Three-Dimensional Imaging for Multiplex Phenotypic Analysis of Pancreatic Microtumors Grown on a Minipillar Array Chip
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
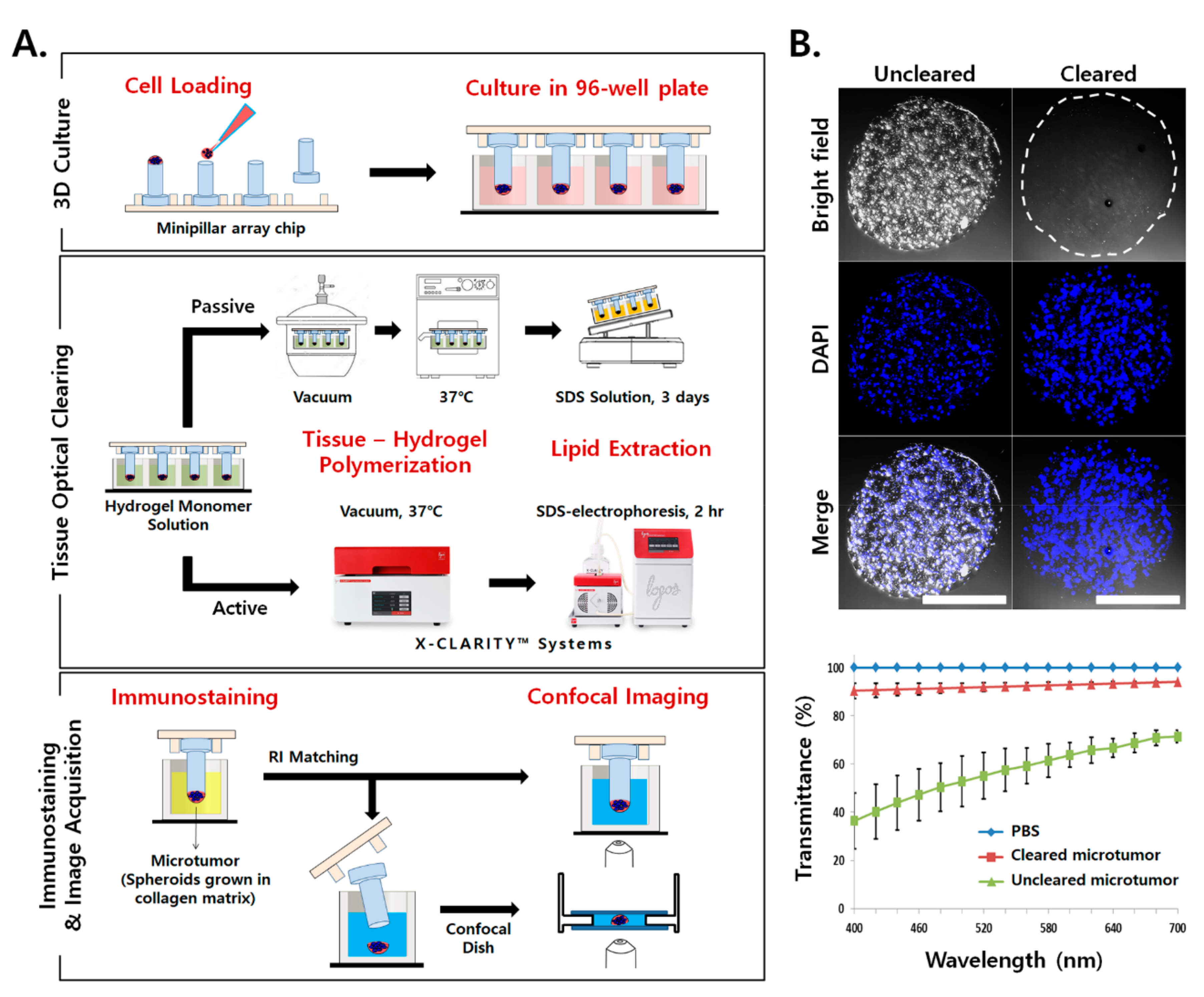
2.1. Application of TOC for Microtumors Grown in a Collagen Matrix
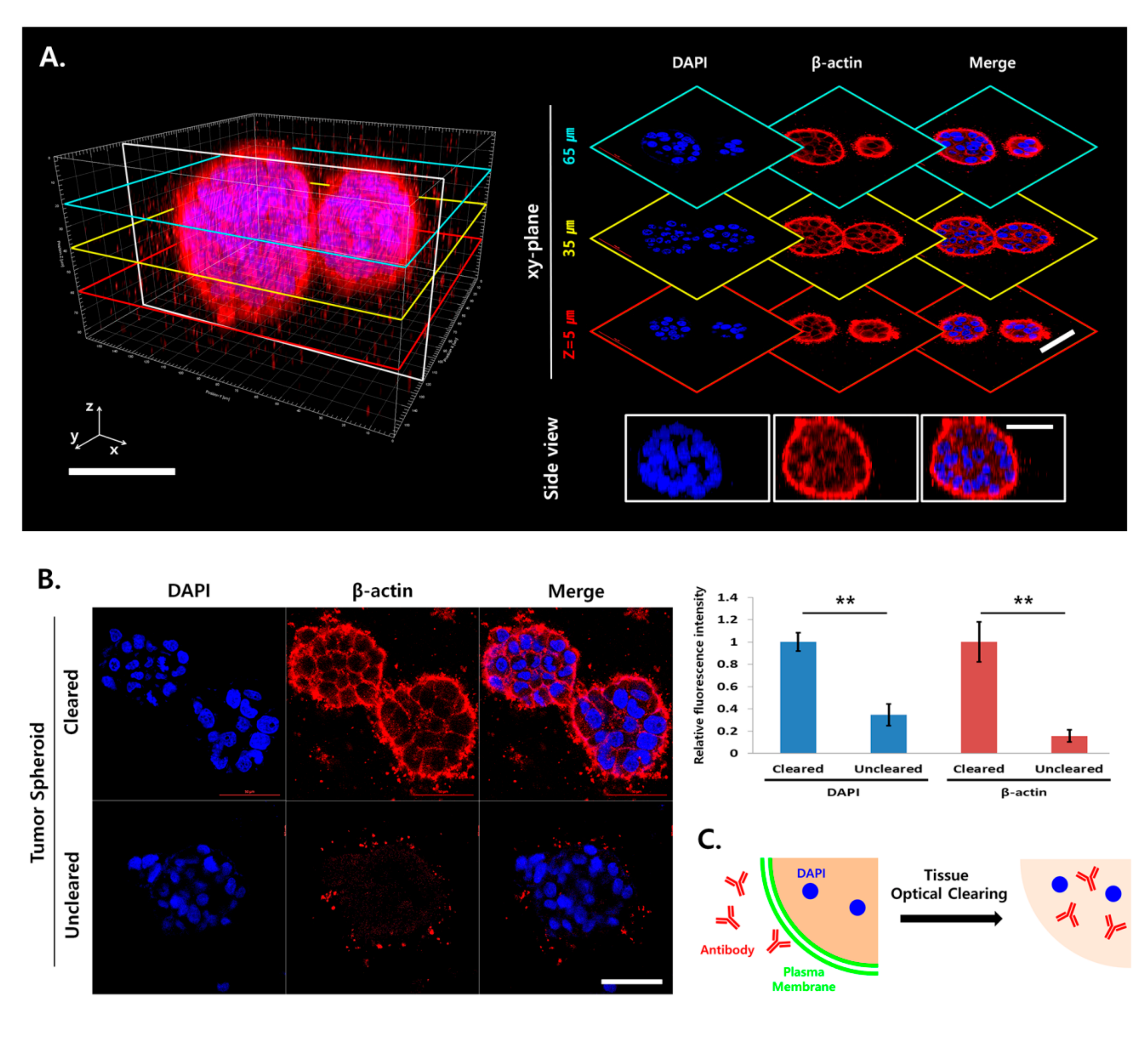
2.2. Light Scattering and Limited Antibody Penetration in TSs
2.3. Increased Antibody Penetration and Light Transmission in TSs by Tissue Clearing
2.4. Tissue Clearing Improved 3D Imaging of the Surrounding Matrix
2.5. Analysis of ECM Remodeling
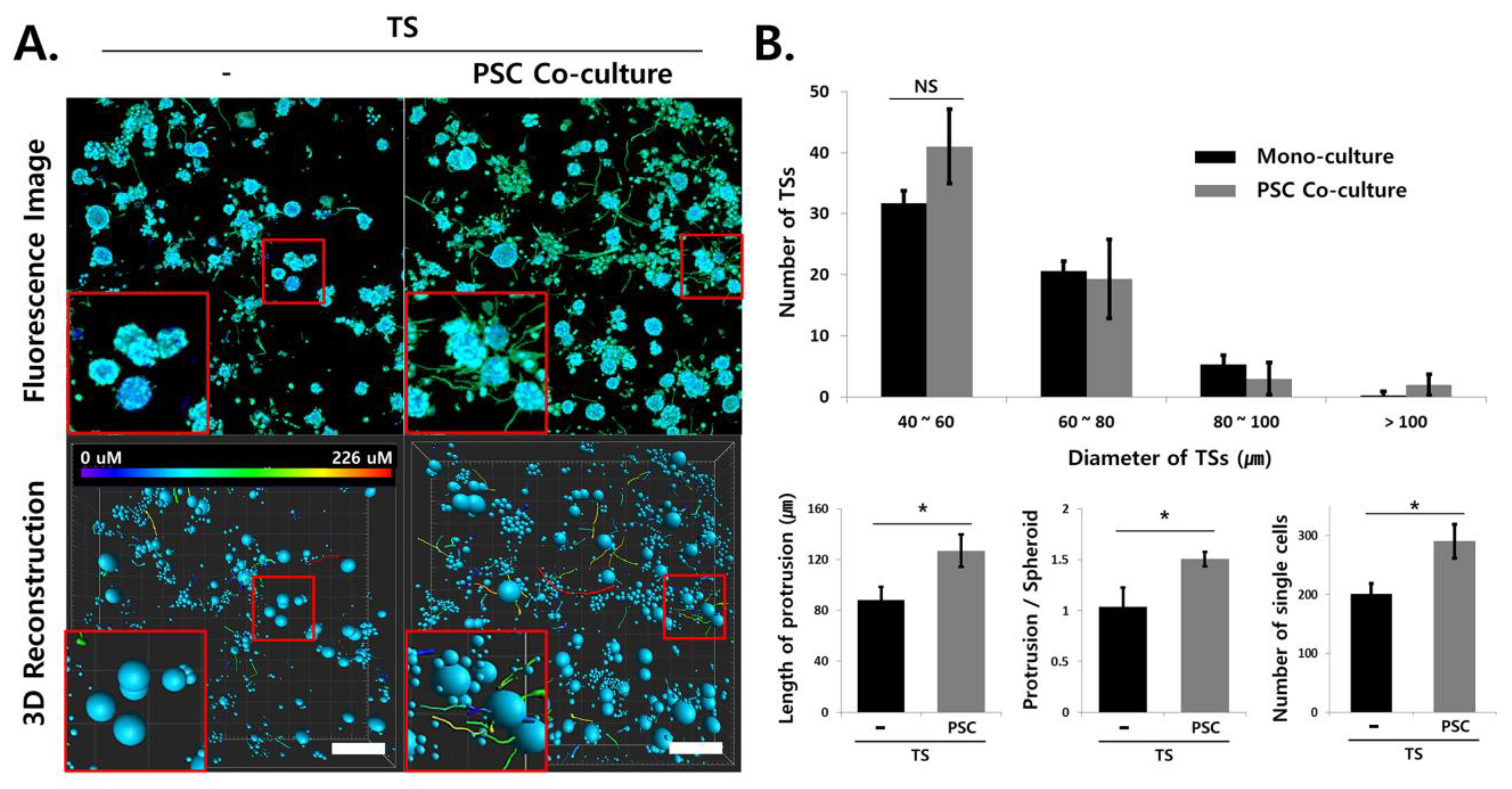
2.6. Multiplex Analysis of Changes in Cellular Protein Expression Induced under Stromal Cell Co-Culturing
2.7. Analysis of Invasive Morphological Phenotypes in TSs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
4.2. Minipillar Array Chips and a Jig for Spheroid Culture and Tissue Clearing
4.3. Culture of Microtumor on Minipillar Array Chips
4.4. TOC
4.5. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.6. Image Acquisition and Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Duval, K.; Grover, H.; Han, L.H.; Mou, Y.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Fredberg, J.; Chen, Z. Modeling Physiological Events in 2D vs. 3D Cell Culture. Physiology (Bethesda) 2017, 32, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, W.; El Assal, R.; Shafiee, H.; Pitteri, S.; Paulmurugan, R.; Demirci, U. Engineering cancer microenvironments for in vitro 3-D tumor models. Mater. Today (Kidlington) 2015, 18, 539–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, A.S.; Barros, A.S.; Costa, E.C.; Moreira, A.F.; Correia, I.J. 3D tumor spheroids as in vitro models to mimic in vivo human solid tumors resistance to therapeutic drugs. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 206–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiswald, L.B.; Bellet, D.; Dangles-Marie, V. Spherical cancer models in tumor biology. Neoplasia 2015, 17, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Lewin Mejia, D.; Chiang, B.; Luker, K.E.; Luker, G.D. Hybrid collagen alginate hydrogel as a platform for 3D tumor spheroid invasion. Acta Biomater. 2018, 75, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kumacheva, E. Hydrogel microenvironments for cancer spheroid growth and drug screening. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaas8998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tibbitt, M.W.; Anseth, K.S. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2009, 103, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berlanga, M.L.; Phan, S.; Bushong, E.A.; Wu, S.; Kwon, O.; Phung, B.S.; Lamont, S.; Terada, M.; Tasdizen, T.; Martone, M.E.; et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of serial mouse brain sections: Solution for flattening high-resolution large-scale mosaics. Front. Neuroanat. 2011, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Hoogt, R.; Estrada, M.F.; Vidic, S.; Davies, E.J.; Osswald, A.; Barbier, M.; Santo, V.E.; Gjerde, K.; van Zoggel, H.; Blom, S.; et al. Protocols and characterization data for 2D, 3D, and slice-based tumor models from the PREDECT project. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 170170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smyrek, I.; Stelzer, E.H. Quantitative three-dimensional evaluation of immunofluorescence staining for large whole mount spheroids with light sheet microscopy. Biomed. Opt. Express 2017, 8, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, J.; Lee, D.W.; Hwang, H.J.; Yeon, S.E.; Lee, M.Y.; Kuh, H.J. Mini-pillar array for hydrogel-supported 3D culture and high-content histologic analysis of human tumor spheroids. Lab. Chip. 2016, 16, 2265–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.; Deisseroth, K. CLARITY for mapping the nervous system. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 508–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epp, J.R.; Niibori, Y.; Liz Hsiang, H.L.; Mercaldo, V.; Deisseroth, K.; Josselyn, S.A.; Frankland, P.W. Optimization of CLARITY for Clearing Whole-Brain and Other Intact Organs. eNeuro 2015, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kabadi, P.K.; Vantangoli, M.M.; Rodd, A.L.; Leary, E.; Madnick, S.J.; Morgan, J.R.; Kane, A.; Boekelheide, K. Into the depths: Techniques for in vitro three-dimensional microtissue visualization. Biotechniques 2015, 59, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nurnberg, E.; Vitacolonna, M.; Klicks, J.; von Molitor, E.; Cesetti, T.; Keller, F.; Bruch, R.; Ertongur-Fauth, T.; Riedel, K.; Scholz, P.; et al. Routine Optical Clearing of 3D-Cell Cultures: Simplicity Forward. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Silva, P.N.; Syed, A.M.; Sindhwani, S.; Rocheleau, J.V.; Chan, W.C. Clarifying intact 3D tissues on a microfluidic chip for high-throughput structural analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 14915–14920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carey, S.P.; Starchenko, A.; McGregor, A.L.; Reinhart-King, C.A. Leading malignant cells initiate collective epithelial cell invasion in a three-dimensional heterotypic tumor spheroid model. Clin. Exp. Metastas. 2013, 30, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaggioli, C.; Hooper, S.; Hidalgo-Carcedo, C.; Grosse, R.; Marshall, J.F.; Harrington, K.; Sahai, E. Fibroblast-led collective invasion of carcinoma cells with differing roles for RhoGTPases in leading and following cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1392U1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorne, J.T.; Segal, T.R.; Chang, S.; Jorge, S.; Segars, J.H.; Leppert, P.C. Dynamic reciprocity between cells and their microenvironment in reproduction. Biol. Reprod. 2015, 92, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.K.; Jang, S.D.; Kim, H.; Chung, S.; Park, J.K.; Kuh, H.J. Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; Oh, M.S.; Lee, D.W.; Kuh, H.J. Multiplex quantitative analysis of stroma-mediated cancer cell invasion, matrix remodeling, and drug response in a 3D co-culture model of pancreatic tumor spheroids and stellate cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.W.; Kang, J.; Hwang, H.J.; Oh, M.S.; Shin, B.C.; Lee, M.Y.; Kuh, H.J. Pitch-tunable pillar arrays for high-throughput culture and immunohistological analysis of tumor spheroids. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4494–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomer, R.; Ye, L.; Hsueh, B.; Deisseroth, K. Advanced CLARITY for rapid and high-resolution imaging of intact tissues. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Josset, E.; Noel, G. Three-dimensional cell culture: A breakthrough in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.W.; Budiman Gosno, E.; Li, Y.S. Fully automatic and robust 3D registration of serial-section microscopic images. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschuh, S.; Schwaha, T.; Metscher, B.D. Showing their true colors: A practical approach to volume rendering from serial sections. BMC Dev. Biol. 2010, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, P.; Lee, M.Y. High Content Imaging (HCI) on Miniaturized Three-Dimensional (3D) Cell Cultures. Biosensors (Basel) 2015, 5, 768–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, S.; Devi, G.R. Three-dimensional culture systems in cancer research: Focus on tumor spheroid model. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 163, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chung, K.; Wallace, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Kalyanasundaram, S.; Andalman, A.S.; Davidson, T.J.; Mirzabekov, J.J.; Zalocusky, K.A.; Mattis, J.; Denisin, A.K.; et al. Structural and molecular interrogation of intact biological systems. Nature 2013, 497, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minchinton, A.I.; Tannock, I.F. Drug penetration in solid tumours. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Huo, S.; Kumar, A.; Wei, T.; Zhang, X.; Jin, S.; Gan, Y.; Wang, P.C.; et al. Size-dependent localization and penetration of ultrasmall gold nanoparticles in cancer cells, multicellular spheroids, and tumors in vivo. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 4483–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kijanka, M.; Dorresteijn, B.; Oliveira, S.; van Bergen en Henegouwen, P.M. Nanobody-based cancer therapy of solid tumors. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2015, 10, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padlan, E.A. Anatomy of the antibody molecule. Mol. Immunol. 1994, 31, 169–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Murray, E.; Bakh, N.; Choi, H.; Ohn, K.; Ruelas, L.; Hubbert, A.; McCue, M.; Vassallo, S.L.; et al. Stochastic electrotransport selectively enhances the transport of highly electromobile molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6274–E6283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mochama, P.; Tyshynsky, R.; Sanders, M.A. Multiplex Immunolabeling and Imaging of Functionally Essential Kidney Structures in X-CLARITY-Cleared Tissue. Microsc. Microanal. 2019, 25, 1260–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DesMarais, V.; Eddy, R.J.; Sharma, V.P.; Stone, O.; Condeelis, J.S. Optimizing leading edge F-actin labeling using multiple actin probes, fixation methods and imaging modalities. Biotechniques 2019, 66, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ungefroren, H.; Sebens, S.; Seidl, D.; Lehnert, H.; Hass, R. Interaction of tumor cells with the microenvironment. Cell Commun. Signal. 2011, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wels, J.; Kaplan, R.N.; Rafii, S.; Lyden, D. Migratory neighbors and distant invaders: Tumor-associated niche cells. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hildebrand, T.; Rüegsegger, P. A new method for the model-independent assessment of thickness in three-dimensional images. J. Microsc. 1997, 185, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemons, T.; Bradshaw, M.; Toshniwal, P.; Chaudhari, N.; Stevenson, A.; Lynch, J.; Fear, M.; Wood, F.; Iyer, K.S.J.R.A. Coherency image analysis to quantify collagen architecture: Implications in scar assessment. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 9661–9669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, M.-S.; Khawar, I.A.; Lee, D.W.; Park, J.K.; Kuh, H.-J. Three-Dimensional Imaging for Multiplex Phenotypic Analysis of Pancreatic Microtumors Grown on a Minipillar Array Chip. Cancers 2020, 12, 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123662
Oh M-S, Khawar IA, Lee DW, Park JK, Kuh H-J. Three-Dimensional Imaging for Multiplex Phenotypic Analysis of Pancreatic Microtumors Grown on a Minipillar Array Chip. Cancers. 2020; 12(12):3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123662
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Min-Suk, Iftikhar Ali Khawar, Dong Woo Lee, Jong Kook Park, and Hyo-Jeong Kuh. 2020. "Three-Dimensional Imaging for Multiplex Phenotypic Analysis of Pancreatic Microtumors Grown on a Minipillar Array Chip" Cancers 12, no. 12: 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123662
APA StyleOh, M.-S., Khawar, I. A., Lee, D. W., Park, J. K., & Kuh, H.-J. (2020). Three-Dimensional Imaging for Multiplex Phenotypic Analysis of Pancreatic Microtumors Grown on a Minipillar Array Chip. Cancers, 12(12), 3662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12123662




