Accurate In-Vivo Quantification of CD19 CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) and Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-Cel) Using Digital PCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
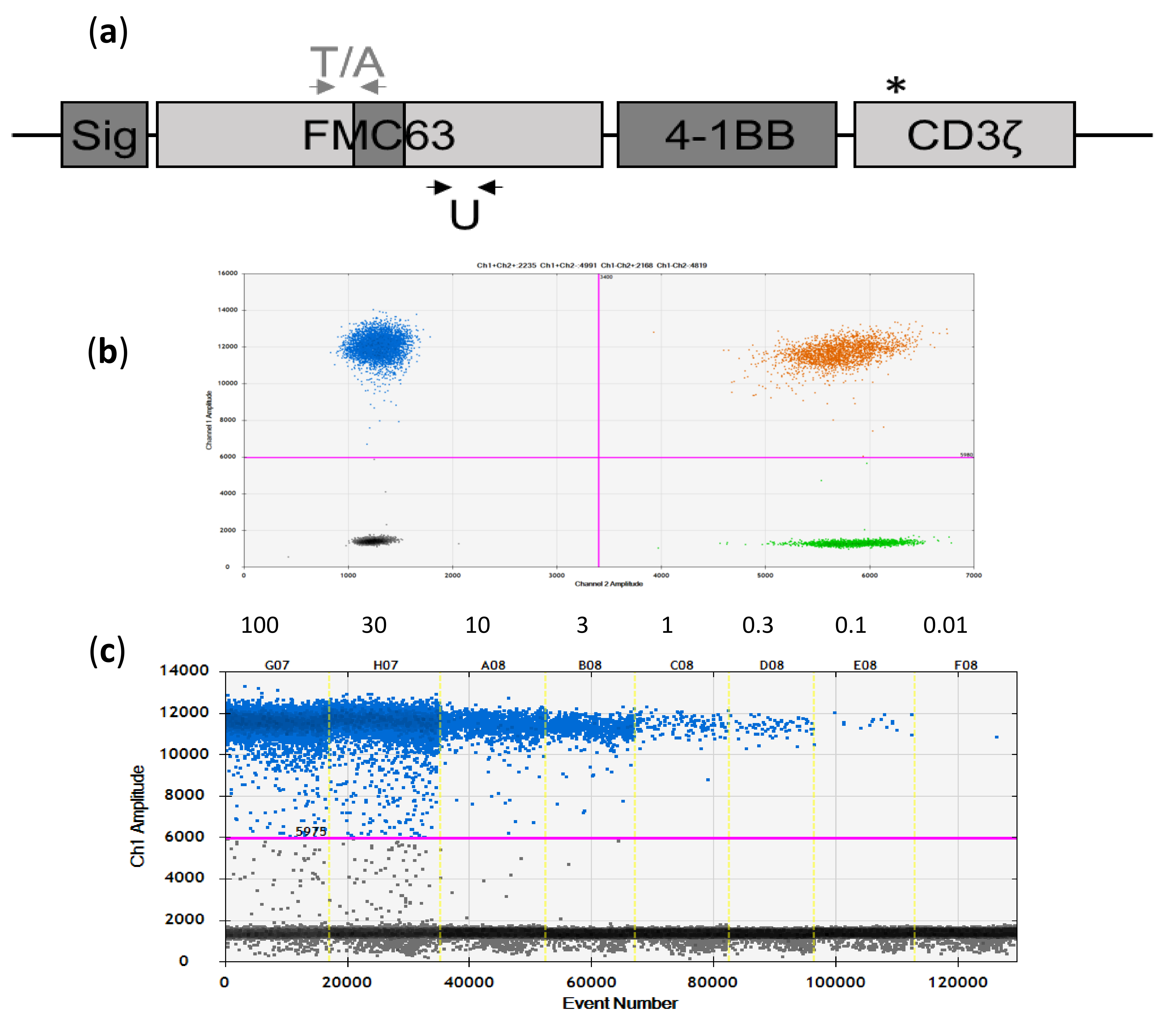
2.1. Development and Initial Testing of Digital-PCR Assays
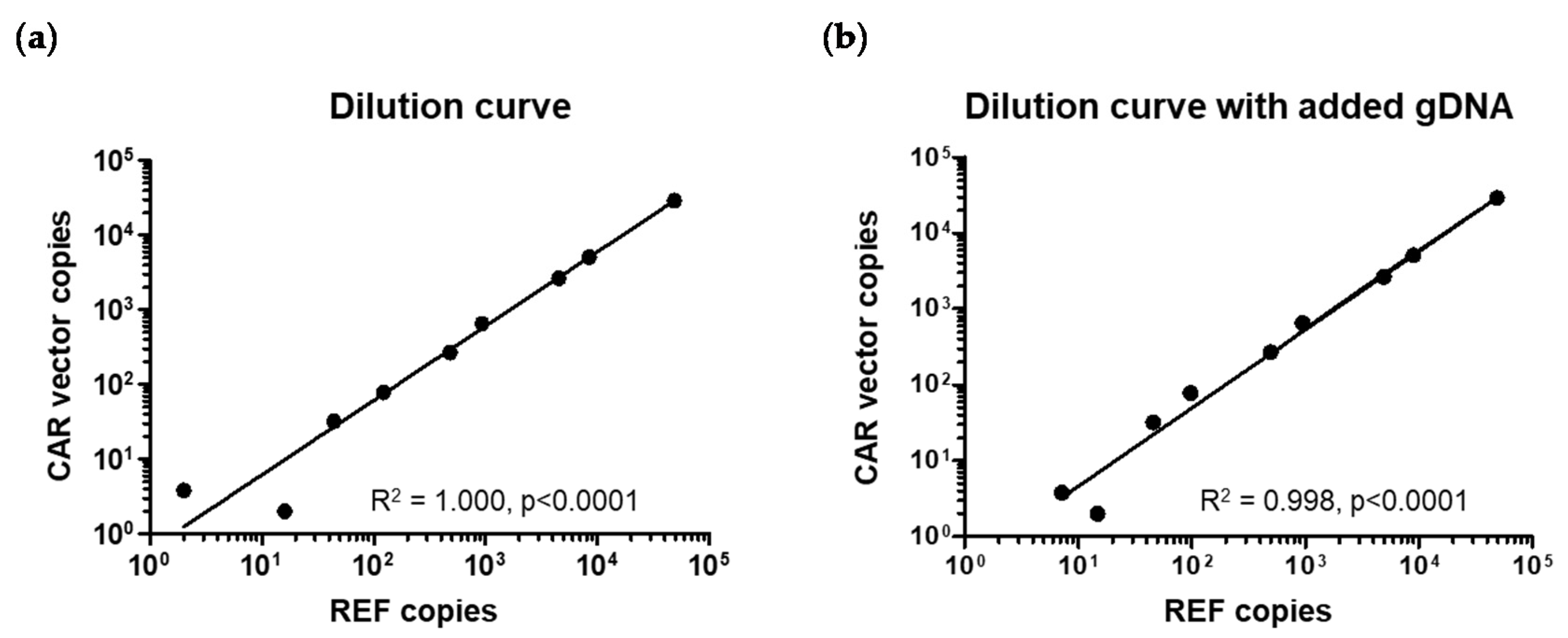
2.2. Assay Specificity, Sensitivity, and Reproducibility
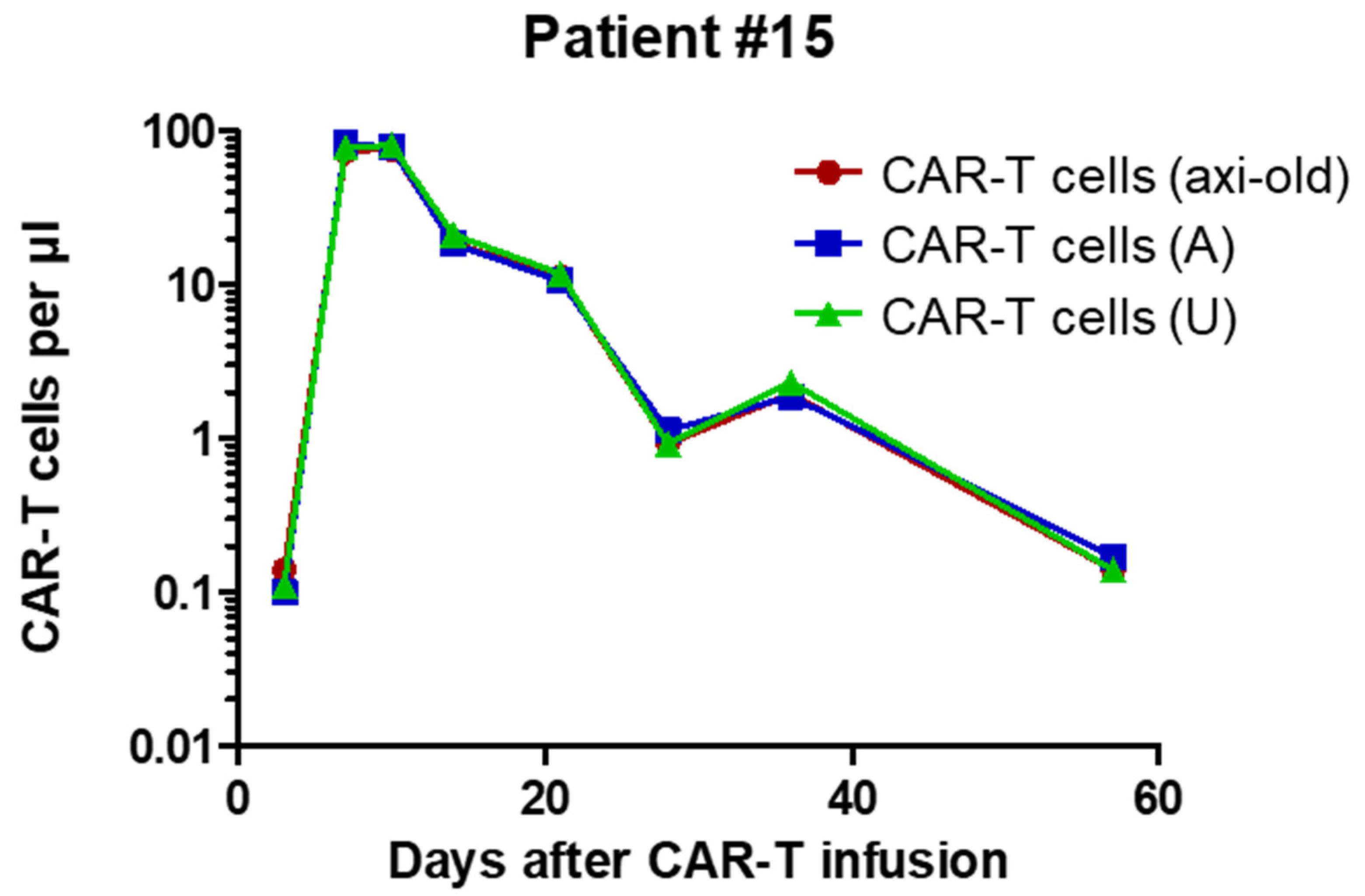
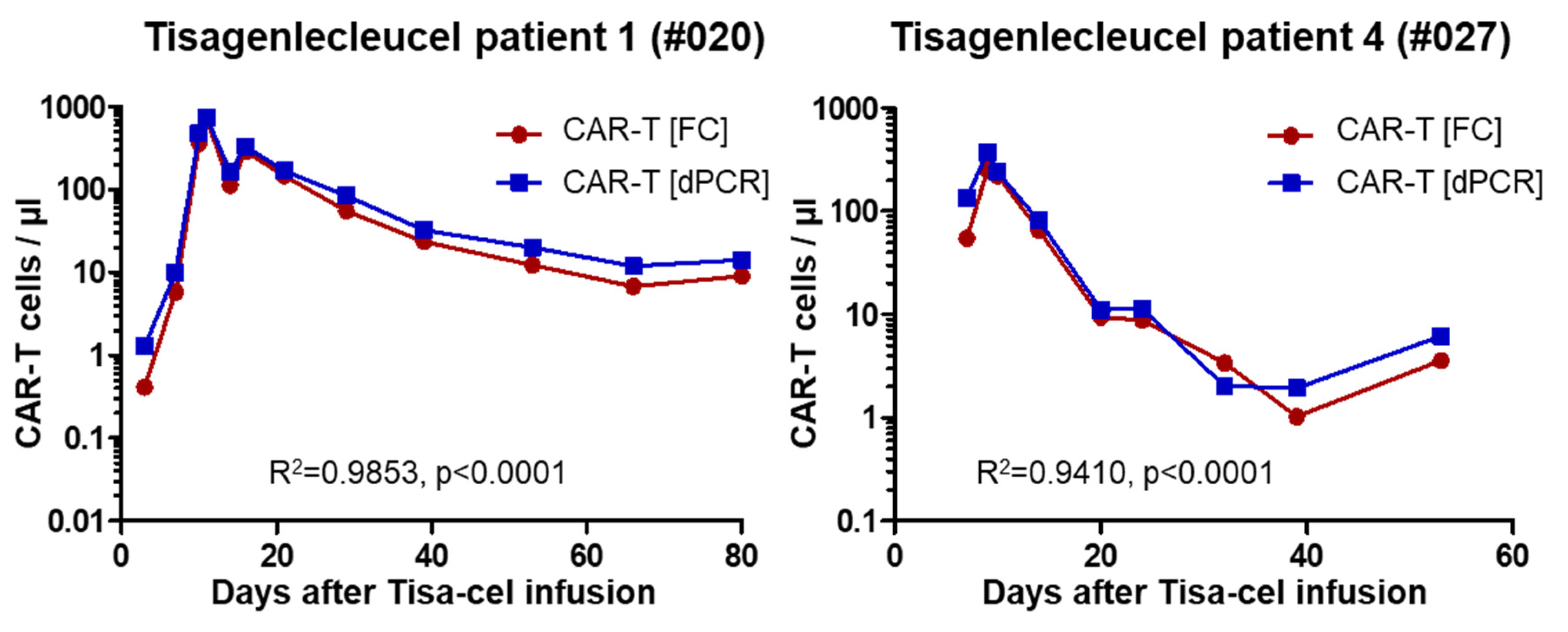
2.3. Analysis of Patient Samples
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of Primers and Probes for Digital PCR
4.2. Genomic DNA and dPCR
4.3. Patients and Patient Material
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. Calculations and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gross, G.; Waks, T.; Eshhar, Z. Expression of immunoglobulin-T-cell receptor chimeric molecules as functional receptors with antibody-type specificity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 10024–10028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshhar, Z.; Waks, T.; Gross, G.; Schindler, D.G. Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and T-cell receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, A.A.; Holzinger, A.; Abken, H. The weal and woe of costimulation in the adoptive therapy of cancer with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-redirected T cells. Curr. Mol. Med. 2013, 13, 1079–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- June, C.H.; Sadelain, M. Chimeric antigen receptor therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, D.L.; Levine, B.L.; Kalos, M.; Bagg, A.; June, C.H. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grupp, S.A.; Kalos, M.; Barrett, D.; Aplenc, R.; Porter, D.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; Teachey, D.T.; Chew, A.; Hauck, B.; Wright, J.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-term safety and activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel in refractory large B cell lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A single-arm, multicentre, phase 1-2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, M.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, P.J.; Neoh, S.H.; Brisco, M.J.; Hughes, E.; Condon, J.; Morley, A.A. Quantitation of targets for PCR by use of limiting dilution. Biotechniques 1992, 13, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W. Digital PCR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9236–9241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccaro, N.; Tota, G.; Anelli, L.; Zagaria, A.; Specchia, G.; Albano, F. Digital PCR: A Reliable Tool for Analyzing and Monitoring Hematologic Malignancies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehse, B.; Badbaran, A.; Berger, C.; Sonntag, T.; Riecken, K.; Geffken, M.; Kröger, N.; Ayuk, F.A. Digital PCR Assays for Precise Quantification of CD19-CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 16, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zola, H.; MacArdle, P.J.; Bradford, T.; Weedon, H.; Yasu, H.; Kurosawa, Y. Preparation and characterization of a chimeric CD19 monoclonal antibody. Immunol. Cell Biol. 1991, 69, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommermeyer, D.; Hill, T.; Shamah, S.M.; Salter, A.I.; Chen, Y.; Mohler, K.M.; Riddell, S.R. Fully human CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptors for T-cell therapy. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochenderfer, J.N.; Feldman, S.A.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, H.; Black, M.A.; Morgan, R.A.; Wilson, W.H.; Rosenberg, S.A. Construction and preclinical evaluation of an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor. J. Immunother. 2009, 32, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzinger, A.; Abken, H. Advances and challenges of car t cells in clinical trials. In Current Immunotherapeutic Strategies in Cancer; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 93–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, A.; Gern, U.; Schmitt, A.; Neuber, B.; Wang, L.; Hückelhoven-Krauss, A.; Michels, B.; Hofmann, S.; Müller-Tidow, C.; Dreger, P.; et al. Optimized assessment of qPCR-Based vector copy numbers as a safety parameter for GMP-Grade CAR T cells and monitoring of frequency in patients. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 17, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehse, B.; Chukhlovin, A.; Kühlcke, K.; Marinetz, O.; Vorwig, O.; Renges, H.; Krüger, W.; Zabelina, T.; Dudina, O.; Finckenstein, F.G.; et al. Real-time quantitative Y chromosome-specific PCR (QYCS-PCR) for monitoring hematopoietic chimerism after sex-mismatched allogeneic stem cell transplantation. J. Hematother. Stem Cell Res. 2001, 10, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehse, B.; Kustikova, O.S.; Bubenheim, M.; Baum, C. Pois(s)on—it’s a question of dose. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Test Sample1 | Axi-Cel Assay | Universal Assay | Mean | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ia | Ib | IIa | IIb | IIIa | IIIb | RPP30 | |||
| CAR-T Cells/µl Blood | |||||||||
| 185 | 0.19 | 0.12 | 0.19 | 0.17 | 0.12 | 0.16 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 0.16 |
| 187 | 0.38 | 0.39 | 0.4 | 0.38 | 0.38 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.34 | 0.38 |
| 196 | 17.82 | 17.9 | 18.1 | 17.7 | 17.15 | 17.83 | 17.77 | 18.11 | 17.80 |
| 201 | 10.72 | 10.05 | 9.4 | 9.03 | 10.11 | 8.82 | 8.6 | 9.49 | 9.53 |
| 204 | 0.66 | 0.76 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.51 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.69 |
| 2912 | 0.04 | 0 | 0.1 | 0 | 0.13 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.16 | 0.07 |
| Patient | #020 | #021 | #024 | #027 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (at CAR infusion) | 10 | 59 | 51 | 7 |
| Sex | male | female | male | female |
| Diagnosis | BPC-ALL 1st relapse | DLBCL 1st relapse (early, refractory) | DLBCL 1st relapse (early) | BPC-ALL 2nd relapse |
| Calculated mVCN | 1.103 | 1.095 | 1.0 | 1.093 |
| CAR-T peak/µl (day) | 743 (11) | 25 (6)1 | 21 (8) | 375 (9) |
| Sample ID | Type of Material | CAR-T Cells per µl | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Axi-Cel Assay | Universal Assay | ||
| 116 | Liquor cerebrospinalis (patient #010) | 27.66 | 27.06 |
| 1171 | Liquor cerebrospinalis (patient #010) | n.d. | 27.31 |
| 133 | Liquor cerebrospinalis (patient #013) | 2.24 | 2.24 |
| 193 | Liquor cerebrospinalis (patient #016) | 32.76 | 33.09 |
| 139 | Ascites (patient #006) | 1.32 | 1.34 |
| CAR-T Cells per Million Cells | |||
| 26 | Bone marrow (patient #005) | 26,432 | 27,467 |
| 97 | Bone marrow (patient #005) | 27,780 | 28,670 |
| 324 | Bone marrow (patient #023) | 7991 | 8506 |
| 234 | Tumor (lymph-node) biopsy (patient#011) | 62,948 | 62,204 |
| 367 | Tumor (lymph-node) biopsy (patient#014) | 19,647 | 19,656 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Badbaran, A.; Berger, C.; Riecken, K.; Kruchen, A.; Geffken, M.; Müller, I.; Kröger, N.; Ayuk, F.A.; Fehse, B. Accurate In-Vivo Quantification of CD19 CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) and Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-Cel) Using Digital PCR. Cancers 2020, 12, 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071970
Badbaran A, Berger C, Riecken K, Kruchen A, Geffken M, Müller I, Kröger N, Ayuk FA, Fehse B. Accurate In-Vivo Quantification of CD19 CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) and Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-Cel) Using Digital PCR. Cancers. 2020; 12(7):1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071970
Chicago/Turabian StyleBadbaran, Anita, Carolina Berger, Kristoffer Riecken, Anne Kruchen, Maria Geffken, Ingo Müller, Nicolaus Kröger, Francis A. Ayuk, and Boris Fehse. 2020. "Accurate In-Vivo Quantification of CD19 CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) and Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-Cel) Using Digital PCR" Cancers 12, no. 7: 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071970
APA StyleBadbaran, A., Berger, C., Riecken, K., Kruchen, A., Geffken, M., Müller, I., Kröger, N., Ayuk, F. A., & Fehse, B. (2020). Accurate In-Vivo Quantification of CD19 CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) and Tisagenlecleucel (Tisa-Cel) Using Digital PCR. Cancers, 12(7), 1970. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071970







