Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patients
2.2. Data Sources and Assessment of Variables
2.3. Flow Cytometry Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Toxicities
3.3. Patient Responses
3.4. Patient Survival
3.5. Comparison of Outcome during the 1st and 2nd Years of CD19-Directed CAR T-Cell Therapies
3.6. Apheresis Product Characteristics
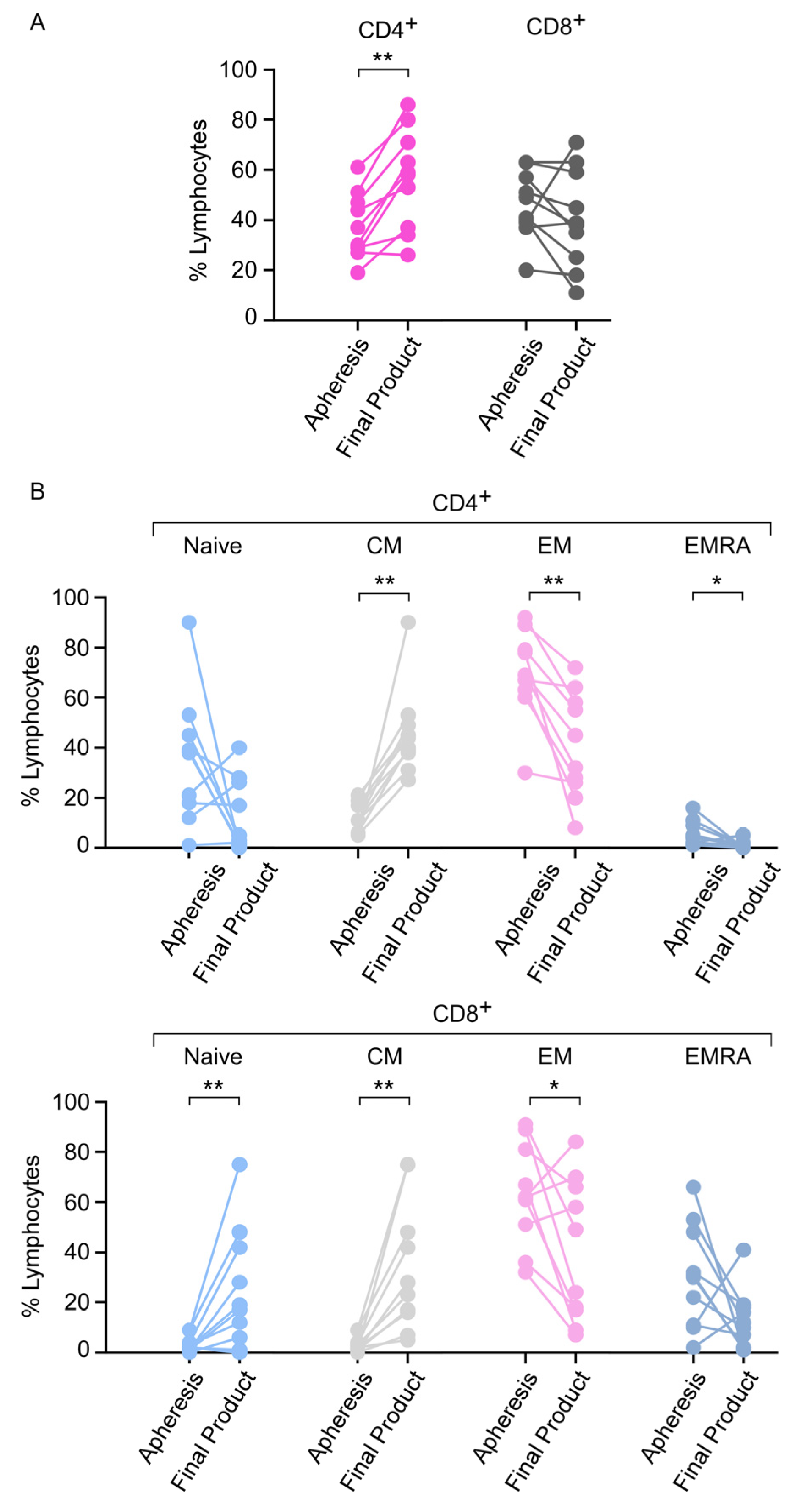
3.7. Phenotype of the CAR T-Cell Final Product
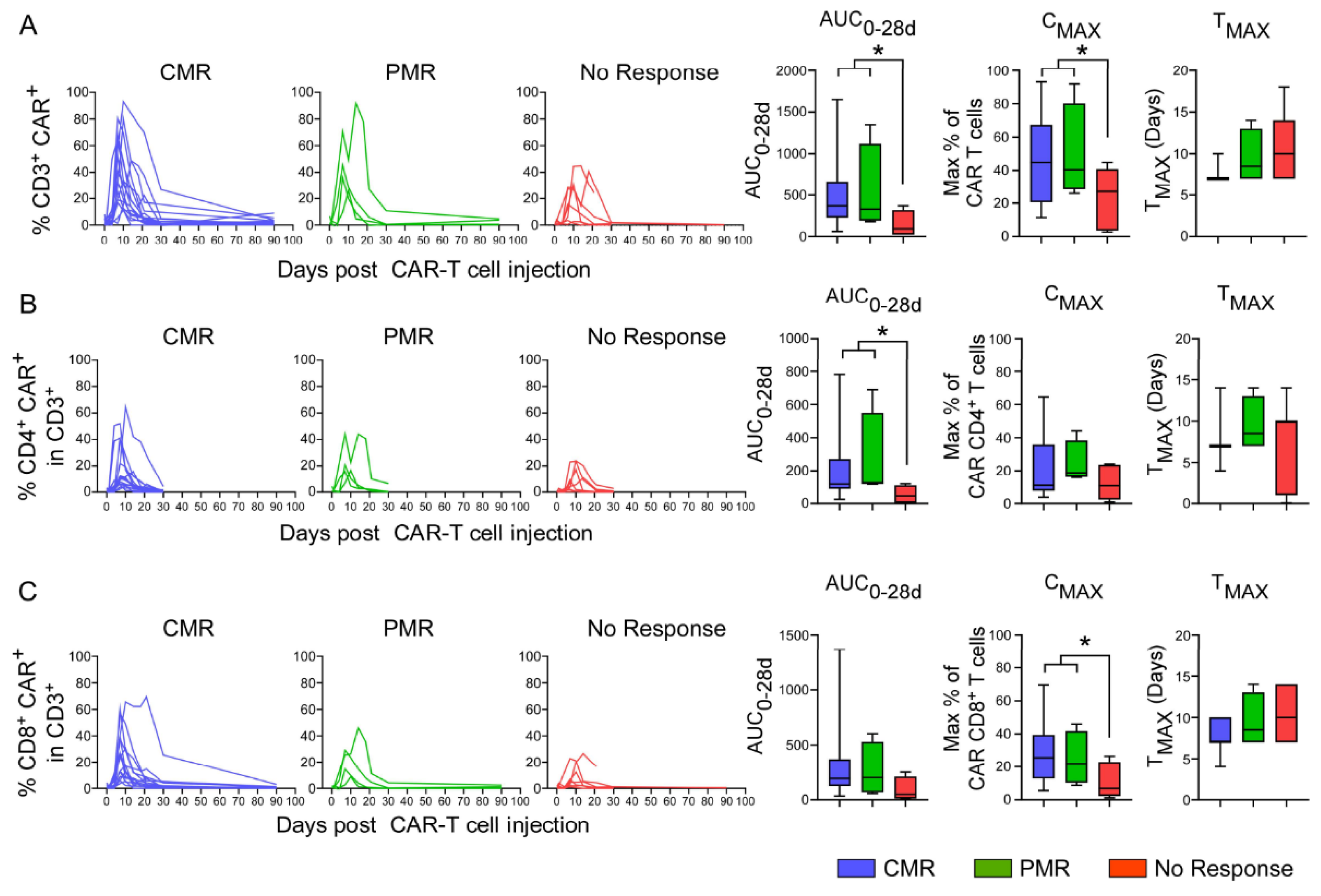
3.8. In Vivo Pharmacokinetics of CAR T-Cells
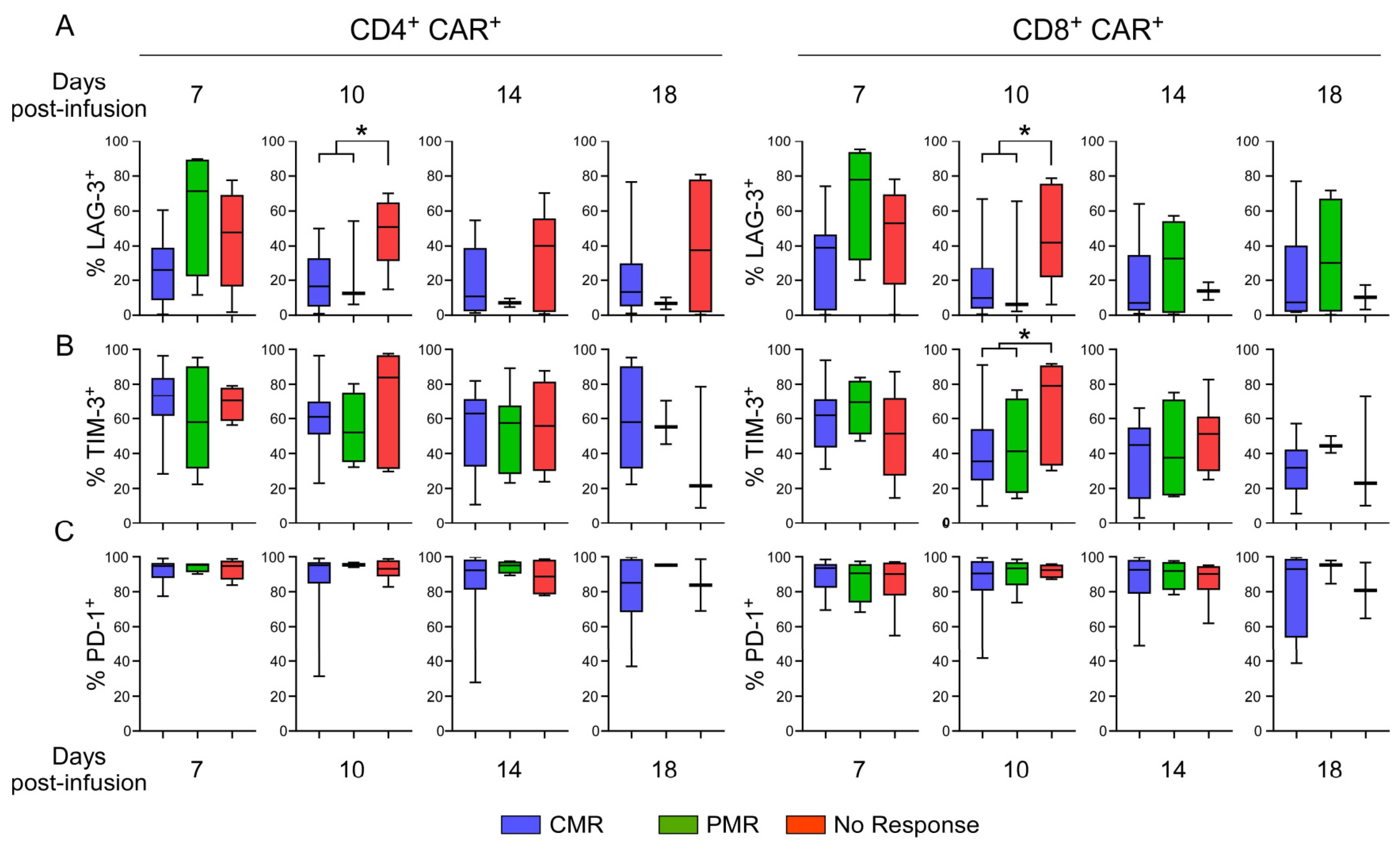
3.9. Evaluation of Exhaustion Phenotype as a Function of Responsiveness to CAR T-Cell Therapy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crump, M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Farooq, U.; Neste, E.V.D.; Kuruvilla, J.; Westin, J.; Link, B.K.; Hay, A.; Cerhan, J.R.; Zhu, L.; et al. Outcomes in Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the International SCHOLAR-1 Study. Blood 2017, 130, 1800–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.A.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Mehta, A.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; et al. Lisocabtagene Maraleucel for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A Multicentre Seamless Design Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, A.H.; Haso, W.M.; Shern, J.F.; Wanhainen, K.M.; Murgai, M.; Ingaramo, M.; Smith, J.P.; Walker, A.J.; Kohler, M.E.; Venkateshwara, V.R.; et al. 4-1BB Costimulation Ameliorates T Cell Exhaustion Induced by Tonic Signaling of Chimeric Antigen Receptors. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawalekar, O.U.; O’Connor, R.S.; Fraietta, J.A.; Guo, L.; McGettigan, S.E.; Posey, A.D.; Patel, P.R.; Guedan, S.; Scholler, J.; Keith, B.; et al. Distinct Signaling of Coreceptors Regulates Specific Metabolism Pathways and Impacts Memory Development in CAR T Cells. Immunity 2016, 44, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Majzner, R.G.; Rietberg, S.P.; Sotillo, E.; Dong, R.; Vachharajani, V.T.; Labanieh, L.; Myklebust, J.H.; Kadapakkam, M.; Weber, E.W.; Tousley, A.M.; et al. Tuning the Antigen Density Requirement for CAR T-Cell Activity. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 702–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savoldo, B.; Ramos, C.A.; Liu, E.; Mims, M.P.; Keating, M.J.; Carrum, G.; Kamble, R.T.; Bollard, C.M.; Gee, A.P.; Mei, Z.; et al. CD28 Costimulation Improves Expansion and Persistence of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells in Lymphoma Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, D.W.; Santomasso, B.D.; Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Turtle, C.J.; Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Park, J.H.; Mead, E.; Pavletic, S.; et al. ASTCT Consensus Grading for Cytokine Release Syndrome and Neurologic Toxicity Associated with Immune Effector Cells. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019, 25, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brudno, J.N.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Toxicities of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells: Recognition and Management. Blood 2016, 127, 3321–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parker, K.R.; Migliorini, D.; Perkey, E.; Yost, K.E.; Bhaduri, A.; Bagga, P.; Haris, M.; Wilson, N.E.; Liu, F.; Gabunia, K.; et al. Single-Cell Analyses Identify Brain Mural Cells Expressing CD19 as Potential Off-Tumor Targets for CAR-T Immunotherapies. Cell 2020, 183, 126–142.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauvais, D.; Bachy, E.; Baruchel, A.; Bay, J.-O.; Caillot, D.; Cartron, G.; Damaj, G.; Furst, S.; Le Gouill, S.; Morschhauser, F.; et al. Eligibility of patients for CAR T-cell: Expert opinion-based collaborative work by the SFGM-TC. Bull. Cancer 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, K.E.; Leukam, M.J.; Riedell, P.A. Refining Patient Selection for CAR T-Cell Therapy in Aggressive Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 799–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesques, P.; Ferrant, E.; Safar, V.; Wallet, F.; Tordo, J.; Dhomps, A.; Karlin, L.; Brisou, G.; Vercasson, M.; Hospital-Gustem, C.; et al. Commercial Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Therapy for Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B Cell Lymphoma in a European Center. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 1324–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellino, L.; Di Blasi, R.; Kanoun, S.; Tessoulin, B.; Rossi, C.; D’Aveni-Piney, M.; Obéric, L.; Bodet-Milin, C.; Bories, P.; Olivier, P.; et al. Predictive Factors of Early Progression after CAR T-Cell Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5607–5615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastoupil, L.J.; Jain, M.D.; Feng, L.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Ghobadi, A.; Lin, Y.; Dahiya, S.; Lunning, M.; Lekakis, L.; Reagan, P.; et al. Standard-of-Care Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results From the US Lymphoma CAR T Consortium. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayuk, F.A.; Berger, C.; Badbaran, A.; Zabelina, T.; Sonntag, T.; Riecken, K.; Geffken, M.; Wichmann, D.; Frenzel, C.; Thayssen, G.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Vivo Expansion and Treatment Outcome in Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma in a Real-World Setting. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 2523–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awasthi, R.; Pacaud, L.; Waldron, E.; Tam, C.S.; Jäger, U.; Borchmann, P.; Jaglowski, S.; Foley, S.R.; Van Besien, K.; Wagner-Johnston, N.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel Cellular Kinetics, Dose, and Immunogenicity in Relation to Clinical Factors in Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Rossi, J.M.; Neelapu, S.S.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Ghobadi, A.; Oluwole, O.O.; Reagan, P.M.; Lekakis, L.J.; Lin, Y.; et al. Tumor Burden, Inflammation, and Product Attributes Determine Outcomes of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4898–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turtle, C.J.; Hanafi, L.-A.; Berger, C.; Gooley, T.A.; Cherian, S.; Hudecek, M.; Sommermeyer, D.; Melville, K.; Pender, B.; Budiarto, T.M.; et al. CD19 CAR-T Cells of Defined CD4+:CD8+ Composition in Adult B Cell ALL Patients. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2123–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cappell, K.M.; Sherry, R.M.; Yang, J.C.; Goff, S.L.; Vanasse, D.A.; McIntyre, L.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Long-Term Follow-Up of Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3805–3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, M.R.; Maziarz, R.T.; Waller, E.K.; Jäger, U.; Westin, J.R.; McGuirk, J.P.; Fleury, I.; Holte, H.; Borchmann, P.; Del Corral, C.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Relapsed/Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Patients without Measurable Disease at Infusion. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 2230–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Q.; Han, G.; Puebla-Osorio, N.; Ma, M.C.J.; Strati, P.; Chasen, B.; Dai, E.; Dang, M.; Jain, N.; Yang, H.; et al. Characteristics of Anti-CD19 CAR T Cell Infusion Products Associated with Efficacy and Toxicity in Patients with Large B Cell Lymphomas. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurent, C.; Baron, M.; Amara, N.; Haioun, C.; Dandoit, M.; Maynadié, M.; Parrens, M.; Vergier, B.; Copie-Bergman, C.; Fabiani, B.; et al. Impact of Expert Pathologic Review of Lymphoma Diagnosis: Study of Patients From the French Lymphopath Network. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 2008–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for Initial Evaluation, Staging, and Response Assessment of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Lugano Classification. JCO 2014, 32, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, J.J.M.; Lhermitte, L.; Böttcher, S.; Almeida, J.; van der Velden, V.H.J.; Flores-Montero, J.; Rawstron, A.; Asnafi, V.; Lécrevisse, Q.; Lucio, P.; et al. EuroFlow Antibody Panels for Standardized N-Dimensional Flow Cytometric Immunophenotyping of Normal, Reactive and Malignant Leukocytes. Leukemia 2012, 26, 1908–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherkassky, L.; Morello, A.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Jones, D.R.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Human CAR T Cells with Cell-Intrinsic PD-1 Checkpoint Blockade Resist Tumor-Mediated Inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3130–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Locke, F.L.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (ZUMA-1): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1-2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gouill, S.; Bachy, E.; Di Blasi, R.; Cartron, G.; Beauvais, D.; Le Bras, F. First Results of Dlbcl Patients Treated with Car-T cells and Enrolled in Descar-T Registry, a French Real-Life Database for Car-T Cells in Hematologic Malignancies. Available online: https://library.ehaweb.org/eha/2021/eha2021-virtual-congress/324624/steven.le.gouill.first.results.of.dlbcl.patients.treated.with.car-t.cells.and.html?f=listing%3D0%2Abrowseby%3D8%2Asortby%3D2%2Asearch%3Dcar-t (accessed on 1 July 2021).
- Jacobson, C.A.; Hunter, B.D.; Redd, R.; Rodig, S.J.; Chen, P.-H.; Wright, K.; Lipschitz, M.; Ritz, J.; Kamihara, Y.; Armand, P.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in the Non-Trial Setting: Outcomes and Correlates of Response, Resistance, and Toxicity. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3095–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ramos, C.A.; Durett, A.; Liu, E.; Dakhova, O.; Liu, H.; Creighton, C.J.; Gee, A.P.; Heslop, H.E.; et al. Closely Related T-Memory Stem Cells Correlate with in Vivo Expansion of CAR.CD19-T Cells and Are Preserved by IL-7 and IL-15. Blood 2014, 123, 3750–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jackson, Z.; Roe, A.; Sharma, A.A.; Lopes, F.B.T.P.; Talla, A.; Kleinsorge-Block, S.; Zamborsky, K.; Schiavone, J.; Manjappa, S.; Schauner, R.; et al. Automated Manufacture of Autologous CD19 CAR-T Cells for Treatment of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stock, S.; Schmitt, M.; Sellner, L. Optimizing Manufacturing Protocols of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Improved Anticancer Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, N.N.; Highfill, S.L.; Shalabi, H.; Yates, B.; Jin, J.; Wolters, P.L.; Ombrello, A.; Steinberg, S.M.; Martin, S.; Delbrook, C.; et al. CD4/CD8 T-Cell Selection Affects Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-Cell Potency and Toxicity: Updated Results From a Phase I Anti-CD22 CAR T-Cell Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1938–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichs, C.S.; Borman, Z.A.; Gattinoni, L.; Yu, Z.; Burns, W.R.; Huang, J.; Klebanoff, C.A.; Johnson, L.A.; Kerkar, S.P.; Yang, S.; et al. Human Effector CD8+ T Cells Derived from Naive Rather than Memory Subsets Possess Superior Traits for Adoptive Immunotherapy. Blood 2011, 117, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lynn, R.C.; Weber, E.W.; Sotillo, E.; Gennert, D.; Xu, P.; Good, Z.; Anbunathan, H.; Lattin, J.; Jones, R.; Tieu, V.; et al. C-Jun Overexpression in CAR T Cells Induces Exhaustion Resistance. Nature 2019, 576, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baird, J.H.; Epstein, D.J.; Tamaresis, J.S.; Ehlinger, Z.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Craig, J.; Claire, G.K.; Frank, M.J.; Muffly, L.; Shiraz, P.; et al. Immune Reconstitution and Infectious Complications Following Axicabtagene Ciloleucel Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Ghobadi, A.; Jacobson, C.A.; Miklos, D.B.; Lekakis, L.J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Lin, Y.; Braunschweig, I.; Hill, B.T.; Timmerman, J.M.; et al. 2-Year Follow-up and High-Risk Subset Analysis of Zuma-1, the Pivotal Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) in Patients with Refractory Large B Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsdottir, H.; Wells, A.D.; Turka, L.A. Dynamics and Requirements of T Cell Clonal Expansion in Vivo at the Single-Cell Level: Effector Function Is Linked to Proliferative Capacity. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 5212–5223. [Google Scholar]
- Fehse, B.; Badbaran, A.; Berger, C.; Sonntag, T.; Riecken, K.; Geffken, M.; Kröger, N.; Ayuk, F.A. Digital PCR Assays for Precise Quantification of CD19-CAR-T Cells after Treatment with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2020, 16, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baras, A.; Bocket, L.; Beauvais, D.; Hallaert, C.; Varlet, P.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Hober, D.; Alidjinou, E.K. A Real-Time Quantitative PCR Targeting the Viral Vector for the Monitoring of Patients Treated with Axicabtagene Ciloleucel. J. Mol. Diagn. 2021, 23, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, T.; Maghnouj, A.; Klein-Scory, S.; Ladigan-Badura, S.; Baraniskin, A.; Thomson, J.; Hasenkamp, J.; Hahn, S.A.; Wulf, G.; Schroers, R. Digital-Droplet PCR for Quantification of CD19-Directed CAR T-Cells. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blache, U.; Weiss, R.; Boldt, A.; Kapinsky, M.; Blaudszun, A.-R.; Quaiser, A.; Pohl, A.; Miloud, T.; Burgaud, M.; Vucinic, V.; et al. Advanced Flow Cytometry Assays for Immune Monitoring of CAR-T Cell Applications. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 658314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demaret, J.; Varlet, P.; Trauet, J.; Beauvais, D.; Grossemy, A.; Hégo, F.; Yakoub-Agha, I.; Labalette, M. Monitoring CAR T-Cells Using Flow Cytometry. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2021, 100, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Characteristics | All Population |
|---|---|
| (n = 60) | |
| Demography | |
| Age, years | |
| Median (range) | 64 (18–79) |
| ≥70, n (%) | 18 (30) |
| Male gender, n (%) | 38 (63) |
| Lymphoma, n (%) | |
| Histology | |
| DLBCL | 43 (71) |
| Transformed follicular lymphoma | 10 (17) |
| High grade DLBCL | 7 (12) |
| Number of previous line therapy | |
| ≤2 lines | 44 (73) |
| >3 lines or more | 16 (27) |
| Autologous SCT | 12 (20) |
| Bridging therapy, n (%) | 54 (90) |
| Characteristics at infusion | |
| Ann Arbor stage, n (%) | |
| No measurable disease | 6 (10) |
| I/II | 18 (30) |
| III/IV | 36 (60) |
| LDH > normal limit, n (%) | 25 (42) |
| PS 3–4, n (%) | 5 (8) |
| Median time between apheresis and infusion, days (range) | 40 (30–174) |
| aaIPI, n (%) | |
| Low | 16 (27) |
| Intermediate-1 | 24 (40) |
| Intermediate-2 | 17 (28) |
| High | 3 (5) |
| Toxicities and Related Treatments | All Population |
|---|---|
| (n = 60) | |
| Cytokine-Releasing Syndrome, n (%) | |
| No CRS | 5 (8) |
| CRS I/II | 52 (87) |
| CRS III/IV | 3 (5) |
| Immune Cell-associated Neurotoxicity, n (%) | |
| No ICANS | 37 (62) |
| ICANS I/II | 16 (27) |
| ICANS III/IV | 7 (11) |
| Treatment of CRS & ICANS, n (%) | |
| Tocilizumab | 44 (73) |
| Corticosteroids | 28 (47) |
| Intensive care unit transfer, n (%) | 17 (28) |
| Hemodynamic failure requiring amines | 2 (3) |
| Renal failure requiring extracorporeal epuration | 1 (2) |
| Respiratory failure requiring high-flow O2 | 1 (2) |
| Neurologic failure requiring ventilation | 1 (2) |
| Documented infections, n (%) | 20 (33) |
| After M1 | 10 (17) |
| Documented bacterial infection | 9 (15) |
| Invasive fungal infection | 5 (8) |
| CMV reactivation | 5 (8) |
| Myelotoxicity | |
| RBC transfusion independency, days (median, range) | 76 (6–654) |
| >3-months RBC transfusion, n (%) | 27 (45) |
| Platelet transfusion independency, days (median, range) | 76 (7–655) |
| >3-months platelets transfusion, n (%) | 24 (40) |
| G-CSF withdrawal, days (median, range) | 61 (4–657) |
| >3-months G-CSF treatment, n (%) | 20 (33) |
| Factors | Adjusted p-Value | Hazard Ratio (IC95%) |
|---|---|---|
| Male Gender vs. Female (reference) | 0.0112 | 3.418 (1.323–8.829) |
| aaIPI | 0.0023 | 2.020 (1.285–3.176) |
| %CD8 effector memory in apheresis product | 0.0643 | 0.975 (0.950–1.001) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lamure, S.; Van Laethem, F.; De Verbizier, D.; Lozano, C.; Gehlkopf, E.; Tudesq, J.-J.; Serrand, C.; Benzaoui, M.; Kanouni, T.; Quintard, A.; et al. Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174279
Lamure S, Van Laethem F, De Verbizier D, Lozano C, Gehlkopf E, Tudesq J-J, Serrand C, Benzaoui M, Kanouni T, Quintard A, et al. Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174279
Chicago/Turabian StyleLamure, Sylvain, François Van Laethem, Delphine De Verbizier, Claire Lozano, Eve Gehlkopf, Jean-Jacques Tudesq, Chris Serrand, Mehdi Benzaoui, Tarik Kanouni, Adeline Quintard, and et al. 2021. "Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174279
APA StyleLamure, S., Van Laethem, F., De Verbizier, D., Lozano, C., Gehlkopf, E., Tudesq, J.-J., Serrand, C., Benzaoui, M., Kanouni, T., Quintard, A., De Vos, J., Tchernonog, E., Platon, L., Ayrignac, X., Ceballos, P., Sirvent, A., François, M., Guedon, H., Quittet, P., ... Cartron, G. (2021). Clinical and Product Features Associated with Outcome of DLBCL Patients to CD19-Targeted CAR T-Cell Therapy. Cancers, 13(17), 4279. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174279






