Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
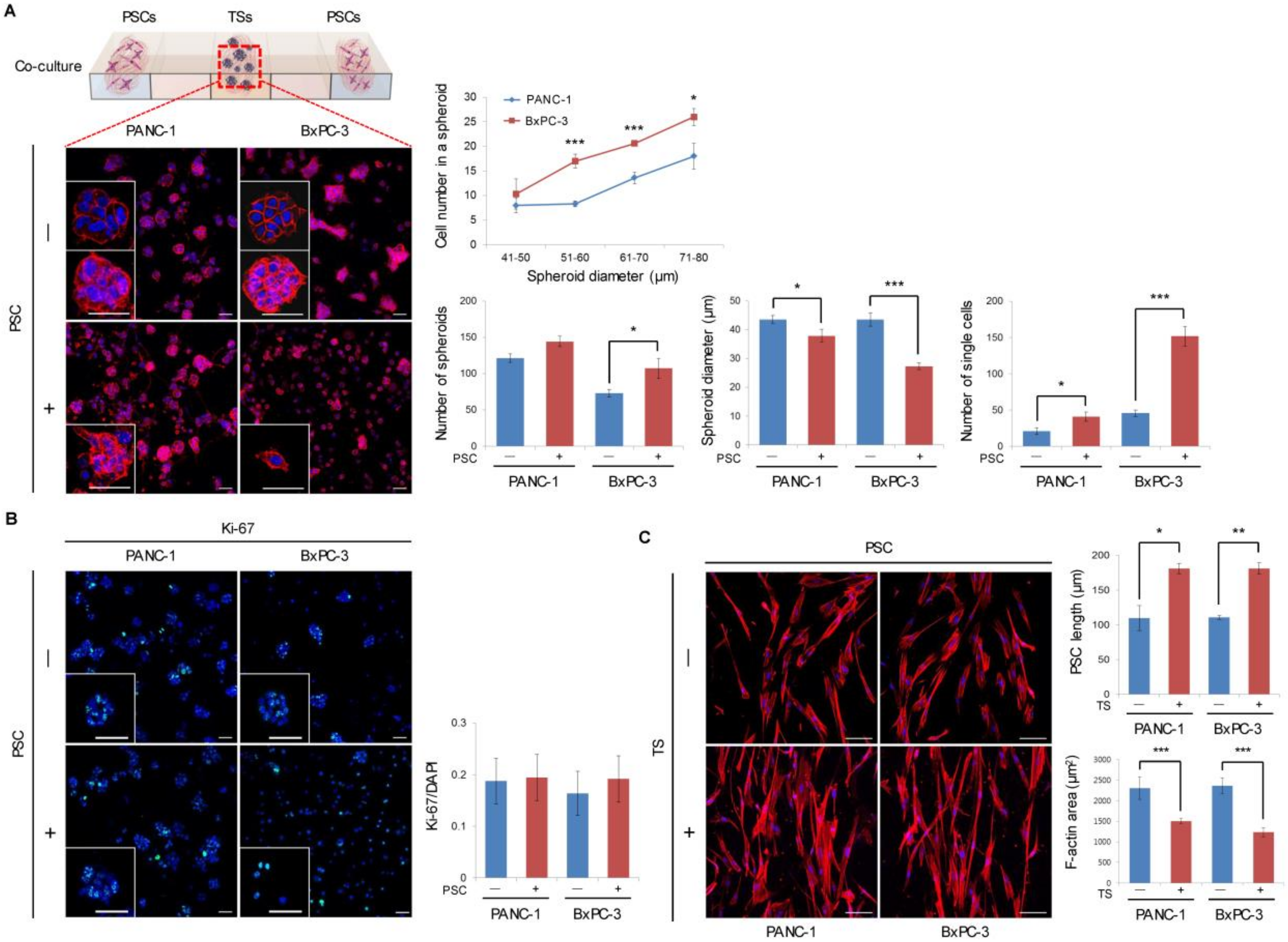
2.1. Formation and Growth of Pancreatic TSs in a Collagen Matrix
2.2. Expression of EMT-Related Factors in TSs
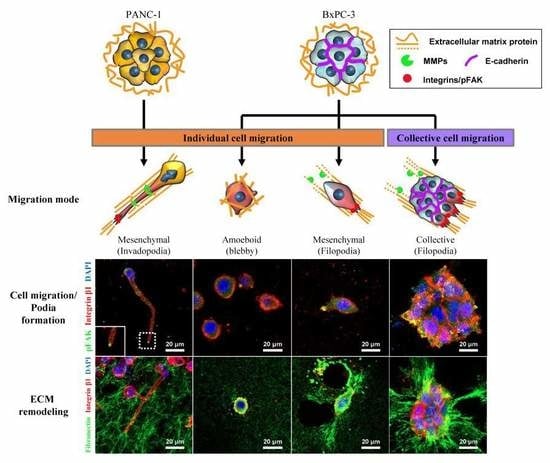
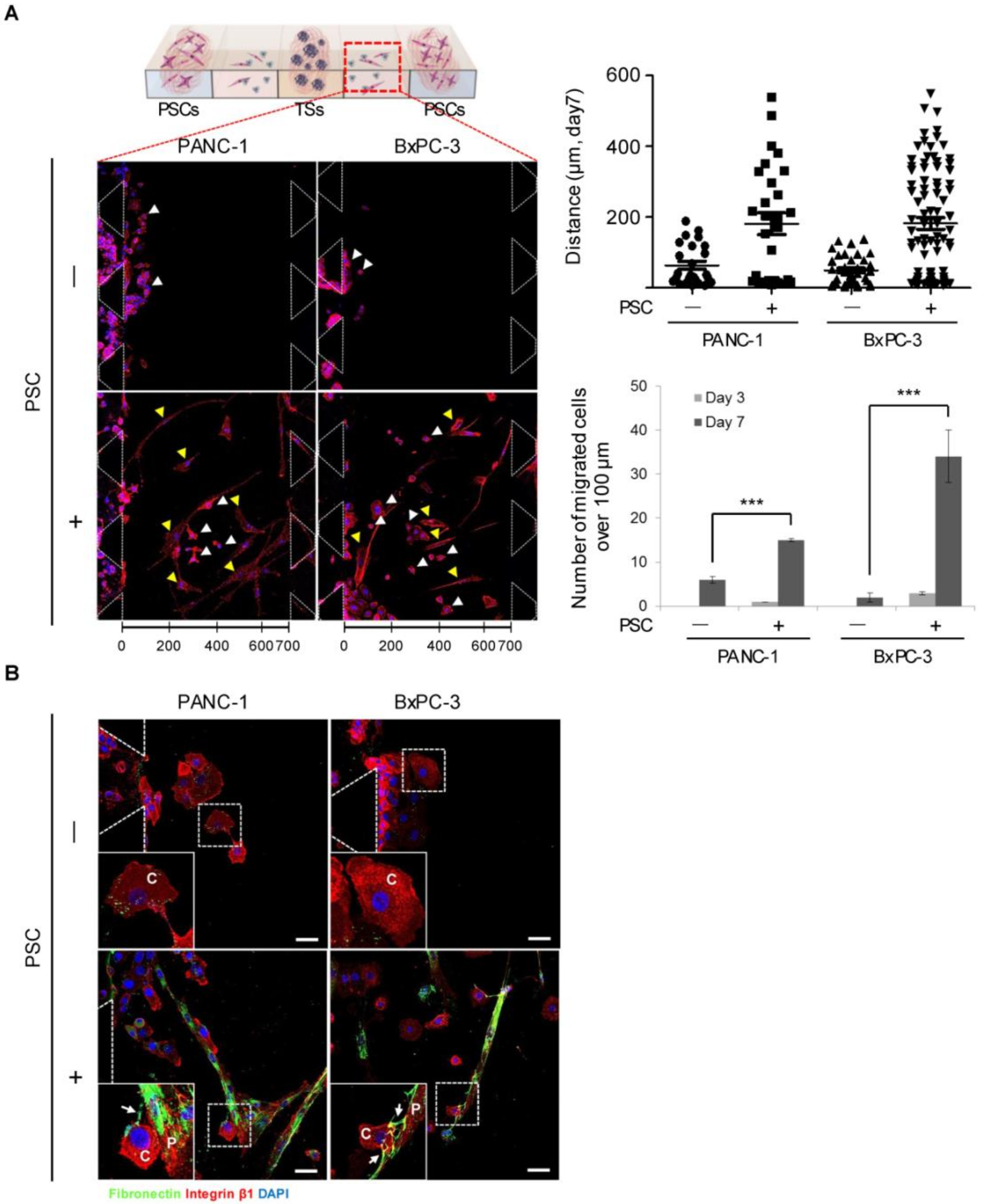
2.3. Differential Modes of Cancer Cell Migration and Focal Adhesion
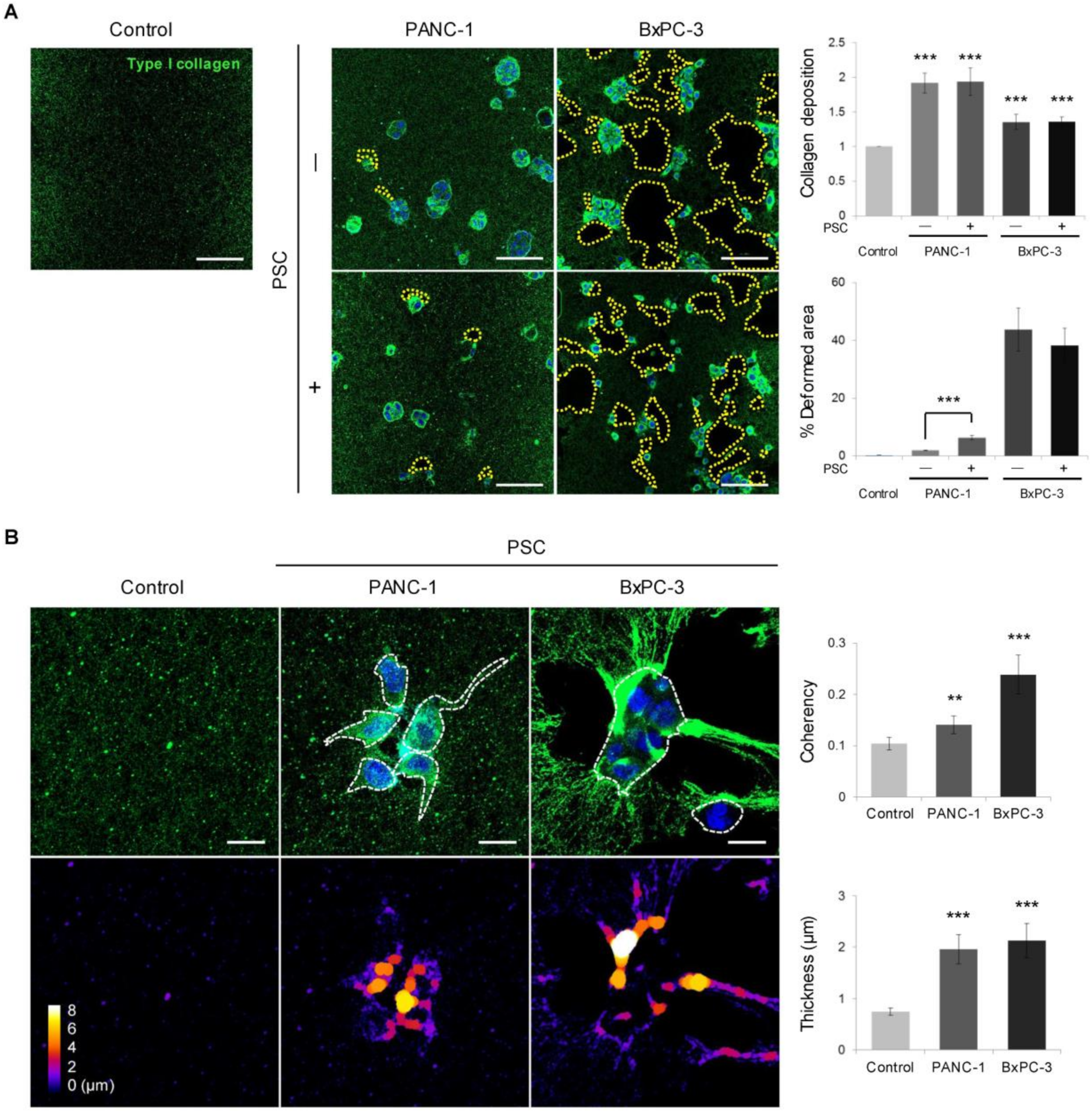
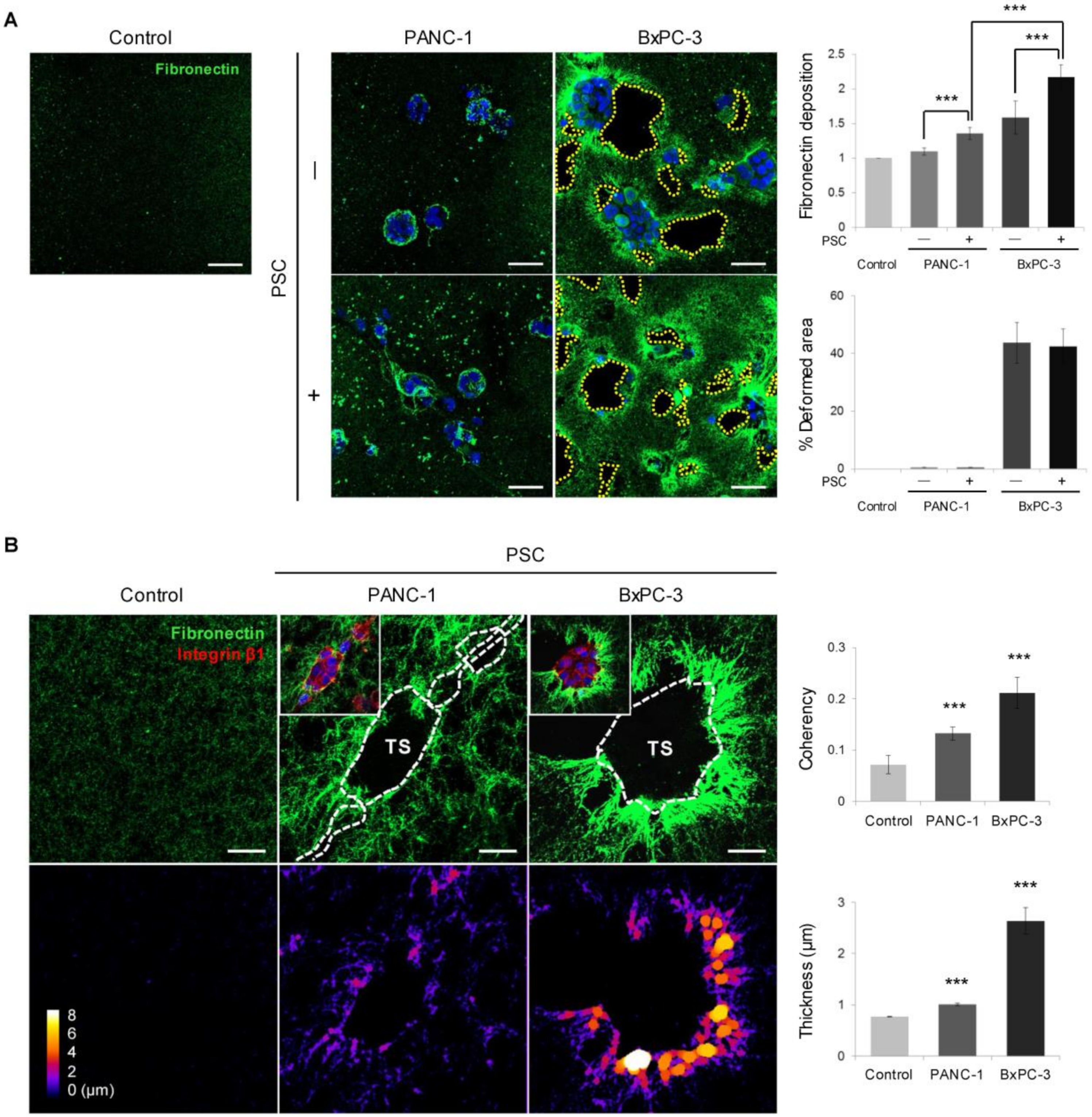
2.4. Remodeling of the Collagen and Fibronectin Matrix
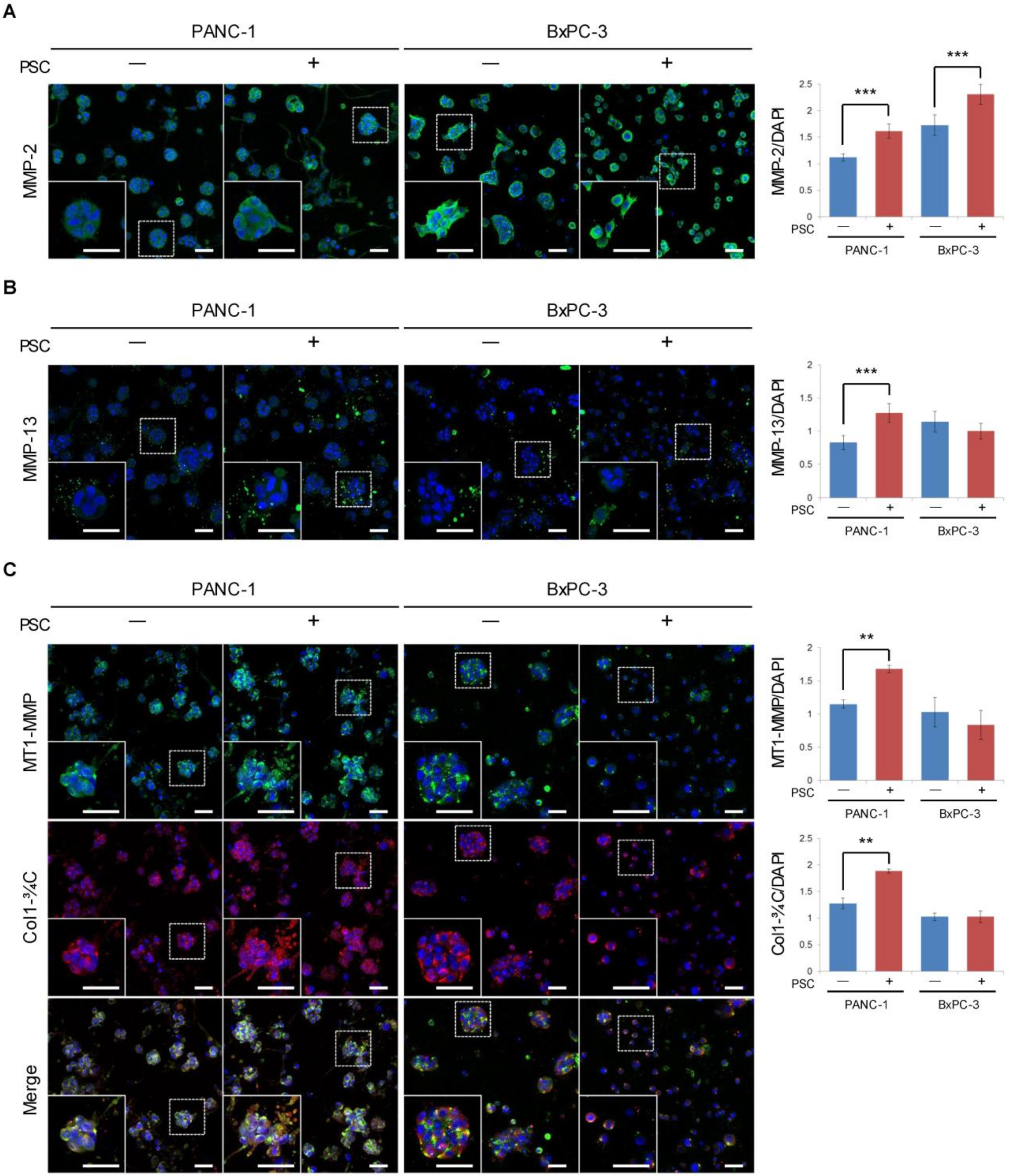
2.5. Expression of MMPs and Cleaved Collagen
2.6. Migration of Cancer Cells out of the Collagen Matrix and Contact with PSCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Fabrication of the Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Microchannel Chip
4.3. Three-Dimensional Spheroid Culture in the Microchannel Chip
4.4. Immunofluorescence Staining and Image Acquisition
4.5. Image Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, B.; Cui, M.; Yang, G.; Wang, H.; Feng, M.; You, L.; Zhao, Y. Tumor microenvironment participates in metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kleeff, J.; Korc, M.; Apte, M.; La Vecchia, C.; Johnson, C.D.; Biankin, A.V.; Neale, R.E.; Tempero, M.; Tuveson, D.A.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. Pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, M.; Jesenofsky, R.; Faissner, R.; Weidenauer, C.; Hagmann, W.; Michl, P.; Heuchel, R.L.; Haas, S.L.; Löhr, J.M. Desmoplasia and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2014, 6, 2137–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neoptolemos, J.P.; Kleeff, J.; Michl, P.; Costello, E.; Greenhalf, W.; Palmer, D.H. Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedl, P.; Wolf, K. Plasticity of cell migration: A multiscale tuning model. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friedl, P.; Alexander, S. Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: Plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 2011, 147, 992–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caswell, P.T.; Zech, T. Actin-Based Cell Protrusion in a 3D Matrix. Trends Cell Biol. 2018, 28, 823–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltavets, V.; Kochetkova, M.; Pitson, S.M.; Samuel, M.S. The Role of the Extracellular Matrix and Its Molecular and Cellular Regulators in Cancer Cell Plasticity. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, K.; Wu, Y.I.; Liu, Y.; Geiger, J.; Tam, E.; Overall, C.; Stack, M.S.; Friedl, P. Multi-step pericellular proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective cancer cell invasion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandya, P.; Orgaz, J.L.; Sanz-Moreno, V. Modes of invasion during tumour dissemination. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 5–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, R.; Lelkes, P.I.; Cukierman, E. Biomechanical and biochemical remodeling of stromal extracellular matrix in cancer. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roma-Rodrigues, C.; Mendes, R.; Baptista, P.V.; Fernandes, A.R. Targeting Tumor Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Wang, D.; Yuan, Z.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y.; An, Y.; Chen, J.; Tu, M.; Lu, Z.; Wei, J.; et al. Persistent activation of pancreatic stellate cells creates a microenvironment favorable for the malignant behavior of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyai, Y.; Esaki, N.; Takahashi, M.; Enomoto, A. Cancer-associated fibroblasts that restrain cancer progression: Hypotheses and perspectives. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Omary, M.B.; Lugea, A.; Lowe, A.W.; Pandol, S.J. The pancreatic stellate cell: A star on the rise in pancreatic diseases. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pickup, M.W.; Mouw, J.K.; Weaver, V.M. The extracellular matrix modulates the hallmarks of cancer. EMBO Rep. 2014, 15, 1243–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamada, K.M.; Sixt, M. Mechanisms of 3D cell migration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 738–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.D.; Yamada, K.M. Mechanosensing via cell-matrix adhesions in 3D microenvironments. Exp. Cell Res. 2016, 343, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antoni, D.; Burckel, H.; Josset, E.; Noel, G. Three-dimensional cell culture: A breakthrough in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5517–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, D.; Puleo, J.; Llave, A.; Mouneimne, G.; Kamm, R.D.; Nikkhah, M. Breast Cancer Cell Invasion into a Three Dimensional Tumor-Stroma Microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.L.; Segall, J.E.; Wu, M. Microfluidic modeling of the biophysical microenvironment in tumor cell invasion. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3221–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Shin, Y.; Chung, S.; Kuh, H.J. Co-Culture of Tumor Spheroids and Fibroblasts in a Collagen Matrix-Incorporated Microfluidic Chip Mimics Reciprocal Activation in Solid Tumor Microenvironment. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.K.; Khawar, I.A.; Jeong, S.Y.; Chung, S.; Kuh, H.J. Microfluidic co-culture of pancreatic tumor spheroids with stellate cells as a novel 3D model for investigation of stroma-mediated cell motility and drug resistance. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrari, R.; Infante, E.; Chavrier, P. Nucleus-Invadopodia Duo during Cancer Invasion. Trends Cell Biol. 2019, 29, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ilina, O.; Campanello, L.; Gritsenko, P.G.; Vullings, M.; Wang, C.; Bult, P.; Losert, W.; Friedl, P. Intravital microscopy of collective invasion plasticity in breast cancer. Dis. Model. Mech. 2018, 11, dmm034330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sapudom, J.; Rubner, S.; Martin, S.; Kurth, T.; Riedel, S.; Mierke, C.T.; Pompe, T. The phenotype of cancer cell invasion controlled by fibril diameter and pore size of 3D collagen networks. Biomaterials 2015, 52, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cukierman, E.; Pankov, R.; Stevens, D.R.; Yamada, K.M. Taking cell-matrix adhesions to the third dimension. Science 2001, 294, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leggett, S.E.; Khoo, A.S.; Wong, I.Y. Multicellular tumor invasion and plasticity in biomimetic materials. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 1460–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deer, E.L.; González-Hernández, J.; Coursen, J.D.; Shea, J.E.; Ngatia, J.; Scaife, C.L.; Firpo, M.A.; Mulvihill, S.J. Phenotype and genotype of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Pancreas 2010, 39, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, Y.; Han, D.; Min, H.; Jin, J.; Yi, E.C.; Kim, Y. Comparative proteomic profiling of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma cell lines. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loukopoulos, P.; Kanetaka, K.; Takamura, M.; Shibata, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Hirohashi, S. Orthotopic transplantation models of pancreatic adenocarcinoma derived from cell lines and primary tumors and displaying varying metastatic activity. Pancreas 2004, 29, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniz, V.P.; Barnes, J.M.; Paliwal, S.; Zhang, X.; Tang, X.; Chen, S.; Zamba, K.D.; Cullen, J.J.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Meyers, S.; et al. The ARF tumor suppressor inhibits tumor cell colonization independent of p53 in a novel mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arumugam, T.; Ramachandran, V.; Fournier, K.F.; Wang, H.; Marquis, L.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Gallick, G.E.; Logsdon, C.D.; McConkey, D.J.; Choi, W. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5820–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fink, S.P.; Mikkola, D.; Willson, J.K.; Markowitz, S. TGF-beta-induced nuclear localization of Smad2 and Smad3 in Smad4 null cancer cell lines. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fischer, K.R.; Durrans, A.; Lee, S.; Sheng, J.; Li, F.; Wong, S.T.; Choi, H.; El Rayes, T.; Ryu, S.; Troeger, J.; et al. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature 2015, 527, 472–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onder, T.T.; Gupta, P.B.; Mani, S.A.; Yang, J.; Lander, E.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aiello, N.M.; Maddipati, R.; Norgard, R.J.; Balli, D.; Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Yamazoe, T.; Black, T.; Sahmoud, A.; Furth, E.E.; et al. EMT Subtype Influences Epithelial Plasticity and Mode of Cell Migration. Dev. Cell. 2018, 45, 681–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Helvert, S.; Storm, C.; Friedl, P. Mechanoreciprocity in cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Guo, S.S.; Fässler, R. Integrin-mediated mechanotransduction. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 215, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Keely, P.J. Mechanical signaling through the cytoskeleton regulates cell proliferation by coordinated focal adhesion and Rho GTPase signaling. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Webb, D.J.; Horwitz, A.F. New dimensions in cell migration. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 690–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.G.; Vignjevic, D.M. Modes of cancer cell invasion and the role of the microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 36, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, C.; Mojares, E.; Del Río Hernández, A. Role of Extracellular Matrix in Development and Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weniger, M.; Honselmann, K.C.; Liss, A.S. The Extracellular Matrix and Pancreatic Cancer: A Complex Relationship. Cancers 2018, 10, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stutchbury, B.; Atherton, P.; Tsang, R.; Wang, D.Y.; Ballestrem, C. Distinct focal adhesion protein modules control different aspects of mechanotransduction. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 1612–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martino, F.; Perestrelo, A.R.; Vinarský, V.; Pagliari, S.; Forte, G. Cellular Mechanotransduction: From Tension to Function. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Takai, K.; Weaver, V.M.; Werb, Z. Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, A.J.; Rajagopalan, P. Extracellular matrix remodeling in 3D: Implications in tissue homeostasis and disease progression. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 10, e1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Boekhorst, V.; Preziosi, L.; Friedl, P. Plasticity of Cell Migration in vivo and in Silico. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 32, 491–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacob, A.; Prekeris, R. The regulation of MMP targeting to invadopodia during cancer metastasis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meirson, T.; Gil-Henn, H. Targeting invadopodia for blocking breast cancer metastasis. Drug Resist. Updat. 2018, 39, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E.S.; Weaver, A.M. A new role for cortactin in invadopodia: Regulation of protease secretion. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Poincloux, R.; Lizárraga, F.; Chavrier, P. Matrix invasion by tumour cells: A focus on MT1-MMP trafficking to invadopodia. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3015–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandya, P.; Orgaz, J.L.; Sanz-Moreno, V. Actomyosin contractility and collective migration: May the force be with you. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2017, 48, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gjorevski, N.; Piotrowski, A.S.; Varner, V.D.; Nelson, C.M. Dynamic tensile forces drive collective cell migration through three-dimensional extracellular matrices. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Inman, D.R.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Trier, S.M.; Keely, P.J. Contact guidance mediated three-dimensional cell migration is regulated by Rho/ROCK-dependent matrix reorganization. Biophys. J. 2008, 95, 5374–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Provenzano, P.P.; Eliceiri, K.W.; Campbell, J.M.; Inman, D.R.; White, J.G.; Keely, P.J. Collagen reorganization at the tumor-stromal interface facilitates local invasion. BMC Med. 2006, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, Y.L.; Ronceray, P.; Xu, G.; Malandrino, A.; Kamm, R.D.; Lenz, M.; Broedersz, C.P.; Guo, M. Cell contraction induces long-ranged stress stiffening in the extracellular matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 4075–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khalil, A.A.; de Rooij, J. Cadherin mechanotransduction in leader-follower cell specification during collective migration. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 376, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Kang, Y. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2019, 49, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandalovičová, A.; Rosel, D.; Fernandes, M.; Veselý, P.; Heneberg, P.; Čermák, V.; Petruželka, L.; Kumar, S.; Sanz-Moreno, V.; Brábek, J. Migrastatics-Anti-metastatic and Anti-invasion Drugs: Promises and Challenges. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 391–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sabeh, F.; Shimizu-Hirota, R.; Weiss, S.J. Protease-dependent versus -independent cancer cell invasion programs: Three-dimensional amoeboid movement revisited. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Teeuwssen, M.; Fodde, R. Cell Heterogeneity and Phenotypic Plasticity in Metastasis Formation: The Case of Colon Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Antin, P.; Berx, G.; Blanpain, C.; Brabletz, T.; Bronner, M.; Campbell, K.; Cano, A.; Casanova, J.; Christofori, G.; et al. Guidelines and definitions for research on epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sontheimer-Phelps, A.; Hassell, B.A.; Ingber, D.E. Modelling cancer in microfluidic human organs-on-chips. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 65–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, D.; Kaushik, S.; Correlo, V.M.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L.; Kundu, S.C. Organ-on-chip models of cancer metastasis for future personalized medicine: From chip to the patient. Biomaterials 2017, 149, 98–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toki, M.I.; Cecchi, F.; Hembrough, T.; Syrigos, K.N.; Rimm, D.L. Proof of the quantitative potential of immunofluorescence by mass spectrometry. Lab. Investig. 2017, 97, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuah, Y.J.; Koh, Y.T.; Lim, K.; Menon, N.V.; Wu, Y.; Kang, Y. Simple surface engineering of polydimethylsiloxane with polydopamine for stabilized mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and multipotency. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, S.-K.; Jang, S.D.; Kim, H.; Chung, S.; Park, J.K.; Kuh, H.-J. Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model. Cancers 2020, 12, 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051305
Kim S-K, Jang SD, Kim H, Chung S, Park JK, Kuh H-J. Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model. Cancers. 2020; 12(5):1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051305
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Seul-Ki, So Dam Jang, Hyunho Kim, Seok Chung, Jong Kook Park, and Hyo-Jeong Kuh. 2020. "Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model" Cancers 12, no. 5: 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051305
APA StyleKim, S. -K., Jang, S. D., Kim, H., Chung, S., Park, J. K., & Kuh, H. -J. (2020). Phenotypic Heterogeneity and Plasticity of Cancer Cell Migration in a Pancreatic Tumor Three-Dimensional Culture Model. Cancers, 12(5), 1305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12051305