Simple Summary
This retrospective study analyzed 237 consecutive patients with coexisting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic hepatitis B (NAFLD-CHB) with long observation period (median follow-up duration, 13 years). The optimal cutoff for the FIB-4 index of 1.77 was calculated based on the maximum Youden index value, and the value was 1.77 with an AUC of 0.70. The significant higher risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) than the patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.35; 95% CI, 1.42–13.24; log-rank test, p = 0.006) were found among the NAFLD-CHB patients whose baseline characteristics were balanced by propensity score matching. The FIB-4 index might be a useful predictor of the development of HCC among NAFLD–CHB patients.
Abstract
Background: The FIB-4 index, a noninvasive tool (FIB-4 index = age × aspartate transaminase (AST)/(platelet count × √alanine aminotransferase (ALT)), is a useful assessment for liver fibrosis. Patients with a high FIB-4 index were reported to have a high risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This study analyzed the clinical association of the FIB-4 index with HCC development in patients with coexisting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic hepatitis B (NAFLD–CHB). Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 237 consecutive patients with NAFLD–CHB between January 2006 and December 2010 at the National Police Hospital in Korea. Patients with HCC at baseline and those diagnosed with HCC within 6 months from baseline were excluded. Propensity score matching analysis (PSM) was adopted to balance the baseline characteristics between patients with low and high FIB-4 index values. The cumulative rates of HCC development were compared between the two groups using the Kaplan–Meier method in the matched population. Results: The median follow-up duration was 13 years (interquartile range, 8.2–15.7). The optimal cutoff for the FIB-4 index of 1.77 was calculated based on the maximum Youden index value, with an AUC of 0.70. Among a total of 237 patients with NAFLD–CHB, HCC developed in 20 patients (8.4%) (14 of the 90 patients with a high FIB-4 index vs. 6 of the 147 patients (4.1%) with a low FIB-4 index; log-rank p = 0.003). Patients with a high FIB-4 index had a significantly and independently higher risk of HCC than those with a low FIB-4 index (adjusted hazard ratio, 4.35; 95%; confidence interval, 1.42–13.24; log-rank test, p = 0.006). Conclusion: A high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) might be a useful marker for predicting the development of HCC in patients with NAFLD–CHB.
1. Introduction
In 2020, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) was the sixth most common cancer and the third most common cause of cancer-related death worldwide [1]. HCC develops mainly in patients with risk factors such as nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), chronic hepatitis B (CHB), and chronic hepatitis C [2].
NAFLD is defined as an excessive accumulation of hepatic steatosis due to a cause other than alcohol consumption [3]. NAFLD is the most common liver disease and is estimated to have a 25% prevalence rate worldwide [4]. The prevalence of NAFLD is approximately 24% in North America, approximately 20–30% in Europe, and approximately 15–40% in Asia [5]. The number of patients with CHB is estimated to be between 240 million and 350 million, and it is particularly common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa [6]. As incidences of NAFLD are rapidly increasing, the number of patients with coexisting NAFLD and CHB (NAFLD–CHB) is also increasing [7].
The prognosis of NAFLD–CHB was reported to be worse than that of either NAFLD or CHB alone. In Asia, it was reported that patients with NAFLD–CHB had a 7.3-fold higher risk of developing HCC than CHB patients without NAFLD [8,9]. Similarly, in North America, CHB patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) had a 1.7-fold higher risk of developing HCC than CHB patients without NASH [7]. Considering the increasing number of patients with NAFLD–CHB, and the fact that this population has a high risk of developing HCC, there is a need for a means of stratifying NAFLD–CHB patients according to their risk of developing HCC.
The FIB-4 index is a noninvasive tool (i.e., FIB-4 index = age × aspartate aminotransferase (AST)/platelet count × √alanine aminotransferase (ALT)) for assessing hepatic fibrosis [10]. The FIB-4 index is easy to use in clinical practice and has a comparable diagnostic capability for advanced fibrosis to that of magnetic resonance elastography [11]. Therefore, the FIB-4 index might be useful for the prediction of the risk of HCC. In previous studies, a high FIB-4 index was reported as a significant risk factor for developing HCC in patients with CHB [12,13,14] and patients with NAFLD [15,16].
In this study, we evaluated the clinical value of the FIB-4 index for the prediction of the development of HCC in patients with NAFLD–CHB.
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design
This study included consecutive patients with NAFLD–CHB seen between January 2006 and December 2010 at the National Police Hospital in Korea. Clinical, laboratory, and imaging data (i.e., abdominal ultrasonography) on the date of the initial visit between January 2006 and December 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. Laboratory evaluations included total bilirubin, AST, ALT, total cholesterol, glucose levels, and viral serology for hepatitis. Body mass index (BMI, weight (kg)/height (m)2), the hepatic-steatosis index score (HSI, 8 × ALT/AST ratio + BMI (+2 if diabetes mellitus; +2 if female)), and FIB-4 index were calculated at baseline [10,17]. Patients were classified as having NAFLD if they had sonographic findings characteristic of NAFLD and/or an HSI score >36. The use of antiviral medication for hepatitis B at baseline was defined as having a prescription within 1 year from baseline, and the use of antiviral agents after baseline was defined as having a prescription for more than a year during the observation period [12]. The use of aspirin or statins was defined by having a prescription for more than 30 days during the observation period.
All patients were monitored at 6-month intervals at minimum based on the international hepatitis B virus (HBV) guidelines for HCC surveillance [18,19]. The cumulative rates of HCC development were compared between the groups with high and low FIB-4 indices using the Kaplan–Meier method.
The development of HCC was diagnosed on the basis of the typical hallmarks of HCC: arterial phase hyperenhancement with washout in the portal venous or delayed phases on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging using contrast agents [20]. Patients were followed-up with until the date of diagnosis of HCC or the last visit before the data cutoff date, which was 31 December 2020.
This study was conducted in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and the principles of good clinical practice. The need to obtain informed consent was waived due to the retrospective design of the study, which was approved by the institutional review board (IRB No.11100176-202102-HR-002).
2.2. Patients
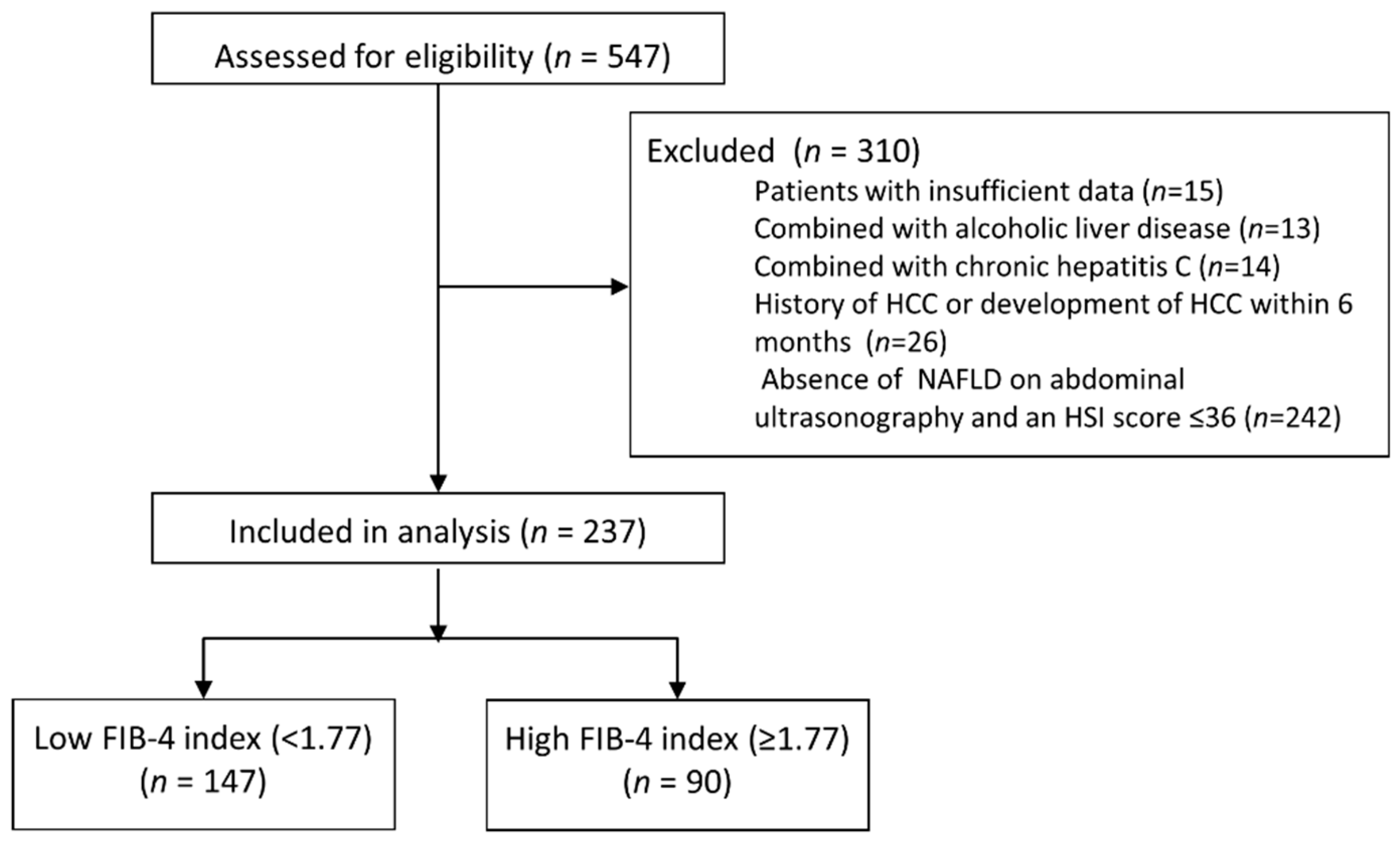
The inclusion criteria for the study subjects were as follows: (i) the persistence of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in serum samples for at least 6 months and (ii) the history of undergoing abdominal ultrasonography at baseline. A total of 547 patients satisfied the inclusion criteria. Among them, 310 patients were excluded based on the following exclusion criteria: (i) insufficient laboratory data (=15), (ii) significant alcohol intake (more than 60 g/day in both sexes; n = 13), (iii) combined with chronic hepatitis C (n = 14), (iv) hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at baseline or a diagnosis of HCC within 6 months after the date of enrollment (n = 26), and (v) absence of NAFLD on abdominal ultrasonography or an HSI score ≤36 (n = 242) (Figure 1) [21]. Finally, 237 patients were included in the study.
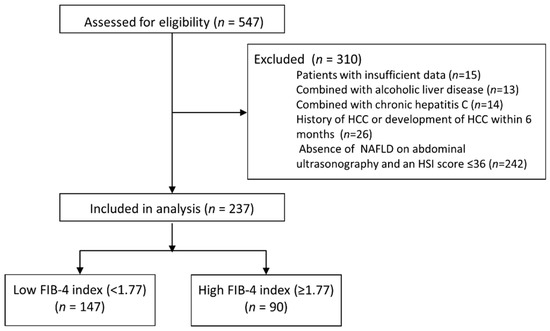
Figure 1.
CONSORT diagram. Of the 547 eligible patients, 310 were excluded from the study in accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Finally, 237 patients were included: 147 in the low FIB-4 group (<1.77) and 90 patients in the high FIB-4 group (≥1.77).
2.3. Statistical Analysis
The patients were divided into two groups according to the optimal cutoff value of the FIB-4 index for the prediction of the development of HCC. Patient baseline characteristics were compared between the two groups using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables and the Mann–Whitney U test for continuous variables. Propensity score matching (PSM) was performed to adjust potential confounders: sex, age, diabetes mellitus, ultrasonographic liver cirrhosis, BMI, history of drug use (i.e., antiviral agents at baseline, antiviral agents after baseline, aspirin, and statin), and HBV DNA levels [22]. The balance of the baseline characteristics between the two groups was re-evaluated after PSM.
To identify independent predictors of developing HCC, univariable Cox proportional hazard analysis and multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis with backward stepwise regression were performed in the PSM cohort. Variables with p < 0.2 in univariable analysis were included in the multivariable analysis. If the variables in the multivariate analysis included two variables with a correlation coefficient greater than or equal to 0.4, only one variable with a lower p-value was included in the multivariable analysis. The correlation coefficients were calculated by using phi correlations between binary variables and biserial correlations between dichotomous and continuous variables. The development of HCC was assessed with Kaplan–Meier curves, and the two groups were compared with a log-rank test. All statistical analyses were performed using R software version 3.5.2 (http://www.r-project.org (accessed on 1 May 2021)). All tests were two-tailed, and p-values < 0.05 were considered significant.
2.4. Sensitivity Analysis
Two sensitivity tests were performed to support the results. First, the sensitivity analysis according to the change of the cutoff value of FIB-4 was performed among entire cohort (n = 237). Severe fibrosis (i.e.; F3-F4) increases the risk of developing HCC [23,24]. The minimum cutoff value of the FIB-4 index for F3-F4 was 1.3, and the maximum cutoff value was 2.67 [25,26,27]. The negative predictive value (NPV) of a FIB-4 cutoff value <1.3 was 90–95%, and the positive predictive value (PPV) of a FIB-4 cutoff value >2.67 was 80%. Based on previous studies on the FIB-4 index, we conducted a sensitivity analysis by dividing the patients into three groups as follows: FIB-4 index < 1.3, 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67, and FIB-4 index > 2.67. For the analysis, one-way ANOVA and the Kruskal–Wallis test were used.
The second sensitivity analysis was performed to verify whether the results were changed according to the NAFLD diagnostic tool. The patients were classified as having NAFLD if they had sonographic findings characteristic of NAFLD.
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
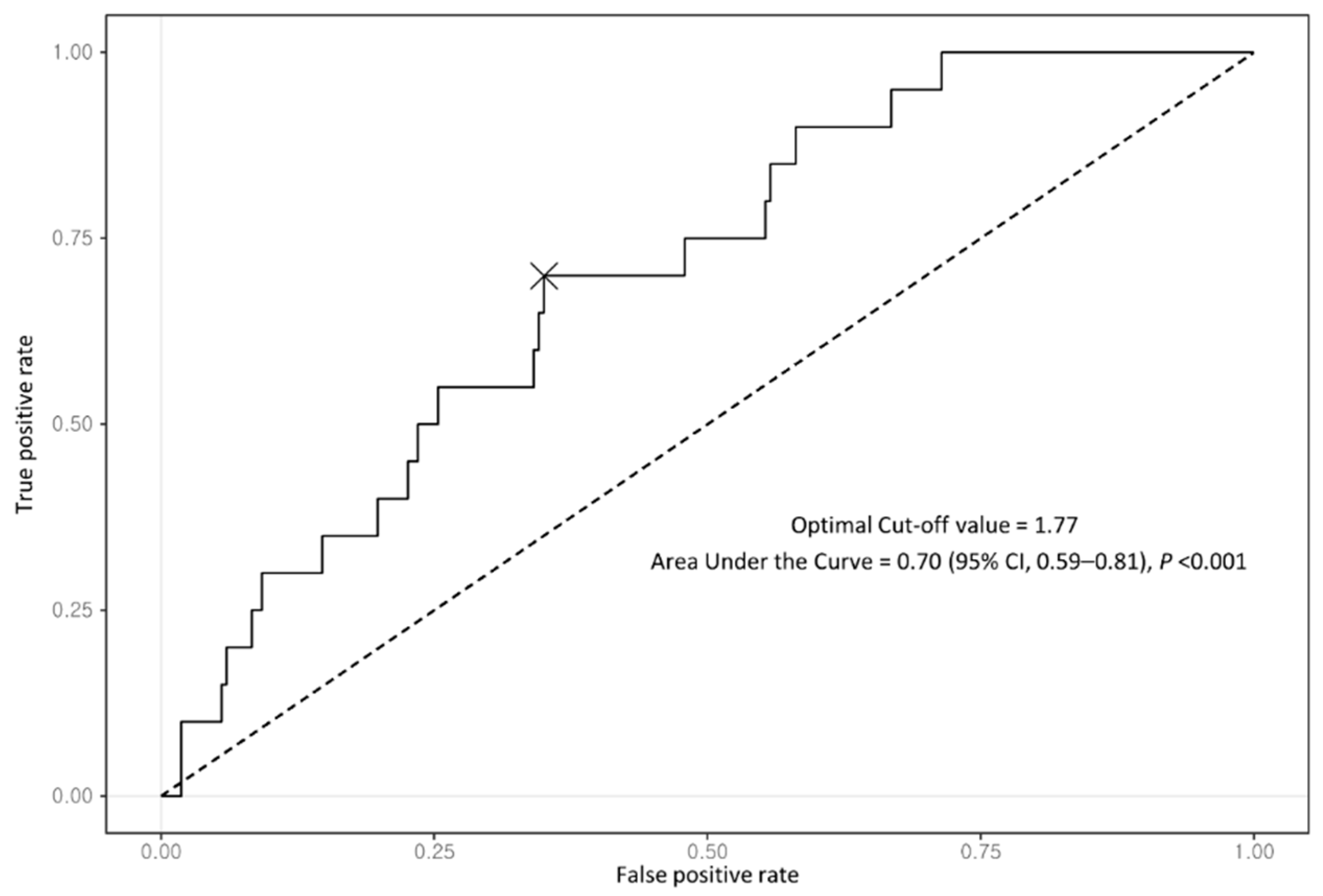
A total of 237 patients with coexisting NAFLD–CHB were included in this analysis. All patients showed positive HBsAg at baseline. Of them, 132 patients (55.7%) were treated with antiviral agents: the largest proportion of patients (72; 54.5%) took entecavir, followed by tenofovir disoproxil (29.5%), lamivudine (8.3%), adefovir (5.3%), and tenofovir alafenamide (2.3%) (Table 1). The median follow-up duration in the entire cohort was 13.0 years (interquartile range (IQR), 8.2–15.7 years). During the follow-up period, 20 patients (8.4%) were newly diagnosed with HCC. All patients were divided into two groups according to the optimal FIB-4 index cutoff, which had the best performance with regard to predicting the development of HCC based on the maximum Youden index value. The optimal cutoff for the FIB-4 index was 1.77 with an area under the curve of 0.70 (95% CI, 0.59–0.81) (Figure 2).

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the NAFLD–CHB patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) and NALFD-CHB patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77).
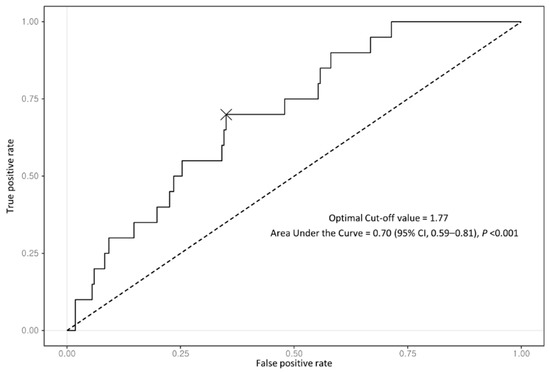
Figure 2.
Receiver operating characteristic curve of FIB-4 index for predicting HCC development in entire cohort.
Among the entire cohort, 90 patients (38.0%) had a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77), and 147 patients (62.0%) had a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) at baseline. During the follow-up period, 14 patients (15.6%) in the high FIB-4 group developed HCC, and 6 patients (4.1%) in the low FIB-4 group developed HCC (log-rank test, p = 0.003). Overall, the median time to the development of HCC from baseline was 8.0 years (IQR, 5.9–10.2 years). There was no significant difference in the time to the development of HCC between the high FIB-4 group and the low FIB-4 group (8.0 years vs. 8.1 years, p = 0.72).
At baseline, there were no significant differences in the proportion of patients with HBeAg positivity and elevated serum HBV DNA levels (>2000 IU/mL) between the two groups. However, the proportion of patients using antiviral agents was significantly higher in the high FIB-4 group than in the low FIB-4 group (64.4% vs. 50.3%, p = 0.047).
After PSM, the baseline characteristics were well balanced between the high and low FIB-4 groups except the FIB-4 index components (Table 1). The variables associated with CHB, including the use of antiviral agents at baseline (36.7% vs. 46.7%, p = 0.23), HBeAg positivity (50.2% vs. 52.2%, p = 0.89), and serum HBV DNA levels (42.2% vs. 38.9%, p = 0.76), were not significantly different between the two groups. In contrast, variables used in the calculation of the FIB-4 index, namely, age (46.5 years vs. 51.5 years, p < 0.001), AST level (24.0 IU/L vs. 49.0 IU/L, p < 0.001), ALT level (34.5 IU/L vs. 63.5 IU/L, p < 0.001), and platelet count (193.0 × 109/L vs. 156.5 × 109/L, p = 0.001), were significantly different between the two groups.
There were two pairs of variables that showed a correlation coefficient greater than or equal to 0.4. The correlation coefficient between the use of antiviral agents at baseline and the use of antiviral agents after base line was 0.68; the correlation coefficient between the use of aspirin and the use of statin was 0.56 (Supplementary Figure S1).
3.2. Risk Factors for Developing HCC in NAFLD–CHB Patients
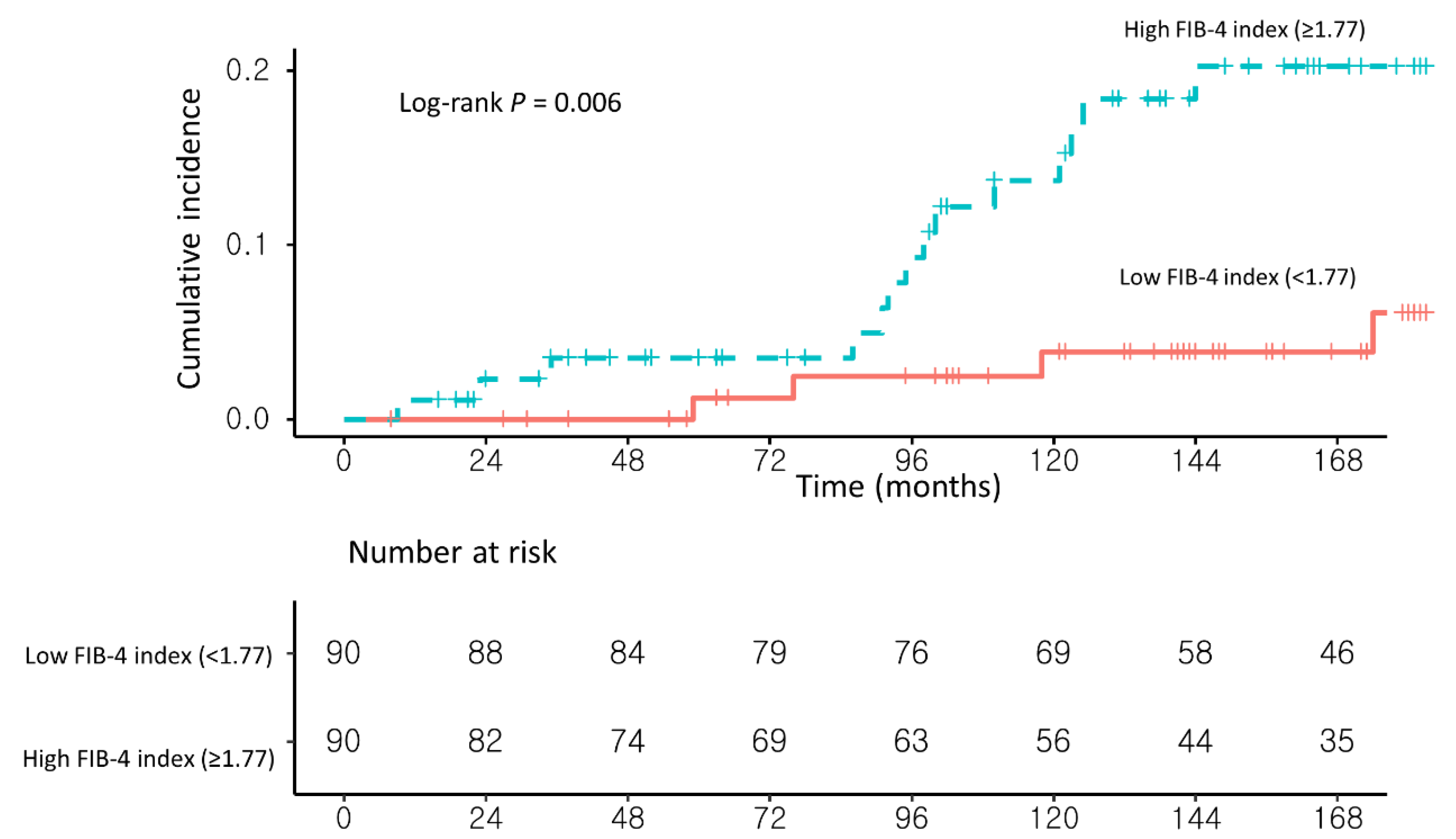
In univariable analysis, a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) and the presence of liver cirrhosis on USG (USG-LC) were significantly associated with the development of HCC. In multivariable Cox proportional hazard analysis with stepwise regression, patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) had a significantly higher risk of HCC development than those with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) (adjusted hazard ratio (Ahr), 4.35; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.42–13.24; log-rank test, p = 0.006; Table 2 and Figure 3).

Table 2.
Risk factors of HCC development in the propensity score matched cohort.
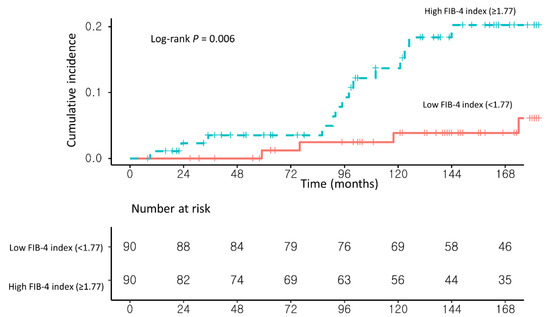
Figure 3.
Propensity score-matched Kaplan–Meier estimates of HCC incidence in (1) NAFLD–CHB patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) and (2) NAFLD–CHB patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77).
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
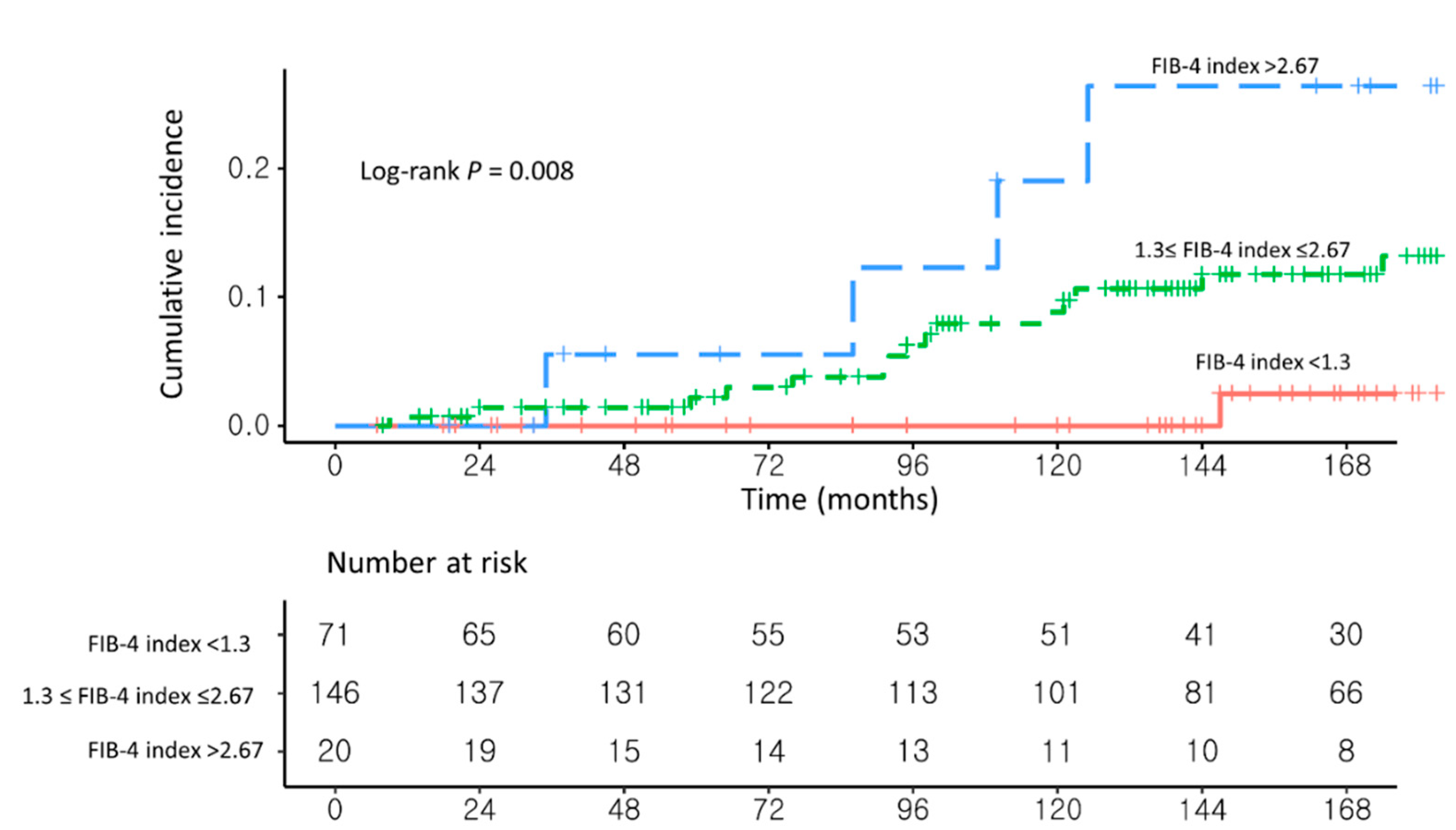
As a sensitivity analysis, the risk factors for HCC development were analyzed in three groups: FiB-4 index < 1.3 (n = 71), 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67 (n = 146), and FIB-4 index > 2.67 (n = 20; Supplementary Table S1). Patients with a FIB-4 index >2.67 had a significantly higher risk of developing HCC than those with a FIB-4 index <1.3 (aHR, 12.51, 95% CI, 1.36–115.03; p = 0.02; Figure 4 and Supplementary Table S2). Similarly, patients with a 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67 had a higher risk of developing HCC than those with a FIB-4 index <1.3 (aHR, 5.10; 95% CI, 0.67–38.88; p = 0.12).
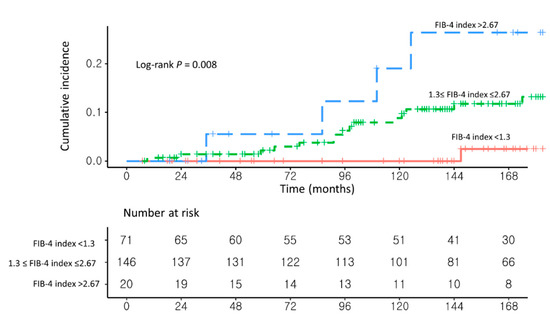
Figure 4.
Unadjusted Kaplan–Meier estimates of HCC incidence in (1) NAFLD–CHB patients with FIB-4 index < 1.3, (2) NAFLD–CHB patients with 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67, and (3) NAFLD–CHB patients with FIB-4 index > 2.67.
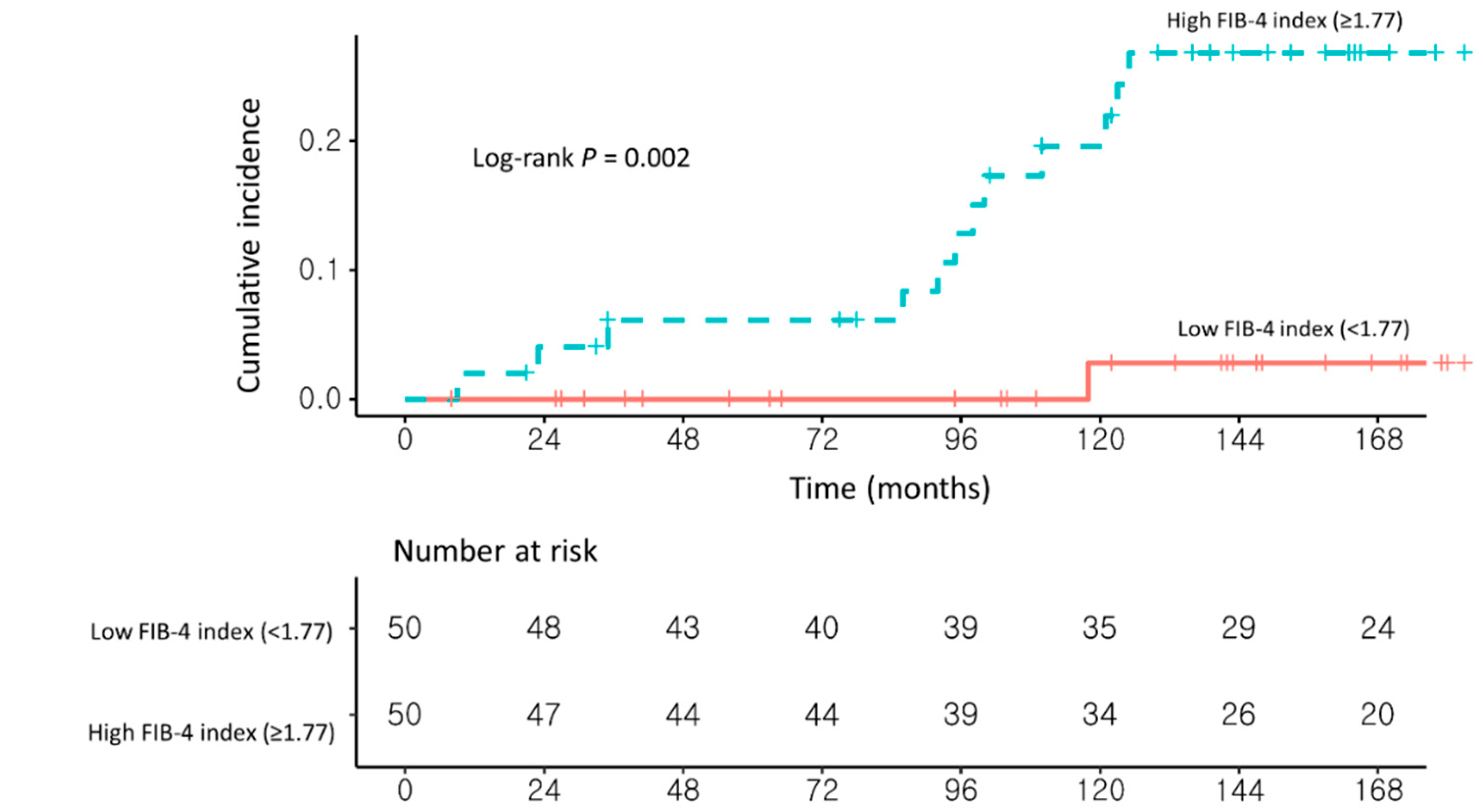
In the second sensitivity analysis, 131 patients were classified as having NAFLD according to ultrasonographic findings. After PSM, patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77; n = 50) had a significantly higher risk of HCC development than those with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77; n = 50; aHR, 20.59; 95% CI, 2.54–166.65; log-rank test, p = 0.002; Figure 5 and Supplementary Table S3).
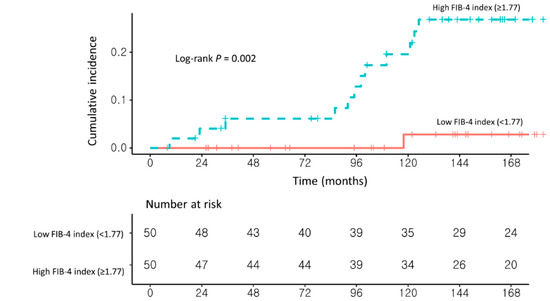
Figure 5.
Propensity score-matched Kaplan–Meier estimates of HCC incidence in (1) NAFLD–CHB patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77) and (2) NAFLD–CHB patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) among ultrasonographic NAFLD patients.
4. Discussion
In this study, the risk of developing HCC was significantly higher in NAFLD–CHB patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) than in those with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77; aHR, 4.35; 95% CI, 1.42–13.24; log-rank p = 0.006). Analysis of long-term follow-up data of NAFLD–CHB patients showed that patients at a higher risk of developing HCC could be identified using the FIB-4 index, which is simple and easy to use in clinical practice.
We were able to estimate hepatic fibrosis with the FIB-4 index based on the patient’s age and the results of simple blood tests (i.e., the AST level, ALT level, and platelet count) [10]. Age, AST and ALT levels, and the platelet count are known to be associated with hepatic fibrosis [28,29,30]. Studies performed after the development of the FIB-4 index verified that the FIB-4 index can be used to identify advanced fibrosis in patients with NAFLD, CHB, or chronic hepatitis C [27,31,32,33,34]. Of course, the gold standard for the diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis is liver biopsy. However, considering the difficulty of performing invasive biopsies in all NAFLD–CHB patients, the FIB-4 index might be suitable as a clinical tool for the evaluation of hepatic fibrosis.
Hepatic fibrosis is a well-known risk factor for the development of HCC [35,36]. Therefore, we hypothesized that the risk of developing HCC could be predicted using the FIB-4 index. Recent studies have suggested a role of the FIB-4 index as a prognostic predictor in patients with CHB or NAFLD. Suh et al. reported that a high FIB-4 index had better predictive value for the development of HCC than USG-LC among patients with CHB [12]. Kanwal et al. also reported that NAFLD patients without cirrhosis and a low FIB-4 index had a significantly lower incidence of HCC than those with a high FIB-4 index (cutoff value = 2.67) [15].
In this study, NAFLD–CHB patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) had a higher risk of developing HCC than patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77). To verify this result, a sensitivity analysis was performed based on the cutoff values used in previous studies: FIB-4 index < 1.3, 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67 (as the gray zone), and FIB-4 index > 2.67 [15,25,26,27]. Consistent with the results of the main analysis, patients with a FIB-4 index >2.67 had a significantly higher risk of developing HCC than patients with a FIB-4 index <1.3 (aHR, 12.51, 95% CI, 1.36–115.03, p = 0.02). The presence of the gray zone enabled the detection of a significant difference between the upper and lower groups.
This study stratified the risk of developing HCC in NAFLD–CHB patients, who are at an elevated risk of developing HCC [8,9]. Chan et al. reported that coexisting NAFLD was an independent risk factor for HCC development by 7.3-folds in CHB patients. Similarly, Lee et al. reported that coexisting NAFLD was associated with a 3-fold increased risk for HCC development in CHB patients. In CHB patients who with an already high risk of developing HCC, the mechanism by which NAFLD–CHB further increases the risk is unclear. Insulin resistance, which is common in patients with NAFLD, may increase the risk of developing HCC [37]. Under the influence of insulin resistance, increased free fatty acids promote intracellular oxidative stress and the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). High ROS levels serially damage DNA and induce hypoadiponectinemia [38]. In one animal experiment, hypoadiponectinemia was associated with a risk of developing HCC [39]. Changes in gut microbiota or increased platelet activation may also influence hepatocarcinogenesis [40,41].
Among NAFLD–CHB patients, those with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) are at high risk for HCC. Surveillance should be based on the risk of developing HCC in the target population, which aims to reduce the patient’s HCC-related death [20]. Patients diagnosed with HCC at a very early stage can expect a 5-year survival rate of 8–90% through resection or ablation treatment [42], and patients diagnosed with HCC at an early stage can expect a 5-year survival rate of 5–60% through resection, liver transplantation or ablation treatment. On the other hand, patients diagnosed at an advanced stage who receive systemic therapies can expect median survival times of 6–8 months. As a tool for screening patients at high-risk of developing HCC, the use of the FIB-4 index in surveillance programs may contribute to improving the prognosis of NAFLD–CHB patients.
Several limitations of this study must be acknowledged. Because the present study was retrospective in nature, there were significant differences in baseline characteristics between the high FIB-4 index and the low FIB-4 index group. To overcome this limitation, we applied two statistical methods: a multivariable Cox proportional hazard model and PSM. In addition, since this was a study conducted on patients at the National Police Hospital in Korea, the cohort was predominantly male (90.3%), and since this study was only conducted in Korea, it did not reflect regional differences, especially between non-Asian countries and Asian countries.
In conclusion, over a mean 13-year follow-up period, patients with a high FIB-4 index (≥1.77) had a significantly higher risk of developing HCC than patients with a low FIB-4 index (<1.77). The FIB-4 index might be a useful predictor of the development of HCC among NAFLD–CHB patients. Large-scale prospective studies are needed in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cancers13102301/s1, Figure S1: The heatmap of correlation coeffients among the propensity score matched cohort, Table S1: Baseline characteristics of the NAFLD-CHB patients with FIB-4 index < 1.3, the NAFLD-CHB patients with 1.3 ≤ FIB-4 index ≤ 2.67, and the NAFLD-CHB patients with FIB-4 index > 2.67, Table S2: Risk factors of HCC development in the entire cohort, and Table S3: Risk factors of HCC development in the propensity score matched cohort among ultrasonographic NAFLD patients.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K., S.W.K. and Y.C.; methodology, M.K. and S.S.K.; software, S.W.K.; validation, Y.C. and J.S.Y.; formal analysis, S.W.K.; data curation, M.K., Y.L. and S.S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K., S.W.K. and Y.C.; writing—review and editing, J.S.Y. and M.L.; funding acquisition, Y.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (HI21C0240) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant, funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (2021R1A2C4001401).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of National Police Hospital, Seoul, Korea (IRB No.11100176-202102-HR-002, 25 March 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable. This study is a retrospective study that is unlikely to cause harm to the patients studied. Therefore, informed consent was waived under IRB review.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- World Health Organization; Globocan. Liver Fact Sheet. Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/11-Liver-fact-sheet.pdf. (accessed on 20 February 2021).
- Refolo, M.G.; Messa, C.; Guerra, V.; Carr, B.I.; D’Alessandro, R. Inflammatory Mechanisms of HCC Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.; Chan, W.K.; Chitturi, S.; Chawla, Y.; Dan, Y.Y.; Duseja, A.; Fan, J.; Goh, K.L.; Hamaguchi, M.; Hashimoto, E.; et al. Asia-Pacific Working Party on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease guidelines 2017-Part 1: Definition, risk factors and assessment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Plank, L.D.; Suk, K.T.; Park, Y.E.; Lee, J.; Choi, J.H.; Heo, N.Y.; Park, J.; Kim, T.O.; Moon, Y.S.; et al. Trends in the prevalence of chronic liver disease in the Korean adult population, 1998–2017. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2020, 26, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacLachlan, J.H.; Cowie, B.C. Hepatitis B virus epidemiology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a021410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.J.; Brouwer, W.P.; Zanjir, W.M.R.; de Man, R.A.; Feld, J.J.; Hansen, B.E.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Patel, K. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Is Associated With Liver-Related Outcomes and All-Cause Mortality in Chronic Hepatitis B. Hepatology 2020, 71, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.W.; Wong, G.L.; Chan, H.Y.; Tong, J.H.; Yu, Y.H.; Choi, P.C.; Chan, H.L.; To, K.F.; Wong, V.W. Concurrent fatty liver increases risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.B.; Ha, Y.; Chon, Y.E.; Kim, M.N.; Lee, J.H.; Park, H.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, S.H.; Rim, K.S.; Hwang, S.G. Association between hepatic steatosis and the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Hui, J.M.; Marchesini, G.; Bugianesi, E.; George, J.; Farrell, G.C.; Enders, F.; Saksena, S.; Burt, A.D.; Bida, J.P.; et al. The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology 2007, 45, 846–854. [Google Scholar]
- Imajo, K.; Kessoku, T.; Honda, Y.; Tomeno, W.; Ogawa, Y.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Taguri, M.; Hyogo, H.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Imaging More Accurately Classifies Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Than Transient Elastography. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 626–637.e627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, B.; Park, S.; Shin, D.W.; Yun, J.M.; Yang, H.K.; Yu, S.J.; Shin, C.I.; Kim, J.S.; Ahn, E.; Lee, H.; et al. High liver fibrosis index FIB-4 is highly predictive of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B carriers. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, T.-C.; Liu, C.-J.; Su, T.-H.; Yang, W.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Yang, H.-C.; Wang, C.-C.; Kuo, S.F.-T.; Liu, C.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; et al. Fibrosis-4 index helps identify HBV carriers with the lowest risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gasteroenterol. 2017, 112, 1564–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Lai, H.C.; Hu, T.H.; Su, W.P.; Lu, S.N.; Lin, C.H.; Hung, C.H.; Chuang, P.H.; Wang, J.H.; Lee, M.H.; et al. Stratification of hepatocellular carcinoma risk through modified FIB-4 index in chronic hepatitis B patients on entecavir therapy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 34, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Mapakshi, S.; Natarajan, Y.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Richardson, P.A.; Li, L.; Desiderio, R.; Thrift, A.P.; Asch, S.M.; et al. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1828–1837.e1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, M.; Loomis, A.K.; van der Lei, J.; Duarte-Salles, T.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Ansell, D.; Pasqua, A.; Lapi, F.; Rijnbeek, P.; Mosseveld, M.; et al. Risks and clinical predictors of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma diagnoses in adults with diagnosed NAFLD: Real-world study of 18 million patients in four European cohorts. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Kim, D.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, C.-H.; Yang, J.I.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Cho, S.-H.; Sung, M.-W.; et al. Hepatic steatosis index: A simple screening tool reflecting nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. Clinical practice guidelines for management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2019, 25, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrault, N.A.; Lok, A.S.; McMahon, B.J.; Chang, K.M.; Hwang, J.P.; Jonas, M.M.; Brown, R.S.; Bzowej, N.H.; Wong, J.B. Update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic hepatitis B: AASLD 2018 hepatitis B guidance. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1560–1599. [Google Scholar]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 182–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of alcohol-related liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 154–181. [Google Scholar]
- Haukoos, J.S.; Lewis, R.J. The Propensity Score. JAMA 2015, 314, 1637–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Kim, W.R.; Coelho, R.; Mettler, T.A.; Benson, J.T.; Sanderson, S.O.; Therneau, T.M.; Kim, B.; Roberts, L.R. Cirrhosis is present in most patients with hepatitis B and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2011, 9, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattovich, G.; Bortolotti, F.; Donato, F. Natural history of chronic hepatitis B: Special emphasis on disease progression and prognostic factors. J. Hepatol. 2008, 48, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Corey, K.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Noureddin, M.; Jacobson, I.; Lam, B.; Clement, S.; Basu, R.; Gordon, S.C.; Ravendhra, N.; et al. Clinical assessment for high-risk patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in primary care and diabetology practices. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2020, 52, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, A.G.; Lydecker, A.; Murray, K.; Tetri, B.N.; Contos, M.J.; Sanyal, A.J.; Nash Clinical Research, N. Comparison of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seko, Y.; Yano, K.; Takahashi, A.; Okishio, S.; Kataoka, S.; Okuda, K.; Umemura, A.; Yamaguchi, K.; Moriguchi, M.; Tanaka, S.; et al. The Appropriate Opportunity for Evaluating Liver Fibrosis by Using the FIB-4 Index in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japan. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macías, J.; Girón-González, J.A.; González-Serrano, M.; Merino, D.; Cano, P.; Mira, J.A.; Arizcorreta-Yarza, A.; Ruíz-Morales, J.; Lomas-Cabeza, J.M.; García-García, J.A.; et al. Prediction of liver fibrosis in human immunodeficiency virus/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients by simple non-invasive indexes. Gut 2006, 55, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, R.J.; Lok, A.S.F. Noninvasive monitoring of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, S57–S64. [Google Scholar]
- Calès, P.; Oberti, F.; Michalak, S.; Hubert-Fouchard, I.; Rousselet, M.C.; Konaté, A.; Gallois, Y.; Ternisien, C.; Chevailler, A.; Lunel, F. A novel panel of blood markers to assess the degree of liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2005, 42, 1373–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, M.; Imajo, K.; Takahashi, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Eguchi, Y.; Sumida, Y.; Yoneda, M.; Kawanaka, M.; Saito, S.; Tokushige, K.; et al. Clinical strategy of diagnosing and following patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease based on invasive and noninvasive methods. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 181–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davyduke, T.; Tandon, P.; Al-Karaghouli, M.; Abraldes, J.G.; Ma, M.M. Impact of Implementing a “FIB-4 First” Strategy on a Pathway for Patients With NAFLD Referred From Primary Care. Hepatol. Commun. 2019, 3, 1322–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.R.; Berg, T.; Asselah, T.; Flisiak, R.; Fung, S.; Gordon, S.C.; Janssen, H.L.; Lampertico, P.; Lau, D.; Bornstein, J.D.; et al. Evaluation of APRI and FIB-4 scoring systems for non-invasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B patients. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fattovich, G.; Stroffolini, T.; Zagni, I.; Donato, F. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Incidence and risk factors. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, S35–S50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Goossens, N.; Hoshida, Y. Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 526–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, L.; Leung, L.; Yen, T.S.; Lee, C.; Chan, J.Y. Liver-specific inactivation of the Nrf1 gene in adult mouse leads to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic neoplasia. Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 2005, 102, 4120–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Fujita, T.; Shimabukuro, M.; Iwaki, M.; Yamada, Y.; Nakajima, Y.; Nakayama, O.; Makishima, M.; Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 114, 1752–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamada, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Tamura, S.; Fukushima, J.; Kiso, S.; Fukui, K.; Igura, T.; Maeda, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; et al. Hypoadiponectinemia accelerates hepatic tumor formation in a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis mouse model. J. Hepatol. 2007, 47, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Bhoori, S.; Castelli, C.; Putignani, L.; Rivoltini, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Morelli, D.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Petito, V.; et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with gut microbiota profile and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malehmir, M.; Pfister, D.; Gallage, S.; Szydlowska, M.; Inverso, D.; Kotsiliti, E.; Leone, V.; Peiseler, M.; Surewaard, B.G.; Rath, D.; et al. Platelet GPIbα is a mediator and potential interventional target for NASH and subsequent liver cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 641–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makary, M.S.; Khandpur, U.; Cloyd, J.M.; Mumtaz, K.; Dowell, J.D. Locoregional therapy approaches for hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advances and management strategies. Cancers 2020, 12, 1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).