Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells in Monoclonal Gammopathies: Methods, Pathogenic Role, and Clinical Implications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Normal Plasma Cell Development and Plasma Cell-Associated Phenotypes in Blood
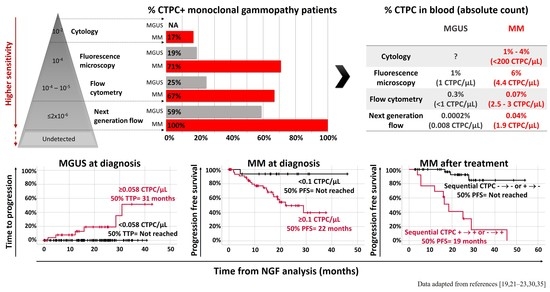
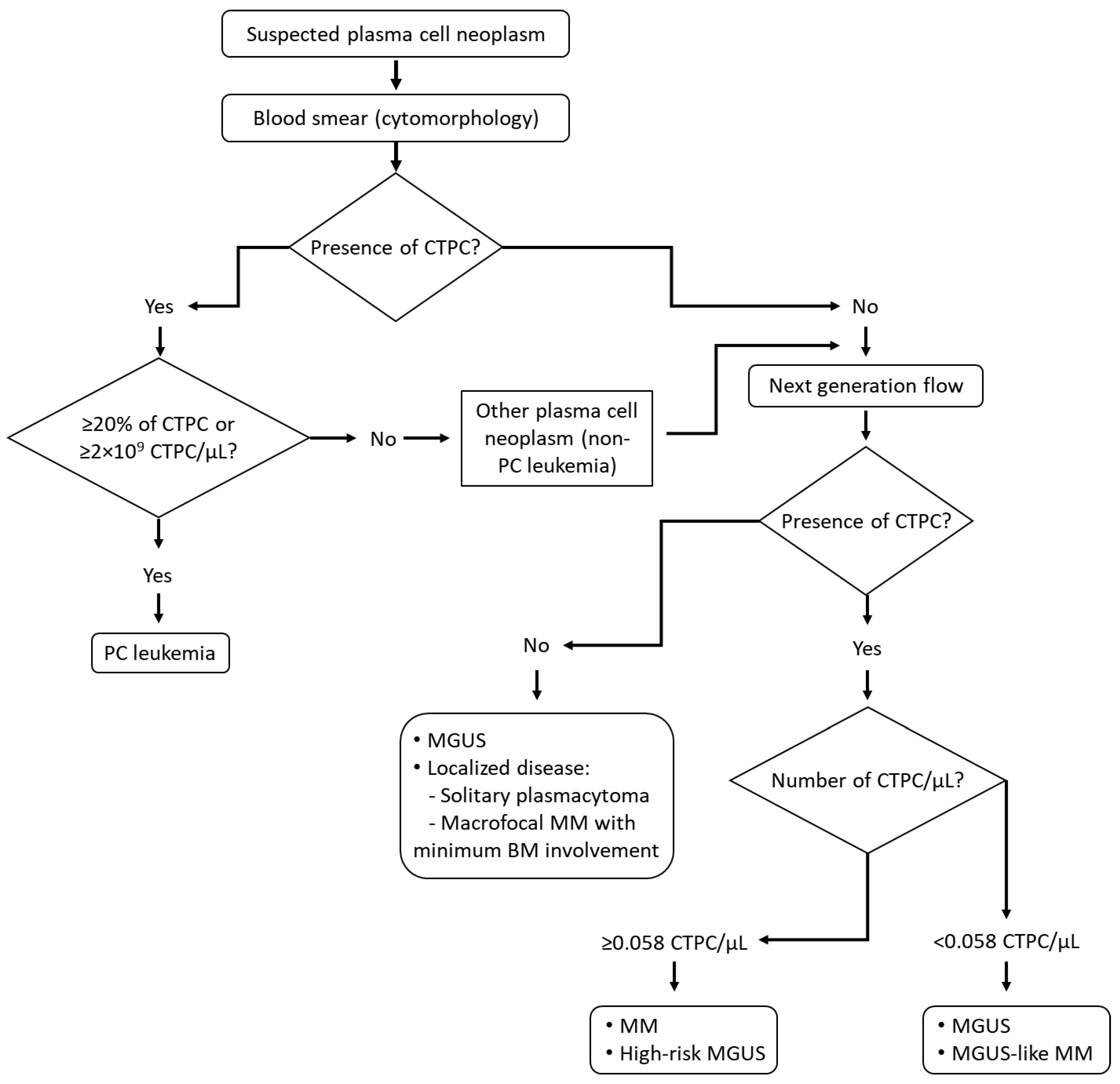
3. Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells
3.1. Circulating Tumor Plasma Cell Detection in Blood Smears by Conventional Cytology
3.2. Fluorescence Microscopy
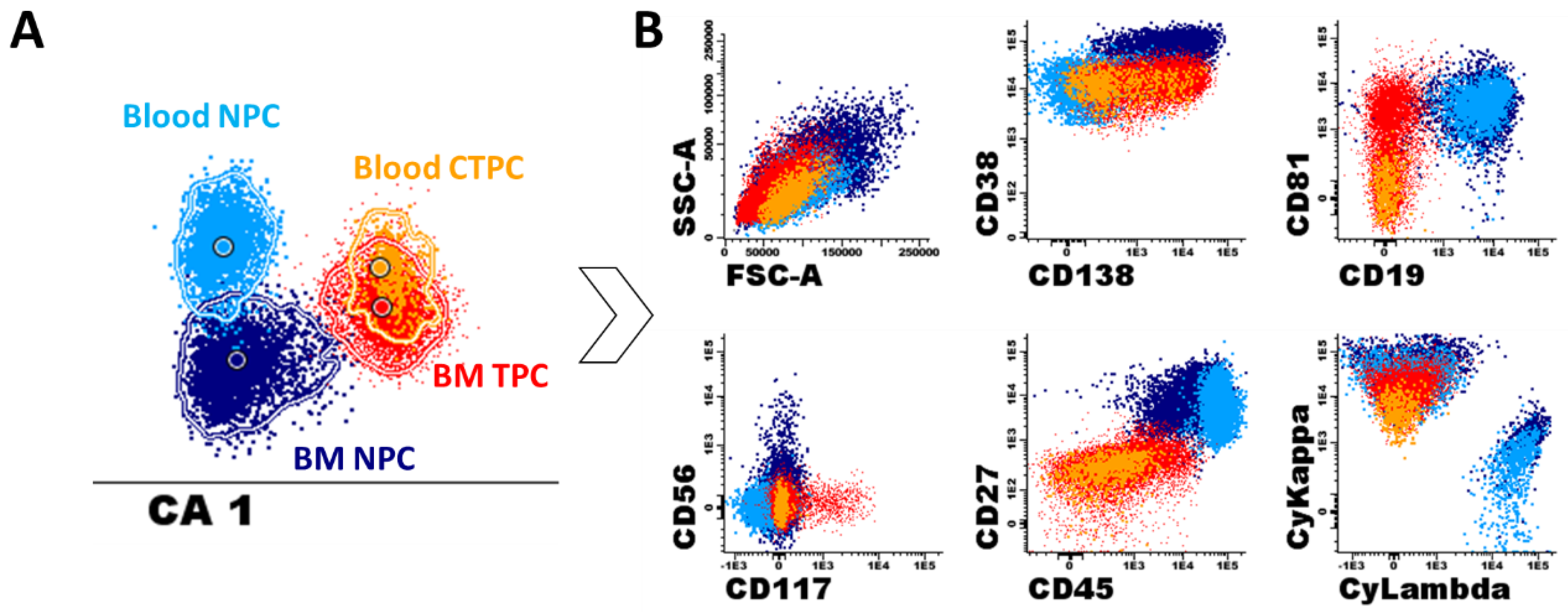
3.3. Conventional Multiparameter Flow Cytometry
3.4. Next Generation Flow Cytometry (NGF)
3.5. Molecular (ASO-qPCR and Next Generation Sequencing) Techniques
4. Biological Features and Physio-Pathological Role of CTPC in Plasma Cell Neoplasms
5. Clinical Implications of CTPC in Plasma Cell Neoplasms
6. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McKenna, R.W.; Kyle, R.A.; Kuehi, W.M.; Grogan, T.M.; Harris, N.L. Plasma cells neoplasms. In World Health Organization Calssification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissue IARC; WHO: Lyon, France, 2008; Volume 4, pp. 200–208. ISBN 9789283224310. [Google Scholar]
- Palumbo, A.A.K. Multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.K.; Rajkumar, V.; Kyle, R.A.; van Duin, M.; Sonneveld, P.; Mateos, M.-V.; Gay, F.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple myeloma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Vincent Rajkumar, S. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 134, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Larson, D.R.; Plevak, M.F.; Offord, J.R.; Dispenzieri, A.; Katzmann, J.A.; Melton, L.J. Prevalence of Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 354, 1362–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landgren, O.; Kyle, R.A.; Pfeiffer, R.M.; Katzmann, J.A.; Caporaso, N.E.; Hayes, R.B.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kumar, S.; Clark, R.J.; Baris, D.; et al. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) consistently precedes multiple myeloma: a prospective study. Blood 2009, 113, 5412–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weiss, B.M.; Abadie, J.; Verma, P.; Howard, R.S.; Kuehl, W.M. A monoclonal gammopathy precedes multiple myeloma in most patients. Blood 2009, 113, 5418–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kyle, R.A.; Remstein, E.D.; Therneau, T.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kurtin, P.J.; Hodnefield, J.M.; Larson, D.R.; Plevak, M.F.; Jelinek, D.F.; Fonseca, R.; et al. Clinical course and prognosis of smoldering (asymptomatic) multiple myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2582–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, R.A.; Child, J.A.; Anderson, K.; Barlogie, B.; Bataille, R.; Bensinger, W.; Bladé, J.; Boccadoro, M.; Dalton, W.; Dimopoulos, M.; et al. Criteria for the classification of monoclonal gammopathies, multiple myeloma and related disorders: A report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 121, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katodritou, E.; Kastritis, E.; Gatt, M.E.; Cohen, Y.C.; Avivi, I.; Pouli, A.; Lalayianni, A.; Lavi, N.; Delibasi, S.; Kyrtsonis, M.-C.; et al. Real-World Data on Incidence, Clinical Characteristics and Outcome of Patients with Macrofocal Multiple Myeloma (MFMM) in the Era of Novel Therapies: A Study of the Greco-Israeli Collaborative Myeloma Working Group. Blood 2018, 132, 3295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Hou, J.; Du, J.; Jin, L.; Peng, L.; Chen, B.; Xi, H.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Zhou, F.; et al. Macrofocal Multple Myeloma Is a Particular Subgroup of Multiple Myeloma. Blood 2015, 126, 1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oriol, A. Multiple myeloma with extramedullary disease. Adv. Ther. 2011, 28, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyle, R.A.; Maldonado, J.E.; Bayrd, E.D. Plasma cell leukemia. Report on 17 cases. Arch. Intern. Med. 1974, 133, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechalekar, A.D.; Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N. Systemic amyloidosis. Lancet 2016, 387, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.A.; Jevremovic, D.; Nandakumar, B.; Buadi, F.K.; Dispenzieri, A.; Dingli, D.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; Go, R.S.; et al. Utilizing Multiparametric Flow Cytometry to Identify Patients with Primary Plasma Cell Leukemia at Diagnosis. Blood 2019, 134, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundesen, M.T.; Lund, T.; Moeller, H.E.H.; Abildgaard, N. Plasma Cell Leukemia: Definition, Presentation, and Treatment. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2019, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fernández De Larrea, C.; Kyle, R.A.; Durie, B.G.M.; Ludwig, H.; Usmani, S.; Vesole, D.H.; Hajek, R.; San Miguel, J.F.; Sezer, O.; Sonneveld, P.; et al. Plasma cell leukemia: Consensus statement on diagnostic requirements, response criteria and treatment recommendations by the International Myeloma Working Group. Leukemia 2013, 27, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Billadeau, D.; Van Ness, B.; Kimlinger, T.; Kyle, R.A.; Therneau, T.M.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E. Clonal circulating cells are common in plasma cell proliferative disorders: A comparison of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, smoldering multiple myeloma, and active myeloma. Blood 1996, 88, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nowakowski, G.S.; Witzig, T.E.; Dingli, D.; Tracz, M.J.; Gertz, M.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Lust, J.A.; Dispenzieri, A.; Greipp, P.R.; Kyle, R.A.; et al. Circulating plasma cells detected by flow cytometry as a predictor of survival in 302 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma. Blood 2005, 106, 2276–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanoja-Flores, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Garcés, J.J.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Mateo, A.; García-Sánchez, O.; Corral-Mateos, A.; Burgos, L.; Blanco, E.; et al. Next generation flow for minimally-invasive blood characterization of MGUS and multiple myeloma at diagnosis based on circulating tumor plasma cells (CTPC). Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Jevremovic, D.; Nandakumar, B.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Kapoor, P.; Leung, N.; et al. Enhancing the R-ISS classification of newly diagnosed multiple myeloma by quantifying circulating clonal plasma cells. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Kyle, R.A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Dispenzieri, A.; Fonseca, R.; Lust, J.A.; Gertz, M.A.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E. Prognostic value of circulating plasma cells in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 5668–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzig, T.E.; Kyle, R.A.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Greipp, P.R. Detection of peripheral blood plasma cells as a predictor of disease course in patients with smouldering multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 1994, 87, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchi, G.; Kyle, R.A.; Larson, D.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Kumar, S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Morice, W.G.; Rajkumar, S.V. High levels of peripheral blood circulating plasma cells as a specific risk factor for progression of smoldering multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2013, 27, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Dispenzieri, A.; Dingli, D.; Timm, M.M.; Morice, W.G.; Lacy, M.Q.; Buadi, F.K.; Go, R.S.; Leung, N.; et al. Quantification of circulating clonal plasma cells via multiparametric flow cytometry identifies patients with smoldering multiple myeloma at high risk of progression. Leukemia 2017, 31, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witzig, T.E.; Gertz, M.A.; Lust, J.A.; Kyle, R.A.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Greipp, P.R. Peripheral blood monoclonal plasma cells as a predictor of survival in patients with multiple myeloma. Blood 1996, 88, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Gupta, V.; Morice, W.G.; Timm, M.M.; Singh, P.P.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Quantification of clonal circulating plasma cells in newly diagnosed multiple myeloma: Implications for redefining high- risk myeloma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 2060–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, G.; Qin, X.; Acharya, C.; Xu, Y.; Deng, S.; Shi, L.; Zang, M.; Sui, W.; Yi, S.; Li, Z.; et al. Multiple myeloma patients with low proportion of circulating plasma cells had similar survival with primary plasma cell leukemia patients. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granell, M.; Calvo, X.; Garcia-Guiñón, A.; Escoda, L.; Abella, E.; Martínez, C.M.; Teixidó, M.; Teresa Gimenez, M.; Senín, A.; Sanz, P.; et al. Prognostic impact of circulating plasma cells in patients with multiple myeloma: Implications for plasma cell leukemia definition. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, M.H.; Park, C.-J.; Kim, B.H.; Cho, Y.-U.; Jang, S.; Lee, D.-H.; Seo, E.-J.; Yoon, D.H.; Lee, J.-H.; Suh, C. Increased circulating plasma cells detected by flow cytometry predicts poor prognosis in patients with plasma cell myeloma. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2018, 94, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Owen, R.G.; Davies, F.E.; Johnson, R.J.; Jones, R.A.; Richards, S.J.; Evans, P.A.; Child, J.A.; Smith, G.M.; Jack, A.S.; et al. Circulating plasma cells in multiple myeloma: Characterization and correlation with disease stage. Br. J. Haematol. 1997, 97, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dingli, D.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Lacy, M.Q.; Hayman, S.R.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Greipp, P.R.; Litzow, M.R.; Gastineau, D.A.; Witzig, T.E.; et al. Flow cytometric detection of circulating myeloma cells before transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma: A simple risk stratification system. Blood 2006, 107, 3384–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonsalves, W.I.; Morice, W.G.; Rajkumar, V.; Gupta, V.; Timm, M.M.; Dispenzieri, A.; Buadi, F.K.; Lacy, M.Q.; Singh, P.P.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Quantification of clonal circulating plasma cells in relapsed multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 167, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanoja-Flores, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Puig, N.; Contreras-Sanfeliciano, T.; Pontes, R.; Corral-Mateos, A.; García-Sánchez, O.; Díez-Campelo, M.; Pessoa de Magalhães, R.J.; García-Martín, L.; et al. Blood monitoring of circulating tumor plasma cells by next generation flow in multiple myeloma after therapy. Blood 2019, 134, 2218–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nutt, S.L.; Hodgkin, P.D.; Tarlinton, D.M.; Corcoran, L.M. The generation of antibody-secreting plasma cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellier, J.; Nutt, S.L. Plasma cells: The programming of an antibody-secreting machine. Eur. J. Immunol. 2019, 49, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kometani, K.; Kurosaki, T. Differentiation and maintenance of long-lived plasma cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2015, 33, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medina, F.; Segundo, C.; Campos-Caro, A.; González-García, I.; Brieva, J.A. The heterogeneity shown by human plasma cells from tonsil, blood, and bone marrow reveals graded stages of increasing maturity, but local profiles of adhesion molecule expression. Blood 2002, 99, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benner, R.; Hijmans, W.; Haaijman, J.J. The bone marrow: The major source of serum immunoglobulins, but still a neglected site of antibody formation. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1981, 46, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Manz, R.A.; Radbruch, A. Plasma cells for a lifetime? Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangye, S.G. Thucydides and longer-lived plasma cells. Blood 2015, 125, 1684–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodnow, C.C.; Vinuesa, C.G.; Randall, K.L.; MacKay, F.; Brink, R. Control systems and decision making for antibody production. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radbruch, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Luger, E.O.; Inamine, A.; Smith, K.G.C.; Dörner, T.; Hiepe, F. Competence and competition: The challenge of becoming a long-lived plasma cell. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mesin, L.; Di Niro, R.; Thompson, K.M.; Lundin, K.E.A.; Sollid, L.M. Long-Lived Plasma Cells from Human Small Intestine Biopsies Secrete Immunoglobulins for Many Weeks In Vitro. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, V.T.; Berek, C. The establishment of the plasma cell survival niche in the bone marrow. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 251, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oracki, S.A.; Walker, J.A.; Hibbs, M.L.; Corcoran, L.M.; Tarlinton, D.M. Plasma cell development and survival. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 237, 140–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Arriba-Méndez, S.; Contreras-Sanfeliciano, T.; Criado, I.; Pelak, O.; Serra-Caetano, A.; Romero, A.; Puig, N.; Remesal, A.; et al. Age-associated distribution of normal B-cell and plasma cell subsets in peripheral blood. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 2208–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suan, D.; Sundling, C.; Brink, R. Plasma cell and memory B cell differentiation from the germinal center. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2017, 45, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro-Shelef, M.; Calame, K.C. Regulation of plasma-cell development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 230–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Perez-Andres, M.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Wentink, M.; Pelak, O.; Martín-Ayuso, M.; Grigore, G.; Torres-Canizales, J.; López-Granados, E.; Kalina, T.; et al. Selection and validation of antibody clones against IgG and IgA subclasses in switched memory B-cells and plasma cells. J. Immunol. Methods 2019, 475, 112372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraux, A.; Klein, B.; Paiva, B.; Bret, C.; Schmitz, A.; Fuhler, G.M.; Bos, N.A.; Johnsen, H.E.; Orfao, A. Circulating human B and plasma cells. Age-associated changes in counts and detailed characterization of circulating normal CD138- and CD138 plasma cells. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1016–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perez-Andres, M.; Paiva, B.; Nieto, W.G.; Caraux, A.; Schmitz, A.; Almeida, J.; Vogt, R.F.; Marti, G.E.; Rawstron, A.C.; Van Zelm, M.C.; et al. Human peripheral blood B-Cell compartments: A crossroad in B-cell traffic. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, S47–S60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalina, T.; Fišer, K.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Kužílková, D.; Cuenca, M.; Bartol, S.J.W.; Blanco, E.; Engel, P.; van Zelm, M.C. CD maps—dynamic profiling of CD1–CD100 surface expression on human leukocyte and lymphocyte subsets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Argüelles, G.; San Miguel, J. Cell Surface Markers in Multiple Myeloma. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1994, 69, 684–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrena, S.; Almeida, J.; Yunta, M.; López, A.; Fernández-Mosteirín, N.; Giralt, M.; Romero, M.; Perdiguer, L.; Delgado, M.; Orfao, A.; et al. Aberrant expression of tetraspanin molecules in B-cell chronic lymphoproliferative disorders and its correlation with normal B-cell maturation. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Vos, J.; Hose, D.; Rème, T.; Tarte, K.; Moreaux, J.; Mahtouk, K.; Jourdan, M.; Goldschmidt, H.; Rossi, J.F.; Cremer, F.W.; et al. Microarray-based understanding of normal and malignant plasma cells. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 210, 86–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jensen, G.S.; Poppema, S.; Mant, M.J.; Pilarski, L.M. Transition in CD45 isoform expression during differentiation of normal and abnormal B cells. Int. Immunol. 1989, 1, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, A.; Gupta, R.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, L.; Jain, P. Analysis of bone marrow plasma cells in patients with solitary bone plasmacytoma. Cancer Ther. 2009, 7, 49–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Barillé, S.; Puthier, D.; Rapp, M.J.; Harousseau, J.L.; Bataille, R.; Amiot, M. Adhesion molecules on human myeloma cells: Significant changes in expression related to malignancy, tumor spreading, and immortalization. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3647–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jego, G.; Robillard, N.; Puthier, D.; Amiot, M.; Accard, F.; Pineau, D.; Harousseau, J.L.; Bataille, R.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C. Reactive plasmacytoses are expansions of plasmablasts retaining the capacity to differentiate into plasma cells. Blood 1999, 94, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llinàs, L.; Lázaro, A.; de Salort, J.; Matesanz-Isabel, J.; Sintes, J.; Engel, P. Expression profiles of novel cell surface molecules on B-cell subsets and plasma cells as analyzed by flow cytometry. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 134, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawstron, A.C.; Orfao, A.; Beksac, M.; Bezdickova, L.; Brooimans, R.A.; Bumbea, H.; Dalva, K.; Fuhler, G.; Gratama, J.; Hose, D.; et al. Report of the European Myeloma Network on multiparametric flow cytometry in multiple myeloma and related disorders. Haematologica 2008, 93, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pojero, F.; Casuccio, A.; Parrino, M.F.; Cardinale, G.; Colonna Romano, G.; Caruso, C.; Gervasi, F. Old and new immunophenotypic markers in multiple myeloma for discrimination of responding and relapsing patients: The importance of “normal” residual plasma cell analysis. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2015, 88, 165–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Johnsen, S.; Segers-Nolten, I.M.J.; Loken, M.R. Identification and characterization of plasma cells in normal human bone marrow by high-resolution flow cytometry. Blood 1990, 76, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harada, H.; Kawano, M.M.; Huang, N.; Harada, Y.; Iwato, K.; Tanabe, O.; Tanaka, H.; Sakai, A.; Asaoku, H.; Kuramoto, A. Phenotypic difference of normal plasma cells from mature myeloma cells. Blood 1993, 81, 2658–2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannizzo, E.; Bellio, E.; Sohani, A.R.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Ferry, J.A.; Dorn, M.E.; Sadowski, C.; Bucci, J.J.; Carulli, G.; Preffer, F. Multiparameter immunophenotyping by flow cytometry in multiple myeloma: The diagnostic utility of defining ranges of normal antigenic expression in comparison to histology. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2010, 78, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robillard, N.; Jego, G.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Pineau, D.; Puthier, D.; Mellerin, M.P.; Barillé, S.; Rapp, M.J.; Harousseau, J.L.; Amiot, M.; et al. CD28, a marker associated with tumoral expansion in multiple myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 1998, 4, 1521–1526. [Google Scholar]
- Mateo, G.; Montalbán, M.A.; Vidriales, M.B.; Lahuerta, J.J.; Mateos, M.V.; Gutiérrez, N.; Rosiñol, L.; Montejano, L.; Bladé, J.; Martínez, R.; et al. Prognostic value of immunophenotyping in multiple myeloma: A study by the PETHEMA/GEM cooperative study groups on patients uniformly treated with high-dose therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 2737–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdan, M.; Caraux, A.; De Vos, J.; Fiol, G.; Larroque, M.; Cognot, C.; Bret, C.; Duperray, C.; Hose, D.; Klein, B. An in vitro model of differentiation of memory B cells into plasmablasts and plasma cells including detailed phenotypic and molecular characterization. Blood 2009, 114, 5173–5181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wells, S.M.; Kantor, A.B.; Stall, A.M. CD43 (S7) expression identifies peripheral B cell subsets. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 5503–5515. [Google Scholar]
- Matesanz-Isabel, J.; Sintes, J.; Llinàs, L.; de Salort, J.; Lázaro, A.; Engel, P. New B-cell CD molecules. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 134, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolf-Oliveira, R.C.M.; Auat, M.; Cardoso, C.C.; Santos-Pirath, I.M.; Lange, B.G.; Pires-Silva, J.; Moraes, A.C.R.; de Dametto, G.C.; Pirolli, M.M.; Colombo, M.D.H.P.; et al. Determination of normal expression patterns of CD86, CD210a, CD261, CD262, CD264, CD358, and CD361 in peripheral blood and bone marrow cells by flow cytometry. Immunol. Lett. 2018, 194, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Christoulas, D.; Bagratuni, T.; Bakogeorgos, M.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Kanellias, N.; Kastritis, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Semaphorin 4D correlates with increased bone resorption, hypercalcemia, and disease stage in newly diagnosed patients with multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luque, R.; Brieva, J.A.; Moreno, A.; Manzanal, A.; Escribano, L.; Villarrubia, J.; Velasco, J.L.; López-Jiménez, J.; Cerveró, C.; Otero, M.J.; et al. Normal and clonal B lineage cells can be distinguished by their differential expression of B cell antigens and adhesion molecules in peripheral blood from multiple myeloma (MM) patients diagnostic and clinical implications. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Muz, B.; Alhallak, K.; Markovic, M.; Gurley, S.; Wang, Z.; Guenthner, N.; Wasden, K.; Fiala, M.; King, J.; et al. Targeting CD47 as a novel immunotherapy for multiple myeloma. Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shin, S.J.; Lee, H.; Jung, G.; Gil, M.; Park, H.; Park, Y.S.; Yoon, D.H.; Suh, C.; Park, C.J.; Huh, J.; et al. Expression of CD99 in multiple myeloma: A clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical study of 170 cases. Korean J. Pathol. 2014, 48, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, M.; Pak, H.K.; Lee, A.N.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.; Roh, J.; Lee, H.; Chung, Y.S.; Park, C.S. CD99 regulates CXCL12-induced chemotaxis of human plasma cells. Immunol. Lett. 2015, 168, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, J.; Browne, C.D.; Ruppert, R.; Féral, C.C.; Fässler, R.; Rickert, R.C.; Ginsberg, M.H. CD98hc facilitates B cell proliferation and adaptive humoral immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2009, 10, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pojero, F.; Casuccio, A.; Giambanco, C.; Bulati, M.; Buffa, S.; Di Bassiano, F.; Gervasi, F.; Caruso, C.; Colonna Romano, G. Bone marrow B lymphocytes in multiple myeloma and MGUS: Focus on distribution of naive cells and memory subsets. Leuk. Res. 2016, 49, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kop, E.N.; Matmati, M.; Pouwels, W.; Leclercq, G.; Tak, P.P.; Hamann, J. Differential expression of CD97 on human lymphocyte subsets and limited effect of CD97 antibodies on allogeneic T-cell stimulation. Immunol. Lett. 2009, 123, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkelmann, R.; Sandrock, L.; Porstner, M.; Roth, E.; Mathews, M.; Hobeika, E.; Reth, M.; Kahn, M.L.; Schuh, W.; Jäck, H.M. B cell homeostasis and plasma cell homing controlled by Krüppel-like factor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011, 108, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tohami, T.; Drucker, L.; Radnay, J.; Shapira, H.; Lishner, M. Expression of tetraspanins in peripheral blood leukocytes: A comparison between normal and infectious conditions. Tissue Antigens 2004, 64, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bischof, D.; Elsawa, S.F.; Mantchev, G.; Yoon, J.; Michels, G.E.; Nilson, A.; Sutor, S.L.; Platt, J.L.; Ansell, S.M.; Von Bulow, G.; et al. Selective activation of TACI by syndecan-2. Blood 2006, 107, 3235–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Takata, K.; Sato, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Ichimura, K.; Tamura, M.; Oka, T.; Yoshino, T. Downregulation of the B-cell receptor signaling component CD79b in plasma cell myeloma: A possible post transcriptional regulation. Pathol. Int. 2011, 61, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.; Montani, E.; Bolli, M.; Garavaglia, G.; Sallusto, F.; Lanzavecchia, A.; Jarrossay, D. A functional BCR in human IgA and IgM plasma cells. Blood 2013, 121, 4110–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Krzysiek, R.; Lefevre, E.A.; Bernard, J.; Foussat, A.; Galanaud, P.; Louache, F.; Richard, Y. Regulation of CCR6 chemokine receptor expression and responsiveness to macrophage inflammatory protein-3α/CCL20 in human B cells. Blood 2000, 96, 2338–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odendahl, M.; Mei, H.; Hoyer, B.F.; Jacobi, A.M.; Hansen, A.; Muehlinghaus, G.; Berek, C.; Hiepe, F.; Manz, R.; Radbruch, A.; et al. Generation of migratory antigen-specific plasma blasts and mobilization of resident plasma cells in a secondary immune response. Blood 2005, 105, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, H.T.; Timm, M.M.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E.; Dispenzieri, A.; Russell, S.J.; Peng, K.W. Oncolytic measles virus targets high CD46 expression on multiple myeloma cells. Exp. Hematol. 2006, 34, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcindor, T.; Kimlinger, T.; Witzig, T.E. High expression of CD59 and CD55 on benign and malignant plasma cells. Leuk. Lymphoma 2006, 47, 919–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terstappen, L.W.M.M.; Nguyen, M.; Lazarus, H.M.; Medof, M.E. Expression of the DAF (CD55) and CD59 antigens during normal hematopoietic cell differentiation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1992, 52, 652–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, H.F.; Hamilton, M.S.; Ball, J.; Drew, M.; Franklin, I.M. Expression of adhesion molecules LFA-3 and N-CAM on normal and malignant human plasma cells. Br. J. Haematol. 1992, 81, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Hao, Y.; Li, Y.; Lyu, C.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Xue, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, R. Upregulation of CD72 expression on CD19+CD27+ memory B cells by CD40L in primary immune thrombocytopenia. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 178, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodríguez-Bayona, B.; Ramos-Amaya, A.; Brieva, J.A. Differential expression of SLAMS and other modulatory molecules by human plasma cells during normal maturation. Immunol. Lett. 2011, 134, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocqueteau, M.; Orfao, A.; Almeida, J.; Bladé, J.; González, M.; García-Sanz, R.; López-Berges, C.; Moro, M.J.; Hernández, J.; Escribano, L.; et al. Immunophenotypic characterization of plasma cells from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance patients: Implications for the differential diagnosis between MGUS and multiple myeloma. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 1655–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez-Andrés, M.; Almeida, J.; Martín-Ayuso, M.; Moro, M.J.; Martín-Nuñez, G.; Galende, J.; Borrego, D.; Rodríguez, M.J.; Ortega, F.; Hernandez, J.; et al. Clonal plasma cells from monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, multiple myeloma and plasma cell leukemia show different expression profiles of molecules involved in the interaction with the immunological bone marrow microenvironment. Leukemia 2005, 19, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Burton, J.D.; Ely, S.; Reddy, P.K.; Stein, R.; Gold, D.V.; Cardillo, T.M.; Goldenberg, D.M. CD74 is expressed by multiple myeloma and is a promising target for therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6606–6611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Abroun, S.; Otsuyama, K.; Asaoku, H.; Kawano, M.M. Heterogeneous expression of CD32 and CD32-mediated growth suppression in human myeloma cells. Haematologica 2006, 91, 920–928. [Google Scholar]
- Banham, A.H.; Colonna, M.; Cella, M.; Micklem, K.J.; Pulford, K.; Willis, A.C.; Mason, D.Y. Identification of the CD85 antigen as ILT2, an inhibitory MHC class I receptor of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J. Leukoc. Biol. 1999, 65, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pojero, F.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja, L.; Pérez, J.J.; Puig, N.; Paiva, B.; Bottcher, S.; van Dongen, J.J.M.; Orfao, A. Utility of CD54, CD229, and CD319 for the identification of plasma cells in patients with clonal plasma cell diseases. Cytom. Part B Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.; Tarte, K.; Jourdan, M.; Mathouk, K.; Moreaux, J.; Jourdan, E.; Legouffe, E.; De Vos, J.; Rossi, J.F. Survival and proliferation factors of normal and malignant plasma cells. Int. J. Hematol. 2003, 78, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.F.; Anderson, K.C.; Tai, Y.T. Targeting B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) in multiple myeloma: Potential uses of BCMA-based immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckinger, A.; Delgado, J.A.; Moser, S.; Moreno, L.; Neuber, B.; Grab, A.; Lipp, S.; Merino, J.; Prosper, F.; Emde, M.; et al. Target Expression, Generation, Preclinical Activity, and Pharmacokinetics of the BCMA-T Cell Bispecific Antibody EM801 for Multiple Myeloma Treatment. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smulski, C.R.; Eibel, H. BAFF and BAFF-receptor in B cell selection and survival. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousef, S.; Marvin, J.; Steinbach, M.; Langemo, A.; Kovacsovics, T.; Binder, M.; Kröger, N.; Luetkens, T.; Atanackovic, D. Immunomodulatory molecule PD-L1 is expressed on malignant plasma cells and myeloma-propagating pre-plasma cells in the bone marrow of multiple myeloma patients. Blood Cancer J. 2015, 5, e285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miguel-Garcia, A.; Matutes, E.; Tarin, F.; Garcia-Talavera, J.; Miguel-Sosa, A.; Carbonell, F.; Catovsky, D. Circulating Ki67 positive lymphocytes in multiple myeloma and benign monoclonal gammopathy. J. Clin. Pathol. 1995, 48, 835–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mizuta, S.; Kawata, T.; Kawabata, H.; Yamane, N.; Mononobe, S.; Komai, T.; Koba, Y.; Ukyo, N.; Tamekane, A.; Watanabe, M. VS38 as a promising CD38 substitute antibody for flow cytometric detection of plasma cells in the daratumumab era. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 110, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Arriba-Méndez, S.; Serrano, C.; Criado, I.; Del Pino-Molina, L.; Silva, S.; Madruga, I.; Bakardjieva, M.; Martins, C.; et al. Defects in memory B-cell and plasma cell subsets expressing different immunoglobulin-subclasses in patients with CVID and immunoglobulin subclass deficiencies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manz, R.A.; Hauser, A.E.; Hiepe, F.; Radbruch, A. Maintenance of serum antibody levels. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 367–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravi, P.; Kumar, S.K.; Roeker, L.; Gonsalves, W.; Buadi, F.; Lacy, M.Q.; Go, R.S.; Dispenzieri, A.; Kapoor, P.; Lust, J.A.; et al. Revised diagnostic criteria for plasma cell leukemia: Results of a Mayo Clinic study with comparison of outcomes to multiple myeloma. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touzeau, C.; Pellat-Deceunynck, C.; Gastinne, T.; Accard, F.; Jego, G.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Robillard, N.; Harousseau, J.L.; Bataille, R.; Moreau, P. Reactive plasmacytoses can mimick plasma cell leukemia: Therapeutical implications. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 207–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounari, E.; Tsavdaridou, V.; Koletsa, T.; Nikolaidou, A.; Kaiafa, G.; Papaioannou, M.; Kostopoulos, I.; Skoura, L. Utility of hematology analyzer and flow cytometry in timely and correct detection of circulating plasma cells: Report of three cases. Cytometry B. Clin. Cytom. 2016, 90, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huhn, S.; Weinhold, N.; Nickel, J.; Pritsch, M.; Hielscher, T.; Hummel, M.; Bertsch, U.; Huegle-Doerr, B.; Vogel, M.; Angermund, R.; et al. Circulating tumor cells as a biomarker for response to therapy in multiple myeloma patients treated within the GMMG-MM5 trial. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vij, R.; Mazumder, A.; Klinger, M.; O’Dea, D.; Paasch, J.; Martin, T.; Weng, L.; Park, J.; Fiala, M.; Faham, M.; et al. Deep Sequencing Reveals Myeloma Cells in Peripheral Blood in Majority of Multiple Myeloma Patients. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2014, 14, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gertz, M.A.; Witzig, T.E.; Pineda, A.A.; Greipp, P.R.; Kyle, R.A.; Litzow, M.R. Monoclonal plasma cells in the blood stem cell harvest from patients with multiple myeloma are associated with shortened relapse-free survival after transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1997, 19, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, R.; Muchtar, E.; Kumar, S.K.; Jevremovic, D.; Buadi, F.K.; Dingli, D.; Dispenzieri, A.; Hayman, S.R.; Hogan, W.J.; Kapoor, P.; et al. Risk stratification in myeloma by detection of circulating plasma cells prior to autologous stem cell transplantation in the novel agent era. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oberle, A.; Brandt, A.; Voigtlaender, M.; Thiele, B.; Radloff, J.; Schulenkorf, A.; Alawi, M.; Akyüz, N.; März, M.; Ford, C.T.; et al. Monitoring multiple myeloma by next-generation sequencing of V(D)J rearrangements from circulating myeloma cells and cell-free myeloma DNA. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korthals, M.; Sehnke, N.; Kronenwett, R.; Schroeder, T.; Strapatsas, T.; Kobbe, G.; Haas, R.; Fenk, R. Molecular Monitoring of Minimal Residual Disease in the Peripheral Blood of Patients with Multiple Myeloma. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, 1109–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcés, J.-J.; Simicek, M.; Vicari, M.; Brozova, L.; Burgos, L.; Bezdekova, R.; Alignani, D.; Calasanz, M.-J.; Growkova, K.; Goicoechea, I.; et al. Transcriptional profiling of circulating tumor cells in multiple myeloma: A new model to understand disease dissemination. Leukemia 2020, 34, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzig, T.E.; Dhodapkar, M.V.; Kyle, R.A.; Greipp, P.R. Quantitation of circulating peripheral blood plasma cells and their relationship to disease activity in patients with multiple myeloma. Cancer 1993, 72, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulk, B.; Schaffer, M.; Gross, S.; Rao, C.; Smirnov, D.; Connelly, M.C.; Chaturvedi, S.; Reddy, M.; Brittingham, G.; Mata, M.; et al. Enumeration and characterization of circulating multiple myeloma cells in patients with plasma cell disorders. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Witzig, T.E.; Meyers, C.; Therneu, T.; Greipp, P.R. A prospective study of CD38/45 flow cytometry and immunofluorescence microscopy to detect blood plasma cells in patients with plasma cell proliferative disorders. Leuk. Lymphoma 2000, 38, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Hieber, M.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Paiva, B.; Flores-Montero, J.; Perez, J.J.; Gutierrez, N.C.; Vidriales, M.B.; Matarraz, S.; San Miguel, J.F.; Orfao, A. CD117 expression in gammopathies is associated with an altered maturation of the myeloid and lymphoid hematopoietic cell compartments and favorable disease features. Haematologica 2011, 96, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Periago, A.; Campillo, J.A.; Mrowiec, A.; Gimeno, L.; Montes, N.R.; Martínez-Sánchez, M.V.; Cabañas-Perianes, V.; García-Garay, C.; Bolarin, J.M.; Blasco-Mogorrón, A.; et al. Circulating aberrant plasma cells allow risk stratification of patients with myeloma. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, E353–E355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moor, I.; Bacher, V.U.; Jeker, B.; Taleghani, B.M.; Mueller, B.U.; Keller, P.; Betticher, D.; Egger, T.; Novak, U.; Pabst, T. Peripheral flow-MRD status at the time of autologous stem cell collection predicts outcome in multiple myeloma. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018, 53, 1599–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, A.J.; Stevenson, P.A.; Libby, E.N.; Becker, P.S.; Coffey, D.G.; Green, D.J.; Hyun, T.S.; Fromm, J.R.; Gopal, A.K.; Holmberg, L.A. Circulating Plasma Cells at the Time of Collection of Autologous PBSC for Transplant in Multiple Myeloma Patients is a Negative Prognostic Factor Even in the Age of Post-Transplant Maintenance Therapy. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1386–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; García-Sánchez, O.; Böttcher, S.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Pérez-Morán, J.-J.; Vidriales, M.-B.; García-Sanz, R.; et al. Next Generation Flow for highly sensitive and standardized detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2094–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiva, B.; Puig, N.; Cedena, M.-T.; Rosiñol, L.; Cordón, L.; Vidriales, M.-B.; Burgos, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Sanoja-Flores, L.; Lopez-Anglada, L.; et al. Measurable Residual Disease by Next-Generation Flow Cytometry in Multiple Myeloma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billadeau, D.; Quam, L.; Thomas, W.; Kay, N.; Greipp, P.; Kyle, R.; Oken, M.M.; Van Ness, B. Detection and quantitation of malignant cells in the peripheral blood of multiple myeloma patients. Blood 1992, 80, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Paiva, B.; Anderson, K.C.; Durie, B.; Landgren, O.; Moreau, P.; Munshi, N.; Lonial, S.; Bladé, J.; Mateos, M.V.; et al. International Myeloma Working Group consensus criteria for response and minimal residual disease assessment in multiple myeloma. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, e328–e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, J.R.; Thoren, K.L. Tracking of low disease burden in multiple myeloma: Using mass spectrometry assays in peripheral blood. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2020, 33, 101142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drayson, M.; Morgan, G.; Jackson, G.; Davies, F.; Owen, R.; Ross, F.; Gregory, W.; Navarro-Coy, N.; Heatley, F.; Bell, S.; et al. Prospective Study of Serum FLC and Other M-Protein Assays: When and How to Measure Response? Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma 2012, 9, S56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Orfao, A.; Chim, C.S. Molecular detection of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 181, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puig, N.; Balanzategui, A.; Martínez, J.; Paiva, B.; García, H.; Fumero, S.; Jimé Nez, C.; Alcoceba, M.; Chilló, M.C.; Sebastián, E.; et al. Critical evaluation of ASO RQ-PCR for minimal residual disease evaluation in multiple myeloma. A comparative analysis with flow cytometry. Leukemia 2014, 28, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paiva, B.; Dongen, J.J.M.; Van Orfao, A. New criteria for response assessment: Role of minimal residual disease in multiple myeloma. Blood 2015, 125, 3059–3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yao, Q.; Bai, Y.; Orfao, A.; Kumar, S.; Chim, C.S. Upgraded Standardized Minimal Residual Disease Detection by Next-Generation Sequencing in Multiple Myeloma. J. Mol. Diagnostics 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishima, Y.; Paiva, B.; Shi, J.; Michor, F.; San Miguel, J.F.; Ghobrial Correspondence, I.M.; Mishima, Y.; Park, J.; Manier, S.; Takagi, S.; et al. The Mutational Landscape of Circulating Tumor Cells in Multiple Myeloma. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ledergor, G.; Weiner, A.; Zada, M.; Wang, S.Y.; Cohen, Y.C.; Gatt, M.E.; Snir, N.; Magen, H.; Koren-Michowitz, M.; Herzog-Tzarfati, K.; et al. Single cell dissection of plasma cell heterogeneity in symptomatic and asymptomatic myeloma. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1867–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manier, S.; Park, J.; Capelletti, M.; Bustoros, M.; Freeman, S.S.; Ha, G.; Rhoades, J.; Liu, C.J.; Huynh, D.; Reed, S.C.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing of cell-free DNA and circulating tumor cells in multiple myeloma. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Witzig, T.E.; Greipp, P.R.; Rajkumar, S.V. Bone marrow angiogenesis and circulating plasma cells in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 272–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vagnoni, D.; Travaglini, F.; Pezzoni, V.; Ruggieri, M.; Bigazzi, C.; Dalsass, A.; Mestichelli, F.; Troiani, E.; Falcioni, S.; Mazzotta, S.; et al. Circulating plasma cells in newly diagnosed symptomatic multiple myeloma as a possible prognostic marker for patients with standard-risk cytogenetics. Br. J. Haematol. 2015, 170, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobrial, I.M. Myeloma as a model for the process of metastasis: Implications for therapy. Blood 2012, 120, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lohr, J.G.; Kim, S.; Gould, J.; Knoechel, B.; Drier, Y.; Cotton, M.J.; Gray, D.; Birrer, N.; Wong, B.; Ha, G.; et al. Genetic interrogation of circulating multiple myeloma cells at single-cell resolution. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Paiva, B.; Paino, T.; Sayagues, J.-M.; Garayoa, M.; San-Segundo, L.; Martin, M.; Mota, I.; Sanchez, M.-L.; Barcena, P.; Aires-Mejia, I.; et al. Detailed characterization of multiple myeloma circulating tumor cells shows unique phenotypic, cytogenetic, functional, and circadian distribution profile. Blood 2013, 122, 3591–3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S.; Rajkumar, S.V.; Greipp, P.R.; Witzig, T.E. Cell proliferation of myeloma plasma cells: Comparison of the blood and marrow compartments. Am. J. Hematol. 2004, 77, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, A.K.; Hu, J.; Quang, P.; Azab, F.; Pitsillides, C.; Awwad, R.; Thompson, B.; Maiso, P.; Sun, J.D.; Hart, C.P.; et al. Hypoxia promotes dissemination of multiple myeloma through acquisition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition-like features. Blood 2012, 119, 5782–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vande Broek, I.; Vanderkerken, K.; Van Camp, B.; Van Riet, I. Extravasation and homing mechanisms in multiple myeloma. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldschmidt, J.M.; Anand, P.; Knoechel, B.; Lohr, J.G. Comprehensive characterization of circulating and bone marrow-derived multiple myeloma cells at minimal residual disease. Semin. Hematol. 2018, 55, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Type of Marker and Function | Target Molecule | Tonsil PC | Blood PC | Bone Marrow PC | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Activation markers | CD71 | Low | − | − | [39,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73] |
| CD37 | Low | − | − | ||
| CD39 | + | + | − | ||
| CD45RB | + | −/+ | − | ||
| CD52 | Low | NT | − | ||
| CD53 | + | − | − | ||
| CD45 | + | Low | −/+ | ||
| CD45RO | − | − | −/+ | ||
| CD45RA | + | + | −/+ | ||
| CD200 | − | − | −/Low | ||
| CD10 | Low | −/Low | −/Low | ||
| CD28 | −/Low | −/Low | −/Low | ||
| CD9 | + | −/Low | + | ||
| CD43 | + | + | + | ||
| CD361 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ||
| CD38 | + | + | ++ | ||
| CD27 | Low | + | ++ | ||
| CD63 | + | + | Low | ||
| Adhesion molecules | CD100 | Low | − | − | [39,52,53,54,57,60,61,62,63,64,66,70,72,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
| CD18 | Low | − | − | ||
| CD62L | − | −/+ | − | ||
| CD47 | + | − | − | ||
| CD11a (LFA-1) | + | −/Low | −/+ | ||
| CD56 (NCAM) | − | − | −/+ | ||
| CD49e (VLA-5) | − | − | −/+ | ||
| CD99 | + | + | + | ||
| CD44 (HCAM) | + | + | + | ||
| CD50 (ICAM-3) | + | −/Low | + | ||
| CD49f (ITGA6) | − | Low | + | ||
| CD98 | + | + | + | ||
| CD54 (ICAM-1) | + | −/+ | + | ||
| CD31 | Low | + | ++ | ||
| CD106 (VCAM-1) | − | − | ++ | ||
| CD49d (VLA-4) | Low | + | ++ | ||
| CD97 | Low | Low | Low | ||
| CD329 (SIGLEC 8) | Low | + | NT | ||
| CD363 (S1PR1) | − | −/+ | − | ||
| CD82 | + | + | + | ||
| CD81 | + | + | + | ||
| CD362 | −/+ | ++ | + | ||
| CD138 | − | −/+ | + | ||
| BCR signalling molecules | CD22 | + | −/Low | − | [39,53,54,70,85,86] |
| CD79b | Low | − | − | ||
| HLA-DR | ++ | −/+ | − | ||
| CD19 | + | Low | −/+ | ||
| CD20 | + | −/+ | −/Low | ||
| CD21 | + | −/+ | −/Low | ||
| CD79a | − | −/+ | + | ||
| Cell migration and chemokine receptors | CD196 (CCR6) | −/+ | − | − | [39,53,57,62,87,88] |
| CD184 (CXCR4) | Low | −/+ | −/+ | ||
| CD185 (CXCR5) | −/+ | −/+ | −/Low | ||
| Complement receptors | CD46 | + | NT | − | [54,64,65,89,90,91,92] |
| CD35 | −/Low | −/Low | −/+ | ||
| CD55 | + | + | + | ||
| CD58 | + | − | + | ||
| CD59 | + | + | + | ||
| Co-stimulatory molecules | CD72 | Low | − | − | [39,54,62,73,93,94,95,96,97,98,99] |
| CD80 (B7-1) | − | Low | − | ||
| CD40 | + | Low | + | ||
| CD86 (B7-2) | Low | + | Low | ||
| CD272 (BTLA) | −/Low | + | Low | ||
| CD126 (IL-6Rα) | Low | + | − | ||
| CD130 (IL-6Rβ) | + | Low | Low | ||
| CD307a (FCRL-1) | − | Low | − | ||
| CD74 | Low | − | − | ||
| CD305 (LAIR1) | − | −/+ | − | ||
| CD32 | Low | + | + | ||
| CD85j | Low | + | + | ||
| CD210a | − | − | Low | ||
| Receptors of the SLAM family | CD84 (SLAMF5) | −/Low | −/+ | − | [54,62,72,94,100] |
| CD352 (SLAMF6) | ++ | ++ | + | ||
| CD150 (SLAMF1) | Low | + | + | ||
| CD48 (SLAMF2) | Low | ++ | + | ||
| CD229 (SLAMF3) | ++ | + | + | ||
| CD319 (SLAMF7) | −/+ | −/+ | + | ||
| PC survival-associated molecules | CD357 (TNFRSF18) | − | Low | − | [39,53,54,62,72,73,94,96,101,102,103,104,105] |
| CD257 (BAFF) | −/+ | −/+ | + | ||
| CD269 (BCMA) | −/Low | Low | + | ||
| CD268 (BAFF-R) | + | − | + | ||
| CD261 (TRAIL-R1) | − | − | + | ||
| CD358 (TNFSF21) | − | − | Low | ||
| CD270 (TNFRSF14) | Low | + | Low | ||
| CD262 (TRAIL-R2) | − | − | Low | ||
| Bcl-2 | − | Low | + | ||
| CD274 (PD-L1) | + | + | − | ||
| CD95 (Fas-L) | Low | + | − | ||
| PC proliferation and Ig production | Ki67 | −/+ | −/+ | −/Low | [39,86,106,107] |
| Vs38c | −/+ | −/+ | + |
| Cytology | IMF | MFC | NGF | ASO-qPCR | NGS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Availability | High | Low | High | High | Intermediate | Limited |
| Applicability | ≈100% | ≈100% | ≈100% | ≈100% | 42% to75% | 80–90% |
| Sensitivity | <10−2 | <10−4 | ≤10−4 | ≤2 × 10−6 | ≤10−5–10−6 | ≤1 × 10−6 |
| Specificity | Limited | Limited | High | High | High | High |
| Standardized | Yes | No | Ongoing | Yes | Yes | Ongoing |
| Quantitative | Yes (high counts) | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Diagnostic sample | Not required | Not required | Not required | Not required | Mandatory | Mandatory |
| Global sample analysis | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No |
| Time to results | <2 h | 4 h | 2–3 h | 3–4 h | 3–4 weeks | ≥7 days |
| Fresh sample | Yes | Yes | Yes (<36 h) | Yes (<36 h) | No | No |
| Sample pre-treatment * | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Data analysis/interpretation | Subjective | Slightly subjective | Slightly subjective | More objective | Slightly subjective | More objective |
| CTPC detection principle | DFN | Ig light-chain restriction | DFN and LAIP | DFN and LAIP | Patient-specific IGH-V(D)J gene rearrangements | Patient-specific IGH-V(D)J gene rearrangements ¥ |
| Additional biological characterization of CTPC | No | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| Prognostic factor in MGUS | NT | Yes | NT | Yes | NT | NT |
| Prognostic factor in SMM | NT | Yes | Yes | Limited | NT | NT |
| Prognostic factor in MM | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Relative Cost | Low | High | Intermediate | Intermediate | Intermediate | High |
| Methodology | Diagnosis | Treated | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGUS | SMM | MM | MM | References | ||||
| TTP/PFS | TTP | OS | PFS | OS | PFS | OS | ||
| Cytology | NT | NT | NT | NT | 1.1 vs. 4.1y a | NT | NT | [30,110] |
| IMF | 138m vs. NR b | 12 vs. 57m c | 49 vs. 148m b | NT | 2.4 vs. 4.5y d | 6.2 vs. 22.5m e | NT | [19,23,25,27,115] |
| MFC | NT | 10m vs. NR b | NT | 25 vs. 43m b (TTNT *) | 54 vs. 89m b | 15.1m vs. 29.6m b | 41m vs. NR b | [22,26] |
| NGF | 31m vs. NR f | 25% vs. 0% at 2y (p > 0.05) g | NT | 22m vs. NR g | 67% vs. 0% at 2y g | 9 vs. 46m b | NT | [21,35] |
| ASO-qPCR | NT | NT | NT | 26 vs. 66m b | 53 vs. 66m (p > 0.05) b | 4 vs. 15m b | 17 vs. 52m b | [118] |
| NGS | NT | NT | NT | 22.6 vs. 47.5mh 26.7 vs. 41.3m i | >55m h,i | NT | NT | [119] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanoja-Flores, L.; Flores-Montero, J.; Pérez-Andrés, M.; Puig, N.; Orfao, A. Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells in Monoclonal Gammopathies: Methods, Pathogenic Role, and Clinical Implications. Cancers 2020, 12, 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061499
Sanoja-Flores L, Flores-Montero J, Pérez-Andrés M, Puig N, Orfao A. Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells in Monoclonal Gammopathies: Methods, Pathogenic Role, and Clinical Implications. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061499
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanoja-Flores, Luzalba, Juan Flores-Montero, Martín Pérez-Andrés, Noemí Puig, and Alberto Orfao. 2020. "Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells in Monoclonal Gammopathies: Methods, Pathogenic Role, and Clinical Implications" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061499
APA StyleSanoja-Flores, L., Flores-Montero, J., Pérez-Andrés, M., Puig, N., & Orfao, A. (2020). Detection of Circulating Tumor Plasma Cells in Monoclonal Gammopathies: Methods, Pathogenic Role, and Clinical Implications. Cancers, 12(6), 1499. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061499