Integration of Systemic Therapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Modern Role for Stereotactic Radiosurgery
3. Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Systemic Therapies
3.1. Chemotherapy
3.2. Targeted Therapies
3.2.1. Anti-Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER-2) Drug Conjugates and Anti HER-2 Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs)
3.2.2. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR)-TKIs
3.2.3. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors
3.2.4. Angiogenesis Inhibitors
3.2.5. BRAF Inhibitors
3.2.6. MEK Inhibitors
3.2.7. Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitors (CDK4/6)
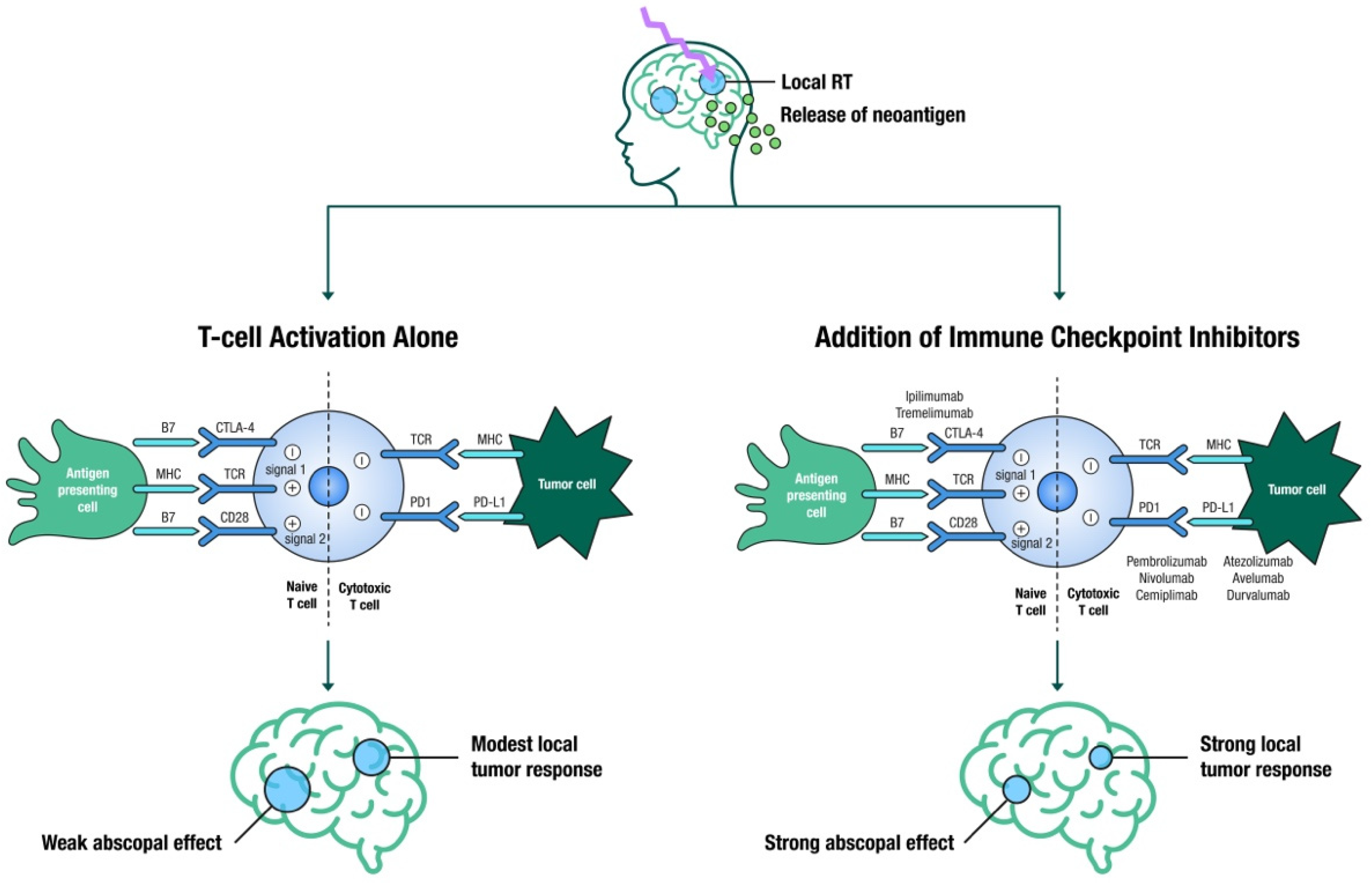
4. SRS and Immunotherapy
4.1. Timing and Sequencing
4.2. Impact of Corticosteroids
4.3. Pseudo-Progression and Radiation Necrosis
5. Future Directions and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suh, J.H.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Sahgal, A.; Chang, E.L. Current approaches to the management of brain metastases. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 279–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.L.; Close, T.P.; Grego, J.M.; Brannon, W.L.; Gonzales, F. Predilection of brain metastasis in gray and white matter junction and vascular border zones. Cancer 1996, 77, 1551–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecha, R.; Gondi, V.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Brastianos, P.K.; Mehta, M.P. Recent advances in managing brain metastasis. F1000Research 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Palmer, J.D.; Trifiletti, D.M.; Gondi, V.; Chan, M.; Minniti, G.; Rusthoven, C.G.; Schild, S.E.; Mishra, M.V.; Bovi, J.; Williams, N.; et al. Multidisciplinary patient-centered management of brain metastases and future directions. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2020, 2, vdaa034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Borius, P.-Y.; Régis, J.; Carpentier, A.; Kalamarides, M.; Valery, C.A.; Latorzeff, I. Safety of radiosurgery concurrent with systemic therapy (chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and/or immunotherapy) in brain metastases: A systematic review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021, 40, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, P.; Lian, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. Radiotherapy in combination with systemic therapies for brain metastases: Current status and progress. Cancer Biol. Med. 2020, 17, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vulpe, H.; Save, A.V.; Xu, Y.; Elliston, C.D.; Garrett, M.D.; Wu, C.-C.; Cheng, S.K.; Jani, A.H.; Bruce, J.N.; McKhann, G.M.; et al. Frameless Stereotactic Radiosurgery on the Gamma Knife Icon: Early Experience From 100 Patients. Neurosurgery 2020, 86, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Atkins, K.M.; Pashtan, I.M.; Bussière, M.R.; Kang, K.H.; Niemierko, A.; Daly, J.E.; Botticello, T.M.; Hurd, M.C.; Chapman, P.H.; Oh, K.; et al. Proton Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases: A Single-Institution Analysis of 370 Patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 101, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, E.J.; Prabhu, A.V.; Sindhu, K.K.; Lazarev, S.; Ruiz-Garcia, H.; Peterson, J.L.; Beltran, C.; Furutani, K.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P.; et al. Proton and Heavy Particle Intracranial Radiosurgery. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperduto, P.W.; Mesko, S.; Li, J.; Cagney, D.; Aizer, A.; Lin, N.U.; Nesbit, E.; Kruser, T.J.; Chan, J.; Braunstein, S.; et al. Survival in Patients With Brain Metastases: Summary Report on the Updated Diagnosis-Specific Graded Prognostic Assessment and Definition of the Eligibility Quotient. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3773–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Jaeckle, K.; Ballman, K.V.; Farace, E.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Barker, F.G.; Deming, R.; Burri, S.H.; et al. Effect of Radiosurgery Alone vs Radiosurgery with Whole Brain Radiation Therapy on Cognitive Function in Patients With 1 to 3 Brain Metastases: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2016, 316, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Ballman, K.V.; Cerhan, J.H.; Anderson, S.K.; Carrero, X.W.; Whitton, A.C.; Greenspoon, J.; Parney, I.F.; Laack, N.N.I.; Ashman, J.B.; et al. Postoperative stereotactic radiosurgery compared with whole brain radiotherapy for resected metastatic brain disease (NCCTG N107C/CEC·3): A multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, H.; Shirato, H.; Tago, M.; Nakagawa, K.; Toyoda, T.; Hatano, K.; Kenjyo, M.; Oya, N.; Hirota, S.; Shioura, H.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 2483–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, E.; Scott, C.; Souhami, L.; Dinapoli, R.; Kline, R.; Loeffler, J.; Farnan, N. Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumors and brain metastases: Final report of RTOG protocol 90-05. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2000, 47, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, E.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Hess, K.R.; Allen, P.K.; Lang, F.F.; Kornguth, D.G.; Arbuckle, R.B.; Swint, J.M.; Shiu, A.S.; Maor, M.H.; et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerosa, M.; Nicolato, A.; Foroni, R.; Tomazzoli, L.; Bricolo, A. Analysis of long-term outcomes and prognostic factors in patients with non-small cell lung cancer brain metastases treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 102, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Kotecha, R.; Mehta, M.P. The Complexity of Managing Large Brain Metastasis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 483–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.B.; Amsbaugh, M.J.; Burton, E.; Nelson, M.; Williams, B.; Koutourousiou, M.; Nauta, H.; Woo, S. Increasing time to postoperative stereotactic radiation therapy for patients with resected brain metastases: Investigating clinical outcomes and identifying predictors associated with time to initiation. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 136, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bander, E.D.; Yuan, M.; Reiner, A.S.; Panageas, K.S.; Ballangrud, Å.M.; Brennan, C.W.; Beal, K.; Tabar, V.; Moss, N.S. Durable 5-year local control for resected brain metastases with early adjuvant SRS: The effect of timing on intended-field control. Neuro-oncol. Pract. 2021, 8, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.R.; Burri, S.H.; Asher, A.L.; Crocker, I.R.; Fraser, R.W.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Kandula, S.; Zhong, J.; Press, R.H.; et al. Comparing Preoperative With Postoperative Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Resectable Brain Metastases: A Multi-institutional Analysis. Neurosurgery 2016, 79, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routman, D.M.; Yan, E.; Vora, S.; Peterson, J.; Mahajan, A.; Chaichana, K.L.; Laack, N.; Brown, P.D.; Parney, I.F.; Burns, T.C.; et al. Preoperative Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iorio-Morin, C.; Masson-Côté, L.; Ezahr, Y.; Blanchard, J.; Ebacher, A.; Mathieu, D. Early Gamma Knife stereotactic radiosurgery to the tumor bed of resected brain metastasis for improved local control. J. Neurosurg. 2014, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabhu, R.S.; Patel, K.R.; Press, R.H.; Soltys, S.G.; Brown, P.D.; Mehta, M.P.; Asher, A.L.; Burri, S.H. Preoperative Vs Postoperative Radiosurgery For Resected Brain Metastases: A Review. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musunuru, H.B.; Witt, J.S.; Yadav, P.; Francis, D.M.; Kuczmarska-Haas, A.; Labby, Z.E.; Bassetti, M.F.; Howard, S.P.; Baschnagel, A.M. Impact of adjuvant fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy dose on local control of brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.M.S.; Miller, J.; Hoffer, S.A.; Mansur, D.B.; Coffey, M.; Lo, S.S.; Sloan, A.E.; Machtay, M. Postoperative hypofractionated stereotactic brain radiation (HSRT) for resected brain metastases: Improved local control with higher BED10. J. Neurooncol. 2018, 139, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, M.; Serizawa, T.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Kawagishi, J.; Yamanaka, K.; Sato, Y.; Jokura, H.; Yomo, S.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with multiple brain metastases (JLGK0901): A multi-institutional prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, R.T.; Masters, A.H.; McTyre, E.R.; Farris, M.K.; Chung, C.; Page, B.R.; Kleinberg, L.R.; Hepel, J.; Contessa, J.N.; Chiang, V.; et al. Initial SRS for Patients With 5 to 15 Brain Metastases: Results of a Multi-Institutional Experience. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ludmir, E.B.; Wang, Y.; Guha-Thakurta, N.; McAleer, M.F.; Settle, S.H.; Yeboa, D.N.; Ghia, A.J.; McGovern, S.L.; Chung, C.; et al. Stereotactic Radiosurgery versus Whole-brain Radiation Therapy for Patients with 4–15 Brain Metastases: A Phase III Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 108, S21–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonadou, D.; Paraskevaidis, M.; Sarris, G.; Coliarakis, N.; Economou, I.; Karageorgis, P.; Throuvalas, N. Phase II randomized trial of temozolomide and concurrent radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 3644–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verger, E.; Gil, M.; Yaya, R.; Viñolas, N.; Villà, S.; Pujol, T.; Quintó, L.; Graus, F. Temozolomide and concomitant whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: A phase II randomized trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 61, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.-J. Targeted drugs for systemic therapy of lung cancer with brain metastases. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 5459–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cagney, D.N.; Martin, A.M.; Catalano, P.J.; Reitman, Z.J.; Mezochow, G.A.; Lee, E.Q.; Wen, P.Y.; Weiss, S.E.; Brown, P.D.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; et al. Impact of pemetrexed on intracranial disease control and radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer receiving stereotactic radiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 511–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.J.; Kummerlowe, M.N.; Redmond, K.J.; Rigamonti, D.; Lim, M.K.; Kleinberg, L.R. Stereotactic Radiosurgery: Treatment of Brain Metastasis Without Interruption of Systemic Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Miller, J.A.; Kotecha, R.; Xiao, R.; Juloori, A.; Ward, M.C.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Peereboom, D.M.; Murphy, E.S.; et al. The risk of radiation necrosis following stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent systemic therapies. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomo, S.; Hayashi, M.; Cho, N. Impacts of HER2-overexpression and molecular targeting therapy on the efficacy of stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases from breast cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 112, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Miller, J.A.; Kotecha, R.; Chao, S.T.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Peereboom, D.M.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Barnett, G.H.; Murphy, E.S.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent HER2-directed therapy is associated with improved objective response for breast cancer brain metastasis. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsai, S.; Miller, J.A.; Juloori, A.; Chao, S.T.; Kotecha, R.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Murphy, E.S.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery with concurrent lapatinib is associated with improved local control for HER2-positive breast cancer brain metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2019, 132, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.A.; Moughan, J.; Sperduto, P.W.; De Los Santos, J.F.; Peereboom, D.; Ogunleye, T.B.; Boulter, D.; Cho, K.H.; Shin, K.H.; Zoberi, I.; et al. NRG Oncology/RTOG 1119: PHASE II Randomized Study of Whole Brain Radiotherapy/Stereotactic Radiosurgery with Concurrent Lapatinib in Patients with Brain Metastases from HER2-Positive Breast Cancer—A Collaborative Study of NRG and KROG (NCT01622868). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2020, 108, S174–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraud, A.; Xu, H.P.; Beuzeboc, P.; Kirova, Y.M. Preliminary experience of the concurrent use of radiosurgery and T-DM1 for brain metastases in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 131, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, P.K.; Cittelly, D.M.; Robin, T.P.; Carlson, J.A.; Stuhr, K.A.; Contreras-Zarate, M.J.; Lai, S.; Ormond, D.R.; Rusthoven, C.G.; Gaspar, L.E.; et al. Combination of Trastuzumab Emtansine and Stereotactic Radiosurgery Results in High Rates of Clinically Significant Radionecrosis and Dysregulation of Aquaporin-4. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3946–3953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, M.N.; Walker, C.; Thawani, C.; Naz, A.; Figura, N.B.; Kushchayev, S.; Etame, A.; Yu, H.-H.M.; Robinson, T.J.; Liu, J.; et al. Trastuzumab Emtansine (T-DM1) and stereotactic radiation in the management of HER2+ breast cancer brain metastases. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 223. [Google Scholar]
- Johung, K.L.; Yao, X.; Li, F.; Yu, J.B.; Gettinger, S.N.; Goldberg, S.; Decker, R.H.; Hess, J.A.; Chiang, V.L.; Contessa, J.N. A clinical model for identifying radiosensitive tumor genotypes in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5523–5532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnuson, W.J.; Lester-Coll, N.H.; Wu, A.J.; Yang, T.J.; Lockney, N.A.; Gerber, N.K.; Beal, K.; Amini, A.; Patil, T.; Kavanagh, B.D.; et al. Management of Brain Metastases in Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor-Naïve Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Retrospective Multi-Institutional Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yomo, S.; Serizawa, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Higuchi, Y.; Sato, Y.; Shuto, T.; Akabane, A.; Jokura, H.; Kawagishi, J.; Aoyama, H. The impact of EGFR-TKI use on clinical outcomes of lung adenocarcinoma patients with brain metastases after Gamma Knife radiosurgery: A propensity score-matched analysis based on extended JLGK0901 dataset (JLGK0901-EGFR-TKI). J. Neurooncol. 2019, 145, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, W.S.; Kwon, D.H.; Cho, Y.H.; Choi, C.-M. Effects of an Epithelial Growth Factor Receptor-Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Add-on in Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases Originating from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2015, 58, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Gong, L.; Fang, L.; Lu, H.; Qin, J.; Han, N.; Xie, F.; Qiu, G.; Huang, Z. Effects of icotinib with and without radiation therapy on patients with EGFR mutant non-small cell lung cancer and brain metastases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erickson, A.W.; Brastianos, P.K.; Das, S. Assessment of Effectiveness and Safety of Osimertinib for Patients with Intracranial Metastatic Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e201617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Nagpal, S.; Wakelee, H.A.; Li, G.; Soltys, S.G.; Neal, J.W. Osimertinib for EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer with Brain Metastases: Results from a Single-Center Retrospective Study. Oncologist 2019, 24, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakuda, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Kenmotsu, H.; Fukuda, M.; Takeshita, M.; Suetsugu, T.; Kirita, K.; Ebi, N.; Hataji, O.; Miura, S.; et al. A phase II study of Osimertinib for patients with radiotherapy-naïve CNS metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer: Treatment rationale and protocol design of the OCEAN study (LOGIK 1603/WJOG 9116L). BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Nowak, K.A.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Winchester, C.-L.; Dalal, K.; Giacalone, N.J.; Liu, N.; Werner-Wasik, M.; Wasik, M.A.; Dicker, A.P.; et al. ALK inhibitor PF02341066 (crizotinib) increases sensitivity to radiation in non-small cell lung cancer expressing EML4-ALK. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Wei, Q.; Schwager, C.; Moustafa, M.; Zhou, C.; Lipson, K.E.; Weichert, W.; Debus, J.; Abdollahi, A. Synergistic effects of crizotinib and radiotherapy in experimental EML4-ALK fusion positive lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 114, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johung, K.L.; Yeh, N.; Desai, N.B.; Williams, T.M.; Lautenschlaeger, T.; Arvold, N.D.; Ning, M.S.; Attia, A.; Lovly, C.M.; Goldberg, S.; et al. Extended Survival and Prognostic Factors for Patients With ALK-Rearranged Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Brain Metastasis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sofia Vala, I.; Martins, L.R.; Imaizumi, N.; Nunes, R.J.; Rino, J.; Kuonen, F.; Carvalho, L.M.; Rüegg, C.; Grillo, I.M.; Barata, J.T.; et al. Low doses of ionizing radiation promote tumor growth and metastasis by enhancing angiogenesis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11222. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, E.; Pan, L.; Dai, J.; Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Mei, G.; Sheng, X. A new strategy of CyberKnife treatment system based radiosurgery followed by early use of adjuvant bevacizumab treatment for brain metastasis with extensive cerebral edema. J. Neurooncol. 2014, 119, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomo, S.; Hayashi, M. Salvage stereotactic radiosurgery with adjuvant use of bevacizumab for heavily treated recurrent brain metastases: A preliminary report. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 127, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinde, J.; Carron, R.; Tomasini, P.; Greillier, L.; Régis, J.; Barlesi, F. Bevacizumab Plus Radiosurgery for Nonsquamous Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients with Brain Metastases: Safe Combination? World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, e1–e1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, E.J.; Brown, A.P.; Asano, H.; Mandler, M.; Burgan, W.E.; Carter, D.; Camphausen, K.; Citrin, D. In vitro and in vivo radiosensitization with AZD6244 (ARRY-142886), an inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 kinase. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3050–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sambade, M.J.; Peters, E.C.; Thomas, N.E.; Kaufmann, W.K.; Kimple, R.J.; Shields, J.M. Melanoma cells show a heterogeneous range of sensitivity to ionizing radiation and are radiosensitized by inhibition of B-RAF with PLX-4032. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 98, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kotecha, R.; Miller, J.A.; Venur, V.A.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Chao, S.T.; Suh, J.H.; Barnett, G.H.; Murphy, E.S.; Funchain, P.; Yu, J.S.; et al. Melanoma brain metastasis: The impact of stereotactic radiosurgery, BRAF mutational status, and targeted and/or immune-based therapies on treatment outcome. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ly, D.; Bagshaw, H.P.; Anker, C.J.; Tward, J.D.; Grossmann, K.F.; Jensen, R.L.; Shrieve, D.C. Local control after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in patients with melanoma with and without BRAF mutation and treatment. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 123, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wolf, A.; Zia, S.; Verma, R.; Pavlick, A.; Wilson, M.; Golfinos, J.G.; Silverman, J.S.; Kondziolka, D. Impact on overall survival of the combination of BRAF inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with melanoma brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2016, 127, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastorakos, P.; Xu, Z.; Yu, J.; Hess, J.; Qian, J.; Chatrath, A.; Taylor, D.G.; Kondziolka, D.; Warnick, R.; Chiang, V.; et al. BRAF V600 Mutation and BRAF Kinase Inhibitors in Conjunction With Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Intracranial Melanoma Metastases: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Neurosurgery 2019, 84, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaudy-Marqueste, C.; Carron, R.; Delsanti, C.; Loundou, A.; Monestier, S.; Archier, E.; Richard, M.A.; Regis, J.; Grob, J.J. On demand Gamma-Knife strategy can be safely combined with BRAF inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma brain metastases. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2014, 25, 2086–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Lee, C.-C.; Ramesh, A.; Mueller, A.C.; Schlesinger, D.; Cohen-Inbar, O.; Shih, H.-H.; Sheehan, J.P. BRAF V600E mutation and BRAF kinase inhibitors in conjunction with stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial melanoma metastases. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, B.G.; Ahmed, K.A.; Johnstone, P.A.S.; Yu, H.-H.M.; Etame, A.B. Initial experience with combined BRAF and MEK inhibition with stereotactic radiosurgery for BRAF mutant melanoma brain metastases. Melanoma Res. 2016, 26, 382–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, E.S.; Lo, S.; Drummond, M.; Fogarty, G.B.; Menzies, A.M.; Guminski, A.; Shivalingam, B.; Clarke, K.; Long, G.V.; Hong, A.M. Survival of patients with melanoma brain metastasis treated with stereotactic radiosurgery and active systemic drug therapies. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 75, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosacki, C.; Bouleftour, W.; Sotton, S.; Vallard, A.; Daguenet, E.; Ouaz, H.; Cojoracu, I.; Moslemi, D.; Molekzadehmoghani, M.; Magné, N. CDK 4/6 inhibitors combined with radiotherapy: A review of literature. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 26, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteway, S.L.; Harris, P.S.; Venkataraman, S.; Alimova, I.; Birks, D.K.; Donson, A.M.; Foreman, N.K.; Vibhakar, R. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 6 suppresses cell proliferation and enhances radiation sensitivity in medulloblastoma cells. J. Neurooncol. 2013, 111, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figura, N.B.; Potluri, T.K.; Mohammadi, H.; Oliver, D.E.; Arrington, J.A.; Robinson, T.J.; Etame, A.B.; Tran, N.D.; Liu, J.K.; Soliman, H.; et al. CDK 4/6 inhibitors and stereotactic radiation in the management of hormone receptor positive breast cancer brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 2019, 144, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElJalby, M.; Pannullo, S.C.; Schwartz, T.H.; Parashar, B.; Wernicke, A.G. Optimal Timing and Sequence of Immunotherapy When Combined with Stereotactic Radiosurgery in the Treatment of Brain Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2019, 127, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, T.; Kiecker, F.; Schaefer, S.; Stege, H.; Kaehler, K.; Terheyden, P.; Gesierich, A.; Gutzmer, R.; Haferkamp, S.; Uttikal, J.; et al. Combined immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab with and without local therapy in patients with melanoma brain metastasis: A DeCOG* study in 380 patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishna, R.; Formenti, S. Radiosurgery and Immunotherapy in the Treatment of Brain Metastases. World Neurosurg. 2019, 130, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tazi, K.; Hathaway, A.; Chiuzan, C.; Shirai, K. Survival of melanoma patients with brain metastases treated with ipilimumab and stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.R.; Shoukat, S.; Oliver, D.E.; Chowdhary, M.; Rizzo, M.; Lawson, D.H.; Khosa, F.; Liu, Y.; Khan, M.K. Ipilimumab and Stereotactic Radiosurgery Versus Stereotactic Radiosurgery Alone for Newly Diagnosed Melanoma Brain Metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 40, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silk, A.W.; Bassetti, M.F.; West, B.T.; Tsien, C.I.; Lao, C.D. Ipilimumab and radiation therapy for melanoma brain metastases. Cancer Med. 2013, 2, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kotecha, R.; Kim, J.M.; Miller, J.A.; Juloori, A.; Chao, S.T.; Murphy, E.S.; Peereboom, D.M.; Mohammadi, A.M.; Barnett, G.H.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; et al. The impact of sequencing PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastasis. Neuro Oncol. 2019, 21, 1060–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomeranz Krummel, D.A.; Nasti, T.H.; Izar, B.; Press, R.H.; Xu, M.; Lowder, L.; Kallay, L.; Rupji, M.; Rosen, H.; Su, J.; et al. Impact of Sequencing Radiation Therapy and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in the Treatment of Melanoma Brain Metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 108, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cohen-Inbar, O.; Shih, H.-H.; Xu, Z.; Schlesinger, D.; Sheehan, J.P. The effect of timing of stereotactic radiosurgery treatment of melanoma brain metastases treated with ipilimumab. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 127, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qian, J.M.; Yu, J.B.; Kluger, H.M.; Chiang, V.L.S. Timing and type of immune checkpoint therapy affect the early radiographic response of melanoma brain metastases to stereotactic radiosurgery. Cancer 2016, 122, 3051–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Skrepnik, T.; Sundararajan, S.; Cui, H.; Stea, B. Improved time to disease progression in the brain in patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with concurrent delivery of radiosurgery and ipilimumab. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1283461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arbour, K.C.; Mezquita, L.; Long, N.; Rizvi, H.; Auclin, E.; Ni, A.; Martínez-Bernal, G.; Ferrara, R.; Lai, W.V.; Hendriks, L.E.L.; et al. Impact of Baseline Steroids on Efficacy of Programmed Cell Death-1 and Programmed Death-Ligand 1 Blockade in Patients With Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2872–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellayappan, B.; Tan, C.L.; Yong, C.; Khor, L.K.; Koh, W.Y.; Yeo, T.T.; Detsky, J.; Lo, S.; Sahgal, A. Diagnosis and Management of Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbeling, H.G.; Schapira, E.F.; Horick, N.K.; Goodwin, K.E.H.; Lin, J.J.; Oh, K.S.; Shaw, A.T.; Mehan, W.A.; Shih, H.A.; Gainor, J.F. Safety of Combined PD-1 Pathway Inhibition and Intracranial Radiation Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, A.M.; Cagney, D.N.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; Redig, A.J.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases Treated With Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehrer, E.J.; Peterson, J.; Brown, P.D.; Sheehan, J.P.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A.; Zaorsky, N.G.; Trifiletti, D.M. Treatment of brain metastases with stereotactic radiosurgery and immune checkpoint inhibitors: An international meta-analysis of individual patient data. Radiother. Oncol. 2019, 130, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial Registration No. | Study Location | Tumor Type | Study Design | Systemic Therapy Agent | n | Primary Endpoint | Study Start Date | Estimated Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT04147728 | Peking University Third Hospital | NSCLC | Phase II | Anlotinib | 50 | EI | Dec 2019 | Dec 2022 |
| NCT04643847 | First People’s Hospital of Hangzhou | NSCLC | Phase II | Almonertinib | 47 | DOR | Nov 2020 | Nov 2023 |
| NCT02726568 | Betta Pharmaceuticals Co., Ltd. | NSCLC | Phase II | Icotinib | 30 | PFS | Mar 2016 | Dec 2022 |
| NCT03535363 | Case Comprehensive Cancer Center | NSCLC | Phase I | Osimertinib | 6 | MTD | Oct 2018 | Aug 2021 |
| NCT03769103 | British Columbia Cancer Agency | NSCLC | Phase II | Osimertinib | 76 | PFS | Mar 2019 | April 2025 |
| NCT03497767 | Trans-Tasman Radiation Oncology Group | NSCLC | Phase II | Osimertinib | 80 | PFS | Aug 2019 | March 2024 |
| NCT04856475 | Jules Bordet Institute | Breast | Phase II | Neratinib | 104 | ORR | July 2021 | July 2025 |
| NCT03190967 | National Cancer Institute (NCI) | Breast | Phase I/II | T-DM1 and Metronomic Temozolomide | 125 | MTD | April 2018 | June 2023 |
| NCT04585724 | Emory University | Breast | Phase I | Abemaciclib, Ribociclib, or Palbociclib | 25 | AE | June 2020 | Oct 2021 |
| NCT04074096 | UNICANCER | Melanoma | Phase II | Binimetinib and Encorafenib | 150 | PFS | Sep 2021 | Sep 2028 |
| NCT03898908 | Grupo Español Multidisciplinar de Melanoma | Melanoma | Phase II | Binimetinib and Encorafenib | 38 | ORR | July 2019 | Oct 2023 |
| NCT03430947 | Technische Universität Dresden | Melanoma | Phase II | Vemurafenib and Cobimetinib | 20 | ORR | July 2018 | July 2022 |
| NCT02974803 | Canadian Cancer Trials Group | Melanoma | Phase II | Dabrafenib and Trametinib | 6 | ORR | Nov 2016 | June 2021 |
| Trial Registration No. | Study Location | Tumor Type | Study Design | Immunotherapy Agent | n | Primary Endpoint | Study Start Date | Estimated Completion Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT03483012 | Dana-Farber Cancer Institute | Breast | Phase II | Atezolizumab | 45 | PFS | Sep 2021 | Sep 2025 |
| NCT03449238 | Weill Medical College of Cornell University | Breast | Phase II | Pembrolizumab | 41 | RR, OS | Nov 2018 | Dec 2026 |
| NCT03807765 | H. Lee Moffitt Cancer Center and Research Institute | Breast | Phase I | Nivolumab | 14 | DLT | Jan 2019 | Jan 2022 |
| NCT02886585 | Massachusetts General Hospital | Any solid tumor | Phase II | Pembrolizumab | 102 | RR, OS | Oct 2016 | Sep 2022 |
| NCT02097732 | University of Michigan Rogel Cancer Center | Melanoma | Phase II | Ipilimumab | 40 | LC | April 2014 | July 2020 |
| NCT03340129 | Melanoma Institute Australia | Melanoma | Phase II | Nivolumab & Ipilimumab | 218 | NSCD | Aug 2019 | Aug 2025 |
| NCT03297463 | Masonic Cancer Center, University of Minnesota | Melanoma | Phase I/II | Ipilimumab | 40 | MTD, ORR | Jan 2018 | Feb 2020 |
| NCT02716948 | Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center | Melanoma | Phase I | Nivolumab | 90 | AE | Jun 2016 | Mar 2023 |
| NCT02858869 | Emory University | Melanoma, NSCLC | Phase I | Pembrolizumab | 30 | DLT | Oct 2016 | Oct 2021 |
| NCT02696993 | M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | NSCLC | Phase I/II | Nivolumab & Ipilimumab | 88 | DLT, PFS | Dec 2016 | Dec 2020 |
| NCT02978404 | Centre hospitalier de l’Université de Montréal (CHUM) | NSCLC, RCC | Phase II | Nivolumab | 26 | PFS | Jun 2017 | Jun 2022 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tonse, R.; Tom, M.C.; Mehta, M.P.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Kotecha, R. Integration of Systemic Therapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Cancers 2021, 13, 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153682
Tonse R, Tom MC, Mehta MP, Ahluwalia MS, Kotecha R. Integration of Systemic Therapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153682
Chicago/Turabian StyleTonse, Raees, Martin C. Tom, Minesh P. Mehta, Manmeet S. Ahluwalia, and Rupesh Kotecha. 2021. "Integration of Systemic Therapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153682
APA StyleTonse, R., Tom, M. C., Mehta, M. P., Ahluwalia, M. S., & Kotecha, R. (2021). Integration of Systemic Therapy and Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases. Cancers, 13(15), 3682. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153682







