Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Breast Cancer
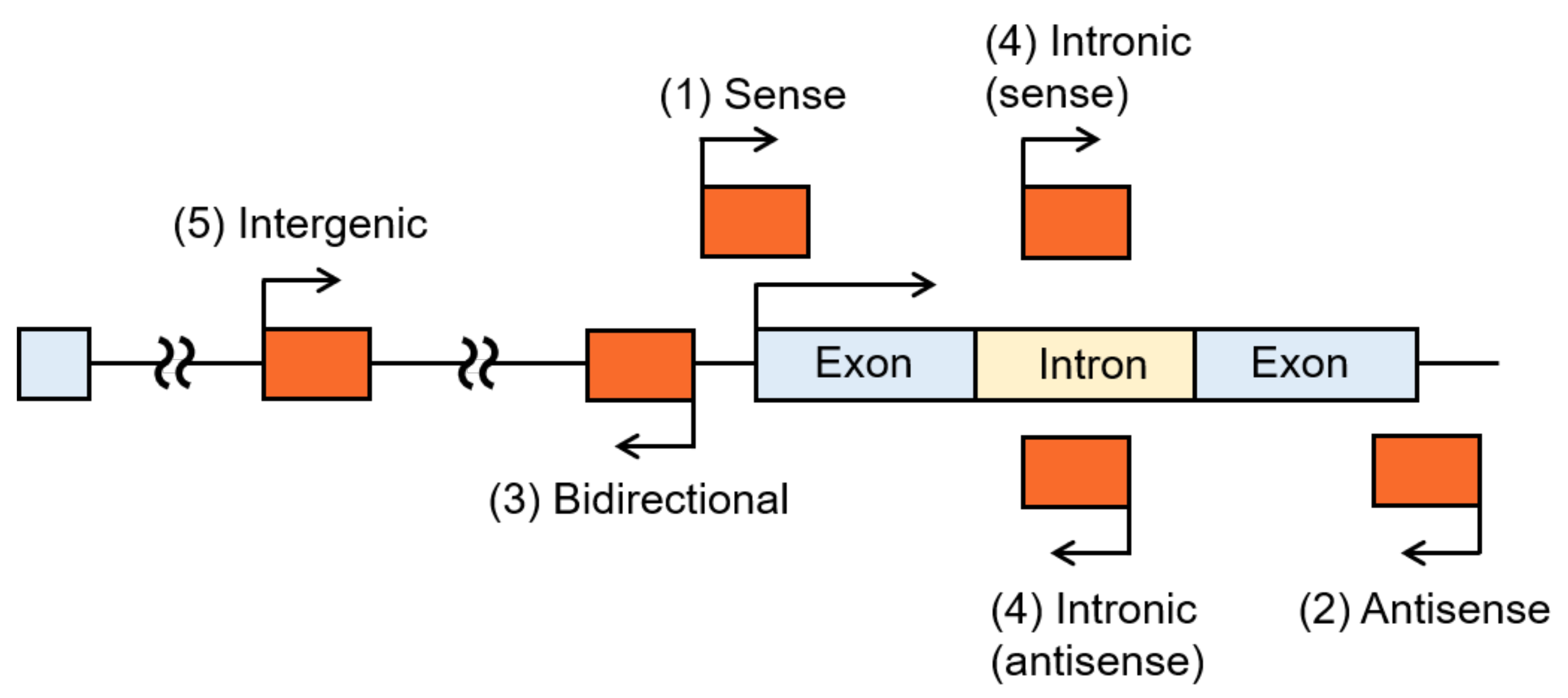
3. LncRNAs
4. LncRNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer
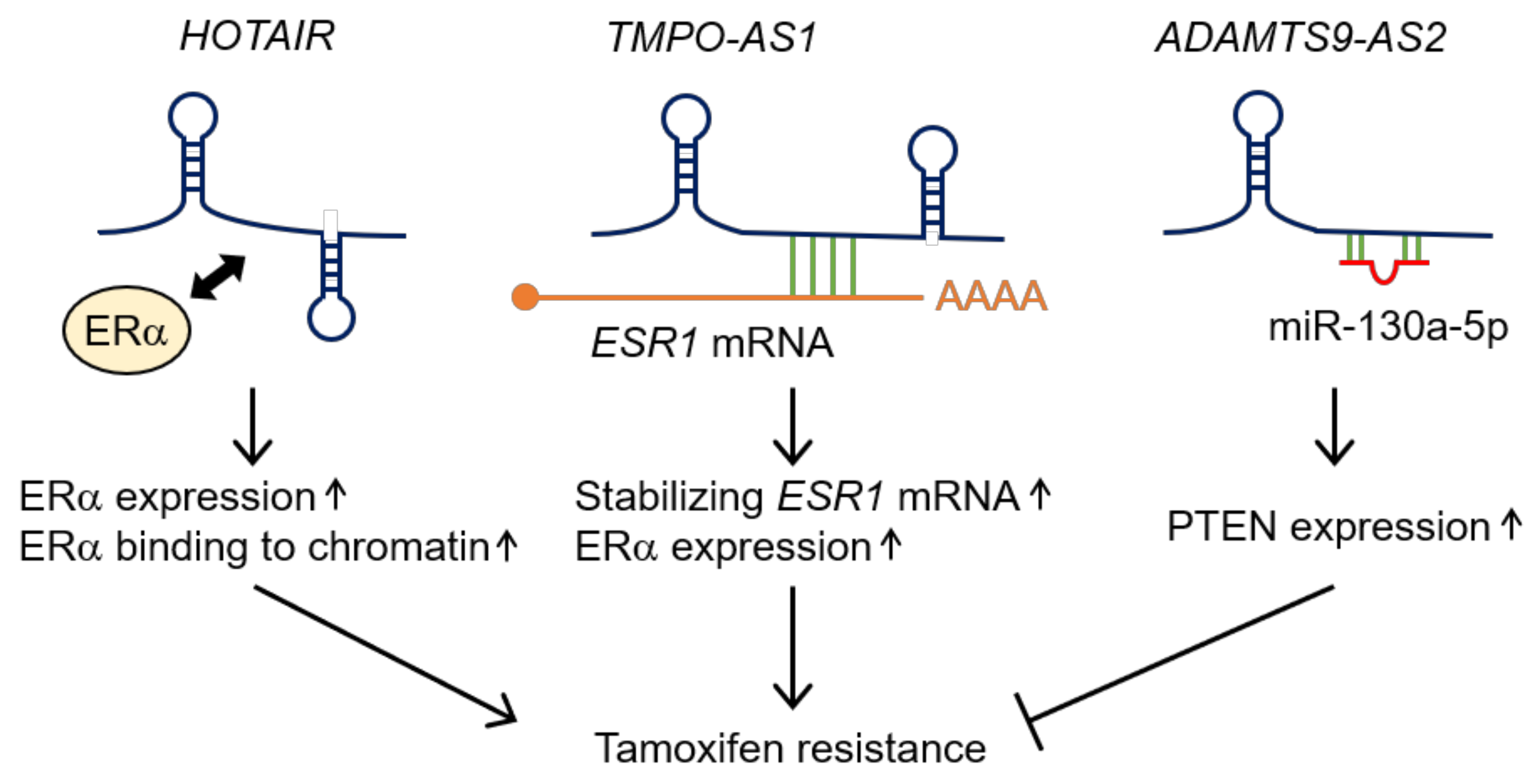
4.1. Antisense LncRNAs
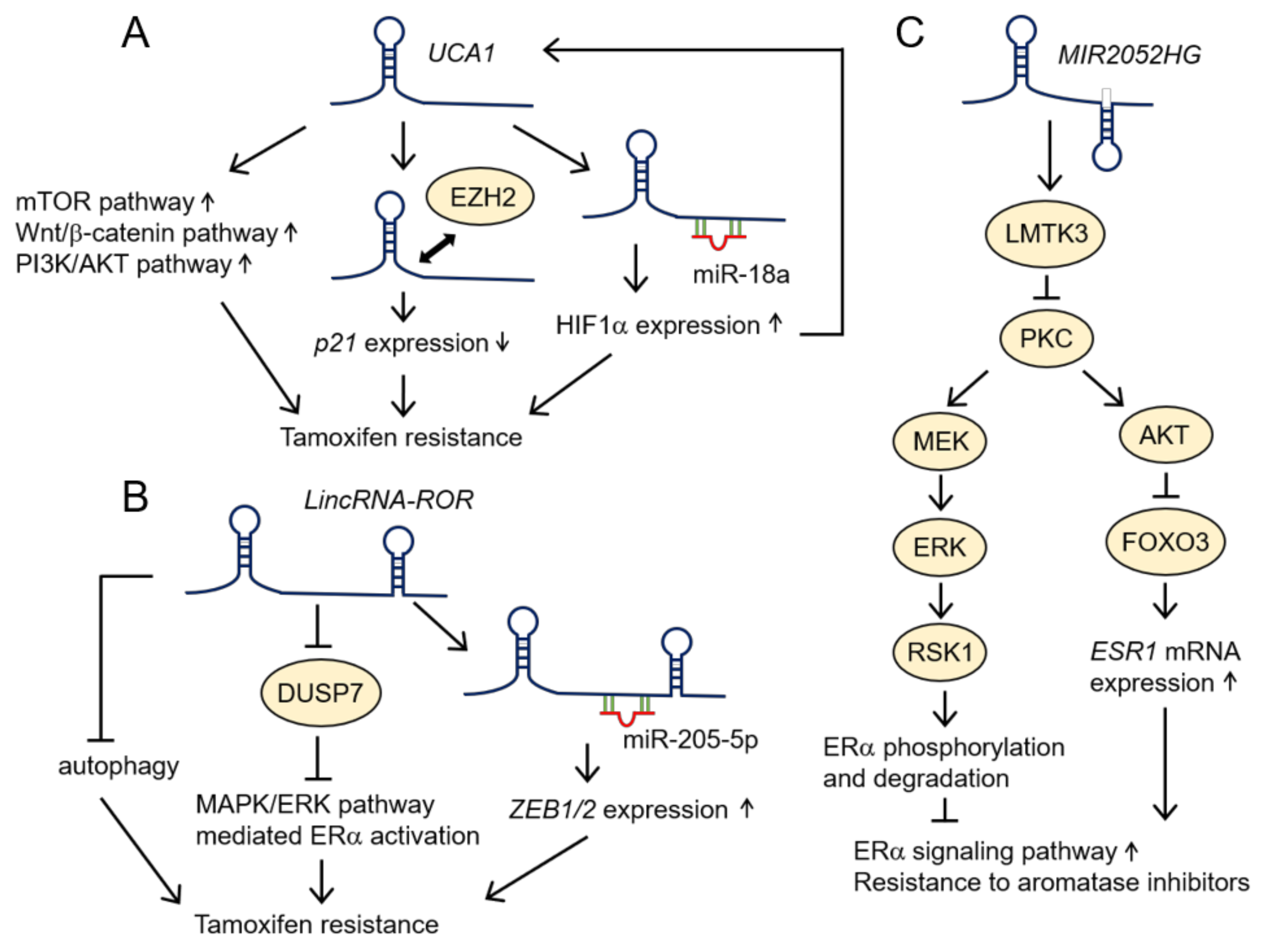
4.2. LincRNAs
4.3. LncRNAs Belonging to Multiple Categories
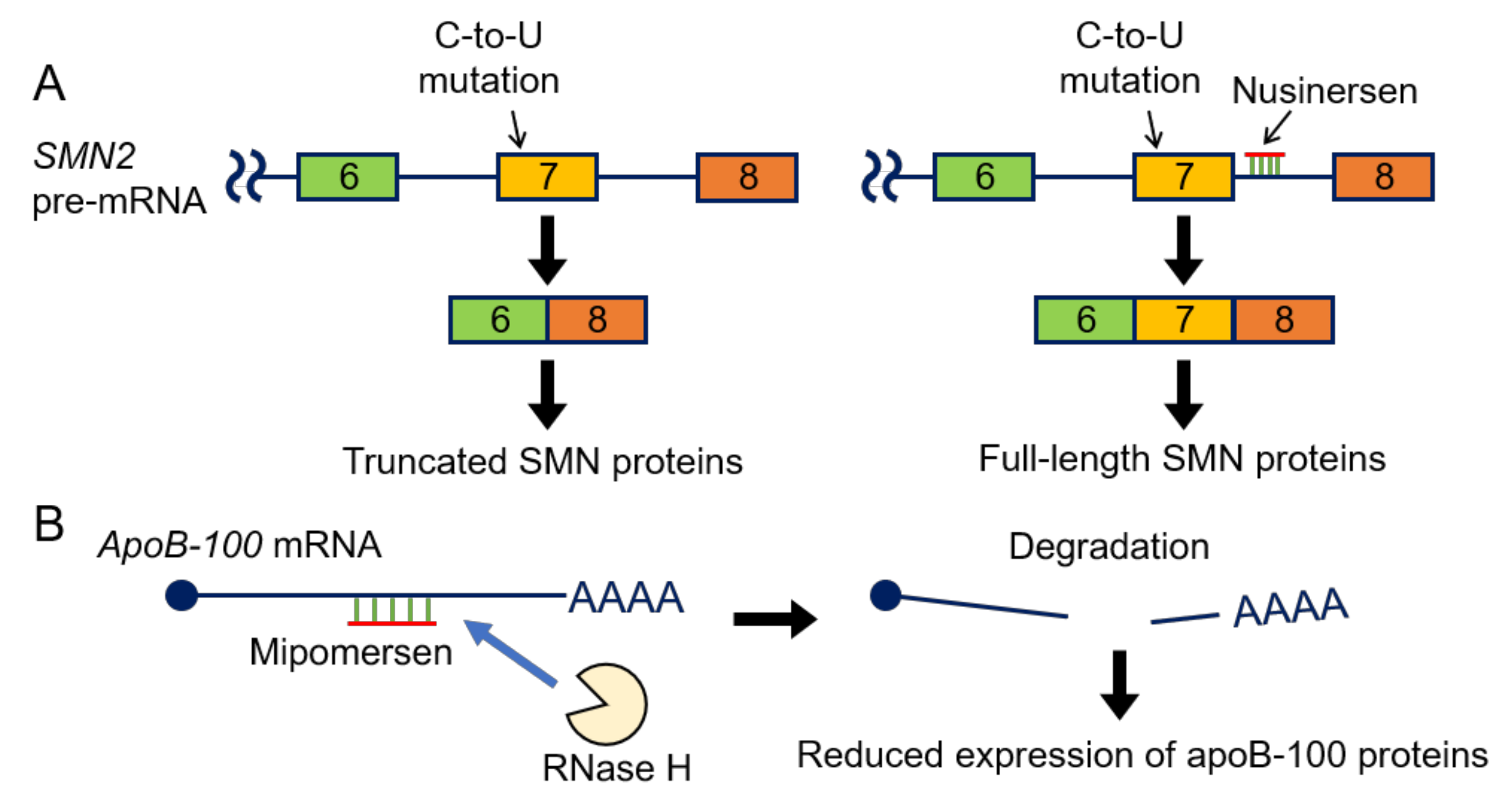
5. Antisense Oligonucleotides (ASOs) in Clinical Use
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harbeck, N.; Gnant, M. Breast cancer. Lancet 2017, 389, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA: A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative Annotation of Human Large Intergenic Noncoding RNAs Reveals Global Properties and Specific Subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, M.K.; Niknafs, Y.S.; Malik, R.; Singhal, U.; Sahu, A.; Hosono, Y.; Barrette, T.R.; Prensner, J.R.; Evans, J.R.; Zhao, S.; et al. The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Alvarez-Dominguez, J.R.; Lodish, H.F. Regulation of mammalian cell differentiation by long non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep. 2012, 13, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grote, P.; Herrmann, B.G. Long noncoding RNAs in organogenesis: making the difference. Trends Genet. 2015, 31, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perry, R.B.; Ulitsky, I. The functions of long noncoding RNAs in development and stem cells. Development 2016, 143, 3882–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Diermeier, S.D.; Spector, D.L. Therapeutic Targeting of Long Non-Coding RNAs in Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 257–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, H.; Maheronnaghsh, M.; Molaei, F.; Mashouri, L.; Reza Aref, A.; Momeny, M.; Alahari, S.K. Long noncoding RNAs and exosomal lncRNAs: classification, and mechanisms in breast cancer metastasis and drug resistance. Oncogene 2020, 39, 953–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perou, C.M.; Sørlie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; Rees, C.A.; Pollack, J.R.; Ross, D.T.; Johnsen, H.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2000, 406, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørlie, T.; Perou, C.M.; Tibshirani, R.; Aas, T.; Geisler, S.; Johnsen, H.; Hastie, T.; Eisen, M.B.; van de Rijn, M.; Jeffrey, S.S.; et al. Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10869–10874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yersal, O.; Barutca, S. Biological subtypes of breast cancer: Prognostic and therapeutic implications. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilton, H.N.; Clarke, C.L.; Graham, J.D. Estrogen and progesterone signalling in the normal breast and its implications for cancer development. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 466, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisken, C. Progesterone signalling in breast cancer: a neglected hormone coming into the limelight. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renoir, J.M.; Marsaud, V.; Lazennec, G. Estrogen receptor signaling as a target for novel breast cancer therapeutics. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhardt, S.A.; Boonyaratanakornkit, V.; Edwards, D.P. Progesterone receptor transcription and non-transcription signaling mechanisms. Steroids 2003, 68, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Nawaz, Z. Progesterone receptors—animal models and cell signaling in breast cancer: Role of steroid receptor coactivators and corepressors of progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2002, 4, 182–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinbolt, R.E.; Mangini, N.; Hill, J.L.; Levine, L.B.; Dempsey, J.L.; Singaravelu, J.; Koehler, K.A.; Talley, A.; Lustberg, M.B. Endocrine Therapy in Breast Cancer: The Neoadjuvant, Adjuvant, and Metastatic Approach. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2015, 31, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.K.; Bihani, T. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) in cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 186, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Gray, R.; Braybrooke, J.; Davies, C.; Taylor, C.; McGale, P.; Peto, R.; Pritchard, K.I.; Bergh, J.; Dowsett, M.; et al. 20-Year Risks of Breast-Cancer Recurrence after Stopping Endocrine Therapy at 5 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlFakeeh, A.; Brezden-Masley, C. Overcoming endocrine resistance in hormone receptor–positive breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018, 25, S18–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.S.; Clark, A.S.; Tchou, J.; Zhang, P.; Freedman, G.M. Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57 Suppl 1, 9S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; et al.; The FANTOM Consortium The Transcriptional Landscape of the Mammalian Genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, K.; Henderson, L.; Bonetti, A.; Carninci, P. Discovery and functional analysis of lncRNAs: Methodologies to investigate an uncharacterized transcriptome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gene Regul. Mech. 2016, 1859, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwakawa, H.O.; Tomari, Y. The Functions of MicroRNAs: mRNA Decay and Translational Repression. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 651–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GENCODE. Available online: https://www.gencodegenes.org/ (accessed on 31 March 2020).
- Ponting, C.P.; Oliver, P.L.; Reik, W. Evolution and Functions of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2009, 136, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, X.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhang, A.; Fong, K.W.; Kim, J.; Song, B.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.C.; Yu, J. LncRNA HOTAIR enhances ER signaling and confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 2746–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional Demarcation of Active and Silent Chromatin Domains in Human HOX Loci by Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajagopal, T.; Talluri, S.; Akshaya, R.L.; Dunna, N.R. HOTAIR LncRNA: A novel oncogenic propellant in human cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2020, 503, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNA as Modular Scaffold of Histone Modification Complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Fang, R.; Cai, X.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. HBXIP and LSD1 Scaffolded by lncRNA Hotair Mediate Transcriptional Activation by c-Myc. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 293–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portoso, M.; Ragazzini, R.; Brenčič, Ž; Moiani, A.; Michaud, A.; Vassilev, I.; Wassef, M.; Servant, N.; Sargueil, B.; Margueron, R. PRC 2 is dispensable for HOTAIR -mediated transcriptional repression. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 981–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Ren, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, D. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Modulates MiR-206-mediated Bcl-w Signaling to Facilitate Cell Proliferation in Breast Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Geng, D.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Sun, M. LncRNA HOTAIR influences cell growth, migration, invasion, and apoptosis via the miR-20a-5p/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitobe, Y.; Ikeda, K.; Suzuki, T.; Takagi, K.; Kawabata, H.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Inoue, S. ESR1-Stabilizing Long Noncoding RNA TMPO-AS1 Promotes Hormone-Refractory Breast Cancer Progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 39, e00261-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liang, B.; Hou, S. TMPO-AS1 promotes cervical cancer progression by upregulating RAB14 via sponging miR-577. J. Gene Med. 2019, 21, e3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Zhao, J. LncRNA TMPO-AS1 serves as a ceRNA to promote osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by regulating miR-199a-5p/WNT7B axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 2284–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Z.; Zheng, X.; Fang, Y. Long noncoding RNA TMPO-AS1 promotes progression of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating its natural antisense transcript TMPO. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 516, 486–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.F.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.B. Downregulated lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 in breast cancer enhances tamoxifen resistance by activating microRNA-130a-5p. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1563–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Gong, Q.; Zhao, R.; Chen, T. Upregulated lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 suppresses progression of lung cancer through inhibition of miR-223-3p and promotion of TGFBR3. IUBMB Life 2018, 70, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, F.; Hou, S. Differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs and the prognostic potential in colorectal cancer. Neoplasma 2016, 63, 977–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Liu, C.; Yang, G. Down-regulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 contributes to gastric cancer development via activation of PI3K/Akt pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N.; Hou, J.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, W.; Ma, G.; Chen, B.; Song, Y. Integrated analysis of a competing endogenous RNA network reveals key lncRNAs as potential prognostic biomarkers for human bladder cancer. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e11887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Ma, H.; Fan, S.; Chen, W.; Pan, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; et al. Upregulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 Promotes Salivary Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Metastasis via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk Signaling. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2766–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H.C.; Cai, J.L.; Xu, Q.W.; Li, M.Q.; Chen, Y.C.; Qian, X.P.; Lu, T.J.; Yu, L.Z.; et al. Rapid Identification of UCA1 as a Very Sensitive and Specific Unique Marker for Human Bladder Carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 4851–4858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Q. The prognostic value and mechanisms of lncRNA UCA1 in human cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 7685–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Luo, J. Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Urothelial Carcinoma-Associated 1 (UCA1) Enhances Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancer Cells via Inhibiting mTOR Signaling Pathway. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3860–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, G.; Yang, L.; Qu, J.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, X. Knockdown of Long Non-Coding RNA UCA1 Increases the Tamoxifen Sensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells through Inhibition of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0168406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yu, D.; Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, S. Long non coding RNA UCA1 confers tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer endocrinotherapy through regulation of the EZH2/p21 axis and the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Liu, A.; Tang, X. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 enhances tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells through a miR-18a-HIF1α feedback regulatory loop. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 14733–14743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.-G.; Yang, M.-F.; Ren, Y.-Q.; Wu, C.-H.; Wang, L.-Q. Exosomes mediated transfer of lncRNA UCA1 results in increased tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4362–4368. [Google Scholar]
- Meijer, D.; van Agthoven, T.; Bosma, P.T.; Nooter, K.; Dorssers, L.C. Functional Screen for Genes Responsible for Tamoxifen Resistance in Human Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.F.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Look, M.P.; Meijer, D.; Foekens, J.A.; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. Relevance of BCAR4 in tamoxifen resistance and tumour aggressiveness of human breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.; Meijer, D.; Setyono-Han, B.; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. Characterization of BCAR4, a novel oncogene causing endocrine resistance in human breast cancer cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.F.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Look, M.P.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Sleijfer, S.; Foekens, J.A.; Petricoin, E.F.; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. BCAR4 induces antioestrogen resistance but sensitises breast cancer to lapatinib. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Lin, A.; Li, C.; Liang, K.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Park, P.K.; Qin, L.; Wei, Y.; Hawke, D.H.; et al. lncRNA Directs Cooperative Epigenetic Regulation Downstream of Chemokine Signals. Cell 2014, 159, 1110–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.-S.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Xue, J.-Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Huang, S.; Mo, M.; Zhou, S.-L.; Wu, J. Long non-coding RNA metastasis associated in lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 (MALAT1) interacts with estrogen receptor and predicted poor survival in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 37957–37965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E.; et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin β4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ma, L. New Insights into Long Non-Coding RNA MALAT1 in Cancer and Metastasis. Cancers 2019, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilusz, J.E.; Freier, S.M.; Spector, D.L. 3′ End Processing of a Long Nuclear-Retained Noncoding RNA Yields a tRNA-like Cytoplasmic RNA. Cell 2008, 135, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, D.N.; Pace, N.R. RIBONUCLEASE P: Unity and Diversity in a tRNA Processing Ribozyme. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1998, 67, 153–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maraia, R.J.; Lamichhane, T.N. 3′ processing of eukaryotic precursor tRNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 2, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gast, M.; Schroen, B.; Voigt, A.; Haas, J.; Kuehl, U.; Lassner, D.; Skurk, C.; Escher, F.; Wang, X.; Kratzer, A.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1-derived mascRNA is involved in cardiovascular innate immunity. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.A.; Valenstein, M.L.; Yario, T.A.; Tycowski, K.T.; Steitz, J.A. Formation of triple-helical structures by the 3’-end sequences of MALAT1 and MENβ noncoding RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 19202–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilusz, J.E.; JnBaptiste, C.K.; Lu, L.Y.; Kuhn, C.-D.; Joshua-Tor, L.; Sharp, P.A. A triple helix stabilizes the 3′ ends of long noncoding RNAs that lack poly(A) tails. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 2392–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.N.; Ensminger, A.W.; Clemson, C.M.; Lynch, C.R.; Lawrence, J.B.; Chess, A. A screen for nuclear transcripts identifies two linked noncoding RNAs associated with SC35 splicing domains. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, T.; Shao, F.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Qian, K.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Xu, N.; Wang, Y.; et al. miR-124 downregulation leads to breast cancer progression via LncRNA-MALAT1 regulation and CDK4/E2F1 signal activation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 16205–16216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, C.; Yan, B.; Lu, Q.; Lin, Y.; Ma, L. Reciprocal regulation of Hsa-miR-1 and long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer development. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 7383–7394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Ma, M.; Fu, K. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes proliferation and invasion via targeting miR-129-5p in triple-negative breast cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, B.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. MiR-204/ZEB2 axis functions as key mediator for MALAT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317690998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Gong, H.; Guo, J.; Wu, K.; Jia, Q.; Ding, X. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates BLCAP mRNA expression through binding to miR-339-5p and promotes poor prognosis in breast cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20181284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhao, Y.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Mao, Y. The functional pathway analysis and clinical significance of miR-20a and its related lncRNAs in breast cancer. Cell. Signal. 2018, 51, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, N.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C.; Wen, X.; Jia, L.; Cui, J.; Hoffman, A.R.; Hu, J.-F.; Li, W. Genome-wide target interactome profiling reveals a novel EEF1A1 epigenetic pathway for oncogenic lncRNA MALAT1 in breast cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 714–729. [Google Scholar]
- Pruszko, M.; Milano, E.; Forcato, M.; Donzelli, S.; Ganci, F.; Di Agostino, S.; De Panfilis, S.; Fazi, F.; Bates, D.O.; Bicciato, S.; et al. The mutant p53-ID4 complex controls VEGFA isoforms by recruiting lncRNA MALAT1. EMBO Rep. 2017, 18, 1331–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latorre, E.; Carelli, S.; Raimondi, I.; D’Agostino, V.; Castiglioni, I.; Zucal, C.; Moro, G.; Luciani, A.; Ghilardi, G.; Monti, E.; et al. The Ribonucleic Complex HuR-MALAT1 Represses CD133 Expression and Suppresses Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arun, G.; Diermeier, S.; Akerman, M.; Chang, K.-C.; Wilkinson, J.E.; Hearn, S.; Kim, Y.; MacLeod, A.R.; Krainer, A.R.; Norton, L.; et al. Differentiation of mammary tumors and reduction in metastasis upon Malat1 lncRNA loss. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 34–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Piao, H.L.; Kim, B.J.; Yao, F.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Siverly, A.N.; Lawhon, S.E.; Ton, B.N.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 suppresses breast cancer metastasis. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 1705–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Liang, F.; Zhang, J.-W.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Kang, X.-G. Effects of long noncoding RNA-ROR on tamoxifen resistance of breast cancer cells by regulating microRNA-205. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 79, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, B.; Zhu, H.; Qu, X.; Zhao, L.; Tan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Liao, M.; Wu, X. Inhibition of long non-coding RNA ROR reverses resistance to Tamoxifen by inducing autophagy in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317705790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.X.; Huang, J.G.; Yang, L.; Gong, A.H.; Mo, Y.Y. Linc-RoR promotes MAPK/ERK signaling and confers estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loewer, S.; Cabili, M.N.; Guttman, M.; Loh, Y.H.; Thomas, K.; Park, I.H.; Garber, M.; Curran, M.; Onder, T.; Agarwal, S.; et al. Large intergenic non-coding RNA-RoR modulates reprogramming of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1113–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.; Tu, J.; Cheng, F.; Yang, H.; Yu, F.; Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Zhou, G. Long noncoding RNA ROR promotes breast cancer by regulating the TGF-β pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eades, G.; Wolfson, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, Q. lincRNA-RoR and miR-145 Regulate Invasion in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer via Targeting ARF6. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Huo, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Chen, J.; Sun, H.; An, W.; Jie, J.; Yang, P. LincRNA-RoR/miR-145 promote invasion and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer via targeting MUC1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Cao, J.; Peng, R.; Guo, Q.; Ye, H.; Wang, P.; Wang, K.; Song, C. Functional Variants in Linc-ROR are Associated with mRNA Expression of Linc-ROR and Breast Cancer Susceptibility. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Li, X.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; Yang, Q. LncRNA LINP1 confers tamoxifen resistance and negatively regulated by ER signaling in breast cancer. Cell. Signal. 2020, 68, 109536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Q.; Hu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Fan, L.; Tang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Shan, W.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINP1 regulates repair of DNA double-strand breaks in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Li, Y.; Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Sang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINP1 acts as an oncogene and promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 19, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Yu, H.; Piao, H. lncRNA CYTOR promotes tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer cells via sponging miR-125a-5p. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 45, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Grembergen, O.; Bizet, M.; de Bony, E.J.; Calonne, E.; Putmans, P.; Brohée, S.; Olsen, C.; Guo, M.; Bontempi, G.; Sotiriou, C.; et al. Portraying breast cancers with long noncoding RNAs. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1600220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Zhong, J.; Yu, P.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, T. YY1-regulated LINC00152 promotes triple negative breast cancer progression by affecting on stability of PTEN protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, J.N.; Xie, F.; Ellis, M.J.; Goss, P.E.; Shepherd, L.E.; Chapman, J.W.; Chen, B.E.; Kubo, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Momozawa, Y.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Long Noncoding RNA MIR2052HG Offer a Pharmacogenomic Basis for the Response of Breast Cancer Patients to Aromatase Inhibitor Therapy. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7012–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J.; Ingle, J.N.; Kalari, K.R.; Shepherd, L.E.; Kubo, M.; Goetz, M.P.; Weinshilboum, R.M.; Wang, L. The lncRNA MIR2052HG regulates ERα levels and aromatase inhibitor resistance through LMTK3 by recruiting EGR1. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giamas, G.; Filipović, A.; Jacob, J.; Messier, W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, W.; Shifa, B.A.; Photiou, A.; Tralau-Stewart, C.; et al. Kinome screening for regulators of the estrogen receptor identifies LMTK3 as a new therapeutic target in breast cancer. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 715–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chi, Y.; Chi, W.; Guo, R.; Su, Y.; Xue, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Nie, J.; et al. LINC00309 is associated with short disease-free survival in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, D.; Shao, C.; Zhou, M.; He, Z. Downregulation of lncRNA GAS5 confers tamoxifen resistance by activating miR-222 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2018, 434, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.; King, R.M.; Philipson, L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell 1988, 54, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goustin, A.S.; Thepsuwan, P.; Kosir, M.A.; Lipovich, L. The Growth-Arrest-Specific (GAS)-5 Long Non-Coding RNA: A Fascinating lncRNA Widely Expressed in Cancers. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Watabe, K.; Zhang, X.; Bai, C.; Xu, M.; Wu, F.; Mo, Y.Y. Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, P.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 suppresses triple negative breast cancer progression through inhibition of proliferation and invasion by competitively binding miR-196a-5p. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kino, T.; Hurt, D.E.; Ichijo, T.; Nader, N.; Chrousos, G.P. Noncoding RNA Gas5 Is a Growth Arrest- and Starvation-Associated Repressor of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Pickard, M.R.; de Vera, I.M.; Kuiper, E.G.; Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Conn, G.L.; Kojetin, D.J.; Williams, G.T.; Ortlund, E.A. Conserved sequence-specific lincRNA-steroid receptor interactions drive transcriptional repression and direct cell fate. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, K. A Genetic Variant of rs145204276 in the Promoter Region of Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2019, 19, e415–e421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niknafs, Y.S.; Han, S.; Ma, T.; Speers, C.; Zhang, C.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Iyer, M.K.; Pitchiaya, S.; Malik, R.; Hosono, Y.; et al. The lncRNA landscape of breast cancer reveals a role for DSCAM-AS1 in breast cancer progression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Bu, D.; Long, J.; Chai, W.; Dong, J. LncRNA DSCAM-AS1 acts as a sponge of miR-137 to enhance Tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2880–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, V.; Ferrero, G.; Reineri, S.; Caizzi, L.; Annaratone, L.; Ricci, L.; Cutrupi, S.; Castellano, I.; Cordero, F.; De Bortoli, M. Luminal long non-coding RNAs regulated by estrogen receptor alpha in a ligand-independent manner show functional roles in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 3201–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Li, A.Q.; Zhou, P.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Jin, X.; Liu, Y.R.; Guo, Y.J.; Yang, W.T.; Shao, Z.M.; Xu, X.E. DSCAM-AS1 regulates the G1/S cell cycle transition and is an independent prognostic factor of poor survival in luminal breast cancer patients treated with endocrine therapy. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 6137–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.H.; Li, N.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Qian, X.L.; Wang, Z.H. DSCAM-AS1 promotes tumor growth of breast cancer by reducing miR-204-5p and up-regulating RRM2. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, S.; Abdalla, M.O.A.; Fujiwara, S.; Matsumori, H.; Maehara, K.; Ohkawa, Y.; Iwase, H.; Saitoh, N.; Nakao, M. A cluster of noncoding RNAs activates the ESR1 locus during breast cancer adaptation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoori, Y.; Zendehbad, Z.; Askari, A.; Kouhpayeh, A.; Tavakkoly-Bazzaz, J.; Nariman-Saleh-Fam, Z.; Bastami, M.; Saadatian, Z.; Mansoori, B.; Yousefvand, A.; et al. Breast cancer-linked lncRNA u-Eleanor is upregulated in breast of healthy women with lack or short duration of breastfeeding. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9869–9876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernstein, L. Epidemiology of endocrine-related risk factors for breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2002, 7, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer. Breast cancer and breastfeeding: collaborative reanalysis of individual data from 47 epidemiological studies in 30 countries, including 50302 women with breast cancer and 96973 women without the disease. Lancet 2002, 360, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, W.; Lan, H.; Jiang, H. Association Between Breastfeeding and Breast Cancer Risk: Evidence from a Meta-analysis. Breastfeed. Med. 2015, 10, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, M.O.A.; Yamamoto, T.; Maehara, K.; Nogami, J.; Ohkawa, Y.; Miura, H.; Poonperm, R.; Hiratani, I.; Nakayama, H.; Nakao, M.; et al. The Eleanor ncRNAs activate the topological domain of the ESR1 locus to balance against apoptosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, J.R.; Gorkin, D.U.; Ren, B. Chromatin Domains: The Unit of Chromosome Organization. Mol. Cell 2016, 62, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Sakamoto, C.; Tachiwana, H.; Kumabe, M.; Matsui, T.; Yamashita, T.; Shinagawa, M.; Ochiai, K.; Saitoh, N.; Nakao, M. Endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer model cells are inhibited by soybean glyceollin I through Eleanor non-coding RNA. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 15202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.F.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.Y. A Potential Prognostic Long Noncoding RNA Signature to Predict Recurrence among ER-positive Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Tamoxifen. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, A.A. Treating Disease at the RNA Level with Oligonucleotides. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo, F.; Hua, Y.; Krainer, A.R.; Bennett, C.F. Antisense-based therapy for the treatment of spinal muscular atrophy. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 199, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finkel, R.S.; Mercuri, E.; Darras, B.T.; Connolly, A.M.; Kuntz, N.L.; Kirschner, J.; Chiriboga, C.A.; Saito, K.; Servais, L.; Tizzano, E.; et al. Nusinersen versus Sham Control in Infantile-Onset Spinal Muscular Atrophy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajufo, E.; Rader, D.J. New Therapeutic Approaches for Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Annu. Rev. Med. 2018, 69, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, A.; Jones, P.; Nambi, V. The Role of Antisense Oligonucleotide Therapy in Patients with Familial Hypercholesterolemia: Risks, Benefits, and Management Recommendations. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2015, 17, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistiakov, D.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Orekhov, A.N. New biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of localized prostate cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2018, 52, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| LncRNAs | Effects on Endocrine Therapy Resistance | Molecular Mechanisms Regulating Endocrine Therapy Resistance | Breast Cancer Cells or Tissues Used for Analyzing the Mechanisms of LncRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antisense lncRNAs | |||
| HOTAIR | Up-regulation | Upregulating the activity of ERα under estrogen-starved condition [32] | MCF7 and an MCF7-derived tamoxifen-resistant cell line (TamR MCF7) [32] |
| TMPO-AS1 | Up-regulation | Upregulating ESR1 mRNA stability [41] | MCF7, T47D, and MCF7-derived tamoxifen-resistant cells (OHTR cells), as well as MCF7 cultured under long-term estrogen-deprivation conditions (LTED cells) [41] |
| ADAMTS9-AS2 | Down-regulation | Inhibiting miR-130a-5p activity to increase the expression of PTEN [45] | MCF7 and an MCF7-derived tamoxifen-resistant cell line (MCF-7R) [45] |
| PINK1-AS | Down-regulation | Possibly regulating several relapse or metastasis-related pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and Wnt signaling pathways [123] | ER-positive breast tumors from patients who were primarily treated with tamoxifen as the unique endocrine therapy [123] |
| RP11-259N19.1 | Up-regulation | ||
| KLF3-AS1 | Down-regulation | ||
| PDCD4-AS1 | Down-regulation | ||
| PP14571 | Up-regulation | ||
| RP11-69E11.4 | Down-regulation | ||
| LincRNAs | |||
| UCA1 | Up-regulation | MCF7 and MCF7-derived tamoxifen- and ICI182,780-resistant cell lines (LCC2 and LCC9) [53]; MCF7, T47D, and tamoxifen-resistant cells derived from MCF7 and T47D (MCF-7-R and T47D-R) [54]; LCC2 [55], MCF7, BTB474, LCC2, and LCC9 [56] | |
| BCAR4 | Up-regulation | Upregulating tamoxifen resistance of ZR-75-1 and ICI182,780 resistance of MCF7 in a HER2/ErbB2-, ErbB3-, and ErbB4-dependent manner [58,59,60,61] | ZR-75-1 [58,59,60], MCF7 [61] |
| MALAT1 | Up-regulation [62] | Unknown | |
| LincRNA-ROR | Up-regulation | BT474 [85] | |
| MCF7 [86] | |||
| MCF7, an MCF7-derived tamoxifen-resistant cell line (MCF7/TR5), and MDA-MB-231 [84] | |||
| LINP1 | Up-regulation | Decreasing ERα expression level [92] | MCF7, T47D, tamoxifen-resistant cells derived from MCF7 and T47D (MCF-7/TAMR and T47D/TAMR) [92] |
| CYTOR | Up-regulation | Inhibiting miR-125a-5p to increase the expression of SRF [95] | MCF7-derived tamoxifen-resistant cell lines (MCF7/TAM1 and MCF7/TAM2) [95] |
| MIR2052HG | Up-regulation | Increasing the expression of LMTK3 to upregulate ERα expression [99] | CAMA-1, an MCF7 cell line stably transfected CYP19A1 (MCF7/AC1), and an anastrozole-resistant MCF7 cell line (MCF7/AnaR) [99] |
| LINC00309 | Up-regulation [100] | Unknown | |
| LINC00339 | Down-regulation | Possibly regulating several relapse or metastasis-related pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and Wnt signaling pathways [123] | ER-positive breast tumors from patients who were primarily treated with tamoxifen as the unique endocrine therapy [123] |
| LINC00472 | Down-regulation | ||
| RP11-351I21.11 | Down-regulation | ||
| KB-1460A1.5 | Up-regulation | ||
| Other lncRNAs | |||
| GAS5 | Down-regulation | Inhibiting miR-222 activity to increase the expression of PTEN [102] | MCF-derived, tamoxifen-resistant cell line (MCF-7R) [102] |
| DSCAM-AS1 | Up-regulation | Inhibiting miR-137 to increase EPS8 [111] | MCF7-derived, tamoxifen-resistant cells (TR MCF7) [111] |
| Eleanors | Up-regulation | Increasing the expression of ESR1 [115.120] | MCF7 and MCF7 cultured under long-term estrogen-deprivation conditions (LTED cells) [115,120] |
| PKD1P6-NPIPP1 | Down-regulation | Possibly regulating several relapse or metastasis-related pathways, such as PI3K/AKT and Wnt signaling pathways [123] | ER-positive breast tumors from patients who were primarily treated with tamoxifen as the unique endocrine therapy [123] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takeiwa, T.; Ikeda, K.; Mitobe, Y.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Inoue, S. Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061424
Takeiwa T, Ikeda K, Mitobe Y, Horie-Inoue K, Inoue S. Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061424
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakeiwa, Toshihiko, Kazuhiro Ikeda, Yuichi Mitobe, Kuniko Horie-Inoue, and Satoshi Inoue. 2020. "Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061424
APA StyleTakeiwa, T., Ikeda, K., Mitobe, Y., Horie-Inoue, K., & Inoue, S. (2020). Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Endocrine Therapy Resistance of Breast Cancer. Cancers, 12(6), 1424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061424






