A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies
Abstract
1. MicroRNA Overview
2. Altered MicroRNA Expression in Cancer Cells
2.1. Altered miRNA Profile in Malignancies
2.2. MiRNA Editing as Cancer Therapy
2.3. MiRNA Inhibition Therapies for OncomiRs
2.4. MiRNA Replacement Therapies for Tumor-Suppressor MiRNAs
3. Approaches for MiRNA Therapeutic Delivery
3.1. Local Delivery
3.2. Systemic Delivery
3.3. Viral Delivery
3.4. Non-Viral Delivery
3.5. Nanoparticles
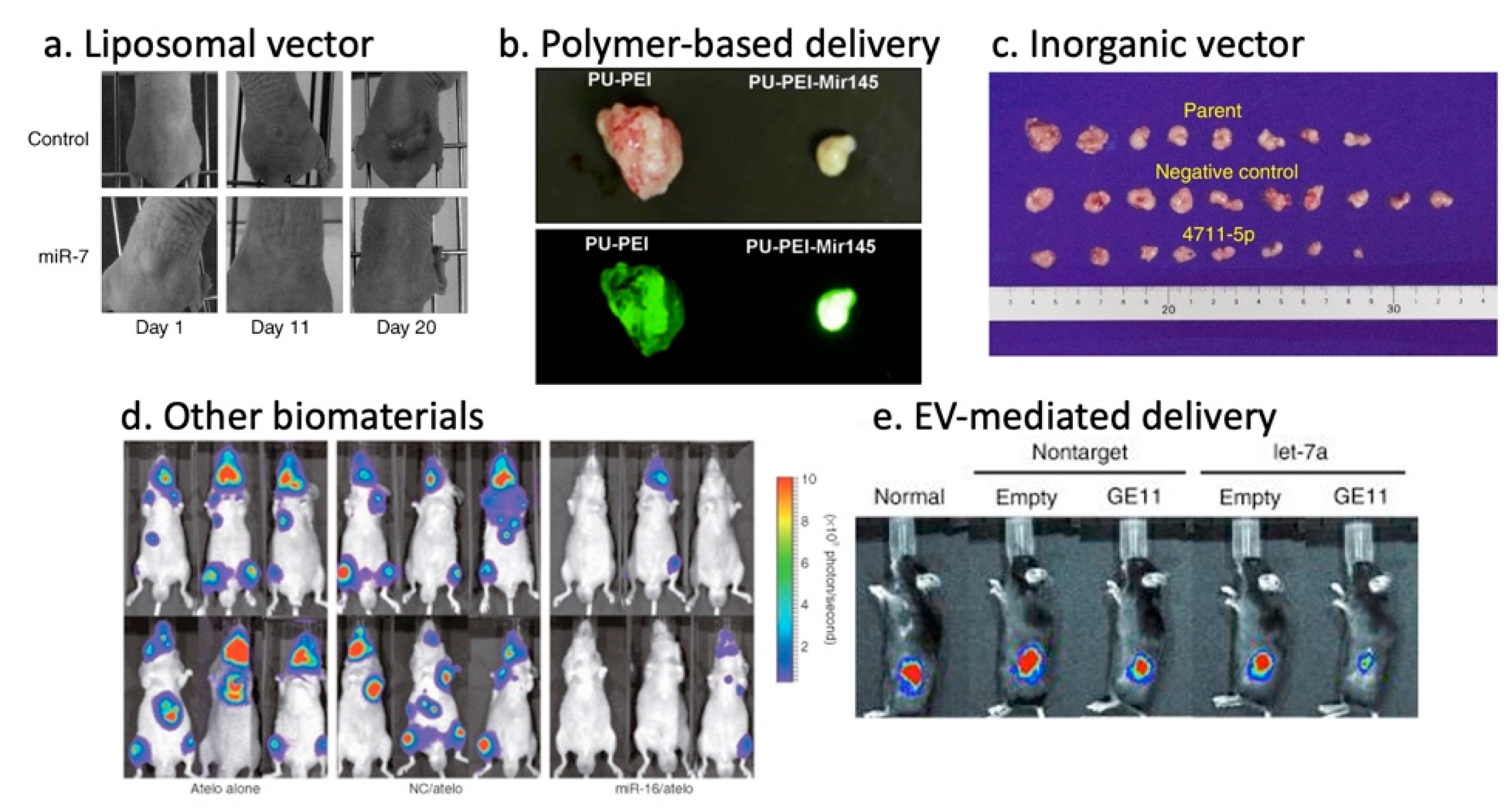
3.5.1. Lipid-Based Vectors
3.5.2. Polymer-Based Vectors
3.5.3. Inorganic Vectors
3.5.4. Other Biomaterials
3.5.5. Exosome/Extracellular Vesicle-Based Vectors
4. MiRNA-Based Therapies in Animal Models and Clinics
4.1. Therapeutic MiRNA Candidates in Preclinical Studies
4.2. Clinical Studies Involving MiRNA-Based Therapy
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Corcoran, M.; Rasool, O.; Ivanova, G.; Ibbotson, R.; Grander, D.; Iyengar, A.; Baranova, A.; Kashuba, V.; Merup, M.; et al. Cloning of two candidate tumor suppressor genes within a 10 kb region on chromosome 13q14, frequently deleted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncogene 1997, 15, 2463–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Dumitru, C.D.; Shimizu, M.; Bichi, R.; Zupo, S.; Noch, E.; Aldler, H.; Rattan, S.; Keating, M.; Rai, K.; et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15524–15529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimmino, A.; Calin, G.A.; Fabbri, M.; Iorio, M.V.; Ferracin, M.; Shimizu, M.; Wojcik, S.E.; Aqeilan, R.I.; Zupo, S.; Dono, M.; et al. miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13944–13949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, M.; Harada, M.; Loven, J.; Castro, J.; Davis, Z.; Oscier, D.; Henriksson, M.; Sangfelt, O.; Grander, D.; Corcoran, M.M. DLEU2, frequently deleted in malignancy, functions as a critical host gene of the cell cycle inhibitory microRNAs miR-15a and miR-16-1. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 2941–2952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Hagedorn, C.H.; Cullen, B.R. Human microRNAs are processed from capped, polyadenylated transcripts that can also function as mRNAs. RNA 2004, 10, 1957–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Radmark, O.; Kim, S.; et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutvagner, G.; McLachlan, J.; Pasquinelli, A.E.; Balint, E.; Tuschl, T.; Zamore, P.D. A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science 2001, 293, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cifuentes, D.; Xue, H.; Taylor, D.W.; Patnode, H.; Mishima, Y.; Cheloufi, S.; Ma, E.; Mane, S.; Hannon, G.J.; Lawson, N.D.; et al. A novel miRNA processing pathway independent of Dicer requires Argonaute2 catalytic activity. Science 2010, 328, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, M.; Kim, V.N. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treiber, T.; Treiber, N.; Meister, G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, W.M.; Lin, Y.G.; Han, L.Y.; Kamat, A.A.; Spannuth, W.A.; Schmandt, R.; Urbauer, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Cheng, J.F.; Nick, A.M.; et al. Dicer, Drosha, and outcomes in patients with ovarian cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.; Kuo, H.H.; Chen, Y.Y.; Diccianni, M.B.; London, W.B.; Chang, C.H.; Yu, A.L. microRNA signature and expression of Dicer and Drosha can predict prognosis and delineate risk groups in neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7841–7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Osada, H.; Tomida, S.; Tatematsu, Y.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yatabe, Y.; Takamizawa, J.; Miyoshi, S.; Mitsudomi, T.; et al. Reduced expression of Dicer associated with poor prognosis in lung cancer patients. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameres, S.L.; Zamore, P.D. Diversifying microRNA sequence and function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinske, L.C.; Franca, G.S.; Torres, H.A.; Ohara, D.T.; Lopes-Ramos, C.M.; Heyn, J.; Reis, L.F.; Ohno-Machado, L.; Kreth, S.; Galante, P.A. miRIAD-integrating microRNA inter- and intragenic data. Database (Oxf.) 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiewicz-Krzeminska, I.; Krzeminski, P.; Corchete, L.A.; Quwaider, D.; Rojas, E.A.; Herrero, A.B.; Gutierrez, N.C. Factors Regulating microRNA Expression and Function in Multiple Myeloma. Noncoding RNA 2019, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulyaeva, L.F.; Kushlinskiy, N.E. Regulatory mechanisms of microRNA expression. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bail, S.; Swerdel, M.; Liu, H.; Jiao, X.; Goff, L.A.; Hart, R.P.; Kiledjian, M. Differential regulation of microRNA stability. RNA 2010, 16, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, M.; Pokrovskaja-Tamm, K.; Soderhall, S.; Heyman, M.; Grander, D.; Corcoran, M. Involvement of miR17 pathway in glucocorticoid-induced cell death in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma 2012, 53, 2041–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Gregory, R.I. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteside, T.L. The tumor microenvironment and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5904–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhome, R.; Goh, R.W.; Bullock, M.D.; Pillar, N.; Thirdborough, S.M.; Mellone, M.; Mirnezami, R.; Galea, D.; Veselkov, K.; Gu, Q.; et al. Exosomal microRNAs derived from colorectal cancer-associated fibroblasts: Role in driving cancer progression. Aging (Albany NY) 2017, 9, 2666–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donnarumma, E.; Fiore, D.; Nappa, M.; Roscigno, G.; Adamo, A.; Iaboni, M.; Russo, V.; Affinito, A.; Puoti, I.; Quintavalle, C.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts release exosomal microRNAs that dictate an aggressive phenotype in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 19592–19608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, K.E.; Zeleniak, A.E.; Fishel, M.L.; Wu, J.; Littlepage, L.E.; Hill, R. Cancer-associated fibroblast exosomes regulate survival and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1770–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au Yeung, C.L.; Co, N.N.; Tsuruga, T.; Yeung, T.L.; Kwan, S.Y.; Leung, C.S.; Li, Y.; Lu, E.S.; Kwan, K.; Wong, K.K.; et al. Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohlhapp, F.J.; Mitra, A.K.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. MicroRNAs as mediators and communicators between cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5857–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Monroig, P.e.C.; Pasculli, B.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAome genome: A treasure for cancer diagnosis and therapy. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.Y.; Ferrajoli, A.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Calin, G.A. microRNA Therapeutics in Cancer-An Emerging Concept. EBioMedicine 2016, 12, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, H.; Lu, H.; Wang, X.; Jin, H. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in cancer: Opportunities and challenges. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 125094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Shen, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wake, L.; Liu, C.; Deffenbacher, K.; Lachel, C.M.; Wang, C.; Rohr, J.; et al. Global microRNA expression profiling uncovers molecular markers for classification and prognosis in aggressive B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramuta, S.; Lee, L.; Ozata, D.M.; Akçakaya, P.; Georgii-Hemming, P.; Xie, H.; Amini, R.M.; Lawrie, C.H.; Enblad, G.; Larsson, C.; et al. Role of microRNAs and microRNA machinery in the pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2013, 3, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Calado, D.P.; Galler, G.; Thai, T.H.; Patterson, H.C.; Wang, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Bender, T.P.; Rajewsky, K. MiR-150 controls B cell differentiation by targeting the transcription factor c-Myb. Cell 2007, 131, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, B.; Shen, L.; Dong, Y.; Lu, Q.; Sun, S.; Liu, S.; Ma, S.; Ma, P.X.; Chen, J. MiRNA-29b suppresses tumor growth through simultaneously inhibiting angiogenesis and tumorigenesis by targeting Akt3. Cancer Lett. 2017, 397, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs-microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinahli, N.; Aghapour, M.; Duijf, P.H.G.; Baradaran, B. Treating cancer with microRNA replacement therapy: A literature review. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 233, 5574–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osaki, M.; Takeshita, F.; Sugimoto, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kobayashi, E.; Yamada, T.; Kawai, A.; Inoue, T.; et al. MicroRNA-143 regulates human osteosarcoma metastasis by regulating matrix metalloprotease-13 expression. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Du, Y.; Xu, J.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, W.; Shu, Y.; Liu, P. MiR-145, miR-133a and miR-133b inhibit proliferation, migration, invasion and cell cycle progression via targeting transcription factor Sp1 in gastric cancer. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1168–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, A.G.; Brown, D.; Winkler, M. The promise of microRNA replacement therapy. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 7027–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.A.; Zamore, P.D. MicroRNA therapeutics. Gene Ther. 2011, 18, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.W.; Ferland-McCollough, D.; Jackson, T.J.; Bushell, M. microRNAs in cancer management. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, e249–e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; He, Q.; Liang, J.; Li, W.; Su, Q.; Chen, Z.; Wan, Q.; Zhou, X.; Cao, L.; Sun, J.; et al. miR-31-5p Is a Potential Circulating Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Oral Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, Y.Y.; Chou, C.H.; Yeh, L.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Chang, K.W.; Liu, C.J.; Fan Chiang, C.Y.; Lin, S.C. MicroRNA miR-31 targets SIRT3 to disrupt mitochondrial activity and increase oxidative stress in oral carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2019, 456, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Ji, F.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Y. MicroRNA-371a-3p promotes progression of gastric cancer by targeting TOB1. Cancer Lett. 2019, 443, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckmann, K.P.; Spiekermann, M.; Balks, T.; Flor, I.; Löning, T.; Bullerdiek, J.; Belge, G. MicroRNAs miR-371-3 in serum as diagnostic tools in the management of testicular germ cell tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 1754–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaihara, N.; Caplen, N.; Bowman, E.; Seike, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; Okamoto, A.; Yokota, J.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Unique microRNA molecular profiles in lung cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Cell 2006, 9, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Zou, S.; Yang, F.; Xu, X.; Bu, W.; Jia, J.; Liu, Z. RUNX3-mediated up-regulation of miR-29b suppresses the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells by targeting KDM2A. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Luo, A.; Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting Fra-1. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Xiao, G.G.; Mao, J.; Lu, Y.; Song, B.; Wang, L.; Fan, S.; Fan, P.; Hou, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Dysregulation of the miR-34a-SIRT1 axis inhibits breast cancer stemness. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 10432–10444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, M.S.; Brenner, A.J.; Sachdev, J.; Borad, M.; Kang, Y.K.; Stoudemire, J.; Smith, S.; Bader, A.G.; Kim, S.; Hong, D.S. Phase I study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, administered twice weekly in patients with advanced solid tumors. Invest. New Drugs 2017, 35, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.J.; Ye, H.; Zeng, C.W.; He, B.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.Q. Dysregulation of miR-15a and miR-214 in human pancreatic cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 3, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonci, D.; Coppola, V.; Musumeci, M.; Addario, A.; Giuffrida, R.; Memeo, L.; D’Urso, L.; Pagliuca, A.; Biffoni, M.; Labbaye, C.; et al. The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 1271–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Schütz, S.; Lawrence, M.; Petri, A.; Obad, S.; Lindholm, M.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, H.F.; Berger, U.; et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008, 452, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Marcucci, G.; Croce, C.M. Targeting microRNAs in cancer: Rationale, strategies and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroig, P.e.C.; Chen, L.; Zhang, S.; Calin, G.A. Small molecule compounds targeting miRNAs for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vester, B.; Wengel, J. LNA (locked nucleic acid): High-affinity targeting of complementary RNA and DNA. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 13233–13241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krützfeldt, J.; Rajewsky, N.; Braich, R.; Rajeev, K.G.; Tuschl, T.; Manoharan, M.; Stoffel, M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature 2005, 438, 685–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, L.; Qu, H.; Fan, Y.; Wu, C. Antagonism of miR-21 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Q.; Jing, Y.; Carpenter, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kung, H.F.; Lai, L.; Jiang, B.H. MiR-21 induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1α expression. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, D.Y.; Huang, L. In vivo delivery of miRNAs for cancer therapy: Challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, K.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, A.; Jia, Z.; Wang, G.; Pu, P.; Kang, C.; Han, L. A lentivirus-mediated miR-23b sponge diminishes the malignant phenotype of glioma cells in vitro and in vivo. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 1573–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, M.D.; Lund, A.H. MicroRNA and cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 590–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kota, J.; Chivukula, R.R.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Wentzel, E.A.; Montgomery, C.L.; Hwang, H.W.; Chang, T.C.; Vivekanandan, P.; Torbenson, M.; Clark, K.R.; et al. Therapeutic microRNA delivery suppresses tumorigenesis in a murine liver cancer model. Cell 2009, 137, 1005–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylianopoulos, T.; Jain, R.K. Combining two strategies to improve perfusion and drug delivery in solid tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 18632–18637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleger, A.; Perkhofer, L.; Seufferlein, T. Smarter drugs emerging in pancreatic cancer therapy. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, D.D.; Terreno, E.; Cabella, C.; Chaabane, L.; Lanzardo, S.; Tei, L.; Visigalli, M.; Aime, S. Evidence for in vivo macrophage mediated tumor uptake of paramagnetic/fluorescent liposomes. NMR Biomed. 2009, 22, 1084–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Crawford, M.; Mao, Y.; Lee, R.J.; Davis, I.C.; Elton, T.S.; Lee, L.J.; Nana-Sinkam, S.P. Therapeutic Delivery of MicroRNA-29b by Cationic Lipoplexes for Lung Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, K.; Takigawa, N.; Ito, S.; Kashihara, H.; Ichihara, E.; Yasuda, T.; Shimizu, K.; Tanimoto, M.; Kiura, K. Liposomal delivery of MicroRNA-7-expressing plasmid overcomes epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor-resistance in lung cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1720–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiggins, J.F.; Ruffino, L.; Kelnar, K.; Omotola, M.; Patrawala, L.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G. Development of a lung cancer therapeutic based on the tumor suppressor microRNA-34. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5923–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trang, P.; Wiggins, J.F.; Daige, C.L.; Cho, C.; Omotola, M.; Brown, D.; Weidhaas, J.B.; Bader, A.G.; Slack, F.J. Systemic delivery of tumor suppressor microRNA mimics using a neutral lipid emulsion inhibits lung tumors in mice. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, M.A.; Valdecanas, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhan, Y.; Bhardwaj, V.; Calin, G.A.; Komaki, R.; Giri, D.K.; Quini, C.C.; Wolfe, T.; et al. Therapeutic delivery of miR-200c enhances radiosensitivity in lung cancer. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Wang, K.; Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, Q.; Liang, T.; Tang, G. A redox-sensitive, oligopeptide-guided, self-assembling, and efficiency-enhanced (ROSE) system for functional delivery of microRNA therapeutics for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomaterials 2016, 104, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.P.; Chien, Y.; Chiou, G.Y.; Cherng, J.Y.; Wang, M.L.; Lo, W.L.; Chang, Y.L.; Huang, P.I.; Chen, Y.W.; Shih, Y.H.; et al. Inhibition of cancer stem cell-like properties and reduced chemoradioresistance of glioblastoma using microRNA145 with cationic polyurethane-short branch PEI. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1462–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.F.; Weirauch, U.; Thomas, M.; Grünweller, A.; Hartmann, R.K.; Aigner, A. MicroRNA replacement therapy for miR-145 and miR-33a is efficacious in a model of colon carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 5214–5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, A.; Chitkara, D.; Behrman, S.W.; Mahato, R.I. Efficacy of gemcitabine conjugated and miRNA-205 complexed micelles for treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 7077–7087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Long, L.; Shi, Z.; Liu, C.; Qiu, M.; Sheng, J.; Pu, P.; Yuan, X.; Ren, Y.; Kang, C. Star-branched amphiphilic PLA-b-PDMAEMA copolymers for co-delivery of miR-21 inhibitor and doxorubicin to treat glioma. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 2322–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.E.; Suh, H.W.; Bahal, R.; Josowitz, A.; Zhang, J.; Song, E.; Cui, J.; Noorbakhsh, S.; Jackson, C.; Bu, T.; et al. Nanoparticle-mediated intratumoral inhibition of miR-21 for improved survival in glioblastoma. Biomaterials 2019, 201, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Lovén, J.; Xu, N.; Meisgen, F.; Wei, T.; Brodin, P.; Jaks, V.; Kasper, M.; Shimokawa, T.; Harada, M.; et al. MicroRNA-203 functions as a tumor suppressor in basal cell carcinoma. Oncogenesis 2012, 1, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, Y.; Mizushima, T.; Wu, X.; Okuzaki, D.; Yokoyama, Y.; Inoue, A.; Hata, T.; Hirose, H.; Qian, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. miR-4711-5p regulates cancer stemness and cell cycle progression via KLF5, MDM2 and TFDP1 in colon cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1037–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiraki, M.; Nishimura, J.; Takahashi, H.; Wu, X.; Takahashi, Y.; Miyo, M.; Nishida, N.; Uemura, M.; Hata, T.; Takemasa, I.; et al. Concurrent Targeting of KRAS and AKT by MiR-4689 Is a Novel Treatment Against Mutant KRAS Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Mizushima, T.; Wu, X.; Okuzaki, D.; Kambara, N.; Ishikawa, S.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Hirose, H.; Yokoyama, Y.; et al. A miR-29b Byproduct Sequence Exhibits Potent Tumor-Suppressive Activities via Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling in. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 977–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akao, Y.; Iio, A.; Itoh, T.; Noguchi, S.; Itoh, Y.; Ohtsuki, Y.; Naoe, T. Microvesicle-mediated RNA molecule delivery system using monocytes/macrophages. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakowski, M.; Buller, B.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Rogers, T.; Osobamiro, O.; Shu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chopp, M. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Ríos, A.J.; Molina-Crespo, Á.; Bouzo, B.L.; López-López, R.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; de la Fuente, M. Exosome-mimetic nanoplatforms for targeted cancer drug delivery. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2019, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, S.; Takanashi, M.; Sudo, K.; Ueda, S.; Ishikawa, A.; Matsuyama, N.; Fujita, K.; Mizutani, T.; Ohgi, T.; Ochiya, T.; et al. Systemically injected exosomes targeted to EGFR deliver antitumor microRNA to breast cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tazawa, H.; Tsuchiya, N.; Izumiya, M.; Nakagama, H. Tumor-suppressive miR-34a induces senescence-like growth arrest through modulation of the E2F pathway in human colon cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15472–15477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeshita, F.; Patrawala, L.; Osaki, M.; Takahashi, R.U.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kosaka, N.; Kawamata, M.; Kelnar, K.; Bader, A.G.; Brown, D.; et al. Systemic delivery of synthetic microRNA-16 inhibits the growth of metastatic prostate tumors via downregulation of multiple cell-cycle genes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Z.; Fan, W.; Hao, J.; Wu, X.; Zeng, G.Q.; Zhang, L.J.; Nie, S.F.; Wang, X.D. Efficient delivery of micro RNA to bone-metastatic prostate tumors by using aptamer-conjugated atelocollagen in vitro and in vivo. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 874–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halle, B.; Marcusson, E.G.; Aaberg-Jessen, C.; Jensen, S.S.; Meyer, M.; Schulz, M.K.; Andersen, C.; Kristensen, B.W. Convection-enhanced delivery of an anti-miR is well-tolerated, preserves anti-miR stability and causes efficient target de-repression: A proof of concept. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 126, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trang, P.; Medina, P.P.; Wiggins, J.F.; Ruffino, L.; Kelnar, K.; Omotola, M.; Homer, R.; Brown, D.; Bader, A.G.; Weidhaas, J.B.; et al. Regression of murine lung tumors by the let-7 microRNA. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1580–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.X.; Chang, Y.; Meng, F.Y.; Wang, M.Y.; Xie, Q.H.; Tang, F.; Li, P.Y.; Song, Y.H.; Lin, J.S. MicroRNA-375 targets AEG-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma and suppresses liver cancer cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3357–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureban, S.M.; May, R.; Mondalek, F.G.; Qu, D.; Ponnurangam, S.; Pantazis, P.; Anant, S.; Ramanujam, R.P.; Houchen, C.W. Nanoparticle-based delivery of siDCAMKL-1 increases microRNA-144 and inhibits colorectal cancer tumor growth via a Notch-1 dependent mechanism. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aagaard, L.; Rossi, J.J. RNAi therapeutics: Principles, prospects and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, B.; Ren, W.; Mo, X.; Zhou, C.; He, H.; Jia, H.; Wang, L.; Jacob, S.T.; Lee, R.J.; et al. Enhanced hepatic delivery of siRNA and microRNA using oleic acid based lipid nanoparticle formulations. J. Control. Release 2013, 172, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Lollo, B.; Freier, S.; Esau, C. Improved targeting of miRNA with antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 2294–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmén, J.; Lindow, M.; Silahtaroglu, A.; Bak, M.; Christensen, M.; Lind-Thomsen, A.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, J.B.; Hansen, H.F.; Straarup, E.M.; et al. Antagonism of microRNA-122 in mice by systemically administered LNA-antimiR leads to up-regulation of a large set of predicted target mRNAs in the liver. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenvang, J.; Petri, A.; Lindow, M.; Obad, S.; Kauppinen, S. Inhibition of microRNA function by antimiR oligonucleotides. Silence 2012, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Uhlmann, E.J.; Gabriely, G.; Volfovsky, N.; Wang, Y.; Teng, J.; Karmali, P.; Marcusson, E.; Peter, M.; Mohan, A.; et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting microRNA-10b in established intracranial glioblastoma: First steps toward the clinic. EMBO Mol. Med. 2016, 8, 268–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N. An overview of viral and nonviral delivery systems for microRNA. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2015, 5, 179–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, C.P.; Dwyer, R.M. Nanoparticle-Based Delivery of Tumor Suppressor microRNA for Cancer Therapy. Cells 2020, 9, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Carrillo, E.; Liu, Y.P.; Berkhout, B. Improving miRNA Delivery by Optimizing miRNA Expression Cassettes in Diverse Virus Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2017, 28, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasar, S.; Salerno, E.; Yuan, Y.; Underbayev, C.; Vollenweider, D.; Laurindo, M.F.; Fernandes, H.; Bonci, D.; Addario, A.; Mazzella, F.; et al. Systemic in vivo lentiviral delivery of miR-15a/16 reduces malignancy in the NZB de novo mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Genes Immun. 2012, 13, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, L.; Chen, Q.; Song, Y.; Xu, S.; Ma, F.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Cao, X.; et al. MicroRNA-494 is required for the accumulation and functions of tumor-expanded myeloid-derived suppressor cells via targeting of PTEN. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5500–5510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Kanasty, R.L.; Eltoukhy, A.A.; Vegas, A.J.; Dorkin, J.R.; Anderson, D.G. Non-viral vectors for gene-based therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 541–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wei, J.; Yu, C.; Han, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, C.; Liao, W.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Non-viral nanocarriers for intracellular delivery of microRNA therapeutics. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 1209–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Jia, L.; Chu, F.; Zhou, Y.; He, Z.; Guo, M.; Chen, C.; Xu, L. Nanostructured lipid carriers for MicroRNA delivery in tumor gene therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakhshandeh, B.; Soleimani, M.; Hafizi, M.; Ghaemi, N. A comparative study on nonviral genetic modifications in cord blood and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Cytotechnology 2012, 64, 523–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, H.J.; Green, J.J.; Tzeng, S.Y. Cancer-Targeting Nanoparticles for Combinatorial Nucleic Acid Delivery. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1901081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintzer, M.A.; Simanek, E.E. Nonviral vectors for gene delivery. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 259–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.Z.; Langer, R.; Farokhzad, O.C. Nanoparticle delivery of cancer drugs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2012, 63, 185–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecot, C.V.; Calin, G.A.; Coleman, R.L.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. RNA interference in the clinic: Challenges and future directions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, H.; Matsumoto, Y.; Mizuno, K.; Chen, Q.; Murakami, M.; Kimura, M.; Terada, Y.; Kano, M.; Miyazono, K.; Uesaka, M.; et al. Accumulation of sub-100 nm polymeric micelles in poorly permeable tumours depends on size. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torchilin, V.P. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Oudhia, S.; Mager, D.E.; Straubinger, R.M. Application of pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis to the development of liposomal formulations for oncology. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yan, X.; Jacobson, O.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.; Tong, X.; Xia, Y.; Ling, D.; Chen, X. Improved Tumor Uptake by Optimizing Liposome Based RES Blockade Strategy. Theranostics 2017, 7, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, D.S.; Kang, Y.K.; Borad, M.; Sachdev, J.; Ejadi, S.; Lim, H.Y.; Brenner, A.J.; Park, K.; Lee, J.L.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Phase 1 study of MRX34, a liposomal miR-34a mimic, in patients with advanced solid tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2020, -1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, C.A.; Rice, K.G. Engineered nanoscaled polyplex gene delivery systems. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 1277–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, R.; Izzo, L. Dendrimer biocompatibility and toxicity. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2215–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, S.; Sun, W.; Kissel, T. Chitosan-based formulations for delivery of DNA and siRNA. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaban, K.; Salva, E.; Akbuga, J. The effects of chitosan/miR-200c nanoplexes on different stages of cancers in breast cancer cell lines. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 95, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaban, K.; Salva, E.; Akbuga, J. In Vitro Dose Studies on Chitosan Nanoplexes for microRNA Delivery in Breast Cancer Cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2017, 27, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaur, S.; Wen, Y.; Song, J.H.; Parikh, N.U.; Mangala, L.S.; Blessing, A.M.; Ivan, C.; Wu, S.Y.; Varkaris, A.; Shi, Y.; et al. Chitosan nanoparticle-mediated delivery of miRNA-34a decreases prostate tumor growth in the bone and its expression induces non-canonical autophagy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29161–29177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dailey, L.A.; Wittmar, M.; Kissel, T. The role of branched polyesters and their modifications in the development of modern drug delivery vehicles. J. Control. Release 2005, 101, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinsley-Bown, A.M.; Fretwell, R.; Dowsett, A.B.; Davis, S.L.; Farrar, G.H. Formulation of poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microparticles for rapid plasmid DNA delivery. J. Control. Release 2000, 66, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Jing, A.; Wang, J.; Hu, F.; Feng, W.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, B. Cationic microRNA-delivering nanocarriers for efficient treatment of colon carcinoma in xenograft model. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosco, D.; Cilurzo, F.; Maiuolo, J.; Federico, C.; Di Martino, M.T.; Cristiano, M.C.; Tassone, P.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. Delivery of miR-34a by chitosan/PLGA nanoplexes for the anticancer treatment of multiple myeloma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Nguyen, L.H.; Miller, J.B.; Yan, Y.; Kos, P.; Xiong, H.; Li, L.; Hao, J.; Minnig, J.T.; Zhu, H.; et al. Modular degradable dendrimers enable small RNAs to extend survival in an aggressive liver cancer model. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatsberg, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ofek, P.; Malhotra, S.; Krivitsky, A.; Scomparin, A.; Tiram, G.; Calderón, M.; Haag, R.; Satchi-Fainaro, R. Functionalized nanogels carrying an anticancer microRNA for glioblastoma therapy. J. Control. Release 2016, 239, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokolova, V.; Epple, M. Inorganic nanoparticles as carriers of nucleic acids into cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2008, 47, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilam, A.; Conde, J.; Weissglas-Volkov, D.; Oliva, N.; Friedman, E.; Artzi, N.; Shomron, N. Local microRNA delivery targets Palladin and prevents metastatic breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.J.; Yoo, J.Y.; Shu, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.G.; Jaime-Ramirez, A.C.; Acunzo, M.; Romano, G.; Cui, R.; et al. RNA Nanoparticle-Based Targeted Therapy for Glioblastoma through Inhibition of Oncogenic miR-21. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 1544–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, A.; Prasetyanto, E.A.; Septiadi, D.; Manicardi, A.; Brognara, E.; Gambari, R.; Corradini, R.; De Cola, L. Combined Delivery of Temozolomide and Anti-miR221 PNA Using Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Induces Apoptosis in Resistant Glioma Cells. Small 2015, 11, 5687–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochiya, T.; Nagahara, S.; Sano, A.; Itoh, H.; Terada, M. Biomaterials for gene delivery: Atelocollagen-mediated controlled release of molecular medicines. Curr. Gene Ther. 2001, 1, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, R.J.; Jensen, S.S.; Lim, J.W. Proteomic profiling of exosomes: Current perspectives. Proteomics 2008, 8, 4083–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EL Andaloussi, S.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X.O.; Wood, M.J. Extracellular vesicles: Biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuhrmann, G.; Herrmann, I.; Stevens, M. Cell-derived vesicles for drug therapy and diagnostics: Opportunities and challenges. Nano Today 2015, 10, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Slack, F.J. MicroRNA therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hessvik, N.P.; Llorente, A. Current knowledge on exosome biogenesis and release. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, P.D.; Raposo, G. Exosomes and extracellular vesicles: The path forward. Essays Biochem. 2018, 62, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell Vesicles 2018, 7, 1535750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Würdinger, T.; van Rijn, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Sena-Esteves, M.; Curry, W.T.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumour growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmin, F.; Ladoire, S.; Mignot, G.; Vincent, J.; Bruchard, M.; Remy-Martin, J.; Boireau, W.; Rouleau, A.; Simon, B.; Lanneau, D.; et al. Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, M.; Martin-Jaular, L.; Lavieu, G.; Théry, C. Specificities of secretion and uptake of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for cell-to-cell communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2019, 21, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vickers, K.C.; Palmisano, B.T.; Shoucri, B.M.; Shamburek, R.D.; Remaley, A.T. MicroRNAs are transported in plasma and delivered to recipient cells by high-density lipoproteins. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, X.; Xiang, X.; Grizzle, W.; Sun, D.; Zhang, S.; Axtell, R.C.; Ju, S.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Steinman, L.; et al. Treatment of brain inflammatory diseases by delivering exosome encapsulated anti-inflammatory drugs from the nasal region to the brain. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 1769–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Su, C. Design strategies and application progress of therapeutic exosomes. Theranostics 2019, 9, 1015–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Fliervoet, L.A.L.; van der Meel, R.; Fens, M.H.A.M.; Heijnen, H.F.G.; van Bergen En Henegouwen, P.M.P.; Vader, P.; Schiffelers, R.M. PEGylated and targeted extracellular vesicles display enhanced cell specificity and circulation time. J. Control. Release 2016, 224, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guessous, F.; Alvarado-Velez, M.; Marcinkiewicz, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, J.; Heister, S.; Kefas, B.; Godlewski, J.; Schiff, D.; Purow, B.; et al. Oncogenic effects of miR-10b in glioblastoma stem cells. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 112, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoloso, M.S.; Spizzo, R.; Shimizu, M.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.A. MicroRNAs--the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Reinhardt, F.; Pan, E.; Soutschek, J.; Bhat, B.; Marcusson, E.G.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Bell, G.W.; Weinberg, R.A. Therapeutic silencing of miR-10b inhibits metastasis in a mouse mammary tumor model. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheedy, P.; Medarova, Z. The fundamental role of miR-10b in metastatic cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1674–1688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Callegari, E.; Elamin, B.K.; Giannone, F.; Milazzo, M.; Altavilla, G.; Fornari, F.; Giacomelli, L.; D’Abundo, L.; Ferracin, M.; Bassi, C.; et al. Liver tumorigenicity promoted by microRNA-221 in a mouse transgenic model. Hepatology 2012, 56, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo Cantafio, M.E.; Nielsen, B.S.; Mignogna, C.; Arbitrio, M.; Botta, C.; Frandsen, N.M.; Rolfo, C.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; Di Martino, M.T. Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of a 13-mer LNA-inhibitor-miR-221 in Mice and Non-human Primates. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandi, N.; Zbinden, S.; Gugger, M.; Arnold, M.; Kocher, V.; Hasan, L.; Kappeler, A.; Brunner, T.; Vassella, E. miR-15a and miR-16 are implicated in cell cycle regulation in a Rb-dependent manner and are frequently deleted or down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5553–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Pel, M.E.; Kirschner, M.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Mugridge, N.; Weiss, J.; Williams, M.; Wright, C.; Edelman, J.J.; Vallely, M.P.; et al. Restoring expression of miR-16: A novel approach to therapy for malignant pleural mesothelioma. Ann. Oncol. 2013, 24, 3128–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, G.; Ozpolat, B.; Coleman, R.L.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G. Preclinical and clinical development of siRNA-based therapeutics. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, M.A.; Ivan, C.; Valdecanas, D.; Wang, X.; Peltier, H.J.; Ye, Y.; Araujo, L.; Carbone, D.P.; Shilo, K.; Giri, D.K.; et al. PDL1 Regulation by p53 via miR-34. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Kao, S.C.; Pavlakis, N.; Brahmbhatt, H.; MacDiarmid, J.; Clarke, S.; Boyer, M.; van Zandwijk, N. Clinical development of TargomiRs, a miRNA mimic-based treatment for patients with recurrent thoracic cancer. Epigenomics 2016, 8, 1079–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winata, P.; Williams, M.; McGowan, E.; Nassif, N.; van Zandwijk, N.; Reid, G. The analysis of novel microRNA mimic sequences in cancer cells reveals lack of specificity in stem-loop RT-qPCR-based microRNA detection. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Calin, G.A.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sood, A.K. miRNA Deregulation in Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Delivery Systems | miRNAs | miRNA Type | Drug | Delivery Route | Target Disease | Target Gene | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid-based system | ||||||||
| Cationic liposome | miR-29b | mature-miR | - | Tail-vein | Lung cancer | CDK6, DNMT3B, MCL1 | [72] | |
| Cationic liposome | miR-7 | pre-miR | - | Intratumoral | Lung cancer | IRS-1, RAF-1, EGFR | [73] | |
| Neutral liposome | miR-34a | pre-miR | - | Intravenous | Lung cancer | BCL-2, c-Met | [74] | |
| Neutral liposome | let-7 miR-34a | mimic-miR | - | Intravenous | Lung cancer | KRAS | [75] | |
| Ionizable liposome | miR-200c | plasmid | - | Subcutaneous | Lung cancer | PRDX2, GAPB/Nrf2, SESN1 | [76] | |
| Polymer-based system | ||||||||
| PEI-PEG | miR-34a | dsRNA | - | Tail-vein | Hepatocellular carcinoma | SNAI1 | [77] | |
| Polyurethane-PEI | miR-145 | plasmid | - | Intracranial | Glioblastoma | Oct4, Sox2 | [78] | |
| PEI | miR-145 miR-33a | dsRNA | - | Intraperitoneal Intravenous | Colon carcinoma | c-Myc, ERK5 | [79] | |
| Polymeric micelle | miR-205 | mimic-miR | Gemcitabine | Intratumoral | Pancreatic cancer | ZEB-1, SIP-1, HRAS, LRP-1, CAV-1, E-CAD | [80] | |
| Polymer micelle | anti-miR-21 | dsRNA | Doxorubicin | Intratumoral | Glioma | PTEN | [81] | |
| PACE polymer | anti-miR-21 | dsRNA | Temozolomide | Intracranial | Glioblastoma | PTEN | [82] | |
| PEI | miR-203 | dsRNA | - | Subcutaneous | Basal cell carcinoma | c-JUN | [83] | |
| Inorganic-based system | ||||||||
| Carbonate apatite | miR-4711-5p | mimic-miR | - | Intravenous | Colon cancer | KLF5, TFDP1 | [84] | |
| Carbonate apatite | miR-4689 | mature-miR | - | Intravenous | Metastatic colorectal cancer | KRAS, AKT1 | [85] | |
| Carbonate apatite | miR-29b | mimic-miR | - | Intravenous | KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer | BCL-2, MCL1 | [86] | |
| Extracellular Vesicles-based system | ||||||||
| Exosome | miR-143 | BP-miR | Intravenous | Colon cancer | - | [87] | ||
| Exosome | miR-146b | plasmid | - | Intratumoral | Glioma | - | [88] | |
| Exosome | miR-145 | dsRNA | - | Tail-vein | Lung cancer | CDH2 | [89] | |
| Exosome | miR-122 | plasmid | Sorafenib | Intratumoral Intraperitoneal | Hepatocellular carcinoma | ADAM10, IGF1R, CCNG1 | [90] | |
| Exosome-GE11 peptide | let-7 | mimic-miR | - | Intravenous | Breast Cancer | HMGA2 | [91] | |
| Other Biomaterials | ||||||||
| Atelocollagen | miR-34a | pre-miR | Subcutaneous | Colon cancer | E2F | [92] | ||
| Atelocollagen | miR-16 | pre-miR | Intravenous | Prostate cancer | CDK1, CDK2 | [93] | ||
| Atelocollagen | miR-15, miR-16-1 | miR with 2′-fluoro | - | Prostate cancer | BCL-2, CCND1, WNT3A | [94] | ||
| Delivery Systems | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Viral Vectors | - High gene delivery efficiency | - Highly immunogenic |
| Adenoviral vector | - High gene delivery efficiency - High packaging gene-size capacity - Ability to transfer dividing cell | - Highly immunogenic - Short term transgene expression |
| Adeno-associated viral vector | - High gene delivery efficiency - Long term transgene expression - Organ specificity possible (serotype) - Ability to transfer dividing and non-dividing cells - Low immunogenicity | - Hard production vectors - Low gene-packaging capacity |
| Lentiviral vector | - High gene delivery efficiency - Long term transgene expression - Ability to transfer dividing and non-dividing cells - Low immunogenicity | - Potential genomic integration |
| Lipid-based system | - Ability to functionalize for targeting - Ability to co-deliver gene therapy and chemotherapy - Controllable size - Systemic gene delivery - High packaging gene-size capacity - Non-immunogenic - Transient expression | - Low delivery efficiency in vivo - Nonspecific gene delivery - Cytotoxicity |
| Polymer-based system | - Ability to functionalize for targeting - Ability to co-delivery gene therapy and chemotherapy - Controllable size - Systemic gene delivery - High packaging gene-size capacity - Non-immunogenic - Transient expression | - Low delivery efficiency in vivo - Nonspecific gene delivery - Cytotoxicity |
| Inorganic-based system | - Ability to functionalize for targeting - Controllable size - Systemic gene delivery - High packaging gene-size capacity - Non-immunogenic - Transient expression - Easy to produce | - Low gene delivery efficiency |
| Extracellular Vesicle-based system | - Ability to functionalize for targeting - Ability to co-delivery gene therapy and chemotherapy - Systemic gene delivery - High packaging gene-size capacity - Non-immunogenic - Highly compatibility - Low immune clearance - Organ specificity possible - High stability | - Insufficient studies on EV-based gene therapy - Diverse composition - Low production |
| Company | Name | Therapeutic Agent | Delivery System | Condition or Disease | Clinical Phase, Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRagen Therapeutics | MRG-106 | Anti-miR-155 | LNA-antisense | Cutaneous T-cell Lymphoma (CTCL)/Mycosis Fungoides (MF) | Phase II (NCT03837457), Enrolling by invitation |
| Phase I (NCT03713320), Active, not recruiting | |||||
| miRagen Therapeutics | MRG-106 | Anti-miR-155 | LNA-antisense | CTCL, MF, Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DVBCL), Activated B-cell (ABC) subtype, Adult T-cell Leukemia/Lymphoma (ATLL) | Phase I (NCT02580552), Active, not recruiting |
| Mirna Therapeutics Inc. | MRX-34 | miR-34 mimic | dsRNA liposomal nanoparticle | Melanoma | Phase I (NCT02862145), Withdrawn |
| Mirna Therapeutics Inc. | MRX-34 | miR-34 mimic | dsRNA liposomal nanoparticle | Primary liver cancer, SCLS, Lymphoma, Melanoma, Multiple myeloma, Renal cell carcinoma, NSCLC | Phase I (NCT01829971), Terminated |
| EnGeneIC | MesomiR-1 | miR-16 mimic | EnGeneIC Dream Vector | Malignant pleural mesothelioma, Non-small-cell lung cancer | Phase I (NCT02369198), Completed |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Forterre, A.; Komuro, H.; Aminova, S.; Harada, M. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071852
Forterre A, Komuro H, Aminova S, Harada M. A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers. 2020; 12(7):1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071852
Chicago/Turabian StyleForterre, Alexis, Hiroaki Komuro, Shakhlo Aminova, and Masako Harada. 2020. "A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies" Cancers 12, no. 7: 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071852
APA StyleForterre, A., Komuro, H., Aminova, S., & Harada, M. (2020). A Comprehensive Review of Cancer MicroRNA Therapeutic Delivery Strategies. Cancers, 12(7), 1852. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071852





