Effect of Varying Expression of EpCAM on the Efficiency of CTCs Detection by SERS-Based Immunomagnetic Optofluidic Device
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Cells Cultivation and Preparation of Cell Suspensions
- (i).
- cultured in humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 at the 37 °C as the optimal temperature;
- (ii).
- trypsinized (0.05% trypsin, 0.02% EDTA (Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) solution);
- (iii).
- washed with PBS buffer to reach subconfluency (about 80%);
- (iv).
- finally, cells were collected by centrifugation for 5 min at room temperature at 250× g. The cell pellets were re-suspended in PBS to reach the concentration ca. 0.44 × 106 cells/mL and stored on ice.
2.2. Western Blotting of Cell Lysates
2.3. Immunocytochemistry
2.4. Immunoassay Protocol
2.5. Materials and Reagents
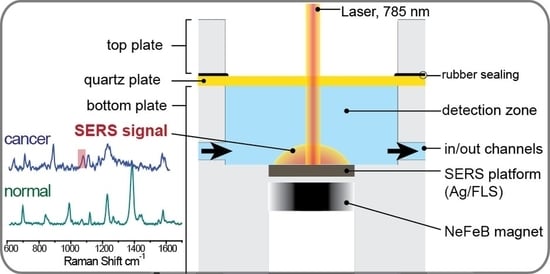
2.5.1. Design and Fabrication of a Microfluidic Chip
2.5.2. Lung Cancer Patients
2.5.3. Preparation of Ag@Fe2O3 Magnetic Nanoparticles
2.5.4. Preparation of the Raman Reporter-Labeled-Immune-Magnetic Nanoparticles (anti-EpCAM/Ag@Fe2O3/p-MBA)
2.5.5. Fabrication and Modification of SERS-Active Silicon Substrate
- (i).
- physical modification of the surface with femtosecond laser,
- (ii).
- sputtering of SERS-active metal layer, and
- (iii).
- chemical modification of the surface.
3. Equipment
3.1. Raman and SERS Measurements
3.2. SEM Measurements
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. EpCAM Expression in Selected Cancer Cell Lines
4.2. SERS-Based Detection Strategy
- (i).
- the first layer composed of anti-EpCAM antibodies captures on the SERS platform via lipoic acid (LA);
- (ii).
- the second layer is consisted of target cancer cell lines with relatively high (LNCaP), medium (PC3), weak (A549), and no EpCAM expressions (HeLa);
- (iii).
- the third layer is composed of the Raman reporter-labeled–immune-magnetic nanoparticles (anti-EpCAM/Ag@Fe2O3/p-MBA).
4.3. Capturing Substrate and Characterization of Raman Reporter-Labeled-Immune-Magnetic Nanoparticles
4.4. SERS Immunomagnetic Detection of CTC in Blood Plasma
4.5. Quantitative Analysis of Cancer Cells
4.6. SERS Immunomagnetic Detection of CTC in Blood from Patients with Metastatic Lung Cancer
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joosse, S.A.; Gorges, T.M.; Pantel, K. Biology, detection, and clinical implications of circulating tumor cells. EMBO Mol. Med. 2015, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pantel, K.; Brakenhoff, R.H.; Brandt, B. Detection, clinical relevance and specific biological properties of disseminating tumour cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehlen, P.; Puisieux, A. Metastasis: A question of life or death. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofanilli, M.; Budd, T.; Ellis, M.J.; Alison, S.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.; Reuben, J.M.; Gerald, D. Circulating Tumor Cells, Disease Progression, and Survival in Metastatic Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. Orig. 2012, 351, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, T.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, W.T.; Pearl, M.L. Clinical significance of circulating tumor cells detected by an invasion assay in peripheral blood of patients with ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2009, 112, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberti, P.A.; Rao, C.G.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Optimization of ferrofluids and protocols for the enrichment of breast tumor cells in blood. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2001, 225, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajba, L.; Guttman, A. Circulating tumor-cell detection and capture using microfluidic devices. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2014, 59, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jordan, N.V.; Bardia, A.; Wittner, B.S.; Benes, C.; Ligorio, M.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, M.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Licausi, J.A.; Desai, R.; et al. HER2 expression identifies dynamic functional states within circulating breast cancer cells. Nature 2016, 537, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murlidhar, V.; Zeinali, M.; Grabauskiene, S.; Ghannad-Rezaie, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Simeone, D.M.; Ramnath, N.; Reddy, R.M.; Nagrath, S. A radial flow microfluidic device for ultra-high-throughput affinity-based isolation of circulating tumor cells. Small 2014, 10, 4895–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bu, J.; Kang, Y.T.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, Y.H.; Chang, H.J.; Kim, H.; Moon, B.I.; Kim, H.G. Dual-patterned immunofiltration (DIF) device for the rapid efficient negative selection of heterogeneous circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4759–4769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamande, J.W.; Hupert, M.L.; Witek, M.A.; Wang, H.; Torphy, R.J.; Dharmasiri, U.; Njoroge, S.K.; Jackson, J.M.; Aufforth, R.D.; Snavely, A.; et al. Modular microsystem for the isolation, enumeration, and phenotyping of circulating tumor cells in patients with pancreatic cancer. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9092–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weissenstein, U.; Schumann, A.; Reif, M.; Link, S.; Toffol-Schmidt, U.D.; Heusser, P. Detection of circulating tumor cells in blood of metastatic breast cancer patients using a combination of cytokeratin and EpCAM antibodies. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, G.; Herrler, M.; Burgess, D.; Manna, E.; Krag, D.; Burke, J.F. Enrichment with anti-cytokeratin alone or combined with anti-EpCAM antibodies significantly increases the sensitivity for circulating tumor cell detection in metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paterlini-Brechot, P.; Benali, N.L. Circulating tumor cells (CTC) detection: Clinical impact and future directions. Cancer Lett. 2007, 253, 180–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleghorn, J.P.; Pratt, E.D.; Denning, D.; Liu, H.; Bander, N.H.; Tagawa, S.T.; Nanus, D.M.; Giannakakou, P.A.; Kirby, B.J. Capture of circulating tumor cells from whole blood of prostate cancer patients using geometrically enhanced differential immunocapture (GEDI) and a prostate-specific antibody. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thege, F.I.; Lannin, T.B.; Saha, T.N.; Tsai, S.; Kochman, M.L.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; Rhim, A.D.; Kirby, B.J. Microfluidic immunocapture of circulating pancreatic cells using parallel EpCAM and MUC1 capture: Characterization, optimization and downstream analysis. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 1775–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikolajczyk, S.D.; Millar, L.S.; Tsinberg, P.; Coutts, S.M.; Zomorrodi, M.; Pham, T.; Bischoff, F.Z.; Pircher, T.J. Detection of EpCAM-Negative and Cytokeratin-Negative Circulating Tumor Cells in Peripheral Blood. J. Oncol. 2011, 2011, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miltenyi, S.; Müller, W.; Weichel, W.; Radbruch, A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry 1990, 11, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riethdorf, S.; Fritsche, H.; Müller, V.; Rau, T.; Schindlbeck, C.; Rack, B.; Janni, W.; Coith, C.; Beck, K.; Jänicke, F.; et al. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of patients with metastatic breast cancer: A validation study of the cell search system. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhuvanendran Nair Gourikutty, S.; Chang, C.P.; Poenar, D.P. An integrated on-chip platform for negative enrichment of tumour cells. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1028, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.Y.; Tsai, S.C.; Hsieh, K.; Lee, G. Bin An integrated microfluidic platform for negative selection and enrichment of cancer cells. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2015, 25, 084007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wen, C.-Y.; Wu, L.-L.; Hong, S.-L.; Hu, J.; Xu, C.-M.; Pang, D.-W.; Zhang, Z.-L. A chip assisted immunomagnetic separation system for the efficient capture and in situ identification of circulating tumor cells. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Feng, X.; Hu, R.; Sun, J.; Du, W.; Liu, B.F. Hydrodynamic gating valve for microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 663, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.M.; Tu, E.; Raymond, D.E.; Yang, J.M.; Zhang, H.; Hagen, N.; Dees, B.; Mercer, E.M.; Forster, A.H.; Kariv, I.; et al. Microfluidic sorting of mammalian cells by optical force switching. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vona, G.; Sabile, A.; Louha, M.; Sitruk, V.; Romana, S.; Schütze, K.; Capron, F.; Franco, D.; Pazzagli, M.; Vekemans, M.; et al. Isolation by Size of Epithelial Tumor Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.L.; Zhu, P.; Makarova, O.V.; Martin, S.S.; Charpentier, M.; Chumsri, S.; Li, S.; Amstutz, P.; Tang, C.M. The systematic study of circulating tumor cell isolation using lithographic microfilters. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 4334–4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarioglu, A.F.; Aceto, N.; Kojic, N.; Donaldson, M.C.; Zeinali, M.; Hamza, B.; Engstrom, A.; Zhu, H.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Miyamoto, D.T.; et al. A microfluidic device for label-free, physical capture of circulating tumor cell clusters. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 685–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Park, S.; Duffy, S.P.; Matthews, K.; Ang, R.R.; Todenhöfer, T.; Abdi, H.; Azad, A.; Bazov, J.; Chi, K.N.; et al. Size and deformability based separation of circulating tumor cells from castrate resistant prostate cancer patients using resettable cell traps. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2278–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamińska, A.; Szymborski, T.; Witkowska, E.; Kijeńska-Gawrońska, E.; Świeszkowski, W.; Niciński, K.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Girstun, A. Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Membrane-Based SERS Platform: A New Diagnostic Approach for ‘Liquid Biopsy’. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gascoyne, P.R.C.; Wang, X.B.; Huang, Y.; Becker, R.F. Dielectrophoretic separation of cancer cells from blood. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 1997, 33, 670–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sano, M.B.; Caldwell, J.L.; Davalos, R.V. Modeling and development of a low frequency contactless dielectrophoresis (cDEP) platform to sort cancer cells from dilute whole blood samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 30, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, S.; Stemke-Hale, K.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Noshari, J.; Anderson, T.E.; Gascoyne, P.R.C. Antibody-independent isolation of circulating tumor cells by continuous-flow dielectrophoresis. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, X.; Peng, Z.; Lin, S.-C.S.; Geri, M.; Li, S.; Li, P.; Chen, Y.; Dao, M.; Suresh, S.; Huang, T.J. Cell separation using tilted-angle standing surface acoustic waves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12992–12997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Antfolk, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Kaneda, S.; Laurell, T.; Fujii, T. Highly efficient single cell arraying by integrating acoustophoretic cell pre-concentration and dielectrophoretic cell trapping. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 4356–4363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iranmanesh, I.; Ramachandraiah, H.; Russom, A.; Wiklund, M. On-chip ultrasonic sample preparation for cell based assays. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 74304–74311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard Huang, L.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. REPORTS Continuous Particle Separation Through Deterministic Lateral Displacement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 84, 3967. [Google Scholar]
- Ozkumur, E.; Shah, A.M.; Ciciliano, J.C.; Emmink, B.L.; Miyamoto, D.T.; Brachtel, E.; Yu, M.; Chen, P.; Morgan, B.; Trautwein, J.; et al. Inertial focusing for tumor antigen-dependent and -independent sorting of rare circulating tumor cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 179ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coumans, F.A.W.; van Dalum, G.; Beck, M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Filter Characteristics Influencing Circulating Tumor Cell Enrichment from Whole Blood. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, S.; Lin, H.; Liu, J.Q.; Balic, M.; Datar, R.; Cote, R.J.; Tai, Y.C. Membrane microfilter device for selective capture, electrolysis and genomic analysis of human circulating tumor cells. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1162, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, W.; Fan, A.; Tran, T.; Danila, D.C.; Keys, D.; Schwartz, M.; Ionescu-Zanetti, C. Mutational Analysis of Circulating Tumor Cells Using a Novel Microfluidic Collection Device and qPCR Assay. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 528–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sajay, B.N.G.; Chang, C.P.; Ahmad, H.; Khuntontong, P.; Wong, C.C.; Wang, Z.; Puiu, P.D.; Soo, R.; Rahman, A.R.A. Microfluidic platform for negative enrichment of circulating tumor cells. Biomed. Microdevices 2014, 16, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Albuquerque, A.; Kaul, S.; Breier, G.; Krabisch, P.; Fersis, N. Multimarker analysis of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood of metastatic breast cancer patients: A step forward in personalized medicine. Breast Care 2012, 7, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gossett, D.R.; Weaver, W.M.; Mach, A.J.; Hur, S.C.; Tse, H.T.K.; Lee, W.; Amini, H.; Di Carlo, D. Label-free cell separation and sorting in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3249–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winer-Jones, J.P.; Vahidi, B.; Arquilevich, N.; Fang, C.; Ferguson, S.; Harkins, D.; Hill, C.; Klem, E.; Pagano, P.C.; Peasley, C.; et al. Circulating tumor cells: Clinically relevant molecular access based on a novel CTC flow cell. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talasaz, A.H.; Powell, A.A.; Huber, D.E.; Berbee, J.G.; Roh, K.-H.; Yu, W.; Xiao, W.; Davis, M.M.; Pease, R.F.; Mindrinos, M.N.; et al. Isolating highly enriched populations of circulating epithelial cells and other rare cells from blood using a magnetic sweeper device. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3970–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Lin, L.; Yang, W.; Xu, J. Enrichment and enumeration of circulating tumor cells by efficient depletion of leukocyte fractions. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2014, 52, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J.; Matera, J.; Miller, M.C.; Repollet, M.; Connelly, M.C.; Rao, C.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Uhr, J.W.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Tumor Cells Circulate in the Peripheral Blood of All Major Carcinomas but not in Healthy Subjects or Patients With Nonmalignant Diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Oh, J.H.; Namkoong, K.; Lee, J.G.; Park, J.M.; Lee, S.S.; Huh, N.; Choi, J.W. Simultaneous capture and in situ analysis of circulating tumor cells using multiple hybrid nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 47, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, D.; Arkenau, H.T.; Ang, J.E.; Ledaki, I.; Attard, G.; Carden, C.P.; Reid, A.H.M.; A’Hern, R.; Fong, P.C.; Oomen, N.B.; et al. Circulating tumour cell (CTC) counts as intermediate end points in castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC): A single-centre experience. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.J.; Punt, C.J.A.; Iannotti, N.; Saidman, B.H.; Sabbath, K.D.; Gabrail, N.Y.; Picus, J.; Morse, M.A.; Mitchell, E.; Miller, M.C.; et al. Prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Wang, C.; Xiao, R.; Sun, Z. Dual-Selective and Dual-Enhanced SERS Nanoprobes Strategy for Circulating Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells Detection. Chem. A Eur. J. 2018, 24, 7060–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhang, R.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X. Novel nitrocellulose membrane substrate for efficient analysis of circulating tumor cells coupled with surface-enhanced raman scattering imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Qian, X.; Beitler, J.J.; Chen, Z.G.; Khuri, F.R.; Lewis, M.M.; Shin, H.J.C.; Nie, S.; Shin, D.M. Detection of circulating tumor cells in human peripheral blood using surface-enhanced raman scattering nanoparticles. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Luo, L.; Yang, S.; Ma, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, C.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Wu, A. Improved SERS nanoparticles for direct detection of circulating tumor cells in the blood. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9965–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, M.Y.; Xu, H.; Natan, M.J.; Cromer, R. SERS Tags for Rapid and Homogeneous Detection of Circulating Tumor Cells in the Presence of Human Whole Blood. J. Am Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 17214–17215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, W.; Paproski, R.J.; Moore, R.; Zemp, R. Detection of circulating tumor cells using targeted surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoparticles and magnetic enrichment. J. Biomed. Opt. 2014, 19, 056014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Choi, N.; Wang, R.; Lee, S.; Moon, K.C.; Yoon, S.Y.; Chen, L.; Choo, J. Simultaneous Detection of Dual Prostate Specific Antigens Using Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering-Based Immunoassay for Accurate Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 4926–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Cheng, Z.; Demello, A.J.; Choo, J. Wash-free magnetic immunoassay of the PSA cancer marker using SERS and droplet microfluidics. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Min, L.; Zhou, N.; Yang, Y.; Su, S.; Huang, W.; Wang, L. Synthesis of novel gold mesoflowers as SERS tags for immunoassay with improved sensitivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 21842–21850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, Y. Facile detection of tumor-derived exosomes using magnetic nanobeads and SERS nanoprobes. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5001–5008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zong, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, N.; Li, L.; Lu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B.; Cui, Y. Screening and multiple detection of cancer exosomes using an SERS-based method. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9053–9062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwizera, E.A.; O’Connor, R.; Vinduska, V.; Williams, M.; Butch, E.R.; Snyder, S.E.; Chen, X.; Huang, X. Molecular detection and analysis of exosomes using surface-enhanced Raman scattering gold nanorods and a miniaturized device. Theranostics 2018, 8, 2722–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Klotzek, S.; Lewandowski, M.; Fleischhacker, M.; Jung, K. Changes in concentration of DNA in serum and plasma during storage of blood samples. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qin, Z.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Zhou, C.; Tong, Y.; Liang, J. Cell-free circulating tumor DNA in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wee, E.J.H.; Wang, Y.; Tsao, S.C.H.; Trau, M. Simple, sensitive and accurate multiplex detection of clinically important melanoma DNA mutations in circulating tumour DNA with SERS nanotags. Theranostics 2016, 6, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armand-Labit, V.; Pradines, A. Circulating cell-free microRNAs as clinical cancer biomarkers. Biomol. Concepts 2017, 8, 61–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, J.D.; Seto, A.G.; Jones, L.P.; Jokela, S.; Dluhy, R.A.; Zhao, Y.P.; Tripp, R.A. Rapid microRNA (miRNA) detection and classification via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 24, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, J.; Primera-Pedrozo, O.M.; Dluhy, R.A.; Zhao, Y.; Tripp, R.A. Quantitative surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy based analysis of microRNA mixtures. Appl. Spectrosc. 2009, 63, 1107–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abell, J.L.; Garren, J.M.; Driskell, J.D.; Tripp, R.A.; Zhao, Y. Label-free detection of micro-RNA hybridization using surface-enhanced raman spectroscopy and least-squares analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 12889–12892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Frontiera, R.R.; Henry, A.I.; Ringe, E.; Van Duyne, R.P. SERS: Materials, applications, and the future. Mater. Today 2012, 15, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischmann, M.; Hendra, P.J.; McQuillan, A.J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1974, 26, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Wang, J.; Hutchison, J.A.; Ma, L.; Zhang, N.; Guo, H.; Hu, Z.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y. Ultrasensitive, multiplex Raman frequency shift immunoassay of liver cancer biomarkers in physiological media. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Ren, J.Q.; Shen, A.G.; Hu, J.M. Splicing Nanoparticles-Based ‘click’ SERS Could Aid Multiplex Liquid Biopsy and Accurate Cellular Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 10649–10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, S.C.H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Behren, A.; Cebon, J.; Trau, M. Characterising the phenotypic evolution of circulating tumour cells during treatment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itzkan, I.; Dasari, R.R.; Feld, M.S.; Kneipp, K.; Kneipp, H. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering and biophysics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2002, 14, R597–R624. [Google Scholar]
- Kusnezow, W.; Hoheisel, J.D. Solid supports for microarray immunoassays. J. Mol. Recognit. 2003, 16, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szymborski, T.; Stepanenko, Y.; Piecyk, P.; Nicinski, K.; Kamińska, A. Polish Patent Application: Sposób Wytwarzania Platformy Krzemowej do Pomiarów Metodą SERS, Platforma Krzemowa do Pomiarów Metodą SERS oraz Zastosowanie Platformy Krzemowej do Pomiarów Metodą SERS Próbek Biologicznych albo Związków Chemicznych; Polish Patent Office: Warsaw, Poland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Trzpis, M.; McLaughlin, P.M.J.; De Leij, L.M.F.H.; Harmsen, M.C. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule: More than a carcinoma marker and adhesion molecule. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 386–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schnell, U.; Cirulli, V.; Giepmans, B.N.G. EpCAM: Structure and function in health and disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Biomembr. 2013, 1828, 1989–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Yang, Y.; Yang, F.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Lei, Z.; Guo, J. Functions of EpCAM in physiological processes and diseases (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1771–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ni, J.; Lipert, R.J.; Dawson, G.B.; Porter, M.D. Immunoassay readout method using extrinsic raman labels adsorbed on immunogold colloids. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 4903–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, D.A.; Haes, A.J.; McFarland, A.D.; Nie, S.; Van Duyne, R.P. Refractive-index-sensitive, plasmon-resonant-scattering, and surface-enhanced Raman-scattering nanoparticles and arrays as biological sensing platforms. Plasmon. Biol. Med. 2004, 5327, 60. [Google Scholar]
- Lutz, B.R.; Dentinger, C.E.; Nguyen, L.N.; Sun, L.; Zhang, J.; April, N.; Chan, S.; Knudsen, B.S. Spectral analysis of multiplex Raman probe signatures. ACS Nano 2009, 2, 2306–2314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salehi, M.; Steinigeweg, D.; Ströbel, P.; Marx, A.; Packeisen, J.; Schlücker, S. Rapid immuno-SERS microscopy for tissue imaging with single-nanoparticle sensitivity. J. Biophotonics 2013, 6, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlücker, S.; Salehi, M.; Bergner, G.; Schütz, M.; Ströbel, P.; Marx, A.; Petersen, I.; Dietzek, B.; Popp, J. Immuno-surface-enhanced coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopy: Immunohistochemistry with target-specific metallic nanoprobes and nonlinear Raman microscopy. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7081–7085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Jeevanandam, P. A facile synthesis of multifunctional iron oxide@Ag core-shell nanoparticles and their catalytic applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 2013, 6126–6136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, V.; Crisa, L.; Beattie, G.M.; Mally, M.I.; Lopez, A.D.; Fannon, A.; Ptasznik, A.; Inverardi, L.; Ricordi, C.; Deerinck, T.; et al. KSA antigen Ep-CAM mediates cell-cell adhesion of pancreatic epithelial cells: Morphoregulatory roles in pancreatic islet development. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 140, 1519–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patriarca, C.; Macchi, R.M.; Marschner, A.K.; Mellstedt, H. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule expression (CD326) in cancer: A short review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.H.; Sun, R.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhang, M.Y.; Lu, J.B.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, L.S.; Yang, X.Z.; Shi, L.; Xiao, R.W.; et al. Epithelial cell adhesion molecule overexpression regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells via the PTEN/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Wit, S.; Van Dalum, G.; Lenferink, A.T.M.; Tibbe, A.G.J.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Groen, H.J.M.; Van Rijn, C.J.M.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. The detection of EpCAM+ and EpCAM− circulating tumor cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Krebs, M.G.; Sloane, R.; Priest, L.; Lancashire, L.; Hou, J.M.; Greystoke, A.; Ward, T.H.; Ferraldeschi, R.; Hughes, A.; Clack, G.; et al. Evaluation and prognostic significance of circulating tumor cells in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1556–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiltermann, T.J.N.; Pore, M.M.; Van den Berg, A.; Timens, W.; Boezen, H.M.; Liesker, J.J.W.; Schouwink, J.H.; Wijnands, W.J.A.; Kerner, G.S.M.A.; Kruyt, F.A.E.; et al. Circulating tumor cells in small-cell lung cancer: A predictive and prognostic factor. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 2937–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.C.; Doyle, G.V.; Terstappen, L.W.M.M. Significance of Circulating Tumor Cells Detected by the CellSearch System in Patients with Metastatic Breast Colorectal and Prostate Cancer. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmelzer, E.; Zhang, L.; Bruce, A.; Wauthier, E.; Ludlow, J.; Yao, H.L.; Moss, N.; Melhem, A.; McClelland, R.; Turner, W.; et al. Human hepatic stem cells from fetal and postnatal donors. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1973–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uhlen, M.; Zhang, C.; Lee, S.; Sjöstedt, E.; Fagerberg, L.; Bidkhori, G.; Benfeitas, R.; Arif, M.; Liu, Z.; Edfors, F.; et al. A pathology atlas of the human cancer transcriptome. Science 2017, 357, eaan2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heine, M.; Freund, B.; Nielsen, P.; Jung, C.; Reimer, R.; Hohenberg, H.; Zangemeister-Wittke, U.; Wester, H.J.; Lüers, G.H.; Schumacher, U. High interstitial fluid pressure is associated with low tumour penetration of diagnostic monoclonal antibodies applied for molecular imaging purposes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Solomon, S.D.; Bahadory, M.; Jeyarajasingam, A.V.; Rutkowsky, S.A.; Boritz, C.; Mulfinger, L. Synthesis and study of silver nanoparticles. J. Chem. Educ. 2007, 84, 322–325. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, A.; Janghorban, K.; Hashemi, B.; Bonavita, A.; Bonyani, M.; Leonardi, S.G.; Neri, G. Synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties of ag@α-Fe2O3 core-shell nanocomposites. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dizaji, A.N.; Yilmaz, M.; Piskin, E. Silver or gold deposition onto magnetite nanoparticles by using plant extracts as reducing and stabilizing agents. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2016, 44, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, J.Q.; Vinckier, C.; Hendriks, J.; Coenegrachts, J. Production of carbon dioxide in a fattening pig house under field conditions. II. Release from the manure. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 3697–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudelski, A. Structures of monolayers formed from different HS-(CH2) 2-X thiols on gold, silver and copper: Comparitive studies by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Lord, R.C. Laser-Excited Raman Spectroscopy of Biomolecules. VI. Polypeptides as Conformational Models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1974, 96, 4750–4752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rygula, A.; Majzner, K.; Marzec, K.M.; Kaczor, A.; Pilarczyk, M.; Baranska, M. Raman spectroscopy of proteins: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2013, 44, 1061–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michota, A.; Bukowska, J. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) of 4-mercaptobenzoic acid on silver and gold substrates. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2003, 34, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, A.; Gupta, V. Methods for the determination of limit of detection and limit of quantitation of the analytical methods. Chronicles Young Sci. 2011, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draga, R.O.P.; Grimbergen, M.C.M.; Vijverberg, P.L.M.; Swol, C.F.P.V.; Jonges, T.G.N.; Kummer, J.A.; Ruud Bosch, J.L.H. In vivo bladder cancer diagnosis by high-volume Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5993–5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Type of Cancer Cell | LOD Calculated via Immune SERS Assay | Intensity of Marker Band at 1078 cm−1 for 100 CTC in Blood Samples in cps (Count per Second) for 100 CTCs in 1 mL of Blood | Relative EpCAM Expression Estimated via Western Blot Method, See Figure 1A |
|---|---|---|---|
| LNCaP | 1 | 9453 | 1.000 |
| PC3 | 3 | 3612 | 0.320 |
| A549 | 4 | 2570 | 0.014 |
| HeLA | 0 | 140 | 0 |
| SERS Immune Assay Sensitivity (CTC in 5 mL of Blood Plasma) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample Number | Metastatic Lung Cancer Patients (5 Samples) | Healthy Patients (5 Samples) |
| Sample #1 | 13 | 0 |
| Sample #2 | 6 | 0 |
| Sample #3 | 8 | 3 |
| Sample #4 | 5 | 0 |
| Sample #5 | 6 | 0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Czaplicka, M.; Niciński, K.; Nowicka, A.; Szymborski, T.; Chmielewska, I.; Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J.; Girstun, A.; Kamińska, A. Effect of Varying Expression of EpCAM on the Efficiency of CTCs Detection by SERS-Based Immunomagnetic Optofluidic Device. Cancers 2020, 12, 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113315
Czaplicka M, Niciński K, Nowicka A, Szymborski T, Chmielewska I, Trzcińska-Danielewicz J, Girstun A, Kamińska A. Effect of Varying Expression of EpCAM on the Efficiency of CTCs Detection by SERS-Based Immunomagnetic Optofluidic Device. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113315
Chicago/Turabian StyleCzaplicka, Marta, Krzysztof Niciński, Ariadna Nowicka, Tomasz Szymborski, Izabela Chmielewska, Joanna Trzcińska-Danielewicz, Agnieszka Girstun, and Agnieszka Kamińska. 2020. "Effect of Varying Expression of EpCAM on the Efficiency of CTCs Detection by SERS-Based Immunomagnetic Optofluidic Device" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113315
APA StyleCzaplicka, M., Niciński, K., Nowicka, A., Szymborski, T., Chmielewska, I., Trzcińska-Danielewicz, J., Girstun, A., & Kamińska, A. (2020). Effect of Varying Expression of EpCAM on the Efficiency of CTCs Detection by SERS-Based Immunomagnetic Optofluidic Device. Cancers, 12(11), 3315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113315