Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Cohort
2.2. Treatment Outcomes of Patients Receiving Nivolumab
2.3. Treatment Outcomes Stratified by Child–Pugh Class
2.4. Treatment Outcomes of Child–Pugh B Patients Receiving Nivolumab
2.5. Predictive Factors Associated with Treatment Response
2.6. Safety of Nivolumab
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population
4.2. Outcome Assessment
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AE | adverse event |
| AHR | adjusted hazard ratio |
| AOR | adjusted odds ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| DCR | disease control rate |
| ECOG | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| mRECIST | modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| OS | overall survival |
| ORR | objective response rate |
| PFS | progression-free survival |
| RECIST | Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors |
| TTP | time to progression |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Park, J.W. Epidemiology of liver cancer in South Korea. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2018, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A.; Cervantes, A.; Chau, I.; Daniele, B.; Llovet, J.M.; Meyer, T.; Nault, J.C.; Neumann, U.; Ricke, J.; Sangro, B.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv238–iv255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinter, M.; Peck-Radosavljevic, M. Review article: Systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 48, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Ricci, S.; Mazzaferro, V.; Hilgard, P.; Gane, E.; Blanc, J.F.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Santoro, A.; Raoul, J.L.; Forner, A.; et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Sangro, B.; Yau, T.; Crocenzi, T.S.; Kudo, M.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Trojan, J.; Welling, T.H.R.; et al. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (CheckMate 040): An open-label, non-comparative, phase 1/2 dose escalation and expansion trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Edeline, J.; Cattan, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Palmer, D.; Verslype, C.; Zagonel, V.; Fartoux, L.; Vogel, A.; et al. Pembrolizumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma previously treated with sorafenib (KEYNOTE-224): A non-randomised, open-label phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruix, J.; Qin, S.; Merle, P.; Granito, A.; Huang, Y.H.; Bodoky, G.; Pracht, M.; Yokosuka, O.; Rosmorduc, O.; Breder, V.; et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambhampati, S.; Bauer, K.E.; Bracci, P.M.; Keenan, B.P.; Behr, S.C.; Gordan, J.D.; Kelley, R.K. Nivolumab in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and Child-Pugh class B cirrhosis: Safety and clinical outcomes in a retrospective case series. Cancer 2019, 125, 3234–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiner, B.; Kirstein, M.M.; Hucke, F.; Finkelmeier, F.; Schulze, K.; von Felden, J.; Koch, S.; Schwabl, P.; Hinrichs, J.B.; Waneck, F.; et al. Programmed cell death protein-1 (PD-1)-targeted immunotherapy in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Efficacy and safety data from an international multicentre real-world cohort. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 49, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelmeier, F.; Czauderna, C.; Perkhofer, L.; Ettrich, T.J.; Trojan, J.; Weinmann, A.; Marquardt, J.U.; Vermehren, J.; Waidmann, O. Feasibility and safety of nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Real-life experience from three German centers. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; Lario, M.; Álvarez-Mon, M. Cirrhosis-associated immune dysfunction: Distinctive features and clinical relevance. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1385–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, A.J.; Fullerton, J.N.; Massey, K.A.; Auld, G.; Sewell, G.; James, S.; Newson, J.; Karra, E.; Winstanley, A.; Alazawi, W.; et al. Immunosuppression in acutely decompensated cirrhosis is mediated by prostaglandin E2. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, W.H.; Baik, S.K. Prostaglandin E2 -mediated immunosuppression and the role of albumin as its modulator. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albillos, A.; Hera Ad Ade, L.; Reyes, E.; Monserrat, J.; Muñoz, L.; Nieto, M.; Prieto, A.; Sanz, E.; Alvarez-Mon, M. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha expression by activated monocytes and altered T-cell homeostasis in ascitic alcoholic cirrhosis: Amelioration with norfloxacin. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 624–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, B. Natural killer cells in liver disease. Hepatology 2013, 57, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Ryoo, B.Y.; Merle, P.; Kudo, M.; Bouattour, M.; Lim, H.Y.; Breder, V.; Edeline, J.; Chao, Y.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab As Second-Line Therapy in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in KEYNOTE-240: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yau, T.; Park, J.; Finn, R.; Cheng, A.-L.; Mathurin, P.; Edeline, J.; Kudo, M.; Han, K.-H.; Harding, J.; Merle, P. CheckMate 459: A randomized, multi-center phase III study of nivolumab (NIVO) vs sorafenib (SOR) as first-line (1L) treatment in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC). In Proceedings of the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) Congress, Barcelona, Spain, 27 September–1 October 2019; pp. v874–v875. [Google Scholar]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, M.G.; Slagter, A.E.; Nuttall, C.; Frizziero, M.; Pihlak, R.; Lamarca, A.; Tariq, N.; Valle, J.W.; Hubner, R.A.; Knox, J.J.; et al. Sorafenib as first-line therapy in patients with advanced Child-Pugh B hepatocellular carcinoma-a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 105, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Matilla, A.; Santoro, A.; Melero, I.; Gracian, A.C.; Acosta-Rivera, M.; Choo, S.P.; El-Khoueiry, A.B.; Kuromatsu, R.; El-Rayes, B.F. Checkmate-040: Nivolumab (NIVO) in patients (pts) with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (aHCC) and Child-Pugh B (CPB) status. In Proceedings of the Liver Metting 2018 by Ameircan Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD), San Francisco, CA, USA, 13 November 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, P.C.; Chao, Y.; Chen, M.H.; Lan, K.H.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, I.C.; Chen, S.C.; Hou, M.C.; Huang, Y.H. Predictors of response and survival in immune checkpoint inhibitor-treated Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucman-Rossi, J.; Villanueva, A.; Nault, J.C.; Llovet, J.M. Genetic landscape and biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1226–1239.e1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yau, T.; Hsu, C.; Kim, T.Y.; Choo, S.P.; Kang, Y.K.; Hou, M.M.; Numata, K.; Yeo, W.; Chopra, A.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Nivolumab in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Sorafenib-experienced Asian cohort analysis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrero, J.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Zhu, A.X.; Finn, R.S.; Abecassis, M.M.; Roberts, L.R.; Heimbach, J.K. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the american association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology 2018, 68, 723–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lencioni, R.; Llovet, J.M. Modified RECIST (mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin. Liver Dis. 2010, 30, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Child–Pugh A (n = 132) | Child–Pugh B (n = 71) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | |||
| Age, mean ± SD, y | 56.9 ± 11.2 | 56.0 ± 9.4 | 0.576 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 115 (87.1) | 56 (78.9) | 0.182 |
| Etiology, HBV/HCV/Other, n (%) | 111/4/17 (84.1/3.0 /12.9) | 57/4/10 (80.3/5.6/14.1) | 0.630 |
| ECOG performance status, n (%) | 0.004 | ||
| 0/1/2 | 64/57/11 (48.5/43.2/8.3) | 18/41/12 (25.4/57.7/16.9) | |
| Tumor characteristics | |||
| BCLC stage, n (%) | 0.822 | ||
| Intermediate/Advanced | 6/126 (4.5/95.5) | 2/69 (2.8/97.2) | |
| Portal vein invasion, n (%) | 46 (34.8) | 42 (59.2) | 0.001 |
| Extrahepatic metastasis, n (%) | 120 (90.9) | 64 (90.1) | >0.999 |
| Involved disease sites, n (%) | |||
| Liver | 104 (78.8) | 66 (93.0) | 0.016 |
| Lung | 79 (59.8) | 48 (67.6) | 0.349 |
| Number of involved disease sites, n (%) | 0.959 | ||
| 1–2/≥3 | 80/52 (60.6/69.4) | 42/29 (59.2/40.8) | |
| α-Fetoprotein, median (IQR), ng/mL | 311 (10, 3392) | 2698 (44, 53727) | 0.001 |
| PIVKA-II, median (IQR), mAU/mL | 1439 (150, 9129) | 6846 (771, 57522) | <0.001 |
| Immunotherapy as systemic, n (%) | 0.218 | ||
| First-line | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.4) | |
| Second-line | 89 (67.4) | 56 (78.9) | |
| Third-line or more | 41 (31.1) | 14 (19.7) | |
| Liver function | |||
| Child–Pugh score, n (%) | – | ||
| 5/6 | 67/65 (50.8/40.2) | – | |
| 7/8/9 | – | 41/15/15 (57.7/21.2/21.2) | |
| Platelet count, n (%) ≥150,000/μL <150,000/μL | 65 (40.2) 67 (50.8) | 26 (36.6) 45 (63.4) | 0.115 |
| Ascites, present, n (%) | 6 (4.5) | 48 (67.6) | <0.001 |
| Albumin, median (IQR), g/dL | 3.6 (3.2, 3.9) | 2.9 (2.6, 3.2) | <0.001 |
| >3.5/2.8–3.5/<2.8, n (%) | 81/51/0 (61.4/38.6 /0.0) | 8/33/30 (11.3/46.5/42.3) | |
| Total bilirubin, median (IQR), mg/dL | 0.7 (0.5, 0.9) | 1.3 (0.9, 2.0) | <0.001 |
| <2/2–3 />3, n (%) | 130/2/0 (98.5/1.5/0.0) | 52/12/7 (73.2/16.9/9.9) | |
| ALBI grade, mean ± SD | −2.33 ± 0.37 | −1.54 ± 0.37 | <0.001 |
| 1/2/3, n (%) | 35/97/0 (26.5/73.5/0.0) | 0/49/22 (0.0/69.0/31.0) | |
| Disposition Characteristics | Child–Pugh A (n = 132) | Child–Pugh B (n = 71) |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment duration, months (IQR) | 1.6 (0.9, 5.0) | 0.9 (0.5, 1.9) |
| Treatment duration, cycles, median (range) mean ± SD | 4 (1–57) 8.5 ± 9.9 | 3 (1–34) 4.3 ± 5.3 |
| Continuing treatment, n (%) | 17 (12.9) | 8 (11.3) |
| Discontinued treatment, n (%) | 115 (87.1) | 63 (88.7) |
| Disease progression, n (%) | 103 (78.0) | 46 (64.8) |
| Death, n (%) | 7 (5.3) | 16 (22.5) |
| Adverse events, n (%) | 5 (3.8) | 1 (1.4) |
| Entire Cohort | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor Responses | Child–Pugh A (n = 132) | Child–Pugh B (n = 71) | p Value a |
| Best overall response, n (%) | |||
| Complete response | 1 (0.8) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Partial response | 20 (15.2) | 2 (2.8) | |
| Stable disease | 35 (26.5) | 14 (19.7) | |
| Progressive disease | 69 (52.3) | 40 (56.3) | |
| Not evaluable b | 7 (5.3) | 15 (21.1) | |
| Objective response c, n (%) | 21 (15.9) | 2 (2.8) | 0.010 |
| Disease control rate d, n (%) | 56 (42.4) | 16 (22.5) | 0.008 |
| Entire Cohort | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Median Time, Week (95% CI) | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||
| Child–Pugh A (n = 132) | Child–Pugh B (n = 71) | HR (95% CI)a | p Value | AHR (95% CI) a | p Value | |
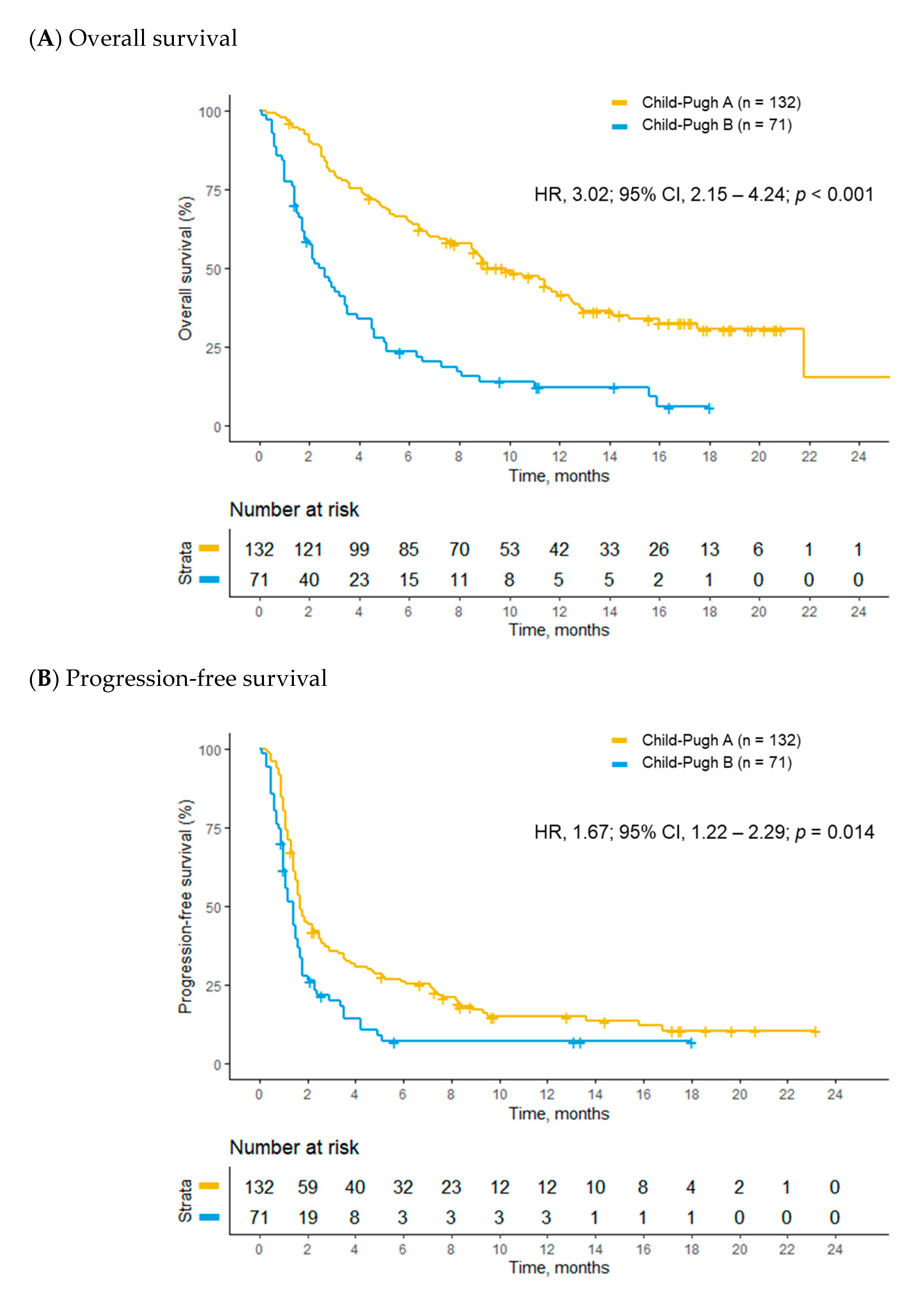
| Overall survival | 42.9 (34.1–54.3) | 11.3 (7.7–15.4) | 3.02 (2.15–4.24) | <0.001 | 2.10 (1.38–3.19) | <0.001 |
| Progression-free survival | 7.4 (7.0–11.0) | 6.0 (4.7–7.6) | 1.67 (1.22–2.29) | 0.014 | 1.17 (0.79–1.72) | 0.430 |
| Time to progression | 7.9 (7.1–11.6) | 6.9 (6.0–10.1) | 1.35 (0.95–1.92) | 0.093 | 1.04 (0.72–1.51) | 0.834 |
| Entire Cohort | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Outcome | Median Time, Week (95% CI) | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | |||
| Child–Pugh B7 (n = 41) | Child–Pugh B8/9 (n = 30) | HR (95% CI) a | p Value | AHR (95% CI) a | p Value | |
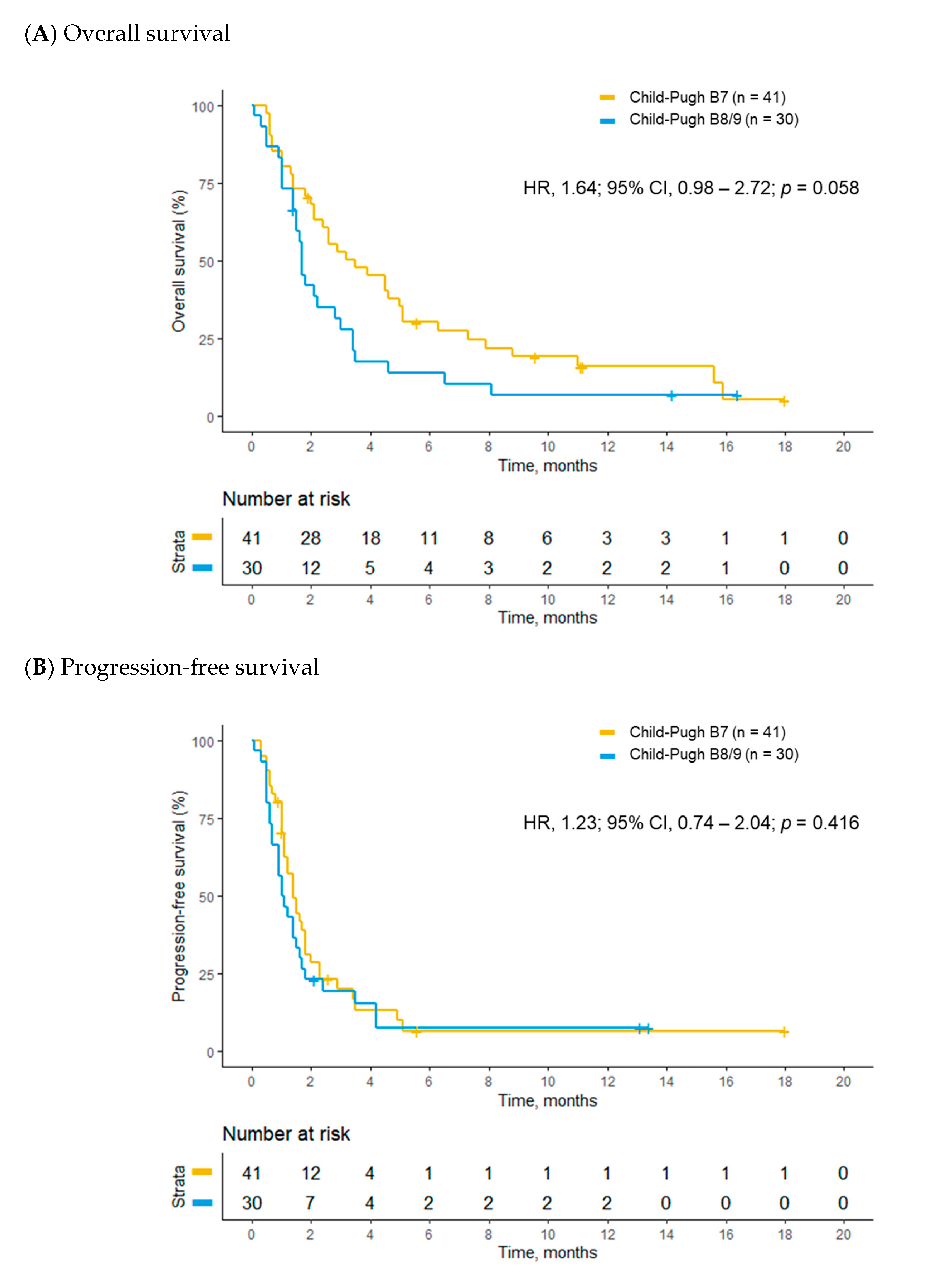
| Overall survival | 15.3 (9.3–22.3) | 7.4 (6.4–14.9) | 1.64 (0.98–2.72) | 0.058 | 1.93 (1.11–3.35) | 0.020 |
| Progression-free survival | 6.3 (5.0–8.0) | 4.8(3.7–7.6) | 1.23 (0.74–2.04) | 0.416 | 1.53 (0.86–2.58) | 0.153 |
| Time to progression | 6.9 (6.0–12.6) | 6.1 (4.6–NA) | 1.04 (0.57–1.88) | 0.895 | 1.30 (0.70–2.40) | 0.408 |
| Characteristics | Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p Value | AOR (95% CI) | p Value | |
| Child–Pugh class A B | 1 (reference) 0.15 (0.03–0.67) | 0.013 * | 1 (reference) 0.21 (0.05–0.93) | 0.040 |
| Age | 1.02 (0.98–1.07) | 0.305 | - | - |
| Sex Female Male | 1 (reference) 2.10 (0.47–9.43) | 0.333 | - | - |
| Ascites, present | 0.23 (0.05–1.04) | 0.056 | - | - |
| α-Fetoprotein, ng/mL <400 ≥400 | 1 (reference) 0.66 (0.27–1.58) | 0.349 | - | - |
| PIVKA-II, mAU/mL <2000 ≥2000 | 1 (reference) 0.37 (0.14–0.93) | 0.035 | 1 (reference) 0.55 (0.21–1.47) | 0.234 |
| Albumin (per 1 g/dL increase) | 1.96 (0.83–4.62) | 0.125 | - | - |
| Total bilirubin (per 1 mg/dL increase) | 0.82 (0.48–1.40) | 0.469 | - | - |
| ALBI grade 1 2 3 | 1 (reference) 0.79 (0.27–2.31) 0.29 (0.03–2.63) | 0.668 0.268 | - | - |
| Etiology HBV Non-HBV etiology | 1 (reference) 2.38 (0.90–6.30) | 0.082 | - | - |
| Portal vein invasion, present | 0.53 (0.21–1.36) | 0.190 | - | - |
| Extrahepatic metastasis, present | 2.44 (0.31–19.22) | 0.396 | - | - |
| Involved disease sites, present | ||||
| Liver | 0.24 (0.09–0.61) | 0.003 | 0.34 (0.13–0.92) | 0.034 |
| Lung | 1.14 (0.46–2.83) | 0.780 | - | - |
| Number of involved disease sites per patient 1–2 ≥3 | 1 (reference) 0.38 (0.14–1.07) | 0.067 | - | - |
| Adverse Events | Child–Pugh A (n = 132) | Child–Pugh B (n = 71) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Any Grade | Grade ≥ 3 | Any Grade | Grade ≥ 3 | |
| Hepatitis | 3 (2.3) | 2 (1.5) | 3 (4.2) | |
| Pneumonitis | 3 (2.3) | 3 (2.3) | ||
| Anorexia | 3 (2.3) | 6 (8.5) | 1 (1.4) | |
| Nausea | 1 (0.8) | 1 (1.4) | ||
| Pain | 1 (0.8) | 3 (4.2) | ||
| Anemia | 3 (2.3) | 3 (4.2) | ||
| Fatigue | 1 (0.8) | 5 (7.0) | ||
| Rash | 2 (1.5) | 1 (1.4) | ||
| Insomnia | 1 (1.4) | |||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, W.-M.; Lee, D.; Shim, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Lim, Y.-S.; Lee, H.C.; Yoo, C.; Park, S.R.; Ryu, M.-H.; Ryoo, B.-Y.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071968
Choi W-M, Lee D, Shim JH, Kim KM, Lim Y-S, Lee HC, Yoo C, Park SR, Ryu M-H, Ryoo B-Y, et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study. Cancers. 2020; 12(7):1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071968
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Won-Mook, Danbi Lee, Ju Hyun Shim, Kang Mo Kim, Young-Suk Lim, Han Chu Lee, Changhoon Yoo, Sook Ryun Park, Min-Hee Ryu, Baek-Yeol Ryoo, and et al. 2020. "Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study" Cancers 12, no. 7: 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071968
APA StyleChoi, W.-M., Lee, D., Shim, J. H., Kim, K. M., Lim, Y.-S., Lee, H. C., Yoo, C., Park, S. R., Ryu, M.-H., Ryoo, B.-Y., & Choi, J. (2020). Effectiveness and Safety of Nivolumab in Child–Pugh B Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Real-World Cohort Study. Cancers, 12(7), 1968. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071968





