Small Molecule Binds with Lymphocyte Antigen 6K to Induce Cancer Cell Death
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
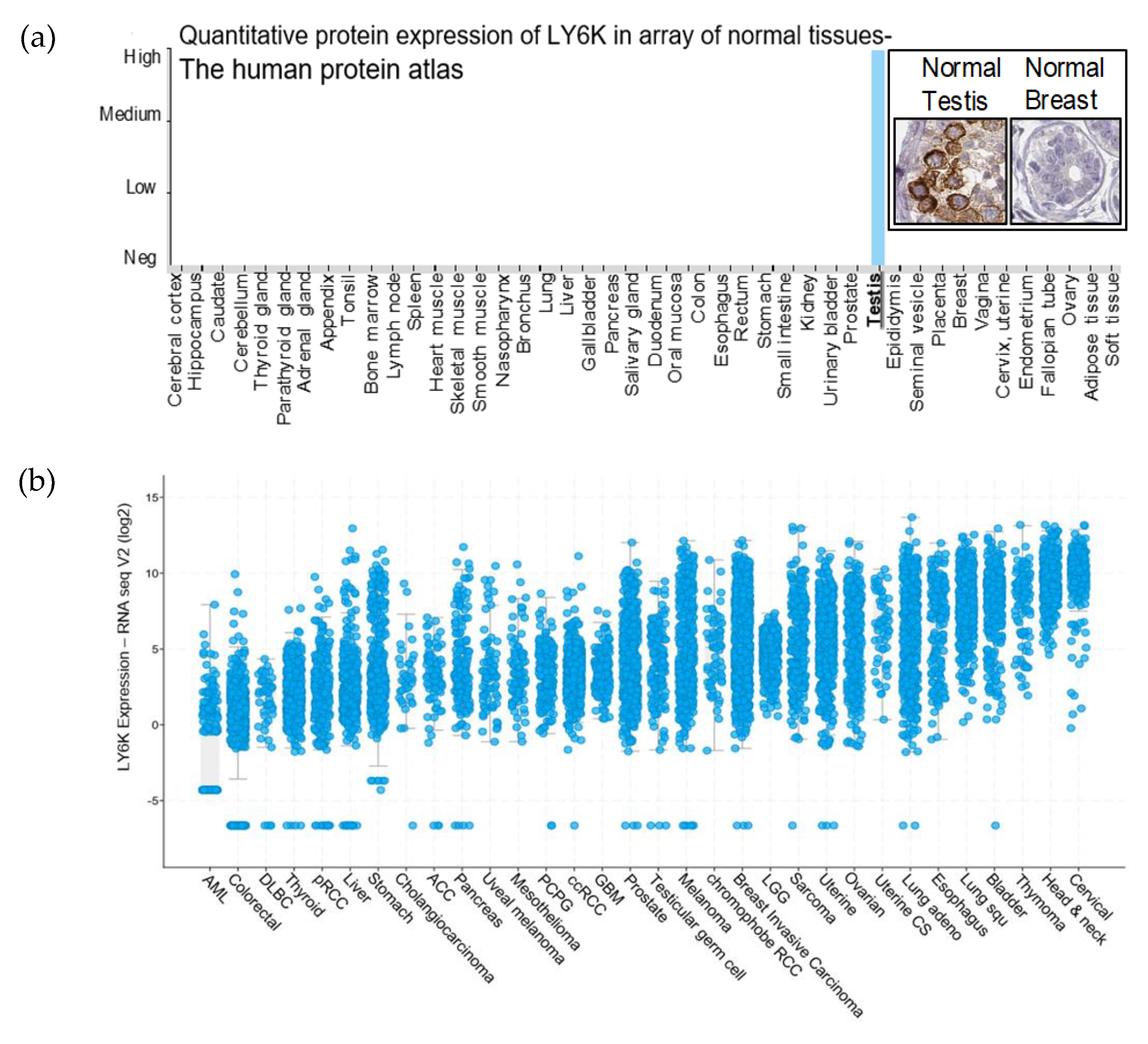
2.1. LY6K Is a Feasible Target to Develop Targeted Therapeutics
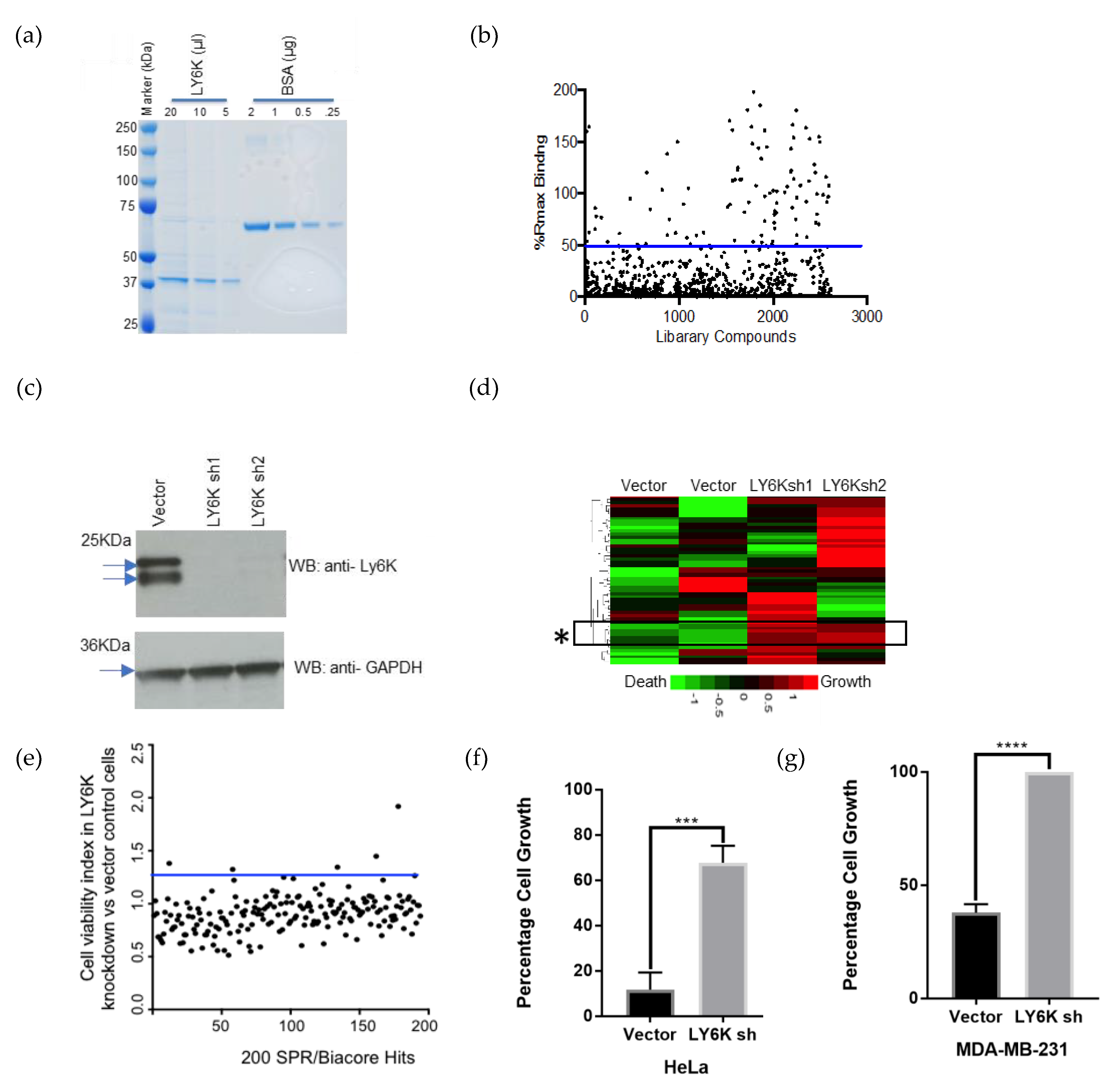
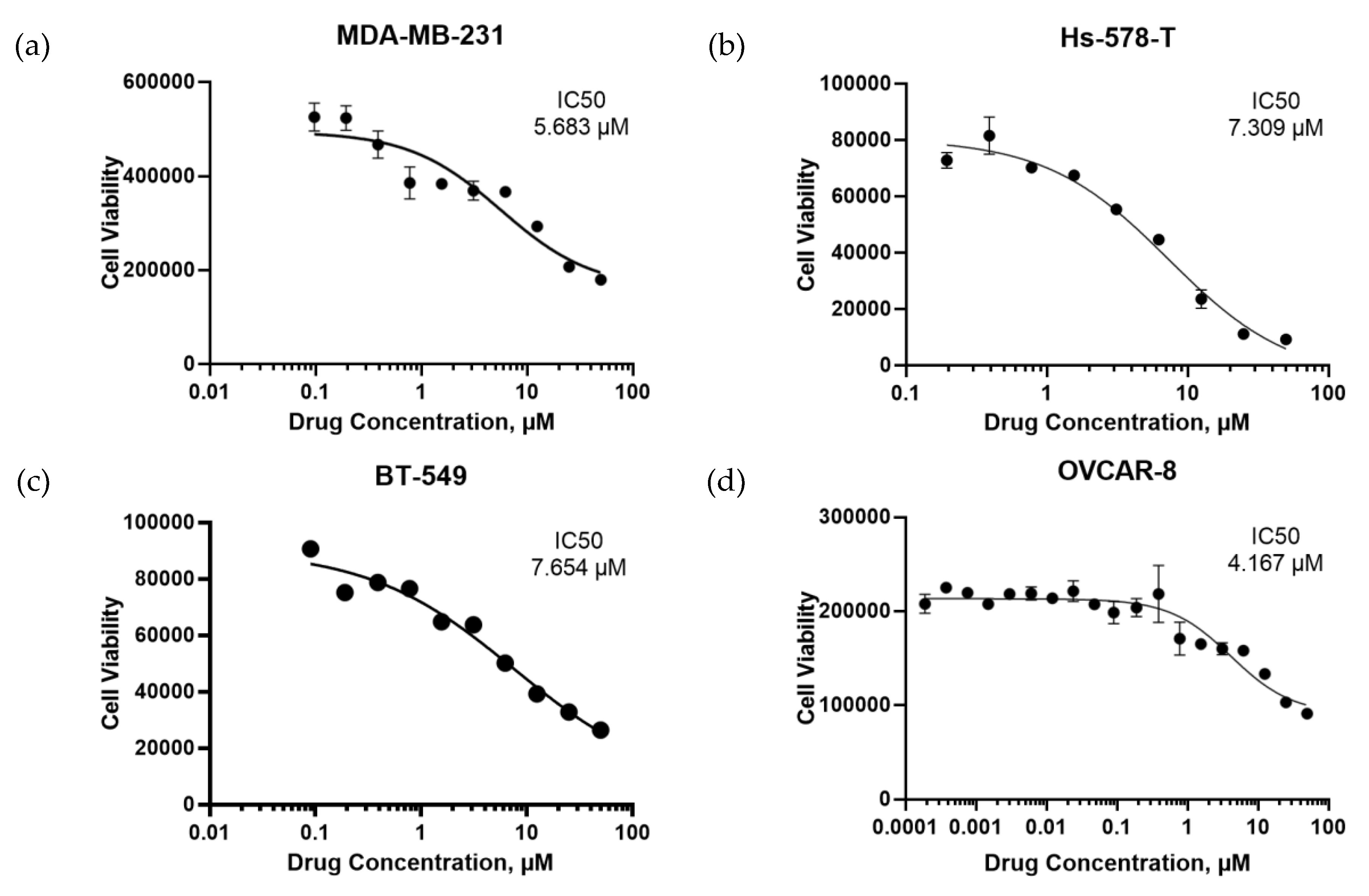
2.2. Identification of a Small Molecule Binder of LY6K
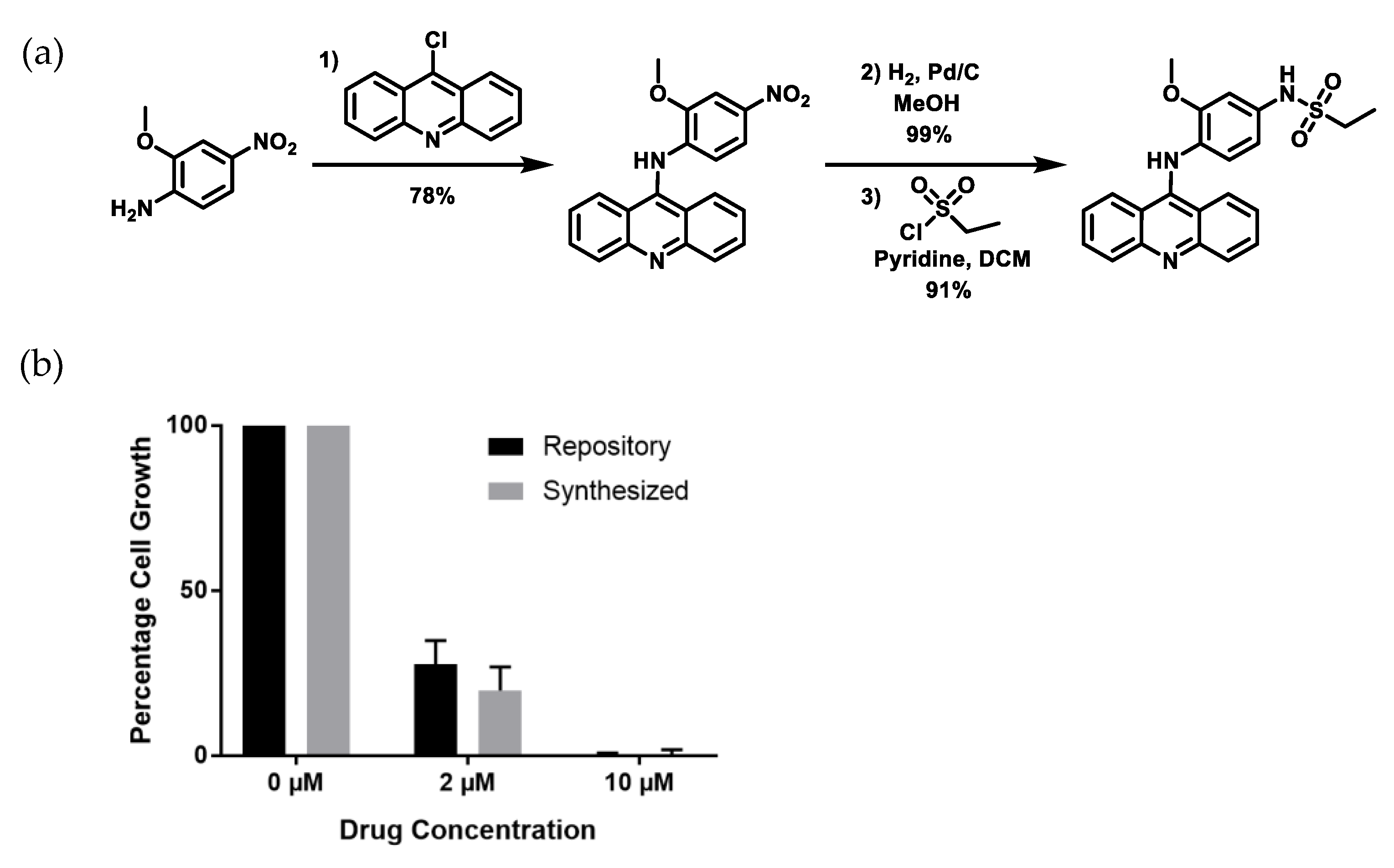
2.3. Re-Synthesized NSC243928 Has Comparable Activity to the Library-Obtained Compound
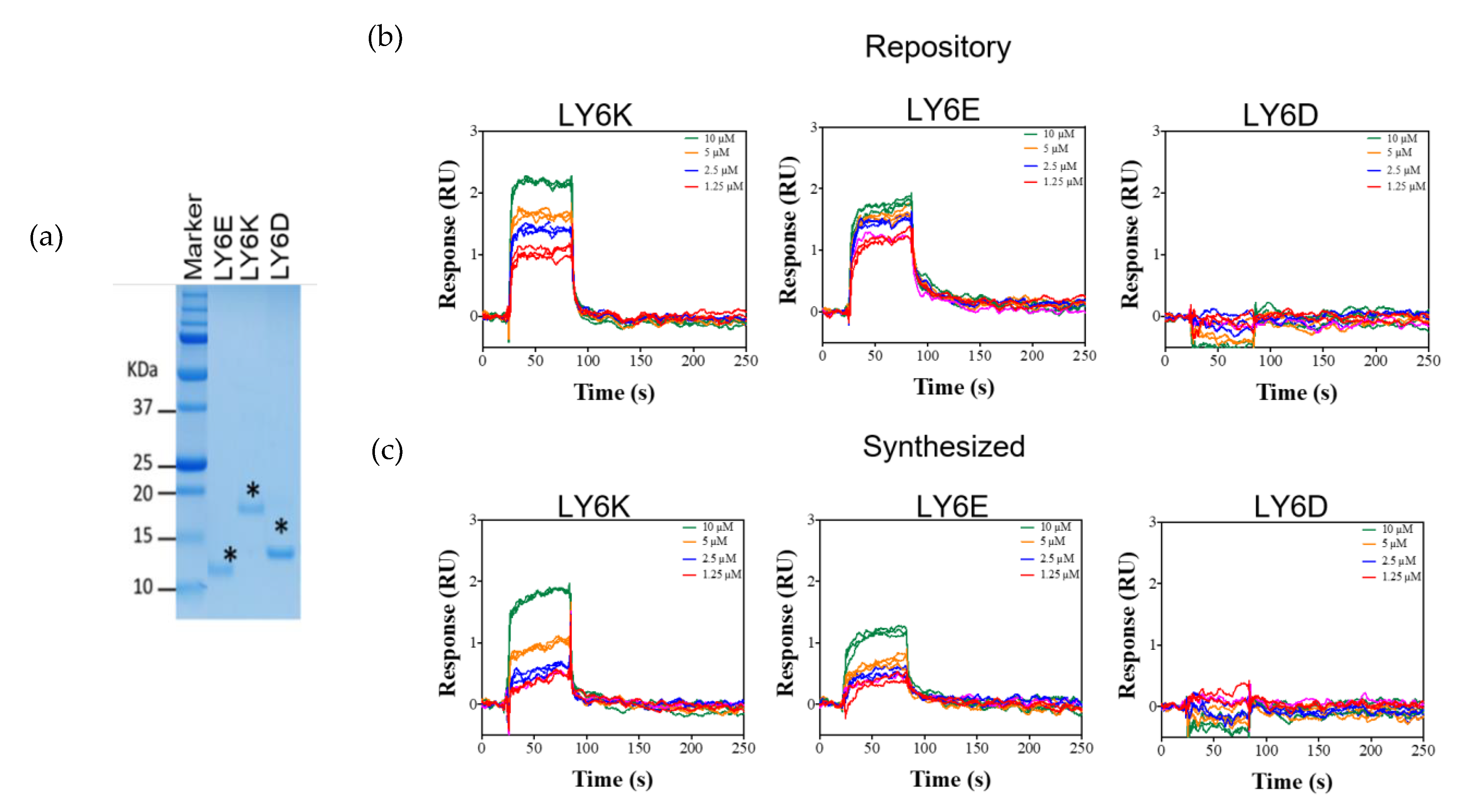
2.4. NSC243928 Shows Specific Binding with the Mature Form of LY6K
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmids
4.2. Mammalian Cell Culture and Transfection
4.3. Purification of Full-Length GST-LY6K Protein from Mammalian Cells
4.4. Purification of Mature Form of LY6K, LY6D, and LY6E Proteins from E. coli
4.5. Small Molecule Library and Preparation of Master Drug Plates
4.6. Surface Plasmon Resonance
4.7. Synthesis of NSC243928
4.8. X-Ray Structure Determination, C22H21N3O3S·H2O (NSC243928)
4.9. Cell Death Assays
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Disclaimer
References
- Loughner, C.L.; Bruford, E.A.; McAndrews, M.S.; Delp, E.E.; Swamynathan, S.; Swamynathan, S.K. Organization, evolution and functions of the human and mouse Ly6/uPAR family genes. Hum. Genom. 2016, 10, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Letessier, A.; Sircoulomb, F.; Ginestier, C.; Cervera, N.; Monville, F.; Gelsi-Boyer, V.; Esterni, B.; Geneix, J.; Finetti, P.; Zemmour, C.; et al. Frequency, prognostic impact, and subtype association of 8p12, 8q24, 11q13, 12p13, 17q12, and 20q13 amplifications in breast cancers. BMC Cancer 2006, 6, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Visapää, H.; Seligson, D.; Eeva, M.; Gaber, F.; Rao, J.; Belldegrun, A.; Palotie, A. 8q24 amplification in transitional cell carcinoma of bladder. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2003, 11, 33–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fromont, G.; Godet, J.; Peyret, A.; Irani, J.; Celhay, O.; Rozet, F.; Cathelineau, X.; Cussenot, O. 8q24 amplification is associated with Myc expression and prostate cancer progression and is an independent predictor of recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Hum. Pathol. 2013, 44, 1617–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, H.; Wei, Q.; Ding, X.; Li, W. Amplification and the clinical significance of circulating cell-free DNA of PVT1 in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Upadhyay, G. Emerging Role of Lymphocyte Antigen-6 Family of Genes in Cancer and Immune Cells. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, H.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, K.M.; Lee, H.W.; Kang, H.G.; Woo, Y.M.; Park, E.Y.; Ko, J.Y.; Suzuki, H.; et al. Epigenetic activation of LY6K predicts the presence of metastasis and poor prognosis in breast carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 55677–55689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuda, R.; Enokida, H.; Chiyomaru, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Sugimoto, T.; Kawakami, K.; Tatarano, S.; Yoshino, H.; Toki, K.; Uchida, Y.; et al. LY6K is a novel molecular target in bladder cancer on basis of integrate genome-wide profiling. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, N.; Takano, A.; Yasui, W.; Inai, K.; Nishimura, H.; Ito, H.; Miyagi, Y.; Nakayama, H.; Fujita, M.; Hosokawa, M.; et al. Cancer-testis antigen lymphocyte antigen 6 complex locus K is a serologic biomarker and a therapeutic target for lung and esophageal carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11601–11611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, L.; McGarvey, P.; Madhavan, S.; Kumar, R.; Gusev, Y.; Upadhyay, G. Distinct lymphocyte antigens 6 (Ly6) family members Ly6D, Ly6E, Ly6K and Ly6H drive tumorigenesis and clinical outcome. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11165–11193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, S.; Yoshitake, H.; Tsukamoto, H.; Matsuura, H.; Kato, K.; Sakuraba, M.; Takamori, K.; Fujiwara, H.; Takeda, S.; Araki, Y. TEX101, a glycoprotein essential for sperm fertility, is required for stable expression of Ly6k on testicular germ cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujihara, Y.; Okabe, M.; Ikawa, M. GPI-anchored protein complex, LY6K/TEX101, is required for sperm migration into the oviduct and male fertility in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2014, 90, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlHossiny, M.; Luo, L.; Frazier, W.R.; Steiner, N.; Gusev, Y.; Kallakury, B.; Glasgow, E.; Creswell, K.; Madhavan, S.; Kumar, R.; et al. Ly6E/K Signaling to TGFbeta Promotes Breast Cancer Progression, Immune Escape, and Drug Resistance. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3376–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mezencev, R.; Wang, L.; McDonald, J.F. Identification of inhibitors of ovarian cancer stem-like cells by high-throughput screening. J Ovarian Res. 2012, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uhlen, M.; Bjorling, E.; Agaton, C.; Szigyarto, C.A.; Amini, B.; Andersen, E.; Andersson, A.C.; Angelidou, P.; Asplund, A.; Asplund, C.; et al. A human protein atlas for normal and cancer tissues based on antibody proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2005, 4, 1920–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, P.Y.; Wang, J.X.; Parisini, E.; Dascher, C.C.; Nigrovic, P.A. Ly6 family proteins in neutrophil biology. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, L.R.; Denny, W.A. Potential antitumor agents. 30. Mutagenic activity of some 9-anilinoacridines: Relationships between structure, mutagenic potential, and antileukemic activity. J. Med. Chem. 1979, 22, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G.; Yin, Y.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Derynck, R.; Glazer, R.I. Stem cell antigen-1 enhances tumorigenicity by disruption of growth differentiation factor-10 (GDF10)-dependent TGF-beta signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 7820–7825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, C.; Stanford, W.L. Concise review: Stem cell antigen-1: Expression, function, and enigma. Stem Cells 2007, 25, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.J.; Hirai, H.; Sakai, R. Evidence that SH2 domains promote processive phosphorylation by protein-tyrosine kinases. Curr. Biol. 1995, 5, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cope, H.; Mutter, R.; Heal, W.; Pascoe, C.; Brown, P.; Pratt, S.; Chen, B. Synthesis and SAR study of acridine, 2-methylquinoline and 2-phenylquinazoline analogues as anti-prion agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 41, 1124–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gellerman, G.; Waintraub, S.; Albeck, A.; Gaisin, V. One-Pot Synthesis of Novel Antiproliferative 9-Aminoacridines. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2011, 2011, 4176–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgaher, W.A.; Sharma, K.K.; Haupenthal, J.; Saladini, F.; Pires, M.; Real, E.; Mely, Y.; Hartmann, R.W. Discovery and Structure-Based Optimization of 2-Ureidothiophene-3-carboxylic Acids as Dual Bacterial RNA Polymerase and Viral Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 7212–7222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruker SAINT (Version 8.38A) in APEX3 (Version 2018.1-0); Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2018.
- Krause, L.; Herbst-Irmer, R.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Stalke, D. Comparison of silver and molybdenum microfocus X-ray sources for single-crystal structure determination. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2015, 48, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. SHELXT-integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL. Acta Crystallogr. C Struct. Chem. 2015, 71, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourhis, L.J.; Dolomanov, O.V.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.; Puschmann, H. The anatomy of a comprehensive constrained, restrained refinement program for the modern computing environment—Olex2 dissected. Acta Crystallogr. A Found. Adv. 2015, 71, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benti, S.; Tiwari, P.B.; Goodlett, D.W.; Daneshian, L.; Kern, G.B.; Smith, M.D.; Uren, A.; Chruszcz, M.; Shimizu, L.S.; Upadhyay, G. Small Molecule Binds with Lymphocyte Antigen 6K to Induce Cancer Cell Death. Cancers 2020, 12, 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020509
Benti S, Tiwari PB, Goodlett DW, Daneshian L, Kern GB, Smith MD, Uren A, Chruszcz M, Shimizu LS, Upadhyay G. Small Molecule Binds with Lymphocyte Antigen 6K to Induce Cancer Cell Death. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):509. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020509
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenti, Senyi, Purushottam B. Tiwari, Dustin W. Goodlett, Leily Daneshian, Grant B. Kern, Mark D. Smith, Aykut Uren, Maksymilian Chruszcz, Linda S. Shimizu, and Geeta Upadhyay. 2020. "Small Molecule Binds with Lymphocyte Antigen 6K to Induce Cancer Cell Death" Cancers 12, no. 2: 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020509
APA StyleBenti, S., Tiwari, P. B., Goodlett, D. W., Daneshian, L., Kern, G. B., Smith, M. D., Uren, A., Chruszcz, M., Shimizu, L. S., & Upadhyay, G. (2020). Small Molecule Binds with Lymphocyte Antigen 6K to Induce Cancer Cell Death. Cancers, 12(2), 509. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020509








