Epstein–Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Establishment of Primary Nasopharyngeal Epithelial Cell Cultures
2.2. EBV Infects a Conventional Monolayer of Nasopharyngeal Epithelial Cells
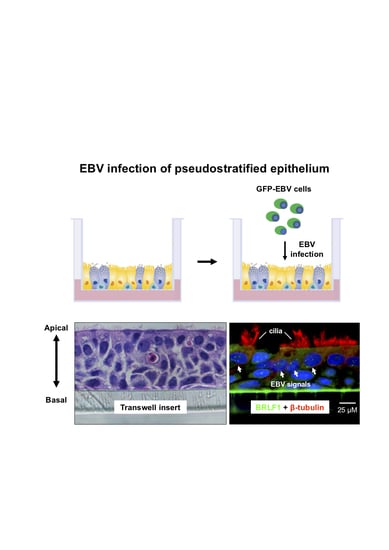
2.3. EBV Infects Pseudostratified Epithelia Formed by Primary Nasopharyngeal Epithelial Cells
2.4. Predominant EBV Infection of the Suprabasal Layer Cells
2.5. EBV Infection Disrupts the Integrity of the Epithelium
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biopsy Collection and Cell Culture
4.2. ALI Culture
4.3. TEER and CBF Measurements
4.4. Immunostaining and ISH
4.5. Virus Production and Infection
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borza, C.M.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Alternate replication in B cells and epithelial cells switches tropism of Epstein-Barr virus. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.P.; Chan, A.T.C.; Le, Q.T.; Blanchard, P.; Sun, Y.; Ma, J. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet 2019, 394, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, S.W.; Tsang, C.M.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W. The role of Epstein–Barr virus in epithelial malignancies. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Middeldorp, J.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A. Epstein-Barr virus infection in ex vivo tonsil epithelial cell cultures of asymptomatic carriers. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12613–12624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heawchaiyaphum, C.; Iizasa, H.; Ekalaksananan, T.; Burassakarn, A.; Kiyono, T.; Kanehiro, Y.; Yoshiyama, H.; Pientong, C. Epstein-Barr virus infection of oral squamous cells. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Q.; Young, L.S.; Niedobitek, G.; Dawson, C.W.; Birkenback, M.; Wang, F.; Rickinson, A.B. Epstein–Barr virus infection and replication in a human epithelial cell system. Nature 1992, 356, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tugizov, S.M.; Berline, J.W.; Palefsky, J.M. Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized tongue and nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caves, E.A.; Cook, S.A.; Lee, N.; Stoltz, D.; Watkins, S.; Shair, K.H.Y. Air-liquid interface method to study Epstein-Barr virus pathogenesis in nasopharyngeal epithelial cells. mSphere 2018, 3, 00152-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Tay, J.K.; Yoshiyama, H.; Loh, K. Establishment of EBV latency in nasopharyngeal tumor epithelial cells by in vivo cell-mediated transfer infection. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2018, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maruo, S.; Yang, L.; Takada, K. Roles of Epstein-Barr virus glycoproteins gp350 and gp25 in the infection of human epithelial cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2001, 82, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, N.; Yoshiyama, H.; Takada, K. Clonal propagation of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) recombinants in EBV-negative Akata cells. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 7260–7263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, L.S.; Dawson, C.W. Epstein-Barr virus and nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Chin. J. Cancer 2014, 33, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, S.T.; Huang, D.P.; Hui, A.B.; Lo, K.W.; Ko, C.W.; Tsang, Y.S.; Wong, N.; Whitney, B.M.; Lee, J.C. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 83, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon-Lowe, C.; Rowe, M. Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized epithelial cells via the basolateral surface by memory B cell-mediated transfer infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nanbo, A.; Kachi, K.; Yoshiyama, H.; Ohba, Y. Epstein-Barr virus exploits host endocytic machinery for cell-to-cell viral transmission. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2989–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faulkner, G.C.; Burrows, S.R.; Khanna, R.; Moss, D.J.; Bird, A.G.; Crawford, D.H. X-Linked agammaglobulinemia patients are not infected with Epstein-Barr virus. J. Virol. 1999, 73, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Petersson, F.; Wang, D.Y.; Loh, K.S. Presence of lytic Epstein-Barr virus infection in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Head Neck 2018, 40, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, R.M.; Zhu, J.; Budgeon, L.; Christensen, N.D.; Meyers, C.; Sample, C.E. Efficient replication of Epstein-Barr virus in stratified epithelium in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16544–16549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.P.; Ho, J.H.; Poon, Y.F.; Chew, E.C.; Saw, D.; Lui, M.; Li, C.L.; Mak, L.S.; Lai, S.H.; Lau, W.H. Establishment of a cell line (NPC/HK1) from a differentiated squamous carcinoma of the nasopharynx. Int. J. Cancer 1980, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawandar, D.M.; Wang, A.; Makielski, K.; Lee, D.; Ma, S.; Barlow, E.; Reusch, J.; Jiang, R.; Wille, C.K.; Greenspan, D.; et al. Differentiation-dependent KLF4 expression promotes lytic Epstein-Barr virus infection in epithelial cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015, 11, e1005195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquitz, A.R.; Mathur, A.; Shair, K.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Infection of Epstein-Barr virus in a gastric carcinoma cell line induces anchorage independence and global changes in gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9593–9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yip, Y.L.; Lin, W.; Deng, W.; Jia, L.; Lo, K.W.; Busson, P.; Vérillaud, B.; Liu, X.; Tsang, C.M.; Lung, M.L.; et al. Establishment of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell line capable of undergoing lytic Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Lab. Investig. 2018, 98, 1093–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathmanathan, R.; Prasad, U.; Sadler, R.; Flynn, K.; Raab-Traub, N. Clonal proliferations of cells infected with Epstein-Barr virus in preinvasive lesions related to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, L.S.; Yap, L.F.; Murray, P.G. Epstein-Barr virus: More than 50 years old and still providing surprises. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.S.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W.; Mak, K.F.; Pak, W.; Chiu, B.; Tse, G.M.; Ding, M.; Li, X.; Lee, J.C.; et al. High frequency of chromosome 3p deletion in histologically normal nasopharyngeal epithelia from southern Chinese. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5365–5370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Tao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, D.; Wang, L.; Petersson, F.; Yoshiyama, H.; Koeffler, P.H.; Goh, B.C.; et al. Non-malignant epithelial cells preferentially proliferate from nasopharyngeal carcinoma biopsy cultured under conditionally reprogrammed conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Yu, F.; Li, C.; Li, Y.; Chao, S.S.; Loh, W.S.; Pan, X.; Shi, L.; Wang, D.Y. The use of nasal epithelial stem/progenitor cells to produce functioning ciliated cells in vitro. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2012, 26, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.T.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhu, H.C.; Wang, F.X.; Li, G.Y.; Wen, D.S.; Li, Y.P.; Tsai, C.H.; Glaser, R. Establishment and characterization of two epithelial tumor cell lines (HNE-1 and HONE-1) latently infected with Epstein-Barr virus and derived from nasopharyngeal carcinomas. Int. J. Cancer 1990, 45, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Li, C.W.; Chao, S.S.; Yu, F.G.; Yu, X.M.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y.; Shen, L.; Gordon, W.; Shi, L.; et al. Impairment of cilia architecture and ciliogenesis in hyperplastic nasal epithelium from nasal polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1282–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisson, J.H.; Stoner, J.A.; Ammons, B.A.; Wyatt, T.A. All-digital image capture and whole-field analysis of ciliary beat frequency. J. Microsc. 2003, 211, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, A.T.; Wolfe, D. Tissue processing and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1180, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, F.; Lu, Y.; Li, Y.; Uchio, Y.; Pangnguriseng, U.A.; Kartika, A.V.; Iizasa, H.; Yoshiyama, H.; Loh, K.S. Epstein–Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity. Cancers 2020, 12, 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092722
Yu F, Lu Y, Li Y, Uchio Y, Pangnguriseng UA, Kartika AV, Iizasa H, Yoshiyama H, Loh KS. Epstein–Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity. Cancers. 2020; 12(9):2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092722
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Fenggang, Yanan Lu, Yingying Li, Yuji Uchio, Utomo Andi Pangnguriseng, Andy Visi Kartika, Hisashi Iizasa, Hironori Yoshiyama, and Kwok Seng Loh. 2020. "Epstein–Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity" Cancers 12, no. 9: 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092722
APA StyleYu, F., Lu, Y., Li, Y., Uchio, Y., Pangnguriseng, U. A., Kartika, A. V., Iizasa, H., Yoshiyama, H., & Loh, K. S. (2020). Epstein–Barr Virus Infection of Pseudostratified Nasopharyngeal Epithelium Disrupts Epithelial Integrity. Cancers, 12(9), 2722. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092722