, M.; et al. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with cancer and their association with all-cause mortality. Heart 2015, 101, 1874–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Nimse, S.B.; Warkad, S.D.; Oh, A.-C.; Kim, T.; Hong, Y.J. Quantification of CYFRA 21-1 and a CYFRA 21-1-anti-CYFRA 21-1 autoantibody immune complex for detection of early stage lung cancer. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 10060–10063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baron, J.A. Screening for cancer with molecular markers: Progress comes with potential problems. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 368–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, N.L.; Hayes, D.F. Cancer biomarkers. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shitrit, D.; Zingerman, B.; Shitrit, A.B.-G.; Shlomi, D.; Kramer, M.R. Diagnostic Value of CYFRA 21-1, CEA, CA 19-9, CA 15-3, and CA 125 Assays in Pleural Effusions: Analysis of 116 Cases and Review of the Literature. Oncologist 2005, 10, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Sheng, S.; Qian, S.Y.; Huo, X. Evaluation of Serum CEA, CA19-9, CA72-4, CA125 and Ferritin as Diagnostic Markers and Factors of Clinical Parameters for Colorectal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamura, K.; Takayama, K.; Izumi, M.; Harada, T.; Furuyama, K.; Nakanishi, Y. Diagnostic value of CEA and CYFRA 21-1 tumor markers in primary lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2013, 80, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaenker, P.; Gray, E.; Ziman, M. Autoantibody Production in Cancer—The Humoral Immune Response toward Autologous Antigens in Cancer Patients. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamay, T.N.; Zamay, G.S.; Kolovskaya, O.S.; Zukov, R.A.; Petrova, M.; Gargaun, A.; Berezovski, M.V.; Kichkailo, A.S. Current and Prospective Protein Biomarkers of Lung Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meaney, C.L.; Zingone, A.; Brown, D.; Yu, Y.; Cao, L.; Ryan, B.M. Identification of serum inflammatory markers as classifiers of lung cancer mortality for stage I adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 40946–40957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, Y.-H.; Luo, L.; Wampfler, J.A.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Chen, Y.-M.; Adjei, A.A.; Midthun, D.E.; Yang, P. 5-year overall survival in patients with lung cancer eligible or ineligible for screening according to US Preventive Services Task Force criteria: A prospective, observational cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1098–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, S.B.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7, 170070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Integrative Analysis of Lung Cancer Etiology and Risk (INTEGRAL) Consortium for Early Detection of Lung Cancer; Guida, F.; Sun, N.; Bantis, L.E.; Muller, D.C.; Li, P.; Taguchi, A.; Dhillon, D.; Kundnani, D.L.; Patel, N.J.; et al. Assessment of Lung Cancer Risk on the Basis of a Biomarker Panel of Circulating Proteins. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e182078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sources of Clinical Samples | Healthy Individuals | Lung Cancer Patients * | IRB No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nowon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Seoul, South Korea | 175 a | - | 2020-EC-01-008 |
| Korea Cancer Central Hospital, Seoul, South Korea | 120 | 50 | KIRAMS 2018-10-006 |
| Ajou Human Bio-Resource Bank (AHBB) | 64 b | - | AJHB-2019-28 |
| Biobank of Gyeongsang National University Hospital, | - | 12 | 2019-021 |
| Asan Bio-Resource Center, Korea Biobank Network | - | 182 | 2019-14(193) |
| Total | 359 | 244 | - |
| Lung Cancer Type | Subtypes | Lung Cancer Stages | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I | Stage II | Stage III | Stage IV | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | Adenoid cystic carcinoma | 1 | 2 | ||
| Bronchioloalveolar adenocarcinoma | 36 | 3 | 5 | ||
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 4 | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 43 | 16 | 9 | 2 | |
| Papillary adenocarcinoma | 40 | 2 | 8 | ||
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Adenosquamous carcinoma | 2 | 2 | 3 | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 18 | 3 | 8 | ||
| Squamous cell carcinoma, keratinizing | 4 | 4 | |||
| Squamous cell carcinoma, large cell, non-keratinizing | 4 | 2 | 1 | ||
| Mucoepidermoid carcinoma | 1 | ||||
| Small Cell | Combined small cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Small cell carcinoma | 2 | ||||
| Large cell carcinoma | Large cell carcinoma | 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| Large cell carcinoma with neuroendocrine feature | 2 | ||||
| Non-small cell carcinoma | Bronchogenic non-small cell carcinoma | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Sarcomatoid carcinoma | 1 | 1 | |||
| Characteristic | Healthy Population (n = 359) | Cancer Patients (n = 244) | p-Value (Healthy vs. Cancer) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (SD) | 57.3 (±12.0) | 62.7 (±9.30) | - |
| Male gender, n (%) | 140 (38.9) | 161 (65.9) | - |
| CIC (pg/mL; SD) | 4.47 (±5.22) | 5.16 (±7.46) | 0.7056 |
| CYFRA 21-1 (pg/mL; SD) | 3.89 (±4.84) | 2.33 (±2.78) | 0.0001 |
| cTnT (pg/mL; SD) | 16.7 (±13.6) | 22.4 (±18.8) | 0.0015 |
| NT-proBNP (pg/mL; SD) | 155.6 (±133.6) | 121.7 (±97.5) | 0.005 |
| CIC/CYFRA 21-1 (SD) | 1.290 (±0.52) | 2.16 (±1.00) | 0.0001 |
| cTnT/NT-proBNP (SD) | 0.11 (±0.04) | 0.19 (±0.06) | 0.0001 |
| LC Index (SD) | 1.45 (±0.73) | 3.90 (±1.87) | 0.0001 |
| Variable | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIC | 6.60 (3.80~10.4) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 64.0 (44.4~79.8) | 59.0 (58.0~59.9) |
| CYFRA 21-1 | 0.00 (0.00~1.50) | 97.3 (95.0 ~98.8) | 0.00 | 57.3 (57.0~57.8) |
| cTnT | 0.00 (0.00~1.50) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 0.00 | 57.3 (57.0~57.8) |
| NT-proBNP | 0.00 (0.00~1.50) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 0.00 | 57.3 (57.0~57.8) |
| CIC/CYFRA 21-1 | 29.5 (23.9~35.7) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 89.0 (80.3~94.0) | 65.6 (63.7~67.4) |
| cTnT/NT-proBNP | 34.0 (28.0~40.3) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 90.2 (82.6~94.8) | 67.0 (65.0~69.0) |
| LC Index | 75.0 (69.1~80.3) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 95.4(91.4~97.5) | 84.3 (81.2~87.0) |
| Cancer Stages (n) | Sensitivity (95% CI) | Specificity (95% CI) | PPV (95% CI) | NPV (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stage I (n = 160) | 77.5 (70.2~83.8) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 93.2 (87.8~96.4) | 90.1 (87.2~92.4) |
| Stage II (n = 32) | 78.1 (60.0~90.0) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 73.5 (58.7~84.5) | 97.9 (96.0~99.0) |
| Stage III (n = 49) | 67.4 (52.5~80.0) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 78.6 (65.2~87.8) | 95.4 (93.2~96.8) |
| Stage IV (n = 3) * | 33.3 (0.80~90.6) | 97.3 (95.0~98.8) | 10.0 (2.00~38.4) | 99.4 (98.7~99.7) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choe, W.; Chae, J.D.; Lee, B.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, S.Y.; Nimse, S.B.; Kim, J.; Warkad, S.D.; Song, K.-S.; Oh, A.-C.; et al. 9G TestTM Cancer/Lung: A Desirable Companion to LDCT for Lung Cancer Screening. Cancers 2020, 12, 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113192
Choe W, Chae JD, Lee B-H, Kim S-H, Park SY, Nimse SB, Kim J, Warkad SD, Song K-S, Oh A-C, et al. 9G TestTM Cancer/Lung: A Desirable Companion to LDCT for Lung Cancer Screening. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113192
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoe, Wonho, Jeong Don Chae, Byoung-Hoon Lee, Sang-Hoon Kim, So Young Park, Satish Balasaheb Nimse, Junghoon Kim, Shrikant Dashrath Warkad, Keum-Soo Song, Ae-Chin Oh, and et al. 2020. "9G TestTM Cancer/Lung: A Desirable Companion to LDCT for Lung Cancer Screening" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113192
APA StyleChoe, W., Chae, J. D., Lee, B.-H., Kim, S.-H., Park, S. Y., Nimse, S. B., Kim, J., Warkad, S. D., Song, K.-S., Oh, A.-C., Hong, Y. J., & Kim, T. (2020). 9G TestTM Cancer/Lung: A Desirable Companion to LDCT for Lung Cancer Screening. Cancers, 12(11), 3192. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113192






