Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Central Nervous System and Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis, Biology, and Functions of MLT
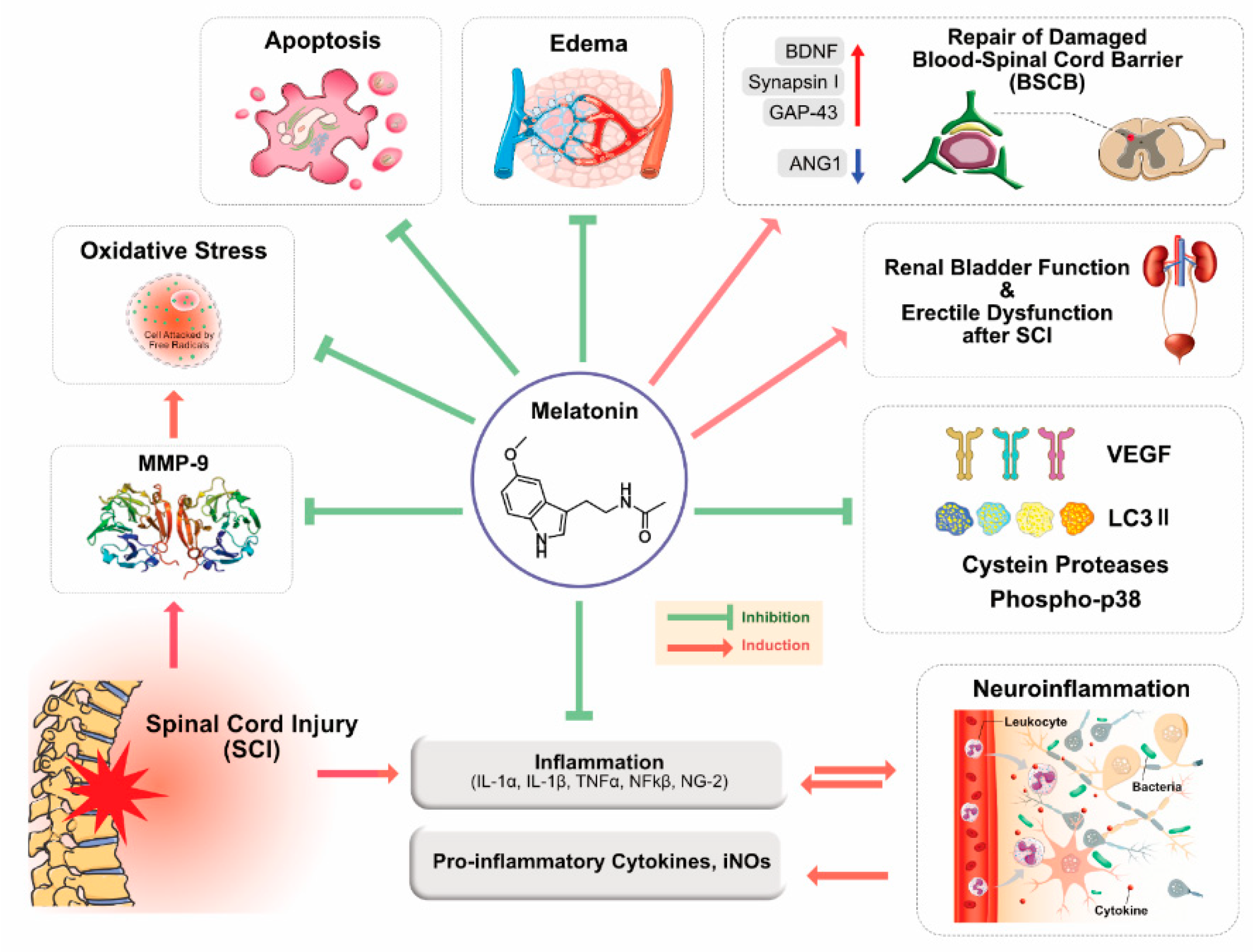
3. Role of MLT in Brain and Spinal Cord Injuries
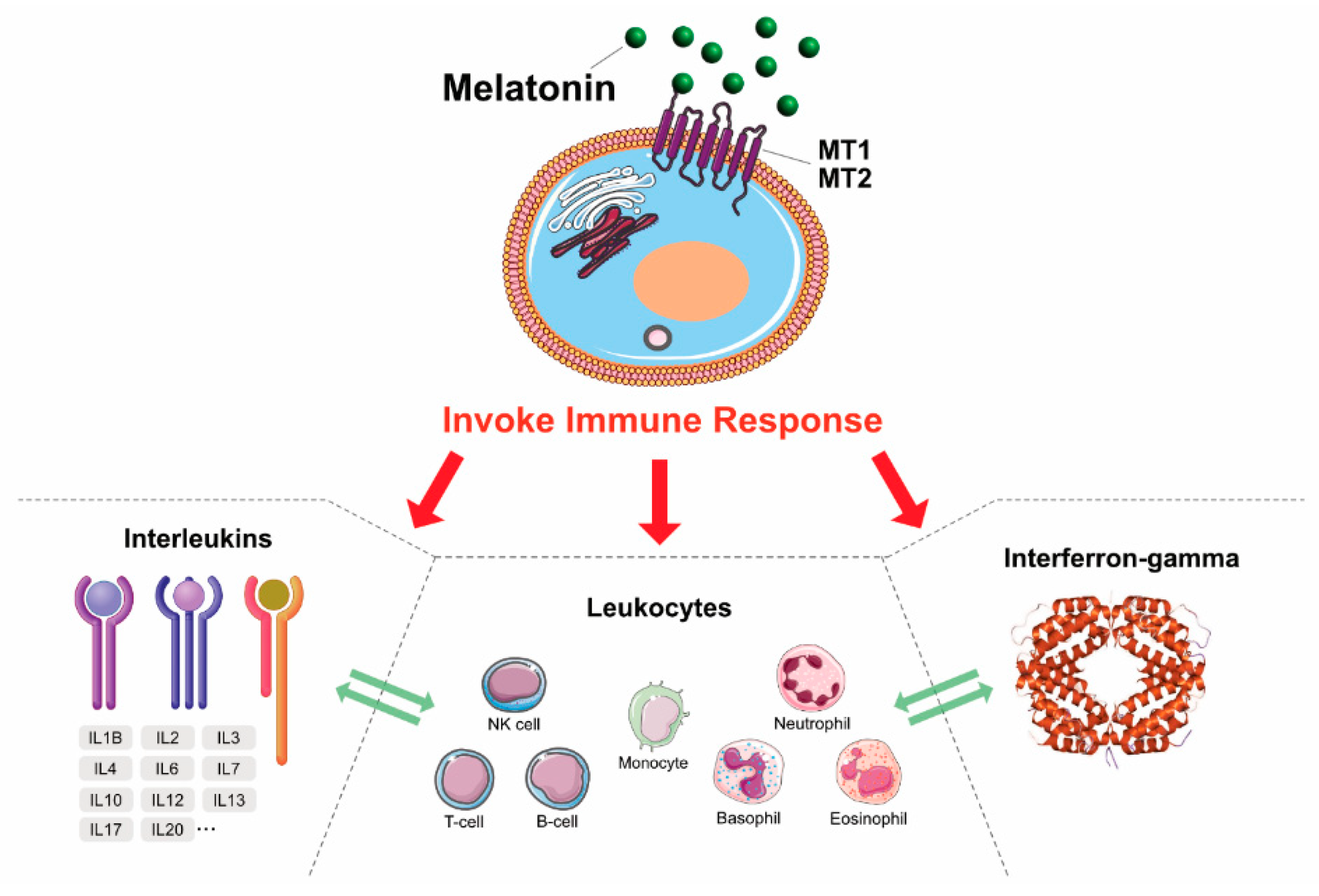
4. MLT: Antioxidant, Neuroprotectant, and Immunomodulatory Agent
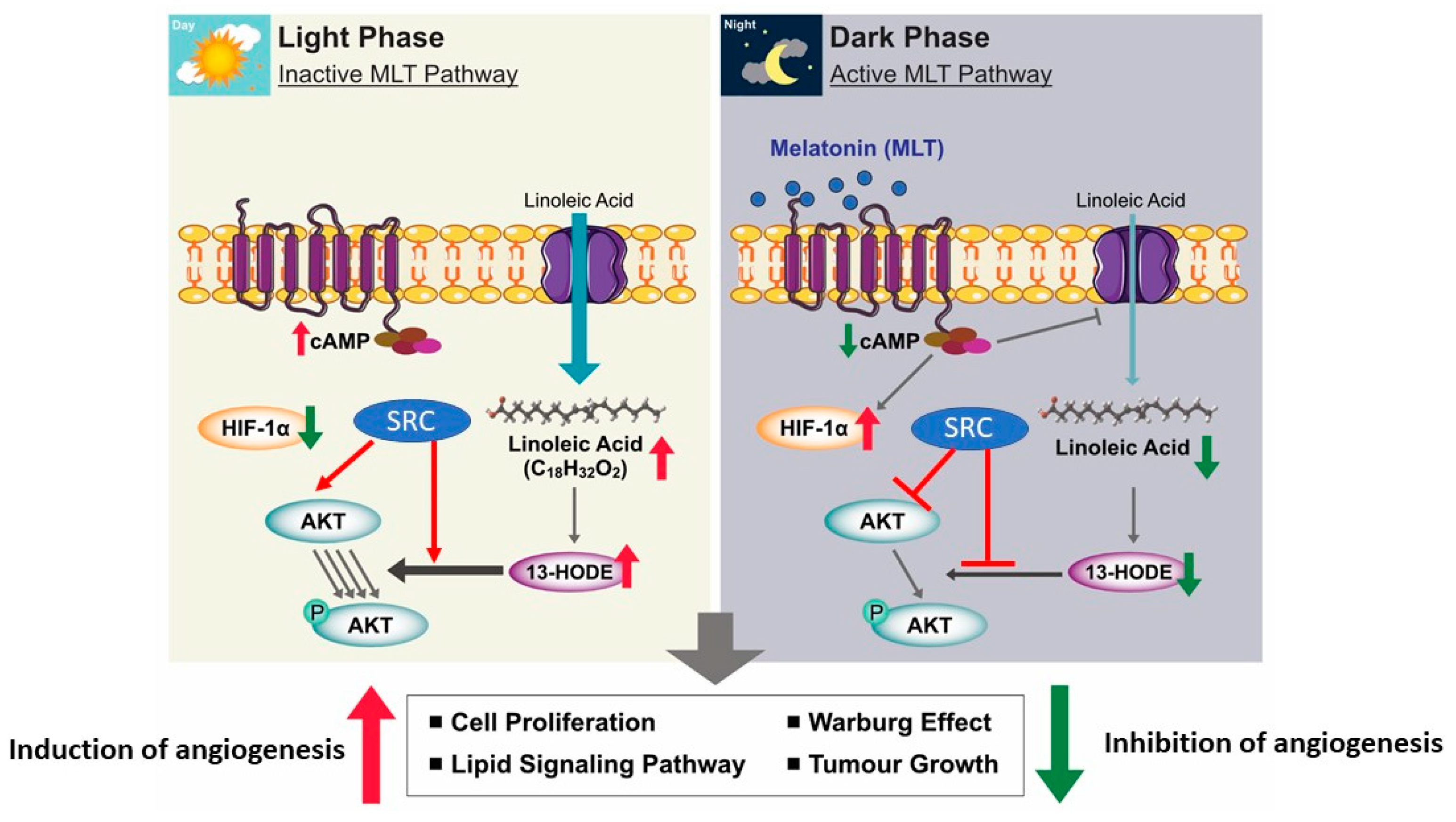
5. MLT as an Anticancer Agent
6. CNS Cancers
7. MLT: A Novel Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of CNS Disorders and Cancers
8. Conclusion and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samantaray, S.; Thakore, N.P.; Matzelle, D.D.; Varma, A.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Neuroprotective drugs in traumatic CNS injury. Open Drug Discov. J. 2010, 2, 174–180. [Google Scholar]
- Samantaray, S.; Das, A.; Thakore, N.P.; Matzelle, D.D.; Reiter, R.J.; Ray, S.K.; Banik, N.L. Therapeutic potential of melatonin in traumatic central nervous system injury. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalala, O.G.; Srikanth, M.; Kessler, J.A. The emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Cooke, M.J.; Shoichet, M.S. Creating permissive microenvironments for stem cell transplantation into the central nervous system. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalatbary, A.R.; Tiraihi, T.; Boroujeni, M.B.; Ahmadvand, H.; Tavafi, M.; Tamjidipoor, A. Effects of epigallocatechin gallate on tissue protection and functional recovery after contusive spinal cord injury in rats. Brain Res. 2010, 1306, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bains, M.; Hall, E.D. Antioxidant therapies in traumatic brain and spinal cord injury. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 2011, 1822, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration; Fitzmaurice, C.; Allen, C.; Barber, R.M.; Barregard, L.; Bhutta, Z.A.; Brenner, H.; Dicker, D.J.; Chimed-Orchir, O.; Dandona, R.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Cancer Incidence, Mortality, Years of Life Lost, Years Lived With Disability, and Disability-Adjusted Life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 524–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaist, D.; A García-Rodríguez, L.; Soerensen, H.T.; Hallas, J.; Friis, S. Use of low-dose aspirin and non-aspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of glioma: A case–control study. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 1189–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Bauchet, L.; Davis, F.G.; Deltour, I.; Fisher, J.L.; Langer, C.E.; Pekmezci, M.; Schwartzbaum, J.; Turner, M.C.; Walsh, K.M.; et al. The epidemiology of glioma in adults: A “state of the science” review. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 896–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, A.; Conconi, S.; Hertens, E.; Skwarlo-Sonta, K.; Markowska, M.; Maestroni, G.J. Evidence for melatonin synthesis in mouse and human bone marrow cells. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin—A pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 350–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin in Aging and Disease—Multiple Consequences of Reduced Secretion, Options and Limits of Treatment. Aging Dis. 2011, 3, 194–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; Venegas, C.; Casado, M.E.D.; Cabello, M.E.L.; López, L.C.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Extrapineal melatonin: Sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2997–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and the electron transport chain. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3883–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacoste, B.; Angeloni, D.; Dominguez-Lopez, S.; Calderoni, S.; Mauro, A.; Fraschini, F.; Descarries, L.; Gobbi, G. Anatomical and cellular localization of melatonin MT1and MT2receptors in the adult rat brain. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 397–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.Y.; Leong, M.K.; Liang, H.; Paxinos, G. Melatonin receptors: Distribution in mammalian brain and their respective putative functions. Brain Struct. Funct. 2017, 222, 2921–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, L.; Ramos, D.; Hataka, A.; Rossignoli, P.S.; Granado, M.D.; Mazzetto, M.C.; Campos, L.; Junior, M.D.G. Day/night expression of MT 1 and MT 2 receptors in hypothalamic nuclei of the primate Sapajus apella. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 81, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin and brain inflammaging. Prog. Neurobiol. 2015, 127, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Watson, N.; Diamandis, T.; Gonzales-Portillo, C.; Reyes, S.; Borlongan, C.V. Melatonin as an antioxidant for stroke neuroprotection. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; LeÓn, J.; Carazo, A.; Khaldy, H. Mitochondrial regulation by melatonin and its metabolites. In Developments in Tryptophan and Serotonin Metabolism; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; pp. 549–557. [Google Scholar]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin role in the mitochondrial function. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin: Signaling mechanisms of a pleiotropic agent. BioFactors 2009, 35, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and the theories of aging: A critical appraisal of melatonin’s role in antiaging mechanisms. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 325–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and the pathologies of weakened or dysregulated circadian oscillators. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 62, e12377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.X.; Jou, M.J.; Galano, A.; Xu, B. Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: One of evolution’s best ideas. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.; Tan, D.-X.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Galano, A.; Zhou, X.J.; Xu, B. Mitochondria: Central Organelles for Melatonin′s Antioxidant and Anti-Aging Actions. Molecules 2018, 23, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Rahim, I.; Acuña-Fernández, C.; Ortiz, F.; Solera-Marín, J.; Sayed, R.; Casado, M.E.D.; Rusanova, I.; López, L.C.; Escames, G. Melatonin, clock genes and mitochondria in sepsis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3965–3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Coto-Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Manchester, L.C.; Fuentes-Broto, L.; Korkmaz, A.; Ma, S.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Alzheimer’s disease: Pathological mechanisms and the beneficial role of melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 52, 167–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.; Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Koppisepi, S. Medical implications of melatonin: Receptor-mediated and receptor-independent actions. Adv. Med. Sci. 2007, 52, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Zawilska, J.B.; Skene, D.J.; Arendt, J. Physiology and pharmacology of melatonin in relation to biological rhythms. Pharmacol. Rep. 2009, 61, 383–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, L.C.; Coto-Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Andersen, L.P.H.; Zhou, Z.; Galano, A.; Vriend, J.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R. Melatonin: An ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Yu, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhao, Z.; Sharma, R.; Reiter, R. Melatonin Synthesis and Function: Evolutionary History in Animals and Plants. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R. Melatonin: Clinical relevance. Best Pr. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 17, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubocovich, M.L.; Markowska, M. Functional MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors in Mammals. Endocrine 2005, 27, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claustrat, B.; Brun, J.; Chazot, G. The basic physiology and pathophysiology of melatonin. Sleep Med. Rev. 2005, 9, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: The chemical expression of darkness. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1991, 79, C153–C158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acarin, L.; González, B.; Castellano, B. Neuronal, astroglial and microglial cytokine expression after an excitotoxic lesion in the immature rat brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3505–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.-C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Jin, X. Melatonin Supplementation, a Strategy to Prevent Neurological Diseases through Maintaining Integrity of Blood Brain Barrier in Old People. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muxel, S.M.; Lapa, M.; Monteiro, A.W.A.; Cecon, E.; Tamura, E.K.; Winter, L.M.F.; Markus, R.P. NF-κB Drives the Synthesis of Melatonin in RAW 264.7 Macrophages by Inducing the Transcription of the Arylalkylamine-N-Acetyltransferase (AA-NAT) Gene. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-J.; Meng, F.-T.; Wu, L.; Zhou, J.-N. Serotoninergic and melatoninergic systems are expressed in mouse embryonic fibroblasts NIH3T3 cells. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34, 236–240. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Reiter, R. Significance of High Levels of Endogenous Melatonin in Mammalian Cerebrospinal Fluid and in the Central Nervous System. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Tan, D.-X.; Lei, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.-T.; Gao, Y.; Kong, J. Melatonin and its potential biological functions in the fruits of sweet cherry. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Antiinflammatory Activity of Melatonin in Central Nervous System. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galano, A.; Alvarez-Idaboy, J.R. Glutathione: Mechanism and kinetics of its non-enzymatic defense action against free radicals. RSC Adv. 2011, 1, 1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.M.; Cardinali, D.P.; Adrien, J.; Agargun, M.Y.; Ahmadi, N.; Ahmed, I.; Arnedt, J.T.; Barbera, J.; Beaulieu-Bonneau, S.; Beitinger, M.E.; et al. Melatonin and mental illness. Sleep Ment. Illn. 2011, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mccarty, M. Minimizing the cancer-promotional activity of cox-2 as a central strategy in cancer prevention. Med. Hypotheses 2012, 78, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, R.; Marani, M.; Blandino, G.; Muti, P.; Strano, S. Melatonin triggers p53Ser phosphorylation and prevents DNA damage accumulation. Oncogene 2011, 31, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mehta, A.; Kaur, G. Potential role of melatonin in prevention and treatment of oral carcinoma. Indian J. Dent. 2014, 5, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardim, B.V.; Ferreira, L.C.; Borin, T.F.; Moschetta, M.G.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Lopes, J.R.; Maschio, L.B.; Leonel, C.; Gonçalves, N.N.; Martins, G.R. Evaluation of the anti-angiogenic action of melatonin in breast cancer. BMC Proc. 2013, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Brzezinski, A.; Brown, G.M. Melatonin and its analogs in insomnia and depression. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Hutchinson, A.J.; Adamah-Biassi, E.B.; Popovska-Gorevski, M.; Dubocovich, M.L. MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors: A Therapeutic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 56, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubocovich, M.L.; Delagrange, P.; Krause, D.N.; Sugden, D.; Cardinali, D.P.; Olcese, J.M. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXV. Nomenclature, classification, and pharmacology of G protein-coupled melatonin receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 343–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bondy, S.C.; Campbell, A. Mechanisms Underlying Tumor Suppressive Properties of Melatonin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suofu, Y.; Li, W.; Jean-Alphonse, F.G.; Jia, J.; Khattar, N.K.; Li, J.; Baranov, S.V.; Leronni, D.; Mihalik, A.C.; He, Y. Dual role of mitochondria in producing melatonin and driving GPCR signaling to block cytochrome c release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7997–E8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pariente, R.; Bejarano, I.; Espino, J.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Pariente, J.A. Participation of MT3 melatonin receptors in the synergistic effect of melatonin on cytotoxic and apoptotic actions evoked by chemotherapeutics. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 985–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, M.; Parvez, S. Role of Melatonin in Traumatic Brain Injury and Spinal Cord Injury. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itoh, N.; Ornitz, D.M. Fibroblast growth factors: From molecular evolution to roles in development, metabolism and disease. J. Biochem. 2010, 149, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, N. Hormone-like (endocrine) Fgfs: Their evolutionary history and roles in development, metabolism, and disease. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 342, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X. The antiapoptotic activity of melatonin in neurodegenerative diseases. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2009, 15, 345–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bars, D.; Thivolle, P.; Vitte, P.; Bojkowski, C.; Chazot, G.; Arendt, J.; Frackowiak, R.; Claustrat, B. PET and plasma pharmacokinetic studies after bolus intravenous administration of [11C]melatonin in humans. Int. J. Radiat. Appl. Instrum. Part B Nucl. Med. Boil. 1991, 18, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekleton, J.A.; Parcell, D.L.; Redman, J.R.; Phipps-Nelson, J.; Ponsford, J.L.; Rajaratnam, S.M. Sleep disturbance and melatonin levels following traumatic brain injury. Neurology 2010, 74, 1732–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiter, R.; Tan, D.-X.; Terron, M.P.; Flores, L.J.; Czarnocki, Z. Melatonin and its metabolites: New findings regarding their production and their radical scavenging actions. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2007, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Reiter, R.J. Pharmacological action of melatonin in shock, inflammation and ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 426, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.; Manchester, L.; Tan, D.-X. Melatonin in walnuts: Influence on levels of melatonin and total antioxidant capacity of blood. Nutrition 2005, 21, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J. Oxidative processes and antioxidative defense mechanisms in the aging brain 1. FASEB J. 1995, 9, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.-J.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Wu, T.-S.; Chen, S.-T.; Chang, G.-L. Melatonin attenuates gray and white matter damage in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; Chun, W.; Kong, P.-J.; Han, J.A.; Cho, B.P.; Kwon, O.-Y.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.-S. Sustained activation of Akt by melatonin contributes to the protection against kainic acid-induced neuronal death in hippocampus. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 40, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paredes, S.D.; Rancan, L.; Kireev, R.; Gonzalez, A.; Louzao, P.; Gonzalez, P.; Rodríguez-Bobada, C.; García, C.; Vara, E.; Tresguerres, J.A. Melatonin Counteracts at a Transcriptional Level the Inflammatory and Apoptotic Response Secondary to Ischemic Brain Injury Induced by Middle Cerebral Artery Blockade in Aging Rats. BioResearch Open Access 2015, 4, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Du, Z.-X.; Zhang, X.-L.; Liu, Q.; Guo, Y.-J.; Li, X.; Hao, A. Protective effect of melatonin on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis in vitro. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 2346–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Dong, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhao, L.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Di, S.; Yue, L.; Liang, G.; et al. Melatonin prevents cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction via a SIRT1-dependent mechanism during ischemic-stroke in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 58, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balduini, W.; Carloni, S.; Perrone, S.; Bertrando, S.; Tataranno, M.; Negro, S.; Proietti, F.; Longini, M.; Buonocore, G. The use of melatonin in hypoxic-ischemic brain damage: An experimental study. J. Matern. Neonatal Med. 2012, 25, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.-Y.; Lee, M.-Y.; Chen, H.-Y.; Kuo, Y.-L.; Lin, S.-C.; Wu, T.-S.; Lee, E.-J. Melatonin attenuates the postischemic increase in blood-brain barrier permeability and decreases hemorrhagic transformation of tissue-plasminogen activator therapy following ischemic stroke in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 40, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalatbary, A.R.; Ahmadvand, H. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of the Epigallocatechin Gallate Following Spinal Cord Trauma in Rat. Iran. Biomed. J. 2011, 15, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.-K.; Liu, J.-T.; Peng, Z.-W.; Fan, H.; Yao, A.-H.; Cheng, P.; Liu, L.; Ju, G.; Kuang, F. Different TLR4 expression and microglia/macrophage activation induced by hemorrhage in the rat spinal cord after compressive injury. J. Neuroinflammation 2013, 10, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guan, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.-X.; Liu, Y.-D.; Liu, Z.-J.; Wu, Q.-C.; Zhang, Y.-J. Melatonin for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeser, V.R.; Loria, R.M. Modulation of traumatic brain injury using progesterone and the role of glial cells on its neuroprotective actions. J. Neuroimmunol. 2011, 237, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, J.; Guillot-Sestier, M.-V.; Town, T. Brain injury, neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2013, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dehghan, F.; Hadad, M.K.; Asadikaram, G.; Najafipour, H.; Shahrokhi, N. Effect of Melatonin on Intracranial Pressure and Brain Edema Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Role of Oxidative Stresses. Arch. Med. Res. 2013, 44, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabadi, S.V.; Maher, T.J. Posttreatment with uridine and melatonin following traumatic brain injury reduces edema in various brain regions in rats. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2010, 1199, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, O.; Acarin, L.; Gonzalez, B.; Castellano, B. NF-kappaB and IkappaBalpha expression following traumatic brain injury to the immature rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 2002, 67, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beni, S.M.; Kohen, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Shohami, E. Melatonin-induced neuroprotection after closed head injury is associated with increased brain antioxidants and attenuated late-phase activation of NF-κB and AP-1. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Readnower, R.D.; Chavko, M.; Adeeb, S.; Conroy, M.D.; Pauly, J.R.; McCarron, R.M.; Sullivan, P.G. Increase in blood-brain barrier permeability, oxidative stress, and activated microglia in a rat model of blast-induced traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 3530–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shlosberg, D.; Benifla, M.; Kaufer, D.; Friedman, A. Blood–brain barrier breakdown as a therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Toklu, H.; Deniz, M.; Yüksel, M.; Keyer-Uysal, M.; Şener, G. The protective effect of melatonin and amlodipine against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative brain injury in rats. Marmara Med. J. 2009, 22, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Hausmann, O.N. Post-traumatic inflammation following spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 2003, 41, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Wang, H.; Qiao, L.; Wang, X. Disruption of Nrf2 enhances the upregulation of nuclear factor-kappaB activity, tumor necrosis factor-, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 after spinal cord injury in mice. Mediat. Inflamm. 2010, 2010, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterniti, I.; Genovese, T.; Crisafulli, C.; Mazzon, E.; Di Paola, R.; Galuppo, M.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Treatment with green tea extract attenuates secondary inflammatory response in an experimental model of spinal cord trauma. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2009, 380, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szczepanik, M. Melatonin and its influence on immune system. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Schiaveto-de-Souza, A.; Da-Silva, C.; Defino, H.L.A.; Del Bel, E.A. Effect of melatonin on the functional recovery from experimental traumatic compression of the spinal cord. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, X.-Q.; Mei, F.; Fan, S.-W.; Gu, C. Protection of erythropoietin on experimental spinal cord injury by reducing the expression of thrombospondin-1 and transforming growth factor-β. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Genovese, T.; Mazzon, E.; Muià, C.; Bramanti, P.; De Sarro, A.; Cuzzocrea, S. Attenuation in the evolution of experimental spinal cord trauma by treatment with melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.; Lee, Y.; Park, S.; Lee, H.J.; Hong, Y.; Kil Lee, S.; Hong, Y. Synergistic effect of melatonin on exercise-induced neuronal reconstruction and functional recovery in a spinal cord injury animal model. J. Pineal. Res. 2010, 48, 270–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, E.; Genovese, T.; Caminiti, R.; Bramanti, P.; Meli, R.; Cuzzocrea, S. Melatonin reduces stress-activated/mitogen-activated protein kinases in spinal cord injury. J. Pineal. Res. 2009, 46, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genovese, T.; Mazzon, E.; Crisafulli, C.; Esposito, E.; Di Paola, R.; Muià, C.; Di Bella, P.; Bramanti, P.; Cuzzocrea, S. Effects of combination of melatonin and dexamethasone on secondary injury in an experimental mice model of spinal cord trauma. J. Pineal. Res. 2007, 43, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asayama, K.; Yamadera, H.; Ito, T.; Suzuki, H.; Kudo, Y.; Endo, S. Double blind study of melatonin effects on the sleep-wake rhythm, cognitive and non-cognitive functions in Alzheimer type dementia. J. Nippon. Med. Sch. 2003, 70, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waldbaum, S.; Patel, M. Mitochondria, oxidative stress, and temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2009, 88, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, S.-K.; Lee, S.-J.; Na, H.-J.; Ha, K.-S.; Han, J.-A.; Lee, H.; Kwon, Y.-G.; Chung, C.-K.; Kim, Y.-M. β-Carotene inhibits inflammatory gene expression in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages by suppressing redox-based NF-κB activation. Exp. Mol. Med. 2005, 37, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloire, G.; Legrand-Poels, S.; Piette, J. NF-κB activation by reactive oxygen species: Fifteen years later. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Circu, M.L.; Aw, T.Y. Reactive oxygen species, cellular redox systems, and apoptosis. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2010, 48, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ates, O.; Cayli, S.R.; Gurses, I.; Turkoz, Y.; Tarim, O.; Cakir, C.O.; Kocak, A. Comparative neuroprotective effect of sodium channel blockers after experimental spinal cord injury. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2007, 14, 658–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-L.; Chang, C.-N.; Chang, S.-J. The effects of pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus on oxidative stress/damage in developing animals. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scannevin, R.H.; Chollate, S.; Jung, M.Y.; Shackett, M.; Patel, H.; Bista, P.; Zeng, W.; Ryan, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Lukashev, M.; et al. Fumarates promote cytoprotection of central nervous system cells against oxidative stress via the nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 341, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ianăş, O.; Olinescu, R.; Bădescu, I. Melatonin involvement in oxidative processes. Endocrinologie 1991, 29, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poeggeler, B.; Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Chen, L.D.; Manchester, L.C. Melatonin, hydroxyl radical-mediated oxidative damage, and aging: A hypothesis. J. Pineal Res. 1993, 14, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.; Manchester, L.; Yan, M.-T.; El-Sawi, M.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Kohen, R.; Allegra, M.; Hardelan, R. Chemical and physical properties and potential mechanisms: Melatonin as a broad spectrum antioxidant and free radical scavenger. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2002, 2, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pieri, C.; Marra, M.; Moroni, F.; Recchioni, R.; Marcheselli, F. Melatonin: A peroxyl radical scavenger more effective than vitamin E. Life Sci. 1994, 55, PL271–PL276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, V. Melatonin oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases. Indian J. Exp. Boil. 2002, 40, 668–679. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, A.M.Y.; Fang, S.F.; Chao, P.L.; Yang, C.H. Melatonin attenuates arsenite-induced apoptosis in rat brain: Involvement of mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum pathways and aggregation of α-synuclein. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.M.Y.; Feng, S.F.; Chao, P.L.; Yang, C.H. Melatonin inhibits arsenite-induced peripheral neurotoxicity. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygur, R.; Aktas, C.; Caglar, V.; Uygur, E.; Erdogan, H.; Ozen, O.A. Protective effects of melatonin against arsenic-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in rat testes. Toxicol. Ind. Heal. 2013, 32, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-L.; Sun, G.-P.; Wei, W.; Wang, Z.-G.; Ge, L.; Fu, W.-Z.; Wang, H. Melatonin and Doxorubicin synergistically induce cell apoptosis in human hepatoma cell lines. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, H.H.; Rao, M.V. Evaluation of in vitro anti-genotoxic potential of melatonin against arsenic and fluoride in human blood cultures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1333–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbulut, K.G.; Gönül, B.; Akbulut, H. The role of melatonin on gastric mucosal cell proliferation and telomerase activity in ageing. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, K.; Swarnakar, S. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-9 and -3 in nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug-induced acute gastric ulcers in mice: Regulation by melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajes Orduna, M.; Pelegrí Gabalda, C.; Vilaplana Hortensi, J.; Pallàs LLiberia, M.; Camins Espuny, A. An evaluation of the neuroprotective effects of melatonin in an in vitro experimental model of age-induced neuronal apoptosis. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M.; Macias, M.; Escames, G.; Reiter, R.J.; Agapito, M.; Ortiz, G.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin-induced increased activity of the respiratory chain complexes I and IV can prevent mitochondrial damage induced by ruthenium red in vivo. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Osuna, C.; Gitto, E. Actions of melatonin in the reduction of oxidative stress. A review. J. Biomed. Sci. 2000, 7, 444–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Martín, M.; Macías, M.; Escames, G.; León, J.; Khaldy, H.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, mitochondria, and cellular bioenergetics. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 30, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Costantino, G.; Mazzon, E.; Micali, A.; De Sarro, A.; Caputi, A.P. Beneficial effects of melatonin in a rat model of splanchnic artery occlusion and reperfusion. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskaloğlu, K.; Sener, T.E.; Kapucu, C.; Ayanoğlu-Dülger, G. Melatonin treatment protects against sepsis-induced functional and biochemical changes in rat ileum and urinary bladder. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Cheung, R.T.F. Pretreatment with melatonin exerts anti-inflammatory effects against ischemia/reperfusion injury in a rat middle cerebral artery occlusion stroke model. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 37, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesudason, E.P.; Baben, B.; Ashok, B.S.; Masilamoni, J.G.; Kirubagaran, R.; Jebaraj, W.C.E.; Jayakumar, R. Anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin on Aβ vaccination in mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 298, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, F.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Doerrier, C.; Dayoub, J.C.; López, L.C.; Venegas, C.; García, J.A.; López, A.; Volt, H.; Sánchez, M.L.; et al. Melatonin blunts the mitochondrial/NLRP3 connection and protects against radiation-induced oral mucositis. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 58, 34–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Gil, B.I.; Moneim, A.E.A.; Ortiz, F.; Shen, Y.-Q.; Soto-Mercado, V.; Mendivil-Perez, M.; Guerra-Librero, A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Molina-Navarro, M.M.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; et al. Melatonin protects rats from radiotherapy-induced small intestine toxicity. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Fan, C.; Hu, W.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Z.; Yan, X.; Deng, C.; Di, S.; Xin, Z.; Wu, G.; et al. Melatonin attenuated early brain injury induced by subarachnoid hemorrhage via regulating NLRP3 inflammasome and apoptosis signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Backhaus, C.; Fadavi, A. Reactions of the NO redox forms NO+, •NO and HNO (protonated NO–) with the melatonin metabolite N1-acetyl-5-methoxykynuramine. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, E.; Pick, E.; Matzkin, H.; Zisapel, N. Melatonin receptors in benign prostate epithelial cells: Evidence for the involvement of cholera and pertussis toxins-sensitive G proteins in their signal transduction pathways. Prostate 1998, 35, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Shrestha, S.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Chen, J.; Yan, F.; Ying, G.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.; Chen, G. Melatonin-mediated mitophagy protects against early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage through inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Permpoonputtana, K.; Govitrapong, P. The anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin on methamphetamine-induced pro-inflammatory mediators in human neuroblastoma dopamine SH-SY5Y cell lines. Neurotox. Res. 2013, 23, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krityakiarana, W.; Zhao, P.M.; Nguyen, K.; Gomez-Pinilla, F.; Kotchabhakdi, N.; De Vellis, J.; Espinosa-Jeffrey, A. Proof-of Concept that an Acute Trophic Factors Intervention After Spinal Cord Injury Provides an Adequate Niche for Neuroprotection, Recruitment of Nestin-Expressing Progenitors and Regeneration. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 431–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterniti, I.; Campolo, M.; Cordaro, M.; Impellizzeri, D.; Siracusa, R.; Crupi, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. PPAR-α modulates the anti-inflammatory effect of melatonin in the secondary events of spinal cord injury. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 54, 5973–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddadi, G.H.; Fardid, R. Oral administration of melatonin modulates the expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) gene in irradiated rat cervical spinal cord. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2015, 20, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lissoni, P.; Meregalli, S.; Nosetto, L.; Barni, S.; Tancini, G.; Fossati, V.; Maestroni, G. Increased survival time in brain glioblastomas by a radioneuroendocrine strategy with radiotherapy plus melatonin compared to radiotherapy alone. Oncology 1996, 53, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Giani, L.; Zerbini, S.; Trabattoni, P.; Rovelli, F. Biotherapy with the pineal immunomodulating hormone melatonin versus melatonin plus aloe vera in untreatable advanced solid neoplasms. Nat. Immun. 1998, 16, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzioni, A.; Luboshitzky, R.; Tiosano, D.; Ben-Harush, M.; Goldsher, D.; Lavie, P. Melatonin replacement corrects sleep disturbances in a child with pineal tumor. Neurology 1996, 46, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappolla, M.A.; Sos, M.; Omar, R.A.; Bick, R.J.; Hickson-Bick, D.L.; Reiter, R.J.; Efthimiopoulos, S.; Robakis, N.K. Melatonin prevents death of neuroblastoma cells exposed to the Alzheimer amyloid peptide. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 1683–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, J.E.; Tai, J.; Hahn, G.; Rothstein, R.R. Melatonin replacement therapy in a child with a pineal tumor. J. Child Neurol. 2001, 16, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Zavarzina, N.Y.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Popovich, I.G.; Zimina, O.A.; Shtylick, A.V.; Arutjunyan, A.V.; Oparina, T.I.; Prokopenko, V.M.; Mikhalski, A.I. Melatonin increases both life span and tumor incidence in female CBA mice. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2001, 56, B311–B323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Granzotto, M.; Rapozzi, V.; Decorti, G.; Giraldi, T. Effects of melatonin on doxorubicin cytotoxicity in sensitive and pleiotropically resistant tumor cells. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 31, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.-H.; Xu, J.-N.; Xu, R.-K.; Pang, S.-F. Inhibitory effects of melatonin on the growth of pituitary prolactin-secreting tumor in rats. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 40, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, V.; Herrera, F.; Carrera-González, M.D.P.; García-Santos, G.; Antolín, I.; Blanco, J.R.; Rodriguez, C. Intracellular Signaling Pathways Involved in the Cell Growth Inhibition of Glioma Cells by Melatonin. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Santos, G.; Antolín, I.; Herrera, F.; Martin, V.; Carrera-González, M.D.P.; Rodriguez, C.; Blanco, J.R. Melatonin induces apoptosis in human neuroblastoma cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P. Biochemotherapy with standard chemotherapies plus the pineal hormone melatonin in the treatment of advanced solid neoplasms. Pathol. Boil. 2007, 55, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Brivio, F.; Fumagalli, L.; Messina, G.; Vigoré, L.; Parolini, D.; Colciago, M.; Rovelli, F. Neuroimmunomodulation in medical oncology: Application of psychoneuroimmunology with subcutaneous low-dose IL-2 and the pineal hormone melatonin in patients with untreatable metastatic solid tumors. Anticancer. Res. 2008, 28, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Casado-Zapico, S.; Rodriguez-Blanco, J.; García-Santos, G.; Martín, V.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.M.; Antolín, I.; Rodriguez, C. Synergistic antitumor effect of melatonin with several chemotherapeutic drugs on human Ewing sarcoma cancer cells: Potentiation of the extrinsic apoptotic pathway. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 48, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.M.; Herrera, F.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Fueyo, J.; Alvarez-Vega, M.A.; Antolín, I.; Rodriguez, C. Melatonin-induced methylation of the ABCG2/BCRP promoter as a novel mechanism to overcome multidrug resistance in brain tumour stem cells. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2005–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blask, D.E.; Brainard, G.C.; Dauchy, R.T.; Hanifin, J.P.; Davidson, L.K.; Krause, J.A.; Sauer, L.A.; Rivera-Bermudez, M.A.; Dubocovich, M.L.; Jasser, S.A. Melatonin-depleted blood from premenopausal women exposed to light at night stimulates growth of human breast cancer xenografts in nude rats. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11174–11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blask, D.E.; Dauchy, R.T.; Dauchy, E.M.; Mao, L.; Hill, S.M.; Greene, M.W.; Belancio, V.P.; Sauer, L.A.; Davidson, L. Light exposure at night disrupts host/cancer circadian regulatory dynamics: Impact on the Warburg effect, lipid signaling and tumor growth prevention. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, V.; Sanchez, A.M.S.; Puente-Moncada, N.; Gomez-Lobo, M.; Álvarez-Vega, M.A.; Antolín, I.; Rodriguez, C. Involvement of autophagy in melatonin-induced cytotoxicity in glioma-initiating cells. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumnongprakhon, P.; Govitrapong, P.; Tocharus, C.; Pinkaew, D.; Tocharus, J. Melatonin Protects Methamphetamine-Induced Neuroinflammation Through NF-κB and Nrf2 Pathways in Glioma Cell Line. Neurochem. Res. 2015, 40, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Pi, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tang, J.; Li, H.; Feng, M.; Deng, P.; et al. Melatonin prevents abnormal mitochondrial dynamics resulting from the neurotoxicity of cadmium by blocking calcium-dependent translocation of Drp1 to the mitochondria. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Zhang, S.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, Z. Melatonin attenuates hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cell aggressive via Smad7/CCL20 in glioma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 93580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- González, A.; González-González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin inhibits angiogenesis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells by downregulation of VEGF. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, J.H.; Shin, E.A.; Kim, S.H. Melatonin disturbs SUMO ylation-mediated crosstalk between c-Myc and nestin via MT 1 activation and promotes the sensitivity of paclitaxel in brain cancer stem cells. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 65, e12496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, G.J.; Kim, S.H.; Kwak, S.; Park, S.H.; Song, J.H.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, K.C. Inhibition of TFEB oligomerization by co-treatment of melatonin with vorinostat promotes the therapeutic sensitivity in glioblastoma and glioma stem cells. J. Pineal Res. 2019, 66, e12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, F.; Shakiba, S.; Mehrzadi, S.; Afshari, K.; Rahimnia, A.H.; Dehpour, A.R. Anticonvulsant effect of melatonin through ATP-sensitive channels in mice. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 34, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, Z.; Wu, L.; Chen, X. The melatonin-MT1 receptor axis modulates tumor growth in PTEN-mutated gliomas. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 496, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, W.A.; Djalilian, H.R.; Nussbaum, E.S.; Cho, K.H. Long-term survival with metastatic cancer to the brain. Med. Oncol. 2000, 17, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilovic, I.; Posner, J.B. Brain metastases: Epidemiology and pathophysiology. J. Neuro Oncol. 2005, 75, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, F.G.; Dolecek, T.A.; McCarthy, B.J.; Villano, J.L. Toward determining the lifetime occurrence of metastatic brain tumors estimated from 2007 United States cancer incidence data. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 1171–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabouret, E.; Chinot, O.; Metellus, P.; Tallet, A.; Viens, P.; Gonçalves, A. Recent trends in epidemiology of brain metastases: An overview. Anticancer. Res. 2012, 32, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar]
- Arvold, N.D.; Lee, E.Q.; Mehta, M.P.; Margolin, K.; Alexander, B.M.; Lin, N.U.; Anders, C.K.; Soffietti, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Updates in the management of brain metastases. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1043–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, M.; Xia, Y.; Bettegowda, C.; Weller, M. Current state of immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 422–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taal, W.; Oosterkamp, H.M.; Walenkamp, A.M.E.; Dubbink, H.J.; Beerepoot, L.V.; Hanse, M.C.J.; Buter, J.; Honkoop, A.H.; Boerman, D.; De Vos, F.Y.F.; et al. Single-agent bevacizumab or lomustine versus a combination of bevacizumab plus lomustine in patients with recurrent glioblastoma (BELOB trial): A randomised controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, J.H.; Hirai, T.; Deng, L.; Chernikova, S.B.; Urata, K.; West, B.; Brown, J.M. Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor inhibition delays recurrence of glioblastoma after radiation by altering myeloid cell recruitment and polarization. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 797–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, D.K.; Yong, Z. Upconverting nanoparticles as nanotransducers for photodynamic therapy in cancer cells. Nanomedince 2008, 3, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricklin, D.; Hajishengallis, G.; Yang, K.; Lambris, J.D. Complement: A key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, S.; Louis, D.N.; Curry, W.T.; Batchelor, T.T.; Dietrich, J. Diagnostic and therapeutic avenues for glioblastoma: No longer a dead end? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Paggio, J.C. Immunotherapy: Cancer immunotherapy and the value of cure. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 268–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussiotis, V.A.; Charest, A. Immunotherapies for malignant glioma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1121–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.; Lim, M. Glioma special issue introduction. Glioma 2019, 2, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Ni, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Lu, X.; Guo, Z.; Yao, S.; Shu, Y.; Xu, R. Thermal analysis in the rat glioma model during directly multipoint injection hyperthermia incorporating magnetic nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 11, 10333–10338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shi, Z.; Liu, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, X. Combined-therapeutic strategies synergistically potentiate glioblastoma multiforme treatment via nanotechnology. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3223–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candolfi, M.; Yagiz, K.; Foulad, D.; Alzadeh, G.E.; Tesarfreund, M.; Muhammad, A.G.; Puntel, M.; Kroeger, K.M.; Liu, C.; Lee, S.; et al. Release of HMGB1 in Response to Proapoptotic Glioma Killing Strategies: Efficacy and Neurotoxicity. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 4401–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozada-Delgado, E.L.; Grafals-Ruiz, N.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E. RNA interference for glioblastoma therapy: Innovation ladder from the bench to clinical trials. Life Sci. 2017, 188, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, F.; Xu, M.; Lu, J.; Mao, L.; Wang, S. The role of exosomal PD-L1 in tumor progression and immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patsoukis, N.; Brown, J.; Petkova, V.; Liu, F.; Li, L.; Boussiotis, V.A. Selective Effects of PD-1 on Akt and Ras Pathways Regulate Molecular Components of the Cell Cycle and Inhibit T Cell Proliferation. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Fan, L.; Wang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, Y.; Bu, L.; Li, X.; et al. Exosomes from Melatonin Treated Hepatocellularcarcinoma Cells Alter the Immunosupression Status through STAT3 Pathway in Macrophages. Int. J. Boil. Sci. 2017, 13, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolchok, J.D.; Sileni, V.C.; Gonzalez, R.; Rutkowski, P.; Grob, J.-J.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Wagstaff, J.; Schadendorf, D.; Ferrucci, P.F.; et al. Overall Survival with Combined Nivolumab and Ipilimumab in Advanced Melanoma. New Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.V.; Atkinson, V.; Lo, S.; Sandhu, S.K.; Guminski, A.D.; Brown, M.P.; Wilmott, J.S.; Edwards, J.; González, M.; Scolyer, R.A.; et al. Combination nivolumab and ipilimumab or nivolumab alone in melanoma brain metastases: A multicentre randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 672–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, E.; Favero, G.; Rodella, L.F.; Rezzani, R. Melatonin’s Antineoplastic Potential Against Glioblastoma. Cells 2020, 9, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, X.; Pang, B.; Gu, G.; Gao, T.; Zhang, R.; Pang, Q.; Liu, Q. Melatonin Inhibits Glioblastoma Stem-like cells through Suppression of EZH2-NOTCH1 Signaling Axis. Int. J. Boil. Sci. 2017, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osanai, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Otsu, M.; Izawa, T.; Sakai, K.; Iwashita, M. Ramelteon, a selective MT1/MT2 receptor agonist, suppresses the proliferation and invasiveness of endometrial cancer cells. Hum. Cell 2017, 30, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, C.-M.; Lin, C.-W.; Yang, J.-S.; Yang, W.-E.; Su, S.-C.; Yang, S.-F. Melatonin inhibits TPA-induced oral cancer cell migration by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation through the histone acetylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21952–21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-W.; Chien, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Su, S.-C.; Hsieh, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-F. Melatonin suppresses TPA-induced metastasis by downregulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression through JNK/SP-1 signaling in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 479–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.-L.; Liu, Y.-F.; Su, C.-W.; Su, S.-C.; Chen, M.-K.; Yang, S.-F.; Lin, C.-W. Functional genetic variant in the Kozak sequence of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX) gene is associated with oral cancer risk. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69384–69396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bouatia-Naji, N.; Bonnefond, A.; Cavalcanti-Proença, C.; Sparsø, T.; Holmkvist, J.; Marchand, M.; Delplanque, J.; Lobbens, S.; Rocheleau, G.; Durand, E.; et al. A variant near MTNR1B is associated with increased fasting plasma glucose levels and type 2 diabetes risk. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39896–39921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Amaral, F.G. Melatonin as a Hormone: New Physiological and Clinical Insights. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 39, 990–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cipolla-Neto, J.; Amaral, F.G.; Afeche, S.C.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin, energy metabolism, and obesity: A review. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ortiz, G.G.; A Benítez-King, G.; A Rosales-Corral, S.; Pacheco-Moisés, F.P.; E Velázquez-Brizuela, I. Cellular and Biochemical Actions of Melatonin which Protect Against Free Radicals: Role in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2008, 6, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seifman, M.; Adamides, A.A.; Nguyen, P.N.; Vallance, A.S.; Cooper, D.J.; Kossmann, T.; Rosenfeld, J.V.; Morganti-Kossmann, C. Endogenous Melatonin Increases in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients after Severe Traumatic Brain Injury and Correlates with Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Disarray. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 28, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bumb, J.; Enning, F.; Mueller, J.; Van Der List, T.; Rohleder, C.; Findeisen, P.; Noelte, I.; Schwarz, E.; Leweke, F. Differential melatonin alterations in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with major depressive disorder and bipolar disorder. Compr. Psychiatry 2016, 68, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angeles-Castellanos, M.; Ramírez-Gonzalez, F.; Ubaldo-Reyes, L.; Rodríguez-Mayoral, O.; Escobar, C. Loss of melatonin daily rhythmicity is asociated with delirium development in hospitalized older adults. Sleep Sci. 2016, 9, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jin, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, K.J.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Yang, Y.; Liu, W. Normobaric hyperoxia combined with minocycline provides greater neuroprotection than either alone in transient focal cerebral ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 240, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Pan, S.; Zhang, H.; Fang, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Xu, K.; Li, Z.; et al. Melatonin protects against blood-brain barrier damage by inhibiting the TLR4/ NF-κB signaling pathway after LPS treatment in neonatal rats. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 31638–31654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; An, R.; Yang, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, H.; Yue, L.; Li, X.; Lin, Y.; Reiter, R.; Qu, Y. Melatonin alleviates brain injury in mice subjected to cecal ligation and puncture via attenuating inflammation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress: The role of SIRT1 signaling. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, L.C.; Escames, G.; Ortiz, F.; Ros, E.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D. Melatonin restores the mitochondrial production of ATP in septic mice. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2006, 27, 623–630. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, F.; García, J.A.; Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Doerrier, C.; López, A.; Venegas, C.; Volt, H.; Sánchez, M.L.; López, L.C.; Escames, G. The beneficial effects of melatonin against heart mitochondrial impairment during sepsis: Inhibition of iNOS and preservation of nNOS. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 56, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, R.; Zhao, L.; Xi, C.; Li, H.; Shen, G.; Liu, H.; Zhang, S.; Sun, L. Melatonin attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 111, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewy, A.J.; Bauer, V.K.; Cutler, N.L.; Sack, R.L. Melatonin treatment of winter depression: A pilot study. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 1998, 77, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewy, A.J.; Emens, J.S.; Lefler, B.J.; Yuhas, K.; Jackman, A. Melatonin Entrains Free-running Blind People According to a Physiological Dose-response Curve. Chrono Int. 2005, 22, 1093–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, G.; Harrold, J.A.; Cutler, D.J. The hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis: Lifting the lid on a black box. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; León, J.; Reiter, R.J. Physiological ischemia/reperfusion phenomena and their relation to endogenous melatonin production. Endocrine 2005, 27, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. On the free radical scavenging activities of melatonin’s metabolites, AFMK and AMK. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 54, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barni, S.; Lissoni, P.; Cazzaniga, M.E.; Ardizzoia, A.; Meregalli, S.; Fossati, V.; Fumagalli, L.; Brivio, F.; Tancini, G. A Randomized Study of Low-Dose Subcutaneous lnterleukin-2 Plus Melatonin versus Supportive Care Alone in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Patients Progressing under 5-Fluorouracil and Folates. Oncology 1995, 52, 243–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Barni, S.; Meregalli, S.; Fossati, V.; Cazzaniga, M.E.; Esposti, D.; Tancini, G. Modulation of cancer endocrine therapy by melatonin: A phase II study of tamoxifen plus melatonin in metastatic breast cancer patients progressing under tamoxifen alone. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 71, 854–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Barni, S.; Mandala, M.; Ardizzoia, A.; Paolorossi, F.; Vaghi, M.; Longarini, R.; Malugani, F.; Tancini, G. Decreased toxicity and increased efficacy of cancer chemotherapy using the pineal hormone melatonin in metastatic solid tumour patients with poor clinical status. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Chilelli, M.; Villa, S.; Cerizza, L.; Tancini, G. Five years survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy and melatonin: A randomized trial. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerea, G.; Vaghi, M.; Ardizzoia, A.; Villa, S.; Bucovec, R.; Mengo, S.; Gardani, G.; Tancini, G.; Lissoni, P. Biomodulation of cancer chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: A randomized study of weekly low-dose irinotecan alone versus irinotecan plus the oncostatic pineal hormone melatonin in metastatic colorectal cancer patients progressing on 5-fluorouracil-containing combinations. Anticancer. Res. 2003, 23, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Seely, D.; Wu, P.; Fritz, H.; Kennedy, D.A.; Tsui, T.; Seely, A.J.; Mills, E. Melatonin as adjuvant cancer care with and without chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zheng, X.; Du, X. Therapeutic strategies of melatonin in cancer patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 7895–7908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.-H.; Kim, J.-H. Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Central Nervous System and Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061567
Gurunathan S, Kang M-H, Kim J-H. Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Central Nervous System and Cancers. Cancers. 2020; 12(6):1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061567
Chicago/Turabian StyleGurunathan, Sangiliyandi, Min-Hee Kang, and Jin-Hoi Kim. 2020. "Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Central Nervous System and Cancers" Cancers 12, no. 6: 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061567
APA StyleGurunathan, S., Kang, M. -H., & Kim, J. -H. (2020). Role and Therapeutic Potential of Melatonin in the Central Nervous System and Cancers. Cancers, 12(6), 1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12061567




