Depth of Remission Following First-Line Treatment Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Progression-Free Survival in Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Evaluated Data
2.2. Staging, Response Assessment and Follow-Up
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics
3.2. First-line treatment and Response
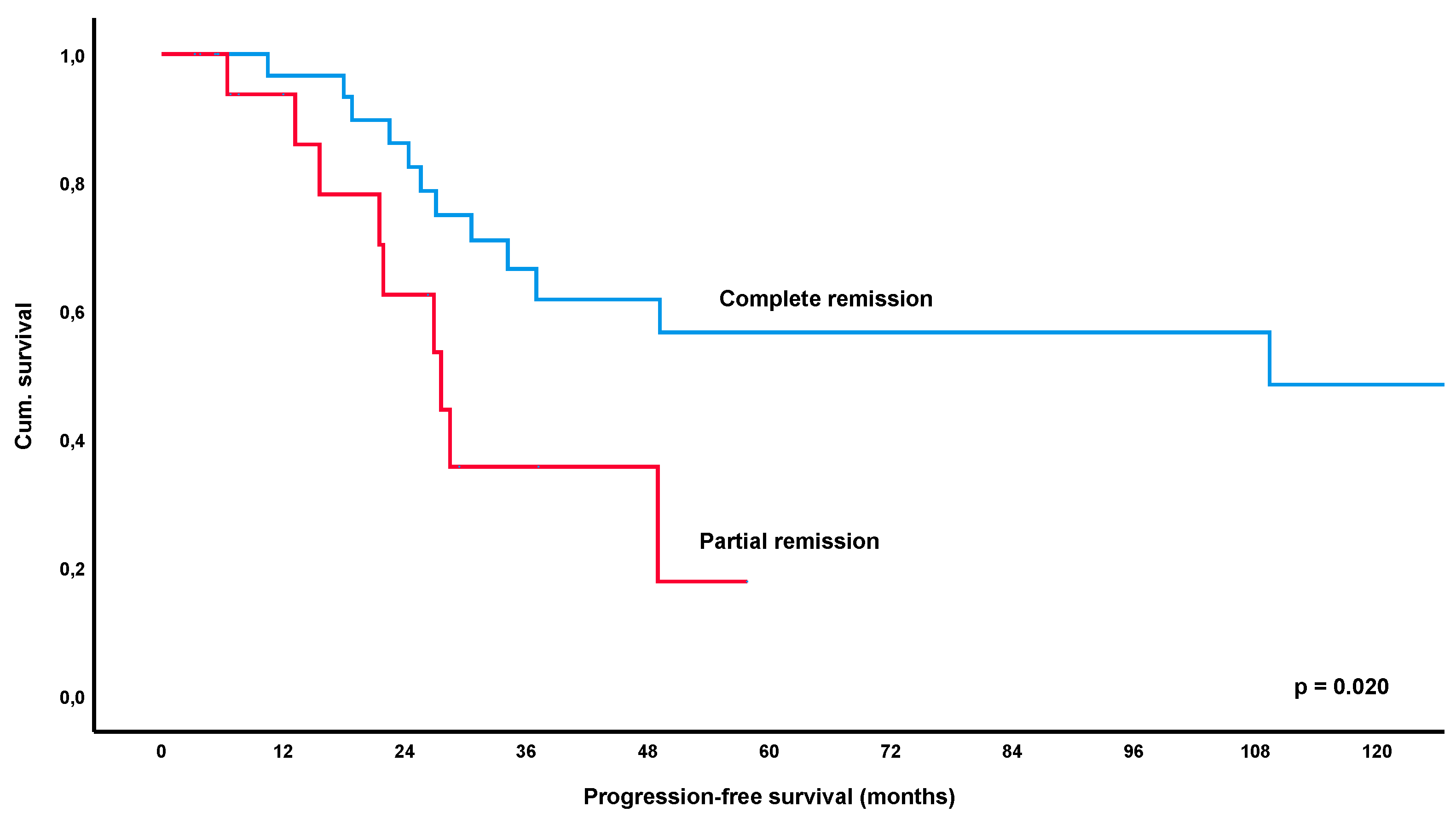
3.3. Progression-Free Survival
3.4. Long-Term Outcome and Overall Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Teras, L.R.; DeSantis, C.E.; Cerhan, J.R.; Morton, L.M.; Jemal, A.; Flowers, C.R. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacon, C.M.; Du, M.Q.; Dogan, A. Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (malt) lymphoma: A practical guide for pathologists. J. Clin. Pathol. 2007, 60, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raderer, M.; Kiesewetter, B.; Ferreri, A.J. Clinicopathologic characteristics and treatment of marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (malt lymphoma). CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 153–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucca, E.; Bertoni, F. The spectrum of malt lymphoma at different sites: Biological and therapeutic relevance. Blood 2016, 127, 2082–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sagaert, X.; Van Cutsem, E.; De Hertogh, G.; Geboes, K.; Tousseyn, T. Gastric malt lymphoma: A model of chronic inflammation-induced tumor development. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruskone-Fourmestraux, A.; Fischbach, W.; Aleman, B.M.; Boot, H.; Du, M.Q.; Megraud, F.; Montalban, C.; Raderer, M.; Savio, A.; Wotherspoon, A.; et al. Egils consensus report. Gastric extranodal marginal zone b-cell lymphoma of malt. Gut 2011, 60, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zucca, E.; Arcaini, L.; Buske, C.; Johnson, P.W.; Ponzoni, M.; Raderer, M.; Ricardi, U.; Salar, A.; Stamatopoulos, K.; Thieblemont, C.; et al. Marginal zone lymphomas: Esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischbach, W.; Goebeler-Kolve, M.E.; Dragosics, B.; Greiner, A.; Stolte, M. Long term outcome of patients with gastric marginal zone b cell lymphoma of mucosa associated lymphoid tissue (malt) following exclusive helicobacter pylori eradication therapy: Experience from a large prospective series. Gut 2004, 53, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Iijima, K.; Ono, S.; Tajika, M.; Tari, A.; Kitadai, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Nagaya, T.; et al. Long-term clinical outcome of gastric malt lymphoma after eradication of helicobacter pylori: A multicentre cohort follow-up study of 420 patients in japan. Gut 2012, 61, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wündisch, T.; Thiede, C.; Morgner, A.; Dempfle, A.; Günther, A.; Liu, H.; Ye, H.; Du, M.-Q.; Kim, T.D.; Bayerdörffer, E.; et al. Long-term follow-up of gastric malt lymphoma after helicobacter pylori eradication. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8018–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andriani, A.; Miedico, A.; Tedeschi, L.; Patti, C.; Di Raimondo, F.; Leone, M.; Schinocca, L.; Romanelli, A.; Bonanno, G.; Linea, C.; et al. Management and long-term follow-up of early stage h. Pylori-associated gastric malt-lymphoma in clinical practice: An italian, multicentre study. Dig. Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, K.D.; Kim, G.H.; Park, S.O.; Lee, K.J.; Moon, J.Y.; Jeon, H.K.; Baek, D.H.; Lee, B.E.; Song, G.A. Treatment outcome for gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma according to helicobacter pylori infection status: A single-center experience. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Copie-Bergman, C.; Wotherspoon, A.C.; Capella, C.; Motta, T.; Pedrinis, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Bertoni, F.; Conconi, A.; Zucca, E.; Ponzoni, M.; et al. Gela histological scoring system for post-treatment biopsies of patients with gastric malt lymphoma is feasible and reliable in routine practice. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Copie-Bergman, C.; Gaulard, P.; Lavergne-Slove, A.; Brousse, N.; Fléjou, J.F.; Dordonne, K.; de Mascarel, A.; Wotherspoon, A.C. Proposal for a new histological grading system for post-treatment evaluation of gastric malt lymphoma. Gut 2003, 52, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fischbach, W.; Goebeler, M.E.; Ruskone-Fourmestraux, A.; Wundisch, T.; Neubauer, A.; Raderer, M.; Savio, A.; Group, E. Most patients with minimal histological residuals of gastric malt lymphoma after successful eradication of helicobacter pylori can be managed safely by a watch and wait strategy: Experience from a large international series. Gut 2007, 56, 1685–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cook, J.R.; Chott, A.; Nakamura, S.; Müller-Hermelink, H.K.; Harris, N.L.; Swerdlow, S.H. Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (malt lymphoma). In WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, revised 4th ed.; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Eds.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 259–262. [Google Scholar]
- Thieblemont, C.; Cascione, L.; Conconi, A.; Kiesewetter, B.; Raderer, M.; Gaidano, G.; Martelli, M.; Laszlo, D.; Coiffier, B.; Lopez Guillermo, A.; et al. A malt lymphoma prognostic index. Blood 2017, 130, 1409–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A.; Alliance, A.L.; Lymphoma, G.; Eastern Cooperative Oncology, G.; et al. Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and response assessment of hodgkin and non-hodgkin lymphoma: The lugano classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raderer, M.; Vorbeck, F.; Formanek, M.; Osterreicher, C.; Valencak, J.; Penz, M.; Kornek, G.; Hamilton, G.; Dragosics, B.; Chott, A. Importance of extensive staging in patients with mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (malt)-type lymphoma. Br. J. Cancer 2000, 83, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesewetter, B.; Lamm, W.; Dolak, W.; Lukas, J.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Weber, M.; Schiefer, A.I.; Kornauth, C.; Bayer, G.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; et al. Transformed mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas: A single institution retrospective study including polymerase chain reaction-based clonality analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hancock, B.W.; Qian, W.; Linch, D.; Delchier, J.C.; Smith, P.; Jakupovic, I.; Burton, C.; Souhami, R.; Wotherspoon, A.; Copie-Bergman, C.; et al. Chlorambucil versus observation after anti-helicobacter therapy in gastric malt lymphomas: Results of the international randomised ly03 trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2009, 144, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teckie, S.; Qi, S.; Chelius, M.; Lovie, S.; Hsu, M.; Noy, A.; Portlock, C.; Yahalom, J. Long-term outcome of 487 patients with early-stage extra-nodal marginal zone lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1064–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, E.J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jung, H.Y.; Jung, K.; Cho, C.J.; Na, H.K.; Jung, K.W.; do Kim, H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, K.D.; et al. Bone marrow involvement is not associated with the clinical outcomes of gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raderer, M.; Streubel, B.; Woehrer, S.; Puespoek, A.; Jaeger, U.; Formanek, M.; Chott, A. High relapse rate in patients with malt lymphoma warrants lifelong follow-up. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 3349–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Parameter | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| Sex (Female/Male) | 51% (70/137)/49% (67/137) |
| Median age (range) | 63 years (22–85 years) |
| Age ≥ 70 years | 28% (38/137) |
| Stage of disease-Ann Arbor | |
| Ann Arbor IE | 66% (90/137) |
| Ann Arbor IIE | 23% (32/137) |
| Ann Arbor IIIE | 1% (1/137) |
| Ann Arbor IV | 10% (14/137) |
| Stage of disease-Lugano | |
| Lugano I | 66% (90/137) |
| Lugano II | 23% (32/137) |
| Lugano IV | 11% (15/137) |
| MALT-IPI | |
| Low risk | 62% (75/122) |
| Intermediate risk | 33% (40/122) |
| High risk | 6% (7/122) |
| Further clinical features | |
| Helicobacter pylori positive | 68% (93/137) |
| Plasmacellular differentiation | 22% (22/101) |
| LDH > upper normal limit | 7% (8/122) |
| Autoimmune disorder | 20% (24/120) |
| Beta-2-micorglobuline > UNL | 15% (19/130) |
| Hepatitis B/C virus | 2% (2/121) |
| Paraproteinemia | 27% (25/91) |
| Median follow-up time (interquartile range) | 56.2 months (26.3–111.6) |
| Treatment/Response | Number of Patients |
|---|---|
| First-line treatment overall collective | |
| Helicobacter pylori eradication | 70% (96/137) |
| Systemic treatment (chemo-/immunotherapy) | 23% (32/137) |
| Local therapy (radiation, surgery) | 4% (5/137) |
| Watch and wait | 3% (4/137) |
| First-line treatment Helicobacter pylori negative | |
| Helicobacter pylori eradication | 50% (22/44) |
| Systemic treatment (chemo-/immunotherapy) | 41% (18/44) |
| Local therapy (radiation, surgery) | 5% (2/44) |
| Watch and wait | 5% (2/44) |
| Response to treatment overall collective | |
| Overall response rate | 67% (86/128) |
| Complete remission | 48% (62/128) |
| Partial remission | 19% (24/128) |
| Stable disease | 30% (38/128) |
| Progressive disease | 3% (4/128) |
| Response to eradication therapy | |
| Overall response rate | 58% (54/93) |
| Complete remission | 38% (35/93) |
| Partial remission | 20% (19/93) |
| Stable disease | 39% (36/93) |
| Progressive disease | 3% (3/93) |
| Response to systemic treatment * | |
| Overall response rate | 90% (27/30) |
| Complete remission | 77% (23/30) |
| Partial remission | 13% (4/30) |
| Stable disease | 7% (2/30) |
| Progressive disease | 3% (1/30) |
| Response to local treatment | |
| Overall response rate | 100% (5/5) |
| Complete remission | 80% (4/5) |
| Partial remission | 20% (1/5) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiesewetter, B.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; Dolak, W.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Raderer, M. Depth of Remission Following First-Line Treatment Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Progression-Free Survival in Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020492
Kiesewetter B, Simonitsch-Klupp I, Dolak W, Mayerhoefer ME, Raderer M. Depth of Remission Following First-Line Treatment Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Progression-Free Survival in Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020492
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiesewetter, Barbara, Ingrid Simonitsch-Klupp, Werner Dolak, Marius E. Mayerhoefer, and Markus Raderer. 2020. "Depth of Remission Following First-Line Treatment Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Progression-Free Survival in Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma" Cancers 12, no. 2: 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020492
APA StyleKiesewetter, B., Simonitsch-Klupp, I., Dolak, W., Mayerhoefer, M. E., & Raderer, M. (2020). Depth of Remission Following First-Line Treatment Is an Independent Prognostic Marker for Progression-Free Survival in Gastric Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma. Cancers, 12(2), 492. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020492








