Metastasis of Uveal Melanoma with Monosomy-3 Is Associated with a Less Glycogenetic Gene Expression Profile and the Dysregulation of Glycogen Storage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of the Genes Involved in Glycogen Synthesis or Breakdown with Regard to the Monosomy-3 Status in the TCGA Cohort
2.2. Expression of the Genes Involved in Glycogen Metabolim with Regard to the Prognostic Factors and Clinical Outcome in the TCGA Cohort
2.3. Validation of Gene Expression in an Independent UM Cohort
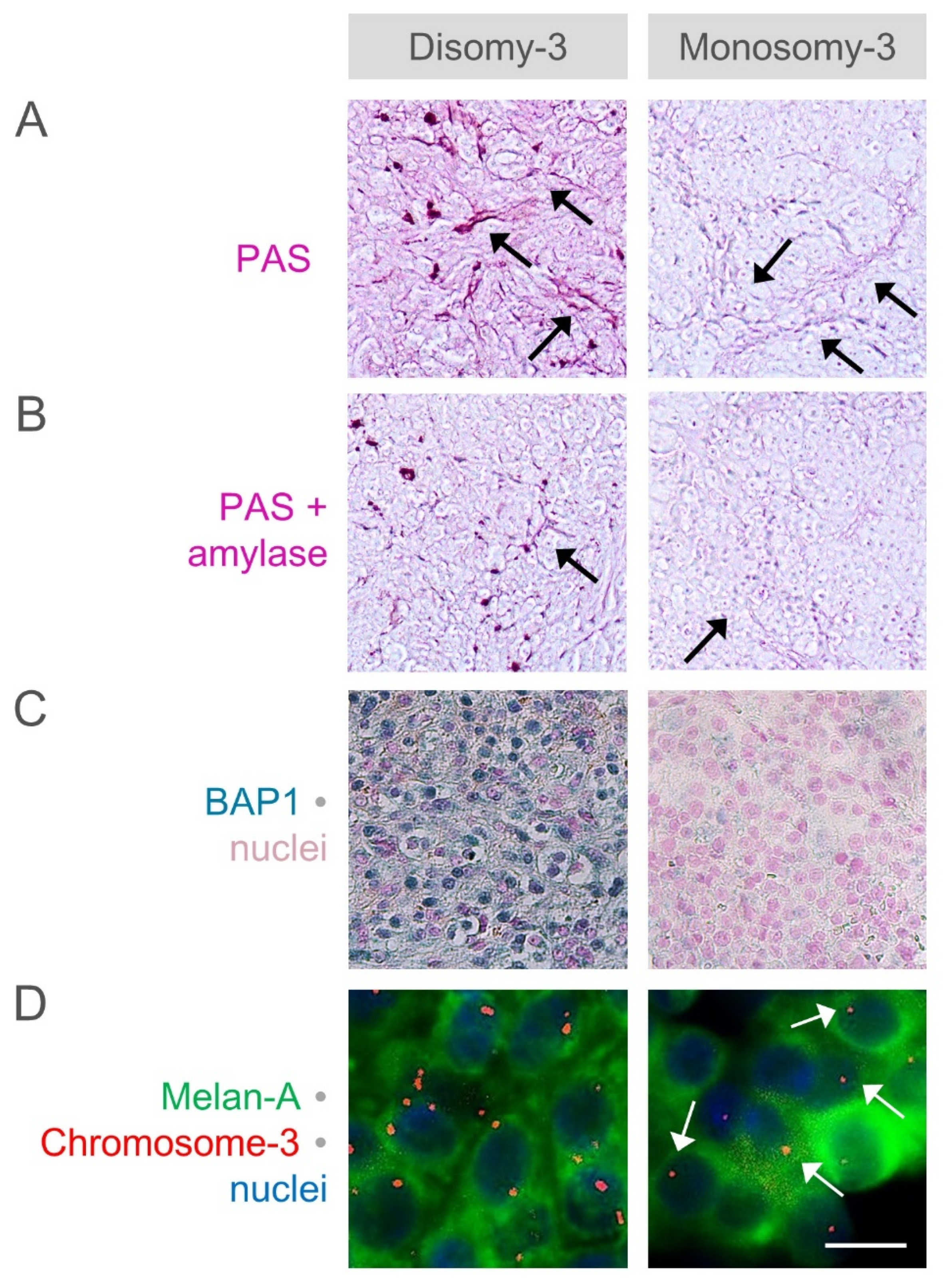
2.4. Analysis of Glycogen Storage in the Primary UM of Our Patients with Regard to the Monosomy-3 Status and Clinical Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Selection
4.2. Analysis of Gene Expression in the UM Cohorts of the TCGA Study and GEO Database
4.3. Differential PAS Staining
4.4. Scoring of PAS Staining Intensity
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Immunomagnetic Enrichment of CMCs
4.7. Immuno-FISH
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lane, A.M.; Kim, I.K.; Gragoudas, E.S. Survival Rates in Patients After Treatment for Metastasis From Uveal Melanoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2018, 136, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rantala, E.S.; Hernberg, M.; Kivelä, T.T. Overall Survival after Treatment for Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Melanoma Res. 2019, 29, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, K.K.; Bollin, K.B.; Patel, S.P. Obstacles to Improving Outcomes in the Treatment of Uveal Melanoma. Cancer 2018, 124, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berus, T.; Halon, A.; Markiewicz, A.; Orlowska-Heitzman, J.; Romanowska-Dixon, B.; Donizy, P. Clinical, Histopathological and Cytogenetic Prognosticators in Uveal Melanoma-A Comprehensive Review. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 6541–6549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coupland, S.E.; Sidiki, S.; Clark, B.J.; McClaren, K.; Kyle, P.; Lee, W.R. Metastatic Choroidal Melanoma to the Contralateral Orbit 40 Years after Enucleation. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill. 1960 1996, 114, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholes, A.G.M.; Damato, B.E.; Nunn, J.; Hiscott, P.; Grierson, I.; Field, J.K. Monosomy 3 in Uveal Melanoma: Correlation with Clinical and Histologic Predictors of Survival. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 1008–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaliki, S.; Shields, C.L.; Shields, J.A. Uveal Melanoma: Estimating Prognosis. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 63, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura, A.; Merz, H.; Reinsberg, M.; Lüke, M.; Jager, M.J.; Grisanti, S.; Lüke, J. Analysis of Monosomy-3 in Immunomagnetically Isolated Circulating Melanoma Cells in Uveal Melanoma Patients. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2016, 29, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.H.; Cebulla, C.M.; Verma, V.; Christopher, B.N.; Carson, W.E.; Olencki, T.; Davidorf, F.H. Monosomy 3 Status of Uveal Melanoma Metastases Is Associated with Rapidly Progressive Tumors and Short Survival. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 100, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krantz, B.A.; Dave, N.; Komatsubara, K.M.; Marr, B.P.; Carvajal, R.D. Uveal Melanoma: Epidemiology, Etiology, and Treatment of Primary Disease. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 2017, 11, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.D.; Topham, A. Incidence of Uveal Melanoma in the United States: 1973–1997. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 956–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zloto, O.; Pe’er, J.; Frenkel, S. Gender Differences in Clinical Presentation and Prognosis of Uveal Melanoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogrusöz, M.; Brouwer, N.J.; de Geus, S.J.R.; Ly, L.V.; Böhringer, S.; van Duinen, S.G.; Kroes, W.G.M.; van der Velden, P.A.; Haasnoot, G.W.; Marinkovic, M.; et al. Prognostic Factors Five Years After Enucleation for Uveal Melanoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papastefanou, V.P.; Islam, S.; Szyszko, T.; Grantham, M.; Sagoo, M.S.; Cohen, V.M.L. Metabolic Activity of Primary Uveal Melanoma on PET/CT Scan and Its Relationship with Monosomy 3 and Other Prognostic Factors. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 98, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zois, C.E.; Harris, A.L. Glycogen Metabolism Has a Key Role in the Cancer Microenvironment and Provides New Targets for Cancer Therapy. J. Mol. Med. Berl. Ger. 2016, 94, 137–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; González-Lucán, M.; Donapetry-García, C.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Ameneiros-Rodríguez, E. Glycogen Metabolism in Humans. BBA Clin. 2016, 5, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, M.; Zweibaum, A.; Fogh, J. Presence of Glycogen and Growth-Related Variations in 58 Cultured Human Tumor Cell Lines of Various Tissue Origins. Cancer Res. 1981, 41, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelletier, J.; Bellot, G.; Gounon, P.; Lacas-Gervais, S.; Pouysségur, J.; Mazure, N.M. Glycogen Synthesis Is Induced in Hypoxia by the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor and Promotes Cancer Cell Survival. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favaro, E.; Bensaad, K.; Chong, M.G.; Tennant, D.A.; Ferguson, D.J.P.; Snell, C.; Steers, G.; Turley, H.; Li, J.-L.; Günther, U.L.; et al. Glucose Utilization via Glycogen Phosphorylase Sustains Proliferation and Prevents Premature Senescence in Cancer Cells. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, J.; Skurat, A.V.; Roach, P.J. Glycogenin-2, a Novel Self-Glucosylating Protein Involved in Liver Glycogen Biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 27589–27597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krag, T.O.; Ruiz-Ruiz, C.; Vissing, J. Glycogen Synthesis in Glycogenin 1-Deficient Patients: A Role for Glycogenin 2 in Muscle. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baughman, J.M.; Rose, C.M.; Kolumam, G.; Webster, J.D.; Wilkerson, E.M.; Merrill, A.E.; Rhoads, T.W.; Noubade, R.; Katavolos, P.; Lesch, J.; et al. NeuCode Proteomics Reveals Bap1 Regulation of Metabolism. Cell Rep. 2016, 16, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halse, R.; Bonavaud, S.M.; Armstrong, J.L.; McCormack, J.G.; Yeaman, S.J. Control of Glycogen Synthesis by Glucose, Glycogen, and Insulin in Cultured Human Muscle Cells. Diabetes 2001, 50, 720–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testoni, G.; Duran, J.; García-Rocha, M.; Vilaplana, F.; Serrano, A.L.; Sebastián, D.; López-Soldado, I.; Sullivan, M.A.; Slebe, F.; Vilaseca, M.; et al. Lack of Glycogenin Causes Glycogen Accumulation and Muscle Function Impairment. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 256–266.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaupel, P.; Schmidberger, H.; Mayer, A. The Warburg Effect: Essential Part of Metabolic Reprogramming and Central Contributor to Cancer Progression. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebelo, M.T.; Joubert, A.M.; Visagie, M.H. Warburg Effect and Its Role in Tumourigenesis. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2019, 42, 833–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, Z.; Çeşmeli, S.; Biray Avcı, Ç. Crucial Players in Glycolysis: Cancer Progress. Gene 2020, 726, 144158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folberg, R.; Hendrix, M.J.; Maniotis, A.J. Vasculogenic Mimicry and Tumor Angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 361–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.G.; Shih, J.; Yau, C.; Gibb, E.A.; Oba, J.; Mungall, K.L.; Hess, J.M.; Uzunangelov, V.; Walter, V.; Danilova, L.; et al. Integrative Analysis Identifies Four Molecular and Clinical Subsets in Uveal Melanoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 204–220.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velho, G.; Petersen, K.F.; Perseghin, G.; Hwang, J.H.; Rothman, D.L.; Pueyo, M.E.; Cline, G.W.; Froguel, P.; Shulman, G.I. Impaired Hepatic Glycogen Synthesis in Glucokinase-Deficient (MODY-2) Subjects. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 1755–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Diaz-Castroverde, S.; Baos, S.; Luque, M.; Di Scala, M.; González-Aseguinolaza, G.; Gómez-Hernández, A.; Beneit, N.; Escribano, O.; Benito, M. Prevalent Role of the Insulin Receptor Isoform A in the Regulation of Hepatic Glycogen Metabolism in Hepatocytes and in Mice. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2702–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Previs, S.F.; Withers, D.J.; Ren, J.M.; White, M.F.; Shulman, G.I. Contrasting Effects of IRS-1 versus IRS-2 Gene Disruption on Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolism in Vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38990–38994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, O.; Fernández-Moreno, M.D.; Zueco, J.A.; Menor, C.; Fueyo, J.; Ropero, R.M.; Diaz-Laviada, I.; Román, I.D.; Guijarro, L.G. Insulin Receptor Substrate-4 Signaling in Quiescent Rat Hepatocytes and in Regenerating Rat Liver. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2003, 37, 1461–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, M.E.; Virkamäki, A.; Landaker, E.J.; Kahn, C.R.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Activation of the Hexosamine Pathway by Glucosamine in Vivo Induces Insulin Resistance of Early Postreceptor Insulin Signaling Events in Skeletal Muscle. Diabetes 1999, 48, 1562–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beale, E.G.; Harvey, B.J.; Forest, C. PCK1 and PCK2 as Candidate Diabetes and Obesity Genes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 48, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.-R.; Zhang, P.-W.; Zhen, Q.; Walther, D.; Wang, X.-B.; Uhl, G.R. KEPI, a PKC-Dependent Protein Phosphatase 1 Inhibitor Regulated by Morphine. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 13312–13320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preisler, N.; Cohen, J.; Vissing, C.R.; Madsen, K.L.; Heinicke, K.; Sharp, L.J.; Phillips, L.; Romain, N.; Park, S.Y.; Newby, M.; et al. Impaired Glycogen Breakdown and Synthesis in Phosphoglucomutase 1 Deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2017, 122, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cong, W.-M.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhou, W.; Yuan, S.; Gao, H.; et al. Phosphoglucomutase 1 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Regulating Glucose Trafficking. PLoS Biol. 2018, 16, e2006483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, S.S.; Weigert, C.; Lehmann, R. Divergent Roles of IRS (Insulin Receptor Substrate) 1 and 2 in Liver and Skeletal Muscle. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 1827–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Rao, S.N.R.; Shankar, S.K.; Satishchandra, P.; Jana, N.R. Lafora Disease Ubiquitin Ligase Malin Promotes Proteasomal Degradation of Neuronatin and Regulates Glycogen Synthesis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2011, 44, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse-Patin, A.; Jeromson, S.; Levesque-Damphousse, P.; Secco, B.; Laplante, M.; Estall, J.L. PGC1A Regulates the IRS1:IRS2 Ratio during Fasting to Influence Hepatic Metabolism Downstream of Insulin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 4285–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinson, J.T.; Chopra, A.; Lowe, A.; Sheng, C.C.; Gupta, R.M.; Kuppusamy, R.; O’Sullivan, J.; Rowe, G.; Wakimoto, H.; Gorham, J.; et al. Integrative Analysis of PRKAG2 Cardiomyopathy IPS and Microtissue Models Identifies AMPK as a Regulator of Metabolism, Survival, and Fibrosis. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 3292–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montori-Grau, M.; Pedreira-Casahuga, R.; Boyer-Díaz, Z.; Lassot, I.; García-Martínez, C.; Orozco, A.; Cebrià, J.; Osorio-Conles, O.; Chacón, M.R.; Vendrell, J.; et al. GNIP1 E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Is a Novel Player in Regulating Glycogen Metabolism in Skeletal Muscle. Metabolism 2018, 83, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, M.S.; Henriksen, A.; Svensson, B. Structure and Function of α-Glucan Debranching Enzymes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2016, 73, 2619–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirschhorn, R.; Huie, M.L.; Kasper, J.S. Computer Assisted Cloning of Human Neutral Alpha-Glucosidase C (GANC): A New Paralog in the Glycosyl Hydrolase Gene Family 31. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13642–13646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longuet, C.; Sinclair, E.M.; Maida, A.; Baggio, L.L.; Maziarz, M.; Charron, M.J.; Drucker, D.J. The Glucagon Receptor Is Required for the Adaptive Metabolic Response to Fasting. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijuin, T.; Takenawa, T. SKIP Negatively Regulates Insulin-Induced GLUT4 Translocation and Membrane Ruffle Formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1209–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T.; Baroja-Fernández, E.; Yamamoto, R.; Muñoz, F.J.; Akazawa, T.; Hong, K.S.; Pozueta-Romero, J. Cloning, Expression and Characterization of a Mammalian Nudix Hydrolase-like Enzyme That Cleaves the Pyrophosphate Bond of UDP-Glucose. Biochem. J. 2003, 370 Pt 2, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auranen, M.; Palmio, J.; Ylikallio, E.; Huovinen, S.; Paetau, A.; Sandell, S.; Haapasalo, H.; Viitaniemi, K.; Piirilä, P.; Tyynismaa, H.; et al. PFKM Gene Defect and Glycogen Storage Disease GSDVII with Misleading Enzyme Histochemistry. Neurol. Genet. 2015, 1, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbull, J.; Girard, J.-M.; Lohi, H.; Chan, E.M.; Wang, P.; Tiberia, E.; Omer, S.; Ahmed, M.; Bennett, C.; Chakrabarty, A.; et al. Early-Onset Lafora Body Disease. Brain J. Neurol. 2012, 135 Pt 9, 2684–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elton, L.; Carpentier, I.; Verhelst, K.; Staal, J.; Beyaert, R. The Multifaceted Role of the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase HOIL-1: Beyond Linear Ubiquitination. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 266, 208–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; Higuchi, T.; Shimada, Y.; Ida, H.; Ohashi, T. TFEB Overexpression Promotes Glycogen Clearance of Pompe Disease IPSC-Derived Skeletal Muscle. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibut, V.; Hennequet-Antier, C.; Le Bihan-Duval, E.; Marthey, S.; Duclos, M.J.; Berri, C. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes in Chickens Differing in Muscle Glycogen Content and Meat Quality. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, P.; Lengyel, E. New Roles for Glycogen in Tumor Progression. Trends Cancer 2019, 5, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B.D.; Cole, S.A.; Hsueh, W.C.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Blangero, J.; MacCluer, J.W.; Hixson, J.E. Linkage of Serum Insulin Concentrations to Chromosome 3p in Mexican Americans. Diabetes 2000, 49, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevim, D.G.; Kiratli, H. Serum Adiponectin, Insulin Resistance, and Uveal Melanoma: Clinicopathological Correlations. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura, A.; Thieme, C.; Brosig, A.; Merz, H.; Ranjbar, M.; Vardanyan, S.; Zuo, H.; Maassen, T.; Kakkassery, V.; Grisanti, S. Lower Levels of Adiponectin and Its Receptor Adipor1 in the Uveal Melanomas with Monosomy-3. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, K.M.; Bhave, S.R.; Ferraro, D.J.; Jaboin, J.J.; Hallahan, D.E.; Thotala, D. GSK-3β: A Bifunctional Role in Cell Death Pathways. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 930710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beurel, E.; Grieco, S.F.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 (GSK3): Regulation, Actions, and Diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 148, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrel, L.; Willard, H.F. X-Inactivation Profile Reveals Extensive Variability in X-Linked Gene Expression in Females. Nature 2005, 434, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotton, A.M.; Ge, B.; Light, N.; Adoue, V.; Pastinen, T.; Brown, C.J. Analysis of Expressed SNPs Identifies Variable Extents of Expression from the Human Inactive X Chromosome. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tukiainen, T.; Villani, A.-C.; Yen, A.; Rivas, M.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Satija, R.; Aguirre, M.; Gauthier, L.; Fleharty, M.; Kirby, A.; et al. Landscape of X Chromosome Inactivation across Human Tissues. Nature 2017, 550, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, L.; Mu, J.; Zong, H.; DePaoli-Roach, A.A.; Roach, P.J. Structure and Chromosomal Localization of the Human Glycogenin-2 Gene GYG2. Gene 2000, 242, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1alpha-Responsive Genes Involved in Oxidative Phosphorylation Are Coordinately Downregulated in Human Diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betancourt, L.H.; Szasz, A.M.; Kuras, M.; Rodriguez Murillo, J.; Sugihara, Y.; Pla, I.; Horvath, Z.; Pawłowski, K.; Rezeli, M.; Miharada, K.; et al. The Hidden Story of Heterogeneous B-Raf V600E Mutation Quantitative Protein Expression in Metastatic Melanoma-Association with Clinical Outcome and Tumor Phenotypes. Cancers 2019, 11, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, C.T.; Fuller, M.; Hopwood, J.J.; Meikle, P.J.; Brooks, D.A. Drug Induced Exocytosis of Glycogen in Pompe Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenacchi, G.; Papa, V.; Costa, R.; Pegoraro, V.; Marozzo, R.; Fanin, M.; Angelini, C. Update on Polyglucosan Storage Diseases. Virchows Arch. Int. J. Pathol. 2019, 475, 671–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedberg-Oldfors, C.; Oldfors, A. Polyglucosan Storage Myopathies. Mol. Aspects Med. 2015, 46, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavanagh, J.B. Corpora-Amylacea and the Family of Polyglucosan Diseases. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 265–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, P.P.; Genoud, C.; Castaño-Díez, D.; Graff-Meyer, A.; Lewis, A.J.; de Gier, Y.; Lauer, M.E.; Britschgi, M.; Bohrmann, B.; Frank, S.; et al. Cerebral Corpora Amylacea Are Dense Membranous Labyrinths Containing Structurally Preserved Cell Organelles. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 18046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, E.; Lin, Y.-S.; Dagher, Z.; Saha, A.; Luo, Z.; Ido, Y.; Ruderman, N.B. Hyperglycemia and Insulin Resistance: Possible Mechanisms. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2002, 967, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathy, D.; Merovci, A.; Basu, R.; Abdul-Ghani, M.; DeFronzo, R.A. Mild Physiologic Hyperglycemia Induces Hepatic Insulin Resistance in Healthy Normal Glucose-Tolerant Participants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019, 104, 2842–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.-S.; Kang, G.; Kim, J.S.; Choi, B.H.; Koo, S.-H. Regulation of Glucose Metabolism from a Liver-Centric Perspective. Exp. Mol. Med. 2016, 48, e218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.C.; Coate, K.C.; Winnick, J.J.; An, Z.; Cherrington, A.D. Regulation of Hepatic Glucose Uptake and Storage in Vivo. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.M.; Goyal, R.K. Liver and Insulin Resistance: New Wine in Old Bottle!!! Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, T.P.; Marliss, E.B. Adiponectin Signaling in the Liver. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.J.; Oh, S.; Quan, S.; Ryu, O.-H.; Jeong, J.-Y.; Hong, K.-S.; Kim, D.-H. Gender Differences in Adiponectin Levels and Body Composition in Older Adults: Hallym Aging Study. BMC Geriatr. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigogora, S.; Zaninotto, P.; Kivimaki, M.; Steptoe, A.; Batty, G.D. Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 and Risk of Depression in Older People: The English Longitudinal Study of Ageing. Transl. Psychiatry 2016, 6, e898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binoux, M. The IGF System in Metabolism Regulation. Diabete Metab. 1995, 21, 330–337. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, D.H.; LeRoith, D. Obesity, Type 2 Diabetes, and Cancer: The Insulin and IGF Connection. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2012, 19, F27–F45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- All-Ericsson, C.; Girnita, L.; Seregard, S.; Bartolazzi, A.; Jager, M.J.; Larsson, O. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Receptor in Uveal Melanoma: A Predictor for Metastatic Disease and a Potential Therapeutic Target. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2002, 43, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel, S.; Zloto, O.; Pe’er, J.; Barak, V. Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 as a Predictive Biomarker for Metastatic Uveal Melanoma in Humans. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The CBio Cancer Genomics Portal: An Open Platform for Exploring Multidimensional Cancer Genomics Data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the CBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruz, T.; Laule, O.; Szabo, G.; Wessendorp, F.; Bleuler, S.; Oertle, L.; Widmayer, P.; Gruissem, W.; Zimmermann, P. Genevestigator V3: A reference expression database for the meta-analysis of transcriptomes. Adv. Bioinform. 2008, 2008, 420747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. The Gene Ontology Resource: 20 Years and Still GOing Strong. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D330–D338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D498–D503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, E.; Wells, J.R.; Ward, L.; Grossniklaus, H.E. Uveal Melanoma Nuclear BRCA1-Associated Protein-1 Immunoreactivity Is an Indicator of Metastasis. Ophthalmology 2018, 125, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura, A.; Lüke, J.; Merz, H.; Reinsberg, M.; Lüke, M.; Jager, M.J.; Grisanti, S. Identification of Circulating Melanoma Cells in Uveal Melanoma Patients by Dual-Marker Immunoenrichment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 4395–4404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandinha, M.T.; Farquharson, M.A.; Roberts, F. Identification of Monosomy 3 in Choroidal Melanoma by Chromosome in Situ Hybridisation. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
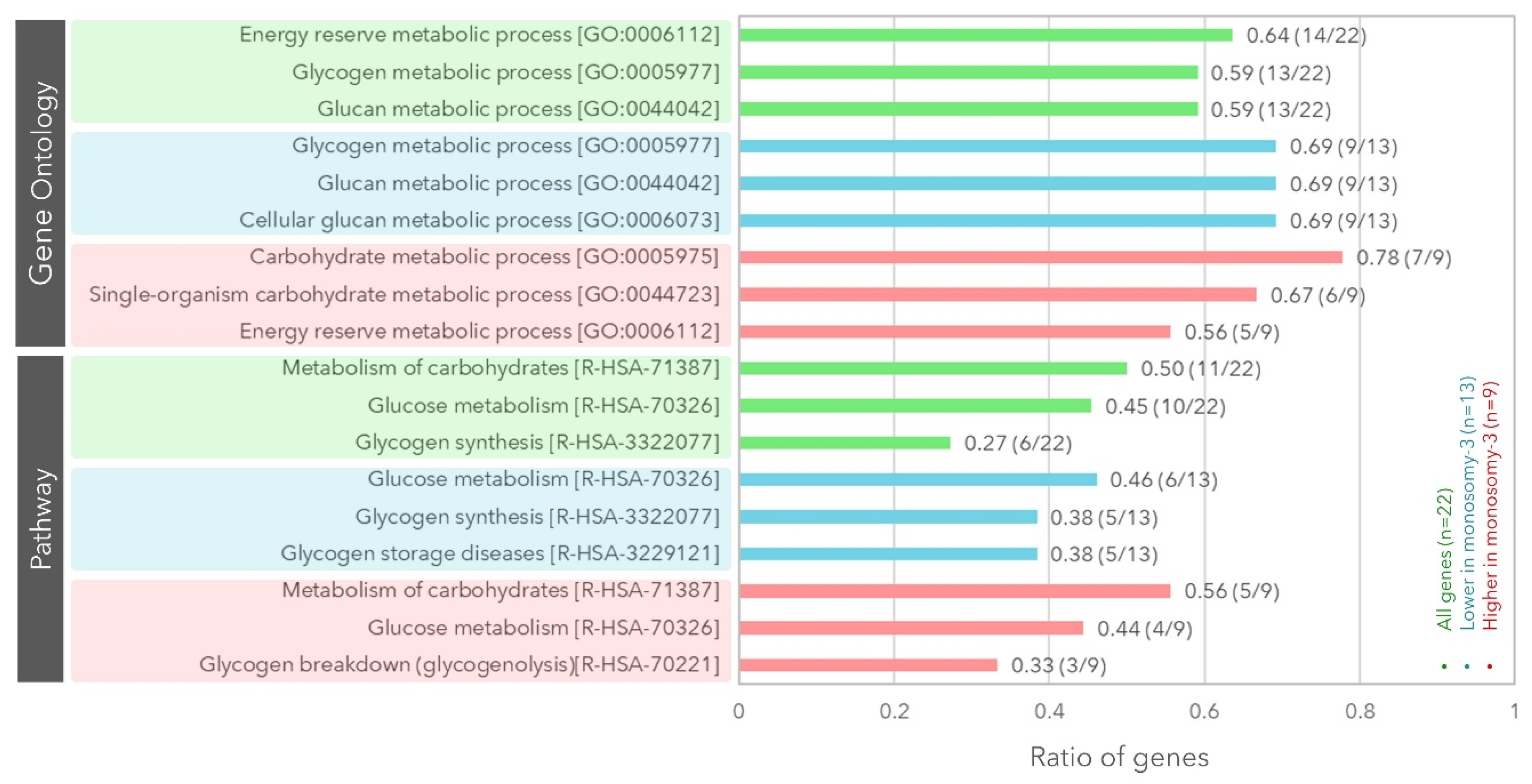
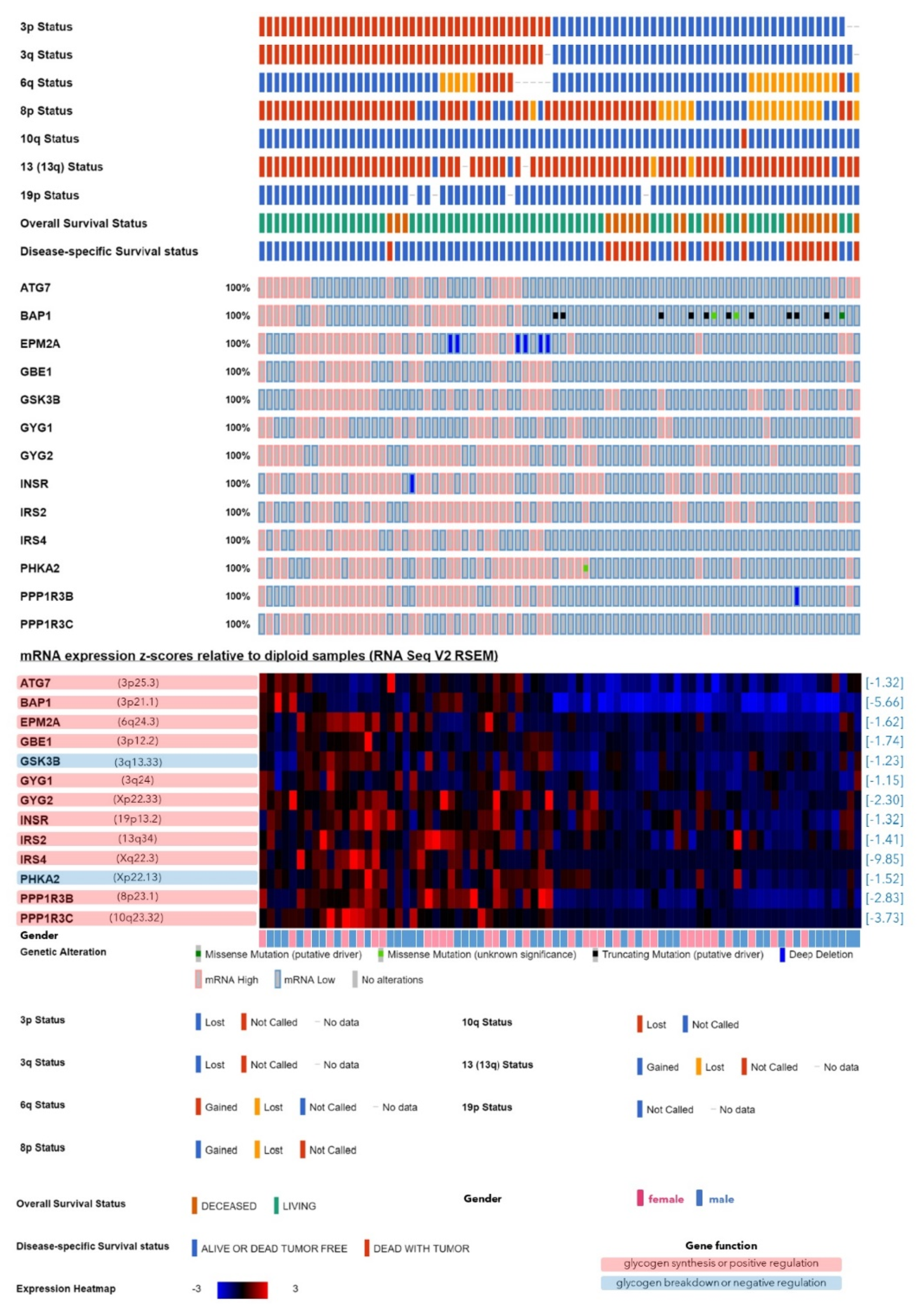
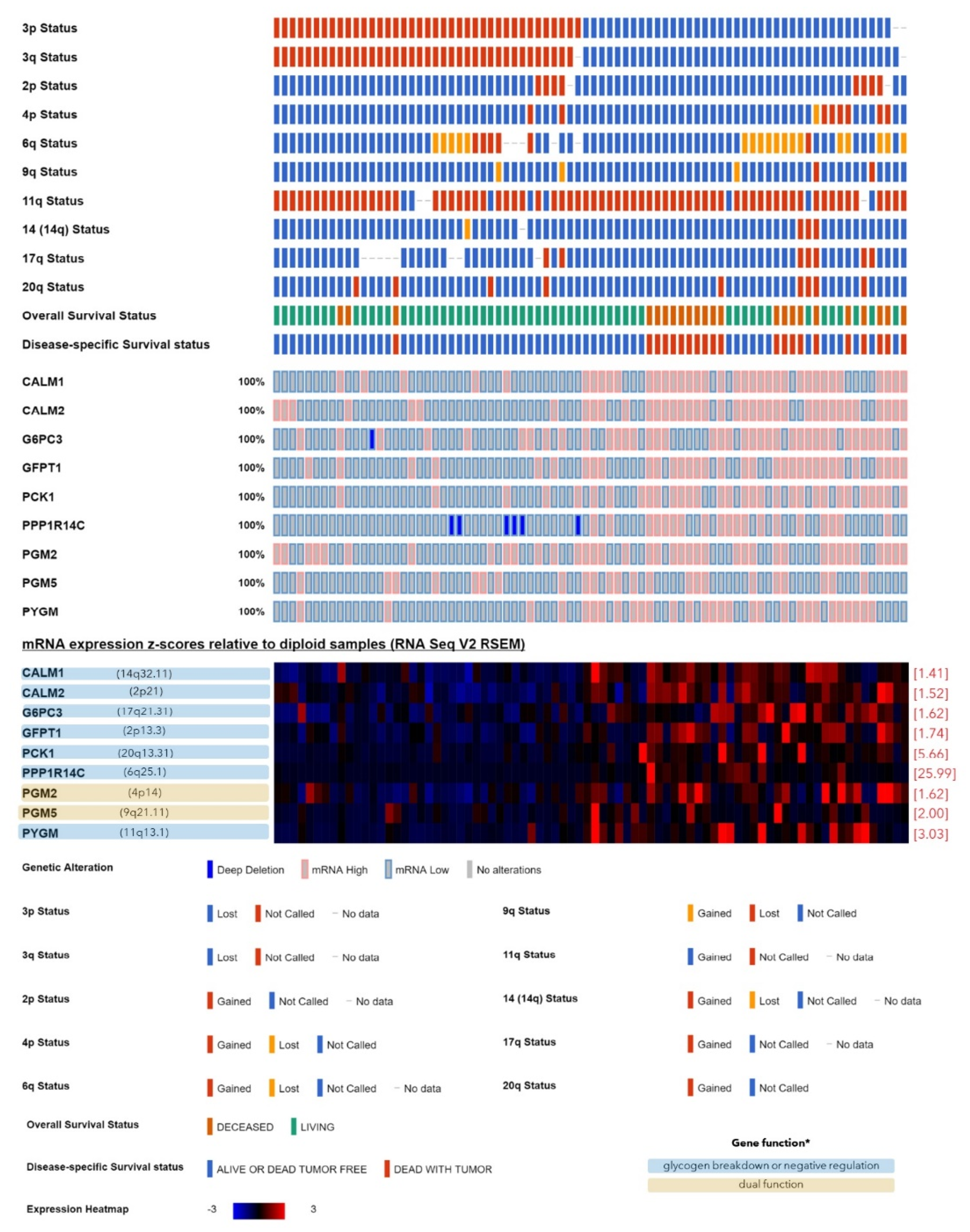

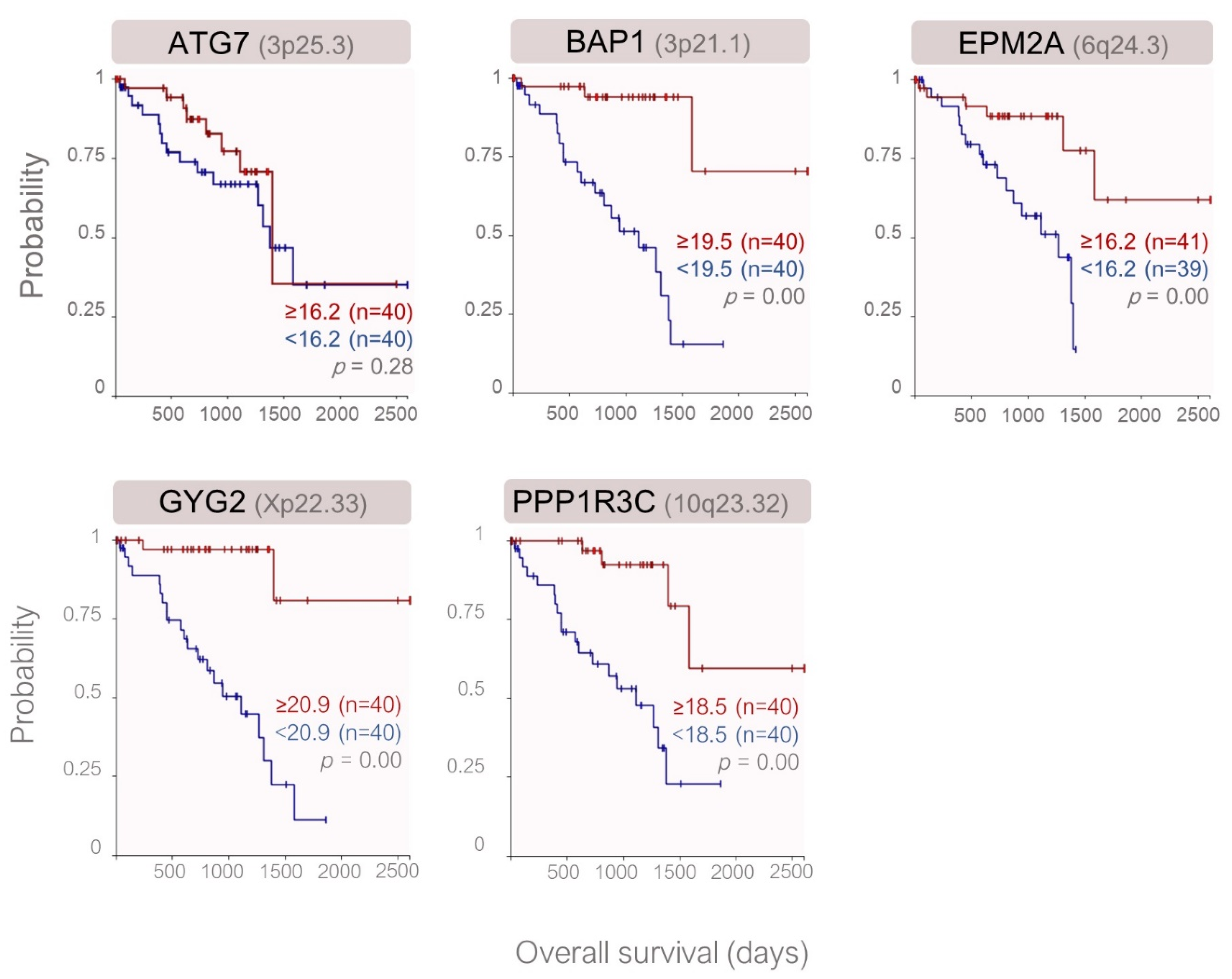

| Symbol | Name | Locus | Function in Glycogen Synthesis [References] | Expression in Monosomy-3 Tumors | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All Patients (n = 77) | Omission of the Patients with an Aberrant Gene Copy Number | ||||||
| Fold Change | p† | Fold Change | p† | ||||
| GBE1 | 1,4-alpha-glucan branching enzyme 1 | 3p12.2 | de novo synthesis [15,16] | −1.74 | 0.00 | n.a. | n.a. |
| GYG1 | glycogenin 1 | 3q24 | de novo synthesis [15,16] | −1.15 | 0.01 | n.a. | n.a. |
| GYG2 | glycogenin 2 | Xp22.33 | de novo synthesis [15,16] | −2.30 | 0.00 | −2.46 | 0.00 |
| ATG7 | autophagy related 7 | 3p25.3 | positive [15] | −1.32 | 0.00 | n.a. | n.a. |
| BAP1 | BRCA1 associated protein 1 | 3p21.1 | positive [22] | −5.66 | 0.00 | n.a. | n.a. |
| EPM2A | EPM2A glucan phosphatase, laforin | 6q24.3 | positive [16] | −1.62 | 0.00 | −1.74 | 0.00 |
| INSR | insulin receptor | 19p13.2 | positive [31] | −1.32 | 0.00 | −1.32 | 0.00 |
| IRS2 | insulin receptor substrate 2 | 13q34 | positive [32] | −1.41 | 0.00 | −1.32 | 0.00 |
| IRS4 | insulin receptor substrate 4 | Xq22.3 | positive [33] | −9.85 | 0.00 | −8.57 | 0.02 |
| PPP1R3B | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3B | 8p23.1 | positive [15,16] | −2.83 | 0.00 | −2.30 | 0.00 |
| PPP1R3C | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3C | 10q23.32 | positive [15,16] | −3.73 | 0.00 | −3.73 | 0.00 |
| CALM1 | calmodulin 1 | 14q32.11 | negative [16] | 1.41 | 0.00 | 1.41 | 0.00 |
| CALM2 | calmodulin 2 | 2p21 | negative [16] | 1.52 | 0.00 | 1.52 | 0.00 |
| G6PC3 | glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit 3 | 17q21.31 | negative [16] | 1.62 | 0.00 | 1.74 | 0.02 |
| GFPT1 | glutamine--fructose-6-phosphate transaminase 1 | 2p13.3 | negative [34] | 1.74 | 0.00 | 1.74 | 0.00 |
| GSK3B | glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta | 3q13.33 | negative [15,23] | −1.23 | 0.00 | n.a. | n.a. |
| PCK1 | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1 | 20q13.31 | negative [35] | 5.66 | 0.00 | 6.96 | 0.00 |
| PHKA2 | phosphorylase kinase regulatory subunit alpha 2 | Xp22.13 | negative [16] | −1.52 | 0.00 | −1.52 | 0.03 |
| PPP1R14C | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 14C | 6q25.1 | negative [36] | 25.99 | 0.00 | 27.86 | 0.00 |
| PYGM | glycogen phosphorylase, muscle associated | 11q13.1 | negative [15,16] | 3.03 | 0.00 | 3.25 | 0.00 |
| PGM2 | phosphoglucomutase 2 | 4p14 | dual [16,38] | 1.62 | 0.00 | 1.52 | 0.02 |
| PGM5 | phosphoglucomutase 5 | 9q21.11 | dual [16,38] | 2.00 | 0.02 | 2.14 | 0.00 |
| All Patients n = 30 | High Glycogen (≥Median) n = 15 | Low Glycogen (<Median) n = 15 | p * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | ||||
| Median (range) | 69 (39–83) | 73 (50–83) | 63 (39–81) | 0.07 |
| Gender (n, %) | ||||
| Female | 14 (46.7) | 6 (40.0) | 8 (53.3) | 0.46 |
| Male | 16 (53.3) | 9 (60.0) | 7 (46.7) | |
| Eye (n, %) | ||||
| Right | 13 (43.3) | 5 (33.3) | 8 (53.3) | 0.27 |
| Left | 17 (56.7) | 10 (66.7) | 7 (46.7) | |
| Irradiation (n, %) | ||||
| No | 15 (50.0) | 8 (53.3) | 7 (46.7) | 0.72 |
| Yes | 15 (50.0) | 7 (46.7) | 8 (53.3) | |
| Tumor size in mm (Median, range) | ||||
| Basis 1 | 12.9 (1.4–18.6) | 12.8 (8.5–18.6) | 13.4 (1.4–17.5) | 0.90 |
| Basis 2 | 12.8 (1.4–21.8) | 14.0 (6.2–21.8) | 12.0 (1.4–19.0) | 0.29 |
| Prominence | 7.9 (0.5–17.8) | 9.0 (0.5–17.8) | 6.6 (0.9–12.8) | 0.17 |
| Monosomy-3 in primary tumor (n, %) | ||||
| No | 16 (53.3) | 12 (80.0) | 4 (26.7) | 0.00 |
| Yes | 14 (46.7) | 3 (20.0) | 11 (73.3) | |
| BAP1 expression, cytoplasmic (n, %) | ||||
| High | 18 (60.0) | 11 (73.3) | 7 (46.7) | 0.14 |
| Low | 12 (40.0) | 4 (26.7) | 8 (53.3) | |
| BAP1 expression, nuclear (n, %) | ||||
| High | 11 (36.7) | 9 (60.0) | 2 (13.3) | 0.01 |
| Low | 19 (63.3) | 6 (40.0) | 13 (86.7) | |
| CMC presence (n, %) † | ||||
| No | 2 (6.9) | 1 (7.1) | 1 (6.7) | 0.96 |
| Yes | 27 (93.1) | 13 (92.9) | 14 (93.3) | |
| CMC number/10 mL blood | ||||
| Median (range) | 1.6 (0.0–10.2) | 1.6 (0.0–10.2) | 1.5 (0.0–7.5) | 0.59 |
| Monosomy-3 in CMCs (n, %) †† | ||||
| No | 8 (29.6) | 5 (35.7) | 3 (23.1) | 0.47 |
| Yes | 19 (70.4) | 9 (64.3) | 10 (76.9) | |
| % CMCs with monosomy-3 | ||||
| Median (range) | 30.4 (0.0–100) | 23.6 (0.0–66.7) | 31.8 (0.0–100) | 0.75 |
| Metastases (n, %) | ||||
| No | 20 (66.7) | 13 (86.7) | 7 (46.7) | 0.02 |
| Yes | 10 (33.3) | 2 (13.3) | 8 (53.3) |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vardanyan, S.; Brosig, A.; Merz, H.; Ranjbar, M.; Kakkassery, V.; Grisanti, S.; Tura, A. Metastasis of Uveal Melanoma with Monosomy-3 Is Associated with a Less Glycogenetic Gene Expression Profile and the Dysregulation of Glycogen Storage. Cancers 2020, 12, 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082101
Vardanyan S, Brosig A, Merz H, Ranjbar M, Kakkassery V, Grisanti S, Tura A. Metastasis of Uveal Melanoma with Monosomy-3 Is Associated with a Less Glycogenetic Gene Expression Profile and the Dysregulation of Glycogen Storage. Cancers. 2020; 12(8):2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082101
Chicago/Turabian StyleVardanyan, Siranush, Anton Brosig, Hartmut Merz, Mahdy Ranjbar, Vinodh Kakkassery, Salvatore Grisanti, and Aysegül Tura. 2020. "Metastasis of Uveal Melanoma with Monosomy-3 Is Associated with a Less Glycogenetic Gene Expression Profile and the Dysregulation of Glycogen Storage" Cancers 12, no. 8: 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082101
APA StyleVardanyan, S., Brosig, A., Merz, H., Ranjbar, M., Kakkassery, V., Grisanti, S., & Tura, A. (2020). Metastasis of Uveal Melanoma with Monosomy-3 Is Associated with a Less Glycogenetic Gene Expression Profile and the Dysregulation of Glycogen Storage. Cancers, 12(8), 2101. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082101






