The Polemic Diagnostic Role of TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies from Breast, Colon and Lung Cancers
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
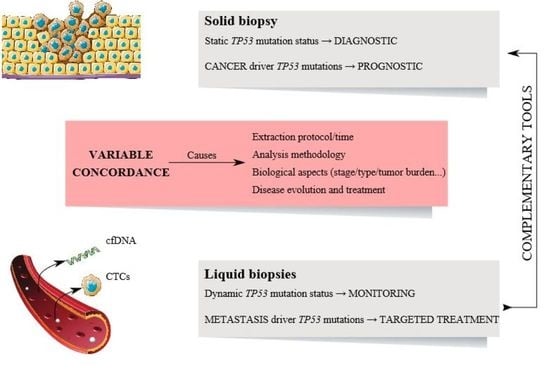
2. Variability of TP53 Status between Liquid and Solid Biopsies
2.1. Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) and Tissue Correlation
2.2. Circulating Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA) and Tissue Correlations
3. Correlation of TP53 Status between CTCS and cfDNA
4. Clinical Utility of TP53 Mutation Identification in Liquid Biopsies
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mantovani, F.; Collavin, L.; Del Sal, G. Mutant p53 as a guardian of the cancer cell. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Tong, J.H.M.; Chan, A.W.H.; Yu, J.; Kang, W.; To, K.F. Targeting the Oncogenic p53 Mutants in Colorectal Cancer and Other Solid Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Wang, A.; Wang, J.; He, Z.; Mao, Y.; Liu, L. Target-based genomic profiling of ctDNA from Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients: A result of real-world data. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 146, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, A.J.; Jaiswal, S. Clonal Hematopoiesis: Pre-Cancer PLUS; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Volume 141, pp. 85–128. [Google Scholar]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, G.S.S.M.A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Huang, T.; Cheng, F.; Huang, K.; Liu, M.; He, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, S.; et al. Monitoring colorectal cancer following surgery using plasma circulating tumor DNA. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 4365–4375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savli, H.; Sertdemir, N.; Aydin, D.; Dursun, B.; Kurtas, O.; Reka, S.; Sunnetci-Akkoyunlu, D.; Eren-Keskin, S.; Uygun, K.; Ozden, E.; et al. TP53, EGFR and PIK3CA gene variations observed as prominent biomarkers in breast and lung cancer by plasma cell-free DNA genomic testing. J. Biotechnol. 2019, 300, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Khan, Z.; Jonas, S.K.; Le-Marer, N.; Patel, H.; Wharton, R.Q.; Tarragona, A.; Ivison, A.; Allen-Mersh, T.G. P53 mutations in primary and metastatic tumors and circulating tumor cells from colorectal carcinoma patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 3499–3504. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.A.; Guttery, D.S.; Hills, A.; Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Page, K.; Rosales, B.M.; Goddard, K.S.; Hastings, R.K.; Luo, J.; Ogle, O.; et al. Faculty Opinions recommendation of Mutation Analysis of Cell-Free DNA and Single Circulating Tumor Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients with High Circulating Tumor Cell Counts. Fac. Opin. Post-Publ. Peer Rev. Biomed. Lit. 2017, 23, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammesheidt, A.; Chen, A.; Braunstein, G.; Anselmo, M.; Jaboni, J.; Viloria, F.; Neidich, J.; Li, X. Mutation detection with a liquid biopsy 96 mutation assay in cancer patients and healthy donors. Cancer Transl. Med. 2017, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Shi, J.; Schmidt, B.; Liu, Q.; Shi, G.; Xu, X.; Liu, C.; Gao, Z.; Guo, T.; Shan, B. Circulating Tumor Cells as a Biomarker to Assist Molecular Diagnosis for Early Stage Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, R.; Wang, M.; Zhu, X.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, A.; Yao, H. Therapeutic effects of lenvatinib in combination with rAd-p53 for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6573–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allard, W.J. Tumor Cells Circulate in the Peripheral Blood of All Major Carcinomas but not in Healthy Subjects or Patients With Nonmalignant Diseases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6897–6904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dawood, S.; Broglio, K.; Valero, V.; Reuben, J.; Handy, B.; Islam, R.; Jackson, S.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Fritsche, H.; Cristofanilli, M. Circulating tumor cells in metastatic breast cancer. Cancer 2008, 113, 2422–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, L.; Han, L.; Tuo, X.; Ma, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X.; Liang, D.; Sun, C.; Wang, Q.; et al. The Discordance of Gene Mutations between Circulating Tumor Cells and Primary/Metastatic Tumor. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2019, 15, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinert, G.; Schölch, S.; Niemietz, T.; Iwata, N.; García, S.A.; Behrens, B.; Voigt, A.; Kloor, M.; Benner, A.; Bork, U.; et al. Immune Escape and Survival Mechanisms in Circulating Tumor Cells of Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navas, M.C.G.; Pérez, D.D.M.; Exposito-Hernandez, J.; Bayarri-Lara, C.I.; Amezcua, V.; Ortigosa, A.; Valdivia, J.; Guerrero, R.; Puche, J.L.G.; Lorente, J.A.; et al. Cooperative and Escaping Mechanisms between Circulating Tumor Cells and Blood Constituents. Cells 2019, 8, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez, S.V.; Bingham, C.; Fittipaldi, P.; Austin, L.; Palazzo, J.; Palmer, G.; Alpaugh, R.K.; Cristofanilli, M. TP53 mutations detected in circulating tumor cells present in the blood of metastatic triple negative breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pailler, E.; Faugeroux, V.; Oulhen, M.; Mezquita, L.; Laporte, M.; Honoré, A.; Lecluse, Y.; Queffelec, P.; Ngo-Camus, M.; Nicotra, C.; et al. Acquired Resistance Mutations to ALK Inhibitors Identified by Single Circulating Tumor Cell Sequencing in ALK-Rearranged Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 6671–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Choi, S.H.; Ahn, S.H.; Son, B.H.; Lee, J.W.; Yu, J.H.; Kwon, N.-J.; Lee, W.C.; Yang, K.-S.; et al. Evaluation of a novel approach to circulating tumor cell isolation for cancer gene panel analysis in patients with breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 3025–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maheswaran, S.; Sequist, L.V.; Nagrath, S.; Ulkus, L.; Brannigan, B.; Collura, C.V.; Inserra, E.; Diederichs, S.; Iafrate, A.J.; Bell, D.W.; et al. Detection of Mutations inEGFRin Circulating Lung-Cancer Cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettegowda, C.; Sausen, M.; Leary, R.J.; Kinde, I.; Wang, Y.; Agrawal, N.; Bartlett, B.R.; Wang, H.; Luber, B.; Alani, R.M.; et al. Detection of Circulating Tumor DNA in Early- and Late-Stage Human Malignancies. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 224ra24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, G.; Mu, Z.; Rademaker, A.W.; Austin, L.; Strickland, K.S.; Costa, R.L.B.; Nagy, R.J.; Zagonel, V.; Taxter, T.J.; Behdad, A.; et al. Cell-Free DNA and Circulating Tumor Cells: Comprehensive Liquid Biopsy Analysis in Advanced Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 24, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shibayama, T.; Low, S.-K.; Ono, M.; Kobayashi, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Fukada, I.; Ito, Y.; Ueno, T.; Ohno, S.; Nakamura, Y.; et al. Clinical significance of gene mutation in ctDNA analysis for hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Wang, D.; Jin, L.; Yao, H.-W.; Zhang, J.-H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, X.-M.; Shen, C.-Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, X.-L.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA detectable in early- and late-stage colorectal cancer patients. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Tian, Z.; Liu, Q.; Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Min, L.; Shan, B. Detection of cancer specific mutations in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer using cell-free DNA by targeted sequencing. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 2351–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Snyder, M.W.; Kircher, M.; Hill, A.J.; Daza, R.M.; Shendure, J. Cell-free DNA Comprises an In Vivo Nucleosome Footprint that Informs Its Tissues-Of-Origin. Cell 2016, 164, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bronkhorst, A.J.; Ungerer, V.; Holdenrieder, S. The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. Biomol. Detect. Quantif. 2019, 17, 100087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Cuesta, L.; Perdomo, S.; Avogbe, P.H.; Leblay, N.; Delhomme, T.M.; Gaborieau, V.; Abedi-Ardekani, B.; Chanudet, E.; Olivier, M.; Zaridze, D.; et al. Identification of Circulating Tumor DNA for the Early Detection of Small-cell Lung Cancer. EBioMedicine 2016, 10, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bingham, C.; Fernandez, S.V.; Fittipaldi, P.; Dempsey, P.W.; Ruth, K.J.; Cristofanilli, M.; Alpaugh, R.K. Mutational studies on single circulating tumor cells isolated from the blood of inflammatory breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 163, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, A.; Chen, X. Current detection technologies for circulating tumor cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 2038–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Oronzo, S.; Lovero, D.; Palmirotta, R.; Stucci, L.S.; Tucci, M.; Felici, C.; Cascardi, E.; Giardina, C.; Cafforio, P.; Silvestris, F. Dissection of major cancer gene variants in subsets of circulating tumor cells in advanced breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, A.M.; Ross, J.S.; Fletcher, J.A. Tumor Suppressor Genes in Breast Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2005, 124, S16–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Fulton, R.S.; McLellan, M.D.; Schmidt, H.; Kalicki-Veizer, J.; McMichael, J.F.; Fulton, L.L.; Dooling, D.J.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; et al. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mu, Z.; Benali-Furet, N.; Uzan, G.; Znaty, A.; Ye, Z.; Paolillo, C.; Wang, C.; Austin, L.; Rossi, G.; Fortina, P.; et al. Detection and Characterization of Circulating Tumor Associated Cells in Metastatic Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapeleris, J.; Kulasinghe, A.; Warkiani, M.E.; Vela, I.; Kenny, L.; O’Byrne, K.; Punyadeera, C. The Prognostic Role of Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) in Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Shiratsuchi, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, G.; Reddy, R.M.; Azizi, E.; Fouladdel, S.; Chang, A.C.; Lin, L.; Jiang, H.; et al. Expansion of CTCs from early stage lung cancer patients using a microfluidic co-culture model. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 12383–12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Janku, F.; Zhang, S.; Waters, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, H.J.; Subbiah, V.; Hong, D.S.; Karp, D.D.; Fu, S.; Cai, X.; et al. Development and Validation of an Ultradeep Next-Generation Sequencing Assay for Testing of Plasma Cell-Free DNA from Patients with Advanced Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5648–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jahangiri, L.; Hurst, T.P. Assessing the Concordance of Genomic Alterations between Circulating-Free DNA and Tumour Tissue in Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shatsky, R.; Parker, B.A.; Bui, N.Q.; Helsten, T.; Schwab, R.B.; Boles, S.G.; Kurzrock, R. Next-Generation Sequencing of Tissue and Circulating Tumor DNA: The UC San Diego Moores Center for Personalized Cancer Therapy Experience with Breast Malignancies. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alborelli, I.; Generali, D.; Jermann, P.; Cappelletti, M.R.; Ferrero, G.; Scaggiante, B.; Bortul, M.; Zanconati, F.; Nicolet, S.; Haegele, J.; et al. Cell-free DNA analysis in healthy individuals by next-generation sequencing: A proof of concept and technical validation study. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Jeong, H.; Choi, J.-W.; Oh, H.E.; Kim, Y.-S. Liquid biopsy prediction of axillary lymph node metastasis, cancer recurrence, and patient survival in breast cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e12862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, C.; Peng, R.; Sun, C. Accuracy of analysis of cfDNA for detection of single nucleotide variants and copy number variants in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, B.J.; Córdoba, G.D.; Aranda, A.G.; Alvarez, M.; Vicioso, L.; Pérez, C.L.; Hernando, C.; Bermejo, B.; Parreño, A.J.; Lluch, A.; et al. Detection of TP53 and PIK3CA Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA Using Next-Generation Sequencing in the Screening Process for Early Breast Cancer Diagnosis. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maxwell, K.N.; Soucier-Ernst, D.; Tahirovic, E.; Troxel, A.B.; Clark, C.; Feldman, M.; Colameco, C.; Kakrecha, B.; Langer, M.; Lieberman, D.; et al. Comparative clinical utility of tumor genomic testing and cell-free DNA in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 164, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delmonico, L.; Costa, M.M.; Fournier, M.V.; Romano, S.D.O.; Nascimento, C.M.D.; Barbosa, A.S.; Moreira, A.D.S.; Scherrer, L.R.; Ornellas, M.H.F.; Alves, G. Mutation profiling in the PIK3CA, TP53, and CDKN2A genes in circulating free DNA and impalpable breast lesions. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2019, 39, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaederle, M.; Husain, H.; Fanta, P.T.; Piccioni, D.E.; Kesari, S.; Schwab, R.B.; Banks, K.C.; Lanman, R.B.; Talasaz, A.; Parker, B.A.; et al. Detection rate of actionable mutations in diverse cancers using a biopsy-free (blood) circulating tumor cell DNA assay. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9707–9717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidard, F.-C.; Madic, J.; Kiialainen, A.; Birzele, F.; Ramey, G.; Leroy, Q.; Frio, T.R.; Raynal, V.; Bernard, V.; Lermine, A.; et al. Abstract PD3-8: Circulating tumor DNA and circulating tumor cells in metastatic triple negative breast cancer patients. Poster Discuss. Abstr. 2015, 136, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.-Y.; Xie, N.; Tian, C.; Yang, X.; Liu, L.; Li, J.; Xiao, H.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Gao, J.; et al. Identifying Circulating Tumor DNA Mutation Profiles in Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients with Multiline Resistance. EBioMedicine 2018, 32, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liang, D.; Patel, A.; Ensor, J.; Patel, T.; Chang, J.; Rodriguez, A. Abstract P6-03-05: Cell-free DNA as molecular tool for monitoring disease progression and response to therapy in breast cancer patients. Poster Sess. Abstr. 2016, 76, P6–03. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, Y.K.; Davis, A.A.; Jain, S.; Santa-Maria, C.; Flaum, L.; Beaubier, N.; Platanias, L.C.; Gradishar, W.; Giles, F.J.; Cristofanilli, M. Concordance of Genomic Alterations by Next-Generation Sequencing in Tumor Tissue versus Circulating Tumor DNA in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 1412–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.-Y.; Hsieh, J.-S.; Chang, M.-Y.; Huang, T.-J.; Chen, F.-M.; Cheng, T.-L.; Alexandersen, K.; Huang, Y.-S.; Tzou, W.-S.; Lin, S.-R. Molecular Detection of APC, K-ras, and p53 Mutations in the Serum of Colorectal Cancer Patients as Circulating Biomarkers. World J. Surg. 2004, 28, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, H.; Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, P.; Huang, T.; Song, L.; Xu, R. Circulating Tumor DNA Is Capable of Monitoring the Therapeutic Response and Resistance in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Patients Undergoing Combined Target and Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisaki, J.; Shinozaki, E.; Takeda, Y.; Wakatsuki, T.; Ichimura, T.; Saiura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takahashi, S.; Noda, T.; Zembutsu, H. Clinical relevance of circulating tumor DNA assessed through deep sequencing in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 8, 408–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansukhani, S.; Barber, L.J.; Kleftogiannis, D.; Moorcraft, S.Y.; Davidson, M.; Woolston, A.; Proszek, P.Z.; Griffiths, B.; Fenwick, K.; Herman, B.; et al. Ultra-Sensitive Mutation Detection and Genome-Wide DNA Copy Number Reconstruction by Error-Corrected Circulating Tumor DNA Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 1626–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mohan, S.; Foy, V.; Ayub, M.; Leong, H.S.; Schofield, P.; Sahoo, S.; Descamps, T.; Kilerci, B.; Smith, N.K.; Carter, M.; et al. Profiling of Circulating Free DNA Using Targeted and Genome-wide Sequencing in Patients with SCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 216–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Topaloğlu, U.; Petty, W.J.; Pagni, M.; Foley, K.L.; Grant, S.C.; Robinson, M.; Bitting, R.L.; Thomas, A.; Alistar, A.T.; et al. Circulating mutational portrait of cancer: Manifestation of aggressive clonal events in both early and late stages. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, M.; Xie, Y.; Li, X.; Qian, Y.; Tu, X.; Yao, X.; Cheng, F.; Xu, F.; Kong, D.; He, B.; et al. Resectable lung lesions malignancy assessment and cancer detection by ultra-deep sequencing of targeted gene mutations in plasma cell-free DNA. J. Med Genet. 2019, 56, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serrano, M.J.; Ortega, F.G.; Alvarez-Cubero, M.J.; Nadal, R.; Sanchez-Rovira, P.; Salido, M.; Rodríguez, M.; García-Puche, J.L.; Delgado-Rodriguez, M.; Solé, F.; et al. EMT and EGFR in CTCs cytokeratin negative non-metastatic breast cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 7486–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delgado-Ureña, M.; Ortega, F.G.; Pérez, D.D.M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, A.; Garcia-Puche, J.L.; Ilyine, H.; Lorente, J.A.; Expósito, J.; Navas, M.C.G.; Delgado-Rodríguez, M.; et al. Circulating tumor cells criteria (CyCAR) versus standard RECIST criteria for treatment response assessment in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, D.D.M.; Bayarri-Lara, C.I.; Sánchez, F.G.O.; Russo, A.; Rodriguez, M.J.M.; Alvarez-Cubero, M.; Serrano, E.M.; Lorente, J.A.; Rolfo, C.; Serrano, M.J.; et al. Post-Surgery Circulating Tumor Cells and AXL Overexpression as New Poor Prognostic Biomarkers in Resected Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2019, 11, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernandez-Garcia, D.; Hills, A.; Page, K.; Hastings, R.K.; Toghill, B.; Goddard, K.S.; Ion, C.; Ogle, O.; Boydell, A.R.; Gleason, K.; et al. Plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) as a predictive and prognostic marker in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamfjord, J.; Guren, T.; Dajani, O.; Johansen, J.; Glimelius, B.; Sorbye, H.; Pfeiffer, P.; Lingjærde, O.; Tveit, K.; Kure, E.; et al. Total circulating cell-free DNA as a prognostic biomarker in metastatic colorectal cancer before first-line oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1088–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, B.; Guan, X.; Ma, F. Plasma cell-free DNA and survival in non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 7, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Frenel, J.-S.; Carreira, S.; Goodall, J.; Roda, D.; Perez-Lopez, R.; Tunariu, N.; Riisnaes, R.; Miranda, S.; Figueiredo, I.; Nava-Rodrigues, D.; et al. Serial Next-Generation Sequencing of Circulating Cell-Free DNA Evaluating Tumor Clone Response To Molecularly Targeted Drug Administration. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4586–4596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vidula, N.; Rich, T.A.; Sartor, O.; Yen, J.; Hardin, A.; Nance, T.; Lilly, M.B.; Nezami, M.A.; Patel, S.P.; Carneiro, B.A.; et al. Routine Plasma-Based Genotyping to Comprehensively Detect Germline, Somatic, and Reversion BRCA Mutations among Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 2546–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidula, N.; Dubash, T.; Lawrence, M.S.; Simoneau, A.; Niemierko, A.; Blouch, E.; Nagy, B.; Roh, W.; Chirn, B.; Reeves, B.A.; et al. Identification of Somatically Acquired BRCA1/2 Mutations by cfDNA Analysis in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 4852–4862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; Yin, Z.; Zhou, B. Coexisting EGFR and TP53 Mutations in Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients Are Associated With COMP and ITGB8 Upregulation and Poor Prognosis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Sun, T.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Yu, R.; Wu, X.; Yan, J.; Shao, Y.W.; Shao, X.; Cao, W.; et al. Monitoring treatment efficacy and resistance in breast cancer patients via circulating tumor DNA genomic profiling. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2020, 8, e1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, Z.; Li, T.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Gong, C.; Wang, B.; Cao, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Characterizations of Cancer Gene Mutations in Chinese Metastatic Breast Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Marchenko, N. ErbB2 inhibition by lapatinib promotes degradation of mutant p53 protein in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 5823–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, F.; Zhu, W.; Guan, Y.; Yang, L.; Xia, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Guan, X.; Yi, Z.; Qian, H.; et al. ctDNA dynamics: A novel indicator to track resistance in metastatic breast cancer treated with anti-HER2 therapy. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 66020–66031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, M.P.; Martens, J.W.; Helmijr, J.C.; Beaufort, C.M.; Van Marion, R.; Krol, N.M.; Monkhorst, K.; Jansen, A.M.T.-; Gelder, M.E.M.-V.; Weerts, M.J.; et al. Cell-free DNA mutations as biomarkers in breast cancer patients receiving tamoxifen. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43412–43418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goetz, M.P.; Suman, V.J.; Reid, J.M.; Northfelt, D.W.; Mahr, M.A.; Ralya, A.T.; Kuffel, M.; Buhrow, S.A.; Safgren, S.L.; McGovern, R.M.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Study of the Tamoxifen Metabolite Z-Endoxifen in Women With Endocrine-Refractory Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendricks, A.; Rosenstiel, P.; Hinz, S.; Burmeister, G.; Röcken, C.; Boersch, K.; Schafmayer, C.; Becker, T.; Franke, A.; Forster, M. Rapid response of stage IV colorectal cancer with APC/TP53/KRAS mutations to FOLFIRI and Bevacizumab combination chemotherapy: A case report of use of liquid biopsy. BMC Med. Genet. 2020, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.M.; Boichard, A.; Kurzrock, R. Mutated TP53 is a marker of increased VEGF expression: Analysis of 7,525 pan-cancer tissues. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2020, 21, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghatalia, P.; Smith, C.H.; Winer, A.; Gou, J.; Kiedrowski, L.A.; Slifker, M.; Saltzberg, P.D.; Bubes, N.; Anari, F.M.; Kasireddy, V.; et al. Clinical Utilization Pattern of Liquid Biopsies (LB) to Detect Actionable Driver Mutations, Guide Treatment Decisions and Monitor Disease Burden During Treatment of 33 Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (mCRC) Patients (pts) at a Fox Chase Cancer Center GI Oncology Subspecialty Clinic. Front. Oncol. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Rousseau, V.; Sun, H.; Lantuejoul, S.; Filipits, M.; Pirker, R.; Popper, H.; Mendiboure, J.; Vataire, A.-L.; Le Chevalier, T.; et al. Significance ofTP53mutations as predictive markers of adjuvant cisplatin-based chemotherapy in completely resected non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Han, Y.; Tan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Yang, S.; He, X.; Zhou, S.; Song, Y.; Pi, J.; et al. Tracking longitudinal genetic changes of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in advanced Lung adenocarcinoma treated with chemotherapy. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.J.; Exposito-Hernández, J.; Guerrero, R.; Lopez-Hidalgo, J.; Aguilar, M.; Lorente, J.A.; De Álava, E.; Navas, M.C.G. From precision medicine to imprecision medicine through limited diagnostic ability to detect low allelic frequency mutations. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canale, M.; Petracci, E.; Delmonte, A.; Chiadini, E.; Dazzi, C.; Papi, M.; Capelli, L.; Casanova, C.; De Luigi, N.; Mariotti, M.; et al. Impact of TP53 Mutations on Outcome in EGFR -Mutated Patients Treated with First-Line Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 23, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christopoulos, P.; Dietz, S.; Kirchner, M.; Volckmar, A.-L.; Endris, V.; Neumann, O.; Ogrodnik, S.; Heussel, C.P.; Herth, F.; Eichhorn, M.; et al. Detection of TP53 Mutations in Tissue or Liquid Rebiopsies at Progression Identifies ALK+ Lung Cancer Patients with Poor Survival. Cancers 2019, 11, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Shao, Y.W.; Lu, S. Concomitant resistance mechanisms to multiple tyrosine kinase inhibitors in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, B.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Yang, J.C.-H. Second and third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Becker, T.M.; Bray, V.; Chua, W.; Ma, Y.; Xu, B.; Lynch, D.; De Souza, P.; Roberts, T. Plasma next generation sequencing and droplet digital PCR-based detection of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations in patients with advanced lung cancer treated with subsequent-line osimertinib. Thorac. Cancer 2019, 10, 1879–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Ulrich, B.C.; Supplee, J.; Kuang, Y.; Lizotte, P.H.; Feeney, N.B.; Guibert, N.M.; Awad, M.M.; Wong, K.-K.; Jänne, P.A.; et al. False-Positive Plasma Genotyping Due to Clonal Hematopoiesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 4437–4443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, Q.; Lu, H. Mutant p53 in cancer therapy—The barrier or the path. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kandioler, D.; Mittlböck, M.; Kappel, S.; Puhalla, H.; Herbst, F.; Langner, C.; Wolf, B.; Tschmelitsch, J.; Schippinger, W.; Steger, G.; et al. TP53 Mutational Status and Prediction of Benefit from Adjuvant 5-Fluorouracil in Stage III Colon Cancer Patients. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beije, N.; Helmijr, J.C.; Weerts, M.J.; Beaufort, C.M.; Wiggin, M.; Marziali, A.; Verhoef, C.; Sleijfer, S.; Jansen, M.P.; Martens, J.W. Somatic mutation detection using various targeted detection assays in paired samples of circulating tumor DNA, primary tumor and metastases from patients undergoing resection of colorectal liver metastases. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1575–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Furuki, H.; Yamada, T.; Takahashi, G.; Iwai, T.; Koizumi, M.; Shinji, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Takeda, K.; Taniai, N.; Uchida, E. Evaluation of liquid biopsies for detection of emerging mutated genes in metastatic colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. (EJSO) 2018, 44, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, R.; Yan, C.; Liu, L.; Tong, Z.; Jiang, W.; Yao, M.; Fang, W.; Chen, Z. Advantage of Next-Generation Sequencing in Dynamic Monitoring of Circulating Tumor DNA over Droplet Digital PCR in Cetuximab Treated Colorectal Cancer Patients. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 12, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gold, B.; Cankovic, M.; Furtado, L.V.; Meier, F.; Gocke, C.D. Do Circulating Tumor Cells, Exosomes, and Circulating Tumor Nucleic Acids Have Clinical Utility? J. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 17, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Heng, J.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Tang, L.; Chen, M.; Wang, S.; Deng, H.; Wang, J. The novel TP53 3′-end methylation pattern associated with its expression would be a potential biomarker for breast cancer detection. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 180, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habli, Z.; Alchamaa, W.; Saab, R.; Kadara, H.; Khraiche, M.L. Circulating Tumor Cell Detection Technologies and Clinical Utility: Challenges and Opportunities. Cancers 2020, 12, 1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rubis, G.; Krishnan, S.R.; Bebawy, M. Liquid Biopsies in Cancer Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Prognosis. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 172–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhao, W.; Liang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, Q.; Miao, K.; Cui, D.; et al. Non-invasive detection of EGFR and TP53 mutations through the combination of plasma, urine and sputum in advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3581–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.D.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Thoburn, C.; Afsari, B.; Danilova, L.; Douville, C.; A Javed, A.; Wong, F.; Mattox, A.; et al. Detection and localization of surgically resectable cancers with a multi-analyte blood test. Science 2018, 359, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Cancer Type | Reference | CTC | cfDNA | Tissue | N | Concordance | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt TP53 Frequency | Mutant TP53 Frequency | wt TP53 Frequency | Mutant TP53 Frequency | wt TP53 Frequency | Mutant TP53 Frequency | ||||
| Breast | 18 | 0% | 100% | N/A | N/A | 100% | 0% | 2 | 100% |
| 34 | 3% | 97% | N/A | N/A | 3% | 97% | 30 | 100% | |
| 31 | 53% | 47% | N/A | N/A | 82% | 18% | 17 | 0% | |
| 30 | 33% | 67% | N/A | N/A | 17% | 83% | 6 | 83% | |
| 9 | 100% | 0% | 60% | 40% | 80% | 20% | 5 | 100% | |
| 42 | N/A | N/A | 30% | 70% | 0% | 100% | 10 | 40% | |
| 43 | N/A | N/A | 62% | 38% | 66% | 34% | 32 | 84% | |
| 44 | N/A | N/A | 86% | 14% | 83% | 17% | 58 | 0% | |
| 46 | N/A | N/A | 15% | 85% | 0% | 100% | 26 | 88% | |
| 39 | N/A | N/A | 20% | 80% | 30% | 70% | 20 | 70% | |
| 48 | N/A | N/A | 61% | 39% | 35% | 65% | 23 | 65% | |
| 49 | N/A | N/A | 76% | 24% | 64% | 36% | 45 | 76% | |
| Colorectal | 8 | 80% | 20% | N/A | N/A | 0% | 100% | 19 | 42% |
| 16 | 58% | 42% | N/A | N/A | 77% | 23% | 31 | 97% | |
| 50 | N/A | N/A | 66% | 34% | 0% | 100% | 38 | 60% | |
| 51 | N/A | N/A | 39% | 61% | 25% | 75% | 36 | 81% | |
| 53 | N/A | N/A | 14% | 86% | 11% | 89% | 28 | 82% | |
| 58 | N/A | N/A | 58% | 42% | 50% | 50% | 12 | 58% | |
| Lung | 36 | 60% | 40% | N/A | N/A | 47% | 53% | 15 | 73% |
| 19 | 0% | 100% | N/A | N/A | 33% | 67% | 3 | 67% | |
| 26 | N/A | N/A | 90% | 10% | 50% | 50% | 10 | 60% | |
| 56 | N/A | N/A | 76% | 24% | 63% | 37% | 120 | 68% | |
| Tumor Type | Stage | Liquid Biopsy | Other Samples | Methodology | Studied Mutations | Drugs | Phase | Participants | Identifier |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metastatic Breast Cancer | Unresectable locally advanced or metastatic HER2-positive | ctDNA | FFPE tumor tissue | NGS | PIK3CA and AKT1 as well as in TP53, ESR1, GATA3, ERBB2 and PTEN, amongst others | Ipatasertib, Trastuzumab, Pertuzumab | 1 | 25 | NCT04253561 |
| Colorectal Cancer | I, II and III | ctDNA | FFPE tumor tissue | targeted resequencing and ddPCR | KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, TP53 and APC | N/A | N/A | 1000 | NCT04050345 |
| Metastatic NSCLC | Advanced biopsy-proven metastatic NSCLC | cfDNA | Tumor biopsy | IHC and NGS | EGFR with concurrent RB1 and TP53 alterations | Osimertinib, Platinum (Cisplatin or Carboplatin) and Etoposide | 1 | 30 | NCT03567642 |
| LUSC and HNSCC | Metastatic SCC of the lung or head and neck | cfDNA and gDNA | Tumor biopsy | Sanger sequencing and ddPCR | MET and TP53 | N/A | N/A | 80 | NCT03938012 |
| NSCLC | I–IIIA | CTCs and ctDNA | Tumor biopsy | NGS and ddPCR | AKT1, KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, DDR2, EGFR, FGFR1, ERBB2 (HER2), MEK1, MET, PIK3CA, PTEN, TP53, MDM2, SOX2 and P63 | N/A | N/A | 50 | NCT03771404 |
| NSCLC | IIIB–MIV | CTCs | N/A | N/A | PD-L1, MSI-H/dMMR, TMB, HLA, POLE, POLD1, DDR, TP53, KRAS, BRCA2, PBRM1, MDM2/4, EGFR, ALK, PTEN, JAK1/2, DNMT3A and STK11. | Elemene plus first-generation EGFR-TKIs/first-generation EGFR-TKIs | 4 | 468 | NCT04401059 |
| NSCLC | III not suitable for curative treatment or IV | ctDNA | Tumor biopsy | NGS | ALK fusion and TP53 alterations | Brigatinib/TKI | 2 | 116 | NCT04318938 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garrido-Navas, M.C.; García-Díaz, A.; Molina-Vallejo, M.P.; González-Martínez, C.; Alcaide Lucena, M.; Cañas-García, I.; Bayarri, C.; Delgado, J.R.; González, E.; Lorente, J.A.; et al. The Polemic Diagnostic Role of TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies from Breast, Colon and Lung Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113343
Garrido-Navas MC, García-Díaz A, Molina-Vallejo MP, González-Martínez C, Alcaide Lucena M, Cañas-García I, Bayarri C, Delgado JR, González E, Lorente JA, et al. The Polemic Diagnostic Role of TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies from Breast, Colon and Lung Cancers. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113343
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarrido-Navas, M. Carmen, Abel García-Díaz, Maria Pilar Molina-Vallejo, Coral González-Martínez, Miriam Alcaide Lucena, Inés Cañas-García, Clara Bayarri, Juan Ramón Delgado, Encarna González, Jose Antonio Lorente, and et al. 2020. "The Polemic Diagnostic Role of TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies from Breast, Colon and Lung Cancers" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113343
APA StyleGarrido-Navas, M. C., García-Díaz, A., Molina-Vallejo, M. P., González-Martínez, C., Alcaide Lucena, M., Cañas-García, I., Bayarri, C., Delgado, J. R., González, E., Lorente, J. A., & Serrano, M. J. (2020). The Polemic Diagnostic Role of TP53 Mutations in Liquid Biopsies from Breast, Colon and Lung Cancers. Cancers, 12(11), 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113343