An Epitope on EGFR Loading Catastrophic Internalization Serve as a Novel Oncotarget for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
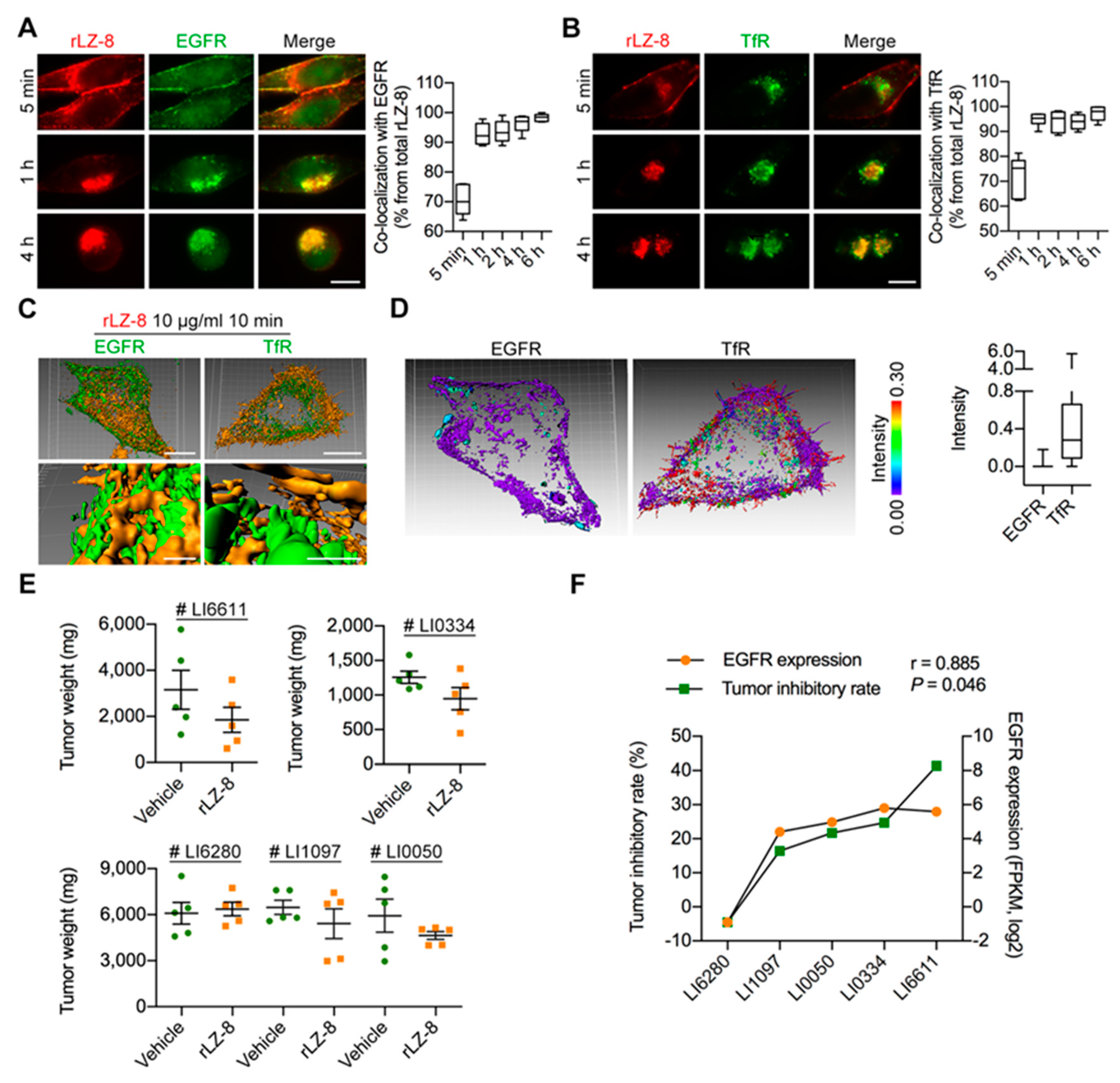
2.1. Attenuation of Tumor Growth and Prolonging Survival Induced in Orthotopic HCC NOG-Mouse Model by rLZ-8
2.2. rLZ-8 Induces Catastrophic Macropinocytosis
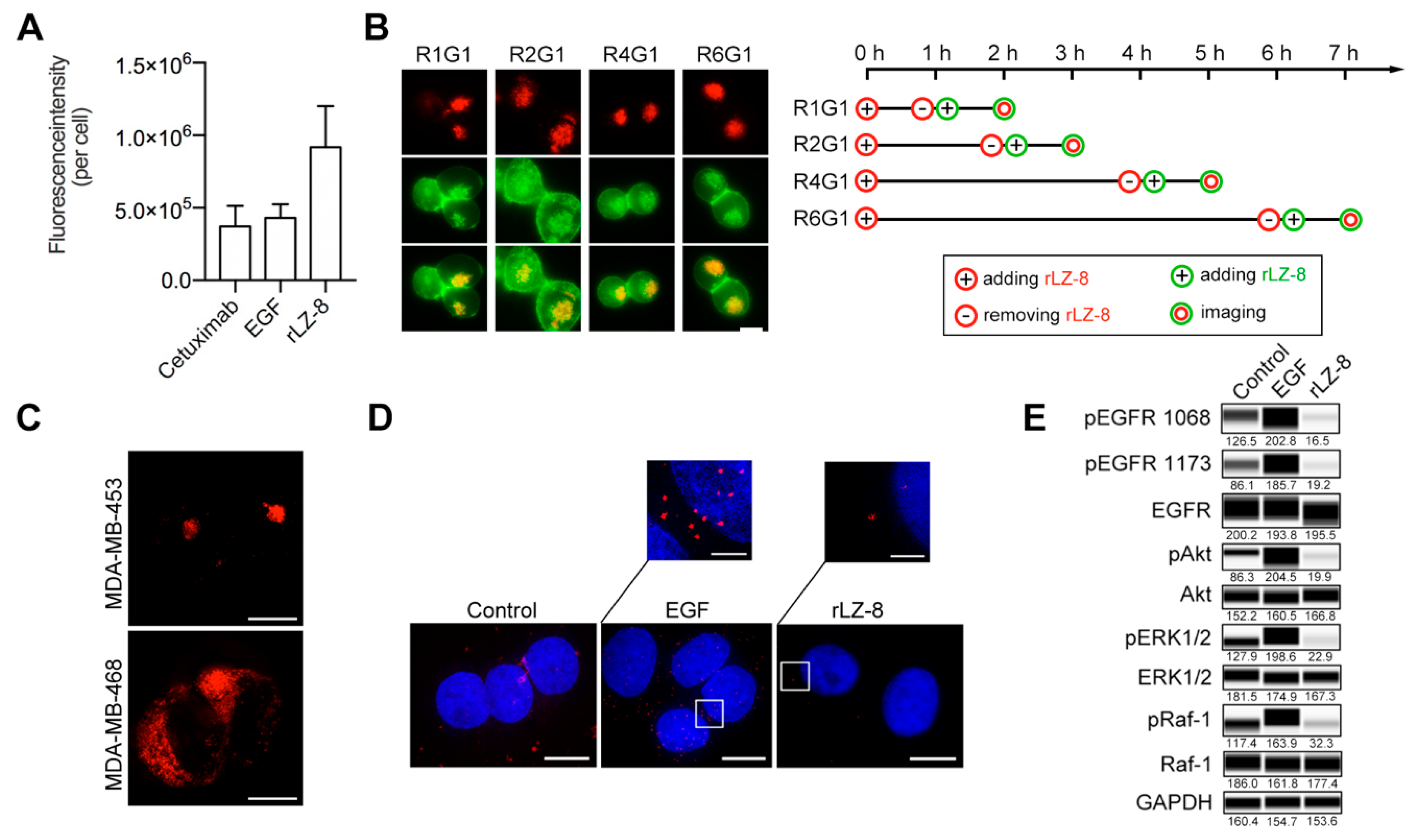
2.3. Endosomal Recycling Is Abrogated by Continuous Internalization of rLZ-8
2.4. EGFR Is the Primary Receptor of rLZ-8 in HCC Cells
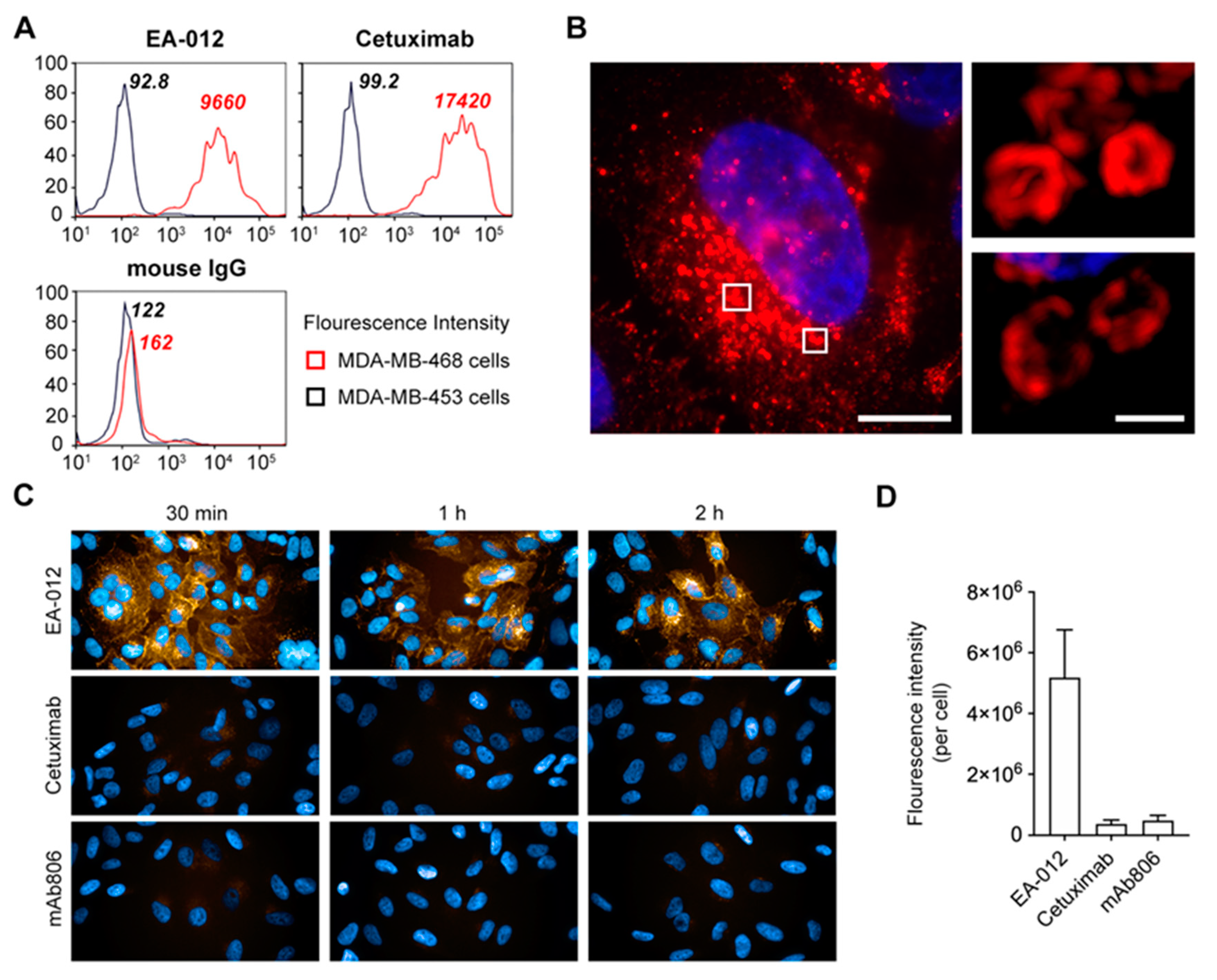
2.5. The Anti-EGFR Antibody Which Possesses Competitive Binding Site with rLZ-8 Could Induce Catastrophic Internalization
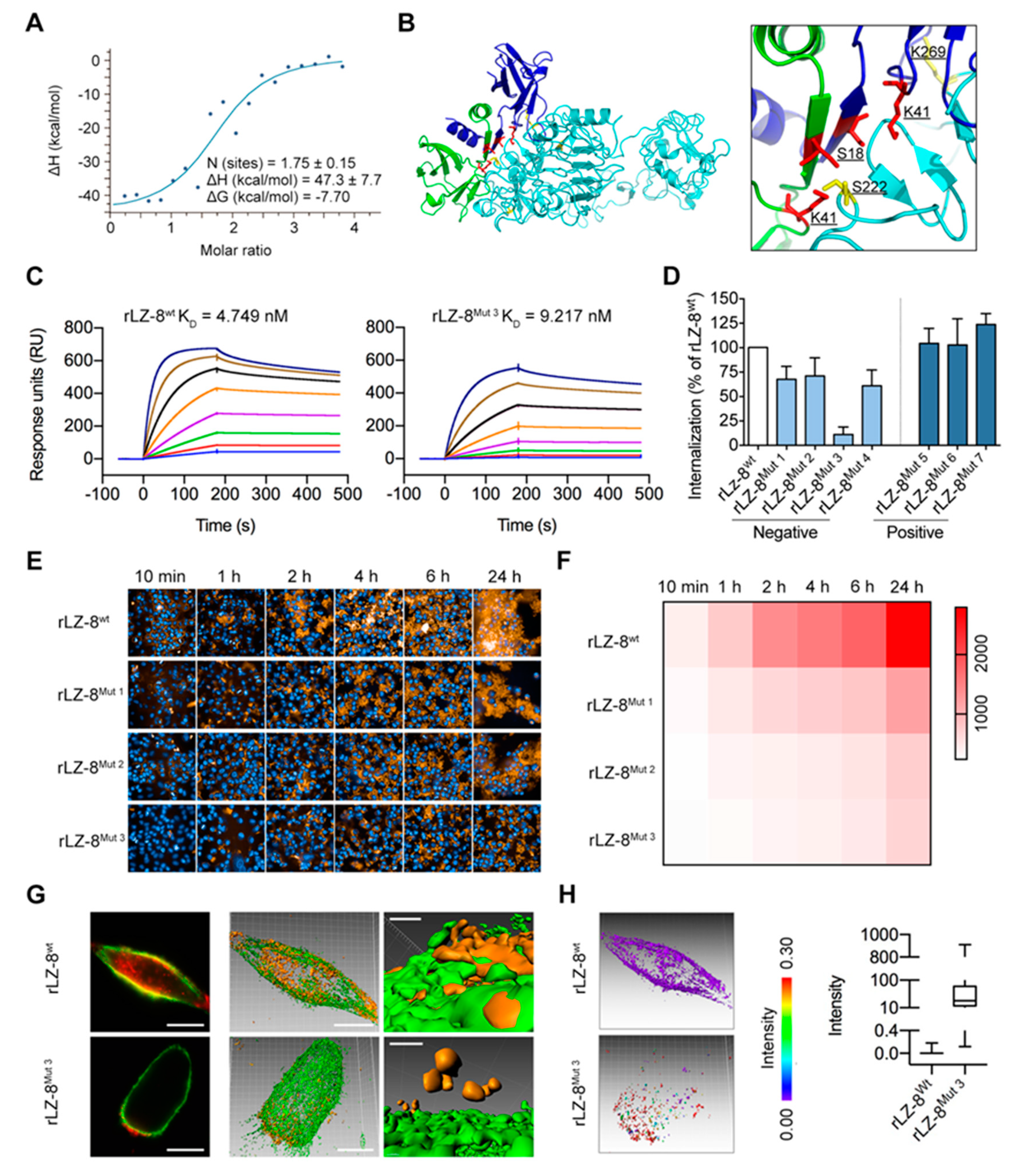
2.6. Mapping the EGFR/rLZ-8 Binding Interface Using Chemical Cross-Linking Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (CXMS) and Molecular Docking
2.7. Targeting S222/K269 Switches Catastrophic EGFR Internalization by Key Residue K41 of rLZ-8
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Recombinant Plasmid Construction and Pichia Pastoris Transformation
4.2. Media and Culture Conditions for rLZ-8 Expression
4.3. Cell Lines
4.4. Cell Viability Assays
4.5. Xenograft Mouse Model In Vivo
4.6. Immunofluorescence, Microscopy Imaging and Analysis
4.7. Chemical Inhibitors
4.8. Isothermal Titration Calorimetry
4.9. Chemical Cross-Linking Coupled with Mass Spectrometry (CXMS) and Molecular Docking
4.10. Determination of Molecular Affinity by Biacore
4.11. Relative Determination of EGFR Dimerization by In Situ PLA
4.12. Western Blot
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tebbutt, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Johns, T.G. Targeting the ERBB family in cancer: Couples therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, N.E.; MacDonald, G. ErbB receptors and signaling pathways in cancer. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2009, 21, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albanell, J.; Gascon, P. Small molecules with EGFR-TK inhibitor activity. CDT 2005, 6, 259–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheeler, D.L.; Dunn, E.F.; Harari, P.M. Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bria, E.; Milella, M.; Cuppone, F.; Novello, S.; Ceribelli, A.; Vaccaro, V.; Sperduti, I.; Gelibter, A.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Cognetti, F.; et al. Outcome of advanced NSCLC patients harboring sensitizing EGFR mutations randomized to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors or chemotherapy as first-line treatment: A meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siena, S.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Balfour, J.; Bardelli, A. Biomarkers predicting clinical outcome of epidermal growth factor receptor–targeted therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1308–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.-M.; Hu, L.; Gu, J.; Wang, R.-Y.; Li, L.; Tang, J.; Zhang, B.-H.; Yan, X.-Z.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Hu, C.-L.; et al. Choline kinase α mediates interactions between the epidermal growth factor receptor and mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells to promote drug resistance and xenograft tumor progression. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1187–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkin, A.; Goh, L.K. Endocytosis and intracellular trafficking of ErbBs. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Goh, L.K.; Sorkin, A. EGF receptor ubiquitination is not necessary for its internalization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16904–16909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wiley, H.S.; Herbst, J.J.; Walsh, B.J.; Lauffenburgerv, D.A.; Rosenfeld, M.G. The role of tyrosine kinase activity in endocytosis, compartmentation, and down-regulation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 11083–11094. [Google Scholar]
- Rappoport, J.Z.; Simon, S.M. Endocytic trafficking of activated EGFR is AP-2 dependent and occurs through preformed clathrin spots. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1301–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sigismund, S.; Woelk, T.; Puri, C.; Maspero, E.; Tacchetti, C.; Transidico, P.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Polo, S. Clathrin-independent endocytosis of ubiquitinated cargos. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2760–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nesterov, A.; Wiley, H.S.; Gill, G.N. Ligand-induced endocytosis of epidermal growth factor receptors that are defective in binding adaptor proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 8719–8723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazazic, M.; Roepstorff, K.; Johannessen, L.E.; Pedersen, N.M.; van Deurs, B.; Stang, E.; Madshus, I.H. EGF-induced activation of the EGF receptor does not trigger mobilization of caveolae. Traffic 2006, 7, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, M.; Brand, T.M.; Starr, M.M.; Li, C.; Huppert, E.J.; Luthar, N.; Pedersen, M.W.; Horak, I.D.; Kragh, M.; Wheeler, D.L. Sym004, a novel EGFR antibody mixture, can overcome acquired resistance to cetuximab. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.W.; Jacobsen, H.J.; Koefoed, K.; Hey, A.; Pyke, C.; Haurum, J.S.; Kragh, M. Sym004: A novel synergistic anti-epidermal growth factor receptor antibody mixture with superior anticancer Efficacy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Martinelli, E.; Belli, V.; Parascandolo, A.; Laukkanen, M.O.; Sforza, V.; Morgillo, F.; Ciardiello, D.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Therapeutic efficacy of SYM004, a mixture of two anti-EGFR antibodies in human colorectal cancer with acquired resistance to cetuximab and MET activation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, e67592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.-R.; Hu, C.-T.; You, R.-I.; Ma, P.-L.; Pan, S.-M.; Lee, M.-C.; Wu, W.-S. Preclinical Trials for Prevention of Tumor Progression of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by LZ-8 Targeting c-Met Dependent and Independent Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Sun, W.-H.; Wu, T.-H.; Tsao, S.-M. Induction of Cbl-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor degradation in Ling Zhi-8 suppressed lung cancer: LZ-8 induces EGFR degradation. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 2596–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manghisi, G.; Elba, S.; Mossa, A.; Giorgio, A.; Aloisio, V.; Perrotta, A.; Tardio, B.; Del Naja, C.; Caturelli, E.; Calandra, M.; et al. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective study of 435 patients. Hepatology 1998, 28, 751–755. [Google Scholar]
- Forner, A.; Reig, M.; Bruix, J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2018, 391, 1301–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Ueno, H.; Morizane, C.; Kojima, Y.; Iwasa, S.; Hagihara, A. Predictive factors of outcome and tumor response to systemic chemotherapy in patients with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 38, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Cao, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhang, X.; McNabola, A.; Wilkie, D.; Wilhelm, S.; Lynch, M.; Carter, C. Sorafenib blocks the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, inhibits tumor angiogenesis, and induces tumor cell apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma model PLC/PRF/5. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11851–11858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strumberg, D.; Richly, H.; Hilger, R.A.; Schleucher, N.; Korfee, S.; Tewes, M.; Faghih, M.; Brendel, E.; Voliotis, D.; Haase, C.G.; et al. Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of the novel Raf kinase and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitor BAY 43-9006 in patients with advanced refractory solid tumors. JCO 2005, 23, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Schwartz, L.; Ricci, S.; Amadori, D.; Santoro, A.; Figer, A.; De Greve, J.; Douillard, J.-Y.; Lathia, C.; Schwartz, B.; et al. Phase II study of sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. JCO 2006, 24, 4293–4300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, A.-L.; Kang, Y.-K.; Chen, Z.; Tsao, C.-J.; Qin, S.; Kim, J.S.; Luo, R.; Feng, J.; Ye, S.; Yang, T.-S.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.-Y.; Choo, S.-P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Z.J.; Heinrich, B.; Steinberg, S.M.; Yu, S.J.; Greten, T.F. Safety in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with immune checkpoint inhibitors as compared to melanoma and non-small cell lung cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikeda, K.; Kudo, M.; Kawazoe, S.; Osaki, Y.; Ikeda, M.; Okusaka, T.; Tamai, T.; Suzuki, T.; Hisai, T.; Hayato, S.; et al. Phase 2 study of lenvatinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.-H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.-W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, B.I.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nalesnik, M.A. Concomitant and isolated expression of TGF-alpha and EGF-R in human hepatoma cells supports the hypothesis of autocrine, paracrine, and endocrine growth of human hepatoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 1995, 58, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, M.; Sato, C.; Sakai, K.; Konishi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Muraoka, M.; Kikuchi-Yanoshita, R.; Nadaoka, Y.; Kanda, H.; Kitagawa, T. Malignant transformation and EGFR activation of immortalized mouse liver epithelial cells caused by HBV enhancer-X from a human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Caner 2000, 85, 518–522. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.-W. Study on the mechanism of epidermal growth factor-induced proliferation of hepatoma cells. WJG 2003, 9, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, Y.; Takeda, T.; Sakon, M.; Tsujimoto, M.; Higashiyama, S.; Noda, K.; Miyoshi, E.; Monden, M.; Matsuura, N. Expression and clinical significance of erb-B receptor family in hepatocellular carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 84, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Philip, P.A.; Mahoney, M.R.; Allmer, C.; Thomas, J.; Pitot, H.C.; Kim, G.; Donehower, R.C.; Fitch, T.; Picus, J.; Erlichman, C. Phase II study of erlotinib (OSI-774) in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer. JCO 2005, 23, 6657–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.B.; Chadha, R.; Glover, K.; Wang, X.; Morris, J.; Brown, T.; Rashid, A.; Dancey, J.; Abbruzzese, J.L. Phase 2 study of erlotinib in patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer 2007, 110, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaseb, A.O.; Garrett-Mayer, E.; Morris, J.S.; Xiao, L.; Lin, E.; Onicescu, G.; Hassan, M.M.; Hassabo, H.M.; Iwasaki, M.; Deaton, F.L.; et al. Efficacy of bevacizumab plus erlotinib for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and predictors of outcome: Final results of a phase II trial. Oncology 2012, 82, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, P.A.; Mahoney, M.R.; Holen, K.D.; Northfelt, D.W.; Pitot, H.C.; Picus, J.; Flynn, P.J.; Erlichman, C. Phase 2 study of bevacizumab plus erlotinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular cancer: Bevacizumab Plus Erlotinib in HCC. Cancer 2012, 118, 2424–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, A.X.; Rosmorduc, O.; Evans, T.R.J.; Ross, P.J.; Santoro, A.; Carrilho, F.J.; Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Thuluvath, P.J.; Llovet, J.M.; et al. SEARCH: A phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of sorafenib plus erlotinib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. JCO 2015, 33, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louafi, S.; Boige, V.; Ducreux, M.; Bonyhay, L.; Mansourbakht, T.; de Baere, T.; Asnacios, A.; Hannoun, L.; Poynard, T.; Taïeb, J. Gemcitabine plus oxaliplatin (GEMOX) in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Results of a phase II study. Cancer 2007, 109, 1384–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, A.; Hiller, K.; Scheer, M.; Munch, R.; Nortemann, B.; Hempel, D.C.; Jahn, D. JCat: A novel tool to adapt codon usage of a target gene to its potential expression host. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, W526–W531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Cheng, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H. The non-small cell lung cancer EGFR extracellular domain mutation, M277E, is oncogenic and drug-sensitive. OTT 2017, 10, 4507–4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howes, M.T.; Kirkham, M.; Riches, J.; Cortese, K.; Walser, P.J.; Simpson, F.; Hill, M.M.; Jones, A.; Lundmark, R.; Lindsay, M.R.; et al. Clathrin-independent carriers form a high capacity endocytic sorting system at the leading edge of migrating cells. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, B.X.; Kim, H.-Y.; Dass, C. Probing three-dimensional structure of bovine serum albumin by chemical cross-linking and mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hornak, V.; Abel, R.; Okur, A.; Strockbine, B.; Roitberg, A.; Simmerling, C. Comparison of multiple Amber force fields and development of improved protein backbone parameters. Proteins 2006, 65, 712–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoo, S.; Xantheas, S.S. Communication: The effect of dispersion corrections on the melting temperature of liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, e121105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Söderberg, O.; Gullberg, M.; Jarvius, M.; Ridderstråle, K.; Leuchowius, K.-J.; Jarvius, J.; Wester, K.; Hydbring, P.; Bahram, F.; Larsson, L.-G.; et al. Direct observation of individual endogenous protein complexes in situ by proximity ligation. Nat. Methods 2006, 3, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Mutations | Mutation Sites |
|---|---|
| rLZ-8Mut 1 | K41A |
| rLZ-8Mut 2 | K41D |
| rLZ-8Mut 3 | K16A/S18A/K41A/D45A |
| rLZ-8Mut 4 | K16A/K41A |
| rLZ-8Mut 5 | L17K |
| rLZ-8Mut 6 | D20H |
| rLZ-8Mut 7 | D70K |
| EGFRMut 1 | S222A/K269A |
| EGFRMut 2 | S196A/S222A/K269A/S282A |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, D.; Fan, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Sun, F. An Epitope on EGFR Loading Catastrophic Internalization Serve as a Novel Oncotarget for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020456
Huang D, Fan Q, Liu Z, Zhang S, Huang W, Li H, Liang C, Sun F. An Epitope on EGFR Loading Catastrophic Internalization Serve as a Novel Oncotarget for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020456
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Dianshuai, Qingjie Fan, Zhiyi Liu, Shuqin Zhang, Wei Huang, Hongrui Li, Chongyang Liang, and Fei Sun. 2020. "An Epitope on EGFR Loading Catastrophic Internalization Serve as a Novel Oncotarget for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy" Cancers 12, no. 2: 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020456
APA StyleHuang, D., Fan, Q., Liu, Z., Zhang, S., Huang, W., Li, H., Liang, C., & Sun, F. (2020). An Epitope on EGFR Loading Catastrophic Internalization Serve as a Novel Oncotarget for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Therapy. Cancers, 12(2), 456. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020456




