Histone Demethylase KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy
Abstract
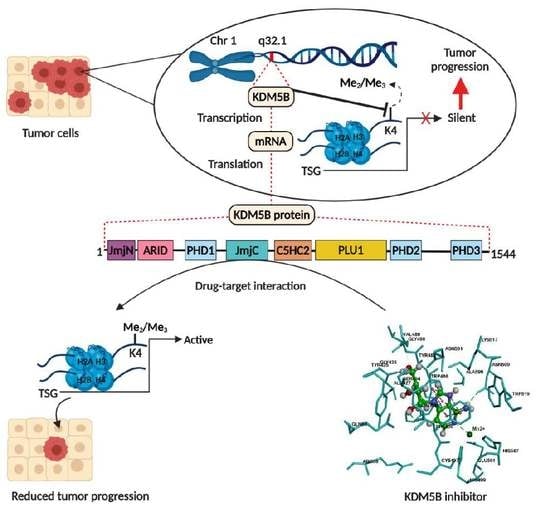
:1. Introduction
2. Structure and Enzymatic Function of KDM5B
3. Significance of KDM5B in Various Cancers
3.1. Breast Cancer
3.2. Lung Cancer
3.3. Melanoma
3.4. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.5. Gastric Cancer
3.6. Colorectal Cancer
3.7. Bladder Cancer
3.8. Prostate Cancer
3.9. KDM5B in Other Cancers
3.10. KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target
4. Molecular Docking Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, S.; Kelly, T.K.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetics in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P.; Tycko, B. The history of cancer epigenetics. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dupont, C.; Armant, D.R.; Brenner, C.A. Epigenetics: Definition, mechanisms and clinical perspective. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2009, 27, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.G.; Allis, C.D.; Chi, P. Chromatin remodeling and cancer, Part I: Covalent histone modifications. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.H.; Nielsen, A.L.; Helgstrand, C.; Lees, M.; Cloos, P.; Kastrup, J.S.; Helin, K.; Olsen, L.; Gajhede, M. Studies of H3K4me3 demethylation by KDM5B/Jarid1B/PLU1 reveals strong substrate recognition in vitro and identifies 2, 4-pyridine-dicarboxylic acid as an in vitro and in cell inhibitor. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1905–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agger, K.; Christensen, J.; Cloos, P.A.; Helin, K. The emerging functions of histone demethylases. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2008, 18, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allis, C.D.; Berger, S.L.; Cote, J.; Dent, S.; Jenuwien, T.; Kouzarides, T.; Pillus, L.; Reinberg, D.; Shi, Y.; Shiekhattar, R. New nomenclature for chromatin-modifying enzymes. Cell 2007, 131, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, Y.; Whetstine, J.R. Dynamic regulation of histone lysine methylation by demethylases. Mol. Cell. 2007, 25, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmeyer, K.M.; Facompre, N.D.; Herlyn, M.; Basu, D. JARID1 histone demethylases: Emerging targets in cancer. Trends Cancer 2017, 3, 713–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevolenskaya, E.V. Histone H3K4 demethylases are essential in development and differentiation. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 85, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotili, D.; Mai, A. Targeting histone demethylases: A new avenue for the fight against cancer. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. AACR 2012, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoadley, K.A.; Yau, C.; Hinoue, T.; Wolf, D.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Drill, E.; Shen, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Cherniack, A.D.; Thorsson, V. Cell-of-origin patterns dominate the molecular classification of 10,000 tumors from 33 types of cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 291–304.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Han, G.; Ye, X.; Xu, B.; Peng, Z.; Ma, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lin, H.; Chen, A.P. JARID1B is a histone H3 lysine 4 demethylase up-regulated in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007, 104, 19226–19231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilsker, D.; Probst, L.; Wain, H.M.; Maltais, L.; Tucker, P.W.; Moran, E. Nomenclature of the ARID family of DNA-binding proteins. Genomics 2005, 86, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wysocka, J.; Swigut, T.; Xiao, H.; Milne, T.A.; Kwon, S.Y.; Landry, J.; Kauer, M.; Tackett, A.J.; Chait, B.T.; Badenhorst, P. A PHD finger of NURF couples histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation with chromatin remodelling. Nature 2006, 442, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilka, E.S.; James, T.; Lisztwan, J.H. Structural definitions of Jumonji family demethylase selectivity. Drug Discov. Today. 2015, 20, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamane, K.; Tateishi, K.; Klose, R.J.; Fang, J.; Fabrizio, L.A.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; Tempst, P.; Zhang, Y. PLU-1 is an H3K4 demethylase involved in transcriptional repression and breast cancer cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2007, 25, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Velupillai, S.; Tumber, A.; Szykowska, A.; Hookway, E.S.; Nowak, R.P.; Strain-Damerell, C.; Gileadi, C.; Philpott, M.; Burgess-Brown, N. Structural analysis of human KDM5B guides histone demethylase inhibitor development. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorosz, J.; Kristensen, L.H.; Aduri, N.G.; Mirza, O.; Lousen, R.; Bucciarelli, S.; Mehta, V.; Sellés-Baiget, S.; Solbak, S.M.Ø.; Bach, A. Molecular architecture of the Jumonji C family histone demethylase KDM5B. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, P.J.; Sundquist, K.; Baeckstrom, D.; Poulsom, R.; Hanby, A.; Meier-Ewert, S.; Jones, T.; Mitchell, M.; Pitha-Rowe, P.; Freemont, P. A novel gene (PLU-1) containing highly conserved putative DNA/chromatin binding motifs is specifically up-regulated in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15633–15645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scibetta, A.G.; Santangelo, S.; Coleman, J.; Hall, D.; Chaplin, T.; Copier, J.; Catchpole, S.; Burchell, J.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. Functional analysis of the transcription repressor PLU-1/JARID1B. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 27, 7220–7235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Catchpole, S.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Hall, D.; Santangelo, S.; Rosewell, I.; Guenatri, M.; Beatson, R.; Scibetta, A.G.; Burchell, J.M.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. PLU-1/JARID1B/KDM5B is required for embryonic survival and contributes to cell proliferation in the mammary gland and in ER+ breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 38, 1267–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, S.; Wu, Z.; Russnes, H.G.; Takagi, S.; Peluffo, G.; Vaske, C.; Zhao, X.; Vollan, H.K.M.; Maruyama, R.; Ekram, M.B. JARID1B is a luminal lineage-driving oncogene in breast cancer. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 762–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitra, D.; Das, P.M.; Huynh, F.C.; Jones, F.E. Jumonji/ARID1 B (JARID1B) protein promotes breast tumor cell cycle progression through epigenetic repression of microRNA let-7e. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 40531–40535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, P.-P.; Miranda, F.; Chan, K.V.; Berlato, C.; Hurst, H.C.; Scibetta, A.G. Histone demethylase KDM5B collaborates with TFAP2C and Myc to repress the cell cycle inhibitor p21cip (CDKN1A). Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Liu, H. Immunohistochemical detection and clinicopathological significance of JARID1B/KDM5B and P16 expression in invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 5417–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamodu, O.A.; Huang, W.-C.; Lee, W.-H.; Wu, A.; Wang, L.S.; Hsiao, M.; Yeh, C.-T.; Chao, T.-Y. Aberrant KDM5B expression promotes aggressive breast cancer through MALAT1 overexpression and downregulation of hsa-miR-448. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, L.P.; Liu, Z.; Labitigan, R.L.D.; Wu, L.; Zheng, D.; Xia, Z.; Pearson, E.L.; Nazeer, F.I.; Cao, J.; Lang, S.M. KDM5 lysine demethylases are involved in maintenance of 3′ UTR length. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Montano, M.M.; Yeh, I.J.; Chen, Y.; Hernandez, C.; Kiselar, J.G.; de la Fuente, M.; Lawes, A.M.; Nieman, M.T.; Kiser, P.D.; Jacobberger, J.; et al. Inhibition of the histone demethylase, KDM5B, directly induces re-expression of tumor suppressor protein HEXIM1 in cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paroni, G.; Bolis, M.; Zanetti, A.; Ubezio, P.; Helin, K.; Staller, P.; Gerlach, L.O.; Fratelli, M.; Neve, R.M.; Terao, M. HER2-positive breast-cancer cell lines are sensitive to KDM5 inhibition: Definition of a gene-expression model for the selection of sensitive cases. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2675–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinohara, K.; Wu, H.-J.; Vigneau, S.; McDonald, T.O.; Igarashi, K.J.; Yamamoto, K.N.; Madsen, T.; Fassl, A.; Egri, S.B.; Papanastasiou, M. KDM5 histone demethylase activity links cellular transcriptomic heterogeneity to therapeutic resistance. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 939–953.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Identification of hub genes to regulate breast cancer metastasis to brain by bioinformatics analyses. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 9522–9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-G.; Zhang, H.-S.; Sun, H.-L.; Liu, H.-Y.; Liu, M.-Y.; Zhou, Z. KDM5B promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and migration via AMPK-mediated lipid metabolism reprogramming. Exp. Cell Res. 2019, 379, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriello, G.; Gatza, M.L.; Beck, A.H.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Rhie, S.K.; Pastore, A.; Zhang, H.; McLellan, M.; Yau, C.; Kandoth, C. Comprehensive molecular portraits of invasive lobular breast cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, B.; Chin, S.-F.; Rueda, O.M.; Vollan, H.-K.M.; Provenzano, E.; Bardwell, H.A.; Pugh, M.; Jones, L.; Russell, R.; Sammut, S.-J. The somatic mutation profiles of 2433 breast cancers refine their genomic and transcriptomic landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, X.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Shen, L.; Pu, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z. JARID1B modulates lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion by regulating p53 expression. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 7133–7142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, S.; Yoshimatsu, M.; Veerakumarasivam, A.; Unoki, M.; Iwai, Y.; Tsunoda, T.; Field, H.I.; Kelly, J.D.; Neal, D.E.; Yamaue, H. Overexpression of the JmjC histone demethylase KDM5B in human carcinogenesis: Involvement in the proliferation of cancer cells through the E2F/RB pathway. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, K.-T.; Huang, W.-C.; Bamodu, O.A.; Lee, W.-H.; Wang, C.-H.; Hsiao, M.; Wang, L.-S.; Yeh, C.-T. Histone demethylase JARID1B/KDM5B promotes aggressiveness of non-small cell lung cancer and serves as a good prognostic predictor. Clin. Epigenetics. 2018, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Liang, X.-H.; Chen, L.-X.; Bao, S.-M.; Yan, Z.-Q. SIRT1 is highly expressed in brain metastasis tissues of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and in positive regulation of NSCLC cell migration. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2357–2365. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Oeck, S.; Glazer, P.M. Hypoxia promotes resistance to EGFR inhibition in NSCLC cells via the histone demethylases, LSD1 and PLU-1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1458–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roesch, A.; Fukunaga-Kalabis, M.; Schmidt, E.C.; Zabierowski, S.E.; Brafford, P.A.; Vultur, A.; Basu, D.; Gimotty, P.; Vogt, T.; Herlyn, M. A temporarily distinct subpopulation of slow-cycling melanoma cells is required for continuous tumor growth. Cell 2010, 141, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roesch, A.; Mueller, A.M.; Stempfl, T.; Moehle, C.; Landthaler, M.; Vogt, T. RBP2-H1/JARID1B is a transcriptional regulator with a tumor suppressive potential in melanoma cells. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, A.; Becker, B.; Schneider-Brachert, W.; Hagen, I.; Landthaler, M.; Vogt, T. Re-expression of the retinoblastoma-binding protein 2-homolog 1 reveals tumor-suppressive functions in highly metastatic melanoma cells. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roesch, A.; Becker, B.; Meyer, S.; Wild, P.; Hafner, C.; Landthaler, M.; Vogt, T. Retinoblastoma-binding protein 2-homolog 1: A retinoblastoma-binding protein downregulated in malignant melanomas. Mod. Pathol. 2005, 18, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roesch, A.; Vultur, A.; Bogeski, I.; Wang, H.; Zimmermann, K.M.; Speicher, D.; Körbel, C.; Laschke, M.W.; Gimotty, P.A.; Philipp, S.E. Overcoming intrinsic multidrug resistance in melanoma by blocking the mitochondrial respiratory chain of slow-cycling JARID1B(high) cells. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 811–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Qi, G.; Tang, F.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Z.; Liang, X.; Li, B.; Yu, S.; Liu, J.; Huang, Q. JARID1B promotes metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition via PTEN/AKT signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 12723–12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, D.; Han, S.; Peng, R.; Jiao, C.; Wang, X.; Yang, X.; Yang, R.; Li, X. Depletion of histone demethylase KDM5B inhibits cell proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulation of cell cycle checkpoint proteins p15 and p27. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shigekawa, Y.; Hayami, S.; Ueno, M.; Miyamoto, A.; Suzaki, N.; Kawai, M.; Hirono, S.; Okada, K.-I.; Hamamoto, R.; Yamaue, H. Overexpression of KDM5B/JARID1B is associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34320–34335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Yan, S.; Yu, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D. Increased Expression of Lysine-Specific Demethylase 5B (KDM5B) Promotes Tumor Cell Growth in Hep3B Cells and is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 7586–7594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, F.; Qi, G.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, G.; Tang, B.; He, S. KDM5B is overexpressed in gastric cancer and is required for gastric cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Feng, L.; Zhu, M.; Shen, Q.; Fang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X. NEK2 promotes proliferation, migration and tumor growth of gastric cancer cells via regulating KDM5B/H3K4me3. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2364–2378. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, J.; Zou, J.; Li, C.; Zheng, G. miR-194 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenesis by targeting KDM5B. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 20, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, D.; Wei, Q.; Han, M.; Feng, L. KDM5B demethylates H3K4 to recruit XRCC1 and promote chemoresistance. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, K.; Haraguchi, N.; Kano, Y.; Kagawa, Y.; Konno, M.; Nishikawa, S.; Hamabe, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Fukusumi, T. Depletion of JARID1B induces cellular senescence in human colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1212–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tarnowski, M.; Czerewaty, M.; Deskur, A.; Safranow, K.; Marlicz, W.; Urasińska, E.; Ratajczak, M.Z.; Starzyńska, T. Expression of cancer testis antigens in colorectal cancer: New prognostic and therapeutic implications. Dis. Markers 2016, 2016, 1987505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Su, Y.; Pan, J.; Zhou, Z.; Song, B.; Xiong, E.; Chen, Z. Connexin 26 is down-regulated by KDM5B in the progression of bladder cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7866–7879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Xie, Y.; Adhiambo, C.; Yang, Q.; Ballard, B.R.; Nakayama, K.I.; Matusik, R.J.; Chen, Z. SKP2 inactivation suppresses prostate tumorigenesis by mediating JARID1B ubiquitination. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 771–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wan, X.; Qiang, W.; Li, T.; Huang, W.; Huang, S.; Wu, D.; Li, Y. MiR-29a suppresses prostate cell proliferation and induces apoptosis via KDM5B protein regulation. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 5329–5339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, E.M.; Laursen, K.B.; Whitchurch, J.; McWilliam, A.; Ødum, N.; Persson, J.L.; Heery, D.M.; Gudas, L.J.; Mongan, N.P. MiR137 is an androgen regulated repressor of an extended network of transcriptional coregulators. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35710–35725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Song, C.; Ding, Y.; Pan, X.; Ge, Z.; Tan, B.-H.; Gowda, C.; Sachdev, M.; Muthusami, S.; Ouyang, H. Transcriptional regulation of JARID1B/KDM5B histone demethylase by ikaros, histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1), and casein kinase 2 (CK2) in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Biol. 2016, 291, 4004–4018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-S.; Lin, Y.-C.; Adebayo, B.O.; Wu, A.; Chen, J.-H.; Peng, Y.-J.; Cheng, M.-F.; Lee, W.-H.; Hsiao, M.; Chao, T.-Y. Silencing JARID1B suppresses oncogenicity, stemness and increases radiation sensitivity in human oral carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 368, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Z.; Song, L.; Hou, Z.; Han, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; Mao, L. PLU-1/JARID1B overexpression predicts proliferation properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2454–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kano, Y.; Konno, M.; Ohta, K.; Haraguchi, N.; Nishikawa, S.; Kagawa, Y.; Hamabe, A.; Hasegawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; Fukusumi, T. Jumonji/Arid1b (Jarid1b) protein modulates human esophageal cancer cell growth. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; An, Q.; Guo, R.-X.; Qiao, Y.-H.; Li, L.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Zhao, X.-L. miR424-5p functions as an anti-oncogene in cervical cancer cell growth by targeting KDM5B via the Notch signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2017, 171, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumari, N.; Nallabelli, N.; Sharma, U.; Rai, A.; Singh, S.K.; Kakkar, N.; Prasad, R. Expression profile of H3K4 demethylases with their clinical and pathological correlation in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Gene 2020, 739, 144498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mao, Y.; Du, G.; He, C.; Han, S. Overexpression of JARID1B is associated with poor prognosis and chemotherapy resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 2465–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuo, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-L.; Adebayo, B.O.; Shih, P.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Wang, L.-S.; Liao, Y.-F.; Hsu, W.-M.; Yeh, C.-T.; Lin, C.-M. JARID1B expression plays a critical role in chemoresistance and stem cell-like phenotype of neuroblastoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, A.; Madsen, B.; Copier, J.; Lu, P.J.; Cooper, L.; Scibetta, A.G.; Burchell, J.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. PLU-1 nuclear protein, which is upregulated in breast cancer, shows restricted expression in normal human adult tissues: A new cancer/testis antigen? Int. J. Cancer 2002, 101, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.-C.; Chang, J.; Wang, L.-C.; Ren, H.-M.; Pang, J.-R.; Liu, H.-M. Lysine demethylase 5B (KDM5B): A potential anti-cancer drug target. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 161, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinemann, B.; Nielsen, J.M.; Hudlebusch, H.R.; Lees, M.J.; Larsen, D.V.; Boesen, T.; Labelle, M.; Gerlach, L.-O.; Birk, P.; Helin, K. Inhibition of demethylases by GSK-J1/J4. Nature 2014, 514, E1–E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westaway, S.M.; Preston, A.G.; Barker, M.D.; Brown, F.; Brown, J.A.; Campbell, M.; Chung, C.-W.; Drewes, G.; Eagle, R.; Garton, N. Cell penetrant inhibitors of the KDM4 and KDM5 families of histone lysine demethylases. 2. Pyrido [3–d] pyrimidin-4 (3 H)-one derivatives. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1370–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavetsias, V.; Lanigan, R.M.; Ruda, G.F.; Atrash, B.; McLaughlin, M.G.; Tumber, A.; Mok, N.Y.; Le Bihan, Y.-V.; Dempster, S.; Boxall, K.J. 8-Substituted Pyrido [3, 4-d] pyrimidin-4 (3 H)-one Derivatives as Potent, Cell Permeable, KDM4 (JMJD2) and KDM5 (JARID1) Histone Lysine Demethylase Inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 1388–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, M.; Gehling, V.S.; Gustafson, A.; Arora, S.; Tindell, C.A.; Wilson, C.; Williamson, K.E.; Guler, G.D.; Gangurde, P.; Manieri, W. An inhibitor of KDM5 demethylases reduces survival of drug-tolerant cancer cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumber, A.; Nuzzi, A.; Hookway, E.S.; Hatch, S.B.; Velupillai, S.; Johansson, C.; Kawamura, A.; Savitsky, P.; Yapp, C.; Szykowska, A. Potent and selective KDM5 inhibitor stops cellular demethylation of H3K4me3 at transcription start sites and proliferation of MM1S myeloma cells. Cell Chem. Biology 2017, 24, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Z.; Shi, L.; Lai, C.; O’Connell, S.M.; Xu, J.; Stansfield, R.K.; Hosfield, D.J.; Veal, J.M.; Stafford, J.A. Structure-based design and discovery of potent and selective KDM5 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1490–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Liang, Q.; Ren, H.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Ma, L.-Y.; Zheng, Y.-C.; Liu, H.-M. Discovery of pyrazole derivatives as cellular active inhibitors of histone lysine specific demethylase 5B (KDM5B/JARID1B). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 192, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleire, L.; Førde, H.E.; Netland, I.A.; Leiss, L.; Skeie, B.S.; Enger, P.Ø. Drug repurposing in cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 124, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyer, L.; Nencka, R.; De Clercq, E.; Seley-Radtke, K.; Růžek, D. Nucleoside analogs as a rich source of antiviral agents active against arthropod-borne flaviviruses. Antivir. Chem. Chemother. 2018, 26, 2040206618761299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damaraju, V.L.; Damaraju, S.; Young, J.D.; Baldwin, S.A.; Mackey, J.; Sawyer, M.B.; Cass, C.E. Nucleoside anticancer drugs: The role of nucleoside transporters in resistance to cancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7524–7536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tănase, C.I.; Drăghici, C.; Cojocaru, A.; Galochkina, A.V.; Orshanskaya, J.R.; Zarubaev, V.V.; Shova, S.; Enache, C.; Maganu, M. New carbocyclic N6-substituted adenine and pyrimidine nucleoside analogues with a bicyclo [2.2. 1] heptane fragment as sugar moiety; synthesis, antiviral, anticancer activity and X-ray crystallography. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 6346–6354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinan, M.; Benckendorff, C.; Smith, M.; Miller, G.J. Recent Advances in the Chemical Synthesis and Evaluation of Anticancer Nucleoside Analogues. Molecules 2020, 25, E2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Chinnasamy, N.; Hong, J.A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xi, S.; Liu, F.; Marquez, V.E.; Morgan, R.A.; Schrump, D.S. Inhibition of histone lysine methylation enhances cancer–testis antigen expression in lung cancer cells: Implications for adoptive immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4192–4204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohamed, T.; Rao, P.P. 2, 4-Disubstituted quinazolines as amyloid-β aggregation inhibitors with dual cholinesterase inhibition and antioxidant properties: Development and structure-activity relationship (SAR) studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 126, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, J.R.; Liu, X.; Gale, M.; Wu, L.; Shanks, J.R.; Zhang, X.; Webber, P.J.; Bell, J.S.; Kales, S.C.; Mott, B.T. Structural basis for KDM5A histone lysine demethylase inhibition by diverse compounds. Cell Chem. Biol. 2016, 23, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jose, A.; Shenoy, G.G.; Sunil Rodrigues, G.; Kumar, N.A.N.; Munisamy, M.; Thomas, L.; Kolesar, J.; Rai, G.; Rao, P.P.N.; Rao, M. Histone Demethylase KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2020, 12, 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082121
Jose A, Shenoy GG, Sunil Rodrigues G, Kumar NAN, Munisamy M, Thomas L, Kolesar J, Rai G, Rao PPN, Rao M. Histone Demethylase KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2020; 12(8):2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082121
Chicago/Turabian StyleJose, Anmi, Gautham G. Shenoy, Gabriel Sunil Rodrigues, Naveena A. N. Kumar, Murali Munisamy, Levin Thomas, Jill Kolesar, Ganesha Rai, Praveen P. N. Rao, and Mahadev Rao. 2020. "Histone Demethylase KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy" Cancers 12, no. 8: 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082121
APA StyleJose, A., Shenoy, G. G., Sunil Rodrigues, G., Kumar, N. A. N., Munisamy, M., Thomas, L., Kolesar, J., Rai, G., Rao, P. P. N., & Rao, M. (2020). Histone Demethylase KDM5B as a Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 12(8), 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12082121