Neuropilin-1 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in HNSCC and Elicits EGFR Activation upon CDDP-Induced Cytotoxic Stress
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Drugs
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Gene Silencing
2.5. Western Blot Analysis
2.6. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.7. TMA and IHC
2.8. Digital Image Analysis and Statistical Analysis
2.9. Caspase Assay
2.10. Colony Forming Assay
3. Results
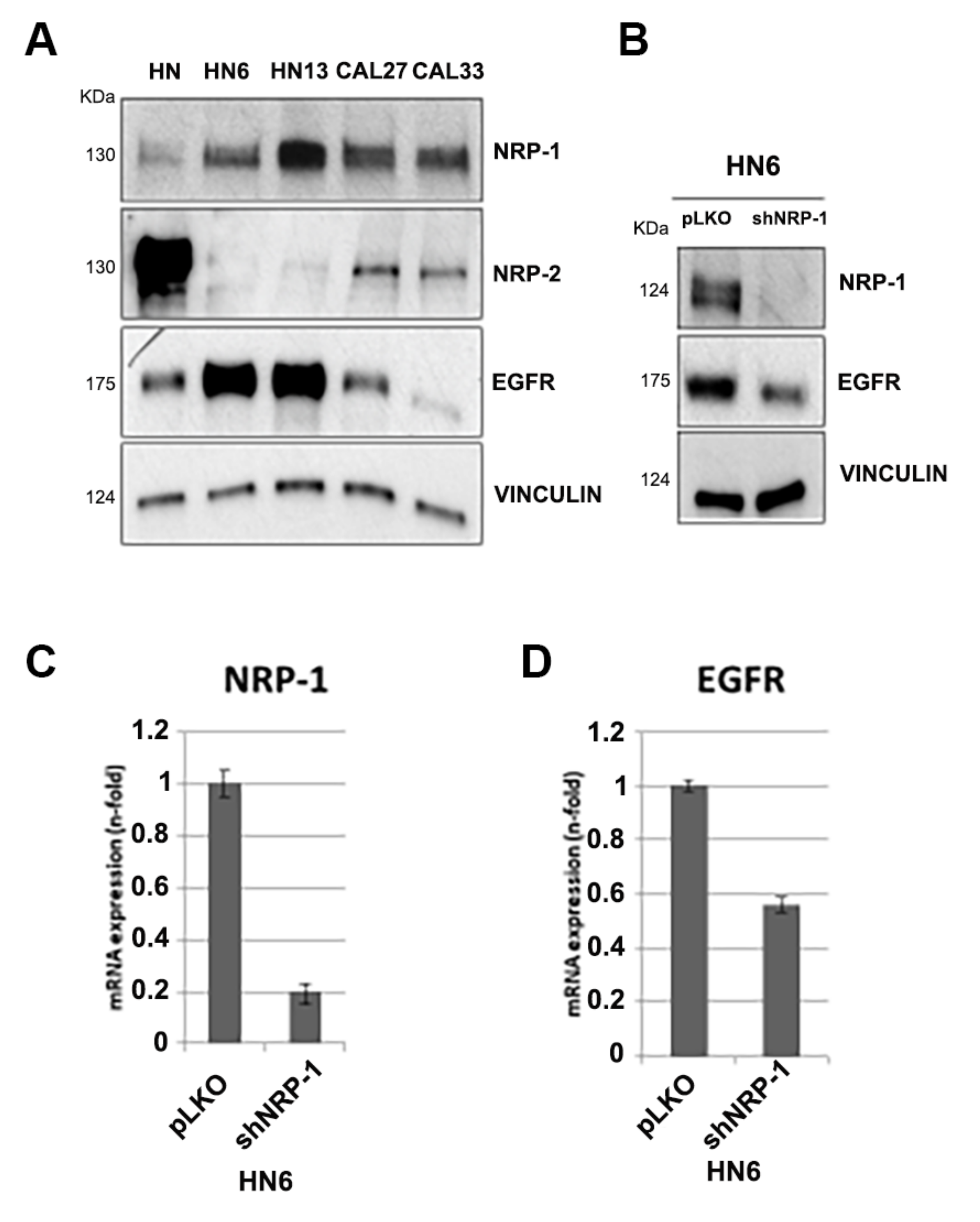
3.1. NRP-1, NRP-2 and EGFR Expression Levels in HNSCC Cell Lines
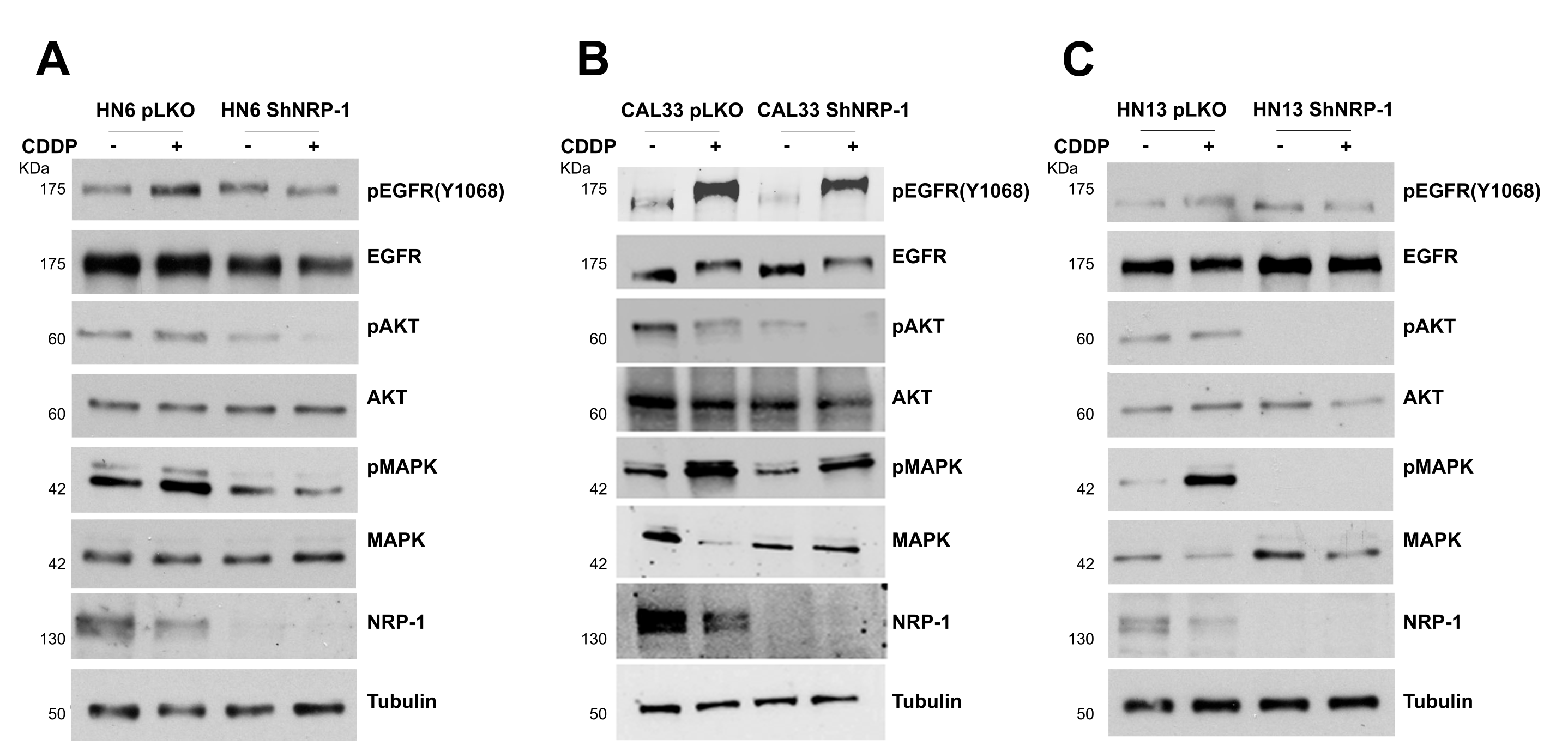
3.2. NRP-1 Sustains EGFR Activation upon CDDP Exposure
3.3. NRP-1 Affects Responsiveness to CDDP Treatment
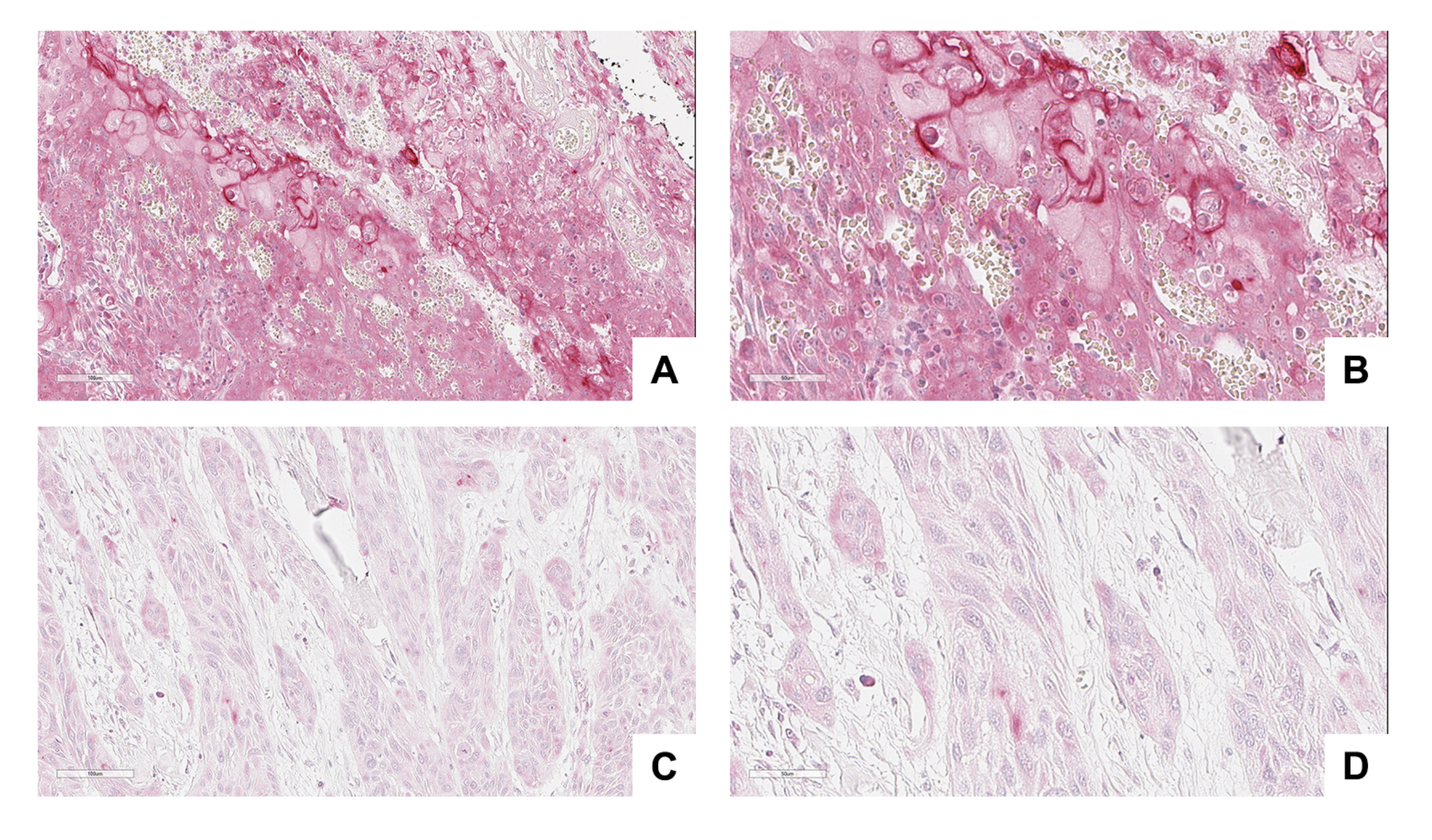
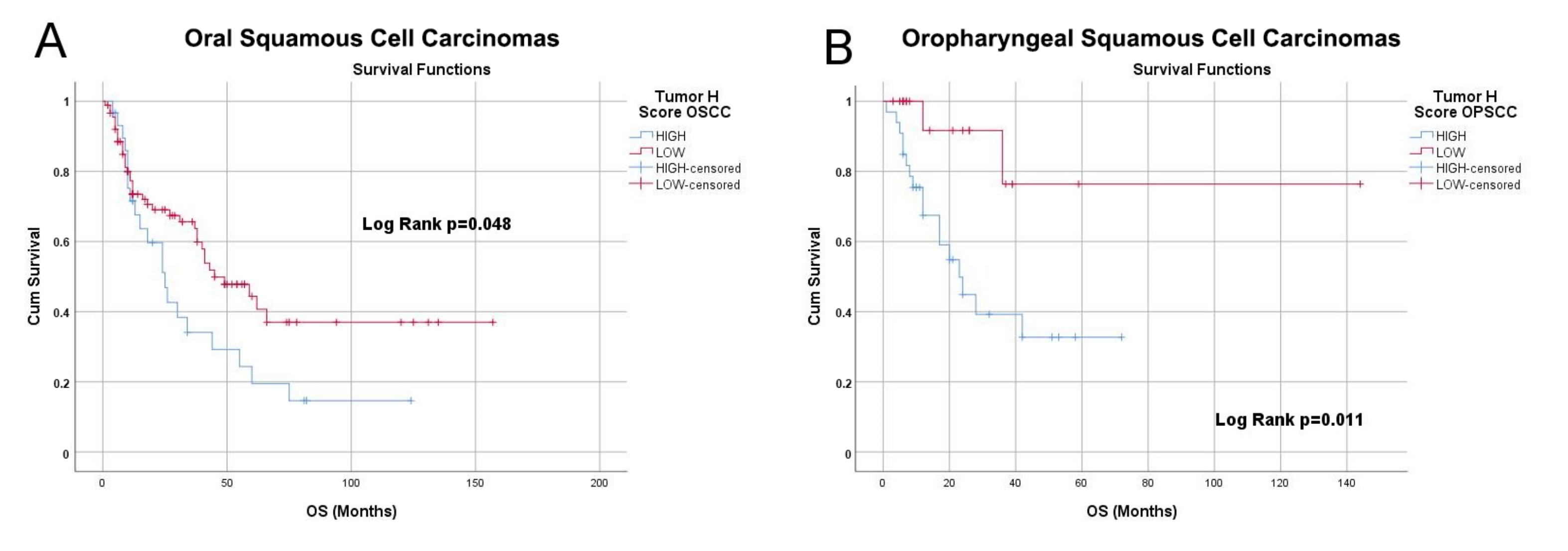
3.4. NRP-1 Expression Level Is a Prognostic Marker for HNSCC Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HNSCC | Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| OSCC | Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| OPSCC | Oropharyngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma |
| NRP-1 | Neuropilin1 |
| MAPK | Map Kinase |
| CDDP | Cisplatin |
| EGF | Epidermal Growth Factor |
| HPV | Human Papilloma Virus |
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, K.K.; Harris, J.; Wheeler, R.; Weber, R.; Rosenthal, D.I.; Nguyen-Tân, P.F.; Westra, W.H.; Chung, C.H.; Jordan, R.C.; Lu, C.; et al. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with oropharyngeal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochner, B.H.; Hansel, D.E.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Konety, B.; Lee, C.; Mckiernan, J.M.; Plimack, E.R.; Reuter, V.E.; Sridhar, S.; Vikram, R.; et al. Ajcc Cancer Staging Man. Am. Jt. Commitee Cancer 2017, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porceddu, S.V.; Daniels, C.; Yom, S.S.; Liu, H.; Waldron, J.; Gregoire, V.; Moore, A.; Veness, M.; Yao, M.; Johansen, J.; et al. Head and Neck Cancer International Group (HNCIG) Consensus Guidelines for the Delivery of Postoperative Radiation Therapy in Complex Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck (cSCCHN). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2020, 107, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, J.B.; Mesia, R.; Rivera, F.; Remenar, E.; Kawecki, A.; Rottey, S.; Erfan, J.; Zabolotnyy, D.; Kienzer, H.; Cupissol, D.; et al. Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and neck cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonner, J.A.; Harari, P.M.; Giralt, J.; Cohen, R.B.; Jones, C.U.; Sur, R.K.; Raben, D.; Baselga, J.; Spencer, S.A.; Zhu, J.; et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for locoregionally advanced head and neck cancer: 5-year survival data from a phase 3 randomised trial, and relation between cetuximab-induced rash and survival. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leemans, C.R.; Braakhuis, B.J.M.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular biology of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.S.; Sougnez, C.; Lichtenstein, L.; Cibulskis, K.; Lander, E.; Gabriel, S.B.; Getz, G.; Ally, A.; Balasundaram, M.; Birol, I.; et al. Comprehensive genomic characterization of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Nature 2015, 517, 576–582. [Google Scholar]
- Leemans, C.R.; Snijders, P.J.F.; Brakenhoff, R.H. The molecular landscape of head and neck cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyankrishna, S.; Grandis, J.R. Epidermal growth factor receptor biology in head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 2666–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temam, S.; Kawaguchi, H.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Jelinek, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, D.D.; Lang, W.; Issa, J.; Lee, J.J.; Mao, L. Epidermal growth factor receptor copy number alterations correlate with poor clinical outcome in patients with head and neck squamous cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 2164–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, C.; Limberg, B.J.; Brian Whitaker, G.; Perman, B.; Leahy, D.J.; Rosenbaum, J.S.; Ginty, D.D.; Kolodkin, A.L. Characterization of neuropilin-1 structural features that confer binding to semaphorin 3A and vascular endothelial growth factor 165. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 18069–18076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodkin, A.L.; Levengood, D.V.; Rowe, E.G.; Tai, Y.; Giger, R.J.; Ginty, D.D. Neuropilin is a semaphorin III receptor. Cell 1997, 90, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prud’homme, G.J.; Glinka, Y. Neuropilins are multifunctional coreceptors involved in tumor initiation, growth, metastasis and immunity. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 921–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soker, S.; Takashima, S.; Miao, H.Q.; Neufeld, G.; Klagsbrun, M. Neuropilin-1 is expressed by endothelial and tumor cells as an isoform- specific receptor for vascular endothelial growth factor. Cell 1998, 92, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzolio, S.; Rabinowicz, N.; Rainero, E.; Lanzetti, L.; Serini, G.; Norman, J.; Neufeld, G.; Tamagnone, L. Neuropilin-1-dependent regulation of EGF-receptor Signaling. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5801–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celetti, A.; Testa, D.; Staibano, S.; Merolla, F.; Guarino, V.; Castellone, M.D.; Iovine, R.; Mansueto, G.; Somma, P.; De Rosa, G.; et al. Overexpression of the Cytokine Osteopontin Identifies Aggressive Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinomas and Enhances Carcinoma Cell Proliferation and Invasiveness. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 8019–8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Leone, V.; Mansueto, G.; Pierantoni, G.M.; Tornincasa, M.; Merolla, F.; Cerrato, A.; Santoro, M.; Grieco, M.; Scaloni, A.; Celetti, A.; et al. CCDC6 represses CREB1 activity by recruiting histone deacetylase 1 and protein phosphatase 1. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4341–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, V.; Langella, C.; Esposito, F.; Arra, C.; Palma, G.; Rea, D.; Paciello, O.; Merolla, F.; De Biase, D.; Papparella, S.; et al. Ccdc6 knock-in mice develop thyroid hyperplasia associated to an enhanced CREB1 activity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 15628–15638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascolo, M.; Ilardi, G.; Romano, M.F.; Celetti, A.; Siano, M.; Romano, S.; Luise, C.; Merolla, F.; Rocco, A.; Vecchione, M.L.; et al. Overexpression of chromatin assembly factor-1 p60, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 and nestin predicts metastasizing behaviour of oral cancer. Histopathology 2012, 61, 1089–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, F.; Merolla, F.; Picardi, I.; Russo, D.; Ilardi, G.; Varricchio, S.; Liotti, F.; Pacelli, R.; Palazzo, L.; Mascolo, M.; et al. CAF-1 subunits levels suggest combined treatments with PARP-inhibitors and ionizing radiation in advanced HNSCC. Cancers 2019, 11, 1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, M.; Ilardi, G.; Merolla, F.; Russo, D.; Vecchione, M.L.; de Rosa, G.; Staibano, S. Tissue microarray-based evaluation of chromatin assembly factor-1 (CAF-1)/p60 as tumour prognostic marker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 11044–11062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, F.; Varricchio, S.; Russo, D.; Merolla, F.; Ilardi, G.; Mascolo, M.; Dell’aversana, G.O.; Califano, L.; Toscano, G.; De Pietro, G.; et al. A machine-learning approach for the assessment of the proliferative compartment of solid tumors on hematoxylin-eosin-stained sections. Cancers 2020, 12, 1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernández, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagy, A.; Munkacsy, G.; Gyorffy, B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriuranpong, V.; Park, J.I.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Patel, V.; Nelkin, B.D.; Gutkind, J.S. Epidermal growth factor receptor-independent constitutive activation of STAT3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is mediated by the autocrine/paracrine stimulation of the interleukin 6/gp130 cytokine system. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 2948–2956. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.; Abba, M.C.; Molinolo, A.A.; Vitale-Cross, L.; Wang, Z.; Zaida, M.; Delic, N.C.; Samuels, Y.; Lyons, J.G.; Gutkind, J.S. The head and neck cancer cell oncogenome: A platform for the development of precision molecular therapies. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 8906–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasten-Pisula, U.; Saker, J.; Eicheler, W.; Krause, M.; Yaromina, A.; Meyer-Staeckling, S.; Scherkl, B.; Kriegs, M.; Brandt, B.; Grénman, R.; et al. Cellular and tumor radiosensitivity is correlated to epidermal growth factor receptor protein expression level in tumors without EGFR amplification. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2011, 80, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Oliveira, R.J.; Melendez, M.; Martinho, O.; Zanon, M.F.; de Souza Viana, L.; Carvalho, A.L.; Reis, R.M. AKT can modulate the in vitro response of HNSCC cells to irreversible EGFR inhibitors. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53288–53301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belcher, R.; Hayes, K.; Fedewa, S.; Chen, A.Y. Current treatment of head and neck squamous cell cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 110, 551–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzweg, T.; Möckelmann, N.; Laban, S.; Knecht, R. Current treatment options for recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer: A post-ASCO 2011 update and review of last year’s literature. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino 2012, 269, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Merolla, F.; Mascolo, M.; Ilardi, G.; Romano, S.; Varricchio, S.; Napolitano, V.; Celetti, A.; Postiglione, L.; Di Lorenzo, P.P.; et al. FKBP51 immunohistochemical expression: A new prognostic biomarker for OSCC? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, D.; Merolla, F.; Varricchio, S.; Salzano, G.; Zarrilli, G.; Mascolo, M.; Strazzullo, V.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Celetti, A.; Ilardi, G. Epigenetics of oral and oropharyngeal cancers (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, P.Y.; Feng, F.Y.; Scheurer, A.M.; Davis, M.A.; Lawrence, T.S.; Nyati, M.K. Synergistic effects of gemcitabine and gefitinib in the treatment of head and neck carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 981–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolla, F.; Ilardi, G.; Di Spigna, G.; Russo, D.; Martino, F.; Varricchio, S.; Dell’Aversana, O.G.; Mascolo, M.; Covelli, B.; Caltabiano, R.; et al. Detection of CAF-1/p60 in peripheral blood as a potential biomarker of HNSCC tumors. Oral Oncol. 2021, 120, 105367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyati, M.K.; Morgan, M.A.; Feng, F.Y.; Lawrence, T.S. Integration of EGFR inhibitors with radiochemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, Q.; Zheng, J.; Fei, J.; An, W.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y. High neuropilin 1 expression was associated with angiogenesis and poor overall survival in resected pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2014, 43, 744–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansel, D.E.; Wilentz, R.E.; Yeo, C.J.; Schulick, R.D.; Montgomery, E.; Maitra, A. Expression of Neuropilin-1 in High-grade Dysplasia, Invasive Cancer, and Metastases of the Human Gastrointestinal Tract. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2004, 28, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, T.; Tokunaga, T.; Hatanaka, H.; Kijima, H.; Yamazaki, H.; Abe, Y.; Osamura, Y.; Inoue, H.; Ueyama, Y.; Nakamura, M. Neuropilin 1 and neuropilin 2 co-expression is significantly correlated with increased vascularity and poor prognosis in nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 95, 2196–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, G.; Tang, Y.; Dong, Z.; McElwee, K.J.; Li, G. Increased expression of neuropilin 1 in melanoma progression and its prognostic significance in patients with melanoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 2268–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Song, X.; Yang, X.; Ma, L.; Zhu, J.; He, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y. Neuropilin-1 Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Stimulating Nuclear Factor-Kappa B and Is Associated with Poor Prognosis in Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, V.; Tamagnone, L. Neuropilins controlling cancer therapy responsiveness. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzolio, S.; Cagnoni, G.; Battistini, C.; Bonelli, S.; Isella, C.; Van Ginderachter, J.A.; Bernards, R.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Giordano, S.; Tamagnone, L. Neuropilin-1 upregulation elicits adaptive resistance to oncogene-targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 3976–3990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhar, M.; Engelberg, D.; Levitzki, A. Cisplatin-induced activation of the EGF receptor. Oncogene 2002, 21, 8723–8731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Schaeybroeck, S.; Karaiskou-McCaul, A.; Kelly, D.; Longley, D.; Galligan, L.; Van Cutsem, E.; Johnston, P. Epidermal growth factor receptor activity determines response of colorectal cancer cells to gefitinib alone and in combination with chemotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7480–7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fury, M.G.; Baxi, S.; Shen, R.; Kelly, K.W.; Lipson, B.L.; Carlson, D.; Stambuk, H.; Haque, S.; Pfister, D.G. Phase II study of saracatinib (AZD0530) for patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Anticancer Res. 2011, 31, 249–253. [Google Scholar]
- De Vlaeminck, Y.; Bonelli, S.; Awad, R.M.; Dewilde, M.; Rizzolio, S.; Lecocq, Q.; Bolli, E.; Santos, A.R.; Laoui, D.; Schoonooghe, S.; et al. Targeting Neuropilin-1 with Nanobodies Reduces Colorectal Carcinoma Development. Cancers 2020, 12, 3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtness, B.; Bauman, J.E.; Galloway, T. Novel targets in HPV-negative head and neck cancer: Overcoming resistance to EGFR inhibition. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, e302–e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Cell Lines | EGFR Mutational Status | References |
|---|---|---|
| CAL33 | wild type | [27] |
| HN6 | amplified | [28] |
| HN13 | mutated (p.H773Y) and amplified | [29] |
| Cisplatin IC 50 (M) | ||
|---|---|---|
| shNRP-1 | pLKO | |
| HN6 | 2.5 | 5.5 |
| CAL33 | 5 | 12 |
| HN13 | 1.9 | 2 |
| N | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| GENDER | F | 76 | 44% |
| M | 96 | 56% | |
| Total | 172 | 100% | |
| AGE | Mean | 63.67 | |
| Median | 64.00 | ||
| Minimum | 33 | ||
| Maximum | 89 | ||
| SITE | NOP | 119 | 69% |
| OP | 53 | 31% | |
| Total | 172 | 100% | |
| GRADE | G1 | 6 | 3% |
| G1/G2 | 8 | 5% | |
| G2 | 47 | 27% | |
| G2/G3 | 18 | 10% | |
| G3 | 76 | 44% | |
| missing | 17 | 10% | |
| Total | 172 | 100% | |
| STAGE AJCC VIIIed. | I | 19 | 11% |
| II | 38 | 22% | |
| III | 20 | 12% | |
| IVA | 78 | 45% | |
| Missing | 17 | 10% | |
| Total | 172 | 100% | |
| F-UP | A&W | 93 | 54% |
| DOD | 79 | 46% | |
| Total | 172 | 100% | |
| F-UP (months) | Mean | 29.36 | |
| Median | 18.00 | ||
| Minimum | 1 | ||
| Maximum | 157 |
| Tumor Neuropilin-1 H-Score | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HIGH | LOW | Total | |||
| SITE | OSCC | Count | 30 | 89 | 119 |
| % within SITE | 25.2% | 74.8% | 100% | ||
| OPSCC | Count | 33 | 20 | 53 | |
| % within SITE | 62.3% | 37.7% | 100% | ||
| Total | Count | 63 | 109 | 172 | |
| % within SITE | 36.6% | 63.4% | 100% | ||
| HPV | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| POS | NEG | ||
| NRP-1 | HIGH | 1 | 32 |
| LOW | 6 | 14 | |
| Site (n of Cases with Valid F-UP) | ||
|---|---|---|
| OSCC (n = 315) | OPSCC (n = 79) | |
| Best cutoff | 10.45 | 10.53 |
| Logrank p value | 0.029 | 0.00023 |
| HR | 0.7 (0.5–0.97) | 4.31 (1.85–10.04 ) |
| FDR | >50% | 1% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Napolitano, V.; Russo, D.; Morra, F.; Merolla, F.; Varricchio, S.; Ilardi, G.; Di Crescenzo, R.M.; Martino, F.; Mascolo, M.; Celetti, A.; et al. Neuropilin-1 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in HNSCC and Elicits EGFR Activation upon CDDP-Induced Cytotoxic Stress. Cancers 2021, 13, 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153822
Napolitano V, Russo D, Morra F, Merolla F, Varricchio S, Ilardi G, Di Crescenzo RM, Martino F, Mascolo M, Celetti A, et al. Neuropilin-1 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in HNSCC and Elicits EGFR Activation upon CDDP-Induced Cytotoxic Stress. Cancers. 2021; 13(15):3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153822
Chicago/Turabian StyleNapolitano, Virginia, Daniela Russo, Francesco Morra, Francesco Merolla, Silvia Varricchio, Gennaro Ilardi, Rosa Maria Di Crescenzo, Francesco Martino, Massimo Mascolo, Angela Celetti, and et al. 2021. "Neuropilin-1 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in HNSCC and Elicits EGFR Activation upon CDDP-Induced Cytotoxic Stress" Cancers 13, no. 15: 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153822
APA StyleNapolitano, V., Russo, D., Morra, F., Merolla, F., Varricchio, S., Ilardi, G., Di Crescenzo, R. M., Martino, F., Mascolo, M., Celetti, A., Tamagnone, L., & Staibano, S. (2021). Neuropilin-1 Expression Associates with Poor Prognosis in HNSCC and Elicits EGFR Activation upon CDDP-Induced Cytotoxic Stress. Cancers, 13(15), 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13153822







