Radiomics in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Nodules: Explorations, Application, and Limitations
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction to Thyroid Cancer
1.1. The Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Thyroid Cancer
1.2. Imaging Techniques for DTC Detection
2. Introduction to Radiomics
2.1. The Definition of Radiomics
2.2. Radiomic Features
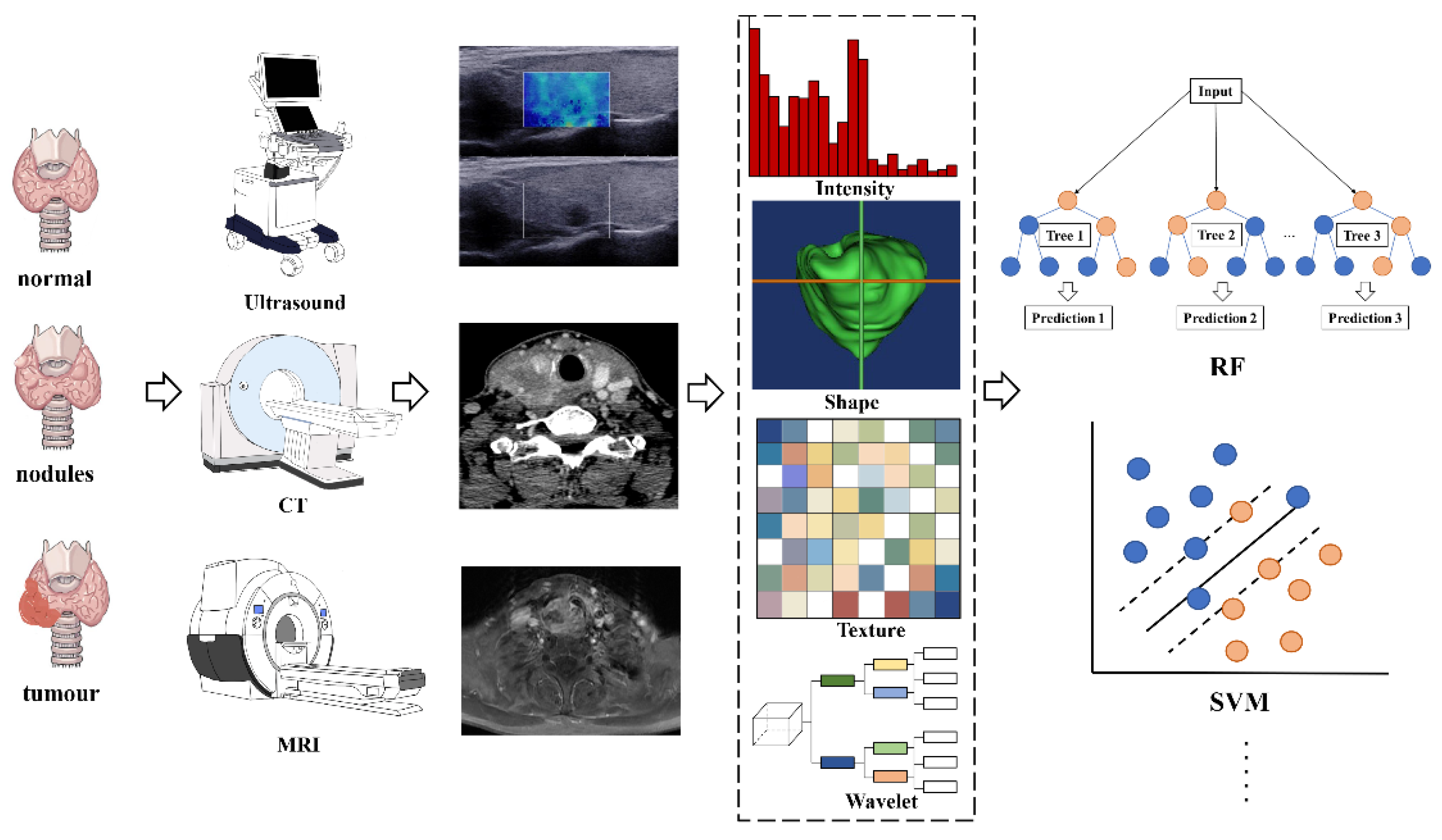
2.3. The Workflow of Radiomics
2.4. Clinical Applications of Radiomics
3. Literature Search Strategy
4. Radiomics in Thyroid Cancer Prediction
5. Radiomics in Thyroid Cancer and Nodule Classification
6. Limitations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bychkov, A.; Saenko, V.; Nakashima, M.; Mitsutake, N.; Rogounovitch, T.; Nikitski, A.; Orim, F.; Yamashita, S. Patterns of FOXE1 expression in papillary thyroid carcinoma by immunohistochemistry. Thyroid 2013, 23, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laetitia, G.; Sven, S.; Fabrice, J. Combinatorial Therapies in Thyroid Cancer: An Overview of Preclinical and Clinical Progresses. Cells 2020, 9, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Deng, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhou, J.; Jia, X.; Xiao, T.; Zhou, S.; Li, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Lymph node metastasis prediction of papillary thyroid carcinoma based on transfer learning radiomics. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, K.; Nagahama, M.; Kitagawa, W.; Ohkuwa, K.; Uruno, T.; Matsuzu, K.; Suzuki, A.; Tomoda, C.; Hames, K.Y.; Akaishi, J.; et al. Distant Metastasis in Pediatric and Adolescent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: Clinical Outcomes and Risk Factor Analyses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e3981–e3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccardo, A.; Siri, G.; Raffa, S.; Castellana, M.; Foppiani, L.; Bottoni, G.; Ugolini, M.; Cistaro, A.; Catrambone, U.; Altrinetti, V.; et al. How to better stratify the risk of differentiated thyroid carcinomas: The key role of radioactive iodine therapy, age, and gender. Eur. J. Nuclear Med. Mol. Imaging 2021, 48, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Guan, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, W.; Li, J.; Xu, K.; Li, C.; Ai, Q.; Lu, W.; Liang, H.; et al. Cancer patients in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A nationwide analysis in China. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, M.E.; McFadden, D.G.; Durante, C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.; Krapcho, M.; Miller, D.; Bishop, K.; Altekruse, S. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2013; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2015.
- Filetti, S.; Durante, C.; Hartl, D.; Leboulleux, S.; Locati, L.D.; Newbold, K.; Papotti, M.G.; Berruti, A. Thyroid cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up†. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2019, 30, 1856–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; Lin, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.; Gao, Q.; Xi, X.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Lai, X.; Zhu, S.; et al. Ultrasound characteristics of cervical lesions in patients with radioiodine refractory differentiated thyroid cancer: A strobe-compliant article. Medicine 2019, 98, e17876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferri, E.L.; Jhiang, S.M. Differentiated thyroid cancer long-term impact of initial therapy. Trans. Am. Clin. Climatol. Assoc. 1995, 106, 151–168, discussion 168–170. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzaferri, E.L.; Kloos, R.T. Clinical review 128: Current approaches to primary therapy for papillary and follicular thyroid cancer. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1447–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, D.S.; Doherty, G.M.; Haugen, B.R.; Kloos, R.T.; Lee, S.L.; Mandel, S.J.; Mazzaferri, E.L.; McIver, B.; Sherman, S.I. Tuttle RM: Management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2006, 16, 109–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naing, S.; Collins, B.J.; Schneider, A.B. Clinical behavior of radiation-induced thyroid cancer: Factors related to recurrence. Thyroid Off. J. Am. Thyroid. Assoc. 2009, 19, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.Y.; Kim, W.Y.; Hwang, T.S.; Lee, S.S.; Kim, H.; Han, H.S.; Lim, S.D.; Kim, W.S.; Yoo, Y.B.; Park, K.S. BRAF and RAS mutations in follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 2013, 24, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, D.S.; Hay, I.D. Prognostic indicators in differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Control. J. Moffitt Cancer Cent. 2000, 7, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegedüs, L. Clinical practice. The thyroid nodule. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1764–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.; Farrell, S.G.; Grossmann, M. Thyroid nodules: Diagnosis and management. Med. J. Aust. 2018, 209, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, D.S.; Gharib, H. Epidemiology of thyroid nodules. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 22, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolotov, S. Genetic Testing in Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma: Indications and Clinical Implications. Rambam Maimonides Med. J. 2016, 7, e0009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Intenzo, C.M.; Dam, H.Q.; Manzone, T.A.; Kim, S.M. Imaging of the thyroid in benign and malignant disease. Semin. Nuclear Med. 2012, 42, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; He, X.; Ma, L.; Li, M.; Sun, L.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, Q. Multimode ultrasonic technique is recommended for the differential diagnosis of thyroid cancer. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, J.S.; Schmidt, R.A.; La Rivière, P.J. Full-field acoustomammography using an acousto-optic sensor. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 2324–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, J.K.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, M.; Johnson, D.; Farrell, S. US Features of thyroid malignancy: Pearls and pitfalls. Radiogr. A Rev. Publ. Radiol. Soc. N. Am. Inc. 2007, 27, 847–860, discussion 845–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonavita, J.A.; Mayo, J.; Babb, J.; Bennett, G.; Oweity, T.; Macari, M.; Yee, J. Pattern recognition of benign nodules at ultrasound of the thyroid: Which nodules can be left alone? AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 193, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, J.K.; Branstetter, B.F.; Gafton, A.R.; Lee, W.K.; Glastonbury, C.M. Imaging of thyroid carcinoma with CT and MRI: Approaches to common scenarios. Cancer Imaging 2013, 13, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rana, K.A.; Meyer, J.; Ibrahim, S.; Ralls, M.; Kent, P.M. The role of imaging of malignant bone tumors in children and young adults. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2013, 37, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.M.; Levin, D.C.; Parker, L.; Frangos, A.J.; Sunshine, J.H. Trends in utilization rates of the various imaging modalities in emergency departments: Nationwide Medicare data from 2000 to 2008. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2011, 8, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang, J.K.; Choudhury, K.R.; Eastwood, J.D.; Esclamado, R.M.; Lyman, G.H.; Shattuck, T.M.; Nguyen, X.V. An exponential growth in incidence of thyroid cancer: Trends and impact of CT imaging. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marcus, C.; Whitworth, P.W.; Surasi, D.S.; Pai, S.I.; Subramaniam, R.M. PET/CT in the management of thyroid cancers. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 202, 1316–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdem, G.; Erdem, T.; Muammer, H.; Mutlu, D.Y.; Firat, A.K.; Sahin, I.; Alkan, A. Diffusion-weighted images differentiate benign from malignant thyroid nodules. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging JMRI 2010, 31, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueller-Weidekamm, C.; Kaserer, K.; Schueller, G.; Scheuba, C.; Ringl, H.; Weber, M.; Czerny, C.; Herneth, A. Can Quantitative Diffusion-Weighted MR Imaging Differentiate Benign and Malignant Cold Thyroid Nodules? Initial Results in 25 Patients. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2008, 30, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Moreira, A.L.; Hatzoglou, V.; Stambuk, H.E.; Gonen, M.; Mazaheri, Y.; Deasy, J.O.; Shaha, A.R.; Tuttle, R.M.; Shukla-Dave, A. Using Diffusion-Weighted MRI to Predict Aggressive Histological Features in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Novel Tool for Pre-Operative Risk Stratification in Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2015, 25, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, J.R.; Byun, B.H.; Hong, S.P.; Chong, A.; Kim, J.; Yoo, S.W.; Kang, S.R.; Kim, D.Y.; Song, H.C.; Bom, H.S.; et al. Comparison of 131I whole-body imaging, 131I SPECT/CT, and 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of metastatic thyroid cancer. Eur. J. Nuclear Med. Mol. Imaging 2011, 38, 1459–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spanu, A.; Nuvoli, S.; Marongiu, A.; Gelo, I.; Mele, L.; Piras, B.; Madeddu, G. Neck lymph node metastasis detection in patients with differentiated thyroid carcinoma (DTC) in long-term follow-up: A (131)I-SPECT/CT study. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barwick, T.; Murray, I.; Megadmi, H.; Drake, W.M.; Plowman, P.N.; A Akker, S.; Chew, S.L.; Grossman, A.B.; Avril, N. Single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/computed tomography using Iodine-123 in patients with differentiated thyroid cancer: Additional value over whole body planar imaging and SPECT. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, M.-J.; Liu, Z.-F.; Zhao, K.; Ruan, L.-X.; Wang, G.-L.; Yang, S.-Y.; Sun, F.; Luo, X.-G. Value of 18F-FDG-PET/PET-CT in differentiated thyroid carcinoma with radioiodine-negative whole-body scan: A meta-analysis. Nuclear Med. Commun. 2009, 30, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ahn, B.-C.; Lee, J. Recurrence detection in differentiated thyroid cancer patients with elevated serum level of antithyroglobulin antibody: Special emphasis on using18F-FDG PET/CT. Clin. Endocrinol. 2010, 72, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; De Jong, E.E.; Van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; LaRue, R.T.; Even, A.J.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conti, A.; Duggento, A.; Indovina, I.; Guerrisi, M.; Toschi, N. Radiomics in breast cancer classification and prediction. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rizzo, S.; Botta, F.; Raimondi, S.; Origgi, D.; Fanciullo, C.; Morganti, A.G.; Bellomi, M. Radiomics: The facts and the challenges of image analysis. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Griethuysen, J.J.M.; Fedorov, A.; Parmar, C.; Hosny, A.; Aucoin, N.; Narayan, V.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pieper, S.; Aerts, H.J.W.L. Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e104–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Traverso, A.; Wee, L.; Dekker, A.; Gillies, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 102, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moyaa, L.; Zakeri, H.; Yamazakic, H.; Liuc, W.; Masa, E.; Koshimura, S. 3D gray level co-occurrence matrix and its application to identifying collapsed buildings. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 149, 14–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergen, B.; Baykara, M. Texture based feature extraction methods for content based medical image retrieval systems. Bio-Med. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 3055–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Materka, A.; Langs, G.; Häggström, I.; Szczypiński, P.; Gibbs, P.; Cook, G. Introduction to Radiomics. J. Nuclear Med. Off. Publ. Soc. Nuclear Med. 2020, 61, 488–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Xing, L.; Napel, S.; Rubin, D.L. Radiomics and Radiogenomics: Technical Basis and Clinical Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Gu, Y.; Basu, S.; Berglund, A.; Eschrich, S.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Forster, K.; Aerts, H.J.; Dekker, A.; Fenstermacher, D.; et al. Radiomics: The process and the challenges. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1234–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, R.; Devaraj, A. Radiomics of pulmonary nodules and lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2017, 6, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; The PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed) 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B. Sonographic features of primary tumor as independent predictive factors for lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Transl. Oncol. Off. Publ. Fed. Span. Oncol. Soc. Natl. Cancer Inst. Mex. 2015, 17, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, D.M.; Leboulleux, S.; Al Ghuzlan, A.; Baudin, E.; Chami, L.; Schlumberger, M.; Travagli, J.-P. Optimization of staging of the neck with prophylactic central and lateral neck dissection for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viola, D.; Materazzi, G.; Valerio, L.; Molinaro, E.; Agate, L.; Faviana, P.; Seccia, V.; Sensi, E.; Romei, C.; Piaggi, P.; et al. Prophylactic central compartment lymph node dissection in papillary thyroid carcinoma: Clinical implications derived from the first prospective randomized controlled single institution study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Ge, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Cui, L. Comparison of the application of B-mode and strain elastography ultrasound in the estimation of lymph node metastasis of papillary thyroid carcinoma based on a radiomics approach. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2018, 13, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Zhou, S.; Yu, J.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chang, C. Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Radiomics Method Based on Preoperative Ultrasound Images. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819831713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Li, C.; Tang, S.; Lv, W.; Yi, A.; Wang, B.; Yu, S.; Cui, X.; Dietrich, C.F. Nomogram Based on Shear-Wave Elastography Radiomics Can Improve Preoperative Cervical Lymph Node Staging for Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Thyroid 2020, 30, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Pan, D.; He, Y.; Wu, Y.; Peng, J.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, J. Using ultrasound features and radiomics analysis to predict lymph node metastasis in patients with thyroid cancer. BMC Surg. 2020, 20, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Zhong, L.Z.; Dong, D.; Fang, M.J.; Dai, Q.; Leng, S.Y.; Zhang, L.W.; Sun, W.; Tian, J.; Zheng, J.J.; et al. Radiomic analysis for preoperative prediction of cervical lymph node metastasis in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2019, 118, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Wei, R.; Wang, L.; Dai, Z.; Duan, S.; Ge, Y.; Wu, P.-Y.; Song, B. MRI-based radiomics analysis to predict preoperative lymph node metastasis in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Gland. Surg. 2020, 9, 1214–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hu, S.; Wang, X.; He, J.; Liu, W.; Yu, C.; Sun, Z.; Ge, Y.; Duan, S. Prediction of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis Using MRI Radiomics Approach in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Feasibility Study. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820969451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, G.W.; Duh, Q.Y.; Heller, K.S.; LiVolsi, V.A.; Mandel, S.J.; Steward, D.L.; Tufano, R.P.; Tuttle, R.M. The prognostic significance of nodal metastases from papillary thyroid carcinoma can be stratified based on the size and number of metastatic lymph nodes, as well as the presence of extranodal extension. Thyroid 2012, 22, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Tomoda, C.; Uruno, T.; Takamura, Y.; Miya, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsuzuka, F.; Kuma, K.; Miyauchi, A. Ultrasonographically and anatomopathologically detectable node metastases in the lateral compartment as indicators of worse relapse-free survival in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2005, 29, 917–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.C.; Liu, T.T.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Y.X.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J.H.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chang, C. An Ultrasound Radiomics Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Central Neck Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Li, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Liu, T.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Chang, C. Ultrasound-Based Radiomic Nomogram for Predicting Lateral Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Acad. Radiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, V.Y.; Han, K.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, E.; Youk, J.H.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kwak, J.Y. Radiomics signature for prediction of lateral lymph node metastasis in conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.-J.; Wei, P.; Ding, Z.; Luo, D.; Qian, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, H.; Cai, W.; Zhang, M. Computed Tomography Radiomics for the Preoperative Prediction of Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Development and External Validation. Res. Sq. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-26914/v1 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Kwon, M.R.; Shin, J.H.; Park, H.; Cho, H.; Kim, E.; Hahn, S.Y. Radiomics Based on Thyroid Ultrasound Can Predict Distant Metastasis of Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhong, L.Z.; Dong, D.; Zheng, J.J.; Fang, M.J.; Yu, C.Y.; Dai, Q.; Zhang, L.W.; Tian, J.; Lu, W.; et al. Computed Tomography Radiomic Nomogram for Preoperative Prediction of Extrathyroidal Extension in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Hu, W.; Sun, X.; Dai, Z.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Ge, Y.; Song, B. Radiomics Based on Multiparametric MRI for Extrathyroidal Extension Feature Prediction in Papillary Thyroid Cancer. BMC Med. Imaging 2020, 21, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Park, V.; Han, K.; Lee, E.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kwak, J.Y. Association between radiomics signature and disease-free survival in conventional papillary thyroid carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, J.H.; Han, K.; Lee, E.; Lee, J.; Kim, E.-K.; Moon, H.J.; Park, V.; Nam, K.H.; Kwak, J.Y. Radiomics in predicting mutation status for thyroid cancer: A preliminary study using radiomics features for predicting BRAFV600E mutations in papillary thyroid carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, E.; Jeon, M.J.; Oh, H.-S.; Han, M.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, T.Y.; Chung, K.-W.; Kim, W.B.; Shong, Y.K.; Song, D.E.; et al. Do aggressive variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma have worse clinical outcome than classic papillary thyroid carcinoma? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 179, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Song, B.; Ye, N.R.; Ren, J.L.; Sun, X.L.; Dai, Z.D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.H.T. Machine learning-based multiparametric MRI radiomics for predicting the aggressiveness of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 122, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schadow, S.; Simons, V.S.; Lochnit, G.; Kordelle, J.; Gazova, Z.; Siebert, H.C.; Steinmeyer, J. Metabolic Response of Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage to Biochemically Characterized Collagen Hydrolysates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; Srivastava, A.; Yu, W.; Liu, C.; Wei, D.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Risk Factors That Influence Surgical Decision-Making for Patients with Low-Risk Differentiated Thyroid Cancer with Tumor Diameters of 1–4 cm. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 12423–12428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.Y.; Choi, H.S.; Park, Y.J.; Lim, J.A.; Ahn, H.Y.; Lee, E.K.; Kim, K.W.; Yi, K.H.; Chung, J.K.; Youn, Y.K.; et al. Changes in the clinicopathological characteristics and outcomes of thyroid cancer in Korea over the past four decades. Thyroid 2013, 23, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Londero, S.C.; Krogdahl, A.; Bastholt, L.; Overgaard, J.; Pedersen, H.B.; Hahn, C.H.; Bentzen, J.; Schytte, S.; Christiansen, P.; Gerke, O.; et al. Papillary thyroid carcinoma in Denmark, 1996–2008: Outcome and evaluation of established prognostic scoring systems in a prospective national cohort. Thyroid 2015, 25, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Alzahrani, A.S.; Carson, K.A.; Viola, D.; Elisei, R.; Bendlova, B.; Yip, L.; Mian, C.; Vianello, F.; Tuttle, R.M.; et al. Association between BRAF V600E mutation and mortality in patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Jama 2013, 309, 1493–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kwon, M.R.; Shin, J.H.; Park, H.; Cho, H.; Hahn, S.Y.; Park, K.W. Radiomics Study of Thyroid Ultrasound for Predicting BRAF Mutation in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: Preliminary Results. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2020, 41, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guth, S.; Theune, U.; Aberle, J.; Galach, A.; Bamberger, C.M. Very high prevalence of thyroid nodules detected by high frequency (13 MHz) ultrasound examination. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, J.P.; Morris, J.C.; Montori, V.M. Thyroid cancer: Zealous imaging has increased detection and treatment of low risk tumours. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed) 2013, 347, f4706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prochazka, A.; Gulati, S.; Holinka, S.; Smutek, D. Classification of Thyroid Nodules in Ultrasound Images Using Direction-Independent Features Extracted by Two-Threshold Binary Decomposition. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2019, 18, 1533033819830748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colakoglu, B.; Alis, D.; Yergin, M. Diagnostic Value of Machine Learning-Based Quantitative Texture Analysis in Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, V.Y.; Lee, E.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, J.; Son, J.; Song, K.; Moon, H.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Kim, G.R.; et al. Combining radiomics with ultrasound-based risk stratification systems for thyroid nodules: An approach for improving performance. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.; Lee, E.; Kang, S.-W.; Han, K.; Park, V.Y.; Kwak, J.Y. Implications of US radiomics signature for predicting malignancy in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 2021, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.-K.; Ren, T.-T.; Yin, Y.-F.; Shi, H.; Wang, H.-X.; Zhou, B.-Y.; Wang, X.-R.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.-F.; Liu, C.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of Two Machine Learning-Based Diagnostic Patterns with Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System for Thyroid Nodules: Diagnostic Performance and Unnecessary Biopsy Rate. Thyroid 2021, 31, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Ge, Y.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhai, J. Construction and Validation of Two-Level CT-Based Radiomics Models Used for Thyroid Cancer Screening in the Population. 2020. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3703901 (accessed on 18 November 2020).
- Zhou, H.; Jin, Y.; Dai, L.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, K.; Tian, J.; Zheng, J. Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant thyroid nodules using deep learning radiomics of thyroid ultrasound images. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 127, 108992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Yue, W.W.; Li, X.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Guo, L.H.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Yang, G. Comparison Study of Radiomics and Deep Learning-Based Methods for Thyroid Nodules Classification Using Ultrasound Images. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 52010–52017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference | Prediction Category | No. Patients | Imaging Method | ROI Segmentation Method | No. Radiomics Features | Model Construction | Validation Method | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liu et al. (2018) [56] | LNM | 75 | US and SEUS | manual | US + SWE: 25 US: 36 SWE: 9 | SVM | LOOCV | US + SEUS: 77 US: 63 SEUS: 71 | US + SEUS: 88 US: 89 SEUS: 75 | US + SEUS:85 US: 83 SEUS: 74 | US+SEUS: 0.90 US: 0.81 SEUS: 0.80 |
| Liu et al. (2019) [57] | LNM | 450 | US images | manual | 50 | SVM | 10-fold CV | 67.9 | 72.5 | 71.1 | 0.783 |
| Jiang et al. (2019) [58] | LNM | training: 147 EV: 90 | SWE images | manual | 4 | LASSO logistic regression | 10-fold CV | training: 80.67 EV: 86.84 | training: 82.7 EV: 73.08 | training: 78.91 EV: 78.89 | training: 0.851 EV: 0.832 |
| Li et al. (2020) [59] | LNM | 126 | US images | manual | 91 | hypothesis-testing and bagging | NA | training: 90 test: 72.7 | training: 86 test: 80 | NA | training: 0.759 test: 0.803 |
| Zhou et al. (2020) [65] | LNM | training: 609 test: 326 | US images | manual | 23 | LASSO logistic regression | NA | training: 82.5 test: 81.6 | training: 78.6 test: 81.0 | training: 79.8 test: 81.2 | training: 0.87 test: 0.858 |
| Tong et al. (2020) [66] | LNM | training: 600 test: 286 | US images | manual | 21 | LASSO logistic regression | NA | training: 74.5 test: 77.4 | training: 82.6 test: 83.1 | NA | training: 0.877 test:0.862 |
| Park et al. (2020) [67] | LNM | training: 400 test: 368 | US images | manual | 14 | LASSO logistic regression | 10-fold CV | NA | NA | NA | training: 0.71 test: 0.621 |
| Yu et al. (2020) [3] | LNM | training: 1013 IT1: 368 IT2: 513 | US images | manual | NA | TLR;SM;RM;NTLR | NA | SM: 72 (training); 43 (IT1); 68 (IT2) RM: 71 (training); 36 (IT1); 47 (IT2) NTLR: 75 (training); 71 (IT1); 67 (IT2) TLR: 94 (training); 83 (IT1); 95 (IT2) | SM: 82 (training); 87 (IT1); 67 (IT2) RM: 57 (training); 72 (IT1); 69 (IT2) NTLR: 81 (training); 81 (IT1); 78 (IT2) TLR: 77 (training); 89 (IT1); 75 (IT2) | SM: 77 (training); 61 (IT1); 67 (IT2) RM: 62 (training); 51 (IT1); 60 (IT2) NTLR: 79 (training); 75 (IT1); 73 (IT2) TLR: 84 (training); 86 (IT1); 84 (IT2) | SM: 0.83(training); 0.67(IT1); 0.67(IT2) RM: 0.64(training); 0.55(IT1); 0.57(IT2) NTLR: 0.82(training); 0.81(IT1); 0.79(IT2) TLR: 0.93(training); 0.93(IT1); 0.93(IT2) |
| Lu et al. (2019) [60] | LNM | training: 154 test: 67 | CT | manual | 8 radiomic sub-signatures | SVM | NA | NA | NA | training: 73.4 test: 64.2 | training: 0.759 test: 0.706 |
| Hu et al. (2020) [61] | LNM | training: 90 test: 39 | MRI | manual | 30 | LASSO logistic regression | NA | T2WI model: 62.2 DWI model: 86.7 T1C+ model: 68.9 Combined model: 88.9 | T2WI model: 87.2 DWI model: 70.2 T1C+ model: 83 Combined model: 72.3 | T2WI model: 75.0 DWI model: 78.3 T1C+ model: 76.1 Combined model: 80.4 | T2WI model: 0.819 DWI model: 0.826 T1C+ model: 0.808 Combined model: 0.835 |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [62] | LNM | 61 | MRI | manual | 10 | RF | LOOCV | T2WI: 83 T2WI-FS: 83 | T2WI: 100 T2WI-FS: 90 | T2WI: 87 T2WI-FS: 82 | T2WI: 0.85 T2WI-FS: 0.80 |
| Kwon et al. (2020) [69] | DM | 169 | US images | manual | 6 | SVM | 5-fold CV | training: 92 test: 80 | training: 87 test: 87 | training: 88 test: 85 | training: 0.93 test: 0.90 |
| Wang et al. (2019) [75] | Aggressiveness | 120 | MRI | manual | 5 | LSSO + GBC LSVM + LRCV LSVM + PAC LSVM + LSVC | 10-fold CV | NA | NA | NA | train: 0.874; 0.979;0.971; 0.805; 0.974 test: 0.915; 0.731; 0.731; 0.885; 0.708 |
| Chen et al. (2020) [70] | ETE | training: 437 test: 187 | CT | manual | 5 | LASSO logistic regression | 10-fold CV | NA | NA | NA | training: 0.791 test: 0.772 |
| Park et al. (2019) [72] | DFS | 768 | US images | manual | 40 | LASSO COX regression | 10-fold CV | NA | NA | NA | 0.777 (C index) |
| Yoon et al. (2020) [73] | BRAF Mutation | training: 387 test: 140 | US images | manual | 8 | LASSO logistic regression | NA | NA | NA | NA | training: 0.718 (C index) test: 0.629 (C index) |
| Kwon et al. (2020) [81] | BRAF Mutation | 96 patients | US images | manual | 43 | logistic regression SVM RF | 5-fold CV | 66.8 (mRMR) | 61.8 (mRMR) | 64.3 (mRMR) | 0.65 (mRMR) |
| Reference | No. Patients/Nodules | Imaging Method | ROI Segmentation | No. Radiomics Features | Model Construction | Validation Method | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) | Accuracy (%) | AUC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prochazka et al. (2019) [84] | 40 nodules in 40 patients | US images | threshold | NA | SVM/RF | LOOCV | NA | NA | NA | RF: 0.9242 SVM: 0.9464 |
| Colakoglu et al. (2019) [85] | 235 nodules in 198 patients | US images | manual | 7 | RF | 10-fold CV | 85.2 | 87.9 | 86.8 | 0.92 |
| Park et al. (2020) [86] | 1624 nodules in 1609 patients training: 1299; test: 325 | US images | manual | 66 | LASSO logistic regression | 10-fold CV | 70.6 | 79.8 | 77.8 | 0.75 |
| Zhao et al. (2020) [88] | training: 743 nodules in 720 patients test: 106 nodules in 102 patients | US and SWE images | manual | 26 | SVM | NA | 74.4 (US) 70.7 (US + SWE) | 72.3 (US) 79.4 (US + SWE) | 73.1 (US) 76.2 (US + SWE) | US: 0.798 US + SWE: 0.834 |
| Zhou et al. (2020) [90] | 1750 nodules in 1734 patients | US images | semi-automated | NA | Deep learning | NA | training: 90.1 IV: 89.3 EV: 89.5 | training: 82.7 IV: 83.5 EV: 84.1 | NA | training: 0.96 IV: 0.95 EV: 0.97 |
| Wang et al. (2020) [91] | 3120 nodules in 1040 patients | US images | semi-automated /manual | 302 | SVM | NA | 51.19 | 75.77 | 66.81 | 0.6371 |
| Yoon et al. (2020) [87] | 155 nodules in 154 patients | US images | manual | 15 | LASSO logistic regression | 10-fold CV | NA | NA | NA | US + Clinical information: 0.839 |
| Yao et al. (2020) [89] | 1372 patients | CT images | manual | 13 | LASSO +RF | 10-fold CV | 68 | 82 | 74 | 0.82 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Diao, W.; Mu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Jia, Z. Radiomics in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Nodules: Explorations, Application, and Limitations. Cancers 2021, 13, 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102436
Cao Y, Zhong X, Diao W, Mu J, Cheng Y, Jia Z. Radiomics in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Nodules: Explorations, Application, and Limitations. Cancers. 2021; 13(10):2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102436
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Yuan, Xiao Zhong, Wei Diao, Jingshi Mu, Yue Cheng, and Zhiyun Jia. 2021. "Radiomics in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Nodules: Explorations, Application, and Limitations" Cancers 13, no. 10: 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102436
APA StyleCao, Y., Zhong, X., Diao, W., Mu, J., Cheng, Y., & Jia, Z. (2021). Radiomics in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer and Nodules: Explorations, Application, and Limitations. Cancers, 13(10), 2436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13102436







