Role of miRNAs in Sigmoid Colon Cancer: A Search for Potential Biomarkers
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
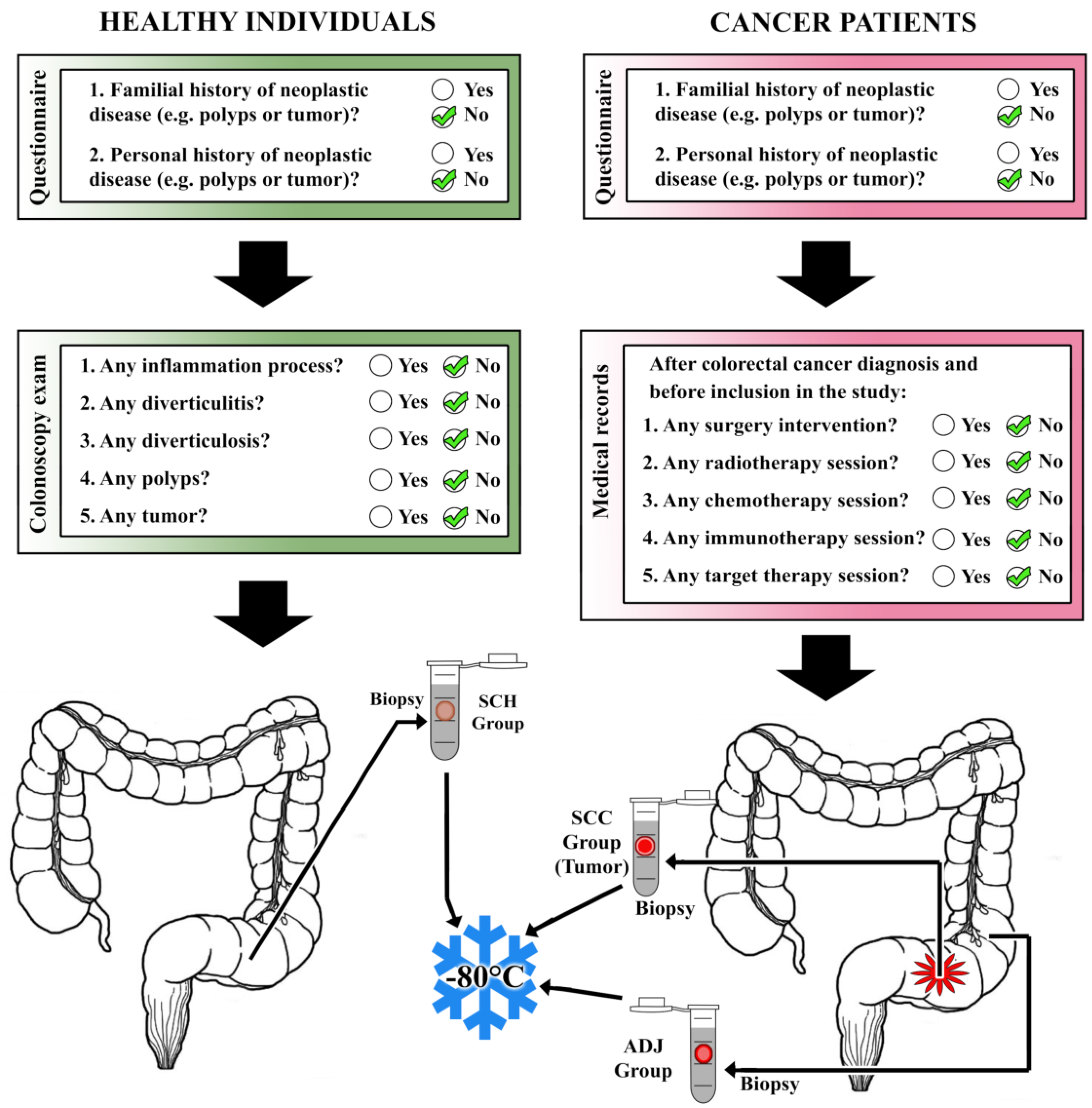
2.1. Biological Material
2.2. Ethics Statement
2.3. RNA Extraction, Small RNA Library Preparation, and Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.5. Identification of the miRNAs’ Target Genes
3. Results
Differentially Expressed miRNAs Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Ervik, M.; Lam, F.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Cancer Today; Global Cancer Observatory: Lyon, France, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schmid, G. The Use of Molecular Markers in the Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer Screening. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 625–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, M.; Sandhu, S.S.; Sharma, A.K. Cancer Molecular Markers: A Guide to Cancer Detection and Management. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52 Pt 1, 39–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, B.; Mert Ozupek, N.; Yerli Tetik, N.; Acar, E.; Bekcioglu, O.; Baskin, Y. Difference Between Left-Sided and Right-Sided Colorectal Cancer: A Focused Review of Literature. Gastroenterol. Res. 2018, 11, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ruan, Q.; Wang, H.; Liang, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, X. Impact of Tumor Site on Lymph Node Status and Survival in Colon Cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 2376–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stintzing, S.; Tejpar, S.; Gibbs, P.; Thiebach, L.; Lenz, H.-J. Understanding the Role of Primary Tumour Localisation in Colorectal Cancer Treatment and Outcomes. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 84, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuipers, E.J.; Grady, W.M.; Lieberman, D.; Seufferlein, T.; Sung, J.J.; Boelens, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Watanabe, T. Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2015, 1, 15065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Duong, H. The Molecular Characteristics of Colorectal Cancer: Implications for Diagnosis and Therapy. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tejpar, S.; Van Cutsem, E. Molecular and Genetic Defects in Colorectal Tumorigenesis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2002, 16, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA Therapeutics: Towards a New Era for the Management of Cancer and Other Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catela Ivkovic, T.; Voss, G.; Cornella, H.; Ceder, Y. MicroRNAs as Cancer Therapeutics: A Step Closer to Clinical Application. Cancer Lett. 2017, 407, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fussey, J.M.; Vaidya, B.; Kim, D.; Clark, J.; Ellard, S.; Smith, J.A. The Role of Molecular Genetics in the Clinical Management of Sporadic Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Systematic Review. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ambros, V.; Bartel, B.; Bartel, D.P.; Burge, C.B.; Carrington, J.C.; Chen, X.; Dreyfuss, G.; Eddy, S.R.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Marshall, M.; et al. A Uniform System for MicroRNA Annotation. RNA 2003, 9, 277–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yiu, A.J.; Yiu, C.Y. Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 1093–1102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA Biogenesis Pathways in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Chen, H. The Role of MicroRNAs in Colorectal Cancer. J. Genet. Genom. 2010, 37, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schee, K.; Fodstad, O.; Flatmark, K. MicroRNAs as Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1592–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â.; Khayat, A.S.; Silva, A.; Alencar, D.O.; Lobato, J.; Luz, L.; Pinheiro, D.G.; Varuzza, L.; Assumpção, M.; Assumpção, P.; et al. Ultra-Deep Sequencing Reveals the MicroRNA Expression Pattern of the Human Stomach. PLoS ONE 2010, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.C.; Assumpção, M.; Hamoy, I.G.; Darnet, S.; Burbano, R.; Khayat, A.; Gonçalves, A.N.; Alencar, D.O.; Cruz, A.; Magalhães, L.; et al. MiRNA Expression Profile for the Human Gastric Antrum Region Using Ultra-Deep Sequencing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, L.L.; Moreira, F.C.; Hamoy, I.G.; Santos, S.; Assumpção, P.; Santana, Á.L.; Santos, Â. Identification of MiRNAs Expression Profile in Gastric Cancer Using Self-Organizing Maps (SOM). Bioinformation 2014, 10, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Darnet, S.; Moreira, F.C.; Hamoy, I.G.; Burbano, R.; Khayat, A.; Cruz, A.; Magalhães, L.; Silva, A.; Santos, S.; Demachki, S.; et al. High-Throughput Sequencing of MiRNAs Reveals a Tissue Signature in Gastric Cancer and Suggests Novel Potential Biomarkers. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2015, 9 (Suppl. 1), 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assumpção, M.B.; Moreira, F.C.; Hamoy, I.G.; Magalhães, L.; Vidal, A.; Pereira, A.; Burbano, R.; Khayat, A.; Silva, A.; Santos, S.; et al. High-Throughput MiRNA Sequencing Reveals a Field Effect in Gastric Cancer and Suggests an Epigenetic Network Mechanism. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2015, 9, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidal, A.F.; Cruz, A.M.P.; Magalhães, L.; Pereira, A.L.; Anaissi, A.K.M.; Alves, N.C.F.; Albuquerque, P.J.B.S.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Demachki, S.; Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â. Hsa-MiR-29c and Hsa-MiR-135b Differential Expression as Potential Biomarker of Gastric Carcinogenesis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2060–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.B.; Magalhães, L.L.; Teófilo, C.R.; Alves, A.P.N.N.; Montenegro, R.C.; Negrini, M.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, Â. Differential Expression of Hsa-MiR-221, Hsa-MiR-21, Hsa-MiR-135b, and Hsa-MiR-29c Suggests a Field Effect in Oral Cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.L.; Magalhães, L.; Moreira, F.C.; Reis-das-Mercês, L.; Vidal, A.F.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, A.M.; Demachki, S.; Anaissi, A.K.M.; Burbano, R.M.R.; Albuquerque, P.; et al. Epigenetic Field Cancerization in Gastric Cancer: MicroRNAs as Promising Biomarkers. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 1560–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.; Moreira, F.; Vinasco-Sandoval, T.; Cunha, A.; Vidal, A.; Ribeiro-Dos-Santos, A.M.; Pinto, P.; Magalhães, L.; Assumpção, M.; Demachki, S.; et al. MiRNome Reveals New Insights Into the Molecular Biology of Field Cancerization in Gastric Cancer. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtius, K.; Wright, N.A.; Graham, T.A. An Evolutionary Perspective on Field Cancerization. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schee, K.; Lorenz, S.; Worren, M.M.; Günther, C.C.; Holden, M.; Hovig, E.; Fodstad, Ø.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Flatmark, K. Deep Sequencing the MicroRNA Transcriptome in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Leng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Tan, Y.; Ni, H.; Dong, X.; Shen, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Different MiR-21-3p Isoforms and Their Different Features in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- IARC. WHO Classification of Tumours of the Digestive System, 5th ed.; WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-92-832-4499-8. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast Universal RNA-Seq Aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq--a Python Framework to Work with High-Throughput Sequencing Data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated Estimation of Fold Change and Dispersion for RNA-Seq Data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Méndez, M.A.; Hödar, C.; Vulpe, C.; González, M.; Cambiazo, V. Discriminant Analysis to Evaluate Clustering of Gene Expression Data. FEBS Lett. 2002, 522, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-Based Map of the Human Proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and Integrative Analysis of Large Gene Lists Using DAVID Bioinformatics Resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics Enrichment Tools: Paths toward the Comprehensive Functional Analysis of Large Gene Lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein-Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozcan, O.; Kara, M.; Yumrutas, O.; Bozgeyik, E.; Bozgeyik, I.; Celik, O.I. MTUS1 and Its Targeting MiRNAs in Colorectal Carcinoma: Significant Associations. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 6637–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Guo, J. Overexpression of MiR-21-5p Promotes Proliferation and Invasion of Colon Adenocarcinoma Cells through Targeting CHL1. Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falzone, L.; Scola, L.; Zanghì, A.; Biondi, A.; Di Cataldo, A.; Libra, M.; Candido, S. Integrated Analysis of Colorectal Cancer MicroRNA Datasets: Identification of MicroRNAs Associated with Tumor Development. Aging (Albany N. Y.) 2018, 10, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasakova, K.; Bezakova, J.; Vician, M.; Reis, R.; Zeman, M.; Herichova, I. Gender-Dependent Expression of Leading and Passenger Strand of MiR-21 and MiR-16 in Human Colorectal Cancer and Adjacent Colonic Tissues. Physiol. Res. 2017, 66 (Suppl. 4), S575–S582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellatt, D.F.; Stevens, J.R.; Wolff, R.K.; Mullany, L.E.; Herrick, J.S.; Samowitz, W.; Slattery, M.L. Expression Profiles of MiRNA Subsets Distinguish Human Colorectal Carcinoma and Normal Colonic Mucosa. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Merhautova, J.; Machackova, T.; Gutierrez-Garcia, I.; Garcia-Solano, J.; Radova, L.; Brchnelova, D.; Slaba, K.; Svoboda, M.; Halamkova, J.; et al. MiR-215-5p Is a Tumor Suppressor in Colorectal Cancer Targeting EGFR Ligand Epiregulin and Its Transcriptional Inducer HOXB9. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zhong, Y.; Cai, S.; Zhou, P.; Yao, L. MicroRNA Expression Profiling in the Colorectal Normal-Adenoma-Carcinoma Transition. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, T.; Duan, J.; Liang, J.; Shi, H.; Zhen, T.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Y.; Han, A. MiR-338-3p Suppresses Colorectal Cancer Proliferation and Progression by Inhibiting MACC1. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2018, 11, 2256–2267. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Q.; Sun, K.; Deng, H.-J.; Lei, S.-T.; Dong, J.-Q.; Li, G.-X. MicroRNA-338-3p Inhibits Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Invasion and Migration by Targeting Smoothened. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 44, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, K.; Su, G.; Deng, H.; Dong, J.; Lei, S.; Li, G. Relationship between MiRNA-338-3p Expression and Progression and Prognosis of Human Colorectal Carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2014, 127, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Dai, S.; Zhen, T.; Shi, H.; Zhang, F.; Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Liang, Y.; Han, A. Clinical and Biological Significance of MiR-378a-3p and MiR-378a-5p in Colorectal Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 1207–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Jin, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Tang, G. Screening MiRNAs for Early Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer by Small RNA Deep Sequencing and Evaluation in a Chinese Patient Population. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2016, 9, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Du, J.; Mao, K.; Wang, X.; Ding, Y.; Wang, F. MicroRNA-143-3p Suppresses Tumorigenesis by Targeting Catenin-Δ1 in Colorectal Cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 3255–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, L.; Fu, J.; Sun, S.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, L.; Niu, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, S. MicroRNA-143-3p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastases by Targeting ITGA6 and ASAP3. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Shi, K.; Wang, Y.; Song, M.; Zhou, W.; Tu, H.; Lin, Z. Clinical Value of Integrated-Signature MiRNAs in Colorectal Cancer: MiRNA Expression Profiling Analysis and Experimental Validation. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37544–37556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.-Q.; Han, F.; Shi, Z.-L.; Yu, L.; Li, X.-F.; Yu, C.; Shen, C.-L.; Wan, D.-W.; Zhu, X.-G.; Li, R.; et al. MiR-133a-3p Targets SUMO-Specific Protease 1 to Inhibit Cell Proliferation and Cell Cycle Progress in Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.; Amar, L.; Gödde, D.; Prinz, C. Extensive Screening of MicroRNA Populations Identifies Hsa-MiR-375 and Hsa-MiR-133a-3p as Selective Markers for Human Rectal and Colon Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27256–27267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, K.-N.; Xiong, B. MiR-182-5p Inhibited Proliferation and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by Targeting MTDH. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1494–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzini, S.; Bisognin, A.; Mandruzzato, S.; Biasiolo, M.; Facciolli, A.; Perilli, L.; Rossi, E.; Esposito, G.; Rugge, M.; Pilati, P.; et al. Impact of MicroRNAs on Regulatory Networks and Pathways in Human Colorectal Carcinogenesis and Development of Metastasis. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishida, N.; Yokobori, T.; Mimori, K.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Ishii, H.; Doki, Y.; Kuwano, H.; Mori, M. MicroRNA MiR-125b Is a Prognostic Marker in Human Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1437–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-M.; Lin, K.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Q. Diverse Functions of MiR-125 Family in Different Cell Contexts. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panganiban, R.P.L.; Pinkerton, M.H.; Maru, S.Y.; Jefferson, S.J.; Roff, A.N.; Ishmael, F.T. Differential MicroRNA Epression in Asthma and the Role of MiR-1248 in Regulation of IL-5. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 1, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Zaynagetdinov, R.; Sherrill, T.P.; Gleaves, L.A.; McLoed, A.G.; Saxon, J.A.; Habermann, A.C.; Connelly, L.; Dulek, D.; Peebles, R.S.; Fingleton, B.; et al. Interleukin-5 Facilitates Lung Metastasis by Modulating the Immune Microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1624–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and Cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R.; Grivennikov, S.I. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity 2019, 51, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, M.W.L.; Galon, J.; Fridman, W.-H.; Smyth, M.J. From Mice to Humans: Developments in Cancer Immunoediting. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 3338–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dranoff, G. Cytokines in Cancer Pathogenesis and Cancer Therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almog, N.; Ma, L.; Schwager, C.; Brinkmann, B.G.; Beheshti, A.; Vajkoczy, P.; Folkman, J.; Hlatky, L.; Abdollahi, A. Consensus Micro RNAs Governing the Switch of Dormant Tumors to the Fast-Growing Angiogenic Phenotype. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e44001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Almog, N.; Briggs, C.; Beheshti, A.; Ma, L.; Wilkie, K.P.; Rietman, E.; Hlatky, L. Transcriptional Changes Induced by the Tumor Dormancy-Associated MicroRNA-190. Transcription 2013, 4, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drasin, D.J.; Guarnieri, A.L.; Neelakantan, D.; Kim, J.; Cabrera, J.H.; Wang, C.-A.; Zaberezhnyy, V.; Gasparini, P.; Cascione, L.; Huebner, K.; et al. TWIST1-Induced MiR-424 Reversibly Drives Mesenchymal Programming While Inhibiting Tumor Initiation. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1908–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Wang, L. MiR-424-5p Participates in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Invasion and Metastasis via SMAD7 Pathway Mediated EMT. Diagn. Pathol. 2016, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Guo, P.; Kang, J.; Wei, Q.; Jia, X.; Zhao, W.; Huai, W.; Qiu, Y.; Sun, L.; et al. MiR-424-5p Reversed Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Anchorage-Independent HCC Cells by Directly Targeting ICAT and Suppressed HCC Progression. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, S.Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, J.-Y.; An, H.J. Clinical Impact of MicroRNAs Associated With Cancer Stem Cells as a Prognostic Factor in Ovarian Carcinoma. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 3538–3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Z. MiR-424-5p Promotes Proliferation of Gastric Cancer by Targeting Smad3 through TGF-β Signaling Pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 75185–75196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Hu, G.; He, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, J.; He, B.; Sun, W. MicroRNA-424-5p Suppresses the Expression of SOCS6 in Pancreatic Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 19, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellam, N.; Pasche, B. Tgf-Beta Signaling Alterations and Colon Cancer. Cancer Treat. Res. 2010, 155, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, W.B.; Yang, V.W. Mitotic Origins of Chromosomal Instability in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Colorectal Cancer Rep. 2007, 3, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koehler, B.C.; Jäger, D.; Schulze-Bergkamen, H. Targeting Cell Death Signaling in Colorectal Cancer: Current Strategies and Future Perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1923–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.J.M. Apoptosis and Colorectal Cancer. Gut 2004, 53, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.-M.; Wu, L.-J.; Xu, J.; Yang, R.; Wu, F.-S. Let-7c MicroRNA Expression and Clinical Significance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2011, 39, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyerinas, B.; Park, S.-M.; Hau, A.; Murmann, A.E.; Peter, M.E. The Role of Let-7 in Cell Differentiation and Cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2010, 17, F19–F36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Peng, D.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Huang, Q.; Lin, Z.; Xu, W.; Qian, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, T.; et al. MiR-215 Suppresses Proliferation and Migration of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2349–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.B.; Zhu, M.N.; Zhu, X.L. MiRNA-215-5p Suppresses the Aggressiveness of Breast Cancer Cells by Targeting Sox9. FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khoshnam, S.E.; Winlow, W.; Farzaneh, M. The Interplay of MicroRNAs in the Inflammatory Mechanisms Following Ischemic Stroke. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henn, D.; Abu-Halima, M.; Wermke, D.; Falkner, F.; Thomas, B.; Köpple, C.; Ludwig, N.; Schulte, M.; Brockmann, M.A.; Kim, Y.-J.; et al. MicroRNA-Regulated Pathways of Flow-Stimulated Angiogenesis and Vascular Remodeling in Vivo. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, G.K.; Goga, A.; Bhaumik, D.; Berger, C.E.; Sullivan, C.S.; Benz, C.C. Coordinate Suppression of ERBB2 and ERBB3 by Enforced Expression of Micro-RNA MiR-125a or MiR-125b. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 1479–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; So, A.Y.-L.; Sinha, N.; Gibson, W.S.J.; Taganov, K.D.; O’Connell, R.M.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-125b Potentiates Macrophage Activation. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5062–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, M.L.; Rios, E.; Durães, C.; Ribeiro, R.; Machado, J.C.; Mantovani, A.; Barbosa, M.A.; Carneiro, F.; Oliveira, M.J. The Two Faces of Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Their Clinical Significance in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.-B.; Zhang, X.-C.; Chen, P.; Ma, L.-M.; Shen, Z.-Q. MiR-378a-3p Inhibits Cellular Proliferation and Migration in Glioblastoma Multiforme by Targeting Tetraspanin 17. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 42, 1957–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois-Camacho, K.; Diaz-Jimenez, D.; De la Fuente, M.; Quera, R.; Simian, D.; Martínez, M.; Landskron, G.; Olivares-Morales, M.; Cidlowski, J.A.; Xu, X.; et al. Inhibition of MiR-378a-3p by Inflammation Enhances IL-33 Levels: A Novel Mechanism of Alarmin Modulation in Ulcerative Colitis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Li, S.-H.; Tian, Y.-X.; Zhu, Q.-Q.; Chen, G.; Pang, Y.-Y.; Hu, X.-H. Role of Downregulated MiR-133a-3p Expression in Bladder Cancer: A Bioinformatics Study. Onco Targets Ther. 2017, 10, 3667–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lei, C.; Du, F.; Sun, L.; Li, T.; Li, T.; Min, Y.; Nie, A.; Wang, X.; Geng, L.; Lu, Y.; et al. MiR-143 and MiR-145 Inhibit Gastric Cancer Cell Migration and Metastasis by Suppressing MYO6. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Nie, J.; Ma, X.; Wei, Y.; Peng, Y.; Wei, X. Targeting PI3K in Cancer: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Slattery, M.L.; Mullany, L.E.; Wolff, R.K.; Sakoda, L.C.; Samowitz, W.S.; Herrick, J.S. The P53-Signaling Pathway and Colorectal Cancer: Interactions between Downstream P53 Target Genes and MiRNAs. Genomics 2019, 111, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbicki, P.M.; Rybarczyk, A. The Hippo Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2015, 53, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.Y.; Gwak, J.W.; Shin, Y.C.; Moon, D.; Ahn, J.; Sol, H.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.; Shin, H.M.; Lee, K.H.; et al. Expression of Hippo Pathway Genes and Their Clinical Significance in Colon Adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4926–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, D.G. Molecular Pathways: Is AMPK a Friend or a Foe in Cancer? Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3836–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laissue, P. The Forkhead-Box Family of Transcription Factors: Key Molecular Players in Colorectal Cancer Pathogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, O.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.H.; Woo, Y.M.; Kang, J.-H.; Yoon, H.-G.; Bae, S.-K.; Songyang, Z.; Oh, S.H.; Choi, Y. Role of the Focal Adhesion Protein TRIM15 in Colon Cancer Development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1853, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, S.M.; Gulhati, P.; Rampy, B.A.; Han, Y.; Rychahou, P.G.; Doan, H.Q.; Weiss, H.L.; Evers, B.M. Novel Expression Patterns of PI3K/Akt/MTOR Signaling Pathway Components in Colorectal Cancer. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 210, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itatani, Y.; Kawada, K.; Sakai, Y. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer and Its Tumor Microenvironment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Gao, P. Toward Normalization of the Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1534735419862352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aran, D.; Camarda, R.; Odegaard, J.; Paik, H.; Oskotsky, B.; Krings, G.; Goga, A.; Sirota, M.; Butte, A.J. Comprehensive Analysis of Normal Adjacent to Tumor Transcriptomes. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Casbas-Hernandez, P.; Sun, X.; Roman-Perez, E.; D’Arcy, M.; Sandhu, R.; Hishida, A.; McNaughton, K.K.; Yang, X.R.; Makowski, L.; Sherman, M.E.; et al. Tumor Intrinsic Subtype Is Reflected in Cancer-Adjacent Tissue. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2015, 24, 406–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]











| Characteristics | Cases (n = 7) | Control (n = 7) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 60.86 ± 10.4 years | 51.85 ± 17.44 years |
| Sex (M/F) | 5 (71.43%)/2 (28.57%) | 3 (42.86%)/4 (57.14%) |
| Tumor grade (Intermediate) | 7 (100%) | - |
| Histological classification | ||
| Non-mucinous adenocarcinoma | 6 (85.71%) | - |
| Mucinous and non-mucinous adenocarcinoma | 1 (14.29%) | - |
| Inflammatory cell infiltrates (Yes) | 7 (100%) | - |
| Tumor budding | ||
| Yes | 1 (14.29%) | - |
| No/Not informed | 5 (71.43%)/1 (14.29%) | - |
| Depth of invasion | ||
| T1, T2 | 2 (28.57%) | - |
| T3, T4 | 4 (57.14%) | - |
| Tx | 1 (14.29%) | - |
| Lymph node involvement | ||
| N0/Nx | 4 (57.14%)/1 (14.29%) | - |
| N1, N2 | 2 (28.57%) | - |
| Distant metastasis | ||
| M0/Mx | 5 (71.43%)/1 (14.29%) | - |
| M1 | 1 (14.29%) | - |
| AJCC stage | ||
| Stage I/Stage II | 2 (28.57%)/1 (14.29%) | - |
| Stage III/Stage IV | 2 (28.57%)/1 (14.29%) | - |
| Unknown | 1 (14.29%) | - |
| Metastasis site (Liver/Not identified) | 1 (14.29%)/6 (85.71%) | - |
| Characteristics | TCGA—miRNA-Seq (n = 3) | TCGA—RNA-Seq (n = 13) | GTEx (n = 173) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 62.66 ± 20.42 years | 64.69 ± 14.51 years | Not informed |
| Sex (M/F) | 33.33%/66.67% | 53.85%/46.15% | 59.24%/40.46% |
| AJCC stage | |||
| Stage I/Stage II | 100% | 84.62% | - |
| Stage III/Stage IV | - | 15.38% | - |
| Unknown | - | - | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marques, D.; Ferreira-Costa, L.R.; Ferreira-Costa, L.L.; Bezerra-Oliveira, A.B.; Correa, R.d.S.; Ramos, C.C.d.O.; Vinasco-Sandoval, T.; Lopes, K.d.P.; Vialle, R.A.; Vidal, A.F.; et al. Role of miRNAs in Sigmoid Colon Cancer: A Search for Potential Biomarkers. Cancers 2020, 12, 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113311
Marques D, Ferreira-Costa LR, Ferreira-Costa LL, Bezerra-Oliveira AB, Correa RdS, Ramos CCdO, Vinasco-Sandoval T, Lopes KdP, Vialle RA, Vidal AF, et al. Role of miRNAs in Sigmoid Colon Cancer: A Search for Potential Biomarkers. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113311
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarques, Diego, Layse Raynara Ferreira-Costa, Lorenna Larissa Ferreira-Costa, Ana Beatriz Bezerra-Oliveira, Romualdo da Silva Correa, Carlos Cesar de Oliveira Ramos, Tatiana Vinasco-Sandoval, Katia de Paiva Lopes, Ricardo Assunção Vialle, Amanda Ferreira Vidal, and et al. 2020. "Role of miRNAs in Sigmoid Colon Cancer: A Search for Potential Biomarkers" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113311
APA StyleMarques, D., Ferreira-Costa, L. R., Ferreira-Costa, L. L., Bezerra-Oliveira, A. B., Correa, R. d. S., Ramos, C. C. d. O., Vinasco-Sandoval, T., Lopes, K. d. P., Vialle, R. A., Vidal, A. F., Silbiger, V. N., & Ribeiro-dos-Santos, Â. (2020). Role of miRNAs in Sigmoid Colon Cancer: A Search for Potential Biomarkers. Cancers, 12(11), 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113311







