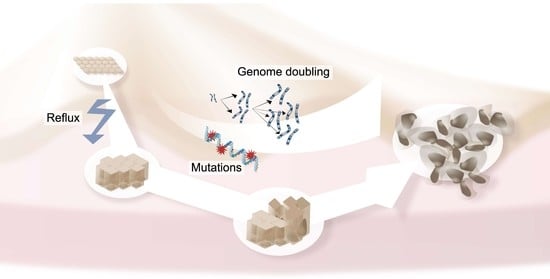
Genomic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Genomics of EAC
2.1. Somatic Variations and Copy Number Alterations
2.1.1. Combining Methods and Expression Levels to Identify Driver Events in EAC
2.1.2. Large-Scale Sequencing of EAC Reveals EAC Helper Genes
2.1.3. Retrospective DNA Sequencing of Short Survivors
2.2. Large-Scale Alterations and Genomic Catastrophes
Loss of Y Chromosome
2.3. Mutational Signatures
Instable Microsatellites Are Rare in EAC
2.4. Comparing EAC with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Gastric Cancer
2.5. Evolution before and towards Metastasis
2.6. Genomic Responses to Therapy
2.7. Genomic Evolution from BE to EAC
3. Transcriptomics of EAC
3.1. RNA Sequencing of the Tumor Microenvironment in EAC
3.2. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing of EAC
4. Clinical Relevance of Molecular Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coleman, H.G.; Xie, S.H.; Lagergren, J. The Epidemiology of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 390–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, B.J.; Li, X.; Galipeau, P.C.; Vaughan, T.L. Barrett’s Oesophagus and Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma: Time for a new synthesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findlay, J.M.; Castro-Giner, F.; Makino, S.; Rayner, E.; Kartsonaki, C.; Cross, W.; Kovac, M.; Ulahannan, D.; Palles, C.; Gillies, R.S.; et al. Differential Clonal Evolution in Oesophageal Cancers in Response to Neo-adjuvant Chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugaesu, N.; Wilson, G.A.; Birkbak, N.J.; Watkins, T.; McGranahan, N.; Kumar, S.; Abbassi-Ghadi, N.; Salm, M.; Mitter, R.; Horswell, S.; et al. Tracking the Genomic Evolution of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma through Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Noorani, A.; Bornschein, J.; Lynch, A.G.; Secrier, M.; Achilleos, A.; Eldridge, M.; Bower, L.; Weaver, J.M.J.; Crawte, J.; Ong, C.A.; et al. A Comparative Analysis of Whole Genome Sequencing of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Pre- and Post-chemotherapy. Genome Res 2017, 27, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Integrated Genomic Characterization of Oesophageal Carcinoma. Nature 2017, 541, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Secrier, M.; Li, X.; de Silva, N.; Eldridge, M.D.; Contino, G.; Bornschein, J.; MacRae, S.; Grehan, N.; O’Donovan, M.; Miremadi, A.; et al. Mutational Signatures in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Define Etiologically Distinct Subgroups with Therapeutic Relevance. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Catenacci, D.V.T.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Davidenko, I.; Murad, A.M.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Ilson, D.H.; Tjulandin, S.; Gotovkin, E.; Karaszewska, B.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Rilotumumab Plus Epirubicin, Cisplatin, and Capecitabine as First-line Therapy in Advanced MET-positive Gastric or Gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (RILOMET-1): A Randomised, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1467–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Ma, X.W.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Lai, N.L.; Zhang, S.X. Cetuximab for Esophageal Cancer: An Updated Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. BMC. Cancer 2018, 18, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsu, A.; Shah, M.A.; Van Cutsem, E.; Rha, S.Y.; Sawaki, A.; Park, S.R.; Lim, H.Y.; Yamada, Y.; Wu, J.; Langer, B.; et al. Bevacizumab in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-line Therapy in Advanced Gastric Cancer: A randomized, double-blind, Placebo-controlled Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3968–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tew, W.P.; Kelsen, D.P.; Ilson, D.H. Targeted Therapies for Esophageal Cancer. Oncologist 2005, 10, 590–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waddell, T.; Chau, I.; Cunningham, D.; Gonzalez, D.; Okines, A.F.; Okines, C.; Wotherspoon, A.; Saffery, C.; Middleton, G.; Wadsley, J.; et al. Epirubicin, Oxaliplatin, and Capecitabine with or without panitumumab for Patients with Previously Untreated Advanced Oesophagogastric Cancer (REAL3): A Randomised, Open-label Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frankell, A.M.; Jammula, S.; Li, X.; Contino, G.; Killcoyne, S.; Abbas, S.; Perner, J.; Bower, L.; Devonshire, G.; Ococks, E.; et al. The landscape of Selection in 551 Esophageal Adenocarcinomas Defines Genomic Biomarkers for the Clinic. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nones, K.; Waddell, N.; Wayte, N.; Patch, A.M.; Bailey, P.; Newell, F.; Holmes, O.; Fink, J.L.; Quinn, M.C.J.; Tang, Y.H.; et al. Genomic Catastrophes Frequently Arise in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Drive Tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulak, A.M.; Stojanov, P.; Peng, S.; Lawrence, M.S.; Fox, C.; Stewart, C.; Bandla, S.; Imamura, Y.; Schumacher, S.E.; Shefler, E.; et al. Exome and Whole-genome sequencing of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Identifies Recurrent Driver Events and Mutational Complexity. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheinbay, E.; Nielsen, M.M.; Abascal, F.; Wala, J.A.; Shapira, O.; Tiao, G.; Hornshoj, H.; Hess, J.M.; Juul, R.I.; Lin, Z.; et al. Analyses of Non-coding Somatic Drivers in 2658 Cancer Whole Genomes. Nature 2020, 578, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mourikis, T.P.; Benedetti, L.; Foxall, E.; Temelkovski, D.; Nulsen, J.; Perner, J.; Cereda, M.; Lagergren, J.; Howell, M.; Yau, C.; et al. Patient-specific Cancer Genes Contribute to Recurrently Perturbed Pathways and Establish Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hao, D.; He, S.; Harada, K.; Pizzi, M.P.; Lu, Y.; Guan, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Sewastjanow-Silva, M.; et al. Integrated Genomic Profiling and Modelling for Risk Stratification in Patients with Advanced Oesophagogastric Adenocarcinoma. Gut 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zack, T.I.; Schumacher, S.E.; Carter, S.L.; Cherniack, A.D.; Saksena, G.; Tabak, B.; Lawrence, M.S.; Zhsng, C.Z.; Wala, J.; Mermel, C.H.; et al. Pan-cancer Patterns of Somatic Copy Number Alteration. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1134–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rausch, T.; Jones, D.T.; Zapatka, M.; Stutz, A.M.; Zichner, T.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Jager, N.; Remke, M.; Shih, D.; Northcott, P.A.; et al. Genome Sequencing of Pediatric Medulloblastoma Links Catastrophic DNA Rearrangements with TP53 Mutations. Cell 2012, 148, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Loeser, H.; Wolwer, C.B.; Alakus, H.; Chon, S.H.; Zander, T.; Buettner, R.; Hillmer, A.M.; Bruns, C.J.; Schroeder, W.; Gebauer, F.; et al. Y Chromosome Loss is a Frequent Event in Barrett’s Adenocarcinoma and Associated with Poor Outcome. Cancers 2020, 12, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Nik-Zainal, S.; Wedge, D.C.; Aparicio, S.A.; Behjati, S.; Biankin, A.V.; Bignell, G.R.; Bolli, N.; Borg, A.; Borresen-Dale, A.L.; et al. Signatures of Mutational Processes in Human Cancer. Nature 2013, 500, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Kim, J.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Huang, M.N.; Tian Ng, A.W.; Wu, Y.; Boot, A.; Covington, K.R.; Gordenin, D.A.; Bergstrom, E.N.; et al. The Repertoire of Mutational Signatures in Human Cancer. Nature 2020, 578, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weaver, J.M.J.; Ross-Innes, C.S.; Shannon, N.; Lynch, A.G.; Forshew, T.; Barbera, M.; Murtaza, M.; Ong, C.J.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; Dunning, M.J.; et al. Ordering of Mutations in Preinvasive Disease Stages of Esophageal Carcinogenesis. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorani, A.; Li, X.; Goddard, M.; Crawte, J.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Secrier, M.; Eldridge, M.D.; Bower, L.; Weaver, J.; Lao-Sirieix, P.; et al. Genomic Evidence Supports a Clonal Diaspora Model for Metastases of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, D.T.; Durham, J.N.; Smith, K.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Aulakh, L.K.; Lu, S.; Kemberling, H.; Wilt, C.; Luber, B.S.; et al. Mismatch Repair Deficiency Predicts Response of Solid Tumors to PD-1 Blockade. Science 2017, 357, 409–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.T.; Cristescu, R.; Bass, A.J.; Kim, K.M.; Odegaard, J.I.; Kim, K.; Liu, X.Q.; Sher, X.; Jung, H.; Lee, M.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Characterization of Clinical Responses to PD-1 Inhibition in Metastatic Gastric Cancer. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polom, K.; Marano, L.; Marrelli, D.; De Luca, R.; Roviello, G.; Savelli, V.; Tan, P.; Roviello, F. Meta-Analysis of Microsatellite Instability in Relation to Clinicopathological Characteristics and Overall Survival in Gastric Cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzykala, B.; Turut, P.; Darrason, G.; Madelain, J.; Dumont, P. Epidemiology of Choroidal Folds. Bull. Soc. Ophtalmol. Fr. 1989, 89, 295–296, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, L.C.; Inam, I.Z.; Saito, Y.; Yoshikawa, T.; Quaas, A.; Hoelscher, A.; Bollschweiler, E.; Fazzi, G.E.; Melotte, V.; Langley, R.E.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus and Mismatch Repair Deficiency Status Differ between Oesophageal and Gastric Cancer: A Large Multi-centre Study. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 94, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasina, R.; Surati, M.; Kawada, I.; Arif, Q.; Carey, G.B.; Kanteti, R.; Husain, A.N.; Ferguson, M.K.; Vokes, E.E.; Villaflor, V.M.; et al. O-6-methylguanine-deoxyribonucleic Acid Methyltransferase Methylation Enhances Response to Temozolomide Treatment in Esophageal Cancer. J. Carcinog. 2013, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, T.; Liu, Y.; Gao, D.; Linghu, E.; Brock, M.V.; Yin, D.; Zhan, Q.; Herman, J.G.; Guo, M. Methylation of CHFR Sensitizes Esophageal Squamous Cell Cancer to Docetaxel and Paclitaxel. Genes Cancer 2015, 6, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.E.; Puccini, A.; Xiu, J.; Raghavan, D.; Lenz, H.J.; Korn, W.M.; Shields, A.F.; Philip, P.A.; Marshall, J.L.; Goldberg, R.M. Comparative Molecular Analyses of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Esophageal Adenocarcinoma, and Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Oncologist 2018, 23, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scott, S.J.; Li, X.; Jammula, S.; Devonshire, G.; Lindon, C.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; D’Avino, P.P. Evidence that Polyploidy in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Originates from Mitotic Slippage Caused by Defective Chromosome Attachments. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 2179–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Sanchez-Vega, F.; Jonsson, P.; Chatila, W.K.; Hechtman, J.F.; Ku, G.Y.; Riches, J.C.; Tuvy, Y.; Kundra, R.; Bouvier, N.; et al. Genetic Predictors of Response to Systemic Therapy in Esophagogastric Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2018, 8, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castiglioni, F.; Tagliabue, E.; Campiglio, M.; Pupa, S.M.; Balsari, A.; Menard, S. Role of Exon-16-Deleted HER2 in Breast Carcinomas. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peters, Y.; Al-Kaabi, A.; Shaheen, N.J.; Chak, A.; Blum, A.; Souza, R.F.; Di Pietro, M.; Iyer, P.G.; Pech, O.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; et al. Barrett Oesophagus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2019, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeki, S.; Fitzgerald, R.C. The Use of Molecular Markers in Predicting Dysplasia and Guiding Treatment. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 29, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, N.; Ransohoff, D.F. Gastroesophageal reflux, barrett esophagus, and esophageal cancer: Scientific review. JAMA 2002, 287, 1972–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, J.; Barr, H.; Wang, K.; Delaney, B. Diagnosis and Management of Barrett’s Oesophagus. BMJ 2010, 341, c4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leedham, S.J.; Preston, S.L.; McDonald, S.A.; Elia, G.; Bhandari, P.; Poller, D.; Harrison, R.; Novelli, M.R.; Jankowski, J.A.; Wright, N.A. Individual Crypt Genetic Heterogeneity and the Origin of Metaplastic Glandular Epithelium in Human Barrett’s Oesophagus. Gut 2008, 57, 1041–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ross-Innes, C.S.; Becq, J.; Warren, A.; Cheetham, R.K.; Northen, H.; O’Donovan, M.; Malhotra, S.; di Pietro, M.; Ivakhno, S.; He, M.; et al. Whole-genome Sequencing Provides New Insights into the Clonal Architecture of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachler, M.D.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Peng, S.; McKenna, A.; Agoston, A.T.; Odze, R.D.; Davison, J.M.; Nason, K.S.; Loda, M.; Leshchiner, I.; et al. Paired Exome Analysis of Barrett’s Esophagus and Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, P.; Mallo, D.; Paulson, T.G.; Li, X.; Sanchez, C.A.; Reid, B.J.; Graham, T.A.; Kuhner, M.K.; Maley, C.C. Evolution of Barrett’s Esophagus through Space and Time at Single-crypt and Whole-biopsy Levels. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Killcoyne, S.; Gregson, E.; Wedge, D.C.; Woodcock, D.J.; Eldridge, M.D.; de la Rue, R.; Miremadi, A.; Abbas, S.; Blasko, A.; Kosmidou, C.; et al. Genomic Copy Number Predicts Esophageal Cancer Years before Transformation. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1726–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jammula, S.; Katz-Summercorn, A.C.; Li, X.; Linossi, C.; Smyth, E.; Killcoyne, S.; Biasci, D.; Subash, V.V.; Abbas, S.; Blasko, A.; et al. Identification of Subtypes of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Based on DNA Methylation Profiles and Integration of Transcriptome and Genome Data. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1682–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, W. Distinct Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Molecular Subtype has Subtype-Specific Gene Expression and Mutation Patterns. BMC. Genom. 2018, 19, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Cui, K.; Liu, C.; Wu, M.; Prochownik, E.V.; Li, Y. The MAP3K13-TRIM25-FBXW7alpha Axis Affects c-Myc Protein Stability and Tumor Development. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, Z.C.; Trotter, E.W.; Torres-Ayuso, P.; Chapman, P.; Wood, H.M.; Nyswaner, K.; Brognard, J. Survival of Head and Neck Cancer Cells Relies upon LZK Kinase-Mediated Stabilization of Mutant p53. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 4961–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Zeng, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Luo, Y.; Sun, W.; Li, S.; Ren, J.; Gong, Y.; et al. Stromal Microenvironment Promoted Infiltration in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A multi-cohort gene-based analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagisetty, K.H.; McEwen, D.P.; Nancarrow, D.J.; Schiebel, J.G.; Ferrer-Torres, D.; Ray, D.; Frankel, T.L.; Lin, J.; Chang, A.C.; Kresty, L.A.; et al. Immune Determinants of Barrett’s Progression to Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. JCI. Insight 2021, 6, e143888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodziejczyk, A.A.; Kim, J.K.; Svensson, V.; Marioni, J.C.; Teichmann, S.A. The Technology and Biology of Single-cell RNA Sequencing. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amezquita, R.A.; Lun, A.T.L.; Becht, E.; Carey, V.J.; Carpp, L.N.; Geistlinger, L.; Marini, F.; Rue-Albrecht, K.; Risso, D.; Soneson, C.; et al. Orchestrating Single-cell Analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirosh, I.; Izar, B.; Prakadan, S.M.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Treacy, D.; Trombetta, J.J.; Rotem, A.; Rodman, C.; Lian, C.; Murphy, G.; et al. Dissecting the Multicellular Ecosystem of Metastatic Melanoma by Single-Cell RNA-seq. Science 2016, 352, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.Z.; Roden, D.L.; Wang, C.; Holliday, H.; Harvey, K.; Cazet, A.S.; Murphy, K.J.; Pereira, B.; Al-Eryani, G.; Bartonicek, N.; et al. Stromal Cell Diversity Associated with Immune Evasion in Human Triple-negative Breast Cancer. EMBO J. 2020, 39, e104063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.; Hong, Y.; Cho, J.H.; Choi, J.W.; Lee, J.I.; Suh, Y.L.; Ku, B.M.; Eum, H.H.; et al. Single-cell RNA Sequencing Demonstrates the Molecular and Cellular Reprogramming of Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Courtois, E.T.; Sengupta, D.; Tan, Y.; Chen, K.H.; Goh, J.J.L.; Kong, S.L.; Chua, C.; Hon, L.K.; Tan, W.S.; et al. Reference Component Analysis of Single-cell Transcriptomes Elucidates Cellular Heterogeneity in Human Colorectal Tumors. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D. and Coussens, L.M.; Accessories to the Crime: Functions of Cells Recruited to the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Underwood, T.J.; Hayden, A.L.; Derouet, M.; Garcia, E.; Noble, F.; White, M.J.; Thirdborough, S.; Mead, A.; Clemons, N.; Mellone, M.; et al. Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Predict Poor Outcome and Promote Periostin-dependent Invasion in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Pathol. 2015, 235, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noble, F.; Mellows, T.; McCormick Matthews, L.H.; Bateman, A.C.; Harris, S.; Underwood, T.J.; Byrne, J.P.; Bailey, I.S.; Sharland, D.M.; Kelly, J.J.; et al. Tumour Infiltrating Lymphocytes Correlate with Improved Survival in Patients with Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, R.P.; White, M.J.; Severson, D.T.; Braden, B.; Bailey, A.; Goldin, R.; Wang, L.M.; Ruiz-Puig, C.; Maynard, N.D.; Green, A.; et al. Single Cell RNA-seq Reveals Profound Transcriptional Similarity between Barrett’s Oesophagus and Oesophageal Submucosal Glands. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, M.; Plum, P.S.; Velazquez Camacho, O.; Folz-Donahue, K.; Thelen, M.; Garcia-Marquez, I.; Wolwer, C.; Busker, S.; Wittig, J.; Franitza, M.; et al. Cell Type-specific Transcriptomics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma as a Scalable Alternative for Single Cell Transcriptomics. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 1170–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Loga, K.; Woolston, A.; Punta, M.; Barber, L.J.; Griffiths, B.; Semiannikova, M.; Spain, G.; Challoner, B.; Fenwick, K.; Simon, R.; et al. Extreme Intratumour Heterogeneity and Driver Evolution in Mismatch Repair Deficient Gastro-oesophageal Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Repana, D.; Nulsen, J.; Dressler, L.; Bortolomeazzi, M.; Venkata, S.K.; Tourna, A.; Yakovleva, A.; Palmieri, T.; Ciccarelli, F.D. The Network of Cancer Genes (NCG): A Comprehensive Catalogue of Known and Candidate Cancer Genes from Cancer Sequencing Screens. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contino, G.; Vaughan, T.L.; Whiteman, D.; Fitzgerald, R.C. The Evolving Genomic Landscape of Barrett’s Esophagus and Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 657–673 e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustgi, A.K.; El-Serag, H.B. Esophageal Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2499–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.; van Lanschot, J.J.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Hospers, G.A.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal or Junctional Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Batran, S.E.; Hartmann, J.T.; Hofheinz, R.; Homann, N.; Rethwisch, V.; Probst, S.; Stoehlmacher, J.; Clemens, M.R.; Mahlberg, R.; Fritz, M.; et al. Biweekly Fluorouracil, Leucovorin, Oxaliplatin, and Docetaxel (FLOT) for Patients with Metastatic Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach or Esophagogastric Junction: A phase II trial of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. Ann. Oncol. 2008, 19, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- den Bakker, C.M.; Smit, J.K.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E.; van Grieken, N.C.T.; Daams, F.; Derks, S.; Cuesta, M.A.; Plukker, J.T.M.; van der Peet, D.L. Non Responders to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiation for Esophageal Cancer: Why Better Prediction is Necessary. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S843–S850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bang, Y.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Feyereislova, A.; Chung, H.C.; Shen, L.; Sawaki, A.; Lordick, F.; Ohtsu, A.; Omuro, Y.; Satoh, T.; et al. Trastuzumab in Combination with Chemotherapy Versus Chemotherapy Alone for Treatment of HER2-positive Advanced Gastric or Gastro-oesophageal Junction Cancer (ToGA): A Phase 3, Open-label, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Kojima, T.; Hochhauser, D.; Enzinger, P.; Raimbourg, J.; Hollebecque, A.; Lordick, F.; Kim, S.B.; Tajika, M.; Kim, H.T.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pembrolizumab for Heavily Pretreated Patients With Advanced, Metastatic Adenocarcinoma or Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Esophagus: The Phase 2 KEYNOTE-180 Study. JAMA. Oncol. 2019, 5, 546–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Janjigian, Y.Y.; Maron, S.B.; Chatila, W.K.; Millang, B.; Chavan, S.S.; Alterman, C.; Chou, J.F.; Segal, M.F.; Simmons, M.Z.; Momtaz, P.; et al. First-line Pembrolizumab and Trastuzumab in HER2-positive Oesophageal, Gastric, or Gastro-oesophageal Junction Cancer: An Open-label, Single-arm, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.H.; Shi, Q.; Sukov, W.R.; Wiktor, A.E.; Khan, M.; Sattler, C.A.; Grothey, A.; Wu, T.T.; Diasio, R.B.; Jenkins, R.B.; et al. Association of HER2/ErbB2 Expression and Gene Amplification with Pathologic Features and Prognosis in Esophageal Adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plum, P.S.; Gebauer, F.; Kramer, M.; Alakus, H.; Berlth, F.; Chon, S.H.; Schiffmann, L.; Zander, T.; Buttner, R.; Holscher, A.H.; et al. HER2/neu (ERBB2) expression and Gene Amplification Correlates with Better Survival in Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. BMC. Cancer 2019, 19, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleespies, A.; Guba, M.; Jauch, K.W.; Bruns, C.J. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Esophageal Cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2004, 87, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Tomasek, J.; Yong, C.J.; Dumitru, F.; Passalacqua, R.; Goswami, C.; Safran, H.; Dos Santos, L.V.; Aprile, G.; Ferry, D.R.; et al. Ramucirumab Monotherapy for Previously Treated Advanced Gastric or gastro-Oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (REGARD): An international, Randomised, Multicentre, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2014, 383, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, H.; Muro, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Oh, S.C.; Bodoky, G.; Shimada, Y.; Hironaka, S.; Sugimoto, N.; Lipatov, O.; Kim, T.Y.; et al. Ramucirumab Plus Paclitaxel Versus Placebo Plus Paclitaxel in Patients with Previously Treated Advanced Gastric or Gastro-oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (RAINBOW): A Double-blind, Randomised Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.S.; Shitara, K.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Lonardi, S.; Al-Batran, S.E.; Van Cutsem, E.; Ilson, D.H.; Alsina, M.; Chau, I.; Lacy, J.; et al. Ramucirumab with Cisplatin and Fluoropyrimidine as First-line Therapy in Patients with Metastatic Gastric or Junctional Adenocarcinoma (RAINFALL): A Double-blind, Randomised, Placebo-controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 420–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Klerk, L.K.; Goedegebuure, R.S.A.; van Grieken, N.C.T.; van Sandick, J.W.; Cats, A.; Stiekema, J.; van der Kaaij, R.T.; Farina Sarasqueta, A.; van Engeland, M.; Jacobs, M.; et al. Molecular Profiles of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy in Oesophageal Cancers to Develop Personalized Treatment Strategies. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 901–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, S. Burned adolescents’ descriptions of their coping strategies. Heart Lung 1988, 17, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gregson, E.M.; Bornschein, J.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Genetic Progression of Barrett’s Oesophagus to Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachler, M.D.; Camarda, N.D.; Deitrick, C.; Kim, A.; Agoston, A.T.; Odze, R.D.; Hornick, J.L.; Nag, A.; Thorner, A.R.; Ducar, M.; et al. Detection of Mutations in Barrett’s Esophagus Before Progression to High-Grade Dysplasia or Adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nahar, R.; Zhai, W.; Zhang, T.; Takano, A.; Khng, A.J.; Lee, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Lim, C.H.; Koh, T.P.T.; Aung, Z.W.; et al. Elucidating the Genomic Architecture of Asian EGFR-Mutant Lung Adenocarcinoma through Multi-region Exome Sequencing. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharahkhani, P.; Fitzgerald, R.C.; Vaughan, T.L.; Palles, C.; Gockel, I.; Tomlinson, I.; Buas, M.F.; May, A.; Gerges, C.; Anders, M.; et al. Genome-wide Association Studies in Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma and Barrett’s Oesophagus: A Large-scale Meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SERVIER, L.L. Servier Medical Art. Available online: https://smart.servier.com (accessed on 29 June 2021).

| Sequencing Approach | Cohort | Main Findings | Study (Consortium) |
|---|---|---|---|
| WGS + SNP-arrays | 22 EACs | - genomic catastrophies are frequent in EAC - chromotripsis appears in about one third of EACs, accompanied by telomere shortening - double minutes with oncogenes such as MYC and MDM2 associate with chromotripsis in EAC - breakage-fusion bridge cycles are frequent and affect driver genes, i.e., MDM2, KRAS - extreme genomic instability can be driven by BRCA2 mutations in EAC | Nones et al., 2014 [14] |
| WES | 8 EACs, spatiotemporal samples n = 40 | - many driver events are early, e.g., TP53, CDKN2A; some are late and subclonal, e.g., PIK3R1, SMAD4 - genome doubling and chromosomal instability are early events leading to amplifications that persist through treatment - high heterogeneity associates with poor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy | Murugaesu et al., 2015 [4] |
| WGS | 129 EACs, including gastro-esophageal junction (Siewert types I and II) | - EAC landscape is highly heterogeneous, point mutations are abundant but with low frequency - dominance of SCNAs over SNVs - large-scale rearrangements are frequent, i.e., chromotripsis, breakage-fusion-bridge cycles - three molecular subtypes based on mutational signatures with therapeutic relevance | Secrier et al., 2016 (OCCAMS) [7] |
| WES + low-pass WGS + SNP arrays + DNA methylation profiling + mRNA-seq + miRNA-seq + proteomic | 72 EACs (+ 90 ESCCs, 36 GEJs of unkown origin, 63 gastric GEJs, 140 gastric fundi or bodies, 143 gastric antral or pyloric, total 559) | - molecular features differentiate EAC from ESCC - EAC resembles chromosomal instable gastric adenocarcinoma - EAC is more commonly hypermethylated than ESCC or gastric cancers | TCGA, 2017 [6] |
| Targeted NGS | 295 patients with metastatic esophageal, gastric and gastro-esophageal junction adenocarcinoma | - HER2 positivity can be detected by NGS - alterations of genes involved in RTK/RAS/PI3K pathway in addition to ERBB2 amplification are predictive for resistance to trastuzumab treatment - patients may lose ERBB2 amplification or gain a resistant isoform during treatment | Janjigian et al., 2017 (MSK-IMPACT) [35] |
| WGS | matched pre- and post-therapy: 10 EACs, unmatched: 62 untreated + 58 treated EACs | - the genome of EAC treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy is similar to untreated EAC - rare cases showing differences pre- and post-therapy arise from endoreduplication | Noorani et al., 2017 (OCCAMS) [5] |
| WGS + WES + RNA-seq | 551 EACs: 379 ICGC (WGS) + 149 from Dulak et al. (WES) + 22 from Nones et al. (WGS). RNA-seq 116/379 ICGC | - combination of methods detects altered non-coding driver elements and driver genes, i.e., TP53, CDKN2A, KRAS, MYC, ERBB2, GATA4, SMAD4, MMP24 - TP53-wt EACs have amplifications of MDM2 - SMAD4 and GATA4 alterations predict poor prognosis - ~50% of EAC cases are potentially sensitive to CDK4/CDK6 inhibitors | Frankell et al., 2019 (OCCAMS) [13] |
| WGS + RNA-seq | 267 EACs from ICGC | - identification of 952 helper genes contributing to cancer progression - helper genes identify six patient subgroups with distinct molecular and clinical features | Mourikis et al., 2019 (OCCAMS) [17] |
| WES + RNA-seq | 40 EACs (stage 4b EGAC (Siewert types I, II and III)) divided into 20 shorter and 20 longer survivors | - similar mutational burden of short and long survivors - intratumoral heterogeneity is higher in short survivors - KMT2C alterations are exclusive for short survivors - loss of chr. 4 is associated with shorter survival | Hao et al., 2020 [18] |
| WGS | 18 EACs, 388 spatiotemporal samples | - EAC progresses via clonal diaspora model with multiple different subclones of the primary tumor spreading and colonizing different or the same metastatic sites | Noorani et al., 2020 [25] |
| Sequencing Approach | Cohort | Main Findings | Study (Consortium) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA-seq | Meta-analysis of three EAC cohorts: n = 88 (TCGA), n = 75 (GSE13898) and n = 52 (GSE19417) | Two molecular subtypes of EAC were identified based on RNA expression levels - Subtype I: basal cell-like; enriched for keratinocyte and epithelial cell differentiation; clusters with normal esophagus and gastric cancer; 24 specific genes mutated including SMAD4; less responsive to chemotherapy - Subtype II: classic EAC-like; clusters with dysplastic BE and ESCC; 30 specific genes mutated including ARID1A; more sensitive to chemotherapy | Guo et al., 2018 [47] |
| WES + RNA-seq | 40 EACs (stage 4b EGAC (Siewert types I, II and III)) divided into 20 shorter and 20 longer survivors | Clustering of EAC samples based on RNA expression: - Long survivors associate with upregulation of immune-related markers, i.e., MPO, LEF1 - Short survivors are enriched for upregulation of tumor promoters, i.e., JAK2, MAP3K13 (please refer to Table 1 for genomics-related findings) | Hao et al., 2020 [18] |
| WGS + WES + RNA-seq | 551 EACs: 379 ICGC (WGS) + 149 from Dulak et al. (WES) + 22 from Nones et al. (WGS). RNA-seq 116/379 ICGC | - 17 known cancer genes are frequently expressed high in EAC, i.e., ERBB2, KRAS, SMAD4, MYC - Copy number loss of tumor suppressors may not result in reduced expression, i.e., for ARID1A - CDKN2A is upregulated and returns to normal expression levels when deleted (please refer to Table 1 for genomics-related findings) | Frankell et al., 2019 (OCCAMS) [13] |
| RNA-seq | 88 EACs + 94 ESCCs for training and 48 EACs (GSE19417) + 179 ESCCs (GSE53625) for validation | - Stratification of patients into two subgroups with high or low stromal activity - High stromal activity (subgroup 2, S2) was associated with high tumor stage and poor prognosis - S2 was enriched for EMT, angiogenesis and stromal infiltration of fibroblasts, endothelial cells and macrophages - Stromal marker genes characterizing S2 comprise genes important for CAF function | Li et al., 2020 [50] |
| RNA-Seq | 65 patient samples: 25 non-dysplastic BEs, 29 high-grade dysplastic BEs, 11 EACs | - Chemokines and cytokines such as IL6 and CXCL8 increase during BE-to-EAC progression - Immune cell populations are high in dysplastic BE but low in EAC (i.e., CD8+ T-cells) - Immune inhibitory signaling, i.e., PD-L1 expression, is high in EAC, supporting trials with immune checkpoint inhibitors | Lagisetty et al., 2021 [51] |
| Single-cell RNA-seq | Total 4237 cells sequenced from 6 patients with BE + 2 patients with normal esophagus | - Distinct cell populations of BE are similar to submucosal gland cells (marker: LEFTY1, OLFM4) - Other cell populations are goblet cell-like and found in BE and colon samples (marker: SPINK4, ITLN1) | Owen et al., 2018 [62] |
| Flow sorting RNA-seq | Spatial sampling from 9 patients with EAC | - As an alternative to single-cell sequencing, specific cell populations from EAC can be labeled and separated using FACS followed by RNA-seq - Fibroblasts from EAC show upregulation of angiogenesis-related genes compared to fibroblasts from normal esophagus | Krämer et al., 2020 [63] |
| Target | Treatment | Cohort Characteristics | Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERBB2 | Trastuzumab | EAC + GEJ + Gastric | Bang et al., 2010 [71] (ToGA) |
| PD-L1 | Pembrolizumab | ESCC + EAC + GEJ | Shah et al., 2019 (KEYNOTE-180 Study) [72] |
| PD-L1 + ERBB2 | Pembrolizumab + Trastuzumab | EAC + GEJ + Gastric | Janjigian et al., 2020 [73] |
| VEGFA | Bevacizumab | GEJ + Gastric | Ohtsu et al., 2021 [10] |
| VEGF2 + ERBB2 | Ramucirumab | GEJ + Gastric GEJ + Gastric GEJ + Gastric | Fuchs et al., 2014 (REGARD) [77] Wilke et al., 2014 (RAINBOW) [78] Fuchs et al., 2019 (RAINFALL) [79] |
| EGFR | Cetuximab | ESCC + EAC + GEJ | Huang et al., 2018 [9] |
| EGFR | Panitumumab | GEJ | Waddell et al., 2013 (REAL3) [12] |
| HGF | Rilotumumab | EAC + GEJ + Gastric | Catenacci et al., 2017 (RILOMET-1) [8] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoppe, S.; Jonas, C.; Wenzel, M.C.; Velazquez Camacho, O.; Arolt, C.; Zhao, Y.; Büttner, R.; Quaas, A.; Plum, P.S.; Hillmer, A.M. Genomic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 4300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174300
Hoppe S, Jonas C, Wenzel MC, Velazquez Camacho O, Arolt C, Zhao Y, Büttner R, Quaas A, Plum PS, Hillmer AM. Genomic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers. 2021; 13(17):4300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174300
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoppe, Sascha, Christoph Jonas, Marten Christian Wenzel, Oscar Velazquez Camacho, Christoph Arolt, Yue Zhao, Reinhard Büttner, Alexander Quaas, Patrick Sven Plum, and Axel Maximilian Hillmer. 2021. "Genomic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma" Cancers 13, no. 17: 4300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174300
APA StyleHoppe, S., Jonas, C., Wenzel, M. C., Velazquez Camacho, O., Arolt, C., Zhao, Y., Büttner, R., Quaas, A., Plum, P. S., & Hillmer, A. M. (2021). Genomic and Transcriptomic Characteristics of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma. Cancers, 13(17), 4300. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13174300