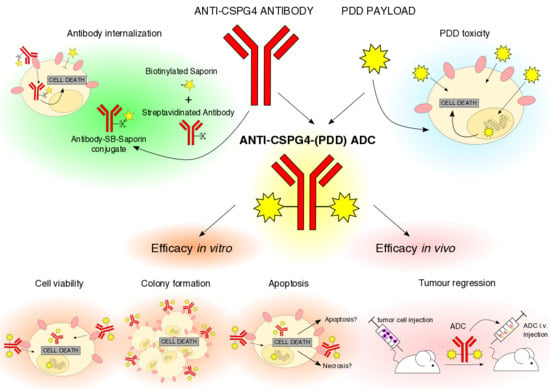
A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Delivering a DNA Mono-Alkylating Payload to Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (CSPG4)-Expressing Melanoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Anti-CSPG4 Monoclonal Antibody Generation and Evaluation of Internalizing Potential by Tumor Cells
2.2. Evaluation of Payload Toxicity across Different Cancer Cell Types
2.3. Generation of Anti-CSPG4(PDD) ADC by Stochastic Conjugation
2.4. Anti-CSPG4-(PDD) ADC Restricts Viability and Promotes Apoptosis of CSPG4-Expressing Melanoma Cells
2.5. Anti-CSPG4-(PDD) Displays Tumor-Growth Restricting Potency in Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. CSPG4 IgG Expression
4.3. Size Exclusion Chromatography
4.4. Antibody-Drug Conjugate Production and Characterization
4.5. DAR by Hydrophobic Interaction HPLC (HIC)
4.6. Residual Toxin Linker by Reverse Phase HPLC (RPLC)
4.7. Monomer Content and Protein Concentration by Size Exclusion HPLC (SEC)
4.8. SDS-PAGE Gel Electrophoresis
4.9. Binding Assay of Anti-CSPG4 IgG
4.10. Cell Viability Assay
4.11. Confocal Microscopy
4.12. Cell Counting and Apoptosis assay
4.13. In Vivo Procedures
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, J.C.; Sun, W.; Khare, P.; Karimi, M.; Wang, X.; Shen, Y.; Ober, R.J.; Ward, E.S. Engineering a HER2-specific antibody-drug conjugate to increase lysosomal delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, D.M.; Bossenmaier, B.; Kollmorgen, G.; Niederfellner, G. Acquired Resistance to Antibody-Drug Conjugates. Cancers (Basel) 2019, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.; Goetsch, L.; Dumontet, C.; Corvaïa, N. Strategies and challenges for the next generation of antibody-drug conjugates. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 315–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barok, M.; Tanner, M.; Köninki, K.; Isola, J. Trastuzumab-DM1 causes tumour growth inhibition by mitotic catastrophe in trastuzumab-resistant breast cancer cells in vivo. Breast Cancer Res. 2011, 13, R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagayama, A.; Ellisen, L.W.; Chabner, B.; Bardia, A. Antibody-Drug Conjugates for the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Clinical Experience and Latest Developments. Target. Oncol. 2017, 12, 719–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, S. Moxetumomab pasudotox: First global approval. Drugs 2018, 78, 1763–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jen, E.Y.; Gao, X.; Li, L.; Zhuang, L.; Simpson, N.E.; Aryal, B.; Wang, R.; Przepiorka, D.; Shen, Y.L.; Leong, R.; et al. FDA Approval Summary: Tagraxofusp-erzs For Treatment of Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, P.A.; Reuben, A.; Cooper, Z.A.; Wargo, J.A. Targeted therapies combined with immune checkpoint therapy. Cancer J. 2016, 22, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wróbel, S.; Przybyło, M.; Stępień, E. The clinical trial landscape for melanoma therapies. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlick, A.C.; Fecher, L.; Ascierto, P.A.; Sullivan, R.J. Frontline Therapy for BRAF-Mutated Metastatic Melanoma: How Do You Choose, and Is There One Correct Answer? Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2019, 39, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foletto, M.C.; Haas, S.E. Cutaneous melanoma: New advances in treatment. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2014, 89, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, R.W.; Barbie, D.A.; Flaherty, K.T. Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Br. J. Cancer 2018, 118, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.; McNeil, C.M.; LoRusso, P.; Patel, M.R.; Kabbarah, O.; Li, C.; Sanabria, S.; Flanagan, W.M.; Yeh, R.-F.; Brunstein, F.; et al. Phase I study of the anti-endothelin B receptor antibody-drug conjugate DEDN6526A in patients with metastatic or unresectable cutaneous, mucosal, or uveal melanoma. Investig. New Drugs 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, P.A.; Pavlick, A.C.; Johnson, D.B.; Hart, L.L.; Infante, J.R.; Luke, J.J.; Lutzky, J.; Rothschild, N.E.; Spitler, L.E.; Cowey, C.L.; et al. A phase 2 study of glembatumumab vedotin, an antibody-drug conjugate targeting glycoprotein NMB, in patients with advanced melanoma. Cancer 2019, 125, 1113–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, A.A.N.; Biondini, M.; Curiel, R.; Siegel, P.M. Targeting GPNMB with glembatumumab vedotin: Current developments and future opportunities for the treatment of cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 179, 127–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, N.C.; Kasamon, Y.L.; Chen, H.; de Claro, R.A.; Ye, J.; Blumenthal, G.M.; Farrell, A.T.; Pazdur, R. FDA Approval Summary: Brentuximab Vedotin in First-Line Treatment of Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Oncologist 2019, 24, e180–e187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Polatuzumab vedotin: First global approval. Drugs 2019, 79, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boshuizen, J.; Koopman, L.A.; Krijgsman, O.; Shahrabi, A.; van den Heuvel, E.G.; Ligtenberg, M.A.; Vredevoogd, D.W.; Kemper, K.; Kuilman, T.; Song, J.-Y.; et al. Cooperative targeting of melanoma heterogeneity with an AXL antibody-drug conjugate and BRAF/MEK inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoli, M.; Ferrone, S.; Wang, X. Functional and clinical relevance of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 109, 73–121. [Google Scholar]
- Price, M.A.; Colvin Wanshura, L.E.; Yang, J.; Carlson, J.; Xiang, B.; Li, G.; Ferrone, S.; Dudek, A.Z.; Turley, E.A.; McCarthy, J.B. CSPG4, a potential therapeutic target, facilitates malignant progression of melanoma. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2011, 24, 1148–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrer, D.C.; Dörrie, J.; Schaft, N. CSPG4 as Target for CAR-T-Cell Therapy of Various Tumor Entities-Merits and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, C.; Li, J.; Luttgen, M.S.; Kolatkar, A.; Kendall, J.T.; Flores, E.; Topp, Z.; Samlowski, W.E.; McClay, E.; Bethel, K.; et al. Limited genomic heterogeneity of circulating melanoma cells in advanced stage patients. Phys. Biol. 2015, 12, 016008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilieva, K.M.; Cheung, A.; Mele, S.; Chiaruttini, G.; Crescioli, S.; Griffin, M.; Nakamura, M.; Spicer, J.F.; Tsoka, S.; Lacy, K.E.; et al. Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 4 and Its Potential As an Antibody Immunotherapy Target across Different Tumor Types. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coats, S.; Williams, M.; Kebble, B.; Dixit, R.; Tseng, L.; Yao, N.-S.; Tice, D.A.; Soria, J.-C. Antibody-Drug Conjugates: Future Directions in Clinical and Translational Strategies to Improve the Therapeutic Index. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5441–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Sun, M.; Lin, L.; Liu, W.; Han, Q.; Wei, M.; Jin, Y. The analysis of key factors related to adcs structural design. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klute, K.; Nackos, E.; Tasaki, S.; Nguyen, D.P.; Bander, N.H.; Tagawa, S.T. Microtubule inhibitor-based antibody-drug conjugates for cancer therapy. Onco Targets Ther. 2014, 7, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kinneer, K.; Meekin, J.; Tiberghien, A.C.; Tai, Y.-T.; Phipps, S.; Kiefer, C.M.; Rebelatto, M.C.; Dimasi, N.; Moriarty, A.; Papadopoulos, K.P.; et al. SLC46A3 as a Potential Predictive Biomarker for Antibody-Drug Conjugates Bearing Noncleavable Linked Maytansinoid and Pyrrolobenzodiazepine Warheads. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 6570–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantaj, J.; Jackson, P.J.M.; Rahman, K.M.; Thurston, D.E. From Anthramycin to Pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD)-Containing Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 462–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ADC Review. Editorial Team Study Demonstrates Superior Efficacy and Cytotoxicity of Femtogenix’s Sequence-Selective DNA-Interactive Payload. Available online: https://www.adcreview.com/news/study-demonstrates-superior-efficacy-and-cytotoxicity-of-femtogenixs-sequence-selective-dna-interactive-payload/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Jackson, P.J.M.; Thurston, D.E.; Rahman, K.M. PDD Compounds. Google Patents, US20180291021A1. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US20180291021A1 (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Femtogenix Presents Efficacy and Toxicity Data on Antibody Drug Conjugates Containing New Generation of DNA-Binding Therapeutic Payloads—Femtogenix. Available online: https://www.femtogenix.com/femtogenix-presents-efficacy-and-toxicity-data-on-antibody-drug-conjugates-containing-new-generation-of-dna-binding-therapeutic-payloads/ (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Dodev, T.S.; Karagiannis, P.; Gilbert, A.E.; Josephs, D.H.; Bowen, H.; James, L.K.; Bax, H.J.; Beavil, R.; Pang, M.O.; Gould, H.J.; et al. A tool kit for rapid cloning and expression of recombinant antibodies. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crescioli, S.; Chiaruttini, G.; Mele, S.; Ilieva, K.M.; Pellizzari, G.; Spencer, D.I.R.; Gardner, R.A.; Lacy, K.E.; Spicer, J.F.; Tutt, A.N.J.; et al. Engineering and stable production of recombinant IgE for cancer immunotherapy and AllergoOncology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1519–1523.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polito, L.; Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Battelli, M.G.; Bolognesi, A. Saporin-S6: A useful tool in cancer therapy. Toxins (Basel) 2013, 5, 1698–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniels-Wells, T.R.; Helguera, G.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Leoh, L.S.; Erb, M.A.; Diamante, G.; Casero, D.; Pellegrini, M.; Martínez-Maza, O.; Penichet, M.L. Insights into the mechanism of cell death induced by saporin delivered into cancer cells by an antibody fusion protein targeting the transferrin receptor 1. Toxicol. In Vitro 2013, 27, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, J.M. CHAPTER 2. Design factors important for antibody–drug conjugate (ADC) payloads. In Cytotoxic Payloads for Antibody–Drug Conjugates; Thurston, D.E., Jackson, P.J.M., Eds.; Drug Discovery; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 31–56. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, M.L.; Fishkin, N.E.; Li, W.; Whiteman, K.R.; Kovtun, Y.; Reid, E.E.; Archer, K.E.; Maloney, E.K.; Audette, C.A.; Mayo, M.F.; et al. A New Class of Antibody-Drug Conjugates with Potent DNA Alkylating Activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beard, R.E.; Zheng, Z.; Lagisetty, K.H.; Burns, W.R.; Tran, E.; Hewitt, S.M.; Abate-Daga, D.; Rosati, S.F.; Fine, H.A.; Ferrone, S.; et al. Multiple chimeric antigen receptors successfully target chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 in several different cancer histologies and cancer stem cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2014, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldres, C.; Savoldo, B.; Hoyos, V.; Caruana, I.; Zhang, M.; Yvon, E.; Del Vecchio, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Ittmann, M.; Ferrone, S.; et al. T lymphocytes redirected against the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan-4 control the growth of multiple solid tumors both in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Katayama, A.; Wang, Y.; Yu, L.; Favoino, E.; Sakakura, K.; Favole, A.; Tsuchikawa, T.; Silver, S.; Watkins, S.C.; et al. Functional characterization of an scFv-Fc antibody that immunotherapeutically targets the common cancer cell surface proteoglycan CSPG4. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7410–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.P.; Crescioli, S.; Sow, H.S.; Bax, H.J.; Hobbs, C.; Ilieva, K.M.; French, E.; Pellizzari, G.; Cox, V.; Josephs, D.H.; et al. In vivo safety profile of a CSPG4-directed IgE antibody in an immunocompetent rat model. Mabs 2020, 12, 1685349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, E.; Tremante, E.; Fraioli, R.; Leonetti, C.; Zamparelli, C.; Boffi, A.; Morea, V.; Ceci, P.; Giacomini, P. Antibody-drug conjugates: Targeting melanoma with cisplatin encapsulated in protein-cage nanoparticles based on human ferritin. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 12278–12285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, M.S.; Kaur, J.; Prasmickaite, L.; Engesæter, B.Ø.; Weyergang, A.; Skarpen, E.; Berg, K.; Rosenblum, M.G.; Mælandsmo, G.M.; Høgset, A.; et al. Enhanced targeting of triple-negative breast carcinoma and malignant melanoma by photochemical internalization of CSPG4-targeting immunotoxins. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2018, 17, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillard, N.; Cascio, F.; Jackson, P.J.M.; Thurston, D.E. Pyridinobenzodiazepines (PDDs) as Sequence-selective DNA Mono-alkylating Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Payloads. In Cytotoxic Payloads for Antibody-Drug Conjugates; Thurston, D.E., Jackson, P.J.M., Eds.; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2019; pp. 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Veillard, N.; Andriollo, P.; Mantaj, J.; Fox, K.R.; Rahman, K.M.; Procopiou, G.; Cascio, F.; Corcoran, D.B.; Pysz, I.; Cooper, P.A.; et al. Abstract 736: Pyridinobenzodiazepines (PDDs): A new class of sequence-selective DNA mono-alkylating ADC payloads with low hydrophobicity. In Experimental and Molecular Therapeutics; American Association for Cancer Research: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018; p. 736. [Google Scholar]
- Walter, R.B.; Gooley, T.A.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Loken, M.R.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; Flowers, D.A.; Bernstein, I.D.; Appelbaum, F.R. CD33 expression and P-glycoprotein-mediated drug efflux inversely correlate and predict clinical outcome in patients with acute myeloid leukemia treated with gemtuzumab ozogamicin monotherapy. Blood 2007, 109, 4168–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hou, J.; Newman, E.; Kim, Y.; Donohue, C.; Liu, X.; Thomas, S.H.; Forman, S.J.; Kane, S.E. CD30 Downregulation, MMAE Resistance, and MDR1 Upregulation Are All Associated with Resistance to Brentuximab Vedotin. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1376–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chekenya, M.; Krakstad, C.; Svendsen, A.; Netland, I.A.; Staalesen, V.; Tysnes, B.B.; Selheim, F.; Wang, J.; Sakariassen, P.Ø.; Sandal, T.; et al. The progenitor cell marker NG2/MPG promotes chemoresistance by activation of integrin-dependent PI3K/Akt signaling. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5182–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorovits, B.; Krinos-Fiorotti, C. Proposed mechanism of off-target toxicity for antibody-drug conjugates driven by mannose receptor uptake. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2013, 62, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, R.M.; Coumbe, B.G.T.; Josephs, D.H.; Mele, S.; Ilieva, K.M.; Cheung, A.; Tutt, A.N.; Spicer, J.F.; Thurston, D.E.; Crescioli, S.; et al. Antibody structure and engineering considerations for the design and function of Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs). Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1395127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, J.; Beavil, R.L.; Calvert, R.A.; Gould, H.J.; Sutton, B.J.; Beavil, A.J. Disulfide linkage controls the affinity and stoichiometry of IgE Fcepsilon3-4 binding to FcepsilonRI. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 16808–16814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonow, D.; Thurston, D.E. Synthesis of DNA-interactive pyrrolo[2,1-c][1,4]benzodiazepines (PBDs). Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 2815–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Suggitt, M.; Coffils, M.; Baig, M.A.H.; Howard, P.W.; Loadman, P.M.; Hartley, J.A.; Jenkins, T.C.; Thurston, D.E. Fluorescent 7-diethylaminocoumarin pyrrolobenzodiazepine conjugates: Synthesis, DNA interaction, cytotoxicity and differential cellular localization. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2008, 18, 2147–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoffmann, R.M.; Crescioli, S.; Mele, S.; Sachouli, E.; Cheung, A.; Chui, C.K.; Andriollo, P.; Jackson, P.J.M.; Lacy, K.E.; Spicer, J.F.; et al. A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Delivering a DNA Mono-Alkylating Payload to Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (CSPG4)-Expressing Melanoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041029
Hoffmann RM, Crescioli S, Mele S, Sachouli E, Cheung A, Chui CK, Andriollo P, Jackson PJM, Lacy KE, Spicer JF, et al. A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Delivering a DNA Mono-Alkylating Payload to Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (CSPG4)-Expressing Melanoma. Cancers. 2020; 12(4):1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041029
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoffmann, Ricarda M., Silvia Crescioli, Silvia Mele, Eirini Sachouli, Anthony Cheung, Connie K. Chui, Paolo Andriollo, Paul J. M. Jackson, Katie E. Lacy, James F. Spicer, and et al. 2020. "A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Delivering a DNA Mono-Alkylating Payload to Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (CSPG4)-Expressing Melanoma" Cancers 12, no. 4: 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041029
APA StyleHoffmann, R. M., Crescioli, S., Mele, S., Sachouli, E., Cheung, A., Chui, C. K., Andriollo, P., Jackson, P. J. M., Lacy, K. E., Spicer, J. F., Thurston, D. E., & Karagiannis, S. N. (2020). A Novel Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Delivering a DNA Mono-Alkylating Payload to Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan (CSPG4)-Expressing Melanoma. Cancers, 12(4), 1029. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041029