Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection: New Insights into the Combined Use of a Radiomic Approach with Advanced Acquisition Protocol
Abstract
1. Introduction
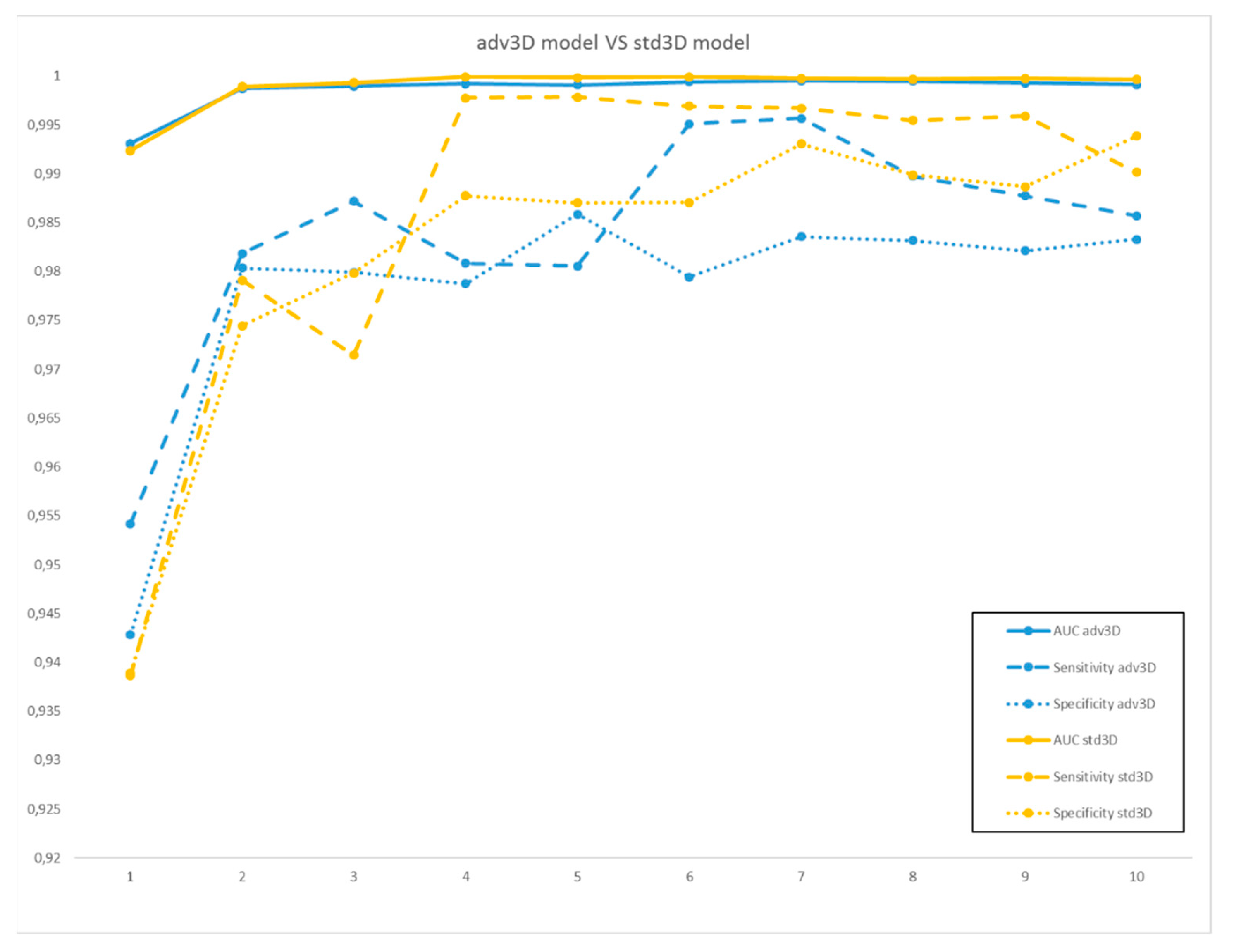
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Cohort
4.2. MR Imaging
4.3. PI-RADS
4.4. ADC and DKI Maps Calculation
4.5. Pharmacokinetic Map Calculation
4.6. Image Preprocessing
4.7. VOI/ROI Segmentation
4.8. Feature Extraction
4.9. Multivariable Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, J.V.; Mulkern, R.V.; Panych, L.P.; Fennessy, F.M.; Fedorov, A.; Maier, S.E.; Tempany, C.M.C. Multiparametric MRI of prostate cancer: An update on state-of-the-art techniques and their performance in detecting and localizing prostate cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2013, 37, 1035–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Rooij, M.; Hamoen, E.H.J.; Fütterer, J.J.; Barentsz, J.O.; Rovers, M.M. Accuracy of multiparametric MRI for prostate cancer detection: A meta-analysis. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fütterer, J.J.; Briganti, A.; De Visschere, P.; Emberton, M.; Giannarini, G.; Kirkham, A.; Taneja, S.S.; Thoeny, H.; Villeirs, G.; Villers, A. Can clinically significant prostate cancer be detected with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging? A systematic review of the literature. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 1045–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinreb, J.C.; Barentsz, J.O.; Choyke, P.L.; Cornud, F.; Haider, M.A.; Macura, K.J.; Margolis, D.; Schnall, M.D.; Shtern, F.; Tempany, C.M.; et al. PI-RADS prostate imaging—Reporting and data system: 2015, version 2. Eur. Urol. 2016, 69, 16–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, G.; Fang, D.; Li, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; He, Q.; Wang, X. The efficiency of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (mpMRI) using PI-RADS Version 2 in the diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer. Clin. Imaging 2016, 40, 885–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.G.; Shafiee, M.J.; Kumar, D.; Khalvati, F.; Haider, M.A.; Wong, A. Discovery radiomics for multi-parametric MRI prostate cancer detection. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1509.00111. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, M.; Fang, M.; Zou, J.; Yang, S.; Yu, D.; Zhong, L.; Hu, C.; Zang, Y.; Dong, D.; Tian, J.; et al. Using biparametric MRI radiomics signature to differentiate between benign and malignant prostate lesions. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoots, I.G. MRI in early prostate cancer detection: How to manage indeterminate or equivocal PI-RADS 3 lesions? Transl. Androl. Urol. 2018, 7, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Reynolds, H.M.; Parameswaran, B.; Wraith, D.; Finnegan, M.E.; Williams, S.; Haworth, A. Multiparametric MRI and radiomics in prostate cancer: A review. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2019, 42, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkrantz, A.B.; Sigmund, E.E.; Johnson, G.; Babb, J.S.; Mussi, T.C.; Melamed, J.; Taneja, S.S.; Lee, V.S.; Jensen, J.H. Prostate cancer: Feasibility and preliminary experience of a diffusional kurtosis model for detection and assessment of aggressiveness of peripheral zone cancer. Radiology 2012, 264, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, S.; Chen, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Yao, Q.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J. Non-Gaussian water diffusion kurtosis imaging of prostate cancer. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 32, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, C.; Shinmoto, H.; Soga, S.; Okamura, T.; Sato, H.; Okuaki, T.; Pang, Y.; Kosuda, S.; Kaji, T. Diffusion kurtosis imaging study of prostate cancer: Preliminary findings. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2014, 40, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancato, V.; Cavaliere, C.; Salvatore, M.; Monti, S. Non-Gaussian models of diffusion weighted imaging for detection and characterization of prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 16837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Gu, Y.; Basu, S.; Berglund, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Forster, K.; Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Dekker, A.; Fenstermacher, D.; et al. Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; Van Stiphout, R.G.P.M.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.L.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aerts, H.J.W.L.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Parmar, C.; Grossmann, P.; Cavalho, S.; Bussink, J.; Monshouwer, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; Rietveld, D.; et al. Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incoronato, M.; Aiello, M.; Infante, T.; Cavaliere, C.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Mirabelli, P.; Monti, S.; Salvatore, M. Radiogenomic analysis of oncological data: A technical survey. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehn, M.; Nardini, C.; Wang, D.S.; McGovern, S.; Jayaraman, M.; Liang, Y.; Aldape, K.; Cha, S.; Kuo, M.D. Identification of noninvasive imaging surrogates for brain tumor gene-expression modules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5213–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, E.; Sirlin, C.B.; Ooi, C.; Adler, A.S.; Gollub, J.; Chen, X.; Chan, B.K.; Matcuk, G.R.; Barry, C.T.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. Decoding global gene expression programs in liver cancer by noninvasive imaging. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Burnside, E.S.; Huang, E.; Drukker, K.; Hoadley, K.A.; Fan, C.; Conzen, S.D.; Zuley, M.; Net, J.M.; et al. Quantitative MRI radiomics in the prediction of molecular classifications of breast cancer subtypes in the TCGA/TCIA data set. npj Breast Cancer 2016, 2, 16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, S.; Aiello, M.; Incoronato, M.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Moscarino, M.; Mirabelli, P.; Ferbo, U.; Cavaliere, C.; Salvatore, M. DCE-MRI pharmacokinetic-based phenotyping of invasive ductal carcinoma: A radiomic study for prediction of histological outcomes. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 5076269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, S.S.F.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Applications and limitations of radiomics. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, R150–R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaddad, A.; Kucharczyk, M.J.; Niazi, T. Multimodal radiomic features for the predicting gleason score of prostate cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaddad, A.; Niazi, T.; Probst, S.; Bladou, F.; Anidjar, M.; Bahoric, B. Predicting Gleason score of prostate cancer patients using radiomic analysis. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, S.; Wei, C.; Wu, J.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Shen, J. Prostate cancer differentiation and aggressiveness: Assessment with a radiomic-based model vs. PI-RADS v2. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermie, I.; Van Besien, J.; De Visschere, P.; Lumen, N.; Decaestecker, K. Which clinical and radiological characteristics can predict clinically significant prostate cancer in PI-RADS 3 lesions? A retrospective study in a high-volume academic center. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 114, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, C.J.; Bao, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.N.; Zhang, Y.D. Machine learning-based analysis of MR radiomics can help to improve the diagnostic performance of PI-RADS v2 in clinically relevant prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4082–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hectors, S.J.; Cherny, M.; Yadav, K.K.; Beksaç, A.T.; Thulasidass, H.; Lewis, S.; Davicioni, E.; Wang, P.; Tewari, A.K.; Taouli, B. Radiomics features measured with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging predict prostate cancer aggressiveness. J. Urol. 2019, 202, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, J.; Perez, I.M.; Movahedi, P.; Merisaari, H.; Pesola, M.; Taimen, P.; Boström, P.J.; Pohjankukka, J.; Kiviniemi, A.; Pahikkala, T.; et al. Radiomics and machine learning of multisequence multiparametric prostate MRI: Towards improved non-invasive prostate cancer characterization. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franiel, T.; Hamm, B.; Hricak, H. Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging and pharmacokinetic models in prostate cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2011, 21, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Dercle, L.; Ammari, S.; Bateson, M.; Durand, P.B.; Haspinger, E.; Massard, C.; Jaudet, C.; Varga, A.; Deutsch, E.; Soria, J.C.; et al. Limits of radiomic-based entropy as a surrogate of tumor heterogeneity: ROI-area, acquisition protocol and tissue site exert substantial influence. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, M.D.; Brown, A.M.; Shih, J.H.; Summers, R.M.; Marko, J.; Law, Y.M.; Sankineni, S.; George, A.K.; Merino, M.J.; Pinto, P.A.; et al. Accuracy and agreement of PIRADSv2 for prostate cancer mpMRI: A multireader study. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 45, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greer, M.D.; Shih, J.H.; Lay, N.; Barrett, T.; Kayat Bittencourt, L.; Borofsky, S.; Kabakus, I.M.; Law, Y.M.; Marko, J.; Shebel, H.; et al. Validation of the dominant sequence paradigm and role of dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging in PI-RADS version 2. Radiology 2017, 285, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghipour, M.; Ziaei, A.; Alessandrino, F.; Hassanzadeh, E.; Harisinghani, M.; Vangel, M.; Tempany, C.M.; Fennessy, F.M. Investigating the role of DCE-MRI, over T2 and DWI, in accurate PI-RADS v2 assessment of clinically significant peripheral zone prostate lesions as defined at radical prostatectomy. Abdom. Radiol. 2019, 44, 1520–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, C.; Velazquez, E.R.; Leijenaar, R.; Jermoumi, M.; Carvalho, S.; Mak, R.H.; Mitra, S.; Shankar, B.U.; Kikinis, R.; Haibe-Kains, B.; et al. Robust radiomics feature quantification using semiautomatic volumetric segmentation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.P.B.; Rose, C.J.; Waterton, J.C.; Carano, R.A.D.; Parker, G.J.M.; Jackson, A. Imaging intratumor heterogeneity: Role in therapy response, resistance, and clinical outcome. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldi, D.; Aiello, M.; Duggento, A.; Salvatore, M.; Cavaliere, C. MR imaging-histology correlation by tailored 3d-printed slicer in oncological assessment. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2019, 2019, 1071453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, H.A.; Hötker, A.M.; Goldman, D.A.; Moskowitz, C.S.; Gondo, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Ehdaie, B.; Woo, S.; Fine, S.W.; Reuter, V.E.; et al. Updated prostate imaging reporting and data system (PIRADS v2) recommendations for the detection of clinically significant prostate cancer using multiparametric MRI: Critical evaluation using whole-mount pathology as standard of reference. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofts, P.S.; Parker, G.J.M. DCE-MRI: Acquisition and analysis techniques. In Clinical Perfusion MRI: Techniques and Applications; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 58–74. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, S.; Staring, M.; Murphy, K.; Viergever, M.A.; Pluim, J.P.W. Elastix: A toolbox for intensity-based medical image registration. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collewet, G.; Strzelecki, M.; Mariette, F. Influence of MRI acquisition protocols and image intensity normalization methods on texture classification. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2004, 22, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haralick, R.M.; Dinstein, I.; Shanmugam, K. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, 3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallières, M.; Freeman, C.R.; Skamene, S.R.; El Naqa, I. A radiomics model from joint FDG-PET and MRI texture features for the prediction of lung metastases in soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities. Phys. Med. Biol. 2015, 60, 5471–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reshef, D.N.; Reshef, Y.A.; Finucane, H.K.; Grossman, S.R.; McVean, G.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Lander, E.S.; Mitzenmacher, M.; Sabeti, P.C. Detecting novel associations in large data sets. Science 2011, 334, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahiner, B.; Chan, H.P.; Hadjiiski, L. Classifier performance prediction for computer-aided diagnosis using a limited dataset. Med. Phys. 2008, 35, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| adv3D | adv2D | std3D |
|---|---|---|
| D—Mean | ADC—Rms | ADC—Mean |
| D—Energy | T2W—Energy | ADC—Energy |
| iAUC—Median | Ktrans—Median | ADC—GLCM Auto Correlation |
| ve—Min | T2—Std | ADC—Max |
| T2W—Max | K—Mad | ADC—Min |
| K—Mad | K—Std | T2W—Max |
| ADC—Max | D—Max | T2W—Std |
| ADC—Min | T2W—Max | T2W—Mean |
| T2W—Std | ADC—Energy | ADC—Rms |
| K—Std | D—Mean | ADC—Median |
| ADC—Energy | ADC—Max | T2W—Variance |
| K—Variance | D—Energy | T2W—Energy |
| T2W—Variance | T2W—Variance | T2W—Rms |
| T2W—Rms | K—Variance | ADC—GLCM Sum Average |
| D—Max | D—Rms | T2W—Median |
| D—Min | D—Median | T2W—Mad |
| T2—Mad | ADC—Mean | T2W—GLCM Correlation |
| Kep—Median | T2W—Mean | ADC—Skewness |
| T2W—Energy | K—Rms | T2W—GLCM Homogeneity |
| T2W—Mean | ADC—Median | T2W—Uniformity |
| D—Rms | T2W—Mad | T2—Entropy |
| Ktrans—Min | Ktrans—Mean | T2—GLCM Dissimilarity |
| Ktrans—Mean | T2W—Median | T2—Min |
| D—Median | iAUC—Median | ADC—Uniformity |
| ADC—Mean | T2W—Rms | ADC—GLCM Correlation |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monti, S.; Brancato, V.; Di Costanzo, G.; Basso, L.; Puglia, M.; Ragozzino, A.; Salvatore, M.; Cavaliere, C. Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection: New Insights into the Combined Use of a Radiomic Approach with Advanced Acquisition Protocol. Cancers 2020, 12, 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020390
Monti S, Brancato V, Di Costanzo G, Basso L, Puglia M, Ragozzino A, Salvatore M, Cavaliere C. Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection: New Insights into the Combined Use of a Radiomic Approach with Advanced Acquisition Protocol. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020390
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonti, Serena, Valentina Brancato, Giuseppe Di Costanzo, Luca Basso, Marta Puglia, Alfonso Ragozzino, Marco Salvatore, and Carlo Cavaliere. 2020. "Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection: New Insights into the Combined Use of a Radiomic Approach with Advanced Acquisition Protocol" Cancers 12, no. 2: 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020390
APA StyleMonti, S., Brancato, V., Di Costanzo, G., Basso, L., Puglia, M., Ragozzino, A., Salvatore, M., & Cavaliere, C. (2020). Multiparametric MRI for Prostate Cancer Detection: New Insights into the Combined Use of a Radiomic Approach with Advanced Acquisition Protocol. Cancers, 12(2), 390. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020390






