Prognostic Significance of KIF11 and KIF14 Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Tissue Material
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
2.3. Immunohistochemical Scoring
2.4. Database Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. KIF11 and KIF14 Immunoexpression in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Adjacent Normal Tissue
3.2. Tumor Characteristics with Respect to KIF11 and KIF14 Immunoexpression
3.3. Correlations between Protein Biomarkers
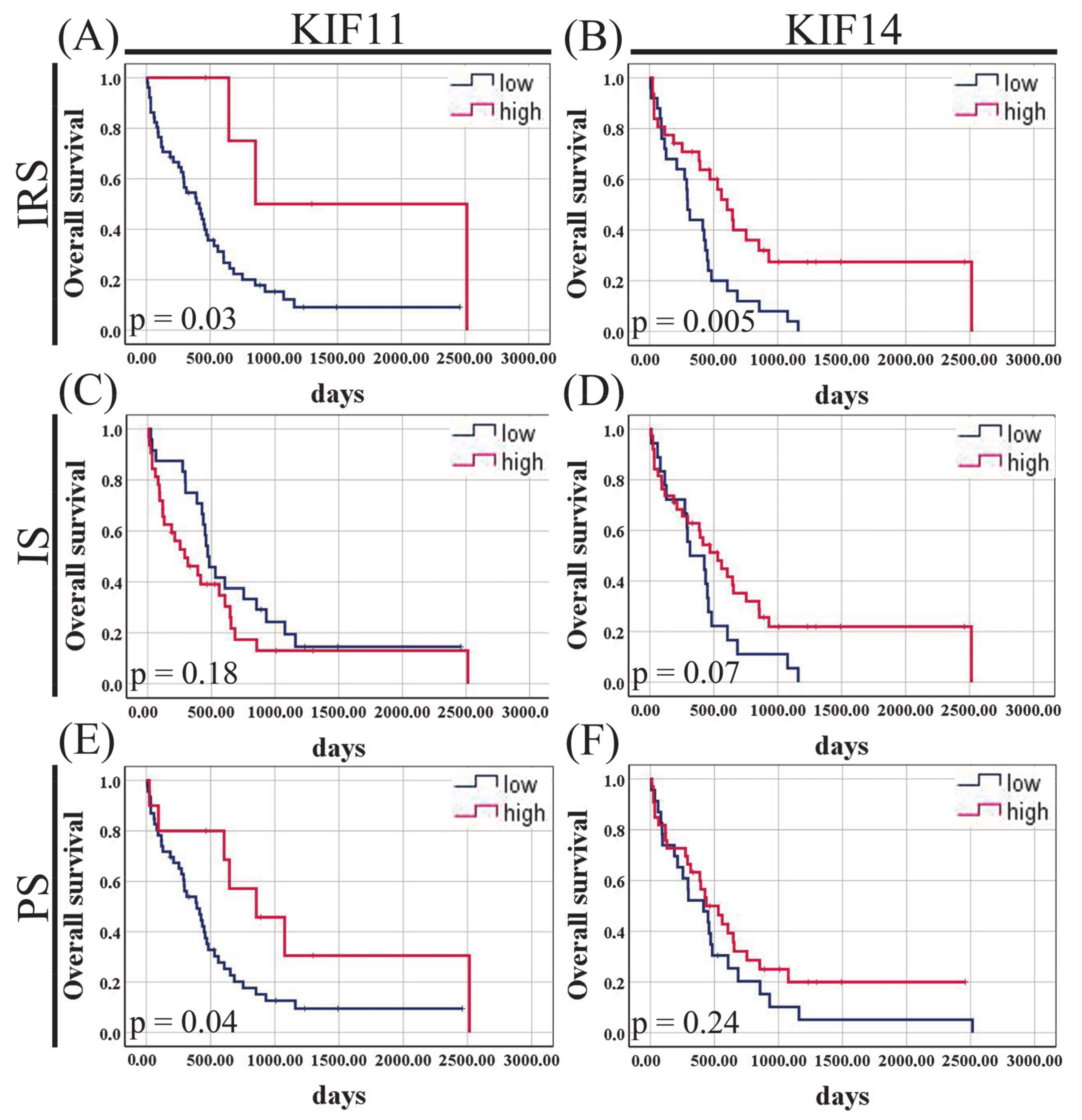
3.4. Relationships to Survival
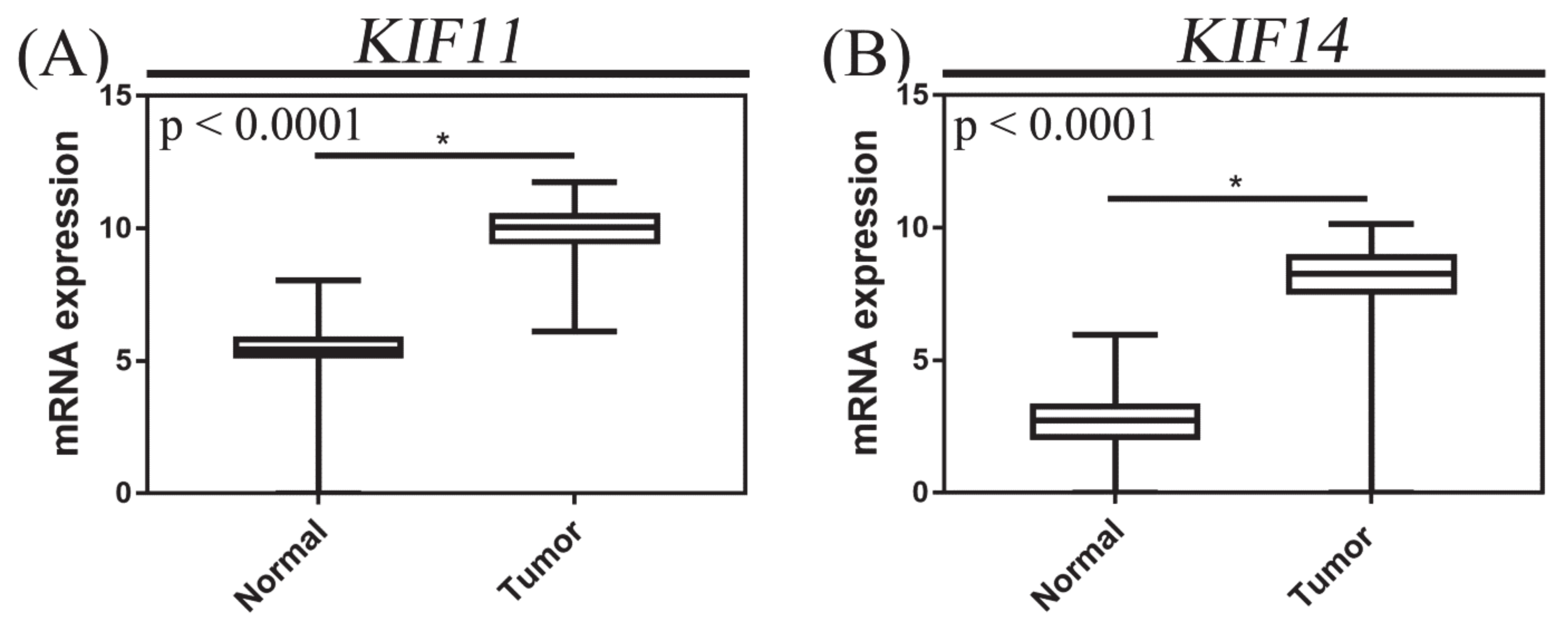
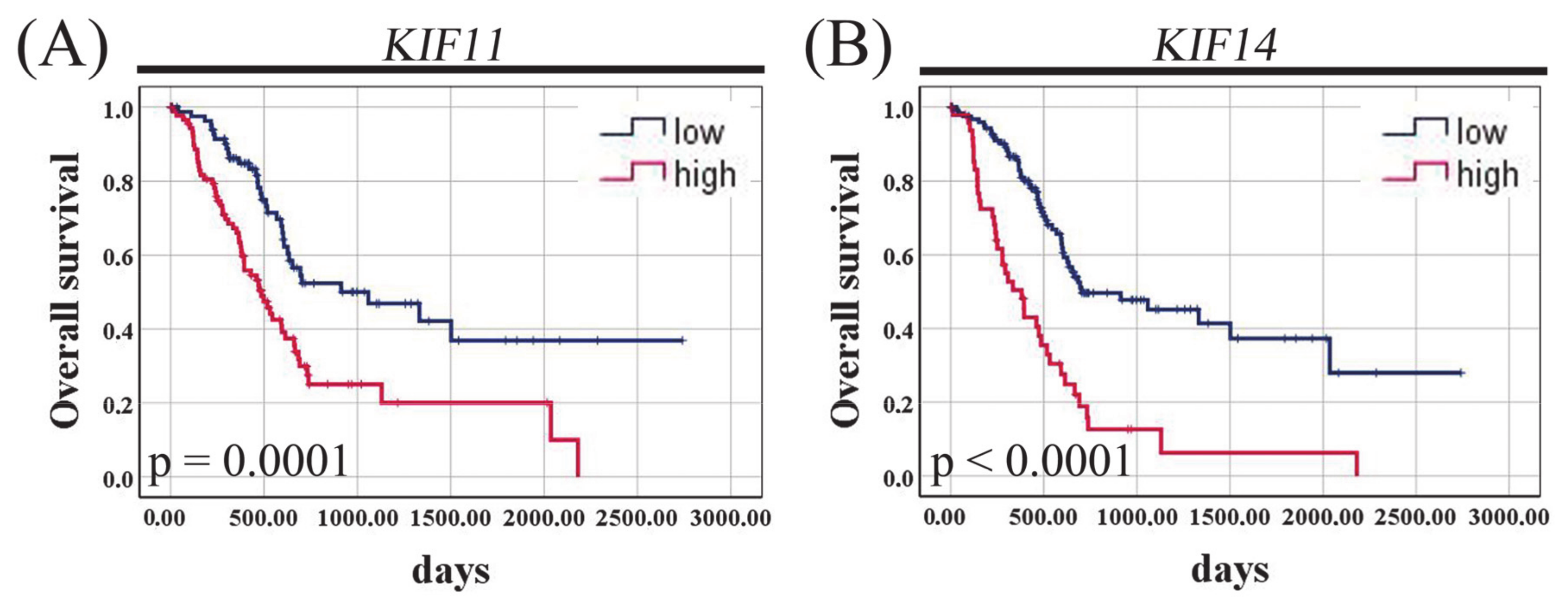
3.5. KIF11 and KIF14 mRNA Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma and Normal Tissue Based on TCGA Datasets
3.6. Correlations between Variables
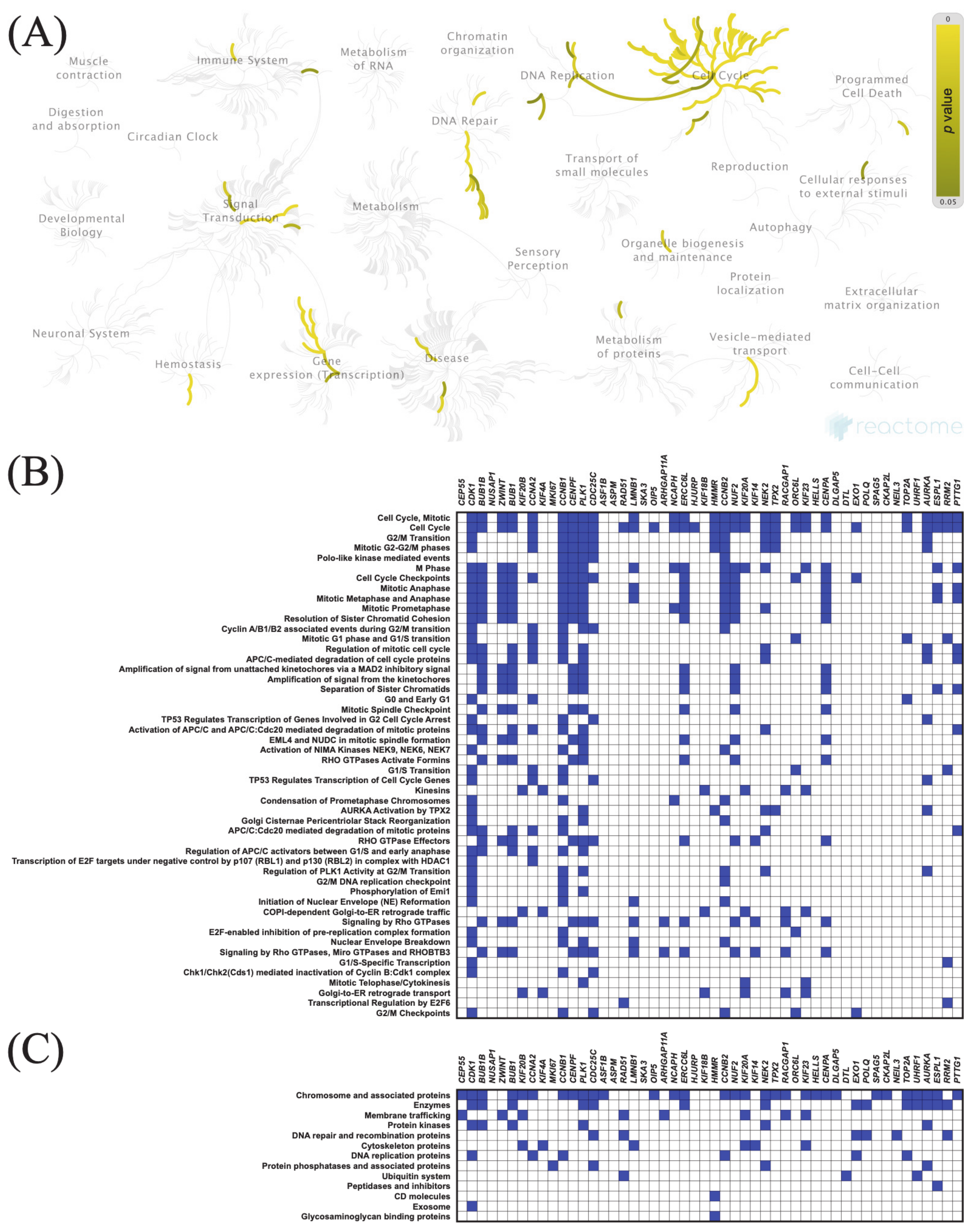
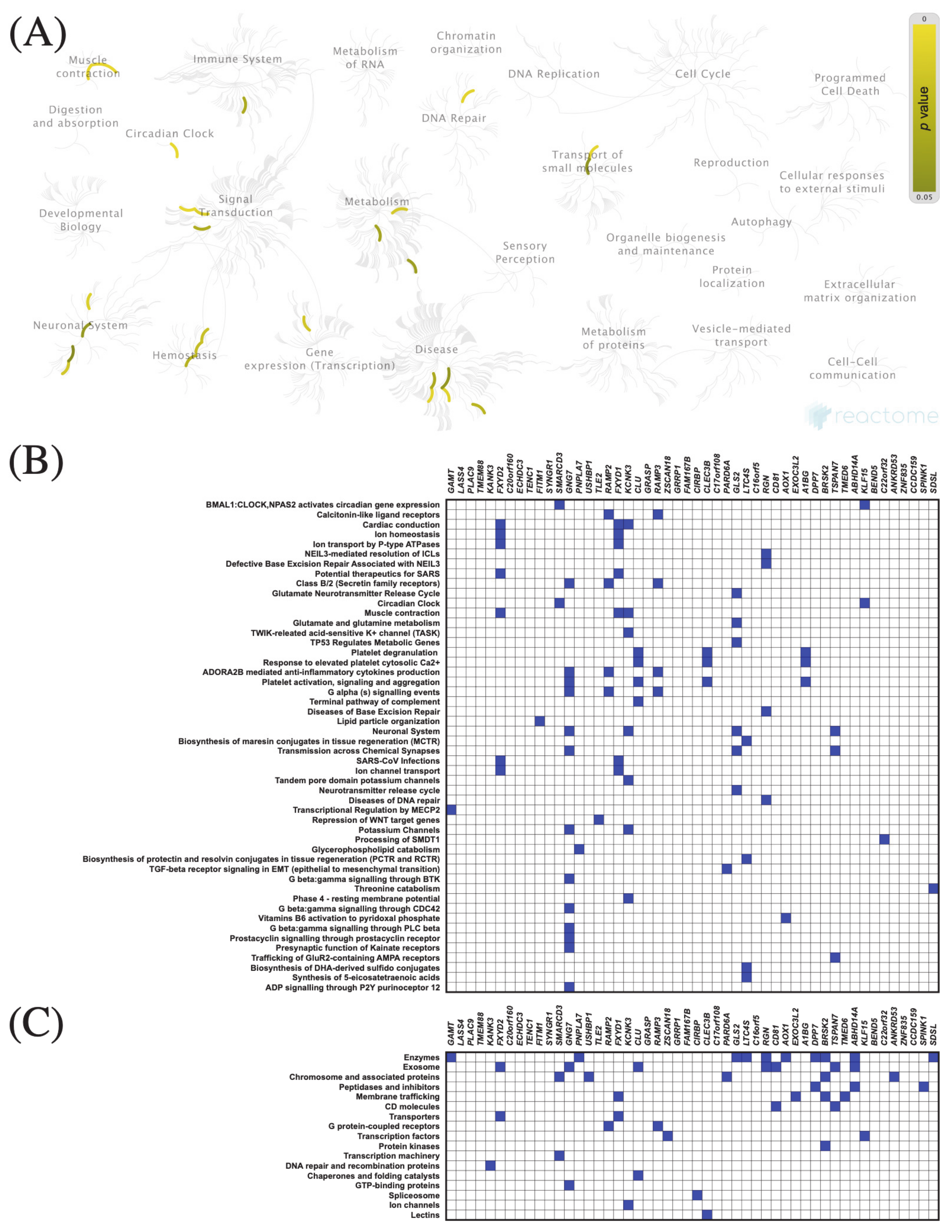
3.7. Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.8. Relationships to Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rawla, P.; Sunkara, T.; Gaduputi, V. Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamska, A.; Domenichini, A.; Falasca, M. Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: Current and Evolving Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, T.J.; Hua, K.; Singh, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of Pancreatic Cancer. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2016, 144, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, H.; Okada, Y.; Hirokawa, N. Analysis of the Kinesin Superfamily: Insights into Structure and Function. Trends Cell Biol. 2005, 15, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, J.; Nemes, S.; Parris, T.Z.; Engqvist, H.; Werner Rönnerman, E.; Kovács, A.; Karlsson, P.; Helou, K. A 17-Marker Panel for Global Genomic Instability in Breast Cancer. Genomics 2020, 112, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Feng, Y.-M. The Role of Kinesin Family Proteins in Tumorigenesis and Progression: Potential Biomarkers and Molecular Targets for Cancer Therapy. Cancer 2010, 116, 5150–5160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, A.; Morse, H.C.; Godfrey, V.L.; Naeem, R.; Justice, M.J. Overexpression of Eg5 Causes Genomic Instability and Tumor Formation in Mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 10138–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sishtla, K.; Pitt, N.; Shadmand, M.; O’Hare, M.N.; Sulaiman, R.S.; Sinn, A.L.; Condon, K.; Pollok, K.E.; Sandusky, G.E.; Corson, T.W. Observations on Spontaneous Tumor Formation in Mice Overexpressing Mitotic Kinesin Kif14. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A.; Buchholz, K.; Neska-Długosz, I.; Durślewicz, J.; Grzanka, D.; Zabrzyński, J.; Sopońska, P.; Grzanka, A.; Gagat, M. Expression of Genomic Instability-Related Molecules: Cyclin F, RRM2 and SPDL1 and Their Prognostic Significance in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogłuszka, M.; Orzechowska, M.; Jędroszka, D.; Witas, P.; Bednarek, A.K. Evaluate Cutpoints: Adaptable Continuous Data Distribution System for Determining Survival in Kaplan-Meier Estimator. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 177, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Bashel, B.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Creighton, C.J.; Ponce-Rodriguez, I.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Varambally, S. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassal, B.; Matthews, L.; Viteri, G.; Gong, C.; Lorente, P.; Fabregat, A.; Sidiropoulos, K.; Cook, J.; Gillespie, M.; Haw, R.; et al. The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D498–D503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Shi, X.; Sun, X.; Luo, Y.; Wu, X.; Yao, C.; Yu, H.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Zhou, J. Dimethylenastron Suppresses Human Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion in Vitro via Allosteric Inhibition of Mitotic Kinesin Eg5. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2011, 32, 1543–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yu, H.; Huo, L.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Zhou, J. Validating the Mitotic Kinesin Eg5 as a Therapeutic Target in Pancreatic Cancer Cells and Tumor Xenografts Using a Specific Inhibitor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 76, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, D.; Ren, H.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, Q.; Han, S.; Hao, J.; Zhou, J. Ectopic Expression of the Microtubule-Dependent Motor Protein Eg5 Promotes Pancreatic Tumourigenesis. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Yi, L.; Gao, Z.; Lou, M.; Yuan, K. High KIF11 Expression Is Associated with Poor Outcome of NSCLC. Tumori J. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; Gangeswaran, R.; Bhakta, V.; Capurso, G.; Lattimore, S.; Akada, M.; Sunamura, M.; Prime, W.; Campbell, F.; Brentnall, T.A.; et al. Proteomic Analysis of Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.-Y.; Li, G.-C.; Ran, J.; Wei, F.-X. Kinesin Family Member 11 Contributes to the Progression and Prognosis of Human Breast Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6618–6626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Zhou, N.; Li, J.; Kong, J.; Guan, X.; Wang, X. Eg5 Overexpression Is Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Dis. Markers 2017, 2017, 2176460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Dai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G. High Kinesin Family Member 11 Expression Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2019, 72, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, L. Department of Clinical Biobank, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, Nantong, Jiangsu 226001, China Eg5 High Expression Predicts Dismal Prognosis in Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Blood Genom. 2019, 3, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Liu, W.; Xiao, H.; Dong, Y.; Sun, L.; Mao, C.; Yin, L.; Jiang, X.; Ao, L.; Cui, Z.; et al. High Expression of SOX30 Is Associated with Favorable Survival in Human Lung Adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peduzzi, P.; Concato, J.; Feinstein, A.R.; Holford, T.R. Importance of Events per Independent Variable in Proportional Hazards Regression Analysis. II. Accuracy and Precision of Regression Estimates. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1995, 48, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, Y.; Thompson, L.L.; Lichtensztejn, Z.; McManus, K.J. KIF11 Silencing and Inhibition Induces Chromosome Instability That May Contribute to Cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2017, 56, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolinjivadi, A.M.; Chong, S.T.; Ngeow, J. Molecular Connections between Circadian Rhythm and Genome Maintenance Pathways. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R55–R66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.K.-W.; Qi, Y.; Xia, T.; Chan, A.K.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Aibaidula, A.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, L.; Yao, Y.; Ng, H.-K. The Kinesin KIF14 Is Overexpressed in Medulloblastoma and Downregulation of KIF14 Suppressed Tumor Proliferation and Induced Apoptosis. Lab. Invest. 2017, 97, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Cui, W.; Yang, B. Up-Regulation of KIF14 Is a Predictor of Poor Survival and a Novel Prognostic Biomarker of Chemoresistance to Paclitaxel Treatment in Cervical Cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Li, C.; Yan, C.; Li, J.; Yan, M.; Liu, B.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Q. KIF14 Promotes Tumor Progression and Metastasis and Is an Independent Predictor of Poor Prognosis in Human Gastric Cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, X.-B.; Zheng, Z.-M. Suppression of KIF14 Expression Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression and Predicts Favorable Outcome. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.-L.; Deng, S.-Z.; Li, C.; Tian, Z.-N.; Song, X.-Q.; Yao, G.-D.; Geng, J.-S. High Expression of KIF14 Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Patients with Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; Xia, L.; Zhao, Y.; Shu, X.-S.; Sun, S.; Ying, Y.; et al. Overexpression of a Novel Candidate Oncogene KIF14 Correlates with Tumor Progression and Poor Prognosis in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45459–45469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, P.-F.; Hong, T.-M.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-L.; Wu, C.-T.; Chang, G.-C.; Jou, Y.-S.; Pan, S.-H.; Yang, P.-C. The Motor Protein KIF14 Inhibits Tumor Growth and Cancer Metastasis in Lung Adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abiatari, I.; DeOliveira, T.; Kerkadze, V.; Schwager, C.; Esposito, I.; Giese, N.A.; Huber, P.; Bergman, F.; Abdollahi, A.; Friess, H.; et al. Consensus Transcriptome Signature of Perineural Invasion in Pancreatic Carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1494–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, R.; Yuan, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Z. Development and Validation of a Metastasis-Related Gene Signature for Predicting the Overall Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6299–6318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, H.N.; Jun, S.; Oh, A.-Y.; Srivastava, M.; Lee, S.; Taniguchi, C.M.; Zhang, S.; Lee, W.S.; Chen, J.; Park, B.-J.; et al. Identification of KIAA1199 as a Biomarker for Pancreatic Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yu, J.; Sun, Z.; Luh, F.; Lin, D.; Shen, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X. Kinesin Family Member 11 Is a Potential Therapeutic Target and Is Suppressed by MicroRNA-30a in Breast Cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jungwirth, G.; Yu, T.; Moustafa, M.; Rapp, C.; Warta, R.; Jungk, C.; Sahm, F.; Dettling, S.; Zweckberger, K.; Lamszus, K.; et al. Identification of KIF11 As a Novel Target in Meningioma. Cancers 2019, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corson, T.W.; Gallie, B.L. KIF14 MRNA Expression Is a Predictor of Grade and Outcome in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1088–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, D.; Colangelo, C.; Williams, K.; Gerstein, M. Comparing Protein Abundance and MRNA Expression Levels on a Genomic Scale. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, N. A Gene’s MRNA Level Does Not Usually Predict Its Protein Level. Available online: https://kendricklabs.com/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/WP1_mRNAvsProtein_KendrickLabs.pdf (accessed on 19 April 2021).
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the Regulation of Protein Abundance from Proteomic and Transcriptomic Analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variables | n (%) | KIF11 IS | p-Value | KIF11 PS | p-Value | KIF11 IRS | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓n = 26 (38.24) | ↑n = 42 (61.76) | ↓n = 58 (85.29) | ↑n = 10 (14.71) | ↓n = 63 (92.65) | ↑n = 5 (7.35) | |||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||||
| ≤ 60 | 29 (42.65) | 12 (41.38) | 17 (58.62) | 0.80 | 22 (75.86) | 7 (24.14) | 0.09 | 25 (86.21) | 4 (13.79) | 0.16 |
| > 60 | 39 (57.35) | 14 (35.90) | 25 (64.10) | 36 (92.31) | 3 (7.69) | 38 (97.44) | 1 (2.56) | |||
| Gender | ||||||||||
| Male | 34 (50.00) | 13 (38.24) | 21 (61.76) | >0.99 | 28 (82.35) | 6 (17.65) | 0.73 | 31 (91.18) | 3 (8.82) | >0.99 |
| Female | 34 (50.00) | 13 (38.24) | 21 (61.76) | 30 (88.24) | 4 (11.76) | 32 (94.12) | 2 (5.88) | |||
| Grading | ||||||||||
| G1 | 5 (7.35) | 1 (20.00) | 4 (80.00) | 0.68 | 5 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | 0.46 | 5 (100.00) | 0 (0.00) | 0.11 |
| G2 | 55 (80.88) | 22 (40.00) | 33 (60.00) | 47 (85.45) | 8 (14.55) | 52 (94.55) | 3 (5.45) | |||
| G3 | 8 (11.77) | 3 (37.50) | 5 (62.50) | 6 (75.00) | 2 (25.00) | 6 (75.00) | 2 (25.00) | |||
| pT status | ||||||||||
| T1 | 10 (15.87) | 5 (50.00) | 5 (50.00) | 0.47 | 10 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | 0.37 | 10 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | 0.60 |
| T2 | 43 (68.25) | 13 (30.23) | 30 (69.77) | 37 (86.05) | 6 (13.95) | 39 (90.70) | 4 (9.30) | |||
| T3-T4 | 10 (15.87) | 4 (40.00) | 6 (60.00) | 8 (80.00) | 2 (20.00) | 9 (90.00) | 1 (10.00) | |||
| pN status | ||||||||||
| N0 | 30 (45.46) | 9 (30.00) | 21 (70.00) | 0.21 | 25 (83.33) | 5 (16.67) | 0.72 | 27 (90.00) | 3 (10.00) | 0.32 |
| N1-N2 | 36 (54.54) | 17 (47.22) | 19 (52.78) | 32 (88.89) | 4 (11.11) | 35 (97.22) | 1 (2.78) | |||
| TNM stage | ||||||||||
| I | 24 (38.71) | 6 (25.00) | 18 (75.00) | 0.20 | 20 (83.33) | 4 (16.67) | 0.29 | 22 (91.67) | 2 (8.33) | 0.54 |
| II | 24 (38.71) | 12 (50.00) | 12 (50.00) | 21 (87.50) | 3 (12.50) | 22 (91.67) | 2 (8.33) | |||
| III-IV | 14 (22.58) | 5 (35.71) | 9 (64.29) | 14 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | 14 (100.0) | 0 (0.00) | |||
| Location | ||||||||||
| Head | 60 (88.24) | 23 (38.33) | 37 (61.67) | >0.99 | 53 (88.33) | 7 (11.67) | 0.09 | 56 (93.33) | 4 (6.67) | 0.48 |
| Body-tail | 8 (11.76) | 3 (37.50) | 5 (62.50) | 5 (62.50) | 3 (37.50) | 7 (87.50) | 1 (12.50) | |||
| VI | ||||||||||
| Absent | 39 (72.22) | 17 (43.59) | 22 (56.41) | >0.99 | 33 (84.62) | 6 (15.38) | >0.99 | 37 (94.87) | 2 (5.13) | >0.99 |
| Present | 15 (27.78) | 7 (46.67) | 8 (53.33) | 13 (86.67) | 2 (13.33) | 14 (93.33) | 1 (6.67) | |||
| PNI Absent Present | 22 (34.38) | 10 (45.45) | 12 (54.55) | 0.59 | 16 (72.73) | 6 (27.27) | 0.05 | 19 (86.36) | 3 (13.64) | 0.11 |
| 42 (65.62) | 15 (35.71) | 27 (64.29) | 39 (92.86) | 3 (7.14) | 41 (97.62) | 1 (2.38) | ||||
| Variables | n (%) | KIF14 IS | p -Value | KIF14 PS | p-Value | KIF14 IRS | p-Value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ↓ n = 21 (30.88) | ↑ n = 47 (69.12) | ↓ n = 31 (45.59) | ↑ n = 37 (54.41) | ↓ n = 30 (44.12) | ↑ n = 38 (55.88) | |||||
| Age (years) | ||||||||||
| ≤ 60 | 29 (42.65) | 8 (27.59) | 21 (72.41) | 0.79 | 14 (48.28) | 15 (51.72) | 0.81 | 14 (48.28) | 15 (51.72) | 0.63 |
| > 60 | 39 (57.35) | 13 (33.33) | 26 (66.67) | 17 (43.59) | 22 (56.41) | 16 (41.03) | 23 (58.97) | |||
| Gender | ||||||||||
| Male | 34 (50.00) | 8 (23.53) | 26 (76.47) | 0.29 | 15 (44.12) | 19 (55.88) | >0.99 | 13 (38.24) | 21 (61.76) | 0.46 |
| Female | 34 (50.00) | 13 (38.24) | 21 (61.76) | 16 (47.06) | 18 (52.94) | 17 (50.00) | 17 (50.00) | |||
| Grading | ||||||||||
| G1 | 5 (7.35) | 1 (20.00) | 4 (80.00) | 0.10 | 3 (60.00) | 2 (40.00) | 0.40 | 2 (40.00) | 3 (60.00) | 0.15 |
| G2 | 55 (80.88) | 20 (36.36) | 35 (63.64) | 26 (47.27) | 29 (52.73) | 27 (49.09) | 28 (50.91) | |||
| G3 | 8 (11.77) | 0 (0.00) | 8 (100.0) | 2 (25.00) | 6 (75.00) | 1 (12.50) | 7 (87.50) | |||
| pT status | ||||||||||
| T1 | 10 (15.87) | 4 (40.00) | 6 (60.00) | 0.56 | 6 (60.00) | 4 (40.00) | 0.40 | 5 (50.00) | 5 (50.00) | 0.83 |
| T2 | 43 (68.25) | 11 (25.58) | 32 (74.42) | 19 (44.19) | 24 (55.81) | 17 (39.54) | 26 (60.47) | |||
| T3-T4 | 10 (15.87) | 2 (20.00) | 8 (80.00) | 3 (30.00) | 7 (70.00) | 4 (40.00) | 6 (60.00) | |||
| pN status | ||||||||||
| N0 | 30 (45.46) | 8 (26.67) | 22 (73.33) | 0.44 | 18 (60.00) | 12 (40.00) | 0.08 | 13 (43.33) | 17 (56.67) | 0.81 |
| N1-N2 | 36 (54.54) | 13 (36.11) | 23 (63.89) | 13 (36.11) | 23 (63.89) | 17 (47.22) | 19 (52.78) | |||
| TNM stage | ||||||||||
| I | 24 (38.71) | 6 (25.00) | 18 (75.00) | 0.43 | 15 (62.50) | 9 (37.50) | 0.12 | 10 (41.67) | 14 (58.33) | 0.86 |
| II | 24 (38.71) | 6 (25.00) | 18 (75.00) | 8 (33.33) | 16 (66.67) | 10 (41.67) | 14 (58.33) | |||
| III-IV | 14 (22.58) | 6 (42.86) | 8 (57.14) | 6 (42.86) | 8 (57.14) | 7 (50.00) | 7 (50.00) | |||
| Location | ||||||||||
| Head | 60 (88.24) | 19 (31.67) | 41 (68.33) | >0.99 | 28 (46.67) | 32 (53.33) | 0.72 | 26 (43.33) | 34 (56.67) | 0.72 |
| Body-tail | 8 (11.76) | 2 (25.00) | 6 (75.00) | 3 (37.50) | 5 (62.50) | 4 (50.00) | 4 (50.00) | |||
| VI | ||||||||||
| Absent | 39 (72.22) | 14 (35.90) | 25 (64.10) | 0.18 | 20 (51.28) | 19 (48.72) | >0.99 | 19 (48.72) | 20 (51.28) | 0.37 |
| Present | 15 (27.78) | 2 (13.33) | 13 (86.67) | 7 (46.67) | 8 (53.33) | 5 (33.33) | 10 (66.67) | |||
| PNI Absent Present | 22 (34.38) | 5 (22.73) | 17 (77.27) | 0.57 | 10 (45.45) | 12 (54.55) | >0.99 | 9 (40.91) | 13 (59.09) | >0.99 |
| 42 (65.62) | 14 (33.33) | 28 (66.67) | 19 (45.24) | 23 (54.76) | 18 (42.86) | 24 (57.14) | ||||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | ||
| Lower | Upper | |||
| KIF11 IRS (low vs. high) | 0.23 | 0.06 | 0.96 | 0.04 |
| KIF11 IS (low vs. high) | 1.49 | 0.82 | 2.71 | 0.19 |
| KIF11 PS (low vs. high) | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.98 | 0.045 |
| KIF14 IRS (low vs. high) | 0.44 | 0.24 | 0.79 | 0.006 |
| KIF14 IS (low vs. high) | 0.58 | 0.32 | 1.06 | 0.08 |
| KIF14 PS (low vs. high) | 0.70 | 0.39 | 1.26 | 0.24 |
| Age (≤60 vs. ≥60) | 1.14 | 0.63 | 2.07 | 0.67 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.97 | 0.54 | 1.75 | 0.93 |
| Grade (G1 vs. G2-G3) | 2.12 | 0.51 | 8.00 | 0.30 |
| pN (absent vs. present) | 1.27 | 0.70 | 2.32 | 0.44 |
| pT (T1-T2 vs. T3-T4) | 1.08 | 0.48 | 2.45 | 0.85 |
| Stage (I-II vs. III-IV) | 2.05 | 1.02 | 4.13 | 0.04 |
| PNI (absent vs. present) | 1.47 | 0.79 | 2.76 | 0.23 |
| VI (absent vs. present) | 2.41 | 1.17 | 4.98 | 0.02 |
| Variable | Multivariate Analysis: IRS | Multivariate Analysis: IS | Multivariate Analysis: PS | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| KIF11 IRS (low vs. high) | 0.06 | 0.005 | 0.64 | 0.02 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KIF11 IS (low vs. high) | - | - | - | - | 3.05 | 1.29 | 7.19 | 0.01 | - | - | - | - |
| KIF11 PS (low vs. high) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.31 | 0.06 | 1.53 | 0.15 |
| KIF14 IRS (low vs. high) | 0.20 | 0.08 | 0.51 | 0.001 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| KIF14 IS (low vs. high) | - | - | - | - | 0.25 | 0.10 | 0.67 | 0.006 | - | - | - | - |
| KIF14 PS (low vs. high) | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.45 | 0.17 | 1.21 | 0.11 |
| Age (≤ 60 vs. ≥ 60) | 1.15 | 0.50 | 2.64 | 0.74 | 1.61 | 0.69 | 3.73 | 0.27 | 1.71 | 0.68 | 4.25 | 0.25 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.93 | 0.37 | 2.30 | 0.87 | 0.80 | 0.32 | 1.98 | 0.63 | 0.87 | 0.33 | 2.29 | 0.78 |
| Grade (G1 vs. G2-G3) | 3.00 | 0.24 | 37.98 | 0.40 | 6.00 | 0.47 | 76.79 | 0.17 | 4.64 | 0.44 | 48.57 | 0.20 |
| pN (absent vs. present) | 1.05 | 0.38 | 2.90 | 0.93 | 1.76 | 0.55 | 5.69 | 0.34 | 1.20 | 0.38 | 3.73 | 0.76 |
| pT (T1-T2 vs. T3-T4) | 2.17 | 0.66 | 7.14 | 0.20 | 2.06 | 0.68 | 6.21 | 0.20 | 1.91 | 0.63 | 5.73 | 0.25 |
| Stage (I-II vs. III-IV) | 2.06 | 0.73 | 5.77 | 0.17 | 1.43 | 0.48 | 4.24 | 0.52 | 1.91 | 0.68 | 5.31 | 0.22 |
| PNI (absent vs. present) | 0.74 | 0.29 | 1.91 | 0.54 | 1.27 | 0.48 | 3.36 | 0.64 | 0.74 | 0.27 | 2.03 | 0.56 |
| VI (absent vs. present) | 3.43 | 1.30 | 9.06 | 0.01 | 4.09 | 1.49 | 11.20 | 0.006 | 1.96 | 0.70 | 5.51 | 0.20 |
| Variables | n (%) | KIF11 | p -Value | KIF14 | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Negative n = 86 | Positive n = 91 | Negative n = 128 | Positive n = 49 | ||||
| Gender | |||||||
| Male | 97 (54.80) | 45 (46.39) | 52 (53.61) | 0.55 | 69 (71.13) | 28 (28.87) | 0.74 |
| Female | 80 (45.20) | 41 (51.25) | 39 (48.75) | 59 (73.75) | 21 (26.25) | ||
| Age | |||||||
| ≤60 | 59 (33.33) | 31 (52.54) | 28 (47.46) | 0.52 | 42 (71.19) | 17 (28.81) | 0.86 |
| >60 | 118 (66.67) | 55 (46.61) | 63 (53.39) | 86 (72.88) | 32 (27.12) | ||
| Grading | |||||||
| G1 | 31 (17.71) | 22 (70.97) | 9 (29.03) | 0.01 | 30 (96.77) | 1 (3.23) | 0.002 |
| G2 | 94 (53.71) | 44 (46.81) | 50 (53.19) | 66 (70.21) | 28 (29.79) | ||
| G3-G4 | 50 (28.57) | 19 (38.00) | 31 (62.00) | 30 (60.00) | 20 (40.00) | ||
| pT status | |||||||
| T1-T2 | 30 (17.14) | 18 (60.00) | 12 (40.00) | 0.17 | 24 (80.00) | 6 (20.00) | 0.37 |
| T3-T4 | 145 (82.86) | 66 (45.52) | 79 (54.48) | 102 (70.34) | 43 (29.66) | ||
| pN status | |||||||
| N0 | 49 (28.49) | 24 (48.98) | 25 (51.02) | >0.99 | 38 (77.55) | 11 (22.45) | 0.35 |
| N1 | 123 (71.51) | 59 (47.97) | 64 (52.03) | 86 (69.92) | 37 (30.08) | ||
| TNM stage | |||||||
| I | 21 (12.00) | 13 (61.90) | 8 (38.10) | 0.24 | 18 (85.71) | 3 (14.29) | 0.20 |
| II-IV | 154 (88.00) | 71 (46.10) | 83 (53.90) | 108 (70.13) | 46 (29.87) | ||
| Variable | Univariate Analysis | Multivariate Analysis: KIF11 | Multivariate Analysis: KIF14 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | HR | 95% CI | p | ||||
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||||
| KIF11 (low vs. high) | 2.25 | 1.47 | 3.45 | 0.0002 | 1.75 | 1.13 | 2.70 | 0.01 | - | - | - | - |
| KIF14 (low vs. high) | 2.99 | 1.97 | 4.54 | <0.0001 | - | - | - | - | 2.65 | 1.70 | 4.15 | <0.0001 |
| Age (≤ 60 vs. ≥ 60) | 1.41 | 0.90 | 2.21 | 0.13 | 1.24 | 0.77 | 1.98 | 0.38 | 1.28 | 0.80 | 2.04 | 0.31 |
| Gender (female vs. male) | 0.81 | 0.54 | 1.23 | 0.33 | 0.78 | 0.51 | 1.20 | 0.26 | 0.84 | 0.54 | 1.30 | 0.41 |
| Grade (G1 vs. G2-G3) | 2.18 | 1.15 | 4.13 | 0.02 | 1.53 | 0.80 | 2.95 | 0.20 | 1.21 | 0.61 | 2.39 | 0.59 |
| pN (absent vs. present) | 2.10 | 1.25 | 3.52 | 0.005 | 2.00 | 1.15 | 3.47 | 0.01 | 2.09 | 1.19 | 3.67 | 0.01 |
| pT (T1-T2 vs. T3-T4) | 2.21 | 1.14 | 4.28 | 0.02 | 1.34 | 0.65 | 2.75 | 0.43 | 1.29 | 0.63 | 2.65 | 0.49 |
| Stage (I-II vs. III-IV) | 0.74 | 0.23 | 2.34 | 0.60 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A.; Neska-Długosz, I.; Buchholz, K.; Durślewicz, J.; Grzanka, D.; Kasperska, A.; Antosik, P.; Zabrzyński, J.; Grzanka, A.; Gagat, M. Prognostic Significance of KIF11 and KIF14 Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123017
Klimaszewska-Wiśniewska A, Neska-Długosz I, Buchholz K, Durślewicz J, Grzanka D, Kasperska A, Antosik P, Zabrzyński J, Grzanka A, Gagat M. Prognostic Significance of KIF11 and KIF14 Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(12):3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123017
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlimaszewska-Wiśniewska, Anna, Izabela Neska-Długosz, Karolina Buchholz, Justyna Durślewicz, Dariusz Grzanka, Anna Kasperska, Paulina Antosik, Jan Zabrzyński, Alina Grzanka, and Maciej Gagat. 2021. "Prognostic Significance of KIF11 and KIF14 Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 12: 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123017
APA StyleKlimaszewska-Wiśniewska, A., Neska-Długosz, I., Buchholz, K., Durślewicz, J., Grzanka, D., Kasperska, A., Antosik, P., Zabrzyński, J., Grzanka, A., & Gagat, M. (2021). Prognostic Significance of KIF11 and KIF14 Expression in Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 13(12), 3017. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13123017








