Smart Biosensors for Cancer Diagnosis Based on Graphene Quantum Dots
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Suitable Properties of GQDs for Designing Nano-Scaled Biosensors
3. Recent Approaches for the Synthesis of GQDs as Biosensing Elements
3.1. Top-Down Approaches
3.2. Bottom-Up Approaches
4. Biosensors Based on GQDs for Cancer Detection
4.1. Intracellular Cancer Cells Sensors
4.2. Immunosensors
4.3. Nucleic Acid Hybridization Sensors
4.4. Circulating Tumor Cells Sensors
5. Conclusions and Future Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramadan, S.; Lobo, R.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Shaforost, O.; Kwong, H.; Tsang, D.; Feng, J.; Yin, T.; Qiao, M.; et al. Carbon-Dot-Enhanced Graphene Field-Effect Transistors for Ultrasensitive Detection of Exosomes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 7854–7864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, L.; Salomone, S.; Libra, M. Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mahato, K.; Kumar, A.; Maurya, P.K.; Chandra, P. Shifting paradigm of cancer diagnoses in clinically relevant samples based on miniaturized electrochemical nanobiosensors and microfluidic devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Shu, J. Multimodal Molecular Imaging: Current Status and Future Directions. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2018, 2018, 1382183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, S. Noninvasive Nanodiagnostics for Cancer. Cancer Biomarkers; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, S.; He, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, J.J. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks in detecting cancer biomarkers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 1338–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, N.; Maekawa, T.; Kumar, D.N.S. Graphene based biosensors—Accelerating medical diagnostics to new-dimensions. J. Mater. Res. 2017, 32, 2860–2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharifi, M.; Avadi, M.R.; Attar, F.; Dashtestani, F.; Ghorchian, H.; Rezayat, S.M.; Saboury, A.A.; Falahati, M. Cancer diagnosis using nanomaterials based electrochemical nanobiosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 126, 773–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirzada, M.; Altintas, Z. Nanomaterials for Healthcare. Sensors 2019, 19, 5311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biju, V. Chemical modifications and bioconjugate reactions of nanomaterials for sensing, imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 744–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Wang, H.; Li, Z. Nanomaterials for Sensing Applications. J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 2016, 2083948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holzinger, M.; Goff, A.L.; Cosnier, S. Nanomaterials for biosensing applications: A review. Front. Chem. 2014, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suvarnaphaet, P.; Pechprasarn, S. Graphene-based materials for biosensors: A review. Sensors 2017, 17, 2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baldo, S.; Buccheri, S.; Ballo, A.; Camarda, M.; La Magna, A.; Castagna, M.E.; Romano, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Di Raimondo, F.; Neri, G.; et al. Carbon nanotube-based sensing devices for human Arginase-1 detection. Sens. Bio Sens. Res. 2016, 7, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, C.; Li, H.; Du, D.; Lin, Y. Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors based on graphene two-dimensional nanomaterials. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 195–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.K.; Singh, E.; Singh, P.; Meyyappan, M.; Nalwa, H.S. A review on graphene-based nanocomposites for electrochemical and fluorescent biosensors. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 8778–8781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Javadi, A.; Gong, S. Sensitive electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of cancer biomarker using quantum dot functionalized graphene sheets as labels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Galvagno, S.; Ferro, S.; De Luca, L.; Monforte, A.M.; Da Ros, T.; Hadad, C.; Prato, M.; Pannecouque, C. Synthesis and anti-HIV activity of carboxylated and drug-conjugated multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Carbon N. Y. 2015, 82, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistone, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Ansari, S.; Milone, C.; Salamò, M.; Galvagno, S.; Cirmi, S.; Navarra, M. Tunable doxorubicin release from polymer-gated multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 515, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Galvagno, S. Functionalization methods of graphene. In Functionalization of Carbon Nanomaterials: Chemistry and Applications; Thakur, V.K., Thakur, M.K., Eds.; Chemical; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 510–537. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Gong, J.; Chen, J.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, W.; Pu, K.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots: From Chemistry and Physics to Applications. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1808283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Ziccarelli, I.; Pistone, A. Graphene quantum dots: Multifunctional nanoplatforms for anticancer therapy. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 6471–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Celesti, C.; Espro, C. Recent Advances on Graphene Quantum Dots as Multifunctional Nanoplatforms for Cancer Treatment. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 1900422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannazzo, D.; Ettari, R.; Giofrè, S.; Eid, A.H.; Bitto, A. Recent advances in nanotherapeutics for multiple myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, S.H.; Kim, D.H.; Jun, G.H.; Hong, S.H.; Jeon, S. Tuning the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots through the charge transfer effect of functional groups. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 1239–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giofrè, S.V.; Tiecco, M.; Celesti, C.; Patanè, S.; Triolo, C.; Gulino, A.; Spitaleri, L.; Scalese, S.; Scuderi, M.; Iannazzo, D. Eco-friendly 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions on graphene quantum dots in natural deep eutectic solvent. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, S.; Namazi, H. Doxorubicin Loaded Carboxymethyl Cellulose/Graphene Quantum dot Nanocomposite Hydrogel Films as a Potential Anticancer Drug Delivery System; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 87, ISBN 4133340191. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, J.; Wang, K.; Sun, L.; Sun, B.; Yang, M.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Dong, L. Application of graphene quantum dots for simultaneous fluorescence imaging and tumor-targeted drug delivery. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 256, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Applications of graphene quantum dots in biomedical sensors. Sensors 2020, 20, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pirsaheb, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Salimi, A. Current advances of carbon dots based biosensors for tumor marker detection, cancer cells analysis and bioimaging. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 115, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.S.; Hola, K.; Ambrosi, A.; Zboril, R.; Pumera, M. Graphene and carbon quantum dots electrochemistry. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 52, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Tang, L.; Teng, K.S.; Lau, S.P. Graphene quantum dots from chemistry to applications. Mater. Today Chem. 2018, 10, 221–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, S.; Jiang, C. Fluorescent carbon dots: Rational synthesis, tunable optical properties and analytical applications. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 40973–40989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.; Hwang, S.W.; Kim, M.K.; Shin, D.Y.; Shin, D.H.; Kim, C.O.; Yang, S.B.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, E.; Choi, S.H.; et al. Anomalous behaviors of visible luminescence from graphene quantum dots: Interplay between size and shape. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 8203–8208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, G.; Yang, G.; Peng, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, J.J. Focusing on luminescent graphene quantum dots: Current status and future perspectives. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4015–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; Yu, W.; et al. Surface chemistry routes to modulate the photoluminescence of graphene quantum dots: From fluorescence mechanism to up-conversion bioimaging applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 4732–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Sun, J.; Zhu, C.; He, P.; Peng, Z.; Ding, G. Supramolecular recognition control of polyethylene glycol modified Ndoped graphene quantum dots: Tunable selectivity for alkali and alkaline-earth metal ions. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 10715–10722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkal, A.; Pradhan, R.; Kadian, S.; Manik, G.; Packirisamy, G. Biofunctionalized Graphene Quantum Dots Based Fluorescent Biosensor toward Efficient Detection of Small Cell Lung Cancer. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 4922–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Graphene quantum dot-based electrochemical immunosensors for biomedical applications. Materials 2020, 13, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, H.; Wu, L.; Wei, W.; Qu, X. Recent advances in graphene quantum dots for sensing. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faridbod, F.; Sanati, A.L. Graphene Quantum Dots in Electrochemical Sensors/Biosensors. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 15, 103–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, V.; Ferlazzo, A.; Iannazzo, D.; Espro, C. Graphene quantum dots by eco-friendly green synthesis for electrochemical sensing: Recent advances and future perspectives. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, Y.R.; Deshmukh, K.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Pasha, S.K.K. Graphene quantum dot based materials for sensing, bio-imaging and energy storage applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 23861–23898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellici, S.; Acord, J.; Power, N.P.; Morgan, D.J.; Coppo, P.; Heil, T.; Saha, B. Rapid synthesis of graphene quantum dots using a continuous hydrothermal flow synthesis approach. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14716–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, S.; Jeong, Y.K.; Jung, K.H.; Son, Y.; Choi, S.C.; An, G.S.; Han, H.; Kim, K.M. Simple preparation of graphene quantum dots with controllable surface states from graphite. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38447–38453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dong, S.; Bi, Q.; Qiao, C.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Zhao, L. Electrochemical sensor for discrimination tyrosine enantiomers using graphene quantum dots and β-cyclodextrins composites. Talanta 2017, 173, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Zhuo, S.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y. Fluorescent graphene quantum dot nanoprobes for the sensitive and selective detection of mercury ions. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2014, 131, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.; Liu, J.; Yan, X.; Kang, L. Graphene oxide derived graphene quantum dots with different photoluminescence properties and peroxidase-like catalytic activity. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50609–50617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Zhong, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, W.; Wang, T. Facile hydrothermal method to prepare graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide with different photoluminescences. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 40422–40426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourinia, H.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Amiri, O.; Farangi, M. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots from corn powder and their application as down conversion effect in quantum dot-dye-sensitized solar cell. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 251, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Shen, J.; Lv, G.; Li, D.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, Z. Green Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Cotton Cellulose. Chem. Select 2019, 4, 2898–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Peng, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, L. One-Pot Facile Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots from Rice Husks for Fe3+ Sensing. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 9144–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jang, M.H.; Ha, H.D.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Seo, T.S. Facile synthetic method for pristine graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide quantum dots: Origin of blue and green luminescence. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3657–3662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Hsieh, C.T.; Chiang, Y.M.; Tzou, D.Y.; Chen, Y.F.; Gandomi, Y.A. Optimization of Graphene Quantum Dots by Chemical Exfoliation from Graphite Powders and Carbon Nanotubes; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 215, ISBN 8863455937. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, S.; Gandla, D.; Venkatesh, Y.; Bangal, P.R.; Ghosh, S.; Yang, Y.; Misra, S. Graphene quantum dots from graphite by liquid exfoliation showing excitation-independent emission, fluorescence upconversion and delayed fluorescence. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 21278–21287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdrazil, L.; Zahradnicek, R.; Mohan, R.; Sedlacek, P.; Nejdl, L.; Schmiedova, V.; Pospisil, J.; Horak, M.; Weiter, M.; Zmeskal, O.; et al. Preparation of graphene quantum dots through liquid phase exfoliation method. J. Lumin. 2018, 204, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhi, J. Facile synthesis of graphene quantum dots based on electrochemical method and their application for specific Fe3+ detection. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2018, 9, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zheng, M.; Su, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, X. Electrochemical synthesis of phosphorus and sulfur co-doped graphene quantum dots as efficient electrochemiluminescent immunomarkers for monitoring okadaic acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joffrion, J.B.; Clower, W.; Wilson, C.G. Tunable excitation-independent emissions from graphene quantum dots through microplasma-assisted electrochemical synthesis. Nano Struct. Nano Objects 2019, 19, 100341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalita, H.; Palaparthy, V.S.; Baghini, M.S.; Aslam, M. Electrochemical synthesis of graphene quantum dots from graphene oxide at room temperature and its soil moisture sensing properties. Carbon N. Y. 2020, 165, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirala, N.R.; Khandelwal, G.; Kumar, B.; Vinita; Prakash, R.; Kumar, V. One step electro-oxidative preparation of graphene quantum dots from wood charcoal as a peroxidase mimetic. Talanta 2017, 173, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, T.; Liao, H.; Yao, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Pan, D.; Sun, L.; et al. Gram-scale synthesis of single-crystalline graphene quantum dots with superior optical properties. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Z.; Nie, Y.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liao, X.; Zhang, J. Facile and large-scale synthesis of graphene quantum dots for selective targeting and imaging of cell nucleus and mitochondria. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; He, J.; Ma, C.; Liu, J.; Xi, F.; Dong, X. One-step synthesis of boron-doped graphene quantum dots for fluorescent sensors and biosensor. Talanta 2019, 199, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, T.V.; Hong, S.H.; Choi, W.M. Facile synthesis of cysteine-functionalized graphene quantum dots for a fluorescence probe for mercury ions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 97598–97603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, M.P.; Lohar, P.H.; Patil, A.G.; Patil, P.O.; Deshmukh, P.K. Controlled synthesis of blue luminescent graphene quantum dots from carbonized citric acid: Assessment of methodology, stability, and fluorescence in an aqueous environment. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 220, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Saievar-Iranizad, E. Synthesis of green-photoluminescent single layer graphene quantum dots: Determination of HOMO and LUMO energy states. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadhwa, S.; John, A.T.; Mathur, A.; Khanuja, M.; Bhattacharya, G.; Roy, S.S.; Ray, S.C. Engineering of luminescent graphene quantum dot-gold (GQD-Au) hybrid nanoparticles for functional applications. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.; Tian, L.; Xiang, W.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, Z. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from natural polymer starch for cell imaging. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresco-Cala, B.; Soriano, M.L.; Sciortino, A.; Cannas, M.; Messina, F.; Cardenas, S. One-pot synthesis of graphene quantum dots and simultaneous nanostructured self-assembly: Via a novel microwave-assisted method: Impact on triazine removal and efficiency monitoring. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 29939–29946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Shen, J.; Yang, Y.; Cui, X.; Yang, G. Bottom-Up Fabrication of Single-Layered Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots through Intermolecular Carbonization Arrayed in a 2D Plane. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15221–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Tang, L.; Xiang, J.; Ji, R.; Lai, S.K.; Yuan, S.; Lau, S.P. Facile preparation of sulphur-doped graphene quantum dots for ultra-high performance ultraviolet photodetectors. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 10447–10451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagheri, Z.; Ehtesabi, H.; Rahmandoust, M.; Ahadian, M.M.; Hallaji, Z.; Eskandari, F.; Jokar, E. New insight into the concept of carbonization degree in synthesis of carbon dots to achieve facile smartphone based sensing platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, X.; Tian, F.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wu, M.; Zhao, J.X. Fabrication of highly fluorescent graphene quantum dots using L-glutamic acid for in vitro/in vivo imaging and sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 4676–4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naik, J.P.; Sutradhar, P.; Saha, M. Molecular scale rapid synthesis of graphene quantum dots (GQDs). J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2017, 7, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, G.L.; Zhao, H.L.; Deng, H.H.; Yang, H.J.; Peng, H.P.; Liu, Y.H.; Chen, W. Fabrication of ultra-small monolayer graphene quantum dots by pyrolysis of trisodium citrate for fluorescent cell imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 4807–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Wang, G.; Mao, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, T.; Wang, M.; Chen, D.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; et al. Green, Rapid, and Universal Preparation Approach of Graphene Quantum Dots under Ultraviolet Irradiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 14470–14477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeresh, S.; Ganesh, H.; Nagaraj, Y.S.; Vandana, M.; Ashokkumar, S.P.; Yesappa, L.; Vijeth, H.; Devendrappa, H. UV-irradiation induced synthesis of reduced graphene quantum dots. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 45, 3968–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Graphene quantum dots: Emergent nanolights for bioimaging, sensors, catalysis and photovoltaic devices. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3686–3699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannazzo, D.; Pistone, A.; Ferro, S.; De Luca, L.; Monforte, A.M.; Romeo, R.; Buemi, M.R.; Pannecouque, C. Graphene Quantum Dots Based Systems As HIV Inhibitors. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3084–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Yang, G.; Su, C.; Zhong, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Guo, Z. One-pot green synthesis of fl ower-liked Au NP @ GQDs nanocomposites for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 725, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.H.; Oh, Y.; Kim, H.; Yoon, H. Exfoliation of 2D Materials for Energy and Environmental Applications. Chem. A Eur. J. 2020, 26, 6360–6401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.L. Graphene quantum dots prepared from chemical exfoliation of multiwall carbon nanotubes: An efficient photocatalyst promoter. Catal. Commun. 2016, 74, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapkota, B.; Benabbas, A.; Lin, H.Y.G.; Liang, W.; Champion, P.; Wanunu, M. Peptide-Decorated Tunable-Fluorescence Graphene Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 9378–9387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Gao, W.; Gupta, B.K.; Liu, Z.; Romero-Aburto, R.; Ge, L.; Song, L.; Alemany, L.B.; Zhan, X.; Gao, G.; et al. Graphene quantum dots derived from carbon fibers. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahirwar, S.; Mallick, S.; Bahadur, D. Electrochemical Method to Prepare Graphene Quantum Dots and Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 8343–8353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tajik, S.; Dourandish, Z.; Zhang, K.; Beitollahi, H.; Le, Q.V.; Jang, H.W.; Shokouhimehr, M. Carbon and graphene quantum dots: A review on syntheses, characterization, biological and sensing applications for neurotransmitter determination. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15406–15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.T.; Pham, H.P.; Tran, Q.T. A Facile Microwave-Assisted Hydrothermal Synthesis of Graphene Quantum Dots for Organic Solar Cell Efficiency Improvement. J. Nanomater. 2020, 2020, 15–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, S.; Kwon, W.; Rhee, S.W. Soft-template synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon nanodots: Tunable visible-light photoluminescence and phosphor-based light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 4221–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, W.; Wu, B.; Li, Z.; Pan, D.; Wu, M. Room-temperature synthesis of graphene quantum dots via electron-beam irradiation and their application in cell imaging. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 309, 374–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Qu, X. Cancer biomarker detection: Recent achievements and challenges. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2963–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumawat, M.K.; Thakur, M.; Gurung, R.B.; Srivastava, R. Graphene Quantum Dots for Cell Proliferation, Nucleus Imaging, and Photoluminescent Sensing Applications. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhou, S.; Garcia, C.; Fan, L.; Zhou, J. PH-Responsive fluorescent graphene quantum dots for fluorescence-guided cancer surgery and diagnosis. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 4928–4933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Than, A.; Chen, J.; Xi, F.; Liu, J.; Chen, P. Graphene quantum dots based fluorescence turn-on nanoprobe for highly sensitive and selective imaging of hydrogen sulfide in living cells. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Zhou, S.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, L.; Voelcker, N.H. Rhodamine-Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots for Detection of Fe3+ in Cancer Stem Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 23958–23966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogaidi, I.A.; Gou, H.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Guo, S.; Melconian, A.K.; Al-Kazaz, A.K.A.; Meng, F.; Wu, N. Detection of the ovarian cancer biomarker CA-125 using chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer to graphene quantum dots. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1344–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadati, A.; Hassanpour, S.; Bahavarnia, F.; Hasanzadeh, M. A novel biosensor for the monitoring of ovarian cancer tumor protein CA 125 in untreated human plasma samples using a novel nano-ink: A new platform for efficient diagnosis of cancer using paper based microfluidic technology. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1639–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y. A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, G.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Guo, Q. A graphene quantum dots based electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for carcinoembryonic antigen detection using poly(5-formylindole)/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 101, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganganboina, A.B.; Doong, R.A. Graphene Quantum Dots Decorated Gold-Polyaniline Nanowire for Impedimetric Detection of Carcinoembryonic Antigen. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Tagi, S.; Solhi, E.; Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Shadjou, N.; Eftekhari, A.; Mahboob, S. An innovative immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of breast cancer specific carbohydrate (CA 15-3) in unprocessed human plasma and MCF-7 breast cancer cell lysates using gold nanospear electrochemically assembled onto thiolated graphene quantum dots. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Baghban, H.N.; Shadjou, N.; Mokhtarzadeh, A. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensing of tumor suppressor protein p53 in unprocessed human plasma and cell lysates using a novel nanocomposite based on poly-cysteine/graphene quantum dots/gold nanoparticle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1348–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafín, V.; Valverde, A.; Martínez-García, G.; Martínez-Periñán, E.; Comba, F.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Campuzano, S.; Pingarrón, J.M. Graphene quantum dots-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes as nanocarriers in electrochemical immunosensing. Determination of IL-13 receptor A2 in colorectal cells and tumor tissues with different metastatic potential. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 284, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafín, V.; Valverde, A.; Garranzo-Asensio, M.; Barderas, R.; Campuzano, S.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Simultaneous amperometric immunosensing of the metastasis-related biomarkers IL-13Rα2 and CDH-17 by using grafted screen-printed electrodes and a composite prepared from quantum dots and carbon nanotubes for signal amplification. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Valipour, A. The potentiality of graphene quantum dots functionalized by nitrogen and thiol-doped (GQDs-N-S) to stabilize the antibodies in designing of human chorionic gonadotropin immunosensor. Nanochem. Res. 2019, 4, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.Y.; Zhao, L.; Lei, W.; Wen, W.; Wang, Y.J.; Bao, T.; Xiong, H.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Wang, S.F. A high-sensitivity electrochemical aptasensor of carcinoembryonic antigen based on graphene quantum dots-ionic liquid-nafion nanomatrix and DNAzyme-assisted signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekari, Z.; Zare, H.R.; Falahati, A. Electrochemical sandwich aptasensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen using graphene quantum dots, gold nanoparticles and nitrogen doped graphene modified electrode and exploiting the peroxidase-mimicking activity of a G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, F.; Arpanaei, A.; Mahmoudifard, M. Highly efficient detection of cancer-derived exosomes using modified core-shell electrospun nanofibers as a capture substrate and antibody immobilized-graphene quantum dots as a signaling agent. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 3670–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.S.; Shan, X.Y.; Chai, L.J.; Ma, J.J.; Chen, J.R.; Feng, H. A universal fluorescence sensing strategy based on biocompatible graphene quantum dots and graphene oxide for the detection of DNA. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5671–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Waghmode, S. Graphene quantum dot-based on-chip electrochemical DNA hybridization sensor for pancreatic cancer. Rep. Electrochem. 2016, 6, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, L.; Xiao, K.; Zhang, X.; Du, C.; Chen, J. A novel signal-off photoelectrochemical biosensor for M.SssI MTase activity assay based on GQDs@ZIF-8 polyhedra as signal quencher. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 150, 111861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pothipor, C.; Jakmunee, J.; Bamrungsap, S.; Ounnunkad, K. An electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of breast cancer clinically related microRNAs based on a gold nanoparticles/graphene quantum dots/graphene oxide film. Analyst 2021, 146, 4000–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.; Xie, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Duan, X.; Ren, J.; Xiao, F.; Wang, S. Pd Nanoparticles Decorated N-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots@N-Doped Carbon Hollow Nanospheres with High Electrochemical Sensing Performance in Cancer Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 22563–22573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, S.; Lan, F.; Liang, L.; Ren, N.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Ultrasensitive Photoelectrochemical Biosensing of Cell Surface N-Glycan Expression Based on the Enhancement of Nanogold-Assembled Mesoporous Silica Amplified by Graphene Quantum Dots and Hybridization Chain Reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 6670–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.; Ji, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, D.; Sun, X. A novel magnetic fluorescent biosensor based on graphene quantum dots for rapid, efficient, and sensitive separation and detection of circulating tumor cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Dang, C.V. Cancer’s molecular sweet tooth and the warburg effect. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 8927–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabassum, R.; Jeong, N.Y.; Jung, J. Therapeutic importance of hydrogen sulfide in age-associated neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashfi, K. The dichotomous role of H2S in cancer cell biology? Déjà vu all over again. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 205–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanaswamy, N.; Govindaraju, T. Aldazine-based colorimetric sensors for Cu2+ and Fe3+. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 161, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristea, C.; Florea, A.; Tertiș, M.; Săndulescu, R. Immunosensors. In Biosensors-Micro and Nanoscale Biosensors Applications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Steele, G.; Andrews, C.; Nakazato, H.; Oikawa, S.; Jessup, J.M. The effect of transfection of the CEA gene on the metastatic behavior of the human colorectal cancer cell line MIP-101. Cancer Lett. 1995, 92, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stovold, R.; Blackhall, F.; Meredith, S.; Hou, J.M.; Dive, C.; White, A. Biomarkers for small cell lung cancer: Neuroendocrine, epithelial and circulating tumour cells. Lung Cancer 2012, 76, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Shadjou, N.; de la Guardia, M. Aptamer-based assay of biomolecules: Recent advances in electro-analytical approach. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventura, A.; Kirsch, D.G.; McLaughlin, M.E.; Tuveson, D.A.; Grimm, J.; Lintault, L.; Newman, J.; Reczek, E.E.; Weissleder, R.; Jacks, T. Restoration of p53 function leads to tumour regression in vivo. Nature 2007, 445, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Yoshimatsu, Y.; Tomizawa, T.; Kunita, A.; Takayama, R.; Morikawa, T.; Komura, D.; Takahashi, K.; Oshima, T.; Sato, M.; et al. Interleukin-13 receptor α2 is a novel marker and potential therapeutic target for human melanoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altree-Tacha, D.; Tyrrell, J.; Haas, T. CDH17 is a more sensitive marker for gastric adenocarcinoma than CK20 and CDX2. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2017, 141, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenman, U.H.; Alfthan, H.; Hotakainen, K. Human chorionic gonadotropin in cancer. Clin. Biochem. 2004, 37, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.; Kim, M.G. Advancements in DNA-assisted Immunosensors. Biochip. J. 2020, 14, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nezlin, R. Use of aptamers in immunoassays. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 70, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliuk, A.B.; Hu, L.; Tao, W.A. Aptamer in bioanalytical applications. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4440–4452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tabar, G.R.H.; Smith, C. DNA aptamers selected as molecular probes for diagnosis of cancerous cells. World Appl. Sci. J. 2010, 8, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.M.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Yu, R.N.; Zhang, M.Z.; Song, J.T.; Zhao, Y. Di Carcino-embryonic antigen detection based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer between quantum dots and graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhong, S.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes: Key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, H.; Yu, Q.; Huang, H.; Fervers, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L. A Circulating Exosome RNA Signature Is a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Pancreatic Cancer, a Systematic Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobhal, G.; Ayupova, D.; Laufersky, G.; Ayed, Z.; Nann, T.; Goreham, R.V. Cadmium-free quantum dots as fluorescent labels for exosomes. Sensors 2018, 18, 3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N. Gold–carbon dots for the intracellular imaging of cancer-derived exosomes. 2D Mater. 2020, 13, 7854–7864. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, J.I.A.; Yusof, N.A. The strategies of DNA immobilization and hybridization detection mechanism in the construction of electrochemical DNA sensor: A review. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2017, 16, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Jia, Y. Multiprobe Assay for Clinical SEPT9 Methylation Based on the Carbon Dot-Modified Liquid-Exfoliated Graphene Field Effect Transistor with a Potential to Present a Methylation Panorama. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 16228–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condrat, C.E.; Thompson, D.C.; Barbu, M.G.; Bugnar, O.L.; Boboc, A.; Cretoiu, D.; Suciu, N.; Cretoiu, S.M.; Voinea, S.C. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Disease: Latest Findings Regarding Their Role in Diagnosis and Prognosis. Cells 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Costa, C.; Abal, M.; López-López, R.; Muinelo-Romay, L. Biosensors for the detection of circulating tumour cells. Sensors 2014, 14, 4856–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lisanti, M.P.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.E.; Lin, Z.; Pavlides, S.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Pestell, R.G.; Howell, A.; Sotgia, F. Hydrogen peroxide fuels aging, inflammation, cancer metabolism and metastasis: The seed and soil also needs “fertilizer”. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2440–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Hu, L.W.; Zhu, H.Y.; Ling, Y.; Tao, J.H.; Xu, C.X. RGO quantum dots/ZnO hybrid nanofibers fabricated using electrospun polymer templates and applications in drug screening involving an intracellular H2O2 sensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 2651–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Tang, H.; Gao, Z.; He, S.; Li, J.; Han, S. Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of tumor cells based on multiple layer CdS quantum dots-functionalized polystyrene microspheres and graphene oxide—Polyaniline composite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, O.M.T. Cancer glycan epitopes: Biosynthesis, structure and function. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 670–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

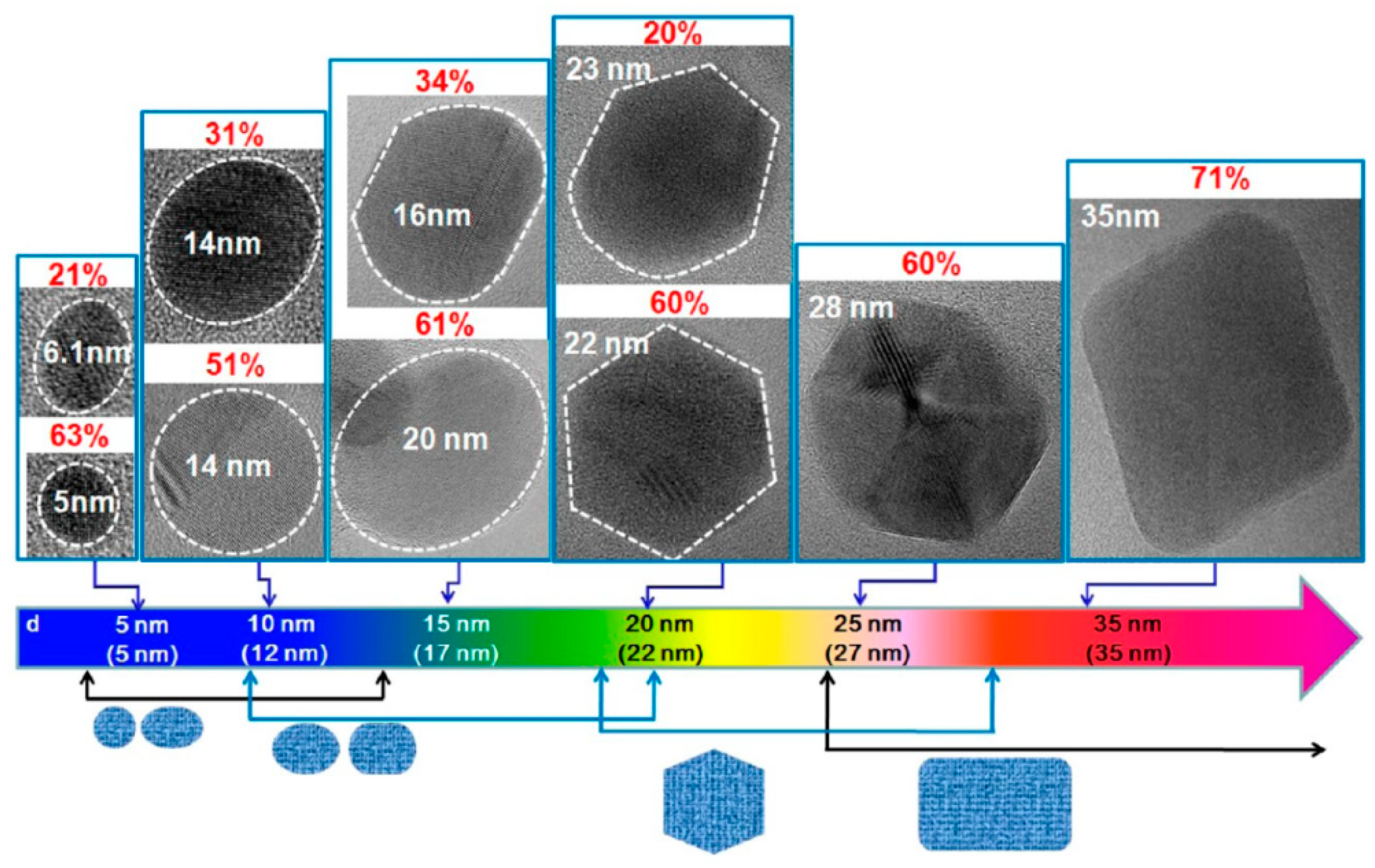

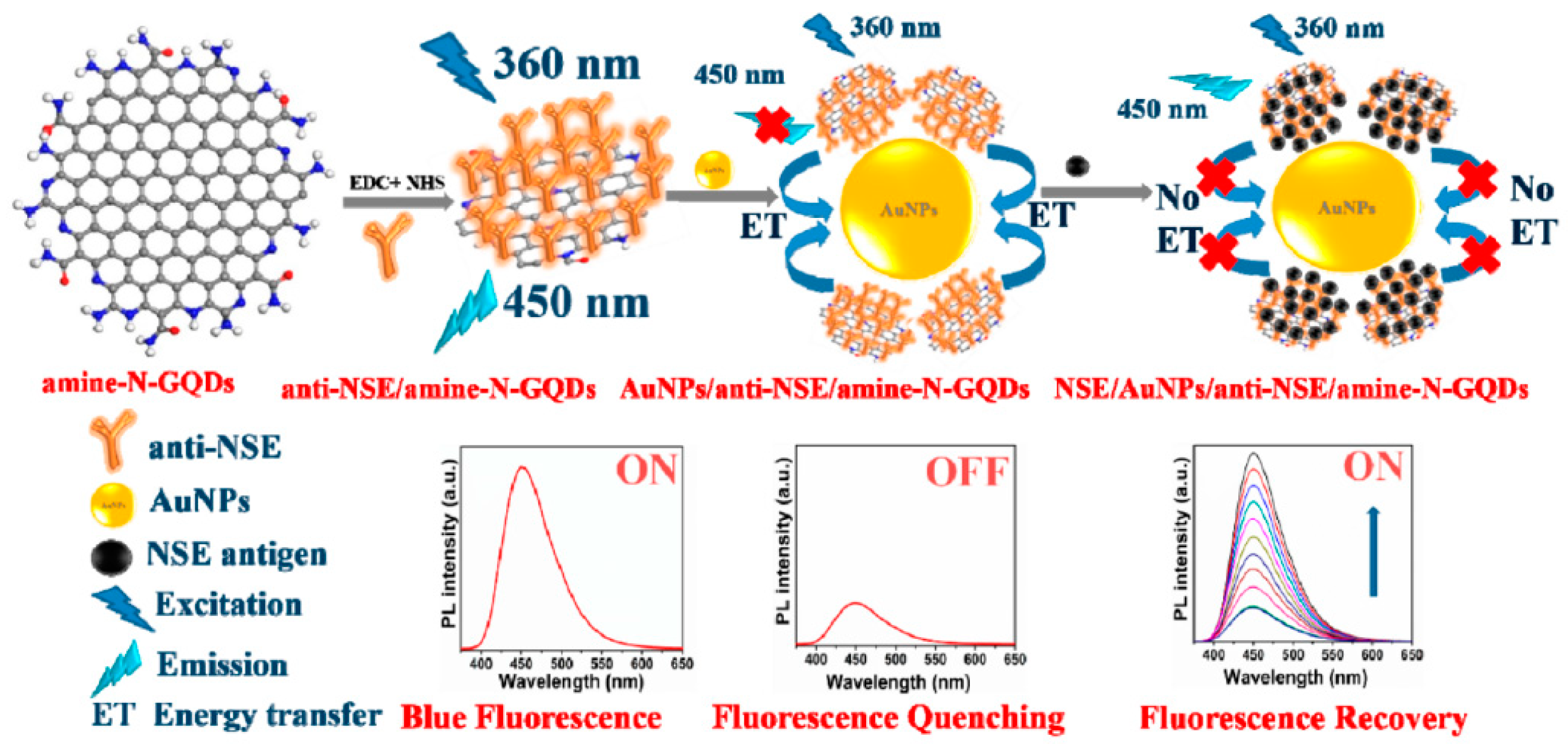

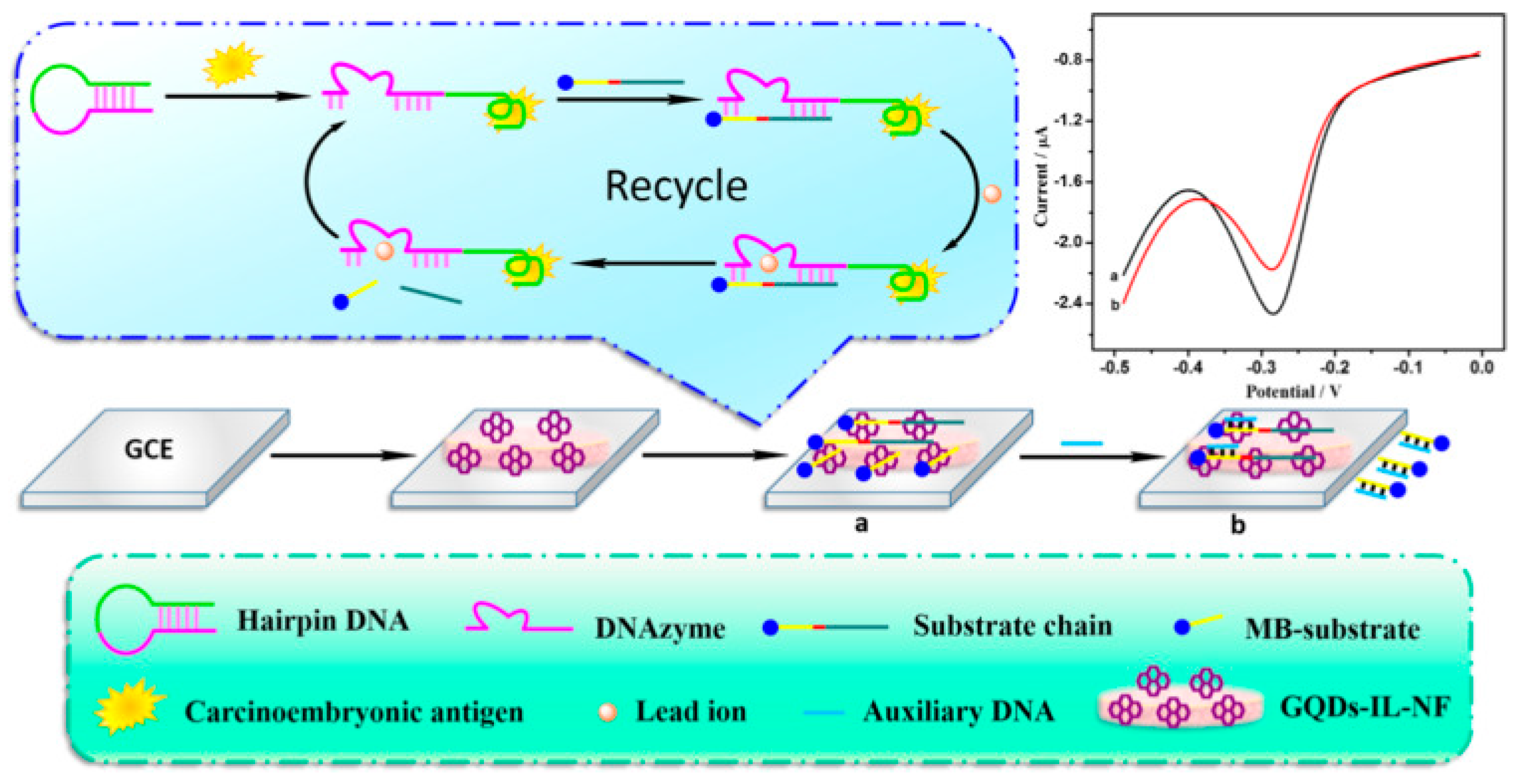

| Approach | Method | Source | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top-down | Hydrothermal | graphite | [47] |
| graphene | [48] | ||
| graphene oxide | [49,50] | ||
| corn powder | [51] | ||
| cellulose | [52] | ||
| rice husk | [53] | ||
| Liquid exfoliation | graphite | [54,55,56,57] | |
| Electrochemical | graphite | [58,59,60] | |
| graphene oxide | [61] | ||
| wood charcoal | [62] | ||
| Bottom-up | Hydrothermal | pyrene | [63] |
| pyrene and polyethyleneimine | [64] | ||
| 1,3,6-trinitropyrene and borax | [65] | ||
| citric acid | [66,67] | ||
| glucose | [68,69] | ||
| starch | [70] | ||
| urea and glucose | [71] | ||
| Template methods | 1,3,5-triamino-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene | [72] | |
| hexa-peri-hexabenzocoronene | [73] | ||
| carbon disuphide | [74] | ||
| Pyrolysis | L-glutamic acid | [75] | |
| citric acid | [76] | ||
| trisodium citrate | [77] | ||
| Irradiation methods | salicylic acid and pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylic acid | [78] | |
| glucose | [79] | ||
| 1,3,6-trinitropyrene | [80] |
| Sensing Material | Biological Material | Analyte | Detection Technique | Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GQDs | L929, HT-1080, MIA, PaCa-2, HeLa, MG-63 cells | pH | optical | −49.96 ± 3.5 mV/pH | [94] |
| S-N-doped GQDs | mice bearing PANC-1, A549 HepG2, U87MG, HeLa cells | pH | optical | switch point at pH 6.8 | [95] |
| GQDs-DNPTYR | MCF-7 cells | H2S | optical | LOD: 2 nM. | [96] |
| RBD-GQDs | Pancreatic CSCs, HeLa cells | Fe3+ | optical | LOD: 0.02 μM | [97] |
| GQDs-cAb | - | CA-125 | chemiluminescence | LOD: 0.05 U mL−1 | [98] |
| Ag–DPA–GQDs | plasma | CA-125 | electrochemical | LOD: 0.001 U mL−1 | [99] |
| PtPd/N-GQDs@Au | serum | CEA | electrochemical | LOD: 2 fg/mL | [100] |
| GQDs@Au | serum | CEA | electrochemiluminescence | LOD: 3.78 fg/mL | [101] |
| N,S-GQDs@Au-PANI | serum | CEA | electrochemical | LOD: 0.01 ng/mL. | [102] |
| amine-N-GQDs@Au | serum | NSE | optical | LOD: 0.09 pg mL−1 | [39] |
| CysA/Au NSs/GQDs | plasma, MCF-7 cells | CA 15-3 | electrochemical | LOD: 0.11 U/mL | [103] |
| P-Cys-GQDs-GNPs | plasma, L929, HCT PC-3, MCF-7 cells | p-53 | electrochemical | LOD: 0.065 fM | [104] |
| MWCNTs/GQDs | lysates from colorectal cancer | IL-13Rα2 | electrochemical | LOD: 0.8 ng mL−1 | [105] |
| MWCNTs/GQDs | lysates from breast and colorectal cancer | IL-13Rα2 CDH-17 | amperometric | LOD: 1.4 ng/mL (IL-13sRα2); 0.03 ng/mL (CDH-17) | [106] |
| GQDs N-S/Au | serum | HCG | electrochemical | LOD: 12.5 fg mL−1 | [107] |
| GQDs-IL-NF | serum | CEA | electrochemical | LOD: 0.34 fg mL−1 | [108] |
| GQD/AuNP/NG/ | serum | CEA | electrochemical | LOD: 3.2 fg mL−1 | [109] |
| GQDs | serum | PCa- exosomes | optical | LOD: 7.5 mg ml−1 | [110] |
| GO/GQDs | - | DNA | optical | LOD: 75.0 pM | [111] |
| GQDs | - | p16 tumor-suppressor gene | electrochemical | LOD: 0.10 pM | [112] |
| GQDs@ZIF-8 | - | M.SssI MTase | photoelectrochemical | LOD: 0.004 U mL−1 | [113] |
| AuNPs/GQDs/GO | serum | miRNA | electrochemical | LOD: 0.04 fM (miRNA-21), 0.33 fM (miRNA-155), 0.28 fM (miRNA-210) | [114] |
| NGQD@NC@Pd HNSs | MDA-MB-231, HBL-100, U87 cells | H2O2 | electrochemical | LOD: 20 nM | [115] |
| ConA-GQDs | MCF-7 cells | N-glycan | electrochemiluminescence | LOD: 21 cells/ mL | [116] |
| Apt@Fe3O4@GQDs/MoS2 | Hep G2, A549, HEK293 cells | EpCAM | optical | LOD: 1.19 nM, | [117] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iannazzo, D.; Espro, C.; Celesti, C.; Ferlazzo, A.; Neri, G. Smart Biosensors for Cancer Diagnosis Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Cancers 2021, 13, 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133194
Iannazzo D, Espro C, Celesti C, Ferlazzo A, Neri G. Smart Biosensors for Cancer Diagnosis Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Cancers. 2021; 13(13):3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133194
Chicago/Turabian StyleIannazzo, Daniela, Claudia Espro, Consuelo Celesti, Angelo Ferlazzo, and Giovanni Neri. 2021. "Smart Biosensors for Cancer Diagnosis Based on Graphene Quantum Dots" Cancers 13, no. 13: 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133194
APA StyleIannazzo, D., Espro, C., Celesti, C., Ferlazzo, A., & Neri, G. (2021). Smart Biosensors for Cancer Diagnosis Based on Graphene Quantum Dots. Cancers, 13(13), 3194. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13133194











