Multifaceted Roles of Caveolin-1 in Lung Cancer: A New Investigation Focused on Tumor Occurrence, Development and Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
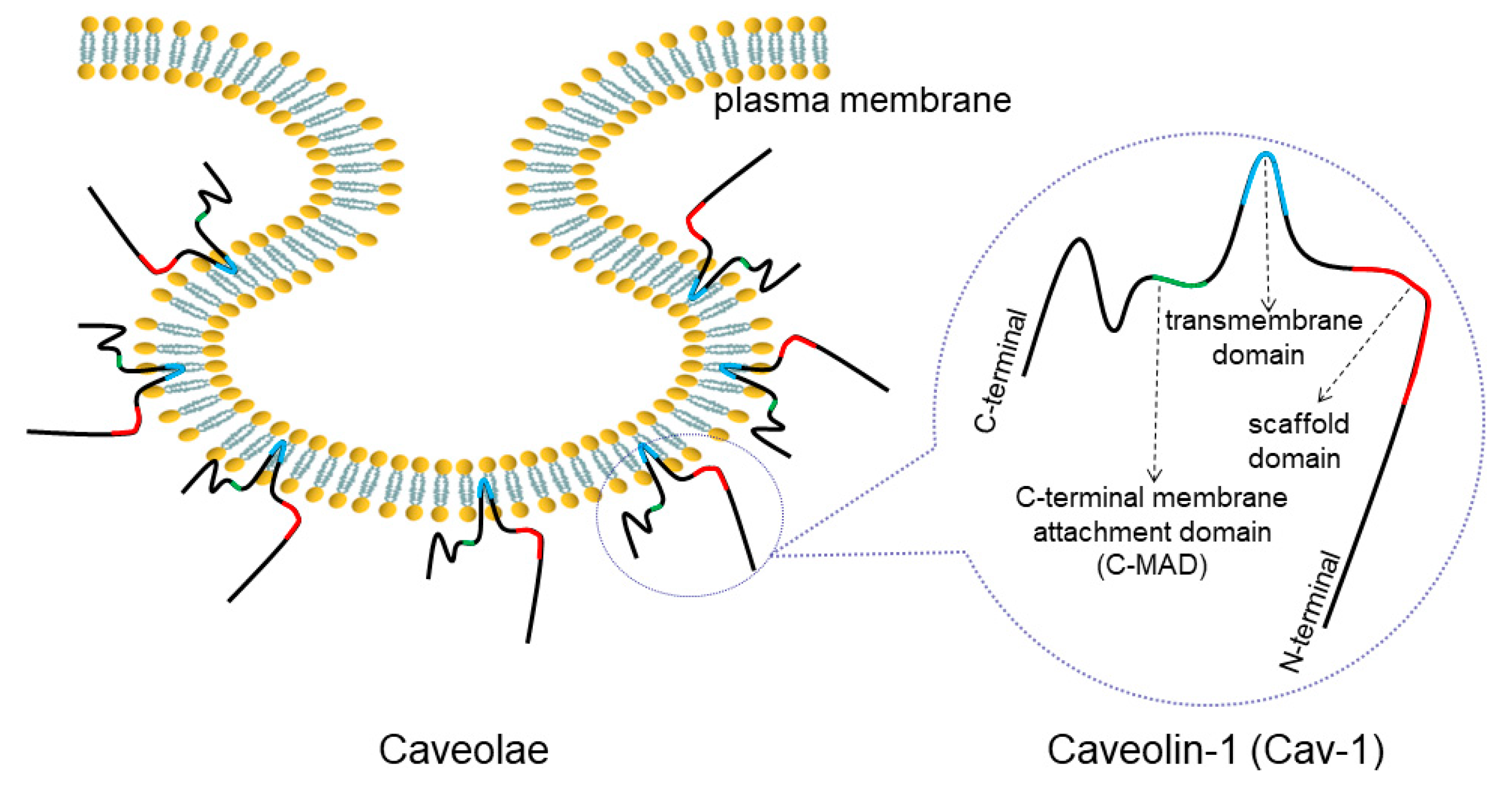
2. Overview of Caveolae and Cav-1
3. Cav-1-Mediated Lung CSC Generation
4. Cav-1 Regulates Lung Cancer Cell Proliferation
5. Cav-1 Participates in Lung Cancer Metastasis
5.1. Cav-1 and Angiogenesis
5.2. Cav-1 and Pseudopods Formation
5.3. Cav-1 and EMT
5.4. Cav-1 Regulates Cell Movement via Multiple Molecules
6. Roles of Cav-1 in Programmed Cell Death
7. The Relationship between Cav-1 and Lung Cancer Prognosis
8. Cav-1 Involved in Lung Cancer Therapy
8.1. Cav-1 and Drug Resistance
8.2. Cav-1 and Cell Senescence
8.3. Multiple Cav-1-Targeted Agents
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: Globocan Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutkowska, A.E.; Antczak, A. Comorbidities in lung cancer. Adv. Respir. Med. 2016, 84, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, S.B.; Crosbie, P.A.; Balata, H.; Chudziak, J.; Hussell, T.; Dive, C. Progress and prospects of early detection in lung cancer. Open Biol. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smart, E.J.; Graf, G.A.; McNiven, M.A.; Sessa, W.C.; Engelman, J.A.; Scherer, P.E.; Okamoto, T.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolins, Liquid-Ordered Domains, and Signal Transduction. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 7289–7304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Echarri, A.; del Pozo, M.A. Caveolae–mechanosensitive membrane invaginations linked to actin filaments. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2747–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parton, R.G.; Pozo, M.A. Caveolae as plasma membrane sensors, protectors and organizers. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, J.; Brick, R.M.; Tuan, R.S. From embryonic development to human diseases: The functional role of caveolae/caveolin. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2016, 108, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, B. Caveolin proteins: A molecular insight into disease. Front. Med. 2016, 10, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.C.T.; Cho, K.A. Versatile Functions of Caveolin-1 in Aging-related Diseases. Chonnam Med. J. 2017, 53, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Williams, T.M.; Lisanti, M.P. The caveolin proteins. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hansen, C.G.; Nichols, B.J. Exploring the caves: Cavins, caveolins and caveolae. Trends Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtun, O.; Tillu, V.A.; Ariotti, N.; Parton, R.G.; Collins, B.M. Cavin family proteins and the assembly of caveolae. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Lu, C.; Ida, L.; Yanagisawa, K.; Usukura, J.; Cheng, J.; Hotta, N.; Shimada, Y.; Isomura, H.; Suzuki, M.; et al. ROR1 sustains caveolae and survival signalling as a scaffold of cavin-1 and caveolin-1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busija, A.R.; Patel, H.H.; Insel, P.A. Caveolins and cavins in the trafficking, maturation, and degradation of caveolae: Implications for cell physiology. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C459–C477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelman, J.A.; Zhang, X.L.; Lisanti, M.P. Genes encoding human caveolin-1 and -2 are co-localized to the D7S522 locus (7q31. 1), a known fragile site (FRA7G) that is frequently deleted in human cancers. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goetz, J.G.; Lajoie, P.; Wiseman, S.M.; Nabi, I.R. Caveolin-1 in tumor progression: The good, the bad and the ugly. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008, 27, 715–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrejón, B.; Cristóbal, I.; Rojo, F.; García-Foncillas, J. Caveolin-1 is Markedly Downregulated in Patients with Early-Stage Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2017, 41, 2625–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechen, K.; Diatchenko, L.; Agoulnik, A.; Scharff, K.M.; Schober, H.; Arlt, K.; Zhumabayeva, B.; Siebert, P.D.; Dietel, M.; Schäfer, R.; et al. Caveolin-1 is down-regulated in human ovarian carcinoma and acts as a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 1635–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-valdivia, N.; Bravo, D.; Huerta, H.; Henriquez, S.; Gabler, F.; Vega, M.; Romero, C.; Calderon, C.; Owen, G.I.; Leyton, L.; et al. Enhanced caveolin-1 expression increases migration, anchorage-independent growth and invasion of endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, Y.; Zeng, X.; He, F.; Liao, Y.; Qian, N.; Toi, M. Caveolin-1 is related to invasion, survival, and poor prognosis in hepatocellular cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 977–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Truong, L.D.; Timme, T.L.; Ren, C.; Wheeler, T.M.; Park, S.H.; Nasu, Y.; Bangma, C.H.; Kattan, M.W.; Scardino, P.T.; et al. Elevated expression of caveolin is associated with prostate and breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar]
- Demirci, N.S.; Dogan, M.; Erdem, G.U.; Kacar, S.; Turhan, T.; Kilickap, S.; Cigirgan, L.C.; Kayacetin, E.; Bozkaya, Y.; Zengin, N. Is plasma caveolin-1 level a prognostic biomarker in metastatic pancreatic cancer? Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Shen, C.; Du, H.; Zhou, Y.; Che, G. Duplex value of caveolin-1 in non-small cell lung cancer: A meta analysis. Fam. Cancer 2014, 13, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Kato, K.; Cho, Y.; Itoh, T.; Morikawa, T.; Okushiba, S.; Kondo, S.; Ohbuchi, T.; Katoh, H. Difference of caveolin-1 expression pattern in human lung neoplastic tissue. Atypical adenomatous hyperplasia, adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2004, 214, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duregon, E.; Senetta, R.; Bertero, L.; Bussolati, B.; Annaratone, L.; Pittaro, A.; Papotti, M.; Marchiò, C.; Cassoni, P. Caveolin 1 expression favors tumor growth and is associated with poor survival in primary lung adenocarcinomas. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, T.Y.; Zhu, T.N.; Cui, Y.J.; Zhang, G.; Song, X.J.; Gao, D.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Zhao, Q.L.; Liu, S.; Su, T.Y.; et al. Expression of caveolin-1 is correlated with lung adenocarcinoma proliferation, migration, and invasion. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.Z.; Guan, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhou, X.; Wangm, N.; Shao, S.; Lin, D. Caveolin-1 interferes cell growth of lung cancer NCI-H446 cell through the interactions with phospho-ERK1/2, estrogen receptor and progestin receptor. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2012, 66, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanuphan, A.; Chunhacha, P.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Chanvorachote, P. Long-Term Nitric Oxide Exposure Enhances Lung Cancer Cell Migration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Chen, H.; Zhu, R.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y.; Fan, K.; Yang, W. Expression of caveolin-1 and its significance in the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 40, 93–96. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, P.; Shen, X.; Qian, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, H.; Xu, C.; Hao, K.; Hu, W.; et al. Expression of caveolin-1 is correlated with disease stage and survival in lung adenocarcinomas. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Xing, L.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; Sun, Y. Relationship between expression of caveolin-1 and pERK1/2 and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. J. Pathol. 2008, 37, 615–619. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.L.; Fan, L.F.; Gao, J.; Ouyang, J.P.; Zhang, Y.X. Differential expression and function of the caveolin-1 gene in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, H.R.; Sung, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Shim, Y.S.; Lee, S.D.; Choi, Y.L.; Kim, M.K.; Chung, D.H. Expression of caveolin-1 is associated with poor prognosis of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. Lung Cancer 2003, 42, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.C.; Kuo, S.H.; Huang, P.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Yang, C.H.; Yang, P.C. Caveolin-1 expression is significantly associated with drug resistance and poor prognosis in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with gemcitabine-based chemotherapy. Lung Cancer 2008, 59, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Di, D.; Zhao, C.; Pan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H. Clinical significance of Gli-1 and Caveolin-1 expression in the human small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2018, 19, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, A.G.; Macleod, K.F. Autophagy, cancer stem cells and drug resistance. J. Pathol. 2019, 247, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Toledo-Guzmán, M.E.; Bigoni-Ordóñez, G.D.; Hernández, M.I.; Ortiz-Sánchez, E. Cancer stem cell impact on clinical oncology. World J. Stem. Cells 2018, 10, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heng, W.S.; Gosens, R.; Kruyt, F.A.E. Lung cancer stem cells: Origin, features, maintenance mechanisms and therapeutic targeting. Biochem. Pharmacol 2019, 160, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villodre, E.S.; Kipper, F.C.; Pereira, M.B.; Lenz, G. Roles of OCT4 in tumorigenesis, cancer therapy resistance and prognosis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 51, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Herlyn, M. The emerging roles of Oct4 in tumor-initiating cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 309, C709–C718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiuthed, A.; Bhummaphan, N.; Luanpitpong, S.; Mutirangura, A.; Aporntewan, C.; Meeprasert, A.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Chanvorachote, P. Nitric oxide promotes cancer cell dedifferentiation by disrupting an Oct4:caveolin-1 complex: A new regulatory mechanism for cancer stem cell formation. J Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 13534–13552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Phiboonchaiyanan, P.P.; Kiratipaiboon, C.; Chanvorachote, P. Ciprofloxacin mediates cancer stem cell phenotypes in lung cancer cells through caveolin-1-dependent mechanism. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 250, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luanpitpong, S.; Wang, L.; Stueckle, T.A.; Tse, W.; Chen, Y.C.; Rojanasakul, Y. Caveolin-1 regulates lung cancer stem-like cell induction and p53 inactivation in carbon nanotube-driven tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 3541–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Feng, Z. Tumor suppressor p53 and its gain-of-function mutants in cancer. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. (Shanghai) 2014, 46, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vijayaraghavan, S.; Moulder, S.; Keyomarsi, K.; Layman, R.M. Inhibiting CDK in Cancer Therapy: Current Evidence and Future Directions. Target. Oncol. 2018, 13, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Moralli, S.; Tarrado-Castellarnau, M.; Miranda, A.; Cascante, M. Targeting cell cycle regulation in cancer therapy. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 138, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golias, C.H.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. Cell proliferation and cell cycle control: A mini review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2004, 58, 1134–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xue, L.; Du, S.; Sun, M.; Hu, J.; Hao, L.; Gong, L.; Yeh, D.; Xiong, H.; Shao, S. Caveolin-1 knockdown is associated with the metastasis and proliferation of human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2012, 66, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, X. Caveolin-1 regulates cell apoptosis and invasion ability in paclitaxel-induced multidrug-resistant A549 lung cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 8937–8947. [Google Scholar]
- Pancotti, F.; Roncuzzi, L.; Maggiolini, M.; Gasperi-Campani, A. Caveolin-1 silencing arrests the proliferation of metastatic lung cancer cells through the inhibition of STAT3 signaling. Cell Signal 2012, 24, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.M.; Ran, B.; Zhang, C.L.; Yan, D.M.; Li, X.H. Estrogen and progesterone promote breast cancer cell proliferation by inducing cyclin G1 expression. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Braz. Pesqui Med. Biol. 2018, 51, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bazzani, L.; Donnini, S.; Giachetti, A.; Christofori, G.; Ziche, M. PGE2 mediates EGFR internalization and nuclear translocation via caveolin endocytosis promoting its transcriptional activity and proliferation in human NSCLC cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 14939–14958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Yin, N.; Liu, H.; Nan, K. Cav-1 promote lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion through lncRNA HOTAIR. Gene 2018, 641, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquemet, G.; Hamidi, H.; Ivaska, J. Filopodia in cell adhesion, 3D migration and cancer cell invasion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wood, S.L.; Pernemalm, M.; Crosbie, P.A.; Whetton, A.D. The role of the tumor-microenvironment in lung cancer-metastasis and its relationship to potential therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 558–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlikos, F.; Harrington, K.J.; Syrigos, K.N. Key molecular mechanisms in lung cancer invasion and metastasis: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2013, 87, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, H.H. Progression and metastasis of lung cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016, 35, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bielenberg, D.R.; Zetter, B.R. The Contribution of Angiogenesis to the Process of Metastasis. Cancer J. (U. S.) 2015, 21, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bremnes, R.M.; Dønnem, T.; Al-Saad, S.; Al-Shibli, K.; Andersen, S.; Sirera, R.; Camps, C.; Marinez, I.; Busund, L.T. The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: Emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2011, 6, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdogan, B.; Webb, D.J. Cancer-associated fibroblasts modulate growth factor signaling and extracellular matrix remodeling to regulate tumor metastasis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gratton, J.P.; Lin, M.I.; Yu, J.; Weiss, E.D.; Jiang, Z.L.; Fairchild, T.A.; Iwakiri, Y.; Groszmann, R.; Claffey, K.P.; Cheng, Y.C.; et al. Selective inhibition of tumor microvascular permeability by cavtratin blocks tumor progression in mice. Cancer Cell 2003, 4, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Claesson-Welsh, L.; Welsh, M. VEGFA and tumour angiogenesis. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 273, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahneh, F.Z.; Baradaran, B.; Zamani, F.; Aghebati-Maleki, L. Tumor angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic therapies. Hum. Antibodies 2013, 22, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimova, I.; Popivanov, G.; Djonov, V. Angiogenesis in cancer - General pathways and their therapeutic implications. J. BUON 2014, 19, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Cardeña, G.; Martasek, P.; Masters, B.S.S.; Skidd, P.M.; Couet, J.; Li, S.; Lisanti, M.P.; Sessa, W.C. Dissecting the interaction between nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and caveolin. Functional significance of the nos caveolin binding domain in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 25437–25440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmitz, M.; Zerr, I.; Althaus, H.H. Effect of cavtratin, a caveolin-1 scaffolding domain peptide, on oligodendroglial signaling cascades. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2011, 31, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, J.; Cheng, M.; Sun, H. Function of inducible nitric oxide synthase in the regulation of cervical cancer cell proliferation and the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, M.I.; Yu, J.; Murata, T.; Sessa, W.C. Caveolin-1 - Deficient mice have increased tumor microvascular permeability, angiogenesis, and growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2849–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Falcon, B.L.; Chintharlapalli, S.; Uhlik, M.T.; Pytowski, B. Antagonist antibodies to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) as anti-angiogenic agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 204–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Om Alblazi, K.M.; Siar, C.H. Cellular protrusions - Lamellipodia, filopodia, invadopodia and podosomes - and their roles in progression of orofacial tumours: Current understanding. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 2187–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawson, C.; Lim, S.T.; Uryu, S.; Chen, X.L.; Calderwood, D.A.; Schlaepfer, D.D. FAK promotes recruitment of talin to nascent adhesions to control cell motility. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 196, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.L.; Lu, S.; Szeto, K.W.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Lasheras, J.C.; Chien, S. FAK and paxillin dynamics at focal adhesions in the protrusions of migrating cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Gao, M.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Liu, X. Inhibition of cell migration by focal adhesion kinase: Time-dependent difference in integrin-induced signaling between endothelial and hepatoblastoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 2573–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tureèková, J.; Vojtìchová, M.; Krausová, M.; Šloncová, E.; Koøínek, V. Focal adhesion kinase functions as an Akt downstream target in migration of colorectal cancer cells. Transl. Oncol. 2009, 2, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, A.; Murakami, H.; Asai, N.; Morone, N.; Watanabe, T.; Kawai, K.; Murakumo, Y.; Usukura, J.; Kaibuchi, K.; Takahashi, M. Akt/PKB regulates actin organization and cell motility via girdin/APE. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, A.; Ping, J.; Takahashi, M. Girdin, a novel actin-binding protein, and its family of proteins possess versatile functions in the Akt and Wnt signaling pathways. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1086, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottner, K.; Faix, J.; Bogdan, S.; Linder, S.; Kerkhoff, E. Actin assembly mechanisms at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 3427–3435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi, H.; Condeelis, J. Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2007, 1773, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Chunhacha, P.; Pongrakhananon, V. Caveolin-1 induces lamellipodia formation via an Akt-dependent pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2014, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.C.; Huang, P.H.; Huang, H.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Yang, P.C.; Hsu, S.M. Up-regulated caveolin-1 accentuates the metastasis capability of lung adenocarcinoma by inducing filopodia formation. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petpiroon, N.; Bhummaphan, N.; Tungsukruthai, S.; Pinkhien, T.; Maiuthed, A.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Chrysotobibenzyl inhibition of lung cancer cell migration through Caveolin-1-dependent mediation of the integrin switch and the sensitization of lung cancer cells to cisplatin-mediated apoptosis. Phytomedicine 2019, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, W.J.; Kim, H.; Park, K.K. The biological role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jolly, M.K.; Ward, C.; Eapen, M.S.; Myers, S.; Hallgren, O.; Levine, H.; Sohal, S.S. Epithelial–mesenchymal transition, a spectrum of states: Role in lung development, homeostasis, and disease. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Legras, A.; Pécuchet, N.; Imbeaud, S.; Pallier, K.; Didelot, A.; Roussel, H.; Gibault, L.; Fabre, E.; Le Pimpec-Barthes, F.; Laurent-Puig, P.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and microRNAs in lung cancer. Cancers (Basel) 2017, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Horejs, C.M. Basement membrane fragments in the context of the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 95, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, N.; Lee, S.; Kim, O.; Park, J.; Na, S.; Lee, J.H. Syntenin promotes VEGF-induced VEGFR2 endocytosis and angiogenesis by increasing ephrin-B2 function in endothelial cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38886–38901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwangbo, C.; Tae, N.; Lee, S.; Kim, O.; Park, O.K.; Kim, J.; Kwon, S.H.; Lee, J.H. Syntenin regulates TGF-â1-induced Smad activation and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting caveolin-mediated TGF-â type i receptor internalization. Oncogene 2016, 35, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.C.; Cheng, W.C.; Huang, Y.C.; Sher, Y.P.; Liou, N.J.; Chien, Y.C.; Lin, P.S.; Lin, P.S.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, W.C. EFHD2 promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and correlates with postsurgical recurrence of stage I lung adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.; Cheriyamundath, S.; Ben-Ze’ev, A. Cell-cell adhesion: Linking Wnt/â-catenin signaling with partial EMT and stemness traits in tumorigenesis. F1000Research 2018, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barrallo-Gimeno, A.; Nieto, M.A. The Snail genes as inducers of cell movement and survival: Implications in development and cancer. Development 2005, 132, 3151–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, O.; Ahn, E.J.; Oh, S.J.; Akanda, M.R.; Oh, I.J.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.K.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Caveolin-1 enhances brain metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer, potentially in association with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition marker SNAIL. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Yi, X. Caveolin-1 promotes an invasive phenotype and predicts poor prognosis in large cell lung carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Li, L.; Zeng, J.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.L.; Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Chang, L.S.; He, D. Inhibitory effect of silibinin on EGFR signal-induced renal cell carcinoma progression via suppression of the EGFR/MMP-9 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 28, 999–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Yeh, D.; Chen, C.; Sun, M.Z.; Shao, S.; Hao, L.; Song, Y.; Gong, L.; Hu, J.; Wang, Q. Caveolin-1 is an important factor for the metastasis and proliferation of human small cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell. Anat. Rec. 2009, 292, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, B.; Köster, D.; Ruez, R.; Gonnord, P.; Bastiani, M.; Abankwa, D.; Stan, R.V.; Butler-Browne, G.; Vedie, B.; Johannes, L.; et al. Cells respond to mechanical stress by rapid disassembly of caveolae. Cell 2011, 144, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kao, Y.C.; Jheng, J.R.; Pan, H.J.; Liao, W.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Kuo, P.L. Elevated hydrostatic pressure enhances the motility and enlarges the size of the lung cancer cells through aquaporin upregulation mediated by caveolin-1 and ERK1/2 signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 863–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewicz, D.; Didiasova, M.; Krüger, M.; Giaimo, B.D.; Borggrefe, T.; Mieth, M.; Hocke, A.C.; Zakrzewicz, A.; Schaefer, L.; Preissner, K.T.; et al. Protein arginine methyltransferase 5 mediates enolase-1 cell surface trafficking in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1816–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Chunhacha, P. Caveolin-1 Regulates Endothelial Adhesion of Lung Cancer Cells via Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Mechanism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luanpitpong, S.; Talbott, S.J.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Nimmannit, U.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Wang, L.; Chanvorachote, P. Regulation of lung cancer cell migration and invasion by reactive oxygen species and caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38832–38840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, X.; Qian, X.; Papageorge, A.; Schetter, A.J.; Vass, W.C.; Liu, X.; Braverman, R.; Robles, A.I.; Lowy, D.R. Functional interaction of tumor suppressor DLC1 and caveolin-1 in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 4405–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, Z.; Yang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Q. Apoptosis, autophagy, necroptosis, and cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2015, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zörnig, M.; Hueber, A.O.; Baum, W.; Evan, G. Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2001, 1551, F1–F37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, H.; Guan, Z.Z.; Okai, I.; Ye, D.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Du, S.; et al. Higher expression of caveolin-1 inhibits human small cell lung cancer (SCLC) apoptosis in vitro. Cancer Invest. 2012, 30, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hu, X.; Chen, S.; Miao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Caveolin-1 knockdown increases the therapeutic sensitivity of lung cancer to cisplatin-induced apoptosis by repressing Parkin-related mitophagy and activating the ROCK1 pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Lou, T.; Pan, J.; Ye, Z.; Yin, Z.; Li, L.; Cheng, W.; Cao, Z. MiR-204 reduces cisplatin resistance in non-small cell lung cancer through suppression of the caveolin-1/AKT/Bad pathway. Aging (Albany N. Y.) 2019, 11, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geletu, M.; Mohan, R.; Arulanandam, R.; Berger-Becvar, A.; Nabi, I.R.; Gunning, P.T.; Raptis, L. Reciprocal regulation of the Cadherin-11/Stat3 axis by caveolin-1 in mouse fibroblasts and lung carcinoma cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2018, 1865, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtek, S.L.; Backos, D.S.; Matheson, C.J.; Reigan, P. Strategies and Approaches of Targeting STAT3 for Cancer Treatment. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongjit, K.; Chanvorachote, P. Caveolin-1 sensitizes cisplatin-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis via superoxide anion-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2011, 358, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, Z.; Livas, T.; Kyprianou, N. Anoikis and EMT: Lethal "Liaisons" during Cancer Progression. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2016, 21, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taddei, M.L.; Giannoni, E.; Fiaschi, T.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis: An emerging hallmark in health and diseases. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Goldstein, D.; Crowe, P.; Yang, J.L. Uncovering a key to the process of metastasis in human cancers: A review of critical regulators of anoikis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1795–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunhacha, P.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Chanvorachote, P. Caveolin-1 Regulates Mcl-1 Stability and Anoikis in Lung Carcinoma Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pengpaeng, P.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Dendrofalconerol A sensitizes anoikis and inhibits migration in lung cancer cells. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 69, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungtabnapa, P.; Nimmannit, U.; Halim, H.; Rojanasakul, Y.; Chanvorachote, P. Hydrogen peroxide inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell anoikis through the inhibition of caveolin-1 degradation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 300, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chanvorachote, P.; Nimmannit, U.; Lu, Y.; Talbott, S.; Jiang, B.H.; Rojanasakul, Y. Nitric oxide regulates lung carcinoma cell anoikis through inhibition of ubiquitin-proteasomal degradation of caveolin-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 28476–28484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sui, A.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, Q. Diagnostic value of serum miR197 and miR145 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 11, 3247–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okuma, Y.; Hosomi, Y.; Nakahara, Y.; Watanabe, K. High plasma levels of soluble programmed cell death ligand 1 are prognostic for reduced survival in advanced lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2017, 104, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.C.; Lee, G.K.; Yoo, S.; Jeon, Y.K. Expression of Caveolin-1 in Pleomorphic Carcinoma of the Lung is Correlated with a Poor Prognosis. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 4631–4637. [Google Scholar]
- Duregon, E.; Senetta, R.; Pittaro, A.; Verdun, L.; Stella, G.; De Blasi, P.; Zorzetto, M. CAVEOLIN-1 expression in brain metastasis from lung cancer predicts worse outcome and radioresistance, irrespective of tumor histotype. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29626–29636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shatz, M.; Lustig, G.; Reich, R.; Liscovitch, M. Caveolin-1 mutants P132L and Y14F are dominant negative regulators of invasion, migration and aggregation in H1299 lung cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 1748–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, E.M.; Williams, T.M.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P.; Shilo, K.; Chatterjee, M.; Mo, X.; Rahmani, M.; Phillips, G.S.; Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Otterson, G.A. Stromal caveolin-1 is associated with response and survival in a phase II trial of nab-paclitaxel with carboplatin for advanced NSCLC patients. Clin. Lung Cancer 2015, 16, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Onion, D.; Isherwood, M.; Shridhar, N.; Xenophontos, M.; Craze, M.L.; Day, L.J.; García-Márquez, M.A.; Pineda, R.G.; Reece-Smith, A.M.; Saunders, J.H.; et al. Multicomponent analysis of the tumour microenvironment reveals low CD8 T cell number, low stromal caveolin-1 and high tenascin-C and their combination as significant prognostic markers in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 1760–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerstenberger, W.; Wrage, M.; Kettunen, E.; Pantel, K.; Anttila, S.; Steurer, S.; Wikman, H. Stromal caveolin-1 and caveolin-2 expression in primary tumors and lymph node metastases. Anal. Cell Pathol. 2018, 2018, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vansteenkiste, J.; Crinò, L.; Dooms, C.; Douillard, J.Y.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Lim, E.; Rocco, G.; Senan, S.; van Schil, P.; Veronesi, G.; et al. 2nd ESMO consensus conference on lung cancer: Early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer consensus on diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1462–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Hassan, O.U.I.; Yang, Y.W.; Buchanan, P. Lung cancer: Biology and treatment options. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2015, 1856, 189–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Du, L.; Morgensztern, D. Chemotherapy for Advanced-Stage Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer J. 2015, 21, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtivelman, E.; Hensing, T.; Simon, G.R.; Dennis, P.A.; Otterson, G.A.; Bueno, R.; Salgia, R. Molecular pathways and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1392–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, W.; Yue, M.; Zheng, N.; Hu, T.; Yang, S.; Dong, Z.; Lu, S.; Mo, S. Caveolin-1 affects tumor drug resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating expressions of P-gp and MRP1. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 9189–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Huang, C.; Bao, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, G. Downregulation of Caveolin-1 increases the sensitivity of drug-resistant colorectal cancer HCT116 cells to 5-Fluorouracil. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.L.; Li, X.; Yang, H.M.; Song, Z.S.; Tong, J.W.; Cao, Q.; Wang, K.S.; Xiao, W.; Xiao, H.B.; Chen, X.Y.; et al. Enhanced expression of caveolin-1 possesses diagnostic and prognostic value and promotes cell migration, invasion and sunitinib resistance in the clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 358, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.P.H.; Galbiati, F.; Volonté, D.; Horwitz, S.B.; Lisanti, M.P. Upregulation of caveolin-1 and caveolae organelles in Taxol-resistant A549 cells. FEBS Lett. 1998, 439, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Zhu, T.; Song, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, S.; Zhao, R. Downregulation of caveolin-1 increased EGFR-TKIs sensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma cell line with EGFR mutation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongvaranon, P.; Pongrakhananon, V.; Chunhacha, P.; Chanvorachote, P. Acquired resistance to chemotherapy in lung cancer cells mediated by prolonged nitric oxide exposure. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 5433–5444. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, M.; Ben-Josef, E.; Robb, R.; Vedaie, M.; Seum, S.; Thirumoorthy, K.; Palanichamy, K.; Harbrecht, M.; Chakravarti, A.; Williams, T.M. Caveolae-mediated endocytosis is critical for albumin cellular uptake and response to albumin-bound chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5925–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pignatta, S.; Orienti, I.; Falconi, M.; Teti, G.; Arienti, C.; Medri, L.; Zanoni, M.; Carloni, S.; Zoli, W.; Amadori, D.; et al. Albumin nanocapsules containing fenretinide: Pre-clinical evaluation of cytotoxic activity in experimental models of human non-small cell lung cancer. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binkhathlan, Z.; Lavasanifar, A. P-glycoprotein Inhibition as a Therapeutic Approach for Overcoming Multidrug Resistance in Cancer: Current Status and Future Perspectives. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 326–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mealey, K.L.; Fidel, J. P-Glycoprotein Mediated Drug Interactions in Animals and Humans with Cancer. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demeule, M.; Jodoin, J.; Gingras, D.; Béliveau, R. P-glycoprotein is localized in caveolae in resistant cells and in brain capillaries. FEBS Lett. 2000, 466, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cai, C.; Chen, J. Overexpression of caveolin-1 induces alteration of multidrug resistance in Hs578T breast adenocarcinoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2004, 111, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.Y.; Lai, T.Y.; Tsai, M.K.; Ou-Yang, P.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wu, S.W.; Hsu, L.C.; Chen, J.S. The influence of a caveolin-1 mutant on the function of P-glycoprotein. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campisi, J. Aging, Cellular Senescence, and Cancer. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 685–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Lee, J.S. Cellular senescence: A promising strategy for cancer therapy. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kasper, M.; Barth, K. Bleomycin and its Role in Inducing Apoptosis and Senescence in Lung Cells - Modulating Effects of Caveolin-1. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linge, A.; Weinhold, K.; Bläsche, R.; Kasper, M.; Barth, K. Downregulation of caveolin-1 affects bleomycin-induced growth arrest and cellular senescence in A549 cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 1964–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galbiati, F.; Volonte’, D.; Liu, J.; Capozza, F.; Frank, P.G.; Zhu, L.; Pestell, R.G.; Lisanti, M.P. Caveolin-1 expression negatively regulates cell cycle progression by inducing G0/G1 arrest via a p53/p21WAF1/Cip1-dependent mechanism. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Linge, A.; Meleady, P.; Henry, M.; Clynes, M.; Kasper, M.; Barth, K. Bleomycin treatment of A549 human lung cancer cells results in association of MGr1-Ag and caveolin-1 in lipid rafts. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenrungruang, S.; Chanvorachote, P.; Sritularak, B.; Pongrakhananon, V. Gigantol, a bibenzyl from Dendrobium draconis, inhibits the migratory behavior of non-small cell lung cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busaranon, K.; Plaimee, P.; Sritularak, B.; Chanvorachote, P. Moscatilin inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and sensitizes anoikis in human lung cancer H460 cells. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 70, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramchu-em, C.; Meksawan, K.; Chanvorachote, P. Zinc sensitizes lung cancer cells to anoikis through down-regulation of Akt and caveolin-1. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.C.; Hwang, J.H.; Jo, E.; Kim, Y.R.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, K.B.; Park, S.J.; Jang, I.S. Cordycepin induces apoptosis by caveolin-1-mediated JNK regulation of Foxo3a in human lung adenocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12211–12224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ecoy, G.A.U.; Chamni, S.; Suwanborirux, K.; Chanvorachote, P.; Chaotham, C. Jorunnamycin A from Xestospongia sp. Suppresses Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition and Sensitizes Anoikis in Human Lung Cancer Cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Liu, F.C.; Pan, C.H.; Lai, M.T.; Lan, S.J.; Wu, C.H.; Sheu, M.J. Suppression of cell growth, migration and drug resistance by ethanolic extract of antrodia cinnamomea in human lung cancer A549 cells and C57BL/6J allograft tumor model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Tissue Type | Histological Type | Tumor Grade | Cav-1 positive Number/Total Sample Number | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-cancer tissue | ----- | ----- | 16/16(100%) | [29] |
| 15/19(78.9%) | [30] | |||
| 20/20(100%) | [31] | |||
| 20/20(100%) | [32] | |||
| Lung cancer tissue | AC | IV | 23/116(19.8%) | [25] |
| AC | I–III | 19/43(44.19%) | [29] | |
| SCC | I–III | 34/107(31.7%) | [33] | |
| AC+SCC+others (LCLC, ASC and carcinoid) | I–IV | 60/115(52.2%) | [30] | |
| AC+SCC+LCLC | I–IV | 105/160(65.7%) | [31] | |
| AC+SCC+LCLC | III and/or IV | 12/73(16.4%) | [34] | |
| AC+SCC+LCLC+ASC | I–III | 69/140(49.3%) | [32] | |
| SCLC | I–IV | 49/70(70%) | [35] |
| Agent | Cell Line | Mode of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| H2O2 and O2·− | H460 | H2O2 and O2·−→ Cav-1↓→ pAKT↓→ migration↓ | [99] |
| Chrysotobibenzyl | H460 H292 | Chrysotobibenzyl→ Cav-1↓→ integrin β1, β3, αv↓ → pFAK↓ and pAKT↓→ migration↓ | [81] |
| Gigantol | H460 | Gigantol→ Cav-1↓→ pAKT↓→ CDC42↓→ EMT↓ and migration↓ | [148] |
| DF-A | H460 | DF-A→ Cav-1↓, Mcl-1↓and Bcl-2↓→ anoikis↑ | [114] |
| Moscatilin | H460 | Moscatilin→ Cav-1↓→ Mcl-1↓→ pAKT↓,pERK↓→ anoikis↑ | [149] |
| Zinc | H460 | Zinc→ Cav-1↓→ pAKT↓→ anoikis↑ | [150] |
| Cordycepin | A549 | Cordycepin→ Cav-1↑→ p-JNK↑→ Foxo3a↑→ Bax↑→ apoptosis↑ | [151] |
| Jorunnamycin A | H460 H292 H23 | Jorunnamycin A→ Cav-1↓→ pAKT↓,pERK↓→ EMT↓ and apoptosis↑ | [152] |
| EEAC | A549 | EEAC→ Cav-1↓→ chemosensitivity to paclitaxel↑ | [153] |
| Albumin-encapsuled fenretinide | A549 | Cav-1 promotes albumin-encapsuled fenretinide uptake into cell→ apoptosis↑ | [136] |
| Bleomycin | A549 | Bleomycin→ Cav-1↑→ p53↑, p21↑→ senescence↑ | [145] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.-B.; Li, J.; Lai, X.-N.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, R.-C.; Xiong, L.-X. Multifaceted Roles of Caveolin-1 in Lung Cancer: A New Investigation Focused on Tumor Occurrence, Development and Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020291
Shi Y-B, Li J, Lai X-N, Jiang R, Zhao R-C, Xiong L-X. Multifaceted Roles of Caveolin-1 in Lung Cancer: A New Investigation Focused on Tumor Occurrence, Development and Therapy. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020291
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yu-Bo, Jun Li, Xing-Ning Lai, Rui Jiang, Rui-Chen Zhao, and Li-Xia Xiong. 2020. "Multifaceted Roles of Caveolin-1 in Lung Cancer: A New Investigation Focused on Tumor Occurrence, Development and Therapy" Cancers 12, no. 2: 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020291
APA StyleShi, Y.-B., Li, J., Lai, X.-N., Jiang, R., Zhao, R.-C., & Xiong, L.-X. (2020). Multifaceted Roles of Caveolin-1 in Lung Cancer: A New Investigation Focused on Tumor Occurrence, Development and Therapy. Cancers, 12(2), 291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020291





