Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising Controller of Cancer Cell States
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CAP Efficacy through Reactive Species
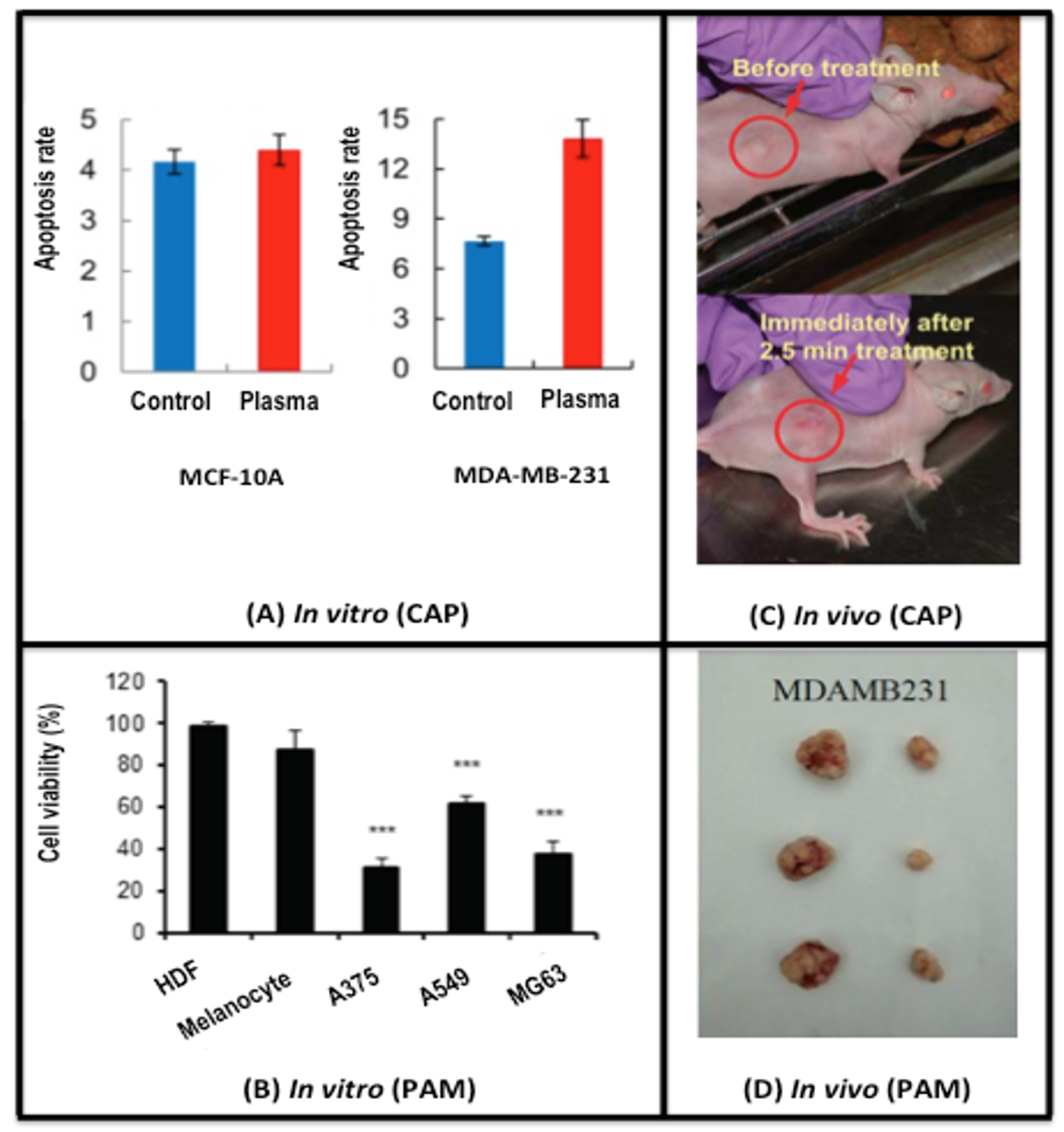
2.1. CAP Alters the Life/Death Transition
2.2. CAP Suppresses the Tumor Angiogenic Switch
2.3. CAP Halts the Tumor Metastatic Transition
2.4. CAP Modulates the Drug Sensitivity of Tumor Cells
3. CAP Safety
4. CAP Administration Approaches
4.1. CAP Generation Sources
4.2. CAP Activated Liquids
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAP | Cold atmospheric plasma |
| CHCPS | Canady Helios Cold Plasma Scapel |
| CSC | Cancer stem cell |
| IR | Ionizing radiation |
| PAM | Plasma-activated medium |
| RONS | Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species |
References
- Spitz, D.R.; Hauer-Jensen, M. Ionizing radiation-induced responses: Where free radical chemistry meets redox biology and medicine. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 1407–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G. The synergistic effect between hydrogen peroxide and nitrite, two long-lived molecular species from cold atmospheric plasma, triggers tumor cells to induce their own cell death. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenova, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Medium Trigger RONS-Based Tumor Cell Apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, G. Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Medium: Antitumor Cell Effects with Inherent Synergistic Potential. Plasma Med. 2019, 9, 57–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mark, P. Plasma Scalpel Takes On Cancer: A New Tool Enters a Pivotal Pilot Study. Available online: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/plasma-scalpel-takes-on-cancer/ (accessed on 1 December 2019).
- Zhou, X.; Cai, D.; Xiao, S.; Ning, M.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, S.; Chen, X.; Ostrikov, K.; Dai, X. InvivoPen: A novel plasma source for in vivo cancer treatment. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dubuc, A.; Monsarrat, P.; Virard, F.; Merbahi, N.; Sarrette, J.P.; Laurencin-Dalicieux, S.; Cousty, S. Use of cold-atmospheric plasma in oncology: A concise systematic review. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privat-Maldonado, A.; Gorbanev, Y.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Reduction of Human Glioblastoma Spheroids Using Cold Atmospheric Plasma: The Combined Effect of Short- and Long-Lived Reactive Species. Cancers 2018, 10, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, C.; Arndt, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Li, Y.; Karrer, S.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment inhibits growth in colorectal cancer cells. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, F.; Mahdikia, H.; Abbaszadeh, H.A.; Abdollahifar, M.A.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Shokri, B. Comparison of Direct and Indirect cold atmospheric-pressure plasma methods in the B16F10 melanoma cancer cells treatment. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, N.; Attri, P.; Yadav, D.K.; Choi, J.; Choi, E.H.; Uhm, H.S. Induced apoptosis in melanocytes cancer cell and oxidation in biomolecules through deuterium oxide generated from atmospheric pressure non-thermal plasma jet. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keidar, M.; Yan, D.; Beilis, I.I.; Trink, B.; Sherman, J.H. Plasmas for Treating Cancer: Opportunities for Adaptive and Self-Adaptive Approaches. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G.; Sersenova, D.; Graves, D.B.; Machala, Z. Dynamics of singlet oxygen-triggered, RONS-based apoptosis induction after treatment of tumor cells with cold atmospheric plasma or plasma-activated medium. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Prasad, K.; Fang, Z.; Speight, R.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikovab, K.K. Cold atmospheric plasma activated water as a prospective disinfectant: The crucial role of peroxynitrite. Green Chem. 2019, 20, 5276–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, D.H.; Park, J.H.; Hong, Y.J.; Uhm, H.S.; Kim, K.N.; Fridman, A.; Choi, E.H. Generation mechanism of hydroxyl radical species and its lifetime prediction during the plasma-initiated ultraviolet (UV) photolysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Kumar, N.; Park, J.H.; Yadav, D.K.; Choi, S.; Uhm, H.S.; Kim, I.T.; Choi, E.H.; Lee, W. Influence of reactive species on the modification of biomolecules generated from the soft plasma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schlegel, J.; Koritzer, J.; Boxhammer, V. Plasma in cancer treatment. Clin. Plasma Med. 2013, 1, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Milberg, J.; Zhang, L.G.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The Specific Vulnerabilities of Cancer Cells to the Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Stimulated Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Xu, Y.; Ning, N.; Cui, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, D.; Chen, H.; Kong, M.G. Alteration of metabolite profiling by cold atmospheric plasma treatment in human myeloma cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralambiev, L.; Wien, L.; Gelbrich, N.; Kramer, A.; Mustea, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B.; Gumbel, D. Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on the Expression of Chemokines, Growth Factors, TNF Superfamily Members, Interleukins, and Cytokines in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Park, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.; Ham, J.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. ChIP-seq analysis reveals alteration of H3K4 trimethylation occupancy in cancer-related genes by cold atmospheric plasma. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 126, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.B.; Kim, B.; Bae, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Differential Epigenetic Effects of Atmospheric Cold Plasma on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keidar, M.; Walk, R.; Shashurin, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Ravi, R.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Trink, B. Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graves, D.B. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maisch, T.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Unger, P.; Heider, J.; Shimizu, T.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Morfill, G.E.; Landthaler, M.; Karrer, S. Investigation of toxicity and mutagenicity of cold atmospheric argon plasma. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2017, 58, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaq, M.; Evans, M.D.; Ostrikov, K.K. Atmospheric pressure gas plasma-induced colorectal cancer cell death is mediated by Nox2-ASK1 apoptosis pathways and oxidative stress is mitigated by Srx-Nrf2 anti-oxidant system. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1843, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Zeng, W.; Xia, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, D.; Liu, D.; Kong, M.G.; Dong, Y. Cold atmospheric plasma induces apoptosis of melanoma cells via Sestrin2-mediated nitric oxide synthase signaling. J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mokhtari, H.; Farahmand, L.; Yaserian, K.; Jalili, N.; Majidzadeh, A.K. The antiproliferative effects of cold atmospheric plasma-activated media on different cancer cell lines, the implication of ozone as a possible underlying mechanism. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 6778–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Daeschlein, G.; Kramer, A.; Sckell, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B. Peroxiredoxin Expression of Human Osteosarcoma Cells Is Influenced by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, G. Intercellular singlet oxygen-mediated bystander signaling triggered by long-lived species of cold atmospheric plasma and plasma-activated medium. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Xiao, H.; Zhu, W.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Zhang, L.G.; Bian, K.; Keidar, M. The role of aquaporins in the anti-glioblastoma capacity of the cold plasma-stimulated medium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 055401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paal, V.V.; Verheyen, C.; Neyt, E.C.; Bogaerts, A. Hampering Effect of Cholesterol on the Permeation of Reactive Oxygen Species through Phospholipids Bilayer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deichman, G.I. Natural selection and early changes of phenotype of tumor cells in vivo: Acquisition of new defense mechanisms. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 78–94. [Google Scholar]
- Böhm, B.; Heinzelmann, S.; Motz, M.; Bauer, G. Extracellular localization of catalase is associated with the transformed state of malignant cells. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 1339–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bauer, G.; Graves, D.B. Mechanisms of Selective Antitumor Action of Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Derived Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. Signal Amplification by Tumor Cells: Clue to the Understanding of the Antitumor Effects of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Plasma-Activated Medium. IEEE. Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2018, 2, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.; Gorbanev, Y.; De Backer, J.; Van Loenhout, J.; Van Boxem, W.; Lemiere, F.; Cos, P.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A. Non-Thermal Plasma as a Unique Delivery System of Short-Lived Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species for Immunogenic Cell Death in Melanoma Cells. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1802062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.; Truong, B.; Patel, S.; Kaushik, N.; Choi, E.H.; Fridman, G.; Fridman, A.; Miller, V. Nanosecond-Pulsed DBD Plasma-Generated Reactive Oxygen Species Trigger Immunogenic Cell Death in A549 Lung Carcinoma Cells through Intracellular Oxidative Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, A.G.; Xiang, B.; Merlino, D.J.; Baybutt, T.R.; Sahu, J.; Fridman, A.; Snook, A.E.; Miller, V. Non-thermal plasma induces immunogenic cell death in vivo in murine CT26 colorectal tumors. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1484978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bekeschus, S.; Kolata, J.; Winterbourn, C.; Kramer, A.; Turner, R.; Weltmann, K.D.; Broker, B.; Masur, K. Hydrogen peroxide: A central player in physical plasma-induced oxidative stress in human blood cells. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, K.I.; Hoan, N.N.; Kim, C.H.; Moon, E.; Choi, K.S.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S. Targeting cancer cells with reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generated by atmospheric-pressure air plasma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virard, F.; Cousty, S.; Cambus, J.P.; Valentin, A.; Kemoun, P.; Clement, F. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Induces a Predominantly Necrotic Cell Death via the Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.; Gebhardt, L.; Arndt, S.; Karrer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma causes a calcium influx in melanoma cells triggering CAP-induced senescence. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Masur, K.; Kolata, J.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A.; Bundscherer, L.; Barton, A.; Kramer, A.; Bröker, B.; Weltmann, K.D. Human mononuclear cell survival and proliferation is modulated by cold atmospheric plasma jet. Plasma Process. Polym. 2013, 10, 706–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.M.; Simms, M.S.; Mann, V.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D.; Frame, F.M. Low temperature plasma treatment induces DNA damage leading to necrotic cell death in primary prostate epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wende, K.; Strassenburg, S.; Haertel, B.; Harms, M.; Holtz, S.; Barton, A.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Lindequist, U. Atmospheric pressure plasma jet treatment evokes transient oxidative stress in HaCaT keratinocytes and influences cell physiology. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 412–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Iseni, S.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Nitrogen shielding of an argon plasma jet and its effects on human immune cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2015, 43, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bundscherer, L.; Bekeschus, S.; Tresp, H.; Hasse, S.; Reuter, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Lindequist, U.; Masur, K. Viability of human blood leucocytes compared with their respective cell lines after plasma treatment. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Asai, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Sahara, J.; Koguchi, H.; Fukuda, N.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Soma, M.; Suzuki-Karasaki, Y. Tumor-selective mitochondrial network collapse induced by atmospheric gas plasma-activated medium. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19910–19927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, S.; Cai, D.; Dai, X. Cold atmospheric plasma conveys selectivity on triple negative breast cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 124, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Unger, P.; Berneburg, M.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Karrer, S. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) activates angiogenesis-related molecules in skin keratinocytes, fibroblasts and endothelial cells and improves wound angiogenesis in an autocrine and paracrine mode. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Bahn, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Jun, S.I.; Lee, K.; Baek, S.J. Induction of cell growth arrest by atmospheric non-thermal plasma in colorectal cancer cells. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S. Cell migration and adhesion of a human melanoma cell line is decreased by cold plasma treatment. Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Seo, S.J.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inhibits thyroid papillary cancer cell invasion via cytoskeletal modulation, altered MMP-2/-9/uPA activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, W.; Lee, S.-J.; Castro, N.J.; Yan, D.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Synergistic Effect of Cold Atmospheric Plasma and Drug Loaded Core-shell Nanoparticles on Inhibiting Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasse, S.; Meder, T.; Freund, E.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Plasma Treatment Limits Human Melanoma Spheroid Growth and Metastasis Independent of the Ambient Gas Composition. Cancers 2020, 12, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Freund, E.; Spadola, C.; Privat-Maldonado, A.; Hackbarth, C.; Bogaerts, A.; Schmidt, A.; Wende, K.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T.; et al. Risk Assessment of kINPen Plasma Treatment of Four Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines with Respect to Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Alessio, M.; Cerella, C.; De Nicola, M.; Bergamaschi, A.; Magrini, A.; Gualandi, G.; Alfonsi, A.M.; Ghibelli, L. Apoptotic GSH extrusion is associated with free radical generation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2003, 1010, 449–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchler, M.J.; Domann, F.E. An epigenetic perspective on the free radical theory of development. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2007, 43, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Jeong, D.; Ham, J.; Park, S.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Cold atmospheric plasma restores tamoxifen sensitivity in resistant MCF-7 breast cancer cell. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köritzer, J.; Boxhammer, V.; Schafer, A.; Shimizu, T.; Klampfl, T.G.; Li, Y.F.; Welz, C.; Schwenk-Zieger, S.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L.; et al. Restoration of sensitivity in chemo-resistant glioma cells by cold atmospheric plasma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eke, I.; Cordes, N. Focal adhesion signaling and therapy resistance in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 31, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szili, E.J.; Hong, S.H.; Oh, J.S.; Gaur, N.; Short, R.D. Tracking the Penetration of Plasma Reactive Species in Tissue Models. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 594–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isbary, G.; Koritzer, J.; Mitra, A.; Li, Y.-F.; Shimizu, T.; Schroeder, J.; Schlegel, J.; Morfill, G.E.; Stolz, W.; Zimmermann, J.L. Ex vivo human skin experiments for the evalution of safety of new cold atmospheric plasma devices. Clin. Plasma Med. 2013, 1, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Garcia, M.C.; Isla-Tejera, B.; Rodero-Serrano, A.; Garcia-Nieto, A.V.; Ruano, J. Clinical and Biological Principles of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Application in Skin Cancer. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuster, M.; Seebauer, C.; Rutkowski, R.; Hauschild, A.; Podmelle, F.; Metelmann, C.; Metelmann, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; et al. Visible tumor surface response to physical plasma and apoptotic cell kill in head and neck cancer. J. Cranio Maxillo Facial Surg. Off. Publ. Eur. Assoc. Cranio Maxillo Facial Surg. 2016, 44, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Simonyan, H.; Cheng, X.; Gjika, E.; Lin, L.; Canady, J.; Sherman, J.H.; Young, C.; Keidar, M. A Novel Micro Cold Atmospheric Plasma Device for Glioblastoma Both In Vitro and In Vivo. Cancers 2017, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Partecke, L.I.; Evert, K.; Haugk, J.; Doering, F.; Normann, L.; Diedrich, S.; Weiss, F.U.; Evert, M.; Huebner, N.O.; Guenther, C.; et al. Tissue tolerable plasma (TTP) induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, J.; Gan, L.; Nie, L.; Sun, F.; Lu, X.; He, G. On the penetration of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generated by a plasma jet into and through mice skin with/without stratum corneum. Phys. Plasmas 2019, 26, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagwal, S.K.; Pasqual-Melo, G.; Bodnar, Y.; Gandhirajan, R.K.; Bekeschus, S. Combination of chemotherapy and physical plasma elicits melanoma cell death via upregulation of SLC22A16. Cell Death. Dis. 2018, 9, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeva, N.Y.; Naidis, G.V. Modeling of Plasmas for Biomedicine. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, G. Targeting Protective Catalase of Tumor Cells with Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Medium (PAM). Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 784–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, X.; Yang, C.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, C.; Zhao, G.; Liu, S. The inhibition effect of cold atmospheric plasma-activated media in cutaneous squamous carcinoma cells. Future Oncol. 2019, 15, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The Application of the Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Activated Solutions in Cancer Treatment. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 769–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Activated Solution: A New Approach for Cancer Treatment. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attri, P.; Park, J.H.; Ali, A.; Choi, E.H. How Does Plasma Activated Media Treatment Differ From Direct Cold Plasma Treatment? Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attri, P.; Bogaerts, A. Perspectives of Plasma-treated Solutions as Anticancer Drugs. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 436–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Kading, A.; Schroder, T.; Wende, K.; Hackbarth, C.; Liedtke, K.R.; van der Linde, J.; von Woedtke, T.; Heidecke, C.D.; Partecke, L.I. Cold Physical Plasma-Treated Buffered Saline Solution as Effective Agent Against Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2018, 18, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Bazaka, K.; Richard, D.J.; Thompson, E.R.W.; Ostrikov, K.K. The Emerging Role of Gas Plasma in Oncotherapy. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscop, E.; Lin, A.; Boxem, W.V.; Loenhout, J.V.; Backer, J.; Deben, C.; Dewilde, S.; Smits, E.; Bogaerts, A.A. Influence of Cell Type and Culture Medium on Determining Cancer Selectivity of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. Cancers 2019, 11, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Boxem, W.; Van der Paal, J.; Gorbanev, Y.; Vanuytsel, S.; Smits, E.; Dewilde, S.; Bogaerts, A. Anti-cancer capacity of plasma-treated PBS: Effect of chemical composition on cancer cell cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girard, P.M.; Arbabian, A.; Fleury, M.; Bauville, G.; Puech, V.; Dutreix, M.; Sousa, J.S. Synergistic Effect of H2O2 and NO2 in Cell Death Induced by Cold Atmospheric He Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurake, N.; Tanaka, H.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, T.; Sekine, M.; Nakamura, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Mizuno, M.; Hori, M. Cell survival of glioblastoma grown in medium containing hydrogen peroxide and/or nitrite, or in plasma-activated medium. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 605, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, C.; Fink, S.; Beier, O.; Horn, K.; Pfuch, A.; Schimanski, A.; Grunler, B.; Hipler, U.C.; Elsner, P. Dose- and Time-Dependent Cellular Effects of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Evaluated in 3D Skin Models. Skin Pharmacol. Physiol. 2016, 29, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; Dai, X.F.; Xiang, L.J.; Cai, D.Y.; Xiao, S.Q.; Ostrikov, K. Quantitative assessment of cold atmospheric plasma anti-cancer efficacy in triple-negative breast cancers. Plasma Process. Polym. 2018, 15, e1800052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Rowe, W.; Ly, L.; Shashurin, A.; Zhuang, T.; Wigh, S.; Basadonna, G.; Trink, B.; Keidar, M.; Canady, J. Treatment of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells with the Canady Cold Plasma Conversion System: Preliminary Results. Plasma 2018, 1, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Yu, G.; Zhou, Z.; Jacobson, O.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, X. Tumor-Specific Drug Release and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation for Cancer Chemo/Chemodynamic Combination Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, W. Cold atmospheric plasma and iron oxide-based magnetic nanoparticles for synergetic lung cancer therapy. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, X.; Bazaka, K.; Thompson, E.W.; Ostrikov, K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising Controller of Cancer Cell States. Cancers 2020, 12, 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113360
Dai X, Bazaka K, Thompson EW, Ostrikov K. Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising Controller of Cancer Cell States. Cancers. 2020; 12(11):3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113360
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Xiaofeng, Kateryna Bazaka, Erik W. Thompson, and Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov. 2020. "Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising Controller of Cancer Cell States" Cancers 12, no. 11: 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113360
APA StyleDai, X., Bazaka, K., Thompson, E. W., & Ostrikov, K. (2020). Cold Atmospheric Plasma: A Promising Controller of Cancer Cell States. Cancers, 12(11), 3360. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12113360




_Ostrikov.png)
